Abstract
Prior research of knowledge sharing between firms mainly focuses on enabling factors, such as benefits resulting from knowledge sharing, leading to an overlook at barriers. Guided by transaction cost economics and social exchange theory, our study constructed an evolutional game model to analyse the dynamic evolution process of the firm’s knowledge sharing behaviour in a setting of supply chain networks. Using a simulation in our game model, we firstly reveal how a long-term strategy for supply chain partners towards knowledge sharing is determined through reaching an equilibrium between enabling factors (revenue gained in various forms) and impeding factors (knowledge leakage) in a dynamic process. Secondly, our analysis demonstrates that the competition or rivalry side of the “co-opetition” relationship acts as the major barrier for knowledge sharing due to the sharer’s concern of knowledge leakage. Thirdly, our model has identified knowledge relevancy as the inherent property of knowledge and the firm’ ability of knowledge inference as two important factors influencing knowledge leakage.
1. Introduction
Supply chain management (SCM) plays a critical role for the modern economy [1], in which individual firms become highly interdependent within supply chain (SC) networks, so that business competition increasingly occurs at a SC level, rather than an individual firm level [2]. Thus, effective SCM has gained extensive attention. According to the knowledge-based view of the firms, knowledge including technology and information, is an important type of firm resource for creating sustainable competitive advantages [3], and knowledge alignment (KA) is thought to be an effective competition strategy [4], so knowledge alignment, knowledge sharing (KS), and mutual learning among SC members have become hot topics of SCM [3,4]. It has been proven that sharing valuable knowledge could help the SC as a whole to build up its competitive advantages by promoting efficient SC coordination [5,6,7]. An effective process of knowledge flow and KS among SC partners could streamline flows of information, money, and products across organizational boundaries, and thus equip the SC with agility, adaptability, and alignment [8]. Meanwhile, from the perspective of manufacturers in supply chains, sharing external knowledge with supply chain members would not only help manufacturers to gain product and customer service quality-based (PCSQ-based) competitive advantages [4], but also enhance mutual learning, understanding, and expectations between supply chain members, leading to the establishment of a jointly-held knowledge base and the creation of collaborative revenues [9]. The Japanese car maker Toyota provides a good example of revenues gained from KS [10]. Toyota shared valuable knowledge with its suppliers, resulting in revenues to all parties in the SC by creating sustainable resources and establishing competitive advantages. Moreover, through smoothing communication processes, knowledge sharing can also play a crucial role in improving relational capabilities with supply chain members, thus support inter-organizational learning practice and enabling the development of absorptive capacity [11].
On the other hand, SC members are in a co-opetition relationship, in which cooperation and competition coexist [12]. Treating SC partners as potential competitors within such a co-opetition relationship, firms tend to be unwilling to share their knowledge and would take actions to prevent the leakage of their core knowledge from opportunistic behaviour of their partners [13], because sharing core or confidential knowledge would lead to a loss of competitive advantages, given the risk of knowledge leakage [14]. However, the existing research mainly focuses on examining factors enabling inter-organizational KS [15,16,17,18]. For example, studies have identified inter-organisational relationships, institutional orientations [5], power [19], and trust [14,20] as enablers of KS. A common feature of these studies is that they are built upon the same assumption that firms are willing to share their knowledge. As a result, this stream of research tends to overlook barriers to KS and thus fails to answer the critical question of what factors influence the firm’s willingness/unwillingness of KS.
More specifically, risk of knowledge leakage acts as one of the most important determinants in decision-making for KS [21]. However, few studies have examined factors influencing knowledge leakage and quantitatively assessed leakage risk, although prior research suggests that knowledge possessed by upstream–downstream SC members tends to have a certain level of relevancy and complementarity, leading to risk of knowledge leakage because the partner firms have the ability to infer the private knowledge of a focal firm [21,22,23]. Moreover, efficient KS among SC members would lead to an increase of the probability in which a focal firm’s confidential information being passed through the SC, resulting a higher occurrence of knowledge leakage [21]. Prior research also suggests that the necessity to exchange proprietary information with others would compromise the organisations’ ability to contain information [24]. Therefore, firms must take factors of knowledge property and risk of knowledge leakage into consideration when marking decisions regarding KS.
Build upon the prior research, our study aims to address the research gap by drawing potential influencing factors from two approaches of transaction cost economics and social exchange theory, and by conducting a modelling analysis of the firm’s KS strategies. Our study contributes to the literature in multiple ways. First, we develop an evolutionary game model on KS by quantitatively analysing firm strategies for various KS levels under different scenarios. In our conceptual model, firms’ KS behaviour is based on four key motivating and deterring factors of revenue, leakage risk, reward, and penalty. More specifically, revenue concept is measured by four dimensions of initial revenue (with no KS), direct revenue gained from KS, synergy revenue of knowledge fusion, and incentive revenue with KS. Leakage risk is addressed in the model by assessing two factors of knowledge relevancy and knowledge inference ability. By integrating these influencing factors within a game theoretical framework, our study examines individual and joint effects of these factors on the firm’s development of the evolutional stable KS strategy. Second, while strongly focusing on enabling factors [25], prior research tends to be less concerned with internal barriers that may hamper efficient KS [26]. Our conceptualisation of KS is able to overcome this shortcoming by treating the competition or rivalry side of the co-opetition relationship as the major barrier for KS due to the sharer’s concern of knowledge leakage. Third, our model has identified and simulated two important factors influencing knowledge leakage of knowledge relevancy as the inherent property of knowledge and the firm’ ability of knowledge inference. Furthermore, by proving equilibrium solutions for the firm’s KS behaviour under different feasibility conditions, our study develop a number of propositions with the aim of helping theory-building for KS and provides managerial implications for management executives and policy makers.
The rest of this paper is organized as the following. Section 2 provides a theoretical foundation by introducing KS concept, theoretical approaches, and the game modelling. Section 3 constructs the evolutionary game model by describing model assumptions, defining influencing factors, and discussing the evolutionary stable KS in the model. Section 4 presents a simulation analysis and results discussion, illustrating individual and concurrent effects of influencing factors; theoretical and managerial implications are also discussed. Section 5 presents concluding remarks, research limitations and future research directions.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. KS in SCs
Knowledge is defined as the skill, intuition and experience that can influence decision making [18]. Following resource-based view [27], knowledge can be regarded as a type of intangible firm resources, such as reputation, employee know-how and organizational culture [28]. Knowledge is classified into two types of explicit knowledge and tacit knowledge. While explicit knowledge, also known as “hard” knowledge, such as numbers, words, data and manuals, can be relatively easily codified and transferred. Tacit knowledge, also known as “soft” knowledge, such as insights, intuitions and hunches, is difficult to codify, transmit or convey. It is slow and costly process and with high uncertainty to transfer such tacit knowledge [18,29,30]. Following knowledge-based theory, the firm is conceptualized as an institution for integrating knowledge, and there are five characteristics of knowledge utilization: transferability, capacity for aggregation, appropriability, specialization in knowledge acquisition and knowledge requirements of production [29]. Our research is based on the first three characteristics, as they are closely related to three basic assumptions of our KS model: (1) knowledge is transferrable, and thus there is KS behaviour; (2) knowledge capacity can be calculated with certain criteria, as knowledge can be accumulated and quantified; and (3) knowledge is imitable or reproducible, and thus a firm can be cautious of being involved in KS due to potential knowledge leakage.
Knowledge sharing is defined as a process for individuals or organizations to mutually exchange their knowledge and further create new ones [18]. A collaborative SC involves seven areas of operational functions such as: design and development, pre-sales, sales, manufacturing, distribution, service and support, and finance. Knowledge sharing can occur in every functional area of the SC process [31]. Knowledge sharing in a SC occurs at the inter-organizational level and is regarded as a means by which organizations gain access to their own and other organizations’ knowledge [17]. Prior research suggests that KS occurs at different levels, such as the operational, or strategic level, and that a high level of KS is associated with strong willingness of involved SC parties to share knowledge with a high level of importance and confidentiality [32,33]. In a SC relationship, output from one firm is normally used as the input for another firm. Strength of KS in a vertical relationship of a SC lies in functional complementarities among SC partners, which leads to a high extent of interdependence [34]. Knowledge sharing in an SC involves activities of exchanging or transferring knowledge between firms either upstream or downstream with the aim to develop new capabilities for effective business operations. Supply chain networks, which usually feature knowledge diffusion among SC members, can help firms to build routines with other partners in order to improve their abilities and adopt new practices via the learning process [35]. Furthermore, greater interdependence between SC functional areas would increase the need for data sharing, facilitating cooperation among SC members [36]. Thus, KS is not only required by the need to coordinate SC activities among SC members, but more importantly, it is the effective means to create new knowledge by extending the existing knowledge or to exploit the existing knowledge in a better way [37].
Prior research suggests that knowledge transfer in a SC is a continuous process, including steps such as knowledge acquisition, internalization, and utilization [34]. Individual firms in the SC can act as knowledge sharer and recipient at the same time. While the knowledge sharer mainly focuses on the supply side of knowledge management, the knowledge recipient tends to pay more attention to knowledge creation on the demand side [7,16].
2.2. Factors Influencing Willingness for KS
Prior research tends to focus on revenues generated from KS and factors influencing the success of KS [14,16,17,18]. More specifically, Cummings [17] has identified five primary contexts that can affect successful implementation of KS: relationship between the source and the recipient, form and location of the knowledge, the recipient’s learning predisposition, the sharer’s knowledge-sharing capability, and the broader environment in which the sharing occurs. Nooshinfard and Nemati-Anaraki [18] have classified influential factors of KS into three levels: individual level (such as trust, perception, attitude, communication and cooperation, and motivation), organizational level (such as management support, reward structure, organisational culture, organisational structure), and technological level (such as social networks, availability of information and communication technology (ICT)) [18].
However, while prior research is largely built on the assumption that firms in a SC have willingness to share knowledge, this assumption itself needs to be addressed by examining factors and conditions under which a firm within a SC is willing to share its knowledge with SC partners. Thus, two related questions need to be answered. First, what factors enable SC partners to be willing to share their knowledge? Second, what factors act as barrier for the firm to share knowledge with SC partners?
Two theoretical approaches of transaction cost economics and social exchange theory are helpful to answer these questions. The neo-classic economics suggests that firms are motivated by a pursuit of profit maximization [38]. Following transaction cost economics, individual firms in a SC would try to minimise their transaction costs by developing the best strategy when pursuing profit maximization [39,40]. Contractual mechanism is a widely used strategy to avoid opportunistic behaviour when being involved with external transactional partners. In this case, through signing complete and detailed contracts, firms are able to protect their own benefits against potential risks and uncertainties rising from opportunistic behaviour of transactional partners [39].
Knowledge sharing has a positive effect on firm performance, either directly or indirectly [10,18,41]. Thus, firms are willing to share their knowledge to increase profits or decrease costs. On the other hand, a firm can also be rather cautious and treat KS as a strategically important decision, especially when the knowledge is related with its core competence [42].
