Repulsive Effect of Stroboscopic Light Barriers on Native Salmonid (Salmo trutta) and Cyprinid (Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Luciobarbus bocagei) Species of Iberia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Target Species
2.3. Test Stimuli
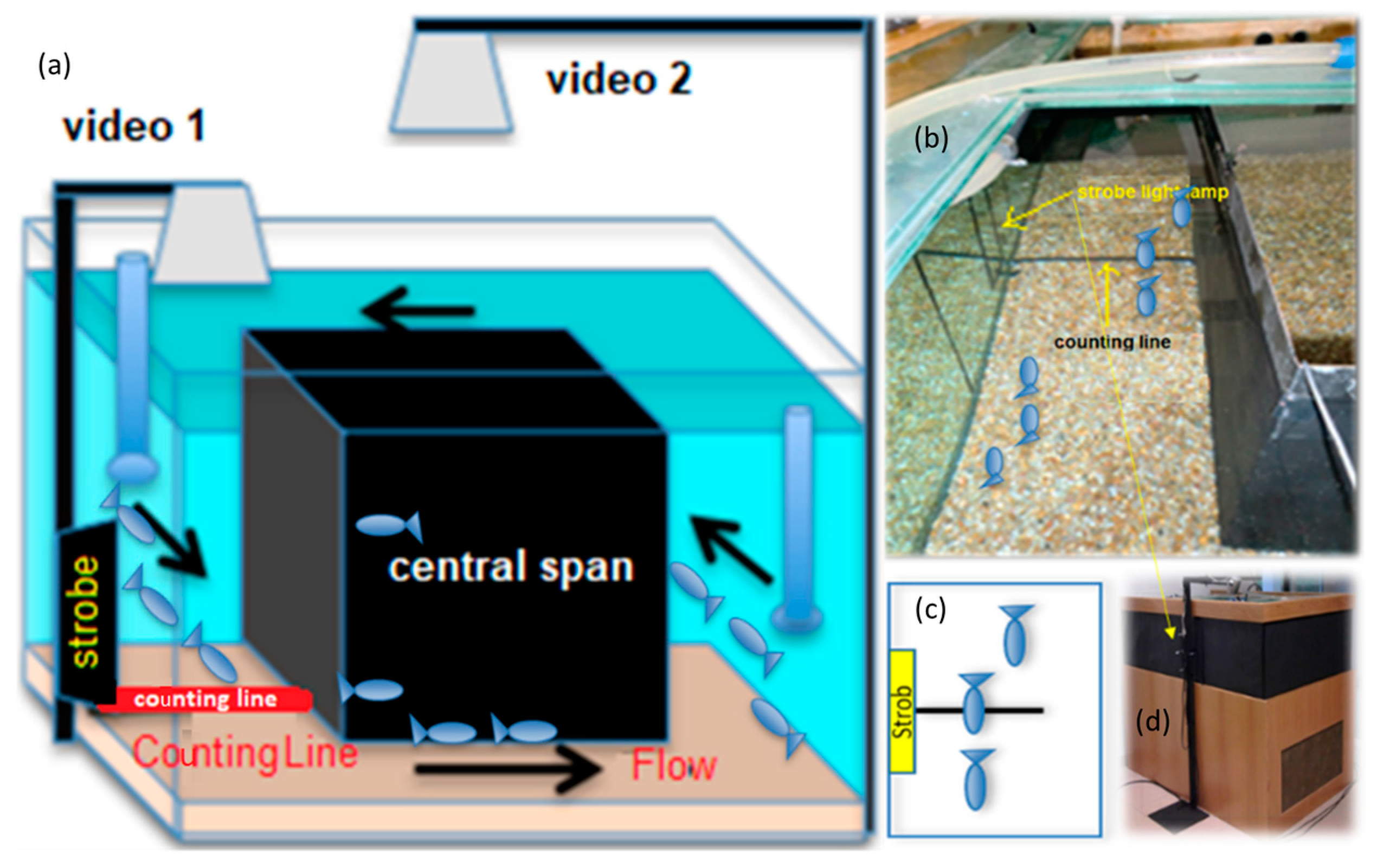
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M. Threatening processes and conservation management of endemic freshwater fish in the Mediterranean basin: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baras, E.; Lucas, M.C. Impacts of man’s modifications of river hydrology on the migration of freshwater fishes: A mechanistic perspective. Int. J. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2001, 1, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Noatch, M.R.; Suski, C.D. Non-physical barriers to deter fish movements. Environ. Rev. 2012, 20, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.J. Population Dynamics and Schooling Behaviour in the Minnow. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Fredrich, F. Preliminary studies on daily migration of chub (Leuciscus cephalus) in the Spree River. In Underwater Biotelemetry, Proceedings of the First Conference and Workshop on Fish Telemetry in Europe, Liège, Belgium, 4–6 April 1995; University of Liège: Liège, Belgium, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.; Baras, E. Migration of Freshwater Fishes; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, D.F.; Pires, A.M.; Collares-Pereira, M.J.; Magalhães, M.F. Variation in fish assemblages across dry-season pools in a Mediterranean stream: Effects of pool morphology, physicochemical factors and spatial context. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2010, 19, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, M.J.; Almeida, J.; Almeida, P.R.; Dellinger, T.; Ferrand de Almeida, N.; Oliveira, M.E.; Palmeirim, J.M.; Queirós, A.I.; Rogado, L.; Santos-Reis, M. Livro Vermelho dos Vertebrados de Portugal; Instituto da Conservação da Natureza: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, A.; Cortes, R.M. PIT telemetry as a method to study the habitat requirements of fish populations: Application to native and stocked trout movements. In Developments in Fish Telemetry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, C.; Rives, J.; Labonne, J. Effect of habitat fragmentation on spawning migration of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.). Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Reino, L.; Porto, M.; Oliveira, J.; Pinheiro, P.; Almeida, P.R.; Cortes, R.; Ferreira, M.T. Complex size-dependent habitat associations in potamodromous fish species. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M. Shifting baselines and the conservation of non-native species. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovidio, M.; Philippart, J.-C. Movement patterns and spawning activity of individual nase Chondrostoma nasus (L.) in flow-regulated and weir-fragmented rivers. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2008, 24, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, C.S.; Amidan, B.G.; Cada, G.F. Simulated Passage through a Modified Kaplan Turbine Pressure Regime: A Supplement to “Laboratory Studies of the Effects of Pressure and Dissolved Gas Supersaturation on Turbine-Passed Fish”; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2002.
- Rytwinski, T.; Algera, D.A.; Taylor, J.J.; Smokorowski, K.E.; Bennett, J.R.; Harrison, P.M.; Cooke, S.J. What are the consequences of fish entrainment and impingement associated with hydroelectric dams on fish productivity? A systematic review protocol. Environ. Evid. 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čada, G.F.; Coutant, C.C.; Whitney, R.R. Development of Biological Criteria for the Design of Advanced Hydropower Turbines; DOE/ID-10578; US Department of Energy, Idaho Operations Office: Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 1997.
