Optimal Coupling of Straw and Synthetic Fertilizers Incorporation on Soil Properties, Active Fe Dynamics, and Greenhouse Gas Emission in Jasminum sambac (L.) Field in Southeastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Measurement of CO2, CH4, and N2O Emissions
2.3. Measurement of Soil Properties
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil and Properties
3.2. Soil Active Fe Dynamics
3.3. Relationship between Soil Fe Dynamics and Soil Properties
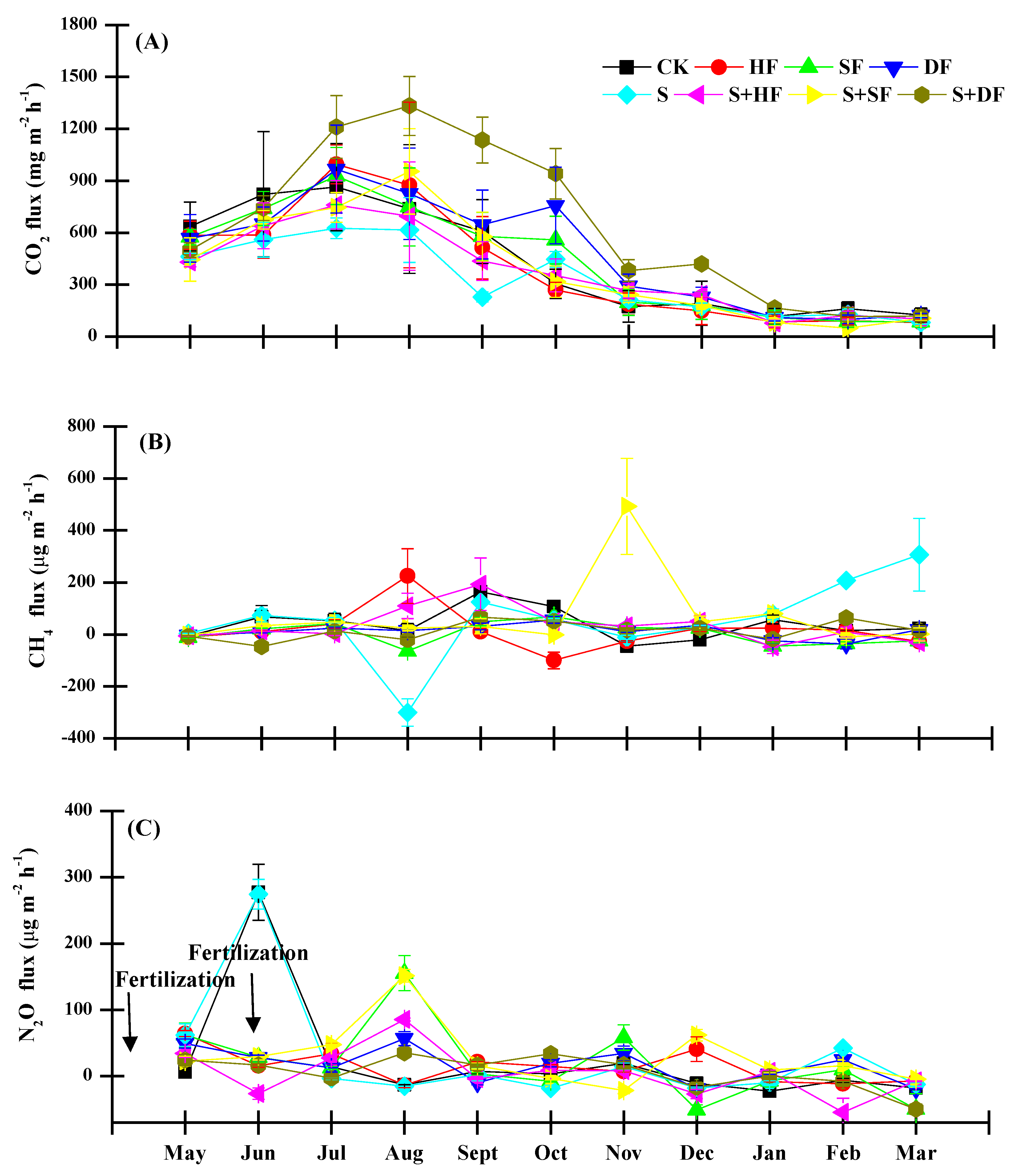
3.4. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
3.5. Relationship Between GHG and Soil Properties
3.6. Plant Height
3.7. General Discriminant Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Straw, Fertilizer Doses, and Their Combination on Soil Properties
4.2. Effects of Straw, Fertilizer Doses, and Their Combination on Active Iron Dynamics in the Soil
4.3. Active Iron Correlations and Their Influencing Factors
4.4. Effects of Straw, Fertilizer Doses, and Their Combination on CO2 Emission
4.5. Effects of Straw, Fertilizer Doses, and Their Combination on CH4 Emission
4.6. Effects of Straw, Fertilizer Doses, and Their Combination on N2O Emission
4.7. Relationship between GHG and Soil Properties
4.8. Best Management Practices to Improve Soil Properties and Reduce GWP
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ford, A.; Gilroy, G. What agriculture will support human life? Curr. Anthropol. 2015, 56, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, D.K.; Verma, T.S.; Deor, B.S.; Mishra, A.; Vermani, A. Enhancing yield and profitability of a western himalayan vegetable production system by balancing nutrient inputs through farmyard manure and synthetic fertilizer applications. J. Sustain. Agric. 2007, 29, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pang, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Li, H. Rice straw incorporation in winter with fertilizer-n application improves soil fertility and reduces global warming potential from a double rice paddy field. Biol. Fert. Soils 2013, 49, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Yan, C.R.; Mei, X.R.; He, W.Q.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in Northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Datta, A.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C.; Bartrons, M.; Peñuelas, J. Rice straw incorporation affects global warming potential differently in early vs. late cropping seasons in Southeastern China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 181, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Yang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, C.; Wang, W. Effects of straw amendment with industrial and agricultural wastes on carbon emission from jasmine plantation. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2017, 37, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.T.; Bai, D.S.; Zhang, F.S.; Jiang, R.F.; Mao, D.R. Effect of acidic rhizosphere fertilizer on the soil pH and Fe availability of calcareous soil. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2003, 9, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z. Seasonal variations of CH4 and N2O emissions in response to water management of paddy fields located in Southeast China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations). OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2010–2030; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Mo, J.M.; Yu, G.R.; Fang, Y.T.; Li, D.J.; Lu, X.K.; Wang, H. Emissions of nitrous oxide from three tropical forests in Southern China in response to simulated nitrogen deposition. Plant Soil 2008, 306, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, W.; Mo, J.; Liu, L.; Dong, S. Increased phosphorus availability mitigates the inhibition of nitrogen deposition on CH4 uptake in an old-growth tropical forest, southern China. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2805–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.; Niklaus, P.A.; Schleppi, P. Soil-atmosphere fluxes of the greenhouse gases CO2, CH4 and N2O in a mountain spruce forest subjected to long-term N addition and to tree girdling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 181, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.H.; Hu, T.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.W.; Hu, H.L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.L. Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Duan, H.; Zhang, D. Responses of soil respiration to elevated carbon dioxide and nitrogen addition in young subtropical forest ecosystems in China. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Hasselquist, N.J.; Palmroth, S.; Zheng, Z.M.; You, W.H. Short-term response of soil respiration to nitrogen fertilization in a subtropical evergreen forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Mo, J.M.; Zhou, G.Y.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.T.; Lu, X.K.; Zhang, T.; Dong, S.F. Methane uptake responses to nitrogen deposition in three tropical forests in southern China. J Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, R.S.; Black, T.A.; Trofymow, J.A.; Roy, R.; Nesic, Z. Soil CO2 and N2O flux dynamics in a nitrogen-fertilized Pacific Northwest Douglas-fir stand. Geoderma 2010, 157, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Megonigal, J.P. Plant species traits regulate methane production in freshwater wetland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.J.; Kiese, R.; Wolf, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on methane uptake and nitrous oxide emissions across three different ecosystem types. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Sardans, J.; Wang, W.; Zeng, C.; Peñuelas, J. Factors related with CH4 and N2O emissions from a paddy field: Clues for management implications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.Q.; Fang, S.H.; Xia, T. Advances of Jasmine Tea processing technology. Tea Fujian 2001, 23, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.F.; Fu, T.L.; Ye, N.X.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, N.H.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, D.S.; Guo, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Lin, G.S.; et al. Fujian Jasmine Tea; Xiamen University Press: Xiamen, Chiana, 2008; pp. 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Zhao, A.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, J. pH buffering capacity of acid soils from tropical and subtropical regions of China as influenced by incorporation of crop straw biochars. J. Soil Sediment. 2012, 12, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Min, Q.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Asensio, D.; Bartrons, M.; Peñuelas, J. Organic cultivation of jasmine and tea increases carbon sequestration by changing plant and soil stoichiometry. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, C.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C.; Liang, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Effects of steel slag application on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yield over multiple growing seasons in a subtropical paddy field in China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 171, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siczek, A.; Frąc, M. Soil microbial activity as influenced by compaction and straw mulching. Int. Agrophys. 2012, 26, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, C.J.; Marschner, H.; Römheld, V. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer form on pH of the bulk soil and rhizosphere, and on the growth, phosphorus, and micronutrient uptake of bean. J. Plant Nutr. 1993, 16, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Shayam, D.; Sharma, Y.K. Effect of paddy straw and paper mill effluent on physico-chemical properties of soil. J. Struct. Chem. 2012, 11, 137–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mcclaugherty, C.A.; Pastor, J.; Aber, J.D.; Melillo, J.M. Forest litter decomposition in relation to soil nitrogen dynamics and litter quality. Ecology 1985, 66, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, C.; Tang, J.; Han, B.; Luo, C. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on the substrate quality of foliar litter in a natural evergreen broad-leaved forest in the rainy area of Western China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7428–7434. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, G.; Fronaeus, S.; Bengtsson-Kloo, L. The kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of hydroxylamine by iron (III). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton 2002, 12, 2548–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C. On the mechanism of microbe inactivation by metallic iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liptzin, D.; Silver, W.L. Effects of carbon additions on iron reduction and phosphorus availability in a humid tropical forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Cruz, M.D.C.; Narcía, A.T.; Ballona, G.C.; Kohler, J.; Caravaca, F.; Roldán, A. Poultry manure and banana waste are effective biofertilizer carriers for promoting plant growth and soil sustainability in banana crops. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chasteen, N.D. Ferroxidase activity of ferritin: Effects of pH, buffer and Fe(II) and Fe(III) concentrations on Fe(II) autoxidation and ferroxidation. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, E.A.; Silver, W.L.; Firestone, M.K. Tropical forest soil microbial communities couple iron and carbon biogeochemistry. Ecology 2010, 91, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lentini, C.J.; Wankel, S.D.; Hansel, C.M. Enriched iron(III)-reducing bacterial communities are shaped by carbon substrate and iron oxide mineralogy. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Liptzin, D. High potential for iron reduction in upland soils. Ecology 2015, 96, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, F.J.; Jones, M.V.; Edwards, C. Effects of salinity on bacterial iron oxidation. Curr. Microbiol. 1984, 10, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Dai, J.; Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, Y. Effects of fe-deficient conditions on Fe uptake and utilization in P-efficient soybean. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 112, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weber, F.A.; Hofacker, A.F.; Voegelin, A.; Kretzschmar, R. Temperature dependence and coupling of iron and arsenic reduction and release during flooding of a contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.G.; Suau, L.J.; Martin, T.A.; Jokela, E.J. Long-term effects of weed control and fertilization on the carbon and nitrogen pools of a slash and loblolly pine forest in north-central Florida. Can. J. For. Res. 2011, 41, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhao, K.; Liu, S. Factors affecting soil respiration in reference with temperature’s role in the global scale. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 1998, 8, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Liu, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Brookes, P.; Wu, J. Tracking the photosynthesized carbon input into soil organic carbon pools in a rice soil fertilized with nitrogen. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inselsbacher, E.; Wanek, W.; Ripka, K.; Hackl, E.; Sessitsch, A.; Strauss, J.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Greenhouse gas fluxes respond to different N fertilizer types due to altered plant-soil-microbe interactions. Plant Soil 2011, 343, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewopo, J.B.; Silveira, M.L.; Xu, S.; Gerber, S.; Sollenberger, L.E.; Martin, T.A. Long-term grassland intensification impacts on particle-size soil carbon fractions: Evidence from carbon-13 abundance. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Gao, H.X.; Liao, H.Y.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Liang, Z.W. An improved fast screening method for single and blended amine-based solvents for post-combustion CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 169, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Rachmilevitch, S.; Xu, J. Root carbon and protein metabolism associated with heat tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3455–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buyanovsky, G.A.; Wagner, G.H. Carbon cycling in cultivated land and its global significance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1998, 4, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, R.J.; Stevens, A.R.J.; Müller, A.C.; Watson, C.J. Evidence that fungi can oxidize NH4+ to NO3− in a grassland soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannert, A.; Bogen, C.; Esperschütz, J.; Koubová, A.; Buegger, F.; Fischer, D.; Radl, V.; Fu, R.; Chroňáková, A.; Evlhottová, D.; et al. Anaerobic oxidation of methane in grassland soils used for cattle husbandry. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3891–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.Q.; Zeng, C.S.; Tong, C. Reviews on electron acceptors of controlling methane production from Wetlands. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2009, 29, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, D.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Tan, M.; Sun, W. Carbon sequestration potential of recommended management practices for paddy soils of China, 1980–2050. Geoderma 2011, 166, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praeg, N.; Wagner, A.O.; Illmer, P. Effects of fertilisation, temperature and water content on microbial properties and methane production and methane oxidation in subalpine soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 65, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Gu, J.; Yu, J.; Han, G.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H. Effects of n fertilizer application on soil N2O emissions and CH4 uptake: A two-year study in an apple orchard in Eastern China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, K.; Bloor, J.M.G.; Ambus, P.; Soussana, J.F. Effects of clover density on N2O emissions and plant-soil n transfers in a fertilised upland pasture. Plant Soil 2011, 343, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Bo, Z.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Tao, W.; Bergmann, J.; Brüggemann, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Kuang, F. Nitrate leaching, direct and indirect nitrous oxide fluxes from sloping cropland in the purple soil area, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, S.; Yano, M.; Nishimura, S.; Akiyama, H.; Hayakawa, A.; Koba, K.; Sudo, S.; Yagi, K.; Makabe, A.; Tobari, Y.; et al. Characterization and production and consumption processes of N2O emitted from temperate agricultural soils determined via isotopomer ratio analysis. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25, GB2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Tong, C.; Ji, Q.; Peñuelas, J. Effects of fertilization on porewater nutrients, greenhouse-gas emissions and rice productivity in a subtropical paddy field. Exp. Agric. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsbursky, R.S.; Saltzman, S. CO2-nitrification relationships in closed soil incubation vessels. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Pan, Y.Z.; Zhao, L. The effects of N, P, K, and Ca on plant growth and nutrient content of Lily leaves. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2012, 21, 274–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, F.; Zhao, J.; Sun, R.G.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, W.P. Spatial distribution of soil nutrients and soil microbes in five arbore-bushe-grass lands at the south-north hills in lanzhou, China. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2010, 25, 990–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, F.; Jia, Y. Effects of shoot removal and soil water content on root respiration of spring wheat and soybean. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 56, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, L.J.; Matson, P.A.; Amundson, R. Effect of land use change on soil carbon in Hawaii. Biogeochemistry 2003, 65, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Townsend, A.R. Increases in soil respiration following labile carbon additions linked to rapid shifts in soil microbial community composition. Biogeochemistry 2007, 82, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.S.; Andresen, L.C.; Beier, C.; Jonasson, S.; Albert, K.R.; Ambus, P.; Arndal, M.F.; Carter, M.S.; Christensen, S.; Holmstrup, M.; et al. Reduced N cycling in response to elevated CO2, warming, and drought in a Danish heathland: Synthesizing results of the CLIMAITE project after two years of treatments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1884–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Crohn, D.M. Effects of soil salinity and carbon availability from organic amendments on nitrous oxide emissions. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillam, K.M.; Zebarth, B.J.; Burton, D.L. Nitrous oxide emissions from denitrification and the partitioning of gaseous losses as affected by nitrate and carbon addition and soil aeration. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalal, R.C.; Wang, W.; Robertson, G.P.; Parton, W.J. Nitrous oxide emission from Australian agricultural lands and mitigation options: A review. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, E.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Peng, B.; Dai, W.; Jiang, P.; Han, S. Pulse increase of soil N2O emission in response to N addition in a temperate forest on Mt Changbai, Northeast China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.Q.; Gao, Y.J.; Tian, X.H. Effect of plastic sheet mulch, wheat straw mulch, and maize growth on water loss by evaporation in dryland areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C. Effects of rice straw incorporation on active soil organic carbon pools in a subtropical paddy field. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zeng, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, D.; Wang, C.; Bartrons, M.; Peñuelas, J. Industrial and agricultural wastes decreased greenhouse-gas emissions and increased rice grain yield in a subtropical paddy field. Exp. Agric. 2018, 54, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Intensified soil acidification from chemical n fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of Southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, C.; Li, Z.G.; Yang, J.F.