In a SC network, individual firms cooperate and compete with each other, forming a co-opetition relationship [12]. In such a co-opetition relationship, risk of knowledge leakage becomes a major barrier for KS [42,43,44,45]. Within a vertical SC relationship, manufacturers are likely to treat their suppliers as potential competitors (e.g., bargaining for material prices, inventory allocations, and specific investments), and thus unwilling to share knowledge given their concern of knowledge leakage, especially when the knowledge is related with their core competence [13,46,47]. Prior research has distinguished direct leakage and inferred leakage as two types of information/knowledge leaking [48]. In the former case, confidential information is mistakenly shared with partners, while in the latter case, confidential information is inferred from non-confidential, shared and fragmented information. Given the risk of knowledge leakage, importance of knowledge protection has been emphasised [49], resulting in a dilemma facing SC members with respect to KS and knowledge protection [50,51].
While transaction cost economics emphasises the maximisation of economic benefits through contractual mechanisms, social exchange theory focuses on the importance of relational mechanisms through trust, commitment and relational norms [52]. Following the social exchange approach, a critical condition for KS would be the establishment of trust between sharing parties [7,53], as inter-organisational trust would be able to encourage information sharing [54,55], to create value through negotiations [56], and to generate familiarity between partners through interpersonal interactions and social exchange [54,56]. Shared goals, relational embeddedness, and influence strategies have been identified as major relational antecedents of inter-organisational trust, which in turn diminishes the probability of opportunistic behaviour, strengthens social bonds between SC partners and secures exchange benefits [20]. Thus, based on social exchange theory, building mutual trust and relational norms between partners would reduce risk associated with KS [14].
Based on social exchange theory, sharing values and goals are also helpful to facilitate the process beneficial to KS. Shared values would enable exchange partners to build up common beliefs in judgement about important or unimportant, appropriate or inappropriate, and right or wrong regarding behaviour, goals and policies [57]. Shared goals increase capability exchange partners to predict and assess the counterparty’s motivations and intentions with respect to business relationships, which direct interactions between SC members and motivate them to contribute, share and combine their intellectual capital [58]. In turn, expected value creation can be realized through collaborative resource sharing. Thus, it is suggested that the more SC partners share common goals, the more favourable will the attitude of SC members be toward KS [18].
Based on two theoretical approaches of transaction cost economics and social exchange theory, our study identifies a number of factors and examines their effects on the behaviour of inter-organizational KS. Instead of assessing individual effects of these influencing factors, we focus on various scenarios regarding the dilemma facing firms on whether or not to share knowledge. More specifically, through a game modelling analysis, our study assesses the firm’s strategy on KS by exploring the facilitating role played by benefits generated from knowledge-sharing and the deterring role played by knowledge leakage risk.
2.3. Application of Game Theory to Analyse KS in SC Relationships
Game theory is about mathematical models of conflict and cooperation between intelligent, rational decision-makers based on economic theories [59]. Prior research has applied game models to analyse inter-organisational relationships involved in SCM. For example, the Nash Bargaining approach was adopted to investigate the effects of trust, coordination, co-learning and co-innovation on collaborative product development (CPD), leading to optimal strategies under different conditions [60]. By constructing a framework with a queuing game and an economic order quantity game, research suggests that benefits generated from scale economies provide strong motivations for firms to be involved in outsourcing [61].
Prior research has also adopted game theory to develop firm strategies for KS. Through building a dynamic game model of KS, Erkal and Minehart [62] examined the impact of inter-firm competition on collaborative behaviour in R&D cooperation. By using evolutionary game model, Liu, et al. [53] analysed the best knowledge-sharing strategies for firms to be engaged in SC collaborative innovation. Through developing a game model for knowledge-sharing strategies at the interpersonal level, Ho, et al. [59] assessed the dynamics of individual behaviour within organizations in terms of KS.
Built upon the prior research, our study derives an evolutionary game model to address the research gap of KS in a SC relationship. Applying the classic game theory and ecological theory, evolutional game modelling provides an effective analytic tool to investigate strategic decision-making behaviour of individuals and/or organisations with bounded rationality. Its principles match well with our research task in analysing KS strategy. Under the condition of bounded rationality, it is unlikely or even impossible for a participant to find the best strategy in a game. The game participants are able to improve their decision-making in selecting an optimum strategy by learning from repeated scenarios in the past. When all parties have improved their strategies, a stable result in the game named Evolutionary Stable Strategy (ESS) is reached [53,63].
3. Model Descriptions and Assumptions
3.1. Model Assumptions and Variables
Our model is built upon a number of assumptions:
Assumption 1 (Participants): To simplify our model setting, we assume that two firms (Firm 1 and Firm 2) in a vertical SC relationship, which can be either manufacturer, supplier, subcontractor, or retailer, play one or more roles in the complex supply network.
Assumption 2 (Context): These two firms cooperate with each other due to their common interests, but they also compete with each other given their different business interests and objectives. Following prior research, KS is assessed as a process of social exchange [64]. Within this context, a firm sharing knowledge is named as knowledge sharer, while a firm receiving knowledge is called knowledge recipient. Each firm has two options in selecting its strategy either of KS or no KS (NKS). Two problems associated with KS can affect the sharer’s willingness to share. The first is free-riding, which occurs when a firm uses the sharer’s knowledge but is reluctant to share its own knowledge. Another is knowledge leakage. A firm can possess some confidential knowledge, which the firm would not like to share with external transaction partners, especially with potential competitors. However, a potential knowledge recipient could get access to the confidential knowledge through collecting, analysing, and acquiring relevant information regarding the confidential knowledge, resulting in knowledge leakage.
Assumption 3 (Information structure): It is an incomplete information game based on bounded rationality. As a firm cannot fully know payoff functions and options of its transaction partner regarding KS. The firm is aware of its own knowledge capacity, the confidential level of its knowledge, and thus its decision-making regarding KS will be based on the total payoff. Moreover, the payoff function of the firm is contingent on the knowledge-sharing behaviour of its transaction partner.
Assumption 4 (Knowledge properties): Following Reference [51], we assume that the shared knowledge, either explicit or tacit, is an objective entity or an objective commodity that can be shared, leaked and managed. Thus, knowledge in our model is measurable, quantifiable and can be accumulated and aggregated.
Our model includes a number of variables, which are assumed as being real numbers and having non-negative values. We define these variables as below.
π1, π2: Initial revenue. It is the benefit gained by two firms under the condition of normal operations with no KS. This is a dormant situation of neither sharing knowledge nor using shared knowledge.
k1, k2: Knowledge capacity. It refers to the maximal quantity of sharable knowledge that can be shared, such as order information, operational knowledge, and strategic knowledge. Respectively, there is private knowledge or sensitive knowledge [43], such as customer information, and competitive knowledge, which a firm would not like to share.
α1, α2: Knowledge-sharing index. It denotes the proportion of knowledge that two firms choose to share. The range of α1, α2 is between (0, 1). The knowledge-sharing level is defined as knowledge-sharing index multiplying knowledge capacity, which can be recorded as kiαi. It is proved that the higher knowledge-sharing level of the focal firm is, the higher revenue it would gain accordingly, but the higher knowledge leakage risk would be [43].
β1, β2: Direct revenue coefficient of KS. This is the effect variable of two firms’ knowledge absorption and transformation. Knowledge sharing means that knowledge is not only accessible to both sides, but also accepted by the recipient [65]. This variable represents maximal revenue when the knowledge in full capacity is shared. Revenue is a motivator for KS. For firm i, direct revenue from actual KS is related to the knowledge quantity kjαj shared by firm j. The larger kjαj is, the greater the knowledge absorption and transformation effect would be. The direct revenue of firm i with its partner sharing knowledge is labeled as kjαjβi.
λ1, λ2: Synergy revenue coefficient of KS. It refers to the additional benefits generated from knowledge creation when the sharable knowledge of two parties is shared in full capacity. In a process of knowledge transfer and absorption, parties may incur additional new knowledge based on knowledge fusion, and accordingly there would be reciprocal benefits created by knowledge fusion. Synergy revenue coefficient is affected by knowledge-sharing. At a particular knowledge-sharing level, the synergy revenue of firm i can be labelled as kj αj βi λi.
η1, η2: Reward coefficient of KS. Prior research suggests that firms are motivated by economic and social reward as incentives to share knowledge [66]. The incentives include both monetary rewards and intrinsic rewards that are associated with social motivations. To simplify the model, the reward coefficient represents both economic and social rewards. Incentive revenue of KS is positively associated with KS level. That is, the higher of KS level is, the greater the incentive revenue would be. Incentive revenue for firm i can be designed as kiαiηi.
δ1, δ2: Knowledge relevancy. It is defined as the correlation between shared knowledge and confidential/private knowledge, and it is a major indicator for the risk of knowledge leakage. Knowledge (both explicit and tacit) can be described in formal methods, such as algebra, logic and set theory, or with informal methods, such as tables, graphs and even natural languages. The relationship between sharable knowledge and confidential knowledge sometimes are complicated and there is a correlation between sharable knowledge and confidential/private/sensitive knowledge [48]. Knowledge relevancy is valued in the range from 0 to 1. The “0” value indicates that the sharable knowledge is not related to confidential knowledge at all, and thus there would be no risk of KS. On the contrary, the “1” value indicates a complete correlation.
μ1, μ2: Knowledge inference ability. Following Reference [48], we defined this variable as the probability that a recipient is able to gain access to private knowledge of a sharer by inferring from the “knowledge obtained through KS” with its ‘‘initial knowledge’’. A recipient’s ability of knowledge inference is the main factor affecting the knowledge-sharing risk. It is expected that the stronger the knowledge inference of the recipient is, the greater KS risk would be for the sharer.
r1, r2: Knowledge leakage risk coefficient. It indicates a firm’s knowledge leakage risk when knowledge is shared at a maximal capacity. Different levels of KS are corresponding with different levels of knowledge leakage risk, which is in turn positively related to knowledge relevancy between the two focal firms. Knowledge leakage risk by inference can be expressed as (kj + kiαi) δiμjri.
c1, c2: Knowledge-sharing cost. Based on transaction cost economics, KS would incur costs, including opportunity cost, technical cost, and time cost that a firm has to pay for KS, as KS requires the time and efforts for the firm to seek and match relevant knowledge.
ρ1, ρ2: Penalty coefficient for the party of no KS (NKS). This is a contract proposition we can design. When one partner shares its knowledge in full capacity but the other acts as an NKS partner, a penalty could be imposed on the NKS partner as a deterrence to the free-riding behaviour. Penalty coefficient is determined by the knowledge-sharing level of the sharing partner. It is expected that the higher level of the sharer’s KS is, the severer the penalty would be for the free-riding partner. The penalty coefficient for firm i of NKS is based on the partner’s knowledge-sharing level, so it can be expressed as kjαjρi.
After describing assumptions and defining variables, we would be able to discuss benefits that firm i gained from KS and they include initial revenue πi, direct revenue kjαjβi, synergy revenue kjαjβiλi, and incentive revenue kiαiηi. When a firm is not aware of how much its partner firm shares knowledge, the firm choose a strategy of either KS or NKS. There would be four scenarios for total benefits generated from a game involved in the two focal firms as described below.
- (1)
- Both Firm 1 and Firm 2 choose KS.
- The revenue of Firm 1 is defined as: .
