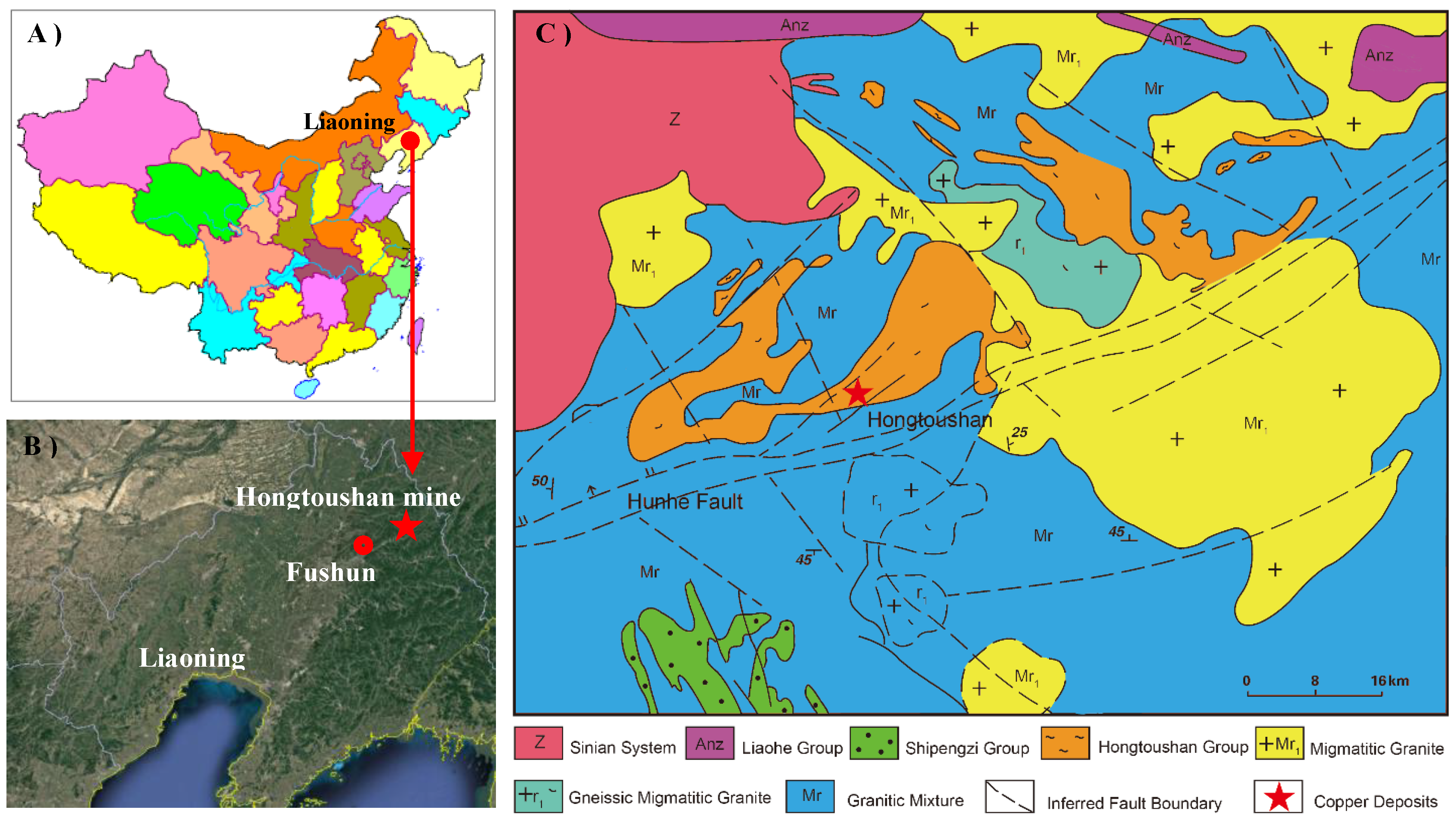
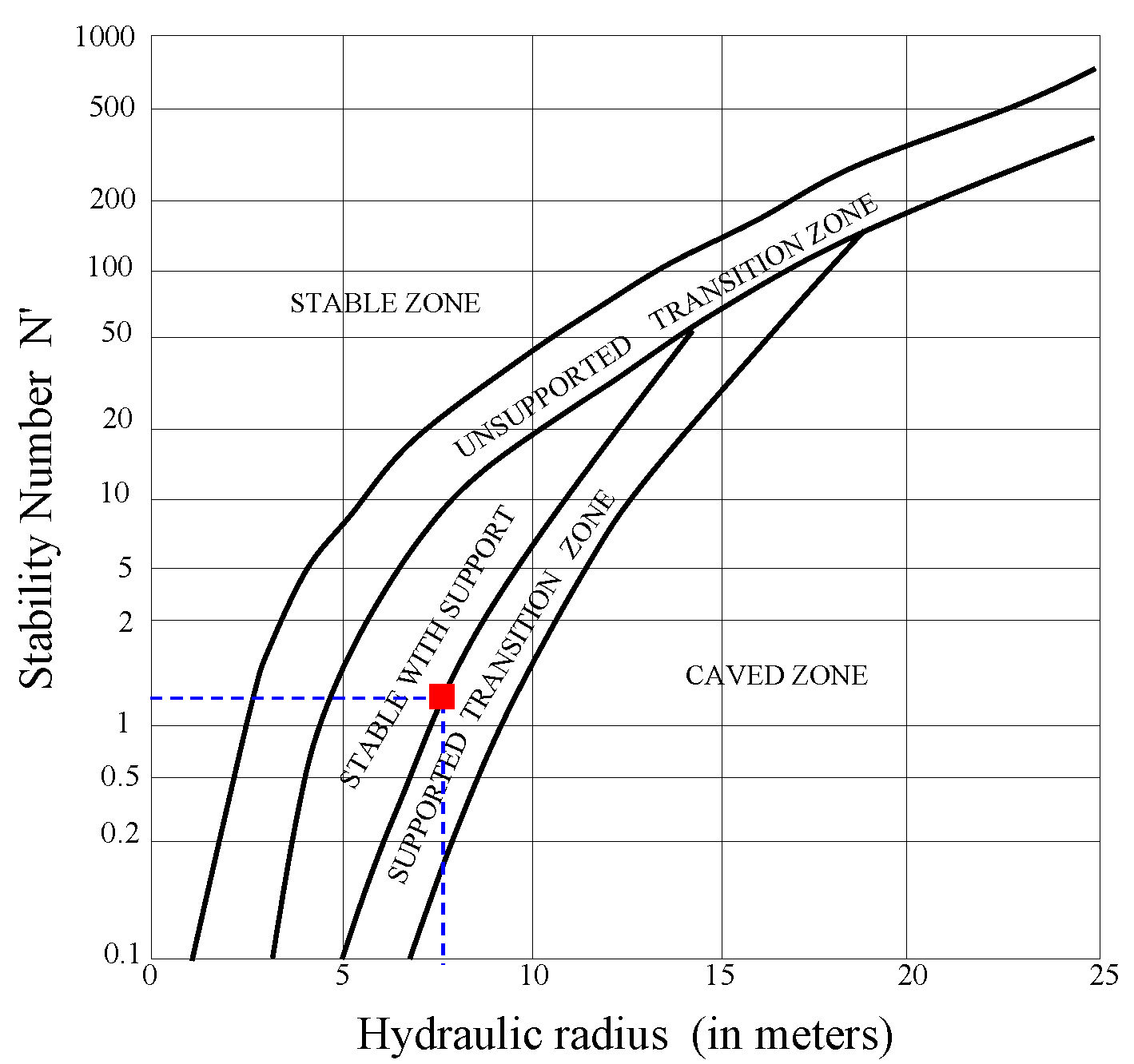
1. Introduction
Stope roof stability is an essential prerequisite for safe working conditions in overhand cut-and-fill mining. Non-anticipated rock collapses and falls from the stope roof are the primary threat to the safety of underground workers and economic extraction of ore bodies. Such accidents account for approximately 40% of all injuries and fatalities in underground base metal mines in China [
1]. The overhand cut-and-fill mining method has been extensively used in underground base metal mines worldwide, with typical stope dimensions of about 20–35 m in width and 50–80 m long in strike, accommodating large mechanized equipment [
2]. In general, roof instabilities observed in the field can be related to ground falls owing to excessive stresses or unfavorable geological structures.
