An Ecological Early Warning Indicator System for Environmental Protection of Scenic Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Impact of Tourist Activity on the Environmental Quality of Scenic Areas
2.2. Studies on Ecological Early Warning Indicator Systems
2.3. Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
3. Research Methods
3.1. First Stage
3.2. Second Stage
- m: Number of indices
- : Geometric mean of the triangular fuzzy numbers
- : Fuzzy weight of every array of fuzzy positive reciprocal matrix
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. Validity and Reliability Analysis for the Indicator Structure
4.2. Indicator Structure Survey Analysis
4.2.1 Indicator Importance Analysis
4.2.2 Factor Analysis
4.3. Fuzzy AHP Survey Analysis
4.3.1. Consistency Test
4.3.2. Weighting Analysis
5. Conclusions and Suggestion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Contribution
5.3. Suggestion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, G.N. Research on model of eco-tourism development in nature reserves of China. Resour. Sci. 1998, 20, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A. Tourism development and nature capital. Ann. Tour. Res. 1999, 1, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.M. Trends in ocean and coastal tourism: The end of the last frontier? Ocean Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y. The Application of multiple criteria decision making and grey relational analysis for evaluating destinations of ecotourism. Taiwan J. Rural Stud. 2004, 4, 75–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Wang, H.Q. Domestic tourism ecological security research. J. Xiangtan Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 30, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, L.C. Recreational impact on biodiversity and spatial distribution of populations in the intertidal zones of Liuchio Hsu. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 69, 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Becken, S.; Mahon, R.; Rennie, H.G.; Shakeela, A. The tourism disaster vulnerability frame work: An application to tourism in small island destinations. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, K. Academic Thought and Technica Progress of Monitoring and Early-warning of the National Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity (V 2014). Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.l.; Yu, X.G.; Li, Q.S. The study of tourism carrying capacity of island in China. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2015, 6, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H. Assessment of ecological impact of tourism waste—Jiuzhai Valley and Yellow Mountain Scenic areas. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 6, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Zhong, L.S.; Wang, X.F. The impact of tourism activities on plants in the Zhangjiajie Forest Park. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2004, 28, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, D.C.; Deng, X.Z.; Zhan, J.Y. Wulingyuan scenic area environmental quality assessment. Geogr. Res. 2004, 23, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, Y.L.; Cao, J.; Chen, L. Impact of restaurant wastewater on Zhejiang Province Anjie County Daxi scenic area. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Suzhou (Eng. Technol.) 2005, 18, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.G.; Zhang, M. Traffic noise pollution and control strategies in Wuhan West Lake scenic area. Environ. Sanit. Eng. 2006, 14, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, J.; Davenport, J.L. The impact of tourism and personal leisure transport on coastal environments: A review estuarine. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, R.C.; Korfmacher, J.L. Air quality at a snowmobile staging area and snow chemistry on and off trail in a Rocky Mountain Subalpine Forest, Snowy Range, Wyoming. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shively, D.D.; Pape, B.M.C.; Mower, R.N.; Zhou, Y.; Barkley, R.R.; Sive, C. Blowing smoke in Yellowstone: Air quality impacts of oversnow motorized recreation in the park. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q. Impact of tourism activities on water quality in Fuzhou National Forest Park. For. Prospect Des. 2008, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.F.; Liu, Y.Y. Primary environmental problems and management strategies for the Xinjiang Tianchi scenic area. J. Zaozhuang Univ. 2007, 24, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Lozano, L.; Granandos-Barba, A.; Garcia-Salgado, M.A. Environmental evaluation and development problems of the Mexican coastal zone. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2005, 48, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.K. Wuyi Mountain tourism resource protection area. Nat. Resour. 1997, 2, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Buddhawong, M. The Development of Environmental Management System Guidelines for Sustainable Tourist Attractions: A Case Study of Bang Saen Beach in Chonburi Province. 2006. Available online: http://mulinet8.li.mahidol.ac.th/e-thesis/4536609.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2012).
