Analysis of Coordinated Development of Energy and Environment in China’s Manufacturing Industry under Environmental Regulation: A Comparative Study of Sub-Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Environmental Regulation and Industry Performance
2.2. Environmental Regulation and Technical Innovation
3. Methodology
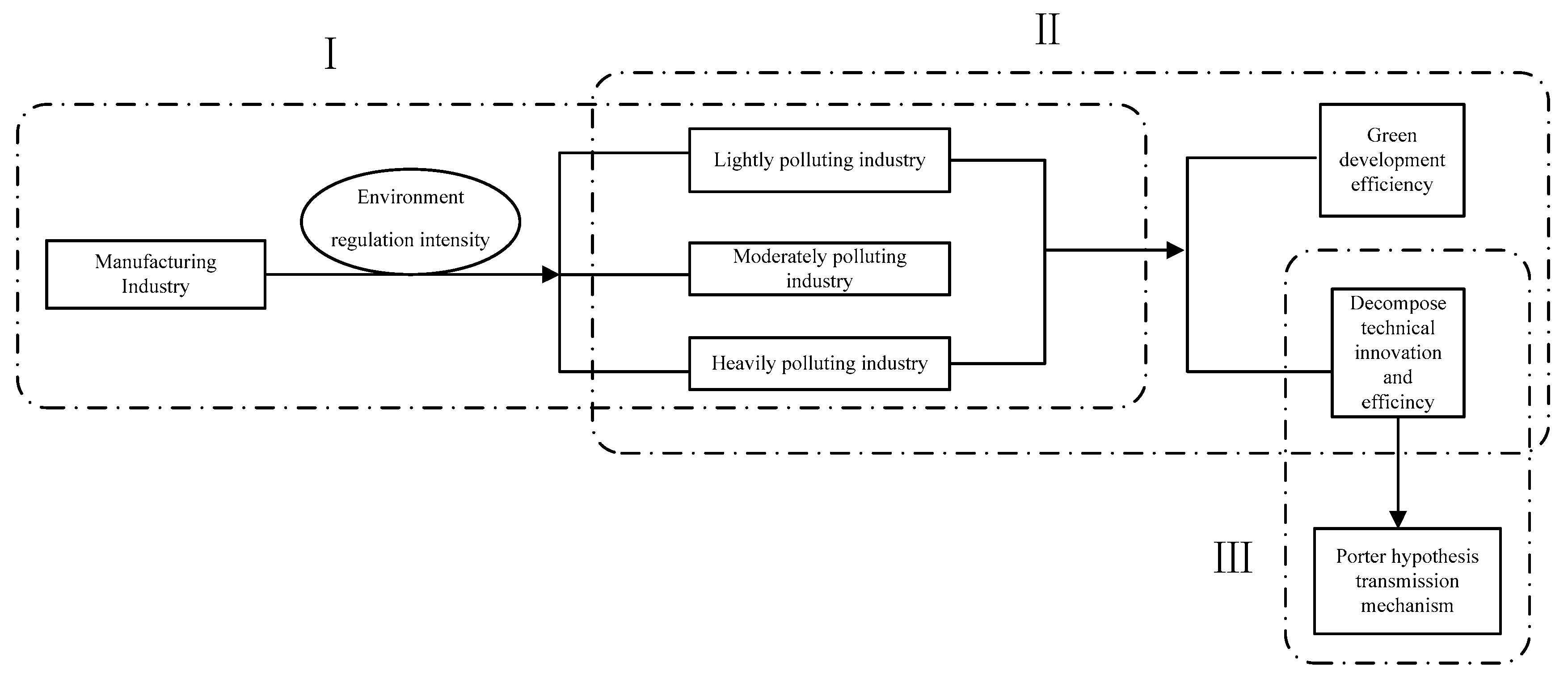
3.1. Industry Division
3.2. SBM with Undesirable Output
3.3. Malmquist Productivity Index
3.4. Econometric Model
4. Indicators and Data
4.1. Indicators of Energy-Environment Efficiency
4.2. Indicators of Econometric Regression
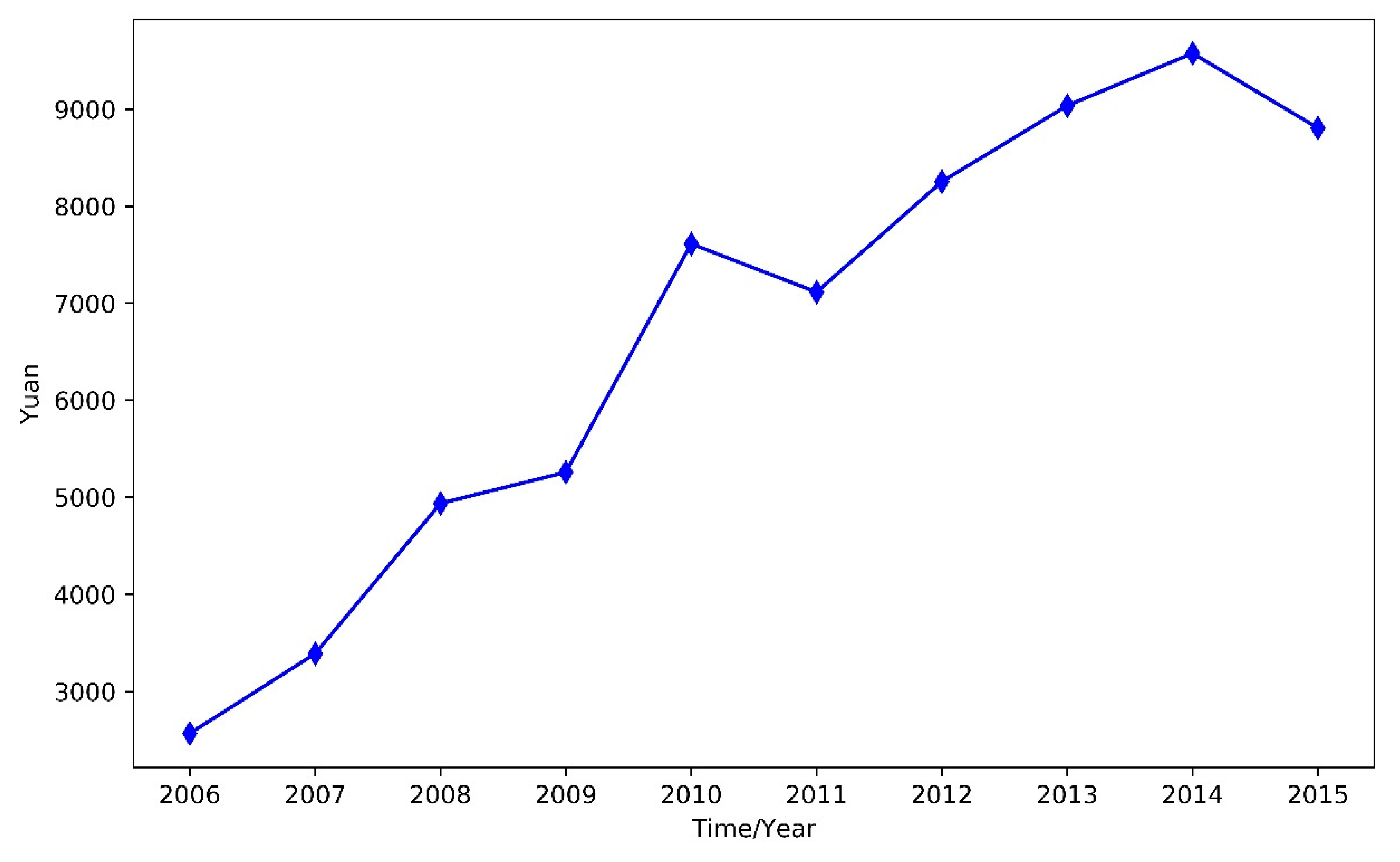
4.2.1. Environmental Regulation (er)
4.2.2. Research and Development Investment (rd)
4.2.3. Governance Transition (gt)
4.2.4. Foreign Indirect Investment (fdi)
5. Empirical Results
5.1. Results of Manufacturing Energy-Environmental Efficiency
5.2. Decomposing Energy-Environmental Technical Progress Efficiency
5.3. Influencing of Environmental Regulation on Technical Progress Efficiency
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impact of energy conservation policies on the green productivity in China’s manufacturing sector: Evidence from a three-stage DEA model. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ke, J.; Ni, C.C.; McNeil, M.; Khanna, N.Z.; Zhou, N.; Fridley, D.; Li, Q. A comparative study of energy consumption and efficiency of Japanese and Chinese manufacturing industry. Energy Policy 2014, 70, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Yang, G.-L. A framework for measuring global Malmquist–Luenberger productivity index with CO2 emissions on Chinese manufacturing industries. Energy 2016, 115, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ai, B.; Li, C.; Pan, X.; Yan, Y. Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, technological innovation and energy efficiency based on large scale provincial panel data in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 144, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, B.; Tao, X.; Xie, R. Measuring regional energy efficiencies in China: A meta-frontier SBM-Undesirable approach. Nat. Hazards 2016, 85, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Ramanathan, U.; Bentley, Y. The debate on flexibility of environmental regulations, innovation capabilities and financial performance—A novel use of DEA. Omega 2018, 75, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, J. The role of environmental regulation and technological innovation in the employment of manufacturing enterprises: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, N. Environmental regulation and environmental productivity: The case of China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 758–766. [Google Scholar]
- Mundaca, L.; Markandya, A. Assessing regional progress towards a ‘Green Energy Economy’. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 1372–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Oates, W.E.; Portney, P.R. Tightening environmental standards: The benefit-cost or the no-cost paradigm? J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.B.; Shadbegian, R.J. Plant vintage, technology, and environmental regulation. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. America’s green strategy. Sci. Am. 1991, 264, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E.; van der Linde, C. Toward a new conception of the environment competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, G. (Ed.) Economies in Transition: The Long-Run View; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, G. The political economy of transition. J. Econ. Perspect. 2002, 16, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.; Hong, X. Regional environmental efficiency evaluation in China: Analysis based on the Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yin, P.; Sun, J.; Chu, J.; Liang, L. Evaluating the environmental efficiency of a two-stage system with undesired outputs by a DEA approach: An interest preference perspective. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 254, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, C.; Lee, J.; Feng, Y.; Chiu, Y. Dynamic environmental efficiency assessment of industrial water pollution. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.-H.; Yuan, Y.-J.; Huang, J.-J. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “Green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Ren, S.; Chen, X. Can environmental regulation promote the coordinated development of economy and environment in China’s manufacturing industry?—A panel data analysis of 28 sub-sectors. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Economic growth model, structural transformation, and green productivity in China. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Shao, Q.; Zhu, X.; He, Q.; Xiang, C.; Wei, G. Environmental regulation, economic growth and air pollution: Panel threshold analysis for OECD countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.; Qin, C.; Ye, X. Environmental regulation, economic network and sustainable growth of urban agglomerations in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manello, A. Productivity growth, environmental regulation and win–win opportunities: The case of chemical industry in Italy and Germany. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, C.; Pazó, C. Environmental protection, innovation and price-setting behavior in Spanish manufacturing firms. Energy Econ. 2017, 68, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, A.M.; Parolini, A.; Winner, H. Environmental regulation and investment: Evidence from European industry data. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; He, Q.; Black, A.; Ghobadian, A.; Gallear, D. Environmental regulations, innovation and firm performance: A revisit of the Porter hypothesis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Liao, H.; Deng, R.; Wang, Q. Different types of environmental regulations and the heterogeneous influence on the environmental total factor productivity: Empirical analysis of China’s industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, R.; Alam, K. Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, innovation, CO2 emissions, population, and economic growth in OECD countries: A panel investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Guo, X. Environmental regulation and green productivity growth: Empirical evidence on the Porter Hypothesis from OECD industrial sectors. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, Y. The influence of enterprises’ bargaining power on the green total factor productivity effect of environmental regulation-evidence from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zhu, L. Technological innovation efficiency in China’s industrial enterprises: A spatial analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.Z.; Yunhui, Z.; Ketao, T.; Weifen, L. Compound effects of environmental regulation and governance transformation in enhancing green competitiveness. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 10, 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tao, F. Selction of optimal environmental regulation intensity for Chinese manufacturing industry-Based on the green TFP perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2012, 290, 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fare, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lindgren, B.; Ross, P. Productivity change in Swedish pharmacies 1980-1989: A non-parametric Malmquist approach. J. Prod. Anal. 1992, 3, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zha, Y. Industrial efficiency evaluation in China: A nonparametric production-frontier approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, A.; Cai, X. Covergence analysis of China’s energy intensity at the industrial sector level. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7730–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Park, K.; Whang, U. Organizational capabilities, export growth and job creation: An investigation of Korean SMEs. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Chen, C.; Yu, Y. Dynamic assessment of environmental efficiency in Chinese industry: A multiple DEA model with a Gini criterion approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez Lopez, J.M.; Sakhel, A.; Busch, T. Corporate investments and environmental regulation: The role of regulatory uncertainty, regulation-induced uncertainty, and investment history. Eur. Manag. J. 2017, 35, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Shi, X. Public appeal, environmental regulation and green investment: Evidence from China. Energy Policy 2018, 119, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shadbegian, R.; Zhang, B. Does environmental regulation affect labor demand in China? Evidence from the textile printing and dyeing industry. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 86, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Zheng, D. Let’s agree to disagree! On payoffs and green tastes in green energy investments. Energy Econ. 2018, 69, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Patry, M.; Lajeunesse, R. Environmental regulation and productivity: Testing the porter hypothesis. J. Product. Anal. 2008, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuckert, J. What shapes the impact of environmental regulation on competitiveness? Evidence from Executive Opinion Surveys. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2014, 10, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, L.; Kotsemir, M.; Vinci, C.P. Knowledge spillover effects: Empirical evidence from Russian regions. Qual. Quant. 2018, 52, 2111–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F. China’s industrial green total factor productivity and its determinants—An empirical study based on ML index and dynamic panel data model. Stat. Res. 2016, 33, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yanrui, W.; Pengfei, Y. Environmental efficiency and environmental total factor productivity growth in China’s regional economies. Econ. Res. J. 2010, 5, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L.; Yu, T.S. The intensity of environmental regulation and technological progress of production. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 2, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, L.; Poncet, S. Environmental policy and exports: Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 296–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mulali, U.; Tang, C.F. Investigating the validity of pollution haven hypothesis in the gulf cooperation council (GCC) countries. Energy Policy 2013, 60, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; He, Y.; Wang, B.; Ye, S.S.; Hua, Y.; Ding, L. Efficiency evaluation of atmospheric pollutants emission in Zhejiang Province China: A DEA-Malmquist based approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.L.; Qu, Y.; Tseng, M.-L. The interaction effects of environmental regulation and technological innovation on regional green growth performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-P. Environmental regulations, induced R&D, and productivity: Evidence from Taiwan’s manufacturing industries. Resour. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 514–532. [Google Scholar]
| Pollution Emission Coefficient | Classification | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| > 0.2042 | Heavily polluting industry | Paper products industry, oil processing industry, non-metallic products industry, chemical industry, chemical fiber manufacturing industry, ferrous metal industry, beverage manufacturing industry, textiles industry, non-ferrous metal industry |
| 0.0367 < < 0.2042 | Moderately polluting industry | Food processing industry, pharmaceutical industry, agricultural and sideline processing industry, cultural, educational, and sports products industry, leather products industry, rubber and plastics industry, garment manufacturing industry, metal products industry |