- Čada, G.F. The development of advanced hydroelectric turbines to improve fish passage survival. Fisheries 2001, 26, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydro, B.C. Developing Measures for the Aquatic Habitat Attribute in BC Hydro’s 2005 Integrated Electricity Plan; Ecofish Research Ltd.: Courtenay, BC, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hamel, M.J.; Brown, M.L.; Chipps, S.R. Behavioral responses of rainbow smelt to in situ strobe lights. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2008, 28, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Mandrak, N.E. Effects of strobe lights on the behaviour of freshwater fishes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2017, 100, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, O.; ENGER, P.; Karlsen, H.E.; Knudsen, F.R. To Intense Infrasound In Juvenile Salmonids. In Proceedings of the American Fisheries Society Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 20–21 August 2001; Volume 26, pp. 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, J.; Turnpenny, A.W.H.; Lambert, D.R.; Nedwell, J.R.; Parmentier, A.; Ollevier, F. Field evaluation of a sound system to reduce estuarine fish intake rates at a power plant cooling water inlet. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolie, M.A.; Harryman, B.; Ament, B. Response of free-ranging kokanee to strobe lights. In Proceedings of the Behavioral Technologies for Fish Guidance: American Fisheries Society Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20–23 May 2001; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Königson, S.; Fjälling, A.; Lunneryd, S.-G. Reactions in individual fish to strobe light. Field and aquarium experiments performed on whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus). Hydrobiologia 2002, 483, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.E.; Barkley, T.L.; Creque, S.M.; Dettmers, J.M.; Stainbrook, K.M. Evaluation of an electric fish dispersal barrier in the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal. In American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010; Volume 74. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, R.W. Effectiveness of electrical fish barriers associated with the Central Arizona Project. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2004, 24, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kates, D.; Dennis, C.; Noatch, M.R.; Suski, C.D. Responses of native and invasive fishes to carbon dioxide: Potential for a nonphysical barrier to fish dispersal. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.G.M. Estudo de Sistemas para Repulsão de Peixes Como Alternativas de Mitigação de Impacto Ambiental em Usinas Hidrelétricas e Canais para Abastecimento de Água. Ph.D. Thesis, UFMG, Belo Horizonte, Brzail, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruebush, B.C. In-situ Tests of Sound-Bubble-Strobe Light Barrier Technologies to Prevent the Range Expansions of Asian Carp. 2011. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2142/26112 (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Stewart, H.A.; Wolter, M.H.; Wahl, D.H. Laboratory investigations on the use of strobe lights and bubble curtains to deter dam escapes of age-0 Muskellunge. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2014, 34, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, D.R.; Hocutt, C.H.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Estuarine fish responses to strobe light, bubble curtains and strobe light/bubble-curtain combinations as influenced by water flow rate and flash frequencies. Fish. Res. 1987, 5, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.L.; Simmons, M.A.; McKinstry, C.A.; Simmons, C.S.; Cook, C.B.; Brown, R.S.; Tano, D.K.; Thorsten, S.L.; Faber, D.M.; Lecaire, R. Strobe Light Deterrent Efficacy Test and Fish Behavior Determination at Grand Coulee Dam Third Powerplant Forebay; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2005.