- Mbaiwa, J.E. The socio-economic and environmental impacts of tourism development on the Okavango Delta, North-Western Botswana. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 54, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Cheng, K. Impacts of ecotourism on wildlife in nature reserves monitoring and management. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.H. Impact of tourism interference on Xiangshan smoke tree forests. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 1997, 21, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, C.M.; Hill, W. Impacts of recreation and tourism on plants in protected areas in Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.X. Ecological security early warning assessment indicator system and methodology research—Kaifeng City. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2006, 31, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.X. Inland River Basin Ecological Security—Hei River. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Meteorology Institute, Nanjing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.X. Ecological security assessment research for scenic tourist areas—Zhangjiajie National Forest Park. Yunnan Geogr. Environ. Res. 2007, 19, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, F.S. Assessment of ecological tourism environmental capacity—Guilin River. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2007, 35, 2380–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.C.; Wu, C.Z. Application of PSR indicator system model for Wuyi Mountain scenic area ecology security assessment. J. Secur. Environ. 2006, 6, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.Z. New conceptual system for tourism environmental capacity. J. Yunnan Norm. Univ. 1999, 5, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N.; Zhang, G.Z. Quantitative analysis of tourism environmental capacity—Jiuzhai Valley. J. Chongqing Inst. Commer. 2000, 6, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H. Fuzzy Set Theory—And Its Applications, 4th ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA; Dodrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 1975, 8, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Chang, C.W.; Lin, H.L. Evaluating the organization performance of Taiwanese hospitals using the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. J. Am. Acad. Bus. 2006, 9, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Van Laarhoven, P.J.M.; Pedrycz, W. A Fuzzy extension of Saaty’s Priority Theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1983, 11, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Hwang, C.L. Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, C.K.; Bai, H. A Fuzzy AHP approach to the determination of importance weights of customer requirements in quality function deployment. J. Intell. Manuf. 2002, 13, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.Y.; Hsu, C.L.; Chen, M.C. A fuzzy multi-criteria decision model for international tourist hotels location selection. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2008, 27, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Cheng, J.S. A concept of balanced scorecard for establishing resort hotel’s performance index—Application of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. J. Qual. 2009, 16, 441–459. [Google Scholar]