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, H.L.; Yost, R.; Wu, H.S. Acid soil is associated with reduced yield, root growth and nutrient uptake in black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Peñuelas, J. Response of soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry to different land uses in a subtropical wetland. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Roy, K.S.; Neogi, S.; Adhya, T.K.; Rao, K.S.; Manna, M.C. Effects of rice straw and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions and carbon storage in tropical flooded soil planted with rice. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Min, Q.; Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C.; Peñuelas, J. Responses of greenhouse-gas emissions to land-use change from rice to jasmine production in subtropical China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
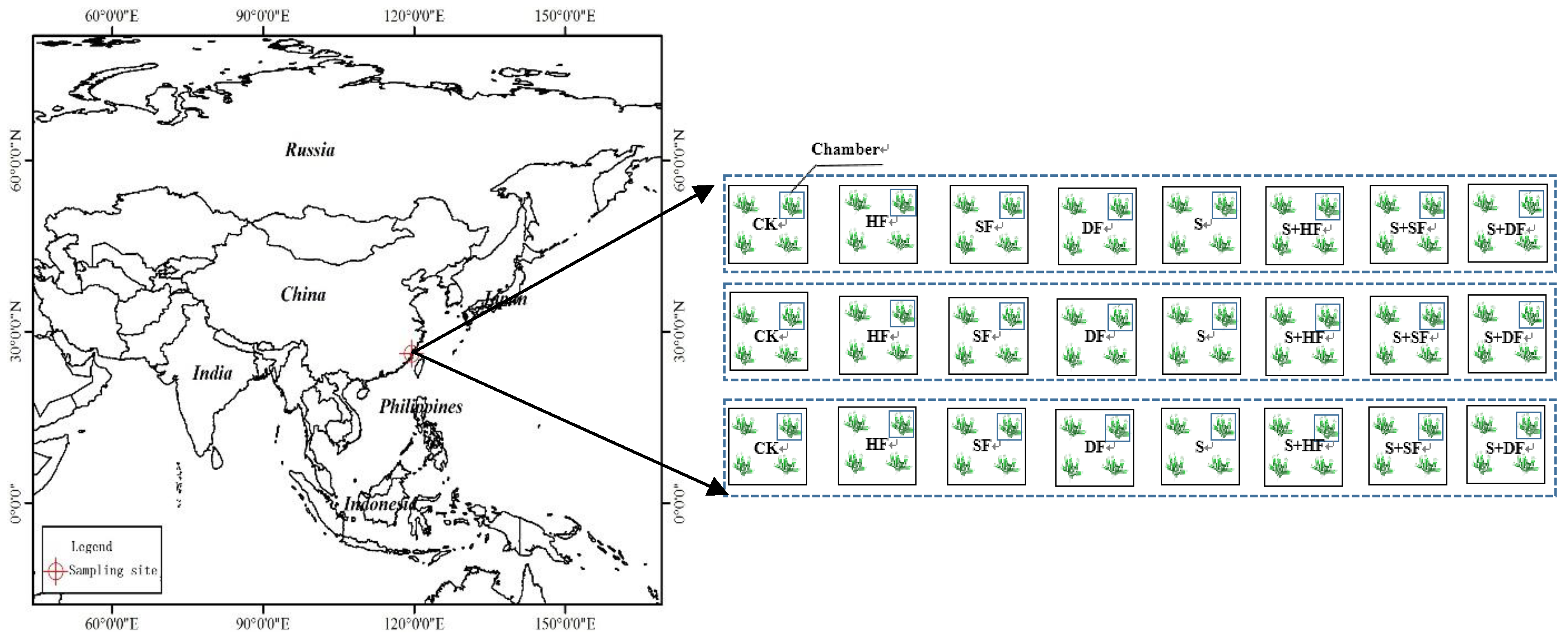





| Treatment | Straw | First Time Fertilizer (One Day after The J. sambac Was Cut) | Second Time Fertilizer (One Day after the First J. sambac Flowers Were Collected) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No fertilizer + no straw (control, CK) | No | No | No |
| Half fertilization + no straw (HF) | No | 65 kg ha−1 | 50 kg ha−1 |
| Standard fertilization + no straw (SF) | No | 130 kg ha−1 | 100 kg ha−1 |
| Double fertilization + no straw (DF) | No | 260 kg ha−1 | 200 kg ha−1 |
| No fertilizer + straw (S) | 3.5 Mg ha−1 | No | No |
| Half fertilization + straw (S + HF) | 3.5 Mg ha−1 | 65 kg ha−1 | 50 kg ha−1 |
| Standard fertilization + straw (S + SF) | 3.5 Mg ha−1 | 130 kg ha−1 | 100 kg ha−1 |
| Double fertilization + straw (S + DF) | 3.5 Mg ha−1 | 260 kg ha−1 | 200 kg ha−1 |
| Index | Variables | df | MS | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | 7 | 2,013,690 | 1.27 | <0.01 | |
| CO2 | Time | 10 | 23,182,135 | 42.71 | <0.01 |
| Treatments × Time | 70 | 4,654,081 | 1.23 | 0.15 | |
| Treatments | 7 | 119,844 | 4.07 | <0.01 | |
| CH4 | Time | 10 | 155,377 | 4.94 | <0.01 |
| Treatments × Time | 70 | 1,689,456 | 7.68 | <0.01 | |
| Treatments | 7 | 20,378 | 11.71 | <0.01 | |
| N2O | Time | 10 | 212,118 | 85.85 | <0.01 |
| Treatments × Time | 70 | 488,849 | 28.26 | <0.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Min, Q.; Abid, A.A.; Sardans, J.; Wu, H.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Peñuelas, J.; Wang, W. Optimal Coupling of Straw and Synthetic Fertilizers Incorporation on Soil Properties, Active Fe Dynamics, and Greenhouse Gas Emission in Jasminum sambac (L.) Field in Southeastern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041092
Wang C, Min Q, Abid AA, Sardans J, Wu H, Lai DYF, Peñuelas J, Wang W. Optimal Coupling of Straw and Synthetic Fertilizers Incorporation on Soil Properties, Active Fe Dynamics, and Greenhouse Gas Emission in Jasminum sambac (L.) Field in Southeastern China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(4):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041092
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chun, Qingwen Min, Abbas Ali Abid, Jordi Sardans, Honghui Wu, Derrick Yuk Fo Lai, Josep Peñuelas, and Weiqi Wang. 2019. "Optimal Coupling of Straw and Synthetic Fertilizers Incorporation on Soil Properties, Active Fe Dynamics, and Greenhouse Gas Emission in Jasminum sambac (L.) Field in Southeastern China" Sustainability 11, no. 4: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041092
APA StyleWang, C., Min, Q., Abid, A. A., Sardans, J., Wu, H., Lai, D. Y. F., Peñuelas, J., & Wang, W. (2019). Optimal Coupling of Straw and Synthetic Fertilizers Incorporation on Soil Properties, Active Fe Dynamics, and Greenhouse Gas Emission in Jasminum sambac (L.) Field in Southeastern China. Sustainability, 11(4), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11041092







