Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Trend and Correlation Analyses
2.3.2. Spatial Variation of Groundwater
2.3.3. Drought Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Changes in Precipitation
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Groundwater Levels
3.3. Spatial Variation of Water Level Changes
3.4. Groundwater Drought
3.5. Sustainability Assessment of Groundwater Resources
3.5.1. Groundwater Budget of the MRB
3.5.2. Groundwater Quality
4. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Year | Amount of Rainfall (mm) | Rainy Day | Rainfall Intensity (Wet Season, mm/d) | Net P. * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | Wet Season | Dry Season | Ratio (Wet/Annual) | Annual | Wet Season | >50 (mm/d) | >100 (mm/d) | |||
| 2005 | 1390 | 1130 | 260 | 81.3 | 128 | 55 | 6 | 2 | 20.5 | 401 |
| 2006 | 1188 | 815 | 373 | 68.6 | 118 | 52 | 2 | 1 | 15.7 | 169 |
| 2007 | 1472 | 1106 | 366 | 75.2 | 127 | 62 | 5 | 1 | 17.8 | 533 |
| 2008 | 1000 | 683 | 317 | 68.3 | 113 | 57 | 3 | 0 | 12.0 | -47 |
| 2009 | 1164 | 842 | 322 | 72.3 | 115 | 46 | 5 | 0 | 18.3 | 73 |
| 2010 | 1463 | 984 | 479 | 67.3 | 136 | 61 | 8 | 1 | 16.1 | 451 |
| 2011 | 1622 | 1168 | 454 | 72.0 | 123 | 58 | 4 | 2 | 20.1 | 582 |
| 2012 | 1360 | 992 | 368 | 73.0 | 123 | 49 | 6 | 0 | 20.2 | 257 |
| 2013 | 1265 | 818 | 447 | 64.7 | 119 | 49 | 5 | 0 | 16.7 | 199 |
| 2014 | 1207 | 756 | 451 | 62.6 | 124 | 57 | 4 | 0 | 13.3 | 19 |
| 2015 | 814 | 332 | 481 | 40.8 | 119 | 38 | 0 | 0 | 8.7 | -376 |
| Year. | Station | pH | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 | NO3-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | G-1 * | 7.8 | 38.4 | 8.8 | 21.5 | 1.8 | 9.5 | 0.8 | 58.0 | 3.1 |
| G-2a | 7.8 | 22.2 | 8.5 | 19.4 | 1.7 | 15.6 | 38.2 | 58.0 | 10.3 | |
| G-2b | 6.6 | 41.1 | 11.9 | 20.2 | 2.5 | 32.2 | 46.8 | 58.0 | 17.2 | |
| G-3a | 6.6 | 34.4 | 21.9 | 9.8 | 3.3 | 19.8 | 31.0 | 152.5 | 0.2 | |
| G-3b | 6.6 | 32.6 | 20.7 | 12.0 | 5.0 | 22.6 | 32.0 | 122.0 | 5.8 | |
| G-4a* | 6.5 | 42.1 | 10.3 | 13.5 | 3.3 | 28.1 | 13.2 | 61.0 | 4.9 | |
| G-4b* | 7.1 | 13.8 | 2.0 | 4.3 | 1.3 | 21.7 | 12.3 | 125.1 | 5.0 | |
| G-5* | 6.5 | 28.6 | 7.7 | 10.5 | 2.8 | 5.0 | 9.9 | 30.5 | 4.0 | |
| 2010 | G-1 | 7.7 | 18.5 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 1.2 | 12.1 | 0.7 | 48.8 | 4.5 |
| G-2a | 6.5 | 22.6 | 10.6 | 25.0 | 1.8 | 20.1 | 41.9 | 51.9 | 9.0 | |
| G-2b | 6.6 | 39.7 | 11.6 | 23.4 | 2.7 | 26.8 | 42.5 | 61.0 | 16.6 | |
| G-3a | 6.8 | 39.2 | 27.1 | 12.0 | 2.9 | 26.9 | 53.4 | 173.9 | 0.3 | |
| G-3b | 7.0 | 34.2 | 22.9 | 14.9 | 4.5 | 25.4 | 41.0 | 128.1 | 5.9 | |
| G-4a | 6.5 | 36.9 | 9.0 | 24.2 | 2.5 | 37.0 | 19.8 | 97.6 | 6.5 | |
| G-4b | 7.2 | 39.2 | 9.3 | 15.0 | 2.1 | 19.1 | 10.7 | 125.1 | 4.8 | |
| G-5 | 7.0 | 34.7 | 4.3 | 9.1 | 2.1 | 9.7 | 22.1 | 82.4 | 5.5 | |
| 2012 | G-1 | 7.5 | 33.9 | 7.7 | 16.4 | 5.0 | 22.6 | 13.6 | 94.6 | 5.5 |