| < 0.0367 | Lightly polluting industry | Tobacco products industry, special-purpose equipment industry, instrument and meter industry, general-purpose equipment manufacturing industry, furniture industry, wood processing industry, printing media industry, communication facilities industry, electrical machinery industry, cardboard manufacturing |
| Indicator | Definition | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Net value of fixed assets (100 million Yuan) | China Industrial Statistical Yearbook |
| Number of employees (10,000 persons) | China Industrial Statistical Yearbook | |
| Energy consumption of industrial sector (Mtce) | China Energy Statistical Yearbook | |
| Desirable outputs | Industrial added value (100 million Yuan) | China Industrial Statistical Yearbook |
| Undesirable outputs | CO2 emissions (Mtce) | China Energy Statistical Yearbook |
| Classification | Industries | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavily polluting industry | Paper products industry | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| Oil processing industry | 1.00 | 0.21 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 | |
| Non-metallic Products industry | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.17 | |
| Chemical industry | 0.34 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.68 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.51 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 0.40 | |
| Chemical fiber manufacturing industry | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.26 | |
| Ferrous metal industry | 0.63 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.68 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 0.65 | |
| Beverage manufacturing industry | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.27 | |
| Textiles industry | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.33 | |
| Non-ferrous metal industry | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Average | 0.40 | |||||||||||
| Moderately polluting industry | Food processing industry | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.27 |
| Pharmaceutical industry | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.40 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.30 | |
| Agricultural and sideline food processing industry | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 0.29 | 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.79 | 0.60 | |
| Cultural, educational, and sports products industry | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.57 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.34 | |
| Leather products industry | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.32 | |
| Rubber and plastics industry | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.18 | |
| Metal products | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.26 | |
| Garment manufacturing industry | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.29 | |
| Average | 0.32 | |||||||||||
| Lightly polluting industry | Tobacco products industry | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Special-purpose equipment industry | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.08 | 0.48 | 0.39 | |
| Instrument and meter industry | 0.20 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 0.40 | |
| General-purpose equipment Manufacturing industry | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.19 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 0.40 | |
| Furniture industry | 1.00 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.46 | |
| Wood processing industry | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| Printing media industry | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.23 | |
| Communication facilities industry | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.90 | |
| Electrical machinery industry | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.82 | 0.68 | |
| Cardboard manufacturing | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.14 | |
| Average | 0.52 | |||||||||||