- The revenue of Firm 2 is defined as: .
- Firm 1 chooses KS, and Firm 2 chooses NKS.
- The revenue of Firm 1 is defined as: .
- The revenue of Firm 2 is defined as:
- (2)
- Firm 1 chooses NKS, and Firm 2 chooses KS.
- The revenue of Firm 1 is defined as:
- The revenue of Firm 2 is defined as:
- (3)
- Both Firm 1 and Firm 2 choose NKS.
- The revenue of Firm 1 is defined as: .
- The revenue of Firm 2 is defined as: .
For a given knowledge-sharing level k1α1 of Firm 1, we further assume that the initial probability of Firm 1 choosing KS is x, and thus the initial probability of choosing NKS would be (1 − x). Similarly, the probability of Firm 2 choosing KS is y, and thus the probability of choosing NKS is (1 − y). The total revenue gained from KS between two firms can be expressed in a payoff function matrix (Table 1).

Table 1.
Game model-based payoff function matrix of knowledge sharing.
3.2. Evolutionary Stable Strategy by Applying Replicator Dynamic Equation
At a given knowledge-sharing level k1α1, when Firm 1 chooses KS, its expected revenue is defined in Equation (1):
When Firm 1 chooses NKS, its expected revenue is:
The average expected revenue for Firm 1 is:
Then, we apply replicator dynamic equation [67] for Firm 1 as follows:
In order to solve stable strategy in Equation (4), we need to obtain the critical value. Based on requirements of the replicator dynamic equation, following two conditions need to be satisfied as:
F(x) = 0, and < 0.
First, let F(x) = 0, we get x* = 0 or x* = 1, and y* =.
Thus, when y*= , there is , that is, every is a stable strategy.
When y*, a stable strategy can be reached only either x* = 0 or x* = 1.
Then, we calculate .
For in Equation (5), it is determined by the initial probability of Firm 1 and Firm 2. Two situations of are discussed as follows.
Situation 1: When , Firm 1 would gain larger revenue if it chooses NKS in comparison to the case in which it chooses KS (seen from Table 1). For any y, it satisfies 0 < y < 1, there is:
Hence, there exists F′(x* = 0) < 0. Thus, the evolutionary stable strategy of Firm 1 is x* = 0, Firm 1 would choose NKS for share knowledge level k1α1.
Situation 2: When , Firm 1 would gain smaller revenue if it chooses NKS in comparison to the case in which it chooses KS (seen from Table 1). Under this situation, is determined by the relative size of and , which contains two different cases.
If y > y*, there is
,
Therefore, F′(x* = 1) <0, so x* = 1 is the stable strategy of Firm 1.
If y < y*, there is
,
Therefore, F′(x* = 0) < 0, then x* = 0 is Firm 1’s stable strategy.
We can conclude that Firm 1’s KS based on its corresponding revenue according to Firm 2’s choice. That is, Firm 2’s initial probability y and stable equilibrium y* have critical influence for Firm 1. When y > y*, the evolutionary strategy of Firm 1 would be KS. While y < y*, the evolutionary strategy would be NKS. Moreover, the smaller y* is, the greater probability that Firm chooses to share k1α1.
Next, we discuss the situation of Firm 2.
At a given knowledge-sharing level k2α2, when Firm 2 chooses KS, its expected revenue is:
When Firm 2 chooses NKS, its expected revenue is:
Thus, we can get the average expected revenue of Firm 2 as:
Replicator dynamic equation is:
Let , there are , and x* =
And
Similarly, we calculate and discuss two situations for Firm 2’s stable strategy.
Situation 3: When ,Firm 2 would gain larger revenue if it chooses NKS in comparison to the case in which it chooses KS (see Table 1. Thus, the evolutionary stable strategy of Firm 2 is to choose NKS for k2α2.
Situation 4: When , Firm 2 would gain smaller revenue if it chooses NKS in comparison to the case in which it chooses KS (see Table 1). In this situation, the evolutionary stable strategy of Firm 2 is determined by two factors. One factor is the initial probability x of Firm 1 in choosing KS. The other factor is the critical value of x*. When x > x*, evolutionary stable strategy of Firm 2 is to choose KS. When x < x*, the evolutionary stable strategy of Firm 2 is to choose NKS. The smaller x* is, the greater probability would be for Firm 2 to choose KS for knowledge-sharing level k2α2.
3.3. An Analysis of Stable Strategy under Different Scenarios
Based on different situations about Firm 1 and Firm 2 discussed above, we discuss four scenarios that simultaneously involve both Firm 1 and Firm 2 as follows.
Scenario 1: When Firm 1 and Firm 2 are in Situation 1 and Situation 3, respectively, that is, the following conditions are satisfied simultaneously:
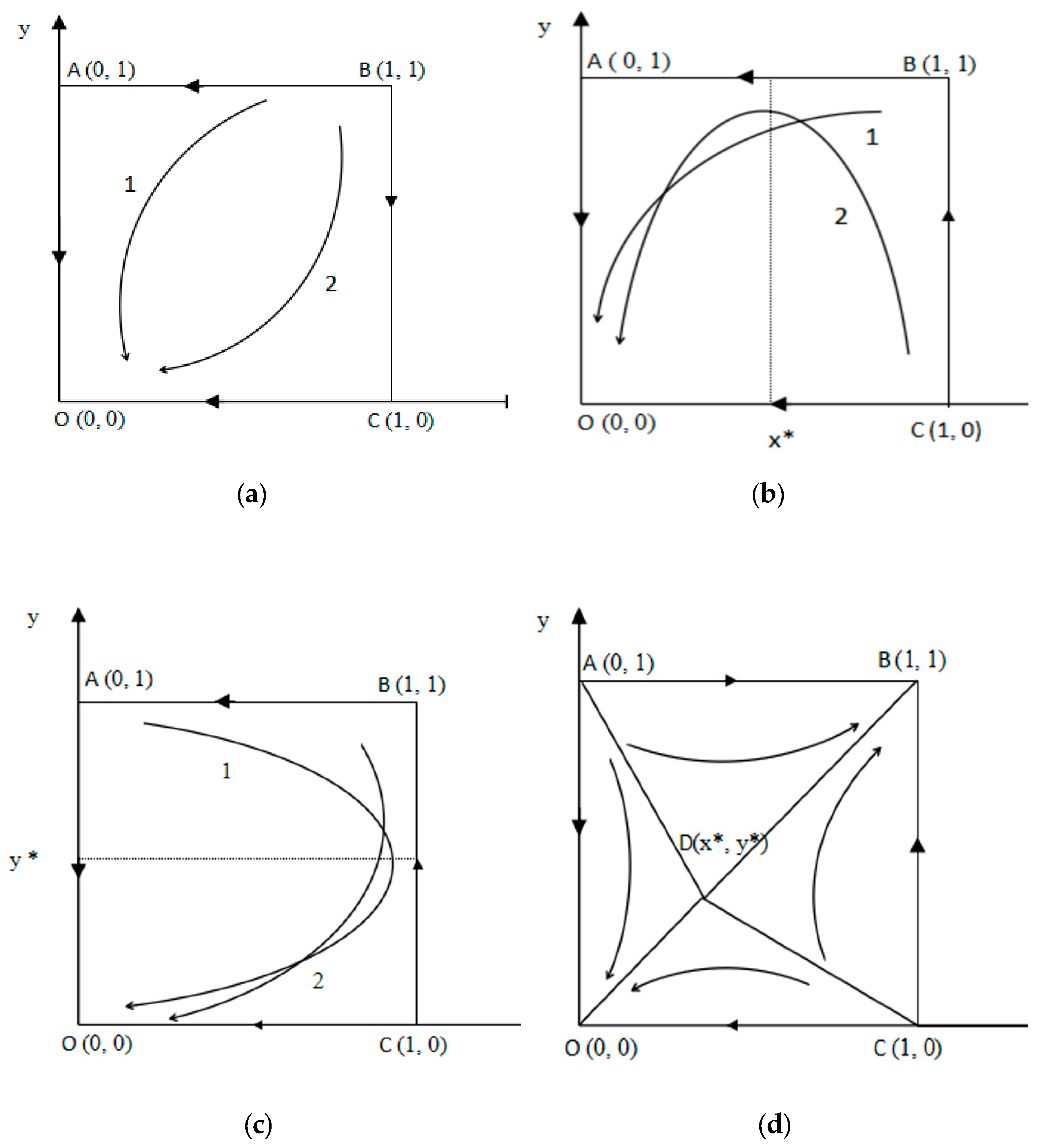
Under this scenario, the revenue both firms gained from choosing KS is less than that when they choose NKS. By continuously learning and improving, both firms would find out that NKS would be better-off than KS, and the system converges to the origin O (0, 0), which shows that the strategy set (NKS, NKS) is a stable result. This evolutionary game phases are shown in Figure 1a.
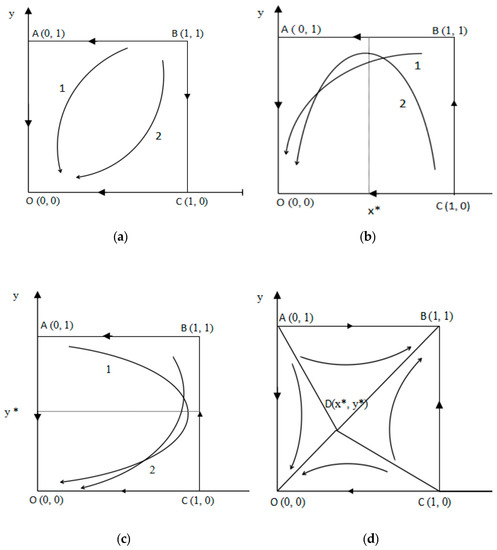
Figure 1.
Scenario 1 (Firms 1 and 2 are in Situations 1 and 3) is described in (a); Scenario 2 (Firms 1 and 2 are in Situations 1 and 4) is described in (b); Scenario 3 (Firms 1 and 2 are in Situations 2 and 3) is described in (c); Scenario 4 (Firms 1 and 2 are in Situations 2 and 4) is described in (d).
Scenario 2: When Firm 1 and 2 are in Situation 1 and Situation 4, respectively, that is, the following conditions are satisfied simultaneously:
For Firm 1, revenue gained from choosing KS is less than that when it chooses NKS. For Firm 2, revenue gained from choosing KS is greater than that when it chooses NKS.
For any y, 0 < y < 1, x* = 0 would be the evolutional stable strategy (ESS) for Firm 1, and it is more likely that Firm 1 would choose NKS. Eventually, the probability of choosing KS for Firm 1 will gradually reduce until it reaches 0.
For Firm 2, x* determines whether or not Firm 2 chooses KS. When x > x*, Firm 2 would prefer to choose KS; When x < x*, with a decreasing probability of KS for Firm 1, KS probability of Firm 2 would also decrease. The system will converge to the origin point O (0, 0). Finally, (NKS, NKS) would be the ESS for both firms. This evolutionary game phases are shown in Figure 1b.