| G-2a | 6.0 | 24.7 | 11.6 | 27.0 | 1.8 | 16.4 | 37.9 | 64.1 | 9.9 | |
| G-2b | 6.2 | 47.2 | 13.9 | 26.5 | 3.2 | 27.9 | 39.4 | 91.5 | 10.6 | |
| G-3a | 6.3 | 42.4 | 26.8 | 12.4 | 2.8 | 27.8 | 47.8 | 164.7 | 1.3 | |
| G-3b | 6.5 | 36.1 | 22.7 | 15.3 | 4.3 | 29.7 | 38.0 | 137.3 | 7.4 | |
| G-4a | 6.3 | 47.0 | 13.5 | 25.6 | 3.5 | 48.9 | 24.4 | 122.0 | 6.0 | |
| G-4b * | 7.1 | 42.2 | 13.1 | 15.7 | 2.3 | 22.4 | 11.5 | 137.3 | 0.1 | |
| G-5 | 6.0 | 19.6 | 3.8 | 7.4 | 4.0 | 9.1 | 15.2 | 45.8 | 7.1 | |
| 2013 | G-1 * | 7.0 | 16.4 | 3.8 | 8.4 | 1.2 | 10.6 | 0.4 | 51.9 | 0.1 |
| G-2a | 6.2 | 37.0 | 11.6 | 23.0 | 2.4 | 20.4 | 39.6 | 70.2 | 10.0 | |
| G-2b | 6.3 | 19.7 | 9.8 | 23.2 | 2.3 | 14.1 | 33.3 | 64.1 | 15.0 | |
| G-3a | 6.4 | 38.4 | 27.0 | 11.7 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 53.5 | 167.8 | 3.2 | |
| G-3b | 6.6 | 33.7 | 22.8 | 14.6 | 3.2 | 30.8 | 40.5 | 128.1 | 5.2 | |
| G-4a | 6.6 | 37.8 | 10.0 | 21.3 | 2.0 | 37.0 | 19.3 | 109.8 | 3.1 | |
| G-4b | 7.3 | 38.8 | 10.1 | 15.5 | 1.5 | 19.5 | 13.4 | 134.2 | 5.9 | |
| G-5 | 6.4 | 14.7 | 2.7 | 7.0 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 16.0 | 24.4 | 5.2 | |
| Year | Station | pH | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 | NO3-N |
| 2014 | G-1 | 8.2 | 15.7 | 3.9 | 7.9 | 1.4 | 10.3 | 0.8 | 45.8 | 3.5 |
| G-2a | 6.5 | 20.2 | 10.1 | 20.8 | 1.8 | 11.8 | 33.9 | 61.0 | 8.2 | |
| G-2b | 6.5 | 37.3 | 12.0 | 21.2 | 3.3 | 19.9 | 36.5 | 82.4 | 16.1 | |
| G-3a | 6.7 | 30.7 | 20.6 | 13.2 | 4.2 | 25.7 | 36.4 | 100.7 | 1.6 | |
| G-3b | 6.8 | 37.6 | 24.4 | 11.0 | 2.6 | 20.3 | 54.1 | 134.2 | 5.0 | |
| G-4a | 6.5 | 39.7 | 12.9 | 21.8 | 2.4 | 34.3 | 23.5 | 106.8 | 6.9 | |
| G-4b | 7.4 | 33.6 | 11.0 | 15.3 | 1.5 | 15.1 | 14.0 | 119.0 | 4.1 | |
| G-5 | 6.3 | 13.2 | 2.7 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 6.1 | 11.2 | 21.4 | 4.2 | |
| 2015 | G-1 | 8.1 | 14.4 | 3.8 | 7.9 | 1.3 | 7.8 | 0.5 | 54.9 | 3.6 |
| G-2a | 6.5 | 23.3 | 9.2 | 25.4 | 1.6 | 19.5 | 32.3 | 61.0 | 11.4 | |
| G-2b | 6.6 | 39.3 | 12.7 | 24.8 | 2.7 | 28.3 | 43.7 | 67.1 | 17.2 | |
| G-3a | 6.7 | 36.6 | 24.4 | 8.0 | 2.2 | 18.5 | 38.0 | 155.6 | 1.7 | |
| G-3b | 6.8 | 30.8 | 22.0 | 13.4 | 3.2 | 28.0 | 34.1 | 112.9 | 5.2 | |
| G-4a | 6.8 | 44.1 | 12.0 | 21.8 | 2.6 | 38.3 | 22.9 | 106.8 | 7.2 | |
| G-4b | 7.6 | 39.0 | 10.8 | 16.8 | 1.5 | 25.2 | 19.5 | 122.0 | 5.0 | |
| G-5 | 6.3 | 23.2 | 4.7 | 21.1 | 3.2 | 29.1 | 19.3 | 21.4 | 9.3 |
| Station | Lat. | Lng. | Use | EC (µS/cm) | pH | Bacteria (population) | NO3-N | Cl | TCE | PCE | 1.1.1-TCE | Toluene | Ethylbenzene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-6-c-1 | 35°50′53.89″N | 126°49′3.94″E | G | 151 | 7.0 | 23.0 | 2.7 | 16.4 | |||||
| K-3-a-1 | 35°57′34.35″N | 126°57′2.64″E | G* | 415 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 51.3 | ||||||
