A Review of Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa: Lessons from Japan and China Case Projects in Tanzania and Kenya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
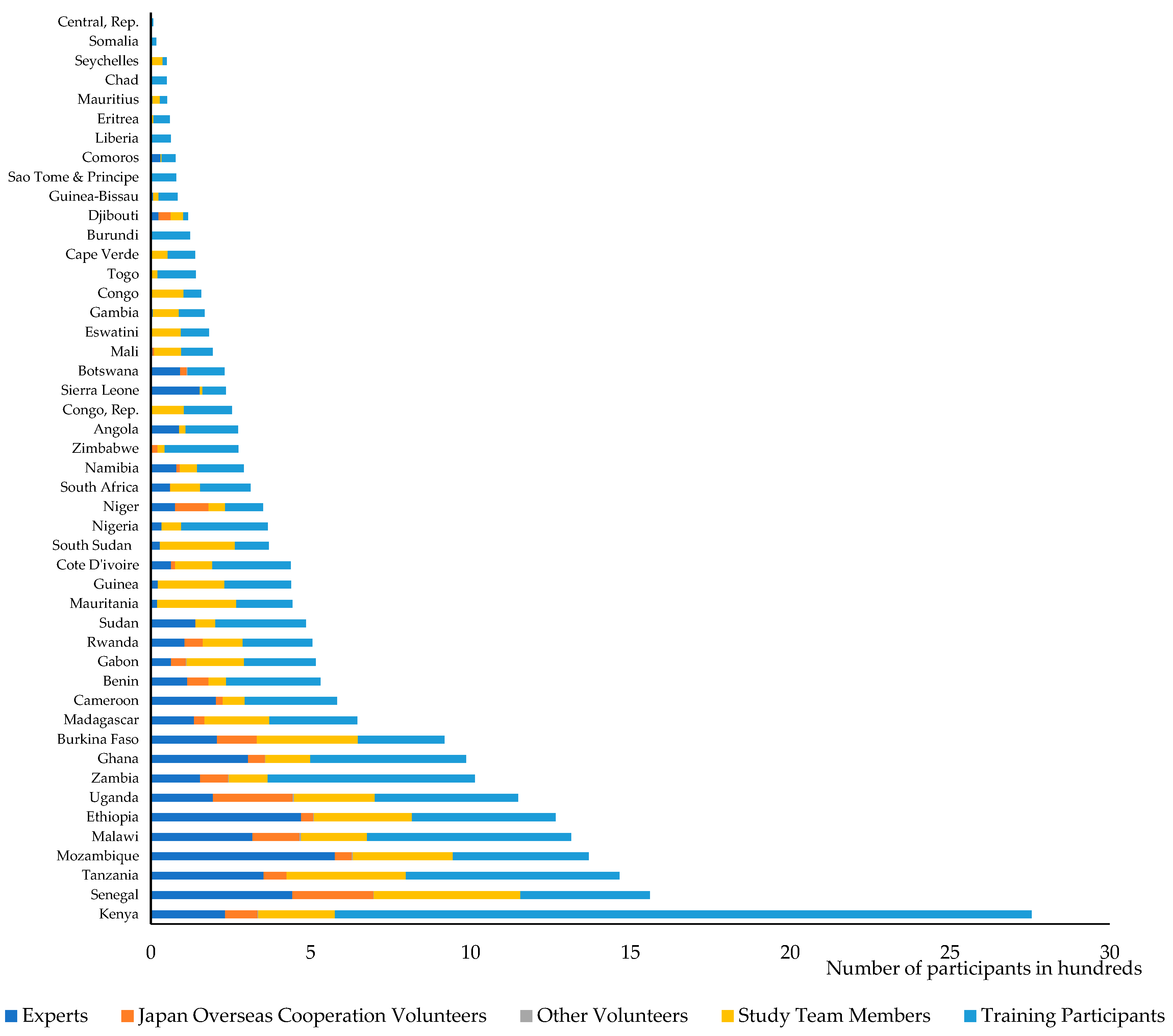
3. Background of China and Japan Participation in Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa
4. Opportunities and Challenges in Agricultural Technical Cooperation Projects
4.1. Case Study 1: Supporting the Adoption of Agricultural Technology Through ATDC in Tanzania
4.2. Case Study 2: Supporting Horticulture Production through SHEP in Kenya
4.3. Case Study 3: Supporting Rice Production through RIDS in Tanzania
5. Success Factors for the Sustainability of Technology Transfer Projects
- Community participation in technical cooperation projects;
- Stakeholders linkages, supports, and commitment to achieve a common objective;
- Perceived benefits of transferred technology in the local community;
- Identification of project environment and nature of agricultural technical project to incorporate sustainability (i.e., nature of technical project versus local environment);
- Fostering autonomy, self-reliance, and utilization of local resources in a technical cooperation project.