- Lythgoe, J.N. Ecology of Vision; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Puckett, K.J.; Anderson, J.J. Behavioral Responses of Juvenile Salmonids to Strobe and Mercury Lights; Fisheries Research Institute: Seattle, WA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, N.S.; Chipps, S.R.; Brown, M.L. Stress response and avoidance behavior of fishes as influenced by high-frequency strobe lights. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.G.M.; Martinez, C.B.; Formagio, P. Uso de luz estroboscópica para repulsão de peixes de áreas de risco em usinas hidrelétricas. SIMPÓSIO Bras. SOBRE PEQUENAS E MÉDIAS CENTRAIS HIDRELÉTRICAS 2006, 5, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ovidio, M.; Parkinson, D.; Philippart, J.-C.; Baras, E. Multiyear homing and fidelity to residence areas by individual barbel (Barbus barbus). Belg. J. Zool. 2007, 137, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, J.-P.; Ovidio, M. The influence of environmental factors on the upstream movements of rheophilic cyprinids according to their position in a river basin. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2018, 27, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Boavida, I.; Almeida, V.; Cooke, S.J.; Pinheiro, A.N. Do artificial velocity refuges mitigate the physiological and behavioural consequences of hydropeaking on a freshwater Iberian cyprinid? Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, C.C.; Whitney, R.R. Fish behavior in relation to passage through hydropower turbines: A review. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 351–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.M.; Pegg, M.A.; Chick, J.H. Response of bighead carp to a bioacoustic behavioural fish guidance system. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2005, 12, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, B.J.; Cupp, A.R.; Fredricks, K.T.; Gaikowski, M.P.; Mensinger, A.F. Acoustical deterrence of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 3383–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilt, C.R. Developing fish passage and protection at hydropower dams. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.W.; Romine, J.G.; Adams, N.S.; Blake, A.R.; Burau, J.R.; Johnston, S.V.; Liedtke, T.L. Using a non-physical behavioural barrier to alter migration routing of juvenile chinook salmon in the sacramento–san joaquin river delta. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedwell, J.R.; Turnpenny, A.W.; Lovell, J.M.; Edwards, B. An investigation into the effects of underwater piling noise on salmonids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2550–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vowles, A.S.; Kemp, P.S. Effects of light on the behaviour of brown trout (Salmo trutta) encountering accelerating flow: Application to downstream fish passage. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 47, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Carlson, T.J. Application of sound and other stimuli to control fish behavior. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1998, 127, 673–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, C.R.; Carlson, T.J. Non-physical fish barrier systems: Their development and potential applications to marine ranching. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, R.S.; Anderson, J.J. Response of juvenile coho and chinook salmon to strobe and mercury vapor lights. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1992, 12, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, C.C. Integrated, multi-sensory, behavioral guidance systems for fish diversion. In Behavioral Technologies for Fish Guidance: American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Taft, E.P.; Dixon, D.A.; Sullivan, C.W. Electric Power Research Institute’s (EPRI) research on behavioral technologies. In Behavioral Technologies for Fish Guidance: American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, P.H.; Christie, A.E.; Sager, D.; Hocutt, C.; Stauffer, J., Jr. Responses of fish to a strobe light/air-bubble barrier. Fish. Res. 1985, 3, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Mesquita, F.; Godinho, H.P.; de Azevedo, P.G.; Young, R.J. A preliminary study into the effectiveness of stroboscopic light as an aversive stimulus for fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 111, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.V.; Winchell, F.C.; Pearsons, T.N. Behavioral Technologies for Fish Guidance: American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.J.; Cocherell, D.