| K-3-b-1 | 35°57′43.35″N | 126°59′12.63″E | G | 153 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 14.6 | |||||
| K-7-d-4-01 | 36° 1′57.38″N | 127°15′35.12″E | G | 179 | 7.3 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 5.4 | |||||
| K-7-b-4-01 | 35°59′19.65″N | 127°12′25.68″E | G | 223 | 6.7 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 10.2 | |||||
| K-7-e-4-01 | 35°56′14.02″N | 127° 9′44.02″E | G | 132 | 7.0 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 13.2 | |||||
| K-7-c-4-01 | 36° 0′28.94″N | 127°12′19.46″E | G | 239 | 6.8 | 5.0 | 6.2 | 17.6 | |||||
| K-7-a-1-01 | 35°53′3.81″N | 127° 9′11.58″E | G | 183 | 6.8 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 23.3 | |||||
| K-1-e-4-01 | 35°51′44.11″N | 127° 4′9.32″E | G | 245 | 6.9 | 2.0 | 3.7 | 17.6 | |||||
| K-1-a-4-01 | 35°48′32.90″N | 127° 9′18.37″E | G | 387 | 7.6 | 1.9 | 4.3 | 32.8 | |||||
| K-1-b-1-01 | 35°49′21.64″N | 127° 8′34.58″E | G | 96 | 7.5 | 4.5 | 2.4 | 23.2 | |||||
| K-1-d-2-01 | 35°51′13.14″N | 127° 8′28.87″E | G* | 218 | 6.8 | 6.0 | 16.9 | ||||||
| K-1-c-4-01 | 35°46′15.28″N | 127° 4′52.51″E | A | 237 | 6.6 | 4.0 | 7.8 | 25.7 | |||||
| FC0201 | 35°56′32.56″N | 127° 7′11.83″E | I | 384 | 6.9 | 10.6 | 9.5 | ||||||
| FC0203 | 35°56′24.83″N | 127° 8′1.24″E | I | 255 | 6.7 | 18.6 | 7.3 | 9.5 | 0.051 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| FC0202 | 35°56′8.75″N | 127° 7′46.78″E | I | 324 | 6.4 | 4.7 | 40.2 | 0.098 | 0.007 | 0.002 | |||
| OC0101 | 35°50′52.60″N | 127° 6′40.85″E | G | 226 | 7.1 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 23.6 | |||||
| OC0102 | 35°50′57.11″N | 127° 6′55.19″E | G | 456 | 7.3 | 24.5 | 3.1 | 36.9 | 0.002 | 0.001 | |||
| IC0102 | 35°51′48.31″N | 127° 4′27.38″E | G | 273 | 7.1 | 13.0 | 3.6 | 20.7 | 0.002 | ||||
| IC0101 | 35°51′34.08″N | 127° 4′44.99″E | G | 115 | 7.3 | 1.1 | 8.7 | ||||||
| OC0103 | 35°51′22.35″N | 127° 6′51.71″E | I | 418 | 6.7 | 0.8 | 23.1 | ||||||
| BC0101 | 35°51′31.58″N | 127° 6′9.80″E | I | 417 | 6.6 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 41.2 | 0.030 | 0.013 | |||
| FC0101 | 35°51′21.05″N | 127° 6′10.34″E | G | 262 | 7.0 | 1.1 | 14.3 | 0.000 | |||||
| BC0103 | 35°51′56.72″N | 127° 6′20.92″E | I | 493 | 6.9 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 29.1 | 0.003 | ||||
| BC0102 | 35°51′52.97″N | 127° 6′10.33″E | I | 522 | 6.7 | 6.0 | 1.7 | 34.5 | 0.004 | 0.001 | |||
| FC0103 | 35°51′51.76″N | 127° 5′53.32″E | I | 480 | 6.6 | 10.0 | 0.3 | 23.4 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |||
| FC0102 | 35°51′35.99″N | 127° 5′39.79″E | G | 482 | 6.9 | 18.7 | 5.3 | 36.8 | 0.001 | ||||
| IC0103 | 35°51′35.97″N | 127° 4′57.47″E | G | 305 | 7.1 | 20.0 | 4.4 | 21.4 | 0.010 | ||||
| FC0301 | 35°56′51.10″ | 126°58′32.62″E | I | 475 | 6.4 | 8.2 | 48.9 | 0.047 | 0.004 | ||||
| FC0302 | 35°56′53.16″N | 126°58′47.79″E | I | 277 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 25.2 | 0.027 | 0.040 | 0.002 | |||