5.1. Community Participation in Technical Cooperation Projects
5.2. Stakeholders Linkages, Supports, and Commitment to Achieve a Common Objective
5.3. Perceived Benefits of Transferred Technology in the Local Community
5.4. Identification of the Project Environment and Nature of Agricultural Technical Project to Incorporate Sustainability
5.5. Fostering Autonomy, Self-Reliance, and Utilization of Local Resources in a Technical Cooperation Project
6. Interaction of the Key Success Factors in System Dynamic Complexity
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tefft, J.F.; Jonasova, M.; Adjao, R.T.O.A.; Morgan, A.M. Food Systems for an Urbanizing World: Knowledge Product; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. World Development Report 2008: Agriculture for Development; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The Future of Food and Agriculture: Trends and Challenges; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; ISBN 9789251095515. [Google Scholar]
- Binswanger-Mkhize, H.; McCalla, A.F. The Changing Context and Prospects for Agricultural and Rural Development in Africa. Handb. Agric. Econ. 2010, 4, 3571–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Pingali, P.L. Green Revolution: Impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12302–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, P.; Dercon, S. African Agriculture in 50 Years: Smallholders in a Rapidly Changing World? World Dev. 2014, 63, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurner, T.W.; Zaichenko, S. Technology transfer into Russia’s agricultural sector-Can public funding replace ailing business engagement? Sci. Public Policy 2018, 45, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiane, O. Agriculture and structural transformation in Africa. In Frontiers in Food Policy: Perspectives on Sub-Saharan Africa; Falcon, W.P., Naylor, R.L., Eds.; The Center on Food Security and the Environment, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014; p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Bräutigam, D.; Tang, X. An Overview of Chinese Agricultural and Rural Engagement in Tanzania. IFPRI Discuss. Pap. 2012, 01214. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Badiane, O.; Zhang, L.; Collins, J.; Zhou, Y. China-Africa Agricultural Modernization Cooperation: Situation, Challenges and the Path Ahead; The International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.; Evers, G.; Seevinck, J.; Cherrou, Y.; Micillo, R. Rapid assessment of aid flows for agricultural development in Sub-Saharan Africa. In Investment Centre Division Discussion Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ssozi, J.; Asongu, S.; Amavilah, V.H. The effectiveness of development aid for agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Econ. Stud. 2019, 46, 284–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, C. Flashback: Fifty Years of donor Aid to African Agriculture; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, T.; Pettersson, G.; Van de Walle, N. An Aid-Institutions Paradox? Cent. Glob. Dev. Work. Pap. 2006, 74, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Christiaensen, L.; Demery, L. Agriculture in Africa: Telling Myths from Facts; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 1464811342. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen, S. Japan’s Official Development Assistance to Sub-Saharan Africa: Patterns, Dynamics, and Lessons. In Japan’s Development Assistance; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2016; pp. 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, S. Technology Transfer for Agriculture Growth in Africa; African Development Bank: Tunis, Tunisia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, X.; Hazell, P.; Thurlow, J. The Role of Agriculture in African Development. World Dev. 2010, 38, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEPAD. African agriculture, transformation and outlook; NEPAD (New Partnership for African Development): Johannesburg, South Africa, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins, S.; Keats, S. Leaping and Learning: Linking Smallholders to Markets in Africa; Agriculture for Impact, Imperial College and Overseas Development Institute: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Feder, G.; Savastano, S. Modern agricultural technology adoption in sub-Saharan Africa: A four-country analysis. In Agriculture and Rural Development in a Globalizing World; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- ACET African Transformation Report 2017: Agriculture Powering Africa’s Economic Transformation; The African Center for Economic Transformation (ACET): Accra, Ghana, 2017.