Stope stability is significantly affected by geology, stress conditions, mining methods, opening dimensions, support technology, and other factors. Numerous studies have addressed the stability analyses of stopes and drifts using empirical, numerical, and analytical methods, as well as in-situ tests and monitoring methods. For example, the pioneering work of Mathews et al. [
3] empirically predicted the stable excavation size for mines at depths below 1000 meters in Canadian hard rock using a stability graph. The Mathews method was later modified by Potvin [
4], which led to the well-known Mathews–Potvin method. Such empirical methods have been intensively reviewed and modified, resulting in several variants that can be applied to many other conditions [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Swart and Handley [
10] designed a stable range of stopes for shallow mining operations using an integrated method included a stability graph, elastic beam theory, and numerical modeling. Sunwoo et al. [
11] predicted the stability of wide underground mine openings using the stability graph. Jordá et al. [
12] analyzed the stability of shallow limestone caves at a maximum depth of 55 m using the stability graph method. Lang [
13] developed a critical span curve to evaluate back stability in cut-and-fill mines, which was later modified by Wang et al. [
14] and Ouchi et al. [
15]. Idris et al. [
16] studied the effects of rock mass property variability on open stope stability using finite element methods (FEM). Li et al. [
17,
18] analyzed the dynamic disasters of deep mining using the analytical and numerical modeling methods. Yang et al. [
19] analyzed the stability of a shallow large-scale stope using stage subsequent filling mining methods in the Sijiaying iron mine in China using physical and numerical modeling methods. Heidarzadeh et al. [
20] evaluated the effect of geometrical parameters on the probability of stope failure in the open stoping method using numerical modeling. Grenon and Hadjigeorgiou [
21] used 3D joint network models and a limit equilibrium analysis to investigate the stability of all potential wedges at the back of a stope. Gao et al. [
22] studied the effect of a dip angle in mining direction on drum loading performance used discrete element method (DEM). Su [
23] adopted nonlinear programming, a genetic algorithm, and a neural network to optimize the stope structure. Fuzzy mathematics and block theory are useful to analyze stope stability [
24,
25]. Many other studies have explored stope stability using instrumentation measurements [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31].
Cable bolts can provide increased stability for various openings in underground mines. The cable bolting patterns for the required stope roof control plans are usually based on past practices. Empirical analyses provide a useful tool for mining engineers to design underground openings and supports [
5]. The rock mass rating (RMR) [
32] and rock mass quality (Q) [
33] are widely used to determine tunneling support requirements. In particular, tunnel support guidelines based on RMR were originally published in the form of a table [
32] that provided recommendations for a tunnel span/diameter of 10 meters. Most guidelines were designed for rockbolting and can be used to select spacings for face support to supplement cable bolts in a fractured rock mass. A design graph for cable bolt density proposed by Potvin [
4] relates cable bolt density to a relative block size factor. This graph was developed from a database made of cable-bolted stope backs and was not intended for the design of hanging walls. Fuller [
34] described a cable design method for a point anchor cable pattern based on beam theory that is commonly applied to layered rock masses. Barton [
35] presented a tabulated series of detailed support recommendations based on different combinations of rock quality, N′. Hutchinson and Diederichs [
36] proposed the cable bolt design graph based on empirical methods and mechanistic assumptions. Hutchinson and Falmagne [
37] optimized cable bolting patterns in cut-and-fill stopes (between the −70 ft and −170 ft levels) at the Chikla mine using observational, empirical, and numerical modeling methods. Liu et al. [
38] applied the empirical rock mass classification and numerical modeling to provide a reliance support design for a shallow large-scale underground water-sealed oil storage cavern. Skrzypkowski et al. [
39,
40] studied the stress–strain characteristic of the long point resin and expansion cable bolt. The literature provides valuable resources for stability analyses and support design of stope. However, systematic studies involving stability analysis and support design of deep large-span stopes are seldom reported. A thorough analysis of stope stability and determination of a reasonable cable bolt support system are crucial to ensure that mining operations are carried out economically, safely, and successfully. Many factors that influence the stability of deep large-span stopes are difficult to monitor during mining. There is therefore no single method for stability analysis and support design. The geomechanics classification or RMR [
41] and stability graph [
4,
5,
36,
42,
43] are the most widely used empirical methods in consideration of the rock mass quality, induced stress, and large-span effects. However, these empirical methods cannot adequately provide the stress, displacement, plastic zone distribution, or safety factor information for deep large-span stopes.
In order to solve the issues mentioned above, this paper summarizes and evaluates the results of stope and rock mass characteristics. An integrated empirical and numerical method to assess potentially unstable stope roof conditions is discussed, and the numerical analysis of support systems obtained from the empirical method is used to evaluate support systems stability for a deep large-span stope. After support installation, the maximum plastic zone thickness and vertical displacement at the stope roof decrease significantly and the safety factor of the unstable wedge block increases significantly, and no sign of rock falls.