| FC0402 | 35°57′25.29″N | 127° 0′18.31″E | I | 96 | 7.0 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 4.2 | 0.001 | ||||
| FC0403 | 35°57′12.95″N | 127° 0′53.84″E | I | 341 | 6.6 | 34.0 | 5.8 | 20.7 | |||||
| FC0401 | 35°57′21.21″N | 127° 1′2.40″E | I | 138 | 6.7 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 9.9 | 0.007 | 0.003 | |||
| GC0101 | 35°57′43.25″N | 127° 1′38.82″E | A | 159 | 7.0 | 22.7 | 2.1 | 10.3 | 0.000 | ||||
| GC0102 | 35°57′43.25″N | 127° 1′38.82″E | A | 116 | 6.7 | 10.0 | 1.2 | 7.7 | |||||
| CC0203 | 35°48′2.26″N | 126°53′12.27″E | G | 393 | 7.1 | 12.0 | 9.4 | 56.1 | |||||
| CC0202 | 35°48′6.75″N | 126°53′11.95″E | G | 125 | 7.3 | 1.4 | 16.2 |
References
- Adger, W.N.; Arnell, N.W.; Tompkins, E.L. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Global Environ. Chang. 2005, 15, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Conticello, F.; Lall, U.; Marotta, L.; Telesca, V. Large scale climate and rainfall seasonality in a Mediterranean Area: Insights from a non-homogeneous Markov model applied to the Agro-Pontino plain. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 668–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern global climate change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Projected changes in drought occurrence under future global warming from multi-model, multi-scenario, IPCC AR4 simulations. Clim. Dynam. 2008, 31, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F.; Roderick, M.L. Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 2012, 491, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Matteo, L.; Dragoni, W.; Maccari, D.; Piacentini, S.M. Climate change, water supply and environmental problems of headwaters: The paradigmatic case of the Tiber, Savio and Marecchia rivers (Central Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, UK, 2007; p. 976. [Google Scholar]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.; Garduno, H.; Evans, R.; Olson, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Han, Z.S. Quaternary Aquifer of the North China Plain—Assessing and achieving groundwater resource sustainability. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.V.; Diaz-Delgado, C. Environmental effects of aquifer overexploitation: A case study in the highlands of Mexico. Environ. Manage. 2002, 29, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, T.P.; Pierce, D.W.; Hidalgo, H.G.; Bonfils, C.; Santer, B.D.; Das, T.; Bala, G.; Wood, A.W.; Nozawa, T.; Mirin, A.A.; et al. Human-induced changes in the hydrology of the western United States. Science 2008, 319, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Dunne, K.A. A Hydrologic Drying Bias in Water-Resource Impact Analyses of Anthropogenic Climate Change. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological Drought Explained; Wiley Periodicals, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Karimov, A.; Smakhtin, V.U.; Mavlonov, A.; Borisov, V.; Gracheva, I.; Miryusupov, F.; Djumanov, J.; Khamzina, T.; Ibragimov, R.; Abdurahmanov, B. Managed Aquifer Recharge: The Solution for Water Shortages in the Fergana Valley; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2013; 51p. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y. Environmental issues of groundwater in Korea: implications for sustainable use. Environ. Conserv. 2011, 38, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Licata, I.; Colombo, L.; Francani, V.; Alberti, L. Hydrogeological Study of the Glacial-Fluvioglacial Territory of Grandate (Como, Italy) and Stochastical Modeling of Groundwater Rising. Appl. Sci-Basel 2018, 8, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, C.D.; Chen, T.H.; Lo, W.C. Effect of rainfall intensity and distribution on groundwater level fluctuations. J. Hydrol. 2007, 332, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Lim, T.K.; Park, C.H. Analysis of the Secular Trend of the Annual and Monthly Precipitation Amount of South Korea. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2009, 9, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Hamm, S.Y.; Jang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Kim, G.B. Relationship between groundwater and climate change in South Korea. Geosci. J. 2014, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Jo, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y. Trends of groundwater data from the Korean National Groundwater Monitoring Stations: indication of any change? Geosci. J. 2011, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMA. Abnormal Climate Report 2016; Korea Meteorological Administration: Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ME; NIER. Korean Climate Change Assessment Report 2014; Ministry of Environment and National Institute of Environmental Research: Sejong, Korea, 2015.
- Choi, G.; Kwon, W.-T.; Boo, K.-O.; Cha, Y.-M. Recent spatial and temporal changes in means and extreme events of temperature and precipitation across the Republic of Korea. J. Korean Geogr. Soc. 2008, 43, 681–700. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Kim, T.W.; Ahn, J.H. Drought frequency analysis using cluster analysis and bivariate probability distribution. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BGR. Groundwater and Climate Change: Challenges and Possibilities; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (BGR) and Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS): Hannover, Germany, 2008; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- MOLIT; K-Water. Groundwater Annual Report; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport (MOLIT) and Korea Water Resources Corporation (K-Water): Daejeon, Korea, 2016; p. 647.