Scenario 3: When Firms 1 and 2 are in Situation 2 and Situation 3, respectively, that is, the following conditions are satisfied simultaneously:
For Firm 1, revenue gained from choosing KS is much greater than that when it chooses NKS, while for Firm 2, revenue of choosing KS is less than that when it chooses NKS. Similar to the situation discussed in Scenario 2, the system would converge to the origin O (0, 0). Finally, (NKS, NKS) would be the ESS for both firms. The evolutionary game phases are shown in Figure 1c.
Scenario 4: When Firm 1 and Firm 2 are in Situation 2 and Situation 4, respectively, that is, the following conditions are satisfied simultaneously.
Under this scenario, for both firms, revenue gained from choosing KS is much greater than that when they choose NKS. In this situation, the final ESS is not only related to the initial KS probability of both firms, but also to the saddle point D (x*, y*), which is expressed as:
With continuous learning and improvement, the ESS for both firms could be either (NKS, NKS) or (KS, KS). The evolutionary game phases are shown in Figure 1d. In the area of , (KS, KS) would be the ESS, while in the area of , (NKS, NKS) would be the ESS. Because the area of can be expressed as , when x* and y* become smaller, the area of would also be reduced. In the meantime, the area of is getting bigger, and the KS probability would become higher, and vice versa. Therefore, the value of saddle point D (x*, y*) is inversely proportional to the area of .
It can be concluded from above discussion that when any one of the inequalities was established in the first three scenarios, no matter what the initial knowledge-sharing probability was, the two firms would eventually choose the ESS of (NKS, NKS). Only in the fourth scenario when revenue gained from choosing KS for both firms was greater than that when they choose NKS, located in the area of , the two firms could adopt the ESS of (KS, KS).
4. Analysis Results and Discussion
4.1. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis and Sharing Strategy Simulation
Our analysis shows that the saddle point D(x*, y*) and related ESS are affected by both initial values and dynamic changes of relevant parameters. Then, we conduct a sensitivity analysis to changes in parameters on KS ESS. Here, we set initial parameters in Table 2, and simulate the evolutionary process of the system with function ode45 and function plot in Matlab 7.0 software. The replicator dynamic Equation (4) and (10) are solved. Finally, the results of main parameters influencing the evolutionary game are tested separately and concurrently, shown in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. The x-axis in all the subsequent figures (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8) represents the time, while the y-axis represents the evolutionary probabilities.

Table 2.
Initial Value of Parameters’ Initialization.
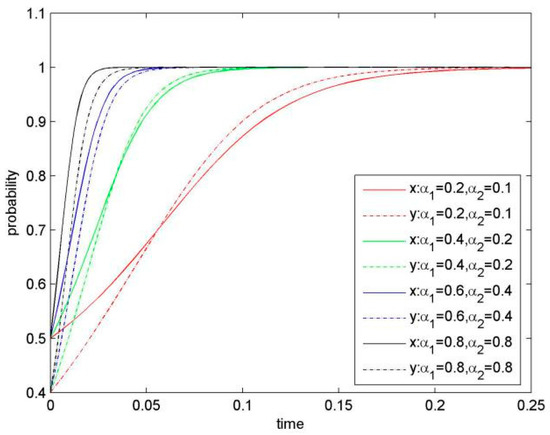
Figure 2.
Evolutionary game phase diagram of the system (when α1 and α2 are improved).
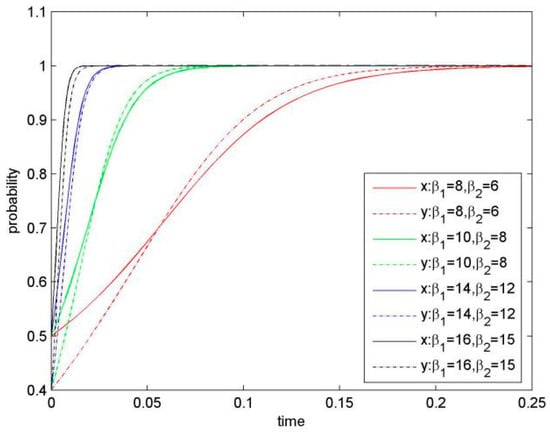
Figure 3.
Evolutionary game phase diagram of the system (when β1 and β2 are improved).
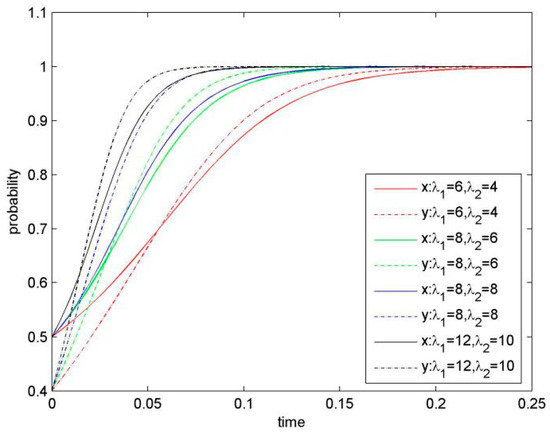
Figure 4.
Evolutionary game phase diagram of the system (when λ1 and λ2 are improved).
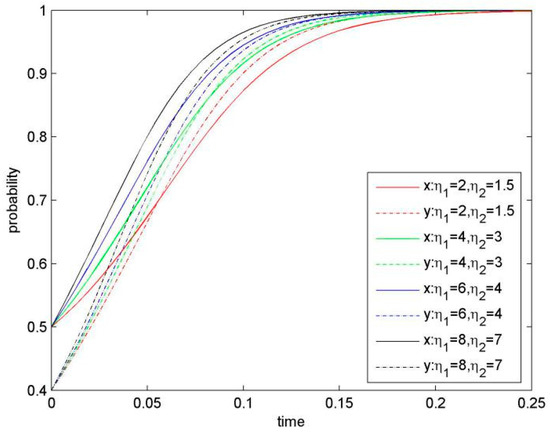
Figure 5.
Evolutionary game phase diagram of the system (when μ1 and μ2 are changed).
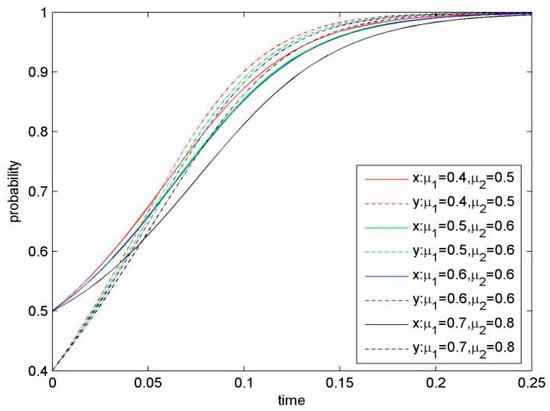
Figure 6.
Evolutionary game phase diagram of the system (when μ1 and μ2 are changed).
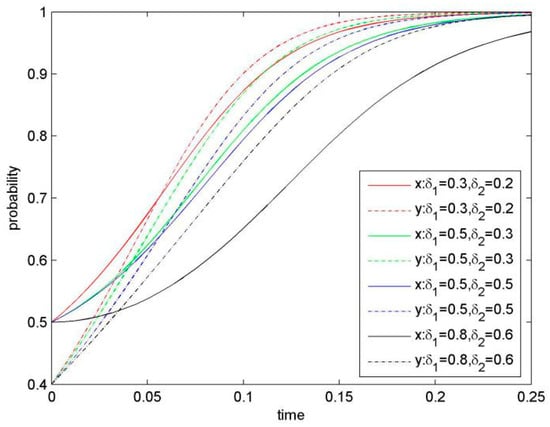
Figure 7.
Evolutionary Game Phase Diagram of the System (when δ1 and δ2 are improved).
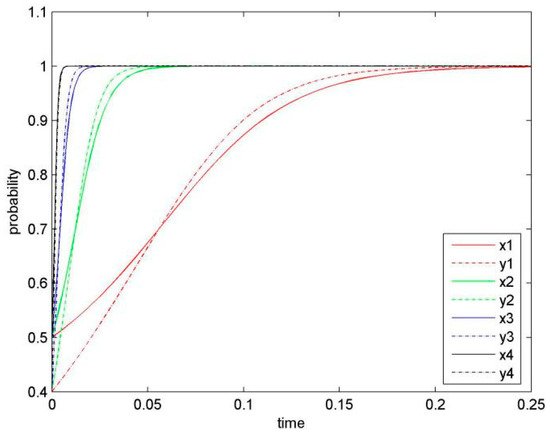
Figure 8.
Dissimilar evolutionary game phases among different systems.
4.1.1. Effect of Knowledge-Sharing Index
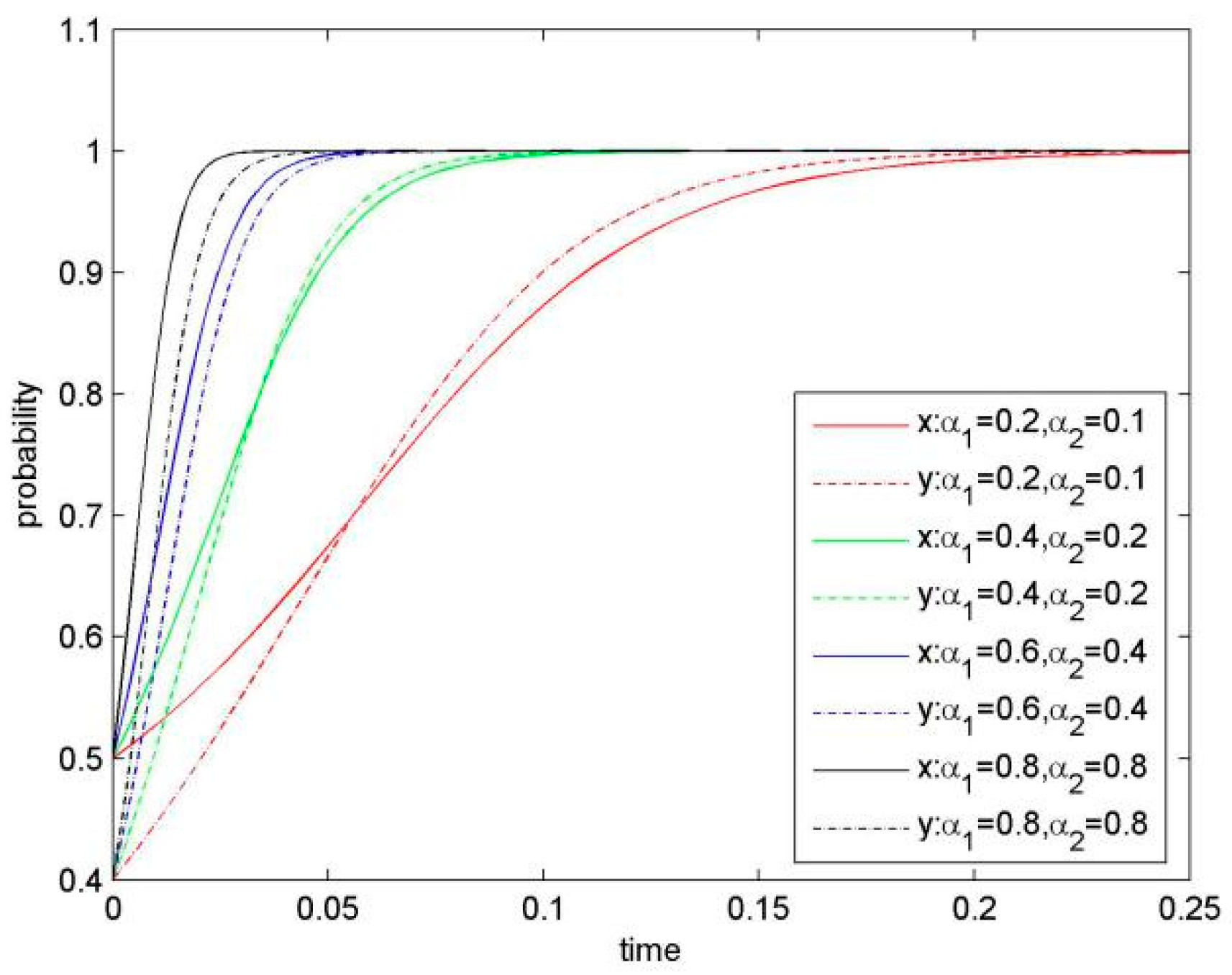
Knowledge-sharing index is an important parameter for our model, and it represents the knowledge-sharing level and has a strong influence on KS behaviour. Figure 2 graphically presents simulation results of the system evolution when increasing knowledge-sharing index (α1 and α2) from its initial value and keeping other parameters as constant. As shown in Figure 2, with steady increase of knowledge-sharing index, converging speed of the system to the stable point (1, 1) is accelerated significantly. As a result, value for the saddle point D (x*, y*) becomes smaller, and sharing possibility for both firms becomes greater.