8. Discussion
This article is a contribution to the stability analyses and cable bolt support design for deep large-span stope at the Hongtoushan mine with complicated geological condition using an integrated empirical and numerical method. The RMR and stability graph are the most widely used empirical methods, which are familiar by rock engineers and have gained a universal acceptance. The empirical methods based on detailed geological surveys and they have been applied to many construction designs. However, these empirical methods cannot adequately provide the stress, displacement, plastic zone distribution, or safety factor information for deep large-span stopes. Therefore, a particular attention has to be given when they are used. In particular, determination of mechanical parameters for jointed rock mass is very sensitive to the field observations. Meanwhile, numerical methods such as the finite difference method are very dependent on the strength parameters of the rock masses. Therefore, both methods should be used with caution and these parameters should be determined reliably according to field data. On the other hand, providing reliable input parameters to numerical methods can produce meaningful calculations on the ground control. In this paper, two methods were used to obtain quantitative stability assessment and optimum cable bolt support design for deep large-span stope roofs.
As mining activity progressed upwards from one layer to another, the tensile stress of the roof had a law of decreasing first and then increasing, and it was always greater than the calculated tensile stress. This was mainly due to the roof being in the relaxation zone after mining the first layer, leading to roof tensile stress being reduced abruptly. As the upper part of the 1-1# stope was the backfill material, the thickness of the remaining ore body continued to decrease during mining, leading to the roof tensile stress continuously increased. In particular, the roof tensile stress increased abruptly when the remaining ore body thickness was reduced to a certain value. Typical cable bolt support systems can be obtained from empirical methods. The long grouting cable bolt support was used in 1-1# stope. The diameter of the cable bolt and cable bolt hole were 17.8 mm and 55 mm, respectively. The long grouting cable bolt was installed in the cable bolt hole by means of cement binders, and it was fixed in the hole along its entire length by applying a suitable cement binder and on the friction principle. The numerical methods verify the feasibility of recommended cable bolt support system. The results proved that the empirical and numerical methods agreed with each other.
Although an integrated empirical and numerical method can address geological and geotechnical uncertainties to a certain extent and is easy to use for engineers. It may be invalid in areas where there is damage owing to blasting or a sudden change in geology, occurrence of weak zones, and so on. Measurements should therefore be carried out during extraction to verify the rock mass behavior and check the validity of the proposed support system or to adapt the support system design. After blasting and mucking, the laser distance meter was employed to survey subsidence displacement of the supported roof. The maximum vertical displacement of the stope roof was 12.5 mm, and verified the rationality of the support systems, obtained from a combination of empirical and numerical methods. However, a deep understanding of the internal stress and displacement of the stope roof on the basis of the above monitoring date is difficult. The multi-point borehole extensometer, stress detector, and microseismic monitoring system should also be carried out during mining.
9. Conclusions
In this research, both the empirical and numerical methods were conducted for stability analysis and cable bolt support design of a deep large-span stope at the Hongtoushan mine in China. On the basis of engineering geological interpretations and considerations together with field investigations, the rock mass surrounding the 1-1# stope was classified by the Q, RMR, and GSI rock mass classification systems. The rock mass properties used as input data for the numerical modeling were obtained from empirical equations related to rock mass classification systems and Hoek–Brown constants. Some stability problems were observed for deep large-span stope roofs according to the results obtained from the empirical and numerical methods in consideration of the rock mass quality, induced stress, and large-span effects. According to the results obtained from empirical methods, with the internationally accepted cable bolt design graph. The long grouting cable bolt as support elements were recommended. As verified with the FLAC3D and UNWEDGE codes, the recommended cable bolt support system was feasible. After support installation, the maximum displacement was reduced from 62.8 to 18.6 mm, the maximum thickness of the plastic zone was reduced from 5.0 to 2.0 m, and the safety factor of the unstable wedge blocks was increased from 0 to 1.6, and there was no sign of rock falls. The results of this research proved that the empirical and numerical methods agreed with each other. Field measurements showed the maximum vertical displacement of the stope roof was 12.5 mm, and verified the rationality of the support systems. The integrated empirical and numerical method was therefore suggested to obtain quantitative stability assessment and optimum cable bolt support design for deep large-span stope roofs. It is applicable in other mines and only needs to derive the geotechnical properties rock masses according to the detailed geological survey and laboratory test.