- Perneger, T.V.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Hudelson, P.M.; Gayet-Ageron, A. Sample size for pre-tests of questionnaires. Qual. Life Res. 2015, 24, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.J. Quantitative Research and Statistical Analysis in Social & Behavioral Sciences; Wunan Publishing: Taipei, Taiwan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, G.S.; Miller, K.K.; Weston, M.A.; Young, K. Being beside the seaside: Beach use and preferences among coastal residents of south-eastern Australia. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.C.; Lin, Y.H. Assessing the management effectiveness of an intertidal attendance control area. Bull. Geogr. Soc. China 2016, 57, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cloquell-Ballester, V.A.; Torres-Sibille, A.D.C.; Cloquell-Ballester, V.A.; Santamarina-Siurana, M.C. Human alteration of the rural landscape: Variations in visual perception. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2012, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Ran, H.; Yang, T.Y.; Xu, Q.Z. Species diversity of butterflies in Fanjing Mountain national nature reserve of Guizhou. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, J.J. Fuzzy Hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1985, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
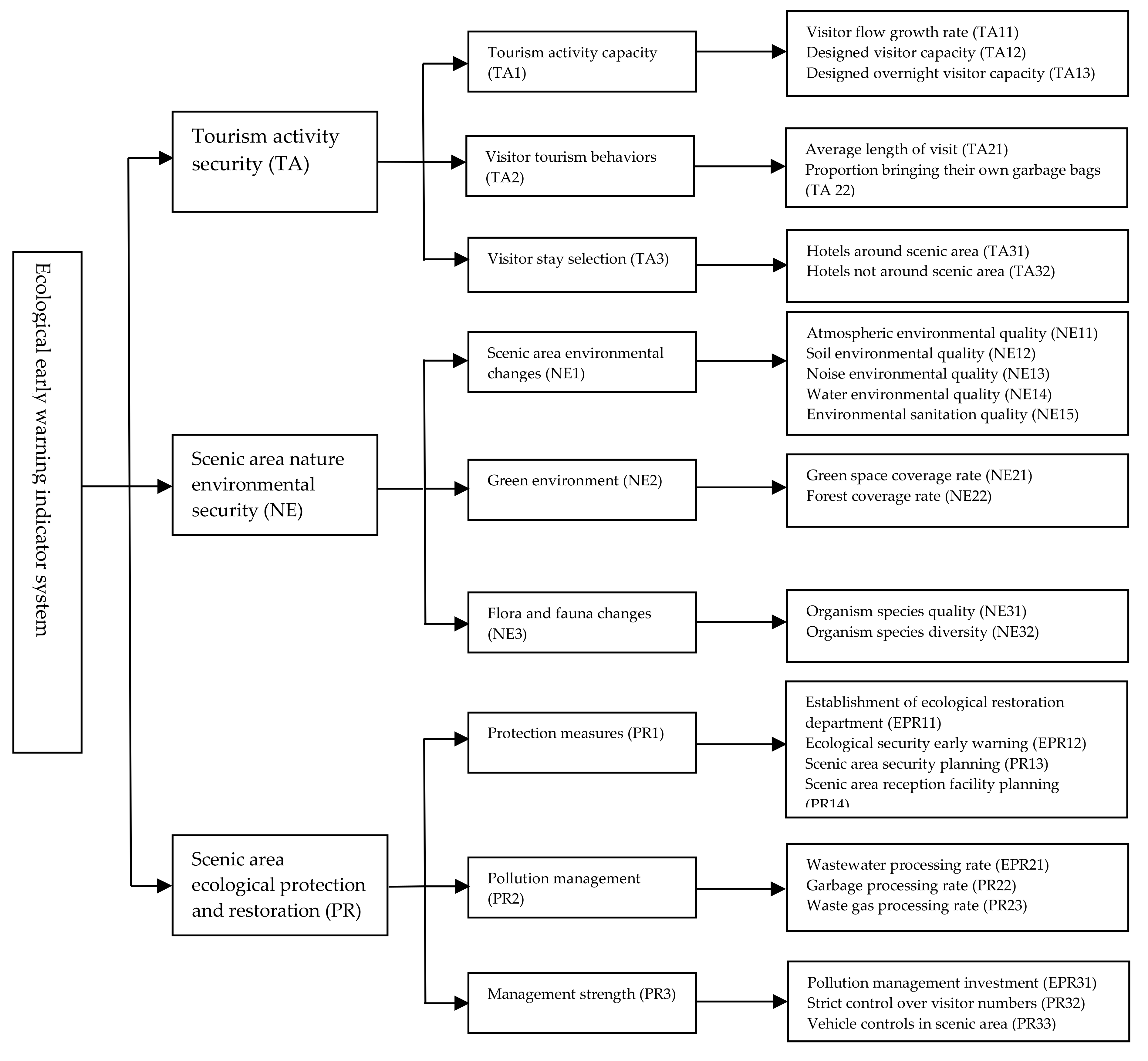
| No. | Indicator | Indicator Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Visitor flow growth rate | Yang [29]; Maguire, et al. [48]; Becken, et al. [7]; Zhang, et al. [9]; Lo and Lin [49]; interviews with scenic area managers |
| 2 | Local population growth rate | |
| 3 | Tourism worker population growth rate | |
| 4 | Designed tourist capacity | Cao [27]; Lo [6]; Becken, et al. [7]; Zhang, et al. [9]; interviews with scenic area managers |
| 5 | Designed overnight tourist capacity | |
| 6 | Average time staying at the scenic area | Suggestions from tourism researchers; stipulated by authors |
| 7 | Proportion of visitors bringing their own garbage bags | |
| 8 | Construction of parking lot for scenic area | Ming [32]; Li and Zhang [33]; Zhao and Li [30]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 9 | Hotels around the scenic area | |
| 10 | Hotels not around the scenic area | |
| 11 | Atmospheric environmental quality | Ming [32]; Li and Zhang [33]; Sun et al. [13]; Yang [29]; Zhang [18]; Cloquell-Ballester, et al. [50]; Lo [6]; Fan, et al. [8] |
| 12 | Soil environmental quality | |
| 13 | Noise environmental quality | |
