Abstract
We evaluated the financial performance of government bond portfolios formed according to socially responsible investment (SRI) criteria. We thus open a discussion on the financial performance of SRI for government bonds. Our sample includes 24 countries over the period of June 2006 to December 2017. Using various financial performance measures, the results suggest that high-rated government bonds, according to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) dimensions, outperform low-ranked bonds under any cut-off, although differences are not statistically significant. These findings suggest that ESG screenings can be used for government bonds without sacrificing financial performance.
1. Introduction
The growth in socially responsible investment (SRI) has been notable. According to the 2016 Global Sustainable Investment Review [1], in 2016, US$22.89 trillion of assets were being professionally managed under responsible investment strategies worldwide, an increase of 25% since 2014. In 2016, 53% of managers in Europe used responsible investment strategies, this proportion being 22% in the U.S. and 51% in Australia and New Zealand. Per the Global Sustainable Investment Association (GSIA) 2016, sustainable investing is an investment approach that considers environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in portfolio selection and management. ESG screening investment processes, which allow an investor to select or exclude investments from the available universe based on ESG criteria, have helped investors to align their personal beliefs and values with their investment decisions. Rising individual awareness of environmental, social, and ethical concerns is now strongly influencing the purchasing decisions of investors [2].
The concept of SRI was originally related to stock selection. However, the proportion of portfolio investors applying SRI criteria to bonds has grown significantly. According to the European Sustainable Investment Forum (EUROSIF, 2016) [3], equities represented over 30% of SRI assets in December 2015, a significant decrease from the previous year’s 50%. A strong increase in bonds simultaneously occurred from the 40% registered in December 2013 to 64% in December 2015. Both corporate bonds and government bonds underwent remarkable growth. The former rose from 21.3% to 51.17% of the bond allocation, while the latter increased from 16.6% to 41.26%.
In this regard, the financial implications of the ESG screening processes on corporate bonds may be closely related to stock selections, since corporate bonds are associated with firms. Previous studies [4,5], which evaluated the financial performance of mutual funds that invested in socially responsible fixed-income stocks, found that the average SRI bond funds performed similarly to conventional funds. These results are in line with most empirical studies about the performance of SRI funds, which showed that they tend to perform similarly to their conventional peers [6]. However, the ESG screening processes for government bonds, since they are not related to firms, can help provide an in-depth understanding of SRI consequences for alternative assets. Despite the SRI government bond market growth and the development of country ratings based on ESG factors, the link between government bond returns and country performance in terms of ESG concerns has been overlooked. To the best of our knowledge, no previous research has evaluated the financial performance of responsible government bond investments.
The main objective of this paper was to fill this gap. We evaluated the financial performance of government bond portfolios formed according to ESG criteria. In contrast with previous studies, which applied firm sustainability ratings, we used sustainability ratings related to countries. We employed the RobecoSAM country sustainability ranking developed by RobecoSAM and Robeco. This ranking is a comprehensive framework for assessing countries’ ESG performance. By focusing on ESG factors, such as aging, competitiveness, and environmental risks, a country’s sustainability ranking offers a view of a country’s strengths and weaknesses.
Previous research has shown that ESG factors are valuable for government bonds. Capelle-Blancard et al. [7] assessed whether ESG performance influences government bond spreads. They found that countries with good ESG performance tended to have less default risk and thus lower bond spreads. Hence, the findings of Hoepner and Neher [8] were reinforced. They found a negative and significant relationship between government debt and a national sustainability rating. We wanted to ascertain whether ESG factors are valuable from a portfolio management perspective. Drut [9] assessed a feasible diversification portfolio problem associated with government bond portfolios. They computed the efficient frontier of portfolios, including government bonds from 20 developed countries and showed that government bond portfolios with high social responsibility scores could be formed without significant loss of diversification. Investors could thus form government bond portfolios based on socially responsible ratings without renouncing the potential for diversification. We wanted to complete a deeper examination and determine whether government bond portfolios formed according to ESG dimensions can be formed without sacrificing financial performance.
We therefore contribute to the existing literature on the financial performance of SRI by examining the impact of ESG screening processes on portfolios of government bonds. Ullmann [10] noted that stakeholders (e.g., investors, customers, and community) have the power to influence management’s corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities and strategies. SRI demands have led firms to pay more attention to their CSR activities and strategies. Hence, our study may lead governments to be more concerned about social, governance, and environmental policies. Given the growth of SRI in international capital markets and the increasing interest of investors in government bonds, our results about the implications of sustainability screening processes on government bonds in an international context are of practical interest for particular and institutional investors, as well as governments worldwide.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents a brief literature review on the financial outcomes of SRI for alternative assets. Section 3 describes the data. Section 4 presents and discusses the empirical analysis and Section 5 summarizes our main findings and presents our concluding remarks.
