Effects of Yak Dung Biomass Black Carbon on the Soil Physicochemical Properties of the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
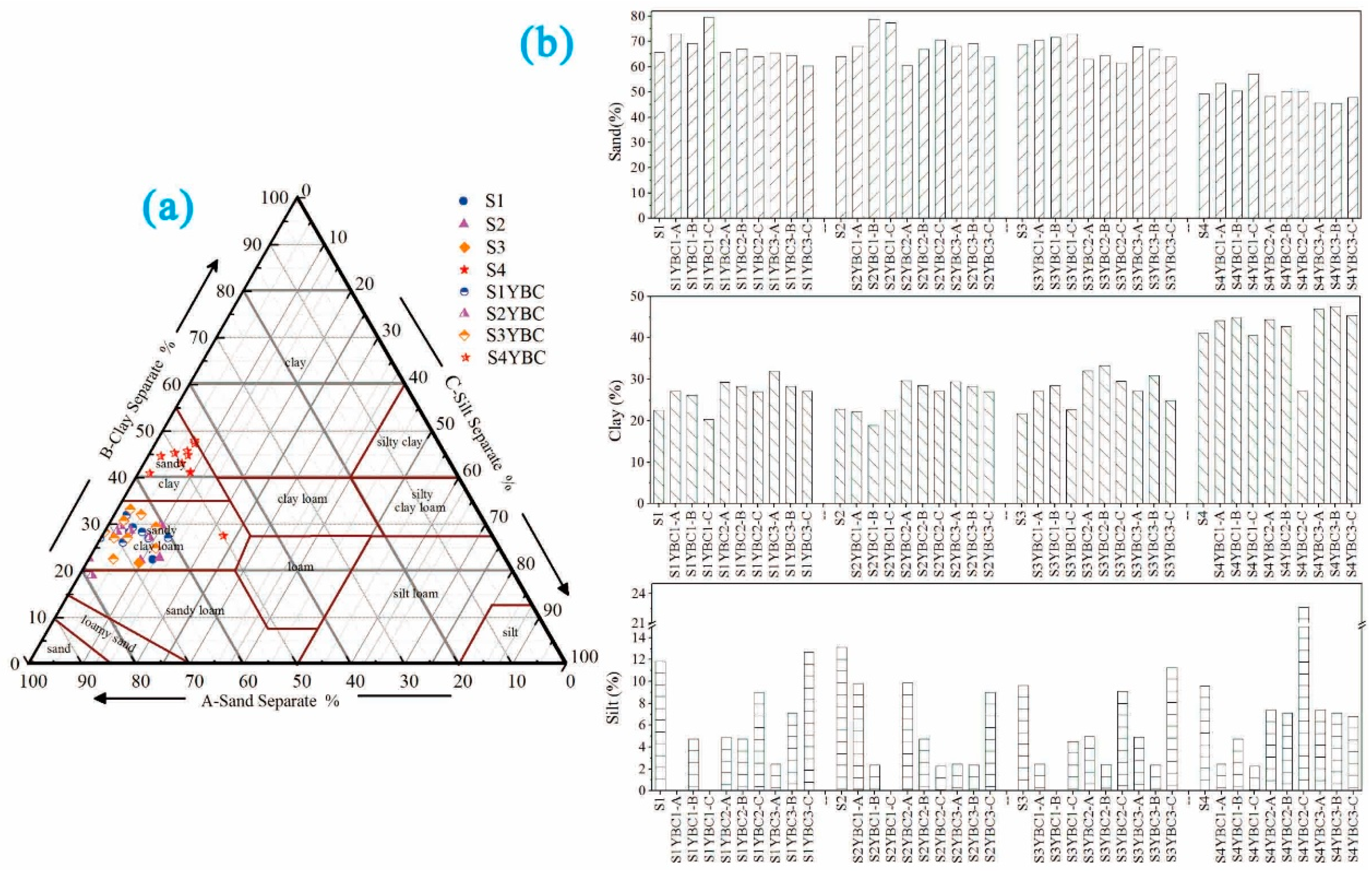
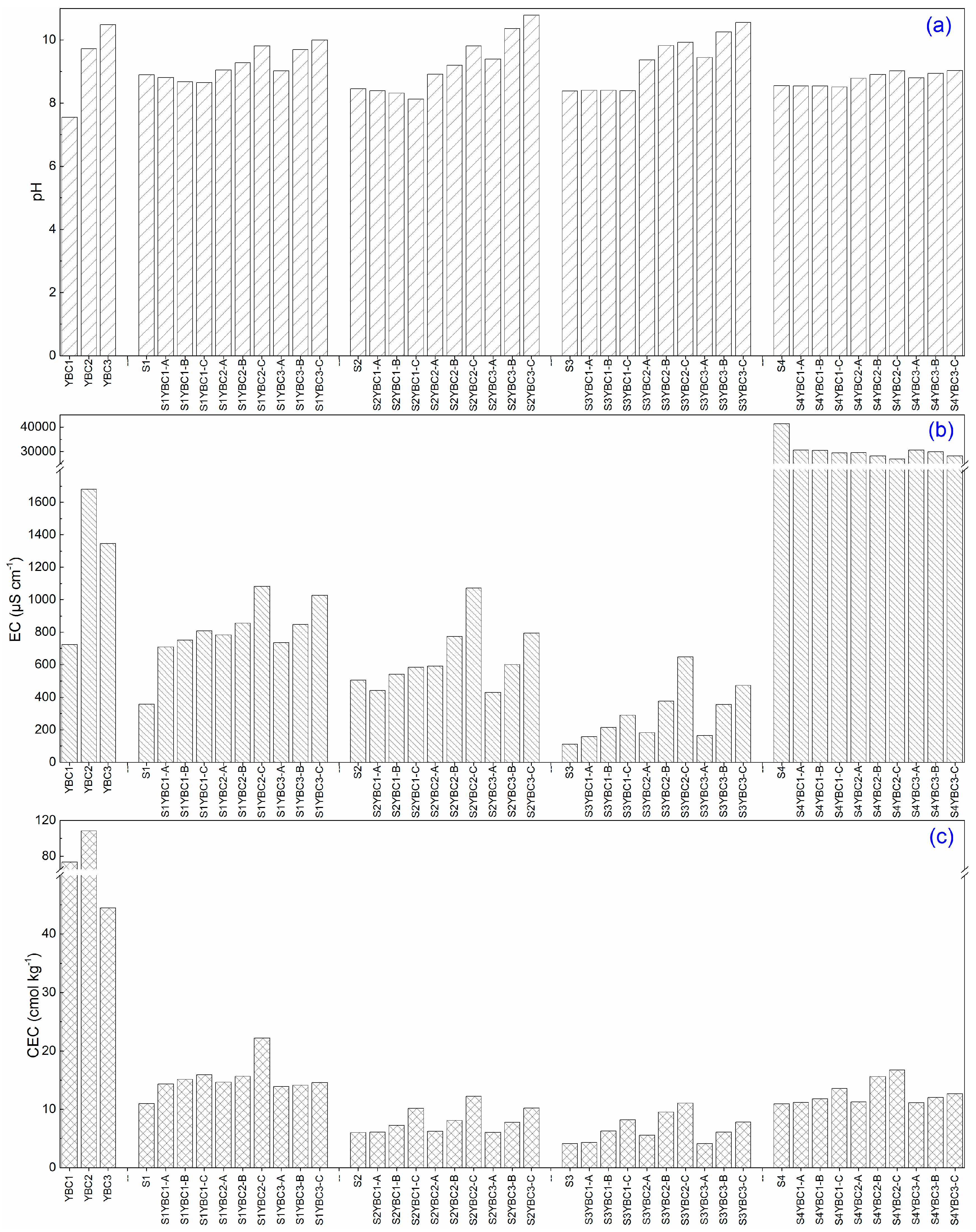
3.1. Change in pH, EC, CEC, and Texture of Soils Affected by Addition of YBCs
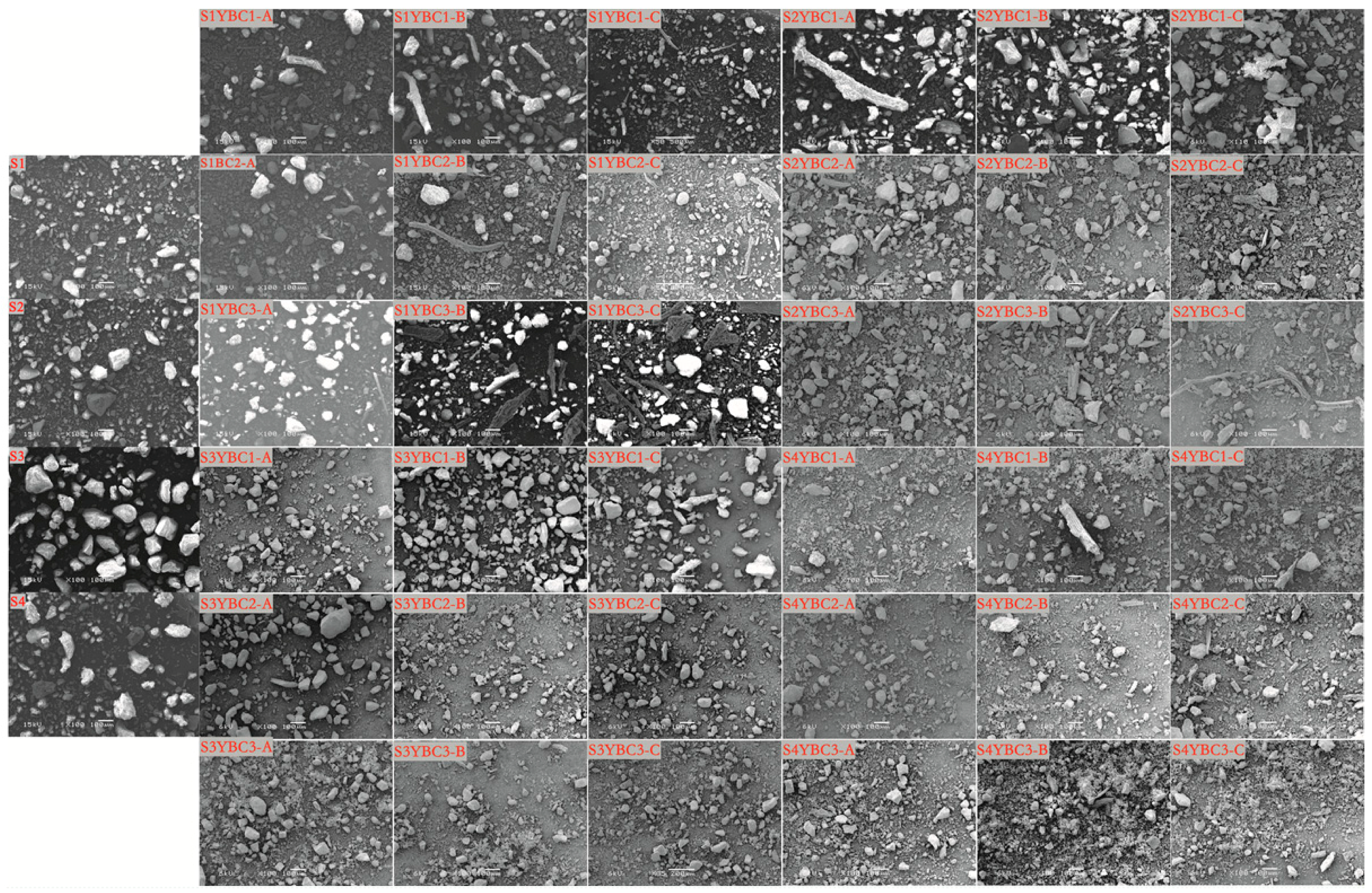
3.2. Effects of Adding YBCs on the Morphologies of Soils
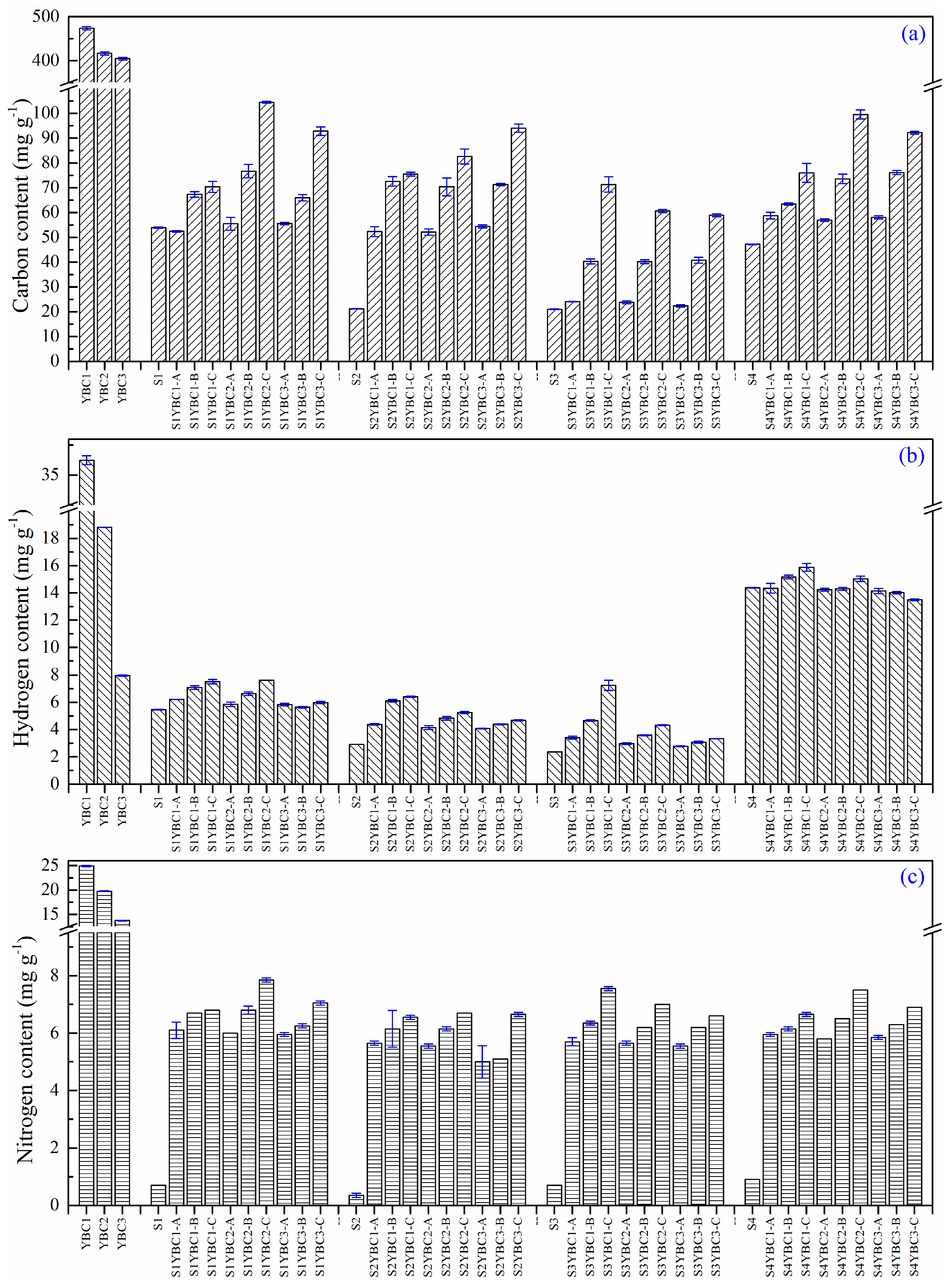
3.3. Changes in CNH Contents of Soil with Addition of YBCs
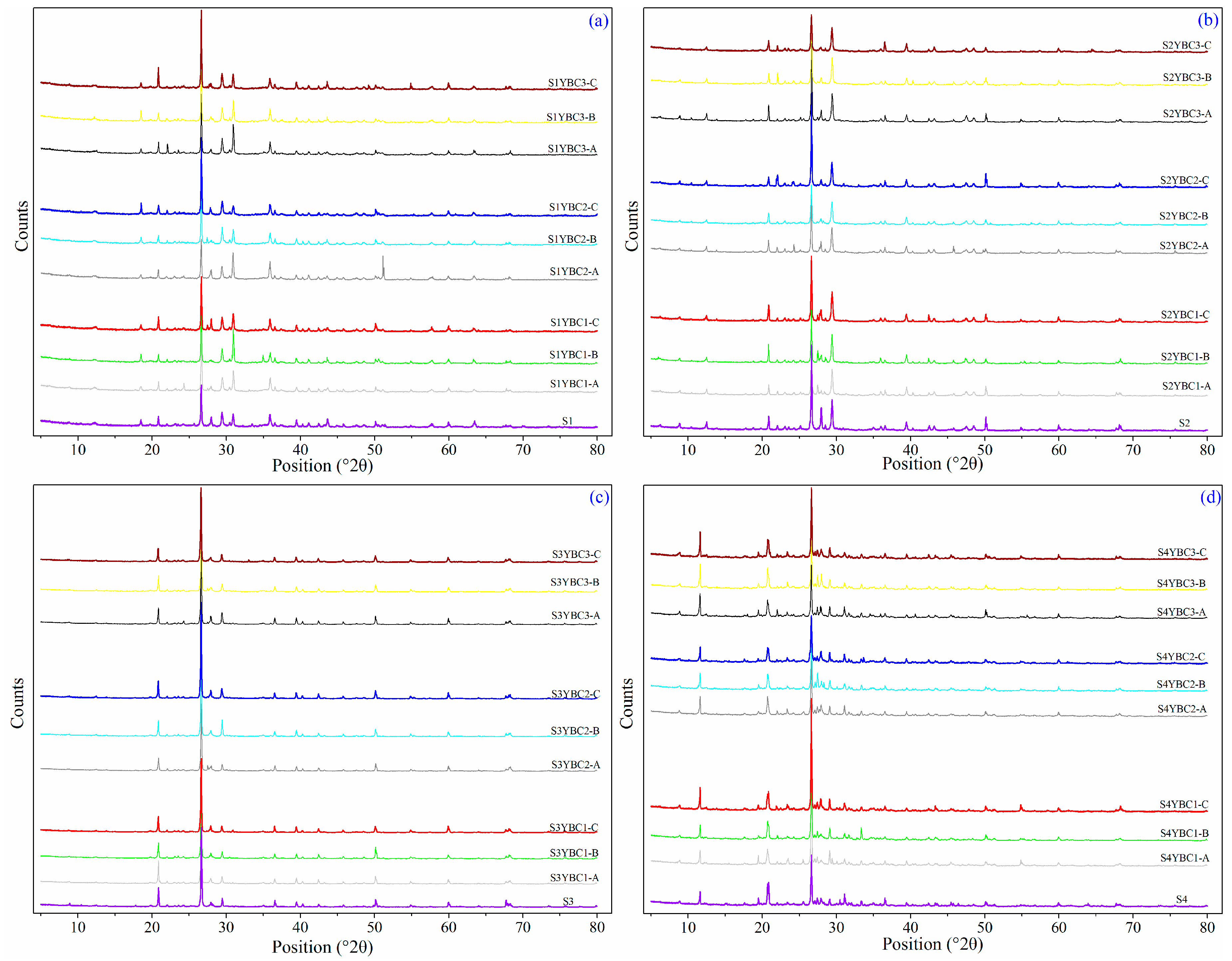
3.4. Changes in Spectral Characteristics and Mineral Constituent of Soil with Addition of YBCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doran, J.W.; Zeiss, M.R. Soil health and sustainability: Managing the biotic component of soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmeier, E.; Mavris, C.; Krebs, R.; Pichler, B.; Egli, M. Black carbon contributes to organic matter in young soils in the Morteratsch proglacial area (Switzerland). Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, J.J.; Gustafsson, O.; Kurt-Karakus, P.; Breivik, K.; Steinnes, E.; Jones, K.C. Relationships between organic matter, black carbon and persistent organic pollutants in European background soils: Implications for sources and environmental fate. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.S.; Sharma, R.; Dahariya, N.S.; Patel, R.K.; Blazhev, B.; Matini, L. Black Carbon and Heavy Metal Contamination of Soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, A.; Lee, S.