- Kiem, A.S.; Austin, E.K. Drought and the future of rural communities: Opportunities and challenges for climate change adaptation in regional Victoria, Australia. Global Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capri, E.; Civita, M.; Corniello, A.; Cusimano, G.; De Maio, M.; Ducci, D.; Fait, G.; Fiorucci, A.; Hauser, S.; Pisciotta, A.; et al. Assessment of nitrate contamination risk: The Italian experience. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobczyk-Karpierz, S.; Sitek, S.; Jakobsen, R.; Kowalczyk, A. Geochemical and isotopic study to determine sources and processes affecting nitrate and sulphate in groundwater influenced by intensive human activity—Carbonate aquifer Gliwice (southern Poland). Appl. Geochem. 2017, 76, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Chung, E.; Woo, N.C. Assessment of Groundwater Drought in the Mangyeong River Basin, Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MLTM. Mangyeong River Basic Plan; Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTM): Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Woo, N.C.; Lee, C.J.; Yoo, K. Characterising Bedrock Aquifer Systems in Korea Using Paired Water-Level Monitoring Data. Water 2017, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Su, X. Linear Regression Analysis: Theory and Computing; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzante, J.R. Resistant, robust and non-parametric techniques for the analysis of climate data: Theory and examples, including applications to historical radiosonde station data. Int. J. Climatol. 1996, 16, 1197–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- McCuen, R.H. Modeling Hydrological Change: Statistical Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.O. Statistical Methods for Environmental Pollution Monitoring; Van Nostrand Rienhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahya, E.; Kalayci, S. Trend analysis of streamflow in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberry, D.O. Unsaturated-zone wedge beneath a large, natural lake. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3401–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicht, R.J.; Walton, W.C. Hydrologic Budget for Three Small Watersheds in Illinois; Illinois State Water Survey, Report on Investigation: Champaign, IL, USA, 1961; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Demlie, M. Assessment and estimation of groundwater recharge for a catchment located in highland tropical climate in central Ethiopia using catchment soil-water balance (SWB) and chloride mass balance (CMB) techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharda, V.N.; Kurothe, R.S.; Sena, D.R.; Pande, V.C.; Tiwari, S.P. Estimation of groundwater recharge from water storage structures in a semi-arid climate of India. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenini, I.; Ben Mammou, A. Groundwater recharge study in arid region: An approach using GIS techniques and numerical modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Kwicklis, E.M.; Fabryka-Martin, J.T.; Bodvarsson, G.S. Estimating recharge at Yucca Mountain, Nevada, USA: comparison of methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Using groundwater levels to estimate recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.S.; Graham, J.P.; Choung, S.; Park, E.; Choi, W.; Kim, Y.S. Local-scale variability in groundwater resources: Cedar Creek Watershed, Wisconsin, USA. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2018, 20, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, F.D.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Pruitt, T. Changes in groundwater recharge under projected climate in the upper Colorado River basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6968–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.E.; Felzer, B.S.; Troy, T.J. Extreme precipitation drives groundwater recharge: the Northern High Plains Aquifer, central United States, 1950-2010. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.W.; Mather, J.R. Instructions and tables for computing potential evapotranspiration and the water balance: in Publications in Climatology: Centerton, NJ. Lab. Clim. 1957, 10, 185–311. [Google Scholar]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA 1979. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Leist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–23 January 1993; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorologic Drought; Research Paper, No. 45; U.S. Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- WMO. Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide; WMO-No. 1090; Svoboda, M., Hayes, M., Wood, D., Eds.; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jaranilla-Sanchez, P.A.; Wang, L.; Koike, T. Modeling the hydrologic responses of the Pampanga River basin, Philippines: A quantitative approach for identifying droughts. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W03514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yi, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Ahn, K.H.; Won, J.H.; Moon, S.H.; Cho, M. Parametric and non-parametric trend analysis of groundwater data obtained from national groundwater monitoring stations. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2006, 11, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water-quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, K.; Ulbrich, U. Potential impacts of climate change on groundwater recharge and streamflow in a central European low mountain range. J. Hydrol. 2003, 284, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.; Ko, K.S.; Koh, D.C.; Yum, B.W.; Lee, K.K. Time Series Analysis of the Responses of the Groundwater Levels at Multi-depth Wells According to the River Stage Fluctuations. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2006, 39, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative contribution of monsoon precipitation and pumping to changes in groundwater storage in india. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makokha, G.O.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.P.; Wang, A.H.; Wang, G.P.; Kuria, D. Quantitative drought monitoring in a typical cold river basin over Tibetan Plateau: An integration of meteorological, agricultural and hydrological droughts. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, P.; Mueller Schmied, H.; Schuh, C.; Portmann, F.T.; Eicker, A. Global-scale assessment of groundwater depletion and related groundwater abstractions: Combining hydrological modeling with information from well observations and GRACE satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5698–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality., Recommendations, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ME. Groundwater Quality Measurement Network Operating Result Report; Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Korea, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, C.L.; Barringer, T.H.; Vowinkel, E.F.; Price, C.V. Relation of Nitrate Concentrations in Ground Water to Well Depth, Well Use, and Land Use in Franklin Township, Gloucester County, New Jersey, 1970–85; Water-Resources Investigations Report 94-4174; U.S. Geological Survey: West Trenton, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