Proposition 1.
For the sharable knowledge, the higher mutual KS level is, the bigger the revenue gained from KS for the two focal firms would be, leading to the result of both firms choosing KS.
4.1.2. Effect of Revenue Coefficient
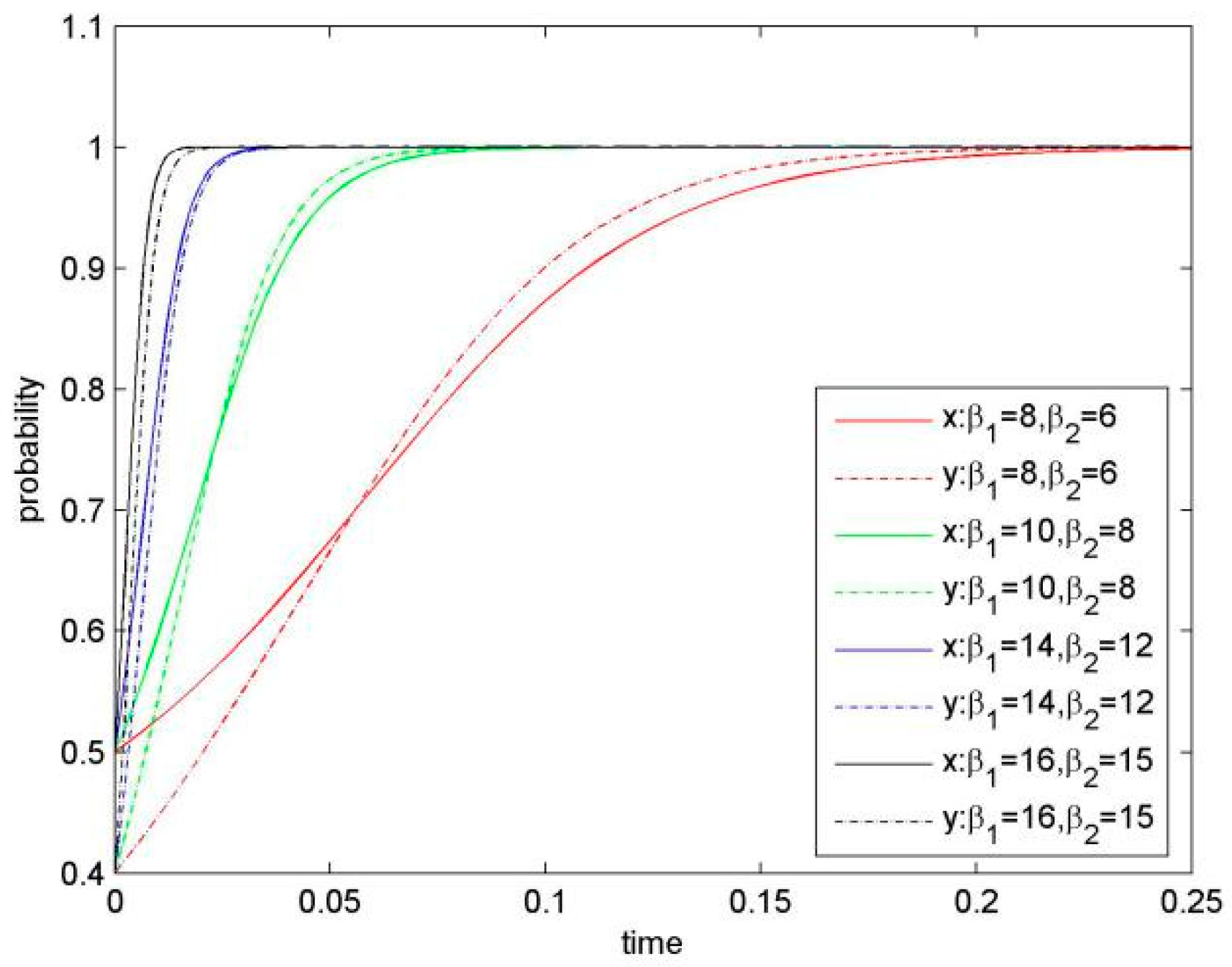
Direct revenue coefficient is a significant parameter influencing KS willingness. Figure 3 illustrates simulation results of the system evolution when keeping β1 and β2 increase, and other parameters constant. A simulation suggests that the larger βi is, the smaller the saddle point D (x*, y*) would be, resulting in a higher probability that the system converges to (1, 1), and thus that the two firms choose ESS of (KS, KS).
Proposition 2.
At a given knowledge-sharing level, a better knowledge usage would generate the greater gain of revenue for involved firms, resulting in enhancement of the firm’s willingness for KS.
4.1.3. Effect of Synergy Revenue Coefficient
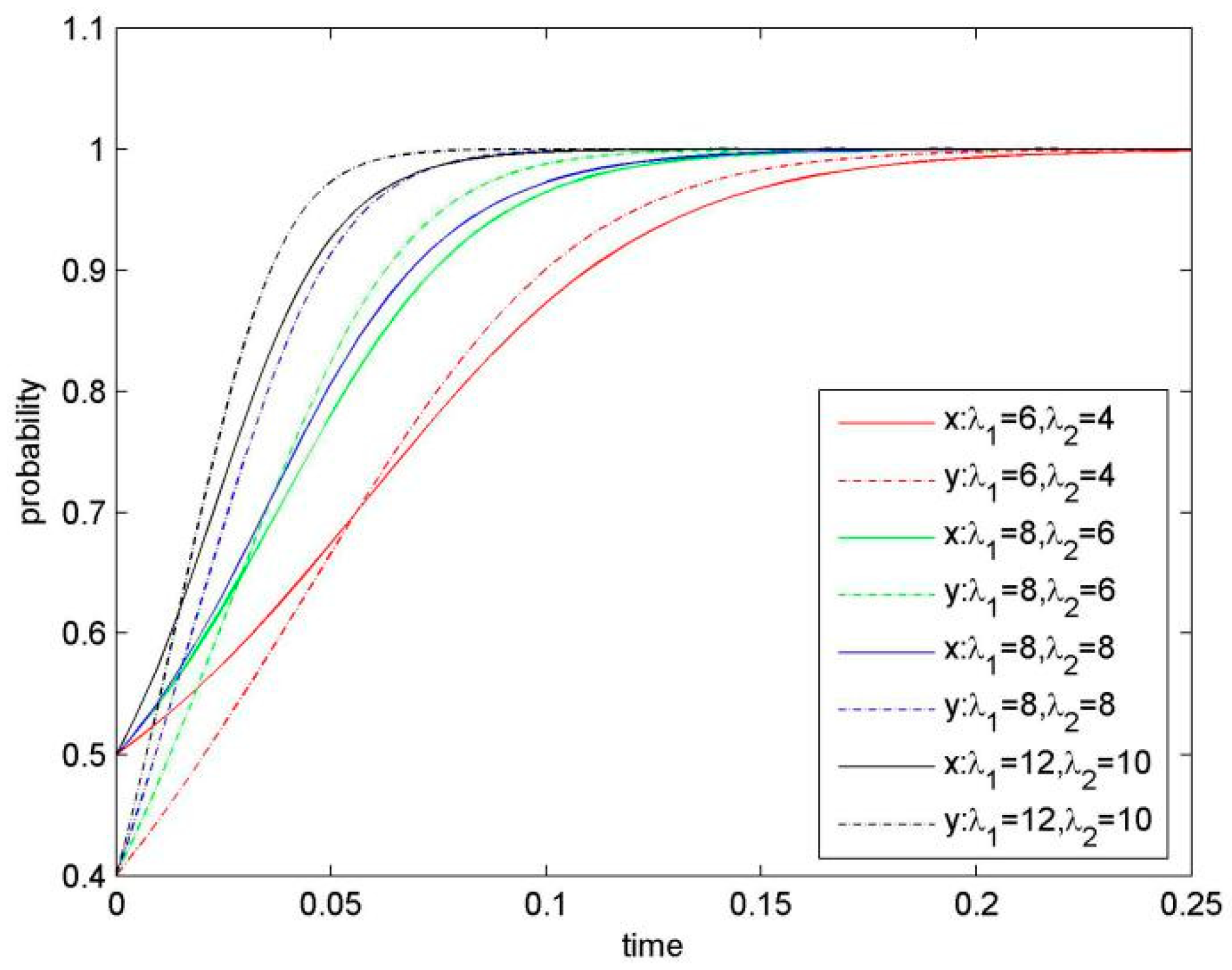
At a given knowledge-sharing level, synergy revenue is the additional revenue generated from an increased knowledge stock and knowledge complementarity for both sides of the KS. Synergy revenue coefficient has a significant impact on KS behaviour. Figure 4 presents simulation results when increasing values for λ1 and λ2 and keeping the other parameters constant. A calculation suggests that the larger the synergy coefficient is, the smaller the value for the saddle point D (x*, y*) would be, resulting in that the system converges to ESS (KS, KS) more quickly.
Proposition 3.
A higher level in knowledge absorption and co-learning, as indicated by a higher synergy revenue coefficient, would be likely to result in creation of new knowledge for both sides, leading to synergy effect of KS.
4.1.4. Effect of Rewards
Rewards, such as monetary rewards to the sharer, provide incentives for the firm’s involvement in KS. At a given knowledge-sharing level, offering monetary rewards would promote KS, since monetary rewards are able to compensate for sharing costs. When we keep improving η1 and η2, and other parameters are constant, the system evolution stage presents simulation results of the system evolution, as shown in Figure 5. Our results indicates that the larger the synergy coefficient is, the smaller value for the saddle point D(x*, y*) would be, resulting in that the system converges to ESS (KS, KS) more quickly.