| 14 | Water environmental quality | |
| 15 | Environmental sanitation quality | Cao [27]; Cloquell-Ballester, et al. [50]; Fan, et al. [8]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 16 | Green space coverage rate | Cao [27]; Yang [29]; Cloquell-Ballester, et al. [50]; Fan, et al. [8]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 17 | Forest coverage rate | Interviews with scenic area managers |
| 18 | Organism species quality | Cao [27]; Yang [29]; Zhao and Li [30]; Mei, et al. [51]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 19 | Organism species diversity | |
| 20 | Establishment of ecological restoration department | Li and Zhang [33]; Zhao and Li [30]; Becken, et al. [7]; Zhang, et al. [9]; interviews with scenic area managers |
| 21 | Construction of ecological security early warnings | |
| 22 | Scenic area ecological security planning | |
| 23 | Scenic area reception facility planning | |
| 24 | Number of environmental protection workers | |
| 25 | Quality of local residents | |
| 26 | Wastewater processing rate | Ming [32]; Li and Zhang [33]; Cao [27]; Yang [29]; Zhao and Li [30]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 27 | Garbage processing rate | |
| 28 | Waste gas processing rate | |
| 29 | Pollution management investments | Lin [4]; Cao [27]; Zhang, et al. [9] |
| 30 | Local GDP around scenic area | |
| 31 | Strict controls over visitor numbers | Interviews with scenic area managers |
| 32 | Vehicle controls in scenic area |
| Fuzzy Number | Definition of Linguistic Term | Triangular Fuzzy Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Equally Important | (1,1,2) | |
| Slightly Important | (2,3,4) | |
| Somewhat Important | (4,5,6) | |
| Very Important | (6,7,8) | |
| Absolutely Important | (8,9,9) |
| Extracted Dimension | Indicator Variable | Factor Loading | Eigenvalue | Variance Explained (%) | Cronbach’s α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism activity security (TA) | 1. Visitor flow growth rate | 0.882 | 12.18 | 47.21 | 0.91 |
| 2. Designed visitor capacity | 0.843 | ||||
| 3. Designed overnight visitor capacity | 0.709 | ||||
| 4. Average time staying at a scenic area | 0.706 | ||||
| 5. Proportion of visitors bringing their own garbage bags | 0.738 | ||||
| 6. Hotels around scenic area | 0.814 | ||||
| 7. Hotels not around scenic area | 0.785 | ||||
| Natural environmental security (NE) | 8. Atmospheric environmental quality | 0.797 | 3.38 | 13.02 | 0.96 |
| 9. Soil environmental quality | 0.781 | ||||
| 10. Noise environmental quality | 0.867 | ||||
| 11. Water environmental quality | 0.875 | ||||
| 12. Environmental sanitation quality | 0.871 | ||||
| 13. Green space coverage rate | 0.792 | ||||
| 14. Forest coverage rate | 0.772 | ||||
| 15. Organism species quality | 0.810 | ||||
| 16. Flora and fauna species diversity | 0.778 | ||||
| Ecological protection and restoration (PR) | 17. Establishment of ecological restoration department | 0.851 | 3.34 | 12.83 | 0.96 |