2. Literature Review
The growth in SRI and its consequences have stimulated empirical studies assessing financial behaviors. Prior studies mainly evaluated the financial performance of SRI investment funds and SRI stock portfolios. As Osthoff [11] noted, many studies compared the performance of SRI investment funds with conventional investments [12,13,14]. In general, these studies found no significant differences between the financial performance of SRI investment funds and conventional funds [5]. Goldreyer and Diltz [15] evaluated the financial performance of U.S. SRI fixed-income funds, invested in both corporate and government bonds. They found that SRI fixed-income funds underperformed their conventional peers. By contrast, 20 years later, Derwall and Koedijk [4] found that U.S. SRI fixed-income funds performed similarly to conventional funds. In European markets, Leite and Cortez [5] showed that financial performance was geographically dependent: UK SRI fixed-income funds underperformed conventional funds, German SRI fixed-income funds outperformed conventional ones and French SRI fixed-income funds showed similar performance to their conventional peers.
Despite all this attention being valuable from a practical point of view, certain limitations are related to fund studies. Brammer et al. [16] and Kempf and Osthoff [17] pointed out that confusing effects, such as fund manager performance and management fees, complicate showing differences in investment fund performance. Evidence provided by Utz and Wimmer [14], Humphrey et al. [18], and Statman and Glushkov [19] showed that the ‘socially responsible’ label might be more akin to a marketing strategy, thus raising doubts among investors whether an SRI fund is really socially responsible. As a consequence, investors may struggle to know the extent to which an SRI fund is really considering social criteria in its selection process. To address these concerns, some studies followed a portfolio stock approach. They formed portfolios, including high- and low-ranked firms according to their ESG scores and investigated their financial differences. These studies found ambiguous results. Van de Velde et al. [20], Galema et al. [21] and Mollet and Ziegler [2] did not find significant financial differences between high- and low-ranked sustainable firms. Derwall et al. [22], Kempf and Osthoff [17], and Eccles et al. [23] showed that high-rated portfolios outperformed low-rated ones, but Brammer et al. [16] and Auer and Schuhmacher [24] found that high-ranked firms underperformed compared to their low-rated counterparts. In this paper, we follow this approach to elude drawbacks related to fund studies.
The financial implications of SRI strategies have led to intensive research on several assets. Surprisingly and despite the growth in investors applying SRI criteria to government bonds, financial performance of SRI government bond portfolios has been overlooked.
3. Data
The samples evaluated mainly focused on developed countries, where valuable information exists on government bond returns and concerns related to SRI behavior, such as the country’s institutional framework, regulatory quality, rule of law, government efficiency, political stability, social cohesion, orderly conflict resolution, environmental vulnerabilities and policies, energy dependency, etc. Our dataset included 24 countries over the period June 2006 to December 2017. The countries were Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The countries assessed further represent a significant share of the world income economy and international bond markets. According to the World Bank country classifications by income level (2018–2019), the countries assessed belong to the leading group, except China and Turkey, which belong to the upper–middle-income economies. The data on government bond monthly total returns were sourced from FTSE Global Government Bond Indices ‘All maturities’, downloaded from the Thomson Reuters database in U.S. dollars. To classify government bonds according to ESG performance, we used the RobecoSAM country sustainability ranking. Robeco and RobecoSAM have jointly developed a comprehensive and systematic framework for determining country sustainability rankings. Sources used by RobecoSAM include international organizations, such as the World Bank, the United Nations and the International Labor Organization, as well as a variety of reputable government agencies, private institutions and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). The framework forms the basis for incorporating environmental, social and governance risk analysis into the construction process for Robeco and RobecoSAM’s government debt portfolios and indices. RobecoSAM’s country sustainability framework is used to evaluate many countries on the basis of a broad range of ESG factors that are considered key risk and return drivers for investors (see Appendix A for an extensive explanation of sustainability dimensions). It consists of 17 indicators, each of which is based on various data series, or sub-indicators, whereby each indicator is assigned a predefined weight out of the total framework. Based on the standardized scores and for each of the indicators and their corresponding weights, countries receive a sustainability score ranging from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest. The resulting scores offer insights into the investment risks and opportunities associated with each country, allowing investors to better compare countries. The weighting scheme is reviewed periodically, reflecting RobecoSAM’s view on the potential impact of each indicator on a country’s risk profile.