Proposition 4.
Rewards toward KS behaviour would facilitate generation of additional synergy revenue, resulting in an enhanced willingness of KS.
4.1.5. Effect of Knowledge Inference Ability
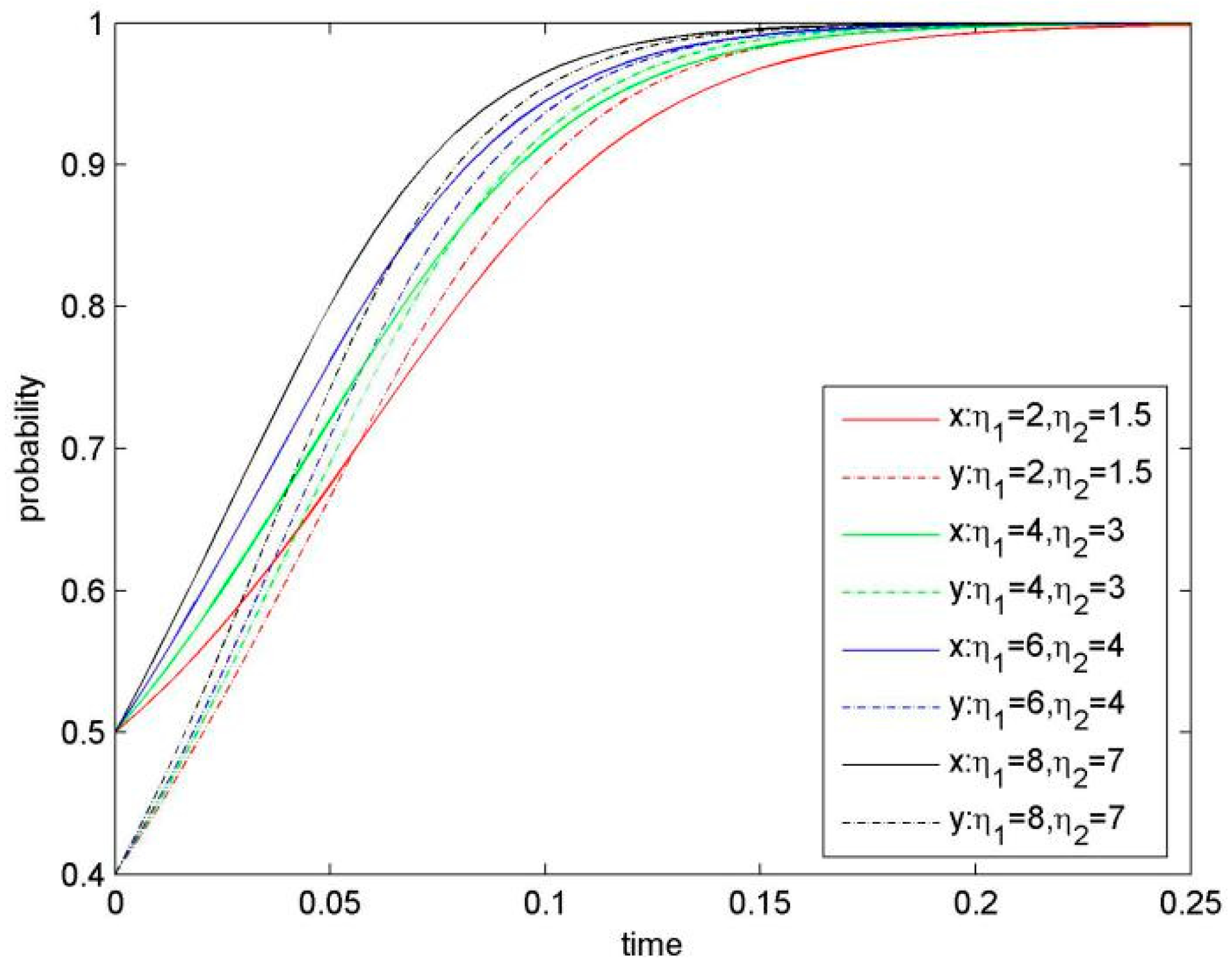
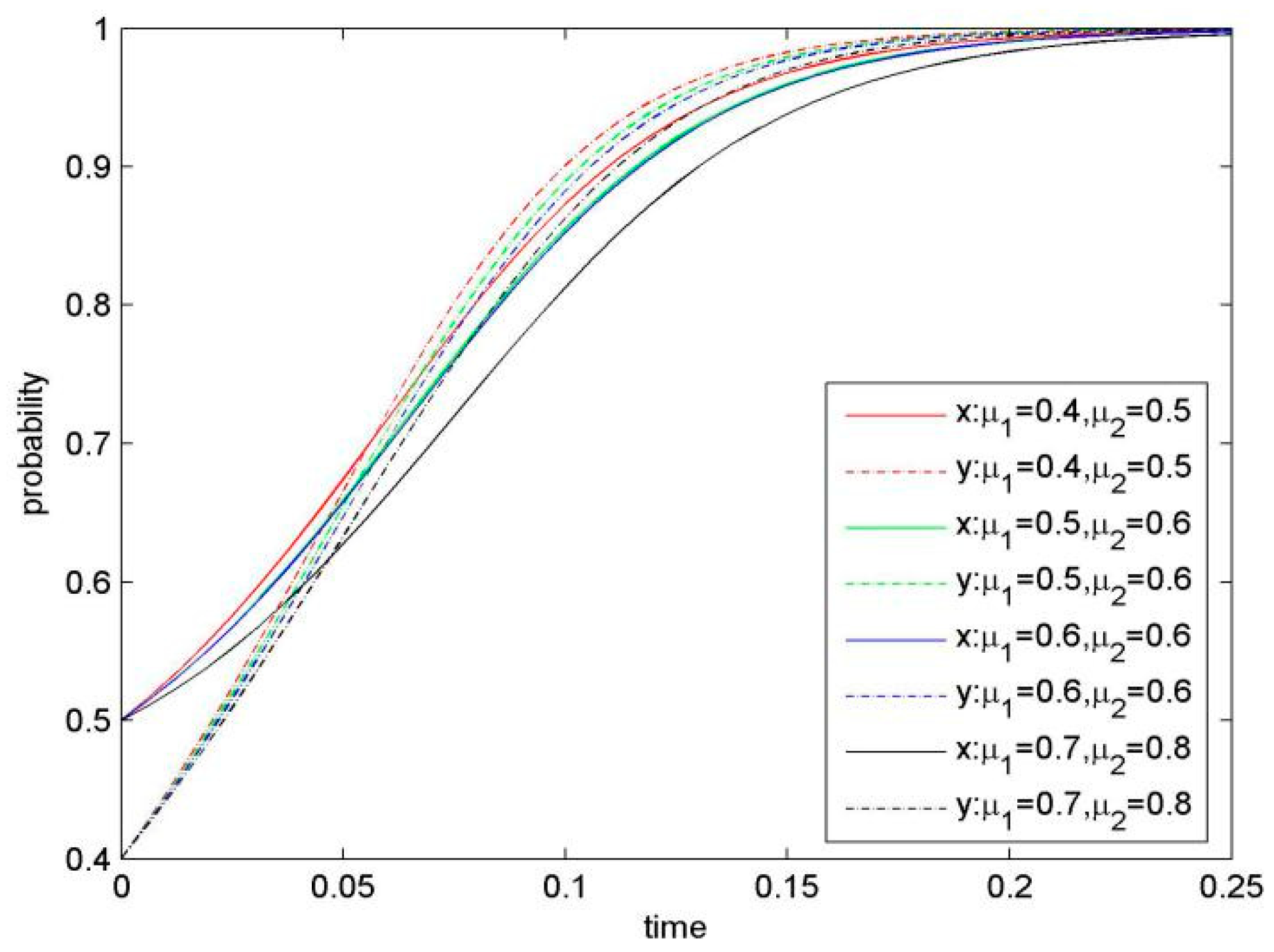
Knowledge inference ability is an important parameter in our model, because it affects the risk of confidential knowledge leakage. Knowledge inference ability is determined by the sharer’s KS level, the recipient’s knowledge stock, knowledge properties (such as relevancy) and the security level of the focal firms’ information and communication technology (ICT). When keeping value for μ1 and μ2 increasing, and other parameters are constant, we get the evolution process for system (Figure 6). The smaller knowledge inference ability (μ1 and μ2) is, the higher speed of the system convergence to stable strategy (KS, KS) would be. Thus, our result demonstrates a negative influence of knowledge inference ability on KS.
Proposition 5.
Knowledge inference ability negatively affects KS, so that when knowledge inference ability is higher, the focal firms would be more likely to choose a stable strategy of NKS.
4.1.6. Effect of Knowledge Relevancy
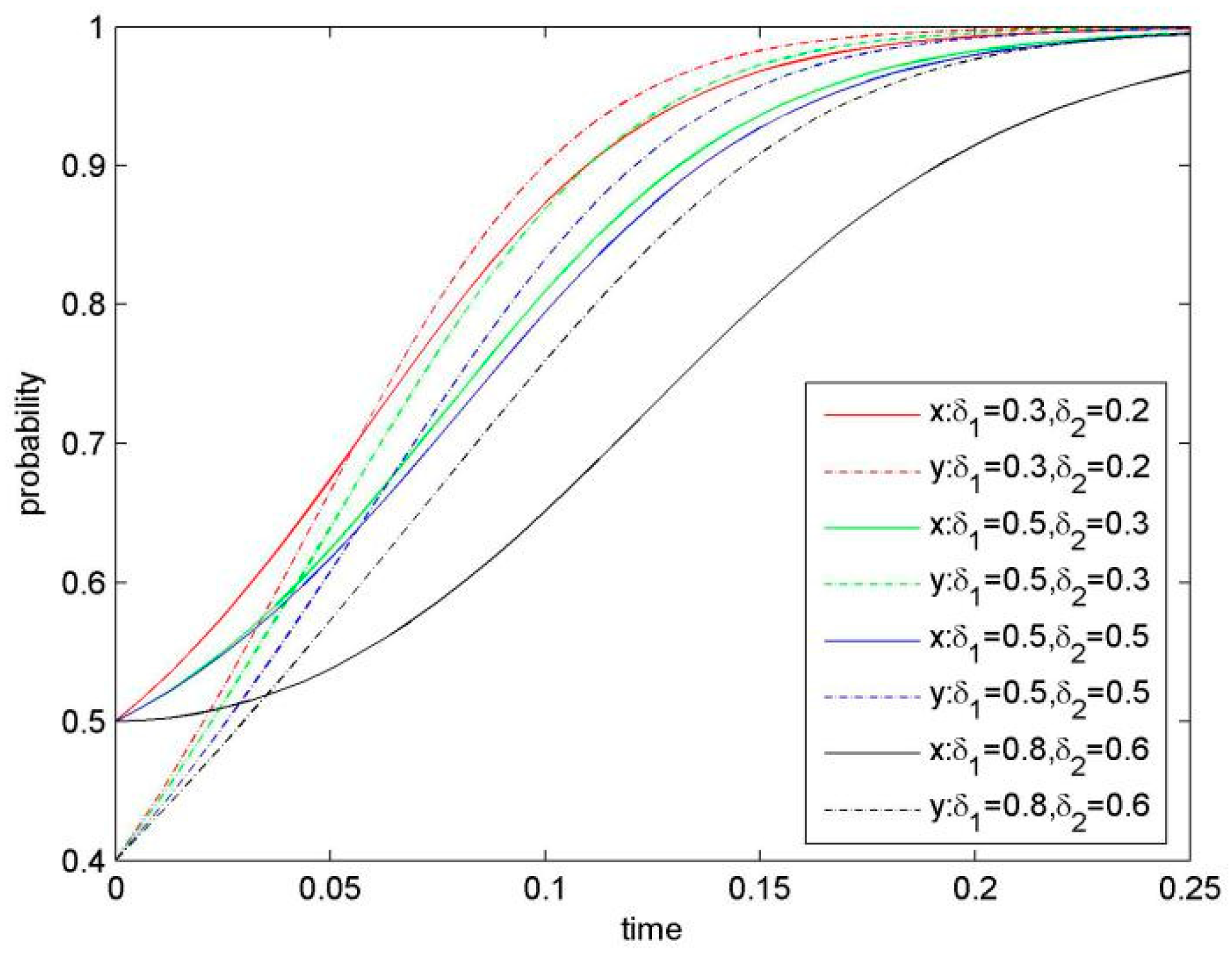
Figure 7 demonstrates our simulation results of the evolution system by keeping the value for knowledge relevancy δ1 and δ2 increased and the other parameters the same. Under this situation it takes a long time for the system to reach the ESS of (KS, KS), because of the increasing value for the saddle point D(x*, y*). Furthermore, it can be predicted that the higher knowledge relevancy, the bigger probability would be for the focal firms to choose NKS.
