Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Study Process
2.3. Optimization of the Land Use Quantity Structures Based on the GMDP Model
2.3.1. Objective Functions Setting
2.3.2. Setting the Constraint Conditions
2.4. Optimization of the Spatial Structure of Land Use Based on the CLUE-S Model
2.4.1. Research Scale
2.4.2. Probability Simulation of Land Use Suitability
2.4.3. CLUE-S Model Input Settings
2.5. Optimization of National Land Space Based on Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions Coordination
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Land Use Quantity Structures
3.2. Optimization of the Spatial Structures of Land Use
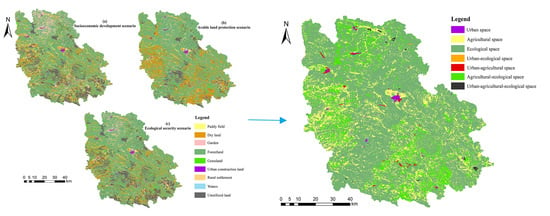
3.3. Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions Coordination
4. Discussion
4.1. Land Use Optimization Methods for Karst Areas
4.2. The Concept of the Coordinated Development of the Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions
4.3. Feasibility Analysis of the Results of National Land Space Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.J.; Wen, Q.K.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. Catena 2016, 137, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiong, K.N. Assessing spatial-temporal evolution processes of karst rocky desertification land: Indications for restoration strategies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S.; Liu, J.W.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, W. Spatial distribution of rock fragments on steep hillslopes in karst region of northwest Guangxi, China. Catena 2011, 84, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cai, Y.L. Multi-scale anthropogenic driving forces of karst rocky desertification in southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Dai, Q.H.; Yuan, Y.F.; Peng, X.D.; Zhao, L.S.; Yang, J. Effects of rainfall intensity on runoff and sediment yields on bare slopes in a karst area, SW China. Geoderma 2018, 330, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Y.; Chen, H.S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.X.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.L. Subsurface flow in a soil-mantled subtropical dolomite karst slope: A field rainfall simulation study. Geomorphology 2015, 250, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Wang, K.L.; Yue, Y.M.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Liao, C.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cai, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, Q.; Yang, X. Effect assessment of the project of grain for green in the karst region in Southwestern China: A case study of Bijie Prefecture. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3255–3264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.K.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.H. Effectiveness of ecological restoration projects in a karst region of southwest China assessed using vegetation succession mapping. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.M.; Li, J.; Yue, T.X.; Zhou, X.; Lan, A.J. Scenarios of land cover in Karst area of southwestern China. Enviorn. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6407–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, H.; Zhong, T.Y. Environmental effects of land-use/cover change caused by urbanization and policies in southwest China Karst area-a case study of Guiyang. Habitat. Int. 2014, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of catchment properties on runoff coefficient in a karst area of southwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Zhang, F.W.; Jiang, Z.C.; Yuan, D.X.; Jiang, Y.J. Assessment of water resource carrying capacity in karst area of Southwest China. Enviorn. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, G.H.; Yuan, D.X.; Polk, J.S. Evolution of major environmental geological problems in karst areas of Southwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Jiang, Z.C.; Yuan, D.X.; Ma, Z.L.; Xie, Y.Q. Temporal and spatial changes of karst rocky desertification in ecological reconstruction region of southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4483–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; He, T.; Chen, H.; Peng, W.; Song, T.; Wang, K.; Lin, D. Impacts of vegetation restoration strategies on soil organic carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a karst area, southwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Li, L.L.; Groves, C.; Yuan, D.; Kambesis, P. Relationships between rocky desertification and spatial pattern of land use in typical karst area, Southwest China. Environ Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.J. Effect of different land use/land cover on karst hydrogeochemistry: A paired catchment study of Chenqi and Dengzhanhe, Puding, Guizhou, SW China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.L.; Weng, Q.H. The impact of land use and land cover changes on land surface temperature in a karst area of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; van de Steeg, J.; Veldkamp, A.; Willemen, L. From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Jin, M.J.; Duan, Z.Y.; Gong, Y.X.; Liu, Y. Examining the effect of land-use function complementarity on intra-urban spatial interactions using metro smart card records. Transportation 2019, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Galler, C.; Von, H.C.; Albert, C. Optimizing environmental measures for landscape multifunctionality: Effectiveness, efficiency and recommendations for agri-environmental programs. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolozzi, R.; Morri, E.; Santolini, R. Delphi-based change assessment in ecosystem service values to support strategic spatial planning in Italian landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, W.; Huelsmann, W.; Marty, M.; Penn-Bressel, G.; Bobylev, N. Climate protection and compact urban structures in spatial planning and local construction plans in Germany. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Li, X. MFOZ planning of Dongguan based on spatial autocorrelation by using genetic algorithms. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 349–357. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. The scientific foundation of major function-oriented zoning in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 339–350. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.R. Classification evaluation and spatial-temporal analysis of “production-living-ecological” spaces in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1290–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.M.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, J.Y. Spatiotemporal patterns of multi-functionality of land use in northeast China. Prog. Geogr. 2016, 35, 232–244. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Dong, Y.X. Spatial differences and influencing factors of land use function in Guangzhou. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 2179–2192. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nian, P.H.; Cai, Y.M.; Xie, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.X.; Ma, S.F. Geographical space comprehensive function zoning in Hunan Province nased on niche theory. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 1958–1968. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.B.; Niu, S.W.; Shi, P.J.; Guo, X.D. The functional zoning of territorial space and the developmental pattern of future space-based on the framework of the major function oriented zoning. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 68–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C.; Lin, H.X.; Qi, X.X. A literature review on optimization of spatial development pattern based on ecological-production-living space. Prog. Geogr. 2017, 36, 378–391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Jin, X.; Gan, L.; Jessup, L.H.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Yang, X.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatial identification and dynamic analysis of land use functions reveals distinct zones of multiple functions in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, J.C.; Lin, Z.L. Conflict or coordination? Assessing land use multi-functionalization using production-living-ecology analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 577, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Yan, J.M.; Chen, H. Land consolidation function unit demarcation based on optimization of production, living and ecology space in peri-urban areas. Trans. CSAE 2018, 34, 243–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Feng, X.M.; Wu, A.B.; Li, R.H. Simulation and optimization of multi-objective land use pattern based on the CLUE-S model: A case study of the three northern counties of Langfang in Hebei Province. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 34, 92–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.C.; Ko, T.T. An interactive dynamic multi-objective programming model to support better land use planning. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, N.; Farahani, R.Z.; Bajgan, H.R.; Sajadieh, M.S. Developing model-based software to optimise wheat storage and transportation: A real-world application. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zeng, Y.N.; Jin, X.B.; Shu, B.R.; Zhou, Y.K.; Yang, X.H. Simulating multi-objective land use optimization allocation using Multi-agent system—A case study in Changsha, China. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Z.; Kang, M.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J. Optimization of land use structure and spatial pattern for the semi-arid loess hilly-gully region in China. Catena 2010, 81, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lv, L.N. A spatiotemporal model ofland use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. Ecol. Model. 2012, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.G.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modelling the potential impacts of urban ecosystem changes on carbon storage under different scenarios by linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.Y.; Hu, Y.C. Assessing temporal-spatial land use simulation effects with CLUE-S and Markov-CA models in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32231–32245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, J. Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ren, X.Y.; Che, Y.; Yang, K. A Coupled SD and CLUE-S model for exploring the impact of land use change on ecosystem service value: A Case Study in Baoshan District, Shanghai, China. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeman, J.; Baysal, G.; Bulley, H.N.N.; Fürst, C. Assessing driving forces of land use and land cover changes by a mixed-method approach in northern-eastern Ghana, West Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 411–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, Q.F.; Liu, J.F. Identification and apportionment of the drivers of land use change on a regional scale: Unbiased recursive partitioning-based stochastic model application. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 217, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; Ladet, S.; Coqué, N.; Gibon, A. Agricultural land-use change and its drivers in mountain landscapes: A case study in the Pyrenees. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Mas, J.F.; Galicia, L. Evaluating drivers of land-use change and transition potential models in a complex landscape in Southern Mexico. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1804–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Lei, K.; Khu, S.; Meng, W.; Qiao, F. Assessment of water environmental carrying capacity for sustainable development using a coupled system dynamics approach applied to the Tieling of the Liao River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Yang, H.C.; Yang, Z.W. Quantitative assessment of resources and environmental carrying capacity in the northwest temperate continental climate ecotope of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Fan, J. Evaluation and analysis of provincial differences in resources and environment carrying capacity in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.M.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.T. Index system of urban resource and environment carrying capacity based on ecological civilization. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 68, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.P.; Li, B.X.; Wang, Y.P.; He, K. Study on temporal and spatial coupling coordination of urbanization and water-soil resources of grain production. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 145–152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Land use ecological risk evaluation in three gorges reservoir area based on normal cloud model. Trans. CSAE 2014, 30, 289–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.Y.; Meng, J.J.; Xiang, Y.Y. Cellular automata-based modelfor developing land use ecological security patterns in semi-arid areas: A case study of Ordos, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, A.R.; Schumchenia, E.J. Toward wind farm monitoring optimization: Assessment of ecological zones from marine landscapes using machine learning algorithms. Hydrobiologia 2015, 756, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, H.; Bardgett, R.D.; Birkhofer, K.; Brady, M.; Byrne, L.; de Ruiter, P.C.; de Vries, F.T.; Gardi, C.; Hedlund, K.; Hemerik, L.; et al. Urban and agricultural soils: Conflicts and trade-offs in the optimization of ecosystem services. Urban Ecosyst. 2014, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.J.; Guo, P.; Li, M.; Guo, S.S.; Zhang, F. A multi-risk assessment framework for agricultural land use optimization. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Nastaran, M.; Sahebgharani, A. Development, application, and comparison of hybrid meta-heuristics for urban land-use allocation optimization: Tabu search, genetic, GRASP, and simulated annealing algorithms. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 60, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjo, P.S.; Lauri, J.; Heikki, L.; Jaana, S.; Eija, H.; Samantha, W.; Mika, K.; Eetu, P. Land use optimization tool for sustainable intensification of high-latitude agricultural systems. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.S.; Guan, X.L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y. Land resources allocation strategies in an urban area involving uncertainty: A case study of Suzhou, in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Environ. Manag. 2014, 53, 894–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Avraamidou, S.; Xiao, X.; Pistikopoulos, E.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y.; Song, F.; Yu, J.; Zhu, M. A food-energy-water nexus approach for land use optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, B.Y.; Huang, J.; Li, S.C. Optimal allocation of land use types in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration based on ecological and economic benefits trade-offs. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 26–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cobuloglu, H.; Büyüktahtakin, I. Food vs. biofuel: An optimization approach to the spatio-temporal analysis of land-use competition and environmental impacts. Appl. Energy 2015, 140, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, M.X. Mining spatial information to investigate the evolution of karst rocky desertification and its human driving forces in Changshun, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakanjac, V.R.; Stevanović, Z.; Stevanović, A.M.; Vakanjac, B.; Marina, C.I. An example of karst catchment delineation for prioritizing the protection of an intact natural area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7643–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrič, M.; Kogovšek, J. Identifying the characteristics of groundwater flow in the Classical Karst area (Slovenia/Italy) by means of tracer tests. Environ Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šturm, T.; Podobnikar, T. A probability model for long-term forest fire occurrence in the Karst forest management area of Slovenia. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2017, 26, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achurra, A.; Rodriguez, P. Biodiversity of groundwater oligochaetes from a karst unit in northern Iberian Peninsula: Ranking subterranean sites for conservation management. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, K.; Breuer, L.; Frede, H.G. Parameter uncertainty and the significance of simulated land use change effects. J. Hydrol. 2003, 273, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Tabeau, A.; Hatna, E. Assessing spatial uncertainties of land allocation using a scenario approach and sensitivity analysis: A study for land use in Europe. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 127, S132–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestele, R.; Alexander, P.; Rounsevell, M.; Arneth, A.; Calvin, K.; Doelman, J.; Eitelberg, D.A.; Engström, K.; Fujimori, S.; Hasegawa, T.; et al. Hotspots of uncertainty in land use and land cover change projections: A global scale model comparison. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3967–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Xu, Q.; Guo, Y.Q. Temporal and spatial evolution of the coupling Coordinated development between tourism resources development and ecological environment in China. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 233–240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.S.; Yuan, X.L.; Cheng, X.X.; Mu, R.M.; Zuo, J. Coordinated development of energy, economy and environment subsystems-A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.F.; Yu, D.Y. Optimization schemes for grassland ecosystem services under climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.J.; Shen, L.Y.; Zhou, L. Empirical study on the contribution of infrastructure to the coordinated development between urban and rural areas: Case study on country road projects. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Konur, D.; Schaefer, B. Economic and environmental comparison of grouping strategies in coordinated multi-item inventory systems. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2016, 67, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zhu, Z.S.; Fan, Y.J. The impact of environmental regulation on the coordinated development of environment and economy in China. Nat. Hazards 2018, 91, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Li, S.N.; Tan, K.; Miao, P.P.; Pu, J.W.; Lu, F.F.; Wang, Q. Land use optimization of plateau lake basin based on town-agriculture-ecological spatial coordination. Trans. CSAE 2019, 35, 296–307. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baró, F.; Palomo, I.; Zulian, G.; Vizcaino, P.; Haase, D.; Gómez, B.E. Mapping ecosystem service capacity, flow and demand for landscape and urban planning: A case study in the Barcelona metropolitan region. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, H.L. Land use transition and land management. Geogr. Res. 2015, 35, 1607–1618. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Qiu, J.L.; Hong, Q.; Chen, L. Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Wang, K.-L.; Liu, B.; Li, R.; Jiao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M.-Y. Spectral indices for estimating ecological indicators of karst rocky desertification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, I.; Soga, M.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Land sparing is crucial for urban ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Classification | Land Use Type | Land Function Type | Dominant Function Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paddy field | Agriculture-ecology | Agriculture |
| 2 | Dry land | Agriculture-ecology | Agriculture |
| 3 | Garden | Agriculture-ecology | Agriculture |
| 4 | Forestland | Agriculture-ecology | Ecology |
| 5 | Grassland | Ecology-agriculture | Ecology |
| 6 | Urban construction land | Urban | Urban |
| 7 | Rural settlement | Agriculture-urban | Agriculture |
| 8 | Waters | Ecology-agriculture | Ecology |
| 9 | Unutilized land | Ecology-agriculture | Ecology |
| Classification | Land Use Types | Scenario Modes | Current Situation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic Development | Arable Land Protection | Ecological Security | |||
| 1 | Paddy field | 295.52 | 184.20 | 196.04 | 387.19 |
| 2 | Dry land | 1034.88 | 1504.28 | 983.4 | 1133.03 |
| 3 | Garden | 670.84 | 373.96 | 373.96 | 363.45 |
| 4 | Forestland | 4321.00 | 4424.80 | 4893.78 | 4113.66 |
| 5 | Grassland | 141.72 | 231.56 | 141.72 | 569.75 |
| 6 | Urban construction land | 52.35 | 51.17 | 51.17 | 58.72 |
| 7 | Rural settlement | 63.27 | 61.85 | 61.85 | 94.16 |
| 8 | Waters | 32.15 | 49.38 | 49.38 | 25.29 |
| 9 | Unutilized land | 1118.36 | 848.89 | 978.79 | 984.84 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Pu, J.; Miao, P.; Wang, Q.; Tan, K. Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6752. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236752
Zhao X, Li S, Pu J, Miao P, Wang Q, Tan K. Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6752. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236752
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaoqing, Sinan Li, Junwei Pu, Peipei Miao, Qian Wang, and Kun Tan. 2019. "Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6752. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236752
APA StyleZhao, X., Li, S., Pu, J., Miao, P., Wang, Q., & Tan, K. (2019). Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China. Sustainability, 11(23), 6752. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236752