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Patrick, P.H.; Sills, M.; Fangue, N.A. Behavioural guidance of Chinook salmon smolts: The variable effects of LED spectral wavelength and strobing frequency. Conserv. Physiol. 2018, 6, coy032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruetz III, C.R.; Hurford, A.L.; Vondracek, B. Interspecific interactions between brown trout and slimy sculpin in stream enclosures. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat: Cornol, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, A.R.; Townsend, C.R. Contrasting predation risks presented by introduced brown trout and native common river galaxias in New Zealand streams. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, N.H.C.; Metcalfe, N.B. The costs of becoming nocturnal: Feeding efficiency in relation to light intensity in juvenile Atlantic salmon. Funct. Ecol. 1997, 11, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, R.A.; Reynolds, W.W.; Casterlin, M.E. Diel locomotor activity patterns of wild brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) in an electronic shuttlebox. Hydrobiologia 1979, 66, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntz, W.R. Visual adaptations to different light environments in Amazonian fishes. Rev. Can. Biol. Exp. 1982, 41, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, N.W. The relationship of ocular morphology to feeding modes and activity periods in shallow marine teleosts from New Zealand. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 26, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Specie (dates) | Trial | Counting Line 1 (n°. of fishes) | Relative Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-test | Testing | ||||
| S. trutta (19/5/2011–8/8/2011) | 350 flashes/min | Day | 2354 | 535 | 77.27 |
| night | 1606 | 819 | 49.00 | ||
| 600 flashes/min | day | 1558 | 189 | 87.87 2 | |
| night | 1328 | 437 | 67.09 3 | ||
| P. duriense (13/6/2011–8/7/2011) | 350 flashes/min | day | 2329 | 1376 | 40.92 |
| night | 2273 | 374 | 64.50 | ||
| 600 flashes/min | day | 3156 | 1298 | 58.87 | |
| night | 1740 | 975 | 43.97 | ||
| L. bocagei (16/6/2011–10/7/2011) | 350 flashes/min | day | 2538 | 1822 | 28.21 |
| night | 2466 | 2176 | 11.76 | ||
| 600 flashes/min | day | 2428 | 1771 | 27.06 | |
| night | 2055 | 1529 | 25.60 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jesus, J.; Teixeira, A.; Natário, S.; Cortes, R. Repulsive Effect of Stroboscopic Light Barriers on Native Salmonid (Salmo trutta) and Cyprinid (Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Luciobarbus bocagei) Species of Iberia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051332
Jesus J, Teixeira A, Natário S, Cortes R. Repulsive Effect of Stroboscopic Light Barriers on Native Salmonid (Salmo trutta) and Cyprinid (Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Luciobarbus bocagei) Species of Iberia. Sustainability. 2019; 11(5):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051332
Chicago/Turabian StyleJesus, Joaquim, Amílcar Teixeira, Silvestre Natário, and Rui Cortes. 2019. "Repulsive Effect of Stroboscopic Light Barriers on Native Salmonid (Salmo trutta) and Cyprinid (Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Luciobarbus bocagei) Species of Iberia" Sustainability 11, no. 5: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051332
APA StyleJesus, J., Teixeira, A., Natário, S., & Cortes, R. (2019). Repulsive Effect of Stroboscopic Light Barriers on Native Salmonid (Salmo trutta) and Cyprinid (Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Luciobarbus bocagei) Species of Iberia. Sustainability, 11(5), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051332