Proposition 6.
Knowledge relevancy negatively affects KS, so that when knowledge relevancy is higher, the focal firms would be more likely to choose a stable strategy of NKS.
4.1.7. Dissimilarity for Different Game Systems
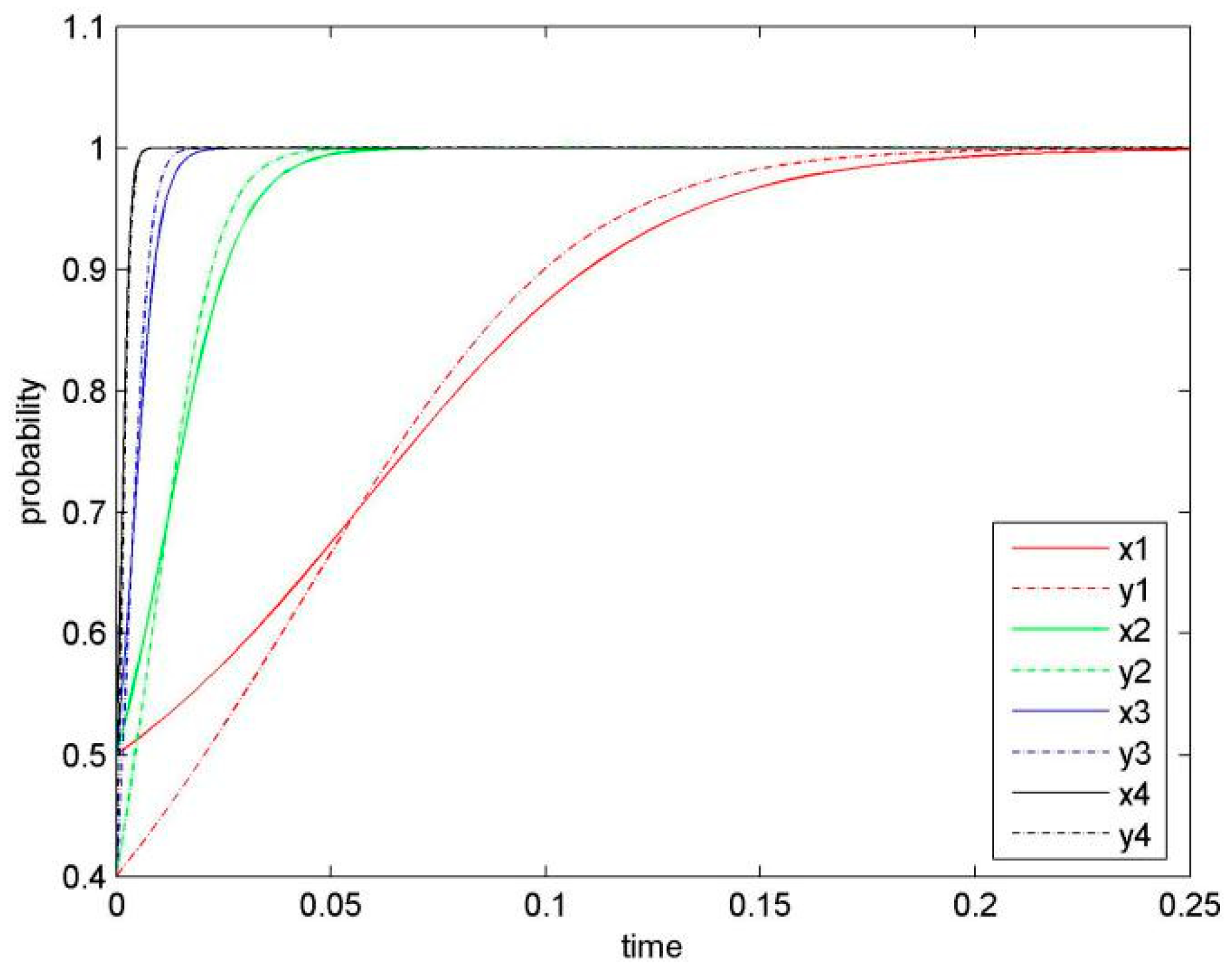
In order to test concurrent effects of parameters on the system, we set as constant variables and change values of remaining parameters sets from low to high, similar to the cases displayed in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. As shown in Figure 8, we obtained four phases of different evolutionary game (as displayed in different colours). The four sets of parameters are given as below:
- (α1 = 0.2, α2 = 0.1; β1 = 8, β2 = 6; λ1 = 6, λ2 = 4; η1 = 2, η2 = 1.5; μ1 = 0.4, μ2 = 0.5; δ1 = 0.3, δ2 = 0.2),
- (α1 = 0.4, α2 = 0.2; β1 = 10, β2 = 8; λ1 = 8, λ2 = 6; η1 = 4, η2. = 3; μ1 = 0.5, μ2 = 0. 6; δ1 = 0.5, δ2 = 0.3),
- (α1 = 0.6, α2 = 0.4; β1 = 14, β2 = 12; λ1 = 8, λ2 = 8; η1 = 6, η2 = 4; μ1 = 0.6, μ2 = 0.6; δ1 = 0.5, δ2 = 0.5),
- (α1 = 0.8, α2 = 0.8; β1 = 16, β2 = 15; λ1 = 12, λ2 = 10; η1 = 8, η2 = 7; μ1 = 0.7, μ2 = 0.8; δ1 = 0.8, δ2 = 0.6).
These four sets of changed parameters denote different KS levels, from low to high, as we define these parameters based on dynamic change of knowledge-sharing index . With the increase of KS level, both sides are inclined to choose (KS, KS) more quickly. In other words, when the KS level increases and the parameters of revenues, knowledge capacity, risks, costs, and penalty are fixed, firms would be more likely to share knowledge mutually. The more knowledge one firm is willing to share, the more the other firm would be encouraged to share. It illustrates a win-win solution for both parties.
Proposition 7.
The KS level of the focal firms positively influences their KS in the future, so that a firm’s high level of KS would be likely lead to KS of the other firm.
4.2. Theoretical Implications
Using an evolutionary game theoretical analysis, we analytically investigated firm strategy of KS and influencing factors on the firm’s KS strategy. Our study contributes to the literature firstly by developing an evolutional game model on the firms’ strategy regarding their KS behaviour. Our analysis demonstrates that revenue gained from knowledge-sharing and risk of knowledge leakage are the most critical factors. Therefore, factors influencing revenue and risk would also be able to influence KS. Based on our analysis, firms would be more likely to choose the stable strategy (KS, KS), when knowledge-sharing index, direct revenue and synergy revenue are increased, and knowledge relevancy and knowledge inference probability are reduced. An analysis of feasibility conditions for the potential scenarios of the focal firms’ KS strategies based on revenue gained and knowledge leakage risk was also completed. We examined the evolutionary stable strategy of KS for each of the two focal firms and cooperative, competitive, simultaneous, and sequential situations of the focal firms’ KS strategies. Furthermore, we also investigated the feasibility conditions of the elasticity parameters for the influencing factors.
Unlike prior research on KS, which strongly focuses on the enabling factors, our study has paid an intensive attention to conceptualize both enabling and hampering factors by identifying free-riding and knowledge leakage as the major barrier for KS. More specifically, our theoretical game analysis has identified knowledge relevancy and firm’s ability of knowledge inference as two major factors leading to knowledge leakage. Thus, our study demonstrates that the barriers to the KS can be either associated the internal attribute of the knowledge (the case of knowledge relevancy), or created by the strategic decisions of the firm (the case of using the firm’s inference probability for selective knowledge access). In this line, our study contributes to the literature by developing a conceptualization of the barriers to KS and providing a better understanding of how these internal barriers affect enabling factors to function effectively and allow efficient KS between SC partners.
4.3. Managerial Implications
Our analysis can be used to assist executives of SCM and policy makers by providing several managerial implications regarding KS.
As suggested by our evolutionary game model analysis, KS behaviour between SC partners would result in generation of extra benefits for the firm involved and the firm’s KS strategy depends on their close collaboration. To facilitate mutual KS, there is a need for the firms to match KS with trust. In the context of SCM, trust is critical to promote a strong partnership and to facilitate collaboration and KS. If firms in a SC do not trust with each other, they would be unable to share knowledge in the long term. On the other hand, it would be also difficult for SC members to trust with each other entirely and to share their entire knowledge. As a result, firms tend to have different levels of sharing willingness, resulting in different knowledge-sharing levels. Prior research suggests that the development of trust is a gradual process, which contains three sequential stages from low to high as calculus-based trust, knowledge-based trust, and identification-based trust [20]. We would like to suggest that firms match different levels of knowledge-sharing with these stages of trust. At the stage of calculus-based trust, SC members could be engaged in sharing of only formal and explicit knowledge. At the stage of knowledge-based trust, firms could share more personal-oriented and tacit knowledge with their SC partners. At the stage of identification-based trust, firms would be able to share knowledge at a maximal level, such as value-adding KS.
