Numerical Study of Sediment Erosion Analysis in Francis Turbine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Erosion Phenomena
2.1. Erosion
2.2. Erosion Model
3. Computer Simulation
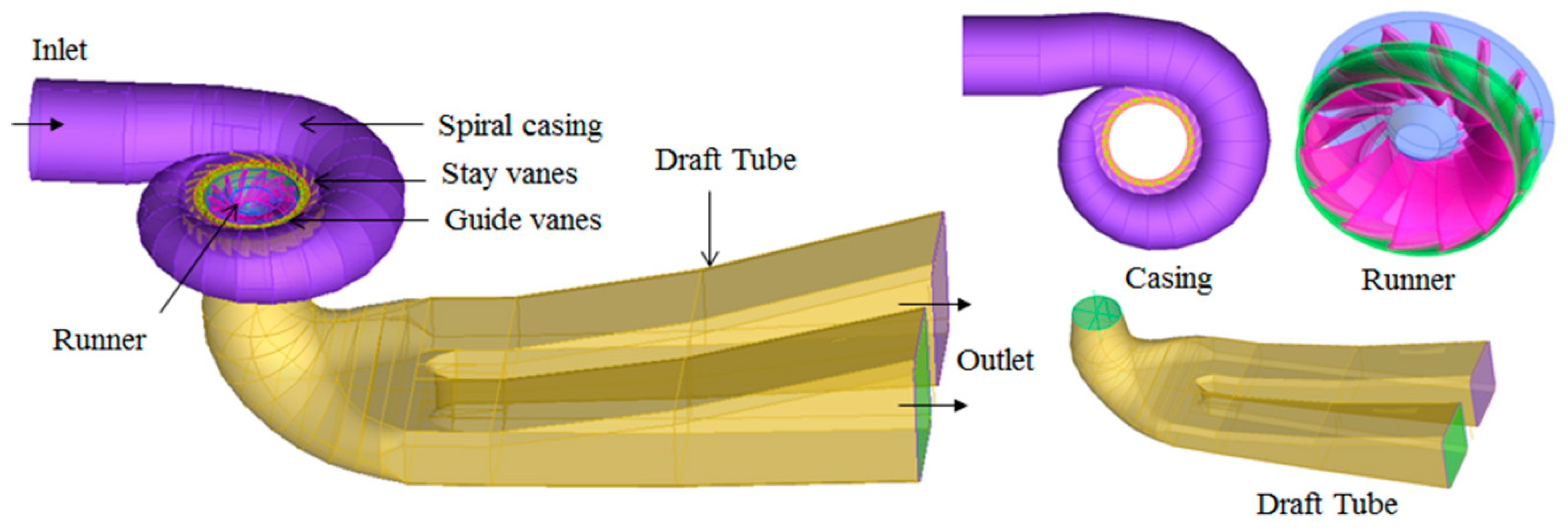
3.1. Geometrical Modeling and Meshing
3.2. Numerical Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Validation of Numerical Results
4.2. Erosion Effects on Performance Characteristics
4.2.1. Effect of Sediment Inflow Rates
4.2.2. Influence of Sediment Particle Shape Factor
4.3. Cavitation-Erosion Effects
4.4. Comparison of Performances at Different Sand Inflow Rates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CFD | Computational Fluid dynamics |
| GCI | Grid convergence index |
| KIMM | Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials |
| SSU | Soongsil University |
| C | Concentration of particle, kg/m3 |
| c | Velocity of particle, m/s |
| df | Degree of freedom |
| E | Erosion rate, mm/yr |
| f(α) | Function of impingement angle |
| f(Vpn) | Function of velocity of particle |
| f | Uncertainty |
| Kmat | Material constant |
| Kenv | Environmental constant |
| k1, k2, k3, k4, k12 | Variable constant |
| Mass of the particle | |
| Mr | Coefficient of water resistance |
| Number rate | |
| n | Exponent number |
| Pf | Abrasive power |
| r | Grid ratio |
| Rθ | Tangential restitution factor |
| R | Radius of curvature on surface |
| S1 | Coefficient of sediment concentration |
| S2 | Coefficient of sediment hardness |
| S3 | Coefficient of sediment particle size |
| S4 | Coefficient of sediment shape |
| V | Velocity, m/s |
| Volume of particle | |
| Vp | Particle impact velocity, m/s |
| W | Erosion rate, mm/year |
| Greek Symbols | |
| α | Impingement angle, degree |
| β | Impact angle, rad |
| μ | coefficient of friction between particle and surface |
| ρ | Density, kg/m3 |
References
- Li, W.F.; Feng, J.J.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.L.; Liao, W.L.; Luo, X.Q. Numerical Investigation of Pressure Fluctuation Reducing in Draft Tube of Francis Turbines. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2015, 8, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.S.; Arya, V. Abrasive and erosive wear characteristics of plasma nitriding and HVOF coatings: Their application in hydro turbines. Wear 2001, 249, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, M.K.; Saini, R.P. A review on silt erosion in hydro turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1974–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, W.; Tilly, G.P. The significance of particles sizes in sand erosion of small gas turbines. R. Aeronaut. Soc. J. 1969, 73, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.F.; Tabakoff, W. Dynamic Behavior of Solid Particles Suspended by Polluted Flow in a Turbine Stage. J. Aircr. 1973, 10, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.F.; Tabakoff, W. Computation and plotting of solid particle flow in rotating cascades. Comput. Fluids 1974, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.; Tabakoff, W. Erosion prediction in turbomachinery resulting from environmental solid particles. J. Aircr. 1975, 12, 471–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Tabakoff, W. Experimental and Numerical Simulations of the Effects of Ingested Particles in Gas Turbine Engines. In AGARD Conference Proceedings; AGARD: London, UK, 1994; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ghenaiet, A. Modeling of Particle Trajectory and Erosion of Large Rotor Blades. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7928347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.S.; Dahlhaug, O.G.; Thapa, B. Sediment erosion in hydro turbines and its effect on the flow around guide vanes of Francis turbine. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chai, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W. A 10-Year Statistical Analysis of Heavy Metals in River and Sediment in Hengyang Segment, Xiangjiang River Basin, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Ai, M. Variation Trend Analysis of Runoff and Sediment Time Series Based on the R/S Analysis of Simulated Loess Tilled Slopes in the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S. Essential design features for efficient sediment management. Int. J. Hydropower Dams 2005, 12, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chamoun, S.; De Cesare, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Managing reservoir sedimentation by venting turbidity currents: A review. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J.; Juez De Cesare, G. Reservoir sedimentation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, H.P.; Shakya, N.M.; Stole, H.; Garg, N.K. Sediment exclusion in Himalayan rivers using hydro cyclone. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 14, 118–133. [Google Scholar]