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Farooq, M.; Song, H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar application to low fertility soils: A review of current status, and future prospects. Geoderma 2019, 337, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Le Villio-Poitrenaud, M.; Houot, S. Improvement of soil aggregate stability by repeated applications of organic amendments to a cultivated silty loam soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, L.; Fang, N.; Shi, Z. Aggregate stability and associated organic carbon and nitrogen as affected by soil erosion and vegetation rehabilitation on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2018, 167, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezketa, E. Soil Aggregate Stability: A Review. J. Sustain. Agric. 1999, 14, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, A.; Levkovitch, I.; Graber, E. pH-Dependent Mineral Release and Surface Properties of Cornstraw Biochar: Agronomic Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9318–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Lehmann, J.; Thies, J.E.; Burton, S.D.; Engelhard, M.H. Oxidation of black carbon by biotic and abiotic processes. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, B. Biochar to improve soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Saikawa, E.; Yokelson, R.J.; Chen, P.; Li, C.; Kang, S. Indoor air pollution from burning yak dung as a household fuel in Tibet. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, M.A.; Boersma, L. A Unifying Quantitative Analysis of Soil Texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Mcbratney, A.B. The Australian soil texture boomerang: A comparison of the Australian and USDA/FAO soil particle-size classification systems. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Canqui, H. Biochar and Soil Physical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 84, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butnan, S.; Deenik, J.L.; Toomsan, B.; Antal, M.J.; Vityakon, P. Biochar characteristics and application rates affecting corn growth and properties of soils contrasting in texture and mineralogy. Geoderma 2015, 237–238, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masulili, A.; Utomo, W.H.; Syechfani, M.S. Rice husk biochar for rice based cropping system in acid soil 1. The characteristics of rice husk biochar and its influence on the properties of acid sulfate soils and rice growth in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 2, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil physical quality: Part I. Theory, effects of soil texture, density, and organic matter, and effects on root growth. Geoderma 2004, 120, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.B.; Hunt, P.G.; Uchimiya, M.; Novak, J.M.; Ro, K.S. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.K.; Joseph, S.D.; Li, F.; Bai, Y.; Shang, Z.; Rawal, A.; Hook, J.M.; Munroe, P.R.; Donne, S.; Taherymoosavi, S.; et al. Pyrolysis of attapulgite clay blended with yak dung enhances pasture growth and soil health: Characterization and initial field trials. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, L.; Huang, H. An overview of the effect of pyrolysis process parameters on biochar stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Liu, S.C.; Chen, H.R.; Chang, Y.M.; Tsai, Y.L. Textural and chemical properties of swine-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use as a soil amendment. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguntunde, P.G.; Fosu, M.; Ajayi, A.E.; van de Giesen, N. Effects of charcoal production on maize yield, chemical properties and texture of soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 39, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Meng, J.; Muhammad, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; He, Y.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. The potential feasibility for soil improvement, based on the properties of biochars pyrolyzed from different feedstocks. J. Soil. Sediment. 2013, 13, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.H.; Wang, C.S. Effects of biochar on soil properties and erosion potential in a highly weathered soil. Catena 2013, 110, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sollins, P.; Robertson, G.P.; Uehara, G. Nutrient mobility in variable- and permanent-charge soils. Biogeochemistry 1988, 6, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, H.; Samson, B.K.; Stephan, H.M.; Songyikhangsuthor, K.; Homma, K.; Kiyono, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Shiraiwa, T.; Horie, T. Biochar amendment techniques for upland rice production in Northern Laos: 1. Soil physical properties, leaf SPAD and grain yield. Field Crops Res. 2009, 111, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, L.R.; Reid, B.J.; Tang, X. Quantifying the influence of biochar on the physical and hydrological properties of dissimilar soils. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Nelissen, V.; Ruysschaert, G.; Manka’Abusi, D.; D’Hose, T.; De Beuf, K.; Al-Barri, B.; Cornelis, W.; Boeckx, P. Impact of a woody biochar on properties of a sandy loam soil and spring barley during a two-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 62, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.X.; Lin, C.S.K.; Ji, X.Y.; Rainey, T.J. Returning biochar to fields: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Voroney, R.P.; Price, G.W. Effects of temperature and processing conditions on biochar chemical properties and their influence on soil C and N transformations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen in natural restoration grassland and Chinese red pine plantation on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2017, 149, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R. Organic carbon and nutrient release from a range of laboratory-produced biochars and biochar–soil mixtures. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Rao, Y.S.; Balaji, T.; Prathima, B.; Jyothi, N.V.V. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using plantain peel extract. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Chandraiah, M. Facile synthesis of zero valent iron magnetic biochar composites for Pb(II) removal from the aqueous medium. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumitru, R.; Papa, F.; Balint, I.; Culita, D.C.; Munteanu, C.; Stanica, N.; Ianculescu, A.; Diamandescu, L.; Carp, O. Mesoporous cobalt ferrite: A rival of platinum catalyst in methane combustion reaction. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2013, 467, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikishore Kumar Reddy, D.; Lee, S.M. Magnetic biochar composite: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application for heavy metal removal. Colloids Surface A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 454, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Addition Amount | pH | EC | CEC | C | N | H | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Addition amount | 1 | ||||||
| pH | 0.062 | 1 | ||||||
| EC | 0.637 * | 0.631 * | 1 | |||||
| CEC | 0.895 ** | −0.021 | 0.678 * | 1 | ||||
| C | 0.994 ** | 0.000 | 0.590 * | 0.896 ** | 1 | |||
| N | 0.911 ** | −0.190 | 0.539 | 0.896 ** | 0.937 ** | 1 | ||
| H | 0.254 | −0.740 ** | −0.312 | 0.172 | 0.315 | 0.484 | 1 | |
| S2 | Addition amount | pH | EC | CEC | C | N | H | |
| Addition amount | 1 | |||||||
| pH | 0.061 | 1 | ||||||
| EC | 0.744 ** | 0.478 | 1 | |||||
| CEC | 0.915 ** | 0.000 | 0.763 ** | 1 | ||||
| C | 0.994 ** | 0.024 | 0.700 ** | 0.913 ** | 1 | |||
| N | 0.921 ** | −0.117 | 0.594 * | 0.907 ** | 0.953 ** | 1 | ||
| H | 0.333 | −0.527 | −0.145 | 0.260 | 0.418 | 0.586 * | 1 | |
| S3 | Addition amount | pH | EC | CEC | C | N | H | |
| Addition amount | 1 | |||||||