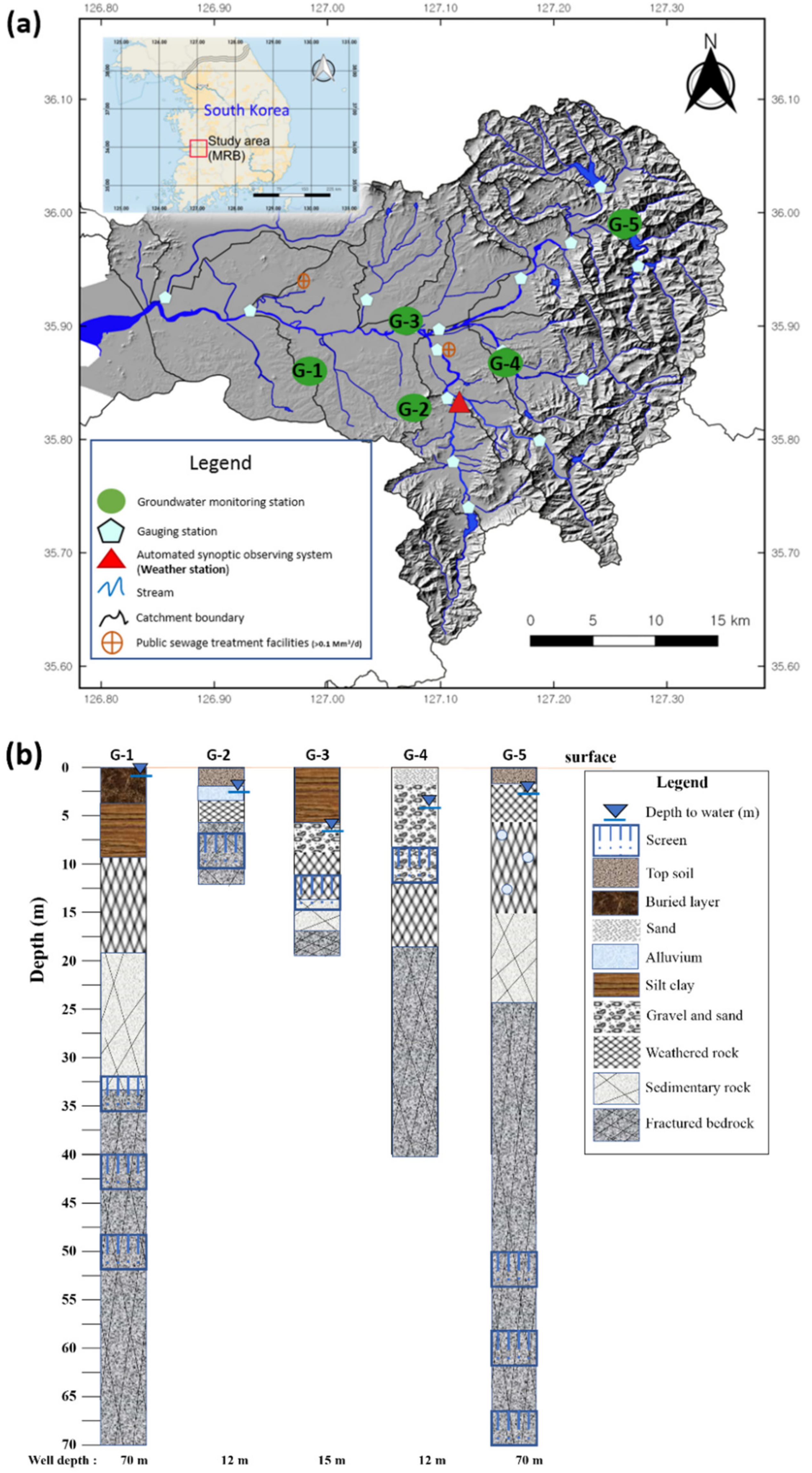







| Well | Aquifer | Aquifer Type a | Well Depth (m) | Water Level (m) | Mean Depth to Water (m) c | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/day) d | Soil Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (a.s.l.) b | Ave. Annual Change | |||||||
| G-1 | Biotite granite (Bedrock) | SC | 70 | 13.67 | 1.58 | 0.55 | 0.34 | Loam |
| G-2 | Gneissic granite (Alluvial) | UC | 12 | 29.95 | 1.96 | 2.75 | 0.01 | Sandy loam |
| G-3 | Schistose granite (Alluvial) | ND | 15 | 9.45 | 1.69 | 6.60 | 0.23 | Loam |
| G-4 | Biotite granite (Alluvial) | SC | 12 | 23.79 | 1.17 | 3.77 | 0.01 | Sandy loam |
| G-5 | Volcanic rocks (Bedrock) | UC | 70 | 68.55 | 1.32 | 2.62 | 0.25 | Loam |
| Observation Well | Trend Analyses | Correlation Coefficients a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | M-K Test * | Sen’s Test * | Lag-time (day) | WL and Rainfall | Period | |||||
| D | M | D | M | D | M | Wet Season | Dry Season | |||
| G-1 | - | - | NT | NT | NT | N | 0 | 0.086 | 0.366 * | −0.162 |
| G-2 | + | + | P | P | P | P | - | −0.035 | −0.199 | −0.233 * |
| G-3 | + | + | P | NT | P | P | 0 | 0.454 ** | 0.164 | 0.124 |
| G-4 | - | - | N | N | N | N | 0 | 0.750 ** | 0.721 ** | 0.268 ** |
| G-5 | - | - | N | N | N | N | 0 | 0.599 ** | 0.722 ** | 0.437 ** |
| Rainfall | - | - | NT | NT | NT | NT | - | - | - | - |
| Year | Mean Recharge Rate (mm) | Amount of Abstraction (1) | Calculated Recharge (2) | Abstraction to Recharge Ratio (%) (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 163.1 | 101,669,325 | 260,908,800 | 39.0 |
| 2006 | 141.0 | 93,147,785 | 225,552,000 | 41.3 |
| 2007 | 229.6 | 95,551,861 | 367,385,600 | 26.0 |
| 2008 | 120.1 | 95,584,978 | 192,227,200 | 49.7 |
| 2009 | 119.9 | 94,772,404 | 191,820,800 | 49.4 |
| 2010 | 215.4 | 96,955,614 | 344,627,200 | 28.1 |
| 2011 | 233.9 | 102,676,289 | 374,294,400 | 27.4 |
| 2012 | 229.1 | 103,082,918 | 366,572,800 | 28.1 |
| 2013 | 175.3 | 104,575,749 | 280,416,000 | 37.3 |
| 2014 | 173.5 | 104,869,683 | 277,571,200 | 37.8 |
| 2015 | 86.4 | - | 138,176,000 | - |
| Mean | 171.5 | 99,288,661 | 274,504,727 | 36.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.M.; Kwon, E.H.; Woo, N.C. Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051486
Lee JM, Kwon EH, Woo NC. Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea. Sustainability. 2019; 11(5):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051486
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae Min, Eun Hye Kwon, and Nam C. Woo. 2019. "Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea" Sustainability 11, no. 5: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051486
APA StyleLee, J. M., Kwon, E. H., & Woo, N. C. (2019). Natural and Human-Induced Drivers of Groundwater Sustainability: A Case Study of the Mangyeong River Basin in Korea. Sustainability, 11(5), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051486