| 18. Construction of ecological security early warnings | 0.801 | ||||
| 19. Ecological security planning for scenic area | 0.828 | ||||
| 20. Scenic area reception facility planning | 0.854 | ||||
| 21. Waste gas processing rate | 0.827 | ||||
| 22. Garbage processing rate | 0.780 | ||||
| 23. Waste water processing rate | 0.866 | ||||
| 24. Pollution management investment | 0.848 | ||||
| 25. Strict control over visitor numbers | 0.766 | ||||
| 26. Vehicle controls in scenic area | 0.814 |
| Target Layer | Dimension Layer (Weight) | Rank | Factor Layer (Weight) | Rank | Indicator Layer (Weight) | Rank | Overall Weight | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological early warning indicator system of scenic areas | TA (0.2970) | 2 | TA1 (0.3718) | 1 | TA11(0.0471) | 6 | 0.01389 | 18 |
| TA12(0.1182) | 4 | 0.03510 | 11 | |||||
| TA13(0.2065) | 2 | 0.06132 | 6 | |||||
| TA2 (0.2726) | 3 | TA21(0.1929) | 3 | 0.05728 | 7 | |||
| TA22(0.0797) | 5 | 0.02366 | 13 | |||||
| TA3 (0.3556) | 2 | TA31(0.3265) | 1 | 0.09695 | 3 | |||
| TA32(0.0291) | 7 | 0.00863 | 23 | |||||
| NE (0.5396) | 1 | NE1 (0.2944) | 2 | NE11(0.0432) | 7 | 0.02330 | 15 | |
| NE12(0.0428) | 9 | 0.02305 | 17 | |||||
| NE13(0.0430) | 8 | 0.02320 | 16 | |||||
| NE14(0.0435) | 6 | 0.02345 | 14 | |||||
| NE15(0.1219) | 3 | 0.06576 | 4 | |||||
| NE2 (0.1934) | 3 | NE21(0.1218) | 4 | 0.06571 | 5 | |||
| NE22(0.0716) | 5 | 0.03915 | 9 | |||||
| NE3 (0.5122) | 1 | NE31(0.3120) | 1 | 0.16833 | 1 | |||
| NE32(0.2002) | 2 | 0.10802 | 2 | |||||
| PR (0.1634) | 3 | PR1 (0.4412) | 2 | PR11(0.0599) | 5 | 0.00975 | 21 | |
| PR12(0.2620) | 3 | 0.04281 | 8 | |||||
| PR13(0.0588) | 7 | 0.00960 | 22 | |||||
| PR14(0.0605) | 4 | 0.00989 | 19 | |||||
| PR2 (0.1115) | 3 | PR21(0.0367) | 9 | 0.00598 | 25 | |||
| PR22(0.0321) | 10 | 0.00524 | 26 | |||||
| PR23(0.0427) | 8 | 0.00698 | 24 | |||||
| PR3 (0.4473) | 1 | PR31(0.0591) | 6 | 0.00965 | 20 | |||
| PR32(0.1568) | 2 | 0.02561 | 12 | |||||
| PR33(0.2314) | 1 | 0.03781 | 10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.-Y.; Lu, J.-L.; Fan, Y.-L. An Ecological Early Warning Indicator System for Environmental Protection of Scenic Areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082344
Lin S-Y, Lu J-L, Fan Y-L. An Ecological Early Warning Indicator System for Environmental Protection of Scenic Areas. Sustainability. 2019; 11(8):2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082344
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shih-Yen, Jun-Liang Lu, and Yu-Lin Fan. 2019. "An Ecological Early Warning Indicator System for Environmental Protection of Scenic Areas" Sustainability 11, no. 8: 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082344
APA StyleLin, S.-Y., Lu, J.-L., & Fan, Y.-L. (2019). An Ecological Early Warning Indicator System for Environmental Protection of Scenic Areas. Sustainability, 11(8), 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082344