- Otsuka, K. Transforming African Agriculture by Promoting Improved Technology and Management Practices. In Background paper for ACET’s Transforming Africa’s Agriculture; ACET: Accra, Ghana, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Shi, G. Historical Transformation of China’s Agriculture: Productivity Changes and Other Key Features. China World Econ. 2018, 26, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarp, F.; Addison, T. Aid, Growth and Employment. ReCom Position Paper. Available online: http://recom.wider.unu.edu/sites/default/files/Position%20paper%20on%20Aid%2C%20Governance%20and%20Fragility_0.pdf, 2014 (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- World Bank. World Development Report 2013: Jobs; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Kalirajan, K.P. Rice green revolution in asia and its transferability to Africa: An introduction. Dev. Econ. 2006, 44, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Sugihara, K. (Eds.) Paths to the Emerging State in Asia and Africa; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-3130-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hayami, Y.; Ruttan, V.W. Agricultural Development: An International Perspective; The Johns Hopkins Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, N. Foreign aid and development in Africa: What the literature says and what the reality is. J. Afr. Stud. Dev. 2009, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Qi, G.; Tang, L.; Mukwereza, L. Science, Technology, and the Politics of Knowledge: The Case of China’s Agricultural Technology Demonstration Centers in Africa. World Dev. 2016, 81, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, P.; Cooper, T.; Hayward, R.; Neuberger, L. A New Era of Sustainability: UN Global Compact-Accenture CEO Study. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2011, 11, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Agola, N.O. Technology Transfer For Economic Growth In Africa—Why It Matters. In Technology Transfer and Economic Growth in Sub-Sahara African Countries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin/McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; ISBN 007238915X. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C. Managing Organizational Growth and Dynamic Complexity. In Dynamic Performance Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rumeser, D.; Emsley, M. Key Success Factors in Implementing System Dynamics in Project Management: Coping with lack of understanding and trust. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference of the System Dynamics Society, System Dynamics Society, Delft, The Netherlands, 17–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pruyt, E. Using Small Models for Big Issues: Exploratory System Dynamics Modelling and Analysis for Insightful Crisis Management. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference of the System Dynamics Society, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, R.E. An Exploratory System Dynamics Model to Investigate the Relationships between Errors that Occur in Construction Documents in Saudi Arabia and their possible causes. Ph.D. Thesis, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Uriona, M.; Grobbelaar, S.S. Innovation system policy analysis through system dynamics modelling: A systematic review. Sci. Public Policy 2019, 46, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, T.M. A project management causal loop diagram. In Proceedings of the Association of Researchers in Construction Management, ARCOM Conference, London, UK, 5–7 September 2005; pp. 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Tang, L.; Xu, X.; Qi, G.; Wang, H. What can Africa Learn from China’s Experience in Agricultural Development? IDS Bull. 2013, 44, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Harding, A.; Anseeuw, W.; Alden, C. Chinese agriculture technology demonstration centres in Southern Africa: The new business of development. Public Sph. 2016, 7–36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Xu, X.; Mao, X. South-South Cooperation and Chinese Foreign Aid; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9789811320019. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, K. Boosting sustainable agricultural growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Incl. Dyn. Dev. Sub-Sahar. Afr. 2013, 73–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sayanagi, N.R.; Aikawa, J. The Motivation of Participants in Successful Development Aid Projects: A Self-Determination Theory Analysis of Reasons for Participating; JICA-RI Working Papper; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 2016.