Our analysis demonstrated knowledge leakage as the major barrier for KS and identified knowledge relevancy and knowledge inference ability as two key factors affecting knowledge leakage. Managerial implications from this analysis are that managers need to pay their attention to reduce the influence from these two influencing factors. First, firms may reduce knowledge leakage risk by hiding explicit knowledge in KS. Based on the knowledge management perspective, tacit knowledge is difficult to express and compile in comparison to explicit knowledge. Therefore, expressing explicit knowledge in a more tacit manner would facilitate KS through reducing knowledge relevancy, leading to a reduction of knowledge leakage risk. Second, an improvement in the contractual governance structure would be helpful to reduce risk of leaking confidential knowledge. In this regard, improving incentive and penalty mechanisms would be able to prevent "free riding" behaviour. Establishing mechanisms for preventing knowledge leakage, such as signing confidentiality agreements with employees who have access to the core knowledge of the firm, would be helpful to reduce risks of knowledge leakage. Third, establishing a better legal environment at the whole society level would be helpful to effectively protect legal rights of intellectual property, including confidential knowledge.
5. Discussion
While KS has become increasingly important for firms in SC networks to improve their competitive advantages, influencing factors and their mechanisms regarding the firm’s KS have not received adequate research attention. This study contributes to the literature by shedding lights on the crucial issue of inter-organizational KS mechanisms and knowledge protection strategies. Drawing factors from two perspectives of the transaction cost economics and social exchange theory, our study constructed an evolutionary game model to analyse the dynamic process of the firm’s development regarding their behaviour in KS. Our model focuses on how the rivalry in the co-opetition competition relationship acts as the major barrier for KS due to the sharer’s concern of knowledge leakage. More specifically, our model identifies knowledge relevancy as the inherent property of knowledge and the firm’ ability of knowledge inference as two important factors resulting in knowledge leakage, and examines how these two impeding factors, together with motivating factors, become the central shaping force in determining the firm’s KS behaviour.
Our study has several limitations, which provide future research directions. First, to simplify our game model, we assume that several important parameters, such as knowledge capacity, as constant. In reality, it is more likely that knowledge capacity for an individual firm would change, which would influence KS. Thus, it would be helpful for future studies to examine how the firm’s KS is influenced by organizational learning. Second, our study is conducted in the context of co-opetition relationships in the SC networks, but this study has not introduced competing parties to the game modelling (e.g., one manufacturer with two distributers), neither considered different features and demands of KS for different players in a SC, such as manufacturer, supplier, subcontractor, and retailers, at the demand or the supply side of SC activities. Future studies may take these conditions into consideration, in order to accurately reflect the business reality. Third, our study examines how KS is reached by both motivating and impeding forces by constructing and simulating an evolutional game model. Future empirical studies would be helpful to verify our evolutional game model.
Author Contributions
Methodology, formal analysis, data curation, project administration, visualization, funding acquisition, writing—original draft preparation, Q.L.; Conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, Y.K.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation, Ministry of Education, the People’s Republic of China (grant No. 16YJC630053) and Shaanxi Social Science Foundation, China (grant No. 2017S019).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, S.; Ragu-Nathan, B.; Ragu-Nathan, T.S.; Rao, S.S. The impact of supply chain management practices on competitive advantage and organizational performance. Omega 2006, 34, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.; Towill, D. An Integrated Model for the Design of Agile Supply Chains. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2011, 31, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fergusson, C.; Perry, D.; Antony, J. A conceptual case-based model for knowledge sharing among supply chain members. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2008, 2, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, C.; Giachetti, C. Aligning knowledge strategy and competitive strategy in small firms. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2015, 3, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Fu, Y.C. Inter-organizational relationships and knowledge sharing through the relationship and institutional orientations in supply chains. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Ho, W.; Edwards, J.S. Supply chain knowledge management: A literature review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 6103–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.C.; Hsu, S.H.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Balasubramanian, S.K.; Shih, S.C. Knowledge sharing—A key role in the downstream supply chain. Inf. Manag. 2012, 49, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L. The Triple-A Supply Chain. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2004, 82, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, R.; Bengtsson, L.; Henriksson, K.; Sparks, J. The interorganizational learning dilemma: Collective knowledge development in strategic alliances. Organ. Sci. 1998, 9, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.H.; Hatch, N.W. Using supplier networks to learn faster. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2004, 45, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.T. Relational capabilities to leverage new knowledge: Managing directors’ perceptions in UK and Portugal old industrial regions. Learn. Organ. 2016, 6, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalebuff, B.J.; Brandenburger, A.; Maulana, A. Co-Opetition; Harper Collins Business: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Spekman, R.E.; Spear, J.; Kamauff, J. Supply chain competency: Learning as a key component. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2002, 7, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Yeh, C.H.; Tu, C.W. Trust and knowledge sharing in green supply chains. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2008, 13, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.B.; Gillian, F.; Thomas, S.; Ratchev, S.; Pawar, K.; Weber, F.; Wunram, M. Inter-and intra-organisational barriers to sharing knowledge in the extended supply-chain. In Proceedings of the eBusiness and eWork, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.L.; Teng, B.S. Transferring R&D knowledge: The key factors affecting knowledge transfer success. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2003, 20, 39–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J. Knowledge Sharing: A Review of the Literature; The World Bank Operations Evaluation Department (OED): Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nooshinfard, F.; Nemati-Anaraki, L. Success factors of inter-organizational knowledge sharing: A proposed framework. Electron. Libr. 2014, 32, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Goh, M.; de Souza, R.; Li, G. Knowledge sharing in collaborative supply chains: Twin effects of trust and power. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 2060–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lin, T.P.; Yen, D.C. How to facilitate inter-organizational knowledge sharing: The impact of trust. Inf. Manag. 2014, 51, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.H.; Wong, W.P.; Chung, L. Information and Knowledge Leakage in Supply Chain. Inf. Syst. Front. 2016, 18, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frishammar, J.; Ericsson, K.; Patel, P.C. The dark side of knowledge transfer: Exploring knowledge leakage in joint R&D projects. Technovation 2015, 41, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, M.H.; Tsai, H.T.; Wu, C.C.; Lu, C.H. A holistic knowledge sharing framework in high-tech firms: Game and co-opetition perspectives. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2006, 36, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Goyal, M. Strategic information management under leakage in a supply chain. Manag. Sci. 2009, 55, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noseleit, F.; Faria, P. Complementarities of internal R&D and alliances with different partner types. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; Audretsch, D.; Sarkar, M. Knowledge spillovers and strategic entrepreneurship. Strat. Entrep. J. 2010, 4, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.; Andriani, P. Analysing intangible resources and managing knowledge in a supply chain context. Eur. Manag. J. 1998, 16, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, B.; Zander, U. Knowledge of the firm, combinative capabilities, and the replication of technology. Organ. Sci. 1992, 3, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hung, H.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Lin, B. A knowledge management architecture in collaborative supply chain. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2002, 42, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.C.; Lai, V.S.; Cheung, W.; Cui, X. Willingness to share information in a supply chain: A partnership-data-process perspective. Inf. Manag. 2012, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M. Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Strategies for Reducing Cost and Improving Service; Financial Times Pitman Publishing: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Gallear, D.; Ghobadian, A. Knowledge transfer: The facilitating attributes in supply-chain partnerships. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2011, 28, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.W.; Chen, P.C.; Chung, C.F. Gaining or losing? The social capital perspective on supply chain members’ knowledge sharing of green practices. Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag. 2014, 26, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Somers, T.M.; Gupta, Y.P. Impact of environmental uncertainty and task characteristics on user satisfaction with data. Inf. Syst. Res. 2004, 15, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, A.; Csepregi, A.; Marchev, J.A. How to extend the ICT used at organizations for transferring and sharing knowledge. IUP J. Knowl. Manag. 2011, 9, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Solli-Sæther, H.; Gottschalk, P. Stage-of growth in outsourcing, offshoring and backsourcing: Back to the future? J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2015, 55, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. Transaction-cost economics: The governance of contractual relations. J. Law Econ. 1979, 22, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. Outsourcing: Transaction Cost Economics and Supply Chain Management. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2008, 44, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.; Petersen, K.J.; Cousins, P.D.; Handfield, R.B. Knowledge sharing in interorganizational product development teams: The effect of formal and informal socialization mechanisms. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2009, 26, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.B. Strategic outsourcing: Leveraging knowledge capabilities. Sloan Manag. Rev. 1999, 40, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Bosua, R.; Scheepers, R. Protecting organizational competitive advantage: A knowledge leakage perspective. Comput. Secur. 2014, 42, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annansingh, F. Exploring the risks of knowledge leakage: An information systems case study approach. In New Research on Knowledge Management Models and Methods; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ritala, P.; Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, P. What’s in it for me? Creating and appropriating value in innovation-related coopetition. Technovation 2009, 29, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, H. Transformational offshore outsourcing: Empirical evidence from alliances in China. J. Oper. Manag. 2008, 26, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.B.; Hilmer, F.G. Strategic outsourcing; The McKinsey Quarterly: Seattle, WA, USA, 1995; pp. 48–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Geng, Y. Modeling and evaluating information leakage caused by inferences in supply chains. Comput. Ind. 2011, 62, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H. Network position and cooperation partners selection strategies for research productivity. Manag. Decis. 2015, 53, 494–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterby-Smith, M.; Lyles, M.A.; Tsang, E.W. Inter-organizational knowledge transfer: Current themes and future prospects. J. Manag. Stud. 2008, 45, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P.; Olander, H.; Michailova, S.; Husted, K. Knowledge sharing, knowledge leaking and relative innovation performance: An empirical study. Technovation 2015, 35, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkpen, A.C.; Tsang, E.W. Social capital, networks, and knowledge transfer. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2005, 30, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Niu, X. Game analysis of the knowledge sharing mechanism for the supply chain collaborative innovation. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2015, 8, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.K., Jr. Trust expectations, information sharing, climate of trust, and negotiation effectiveness and efficiency. Group Organ. Manag. 1999, 24, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.K., Jr. Behaviors, trust, and goal achievement in a win-win negotiating role play. Group Organ. Manag. 1995, 20, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.T.; Dirks, K.T.; Ferrin, D.L. Interpersonal trust within negotiations: Meta-analytic evidence, critical contingencies, and directions for future research. Acad. Manag. J. 2014, 57, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.M.; Hunt, S.D. The Commitment-Trust Theory of Relationship Marketing. J. Mark. 1994, 3, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.S.; Chan, L.S. Social network, social trust and shared goals in organizational knowledge sharing. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Hsu, Y.; Lin, E. Model for knowledge-sharing strategies: A game theory analysis. Eng. Proj. Organ. J. 2011, 1, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenyan, J.; Büyüközkan, G.; Feyzioğlu, O. Modeling collaboration formation with a game theory approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, G.P.; Harker, P.T. Competition and outsourcing with scale economies. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1314–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, N.; Minehart, D. Optimal technology sharing strategies in dynamic games of R&D. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2014, 23, 149–177. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.D.; Jonker, L.B. Evolutionary stable strategies and game dynamics. Math. Biosci. 1978, 40, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanhalli, A.; Tan, B.C.Y.; Wei, K.-K. Contributing Knowledge to Electronic Knowledge Repositories: An Empirical Investigation. MIS Q. 2005, 29, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, N.M. Common Knowledge: How Companies Thrive on Sharing What They Know; Harvard University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bartol, K.M.; Srivastava, A. Encouraging Knowledge Sharing: The Role of Organizational Reward Systems. J. Leadersh. Organ. Stud. 2002, 9, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, J.; Sigund, K. Evolutionary Game Dynamics. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 2003, 40, 479–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).