| Classification | Industries | EC | TC | TFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavily polluting industry | Paper products industry | 0.926 | 1.173 | 1.086 |
| Oil processing industry | 0.924 | 1.195 | 1.104 | |
| Non-metallic products industry | 1.000 | 1.271 | 1.271 | |
| Chemical industry | 0.900 | 1.150 | 1.035 | |
| Chemical fiber manufacturing industry | 0.957 | 1.142 | 1.093 | |
| Ferrous metal industry | 0.869 | 1.227 | 1.066 | |
| Beverage manufacturing industry | 1.027 | 1.089 | 1.119 | |
| Textiles industry | 0.929 | 1.091 | 1.014 | |
| Non-ferrous metal industry | 0.963 | 1.208 | 1.163 | |
| Average | 0.944 | 1.145 | 1.106 | |
| Moderately polluting industry | Food processing industry | 1.044 | 1.083 | 1.130 |
| Pharmaceutical industry | 1.040 | 1.095 | 1.138 | |
| Agricultural and sideline food processing industry | 0.975 | 1.107 | 1.079 | |
| Cultural, educational, and sports products industry | 1.143 | 0.957 | 1.094 | |
| Leather products industry | 0.998 | 0.954 | 0.952 | |
| Rubber and plastics industry | 0.990 | 1.076 | 1.066 | |
| Metal products | 1.054 | 1.054 | 1.111 | |
| Garment manufacturing industry | 1.018 | 1.010 | 1.028 | |
| Average | 1.033 | 1.042 | 1.075 | |
| Lightly polluting industry | Tobacco products industry | 1.000 | 1.188 | 1.188 |
| Special-purpose equipment industry | 1.016 | 1.074 | 1.091 | |
| Instrument and meter industry | 1.033 | 1.012 | 1.046 | |
| General-purpose equipment manufacturing industry | 1.001 | 1.081 | 1.083 | |
| Furniture industry | 1.100 | 0.972 | 1.069 | |
| Wood processing industry | 1.041 | 1.076 | 1.120 | |
| Printing media industry | 1.054 | 1.067 | 1.124 | |
| Communication facilities industry | 1.000 | 1.018 | 1.018 | |
| Electrical machinery industry | 1.041 | 1.045 | 1.087 | |
| Cardboard manufacturing | 0.900 | 1.176 | 1.059 | |
| Average | 1.019 | 1.071 | 1.089 |
| Variables | Coefficients | Variables | Coefficients | Variables | Coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightly polluting industry | Ln(er) | −0.031 * (0.060) | Moderately polluting industry | Ln(er) | −0.194 *** (0.135) | Heavily polluting industry | Ln(er) | 0.204 *** (0.146) |
| Ln(gtrd) | 0.020 ** (0.094) | Ln(gtrd) | 0.359 ** (0.043) | Ln(gtrd) | 0.171 ** (0.140) | |||
| Ln(gt) | 0.003 ** (0.040) | Ln(gt) | 0.138 ** (0.056) | Ln(gt) | 0.021 *** (0.049) | |||
| Ln(errd) | −0.003 * (0.031) | Ln(errd) | 0.065 ** (0.068) | Ln(errd) | 0.061 ** (0.081) | |||
| Ln(rd) | 0.054 * (0.760) | Ln(rd) | 0.352 * (0.333) | Ln(rd) | 0.212 * (0.356) | |||
| Ln(fdi) | −0.247 *** (0.074) | Ln(fdi) | 0.244 ** (0.098) | Ln(fdi) | −0.306 * (0.100) | |||
| _cons | −0.009 ** (0.420) | _cons | −0.547 * (0.906) | _cons | −0.812 ** (1.058) | |||
| Log likelihood | 211.82 | Log likelihood | 312.54 | Log likelihood | −214.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, M.; Shao, Z.; Yang, C.; Tang, X. Analysis of Coordinated Development of Energy and Environment in China’s Manufacturing Industry under Environmental Regulation: A Comparative Study of Sub-Industries. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226510
Cheng M, Shao Z, Yang C, Tang X. Analysis of Coordinated Development of Energy and Environment in China’s Manufacturing Industry under Environmental Regulation: A Comparative Study of Sub-Industries. Sustainability. 2019; 11(22):6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226510
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Manli, Zhen Shao, Changhui Yang, and Xiaoan Tang. 2019. "Analysis of Coordinated Development of Energy and Environment in China’s Manufacturing Industry under Environmental Regulation: A Comparative Study of Sub-Industries" Sustainability 11, no. 22: 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226510
APA StyleCheng, M., Shao, Z., Yang, C., & Tang, X. (2019). Analysis of Coordinated Development of Energy and Environment in China’s Manufacturing Industry under Environmental Regulation: A Comparative Study of Sub-Industries. Sustainability, 11(22), 6510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226510