- Gabl, R.; Gems, B.; Birkner, F.; Hofer, B.; Aufleger, M. Adaptation of an Existing Intake Structure Caused by Increased Sediment Level. Water 2018, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.; Upadhyay, P.; Dahlhaug, O.G.; Timsina, M.; Basnet, R. HVOF coatings for erosion resistance of hydraulic turbines: Experience of Kaligandaki-A Hydropower Plant. In Proceedings of the 2 International Symposium on Water Resources and Renewable Energy Development in Asia, Danang, Vietnam, 10–11 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Egusquiza, E.; Valero, C.; Estévez, A.; Guardo, A.; Coussirat, M. Failures due to ingested bodies in hydraulic turbines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weili, L.; Jinling, L.; Xingqi, L.; Yuan, L. Research on the cavitation characteristic of Kaplan turbine under sediment flow condition. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 12, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zeng, Y.-Z.; Wang, H.-Y.; Ou, S.-B.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, X.-B. Numerical analysis of solid–liquid two-phase turbulent flow in Francis turbine runner with splitter blades in sandy water. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, K.; Suh, S.H. Numerical and experimental investigation of cavitation flows in a multistage centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Sci. Tech. 2018, 32, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Bhingole, P.P. CFD based analysis of combined effect of cavitation and silt erosion on Kaplan turbine. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 2314–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, H.-H.; Park, N.; Suh, S.-H. Numerical Prediction of Sediment Erosion due to Sediment Concentrations in Francis Turbine. In Proceedings of the 7th Asia-Pacific Forum on Renewable Energy (AFORE), Busan, Korea, 15–18 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, B.S.; Thapa, B.; Eltvik, M.; Gjosater, K.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Optimizing runner blade profile of Francis turbine to minimize sediment erosion. In Proceedings of the 26th IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and systems, Beijing, China, 19–23 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.G.; Karelin, V.Y. Abrasive Erosion and Corrosion of Hydraulic Machinery; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Truscott, G.F. A literature survey on abrasive wear in hydraulic machinery. Wear 1972, 20, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neopane, H.P. Sediment Erosion in Hydro Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, G.C.; Souza, F.J.; Martins, D.A. Numerical prediction of the erosion due to particles in elbows. Powder Technol. 2014, 261, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, P. Consideration of the factors influencing wear due to hydraulic transport of solid materials. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Hydraulic Transport and Separation of Solid Materials, Société Hydrotechnique de France, Paris, France, June 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, P.; Dollfus, J. The influence of nature of the pumped mixture and hydraulic characteristics on design and installation of liquid/solid mixture pumps. In Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Hydraulics, January 1958; Volume 2, pp. 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Bovet, T. Contribution to study of the phenomenon of abrasive erosion in the realm of hydraulic turbines. Bull. Tech. Suisse Romande 1958, 84, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Finnie, I. Erosion of Surfaces by Solid Particles. Wear 1960, 3, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, I.M. Tribology, Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials, 1st ed.; Elsevier Limited: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys Inc. ANSYS-CFX (CFX Introduction, CFX Reference Guide, CFX Tutorials, CFX-Pre User’s Guide, CFX-Solver Manager User’s Guide, Theory Guide), Release 16.00; Ansys Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.-W.; Park, N.; Suh, S.-H. Numerical study on sediment erosion of Francis turbine with different operating conditions and sediment inflow rates. Procedia Eng. 2016, 157, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, C.; Cervantes, M.J.; Gandhi, B.K.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Experimental and Numerical Studies for a High Head Francis Turbine at Several Operating Points. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2013, 135, 111102–111117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, J.; Gebart, R. Estimation of Numerical Accuracy for the Flow Field in a Draft Tube. Int. J. Num. Meth. Heat Fluid Flow 1999, 9, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.B.; Ghia, U.; Roache, P.J.; Freitas, C.J.; Coleman, H.; Raad, P.E. Procedure for Estimation and Reporting of Uncertainty due to Discretization in CFD Applications. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Gamiz, U.; Errasti, I.; Gutierrez-Amo, R.; Boyano, A.; Barambones, O. Computational Modelling of Rectangular Sub-Boundary Layer Vortex Generators. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roache, P.J. Conservatism of the Grid Convergence Index in Finite Volume Computations on Steady-State Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2003, 125, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadafalch, J.; Perez-Segarra, R.; Consul, R.; Oliva, A. Verification of Finite Volume Computations on Steady State Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer. J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortiz, R. Transient CFD-Analysis of a High Head Francis Turbine. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Friziger, J.H.; Peric, M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.J.; Zullah, M.A.; Roh, H.W.; Ha, P.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H. CFD validation of performance improvement of a 500 kW Francis turbine. Renew. Energy 2013, 54, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-H.; Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, K.; Suh, S.-H. Flow and Fast Fourier Transform Analyses for Tip Clearance Effect in an Operating Kaplan Turbine. Energies 2019, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD, 1st ed.; DCW Industries, Inc.: La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-Equation Eddy-Viscosity Turbulence Models for Engineering Applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, N.J.; Yoder, D.A.; Engblorn, W.B. Evaluation of modified two-equation turbulence models for jet flow predictions. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEI/IEC-60193, Hydraulic Turbines, Storage Pumps and Pump-Turbines- Model Acceptance Tests; International Standard; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Longo, S.; Di Federico, V.; Chiapponi, L. Non-Newtonian power-law gravity currents propagating in confining boundaries. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Di Federico, V.; Chiapponi, L. A dipole solution for power-law gravity currents in porous formations. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 778, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, K.; Park, N.; Suh, S.-H. Numerical study of sediment erosion and surface roughness analyses in Francis turbine. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computational Heat and Mass Transfer, Cracow, Poland, 21–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]















| Description | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Runner inlet diameter (mm) | 2728 |
| Runner outlet diameter (mm) | 2546 |
| Head (m) | 95 |
| Flow rate (m3/s) | 59.4 |
| Max. power (MW) | 51.6 |
| Rotational speed (rpm) | 257 |
| Runner blade | 13 |
| Guide vane | 24 |
| Stay vane | 23 |
| Description | Elements | Nodes | Min. Y+ | Max. Y+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spiral casing | 14,552,267 | 246,6738 | 0.81 | 476 |
| Runner | 15,868,719 | 268,2908 | 2.71 | 274 |
| Draft tube | 4,368,719 | 785,142 | 1.58 | 66 |
| Total | 34,789,303 | 5,934,788 |
| No. | Nodes | Grid Ratio, r | Efficiency (%) | Error, ea (%) | GCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 963,652 | 2.788 | 90.82 | 0.1515 | 0.02844 |
| 2 | 2,686,965 | 1.337 | 90.96 | 0.9344 | 1.48009 |
| 3 | 3,594,116 | 1.133 | 91.81 | 0.1742 | 0.76761 |
| 4 | 4,072,292 | 1.245 | 91.97 | 0.3153 | 0.71562 |
| 5 | 5,071,234 | 1.170 | 92.26 | 0.1409 | 0.47659 |
| 6 | 5,934,788 | 1.020 | 92.39 | 0.0324 | 0.98898 |
| 7 | 6,055,348 | 0.102 | 92.36 | 0.0866 | 0.10943 |
| Description | Efficiency (%) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-experiment (Fuji Electric Co.) | 93.292 (Exp.) | 0 |
| Reverse design (KIMM) | 92.324 (Sim.) | 1.0485 |
| Simulation (KIMM) | 92.724 (Sim.) | 0.6088 |
| Simulation (SSU) | 92.398 (Sim.) | 0.9579 |
| Experiment (KIMM) | 92.781 (Exp.) | 0.5477 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, K.; Suh, S.-H.; Kim, K.Y. Numerical Study of Sediment Erosion Analysis in Francis Turbine. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051423
Rakibuzzaman M, Kim H-H, Kim K, Suh S-H, Kim KY. Numerical Study of Sediment Erosion Analysis in Francis Turbine. Sustainability. 2019; 11(5):1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051423
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakibuzzaman, Md, Hyoung-Ho Kim, Kyungwuk Kim, Sang-Ho Suh, and Kyung Yup Kim. 2019. "Numerical Study of Sediment Erosion Analysis in Francis Turbine" Sustainability 11, no. 5: 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051423
APA StyleRakibuzzaman, M., Kim, H.-H., Kim, K., Suh, S.-H., & Kim, K. Y. (2019). Numerical Study of Sediment Erosion Analysis in Francis Turbine. Sustainability, 11(5), 1423. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051423