- JICA. JICA-CIDA Joint Evaluation Study Report on the Kilimanjaro Agricultural Development Project (KADP) in Tanzania; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 1998.
- Ikegami, K. A study on technology transfer of paddy cultivation in the Kilimanjaro region, Tanzania. Mem. Fac. Agric. Kinki. Univ. 1995, 28, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- JICA. Evaluation report: Donor Assistance to Tanzania; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 2001.
- Ruttan, V.W. Productivity growth in world agriculture: Sources and constraints. J. Econ. Perspect. 2002, 16, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAFC; JICA. Final Report for Kilimanjaro Agricultural Training Centre Phase II Project; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 2006.
- MAFC; JICA. Project for Supporting Rice Industry Development (TANRICE-2) in The United Republic of Tanzania, 1st ed.; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 2013.
- Sato, M. Japanese aid diplomacy in Africa: An historical analysis. Ritsumeikan Annu. Rev. Int. Stud. 2005, 4, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wild, L.; Denney, L. Informing the Future of Japan’s ODA Positioning Japan’s ODA as a Leader in Its Field; The Overseas Development Institute: London, UK, 2011; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M. Policies and Practices of China’s Foreign Aid: A Comparison with Japan. In Japan’s Development Assistance; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2016; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, B.S. Shinzo Abe: Unleashing the Power of ‘Womenomics’. Wall Str. J. 2013, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, V.L. Chinese Expansion in Africa in the Twenty-First Century: Characteristics and Impacts. In Reclaiming Africa; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H. For Inclusive and Dynamic Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: Challenges and Responses; Japan International Cooperation Agency Research Institute: Osaka, Japan, 2013; 429p.
- JICA. JICA’s Activities in Africa: Quality and Empowerment; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Osaka, Japan, 2016.
- JICA. Africa: Take off? A bright new dawn, a major milestone for Africa; The Magazine of the Japan international cooperation agency; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2010.
- Makundi, H. Diffusing Chinese Rice Technology in Rural Tanzania: Lessons from the Dakawa Agro-Technology Demonstration Center; China Africa Research Initiative: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, C.; Vaz, A.; Mukwereza, L. Chinese State Capitalism? Rethinking the Role of the State and Business in Chinese Development Cooperation in Africa. World Dev. 2016, 81, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Sino-Africa Agricultural Cooperation Experience Sharing, Foreign Economic Cooperation Center, Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. In Proceedings of the Agriculture, Food Safety and Rural Development for Growth and Poverty Reduction; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mgendi, G.S.; Mujawamariya, G.; Isinika, A.C. Consumers preference and market segmentation in developing countries: Rice marketing in Tanzania. Retail Mark. Rev. 2018, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- New Markets Lab; SAGCOT. A Legal Guide to Strengthen Tanzania’s Seed and Input Markets; SAGCOT: Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Technology and Knowledge Transfer: A Case Study of China’s Agricultural Technology Demonstration Center in the United Republic of Tanzania. In South-South Cooperation and Chinese Foreign Aid; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ongeri, B.O. Small Scale Horticultural farming along the Kenyan Highways and Local economic development: Exploring the effect of factor prices. Int. Rev. Res. Emerg. Mark. Glob. Econ. 2014, 1, 102–119. [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa, J. Initiatives of SHEP and SHEP UP-Capacity development of small-scale farmers1 for increased responsiveness to market needs. Incl. Dyn. Dev. Sub-Sahar. Afr. 2013, 143–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sayanagi, N.R. Breaking the Poverty Trap: A Psychological Framework for Facilitating Autonomous Motivation and Sustainable Behavioral Change in Development Aid Beneficiaries. J. Int. Dev. Stud. 2017, 26, 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H. Japan and Africa: A Historical Review of Interaction and Future Prospects. Asia-Pac. Rev. 2017, 24, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampiah, K. Japanese aid to Tanzania: A study of the political marketing of Japan in Africa. Afr. Aff. 1996, 95, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOFA. Country Assistance Evaluation of the United Republic of Tanzania: Third Party Evaluation Report 2016; MOFA: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y.; Kajisa, K.; Otsuka, K. On the possibility of rice green revolution in irrigated and rainfed areas in Tanzania: An assessment of management training and credit programs. In Pursuit of an African Green Revolution; Springer: Toyko, Japan, 2016; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki, T. Trends in Farm Economics under the Tanzania-Kilimanjaro Agricultural Development Plan. Natl. Res. Inst. Agric. Econ. 1989. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Information, A.; Record, M. Institutional Repository Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and Programme Design; WEDC: Loughborough, UK, 2002; ISBN 9781843800057. [Google Scholar]
- Enrique, V.; Lorena, R.; Cynthia, A. The Technology Transfer Systems in Communities, Product Versus Processes. Procedia Eng. 2016, 145, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dahiya, B.; Okitasari, M. Partnering for Sustainable Development: Guidelines for Multi-stakeholder Partnerships to Implement the 2030 Agenda in Asia and the Pacific; United Nations University Institute for the Advanced Study of Sustainability (UNU-IAS): Tokyo, Japan; Bangkok, Japan, 2018; ISBN 978-92-808-4580-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, M.; Bryde, D.; Fearon, D.; Ochieng, E. Stakeholder Engagement: Achieving Sustainability in the Construction Sector. Sustainability 2013, 5, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shen, G.Q.; Ho, M.; Drew, D.S.; Chan, A.P.C. Exploring Critical Success Factors For Stakeholder Management In Construction Projects. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2009, 15, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkerhoff, J.M. Government-nonprofit partnership: A defining framework. Int. J. Manag. Res. Pract. 2002, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D. The Guide to Effective Participation; Delta Press: Brighton, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon, C.S. ‘Sustainability’ in ecological economics, ecology and livelihoods: A review. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2000, 24, 521–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, S. Transforming Government and Public Services Portfolio Management; Ashgate: Aldershot, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781409401636. [Google Scholar]
- Kariuki, J.M. Factors Influencing Sustainability of Non Government Organizations Funded Community Projects in Kenya: A Case of Action Aid Funded Project in Makima Location, Embu County. Masters Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tharp, J. Project Management and Global Sustainability What Is Sustainability? In Proceedings of the PMI Global Congress Proceedings, Dallas, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dill, B. Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) and Norms of Participation in Tanzania: Working against the Grain. Afr. Stud. Rev. 2010, 53, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.J.; Ebner, D. Corporate sustainability strategies: Sustainability profiles and maturity levels. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 18, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, C. The Relationship Between IP, Technology Transfer, and Development-Intellectual Property Watch. Available online: https://www.ip-watch.org/2010/08/30/the-relationship-between-ip-technology-transfer-and-development/ (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Giovannucci, D.; Scherr, S.J.; Nierenberg, D.; Hebebrand, C.; Shapiro, J.; Milder, J.; Wheeler, K. Food and Agriculture: The future of sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 21st Century Rep. Rio 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mgendi, G.; Shiping, M.; Xiang, C. A Review of Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa: Lessons from Japan and China Case Projects in Tanzania and Kenya. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236598
Mgendi G, Shiping M, Xiang C. A Review of Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa: Lessons from Japan and China Case Projects in Tanzania and Kenya. Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236598
Chicago/Turabian StyleMgendi, George, Mao Shiping, and Cheng Xiang. 2019. "A Review of Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa: Lessons from Japan and China Case Projects in Tanzania and Kenya" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236598
APA StyleMgendi, G., Shiping, M., & Xiang, C. (2019). A Review of Agricultural Technology Transfer in Africa: Lessons from Japan and China Case Projects in Tanzania and Kenya. Sustainability, 11(23), 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236598