| pH | 0.007 | 1 | ||||||
| EC | 0.879 ** | 0.361 | 1 | |||||
| CEC | 0.917 ** | −0.047 | 0.869 ** | 1 | ||||
| C | 0.996 ** | −0.056 | 0.844 ** | 0.917 ** | 1 | |||
| N | 0.917 ** | −0.163 | 0.736 ** | 0.906 ** | 0.942 ** | 1 | ||
| H | 0.233 | −0.635 * | −0.090 | 0.168 | 0.299 | 0.447 | 1 | |
| S4 | Addition amount | pH | EC | CEC | C | N | H | |
| Addition amount | 1 | |||||||
| pH | 0.323 | 1 | ||||||
| EC | −0.975 ** | −0.331 | 1 | |||||
| CEC | 0.902 ** | 0.213 | −0.877 ** | 1 | ||||
| C | 0.995 ** | 0.243 | −0.975 ** | 0.903 ** | 1 | |||
| N | 0.917 ** | 0.016 | −0.941 ** | 0.899 ** | 0.945 ** | 1 | ||
| H | −0.045 | −0.660 * | −0.034 | −0.076 | 0.014 | 0.216 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, X.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Gao, C. Effects of Yak Dung Biomass Black Carbon on the Soil Physicochemical Properties of the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061536
Min X, Wu J, Lu J, Gao C. Effects of Yak Dung Biomass Black Carbon on the Soil Physicochemical Properties of the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Xiuyun, Jun Wu, Jian Lu, and Chunliang Gao. 2019. "Effects of Yak Dung Biomass Black Carbon on the Soil Physicochemical Properties of the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061536
APA StyleMin, X., Wu, J., Lu, J., & Gao, C. (2019). Effects of Yak Dung Biomass Black Carbon on the Soil Physicochemical Properties of the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability, 11(6), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061536