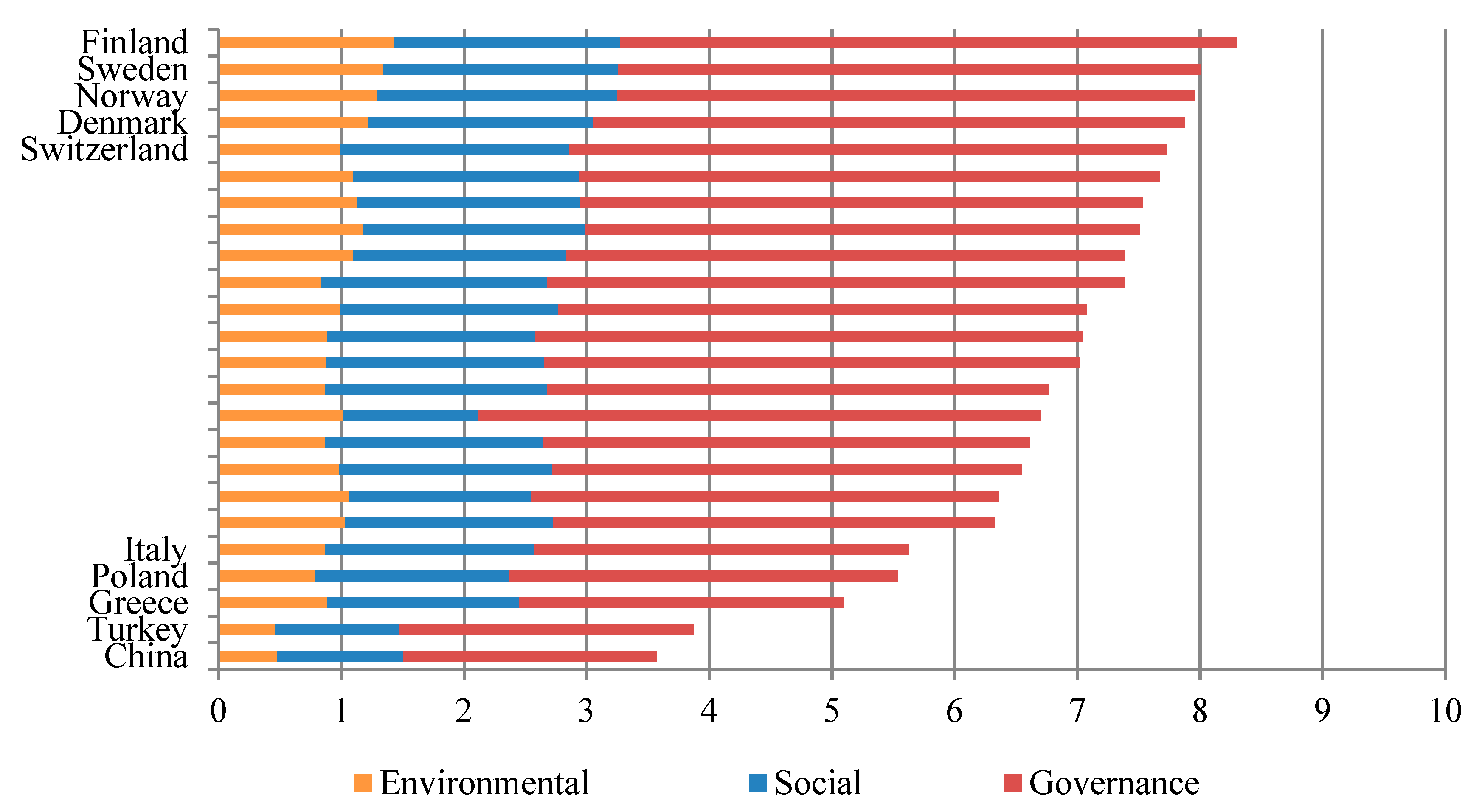
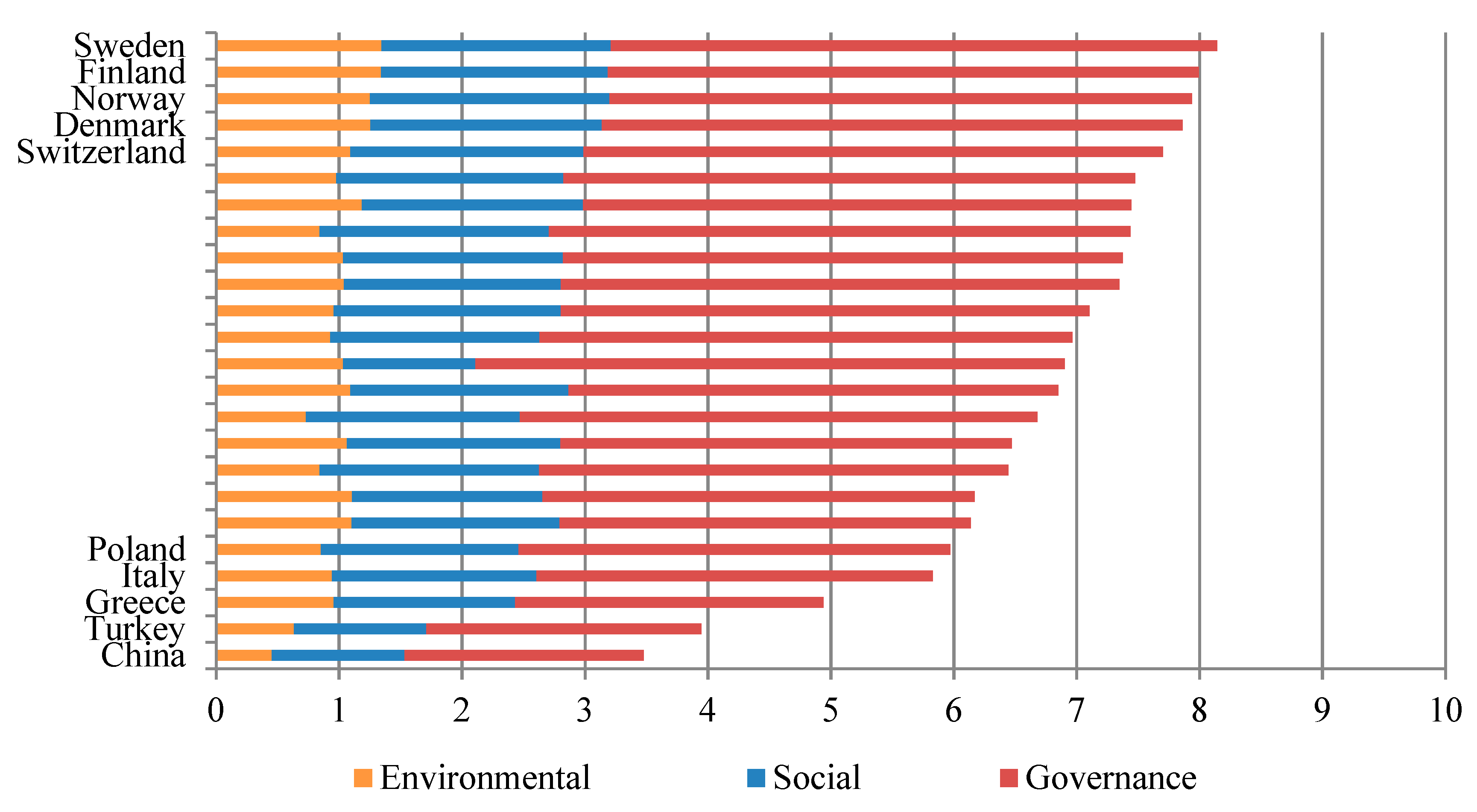
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the top five and bottom five countries according to the country sustainability ranking for the first (2006, first semester) and last (2017, second semester) periods, respectively. The countries at both the top and the bottom have remained the same despite more than 10 years passing between the two classifications. This evidence suggests that a noteworthy traditional and cultural component may exist behind ESG concerns. In this regard, some studies identified that country-specific factors tend to affect the financial performance of SRI [25,26,27]. These figures may highlight a limited capacity of previous policy initiatives to improve ESG standards in low-rated countries.
Figure 1.
Country sustainability ranking. Top five and bottom five countries in the first semester of 2006. Based on the standardized scores and for each of the indicators and their corresponding weights, countries receive a sustainability score ranging from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest (x-axis).
Figure 2.
Country sustainability ranking. Top five and bottom five countries in the second semester of 2017. Based on the standardized scores and for each of the indicators and their corresponding weights, countries receive a sustainability score ranging from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest (x-axis).
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Portfolio Construction
In this paper, we evaluated the financial implications of social responsibility screenings on government bonds. We ranked government bonds at time t according to countries’ ESG scores available at t–1. We then formed a high- and a low-rated portfolio, including ESG outperformers and underperformers, respectively. Since the country sustainability ranking is updated semi-annually, portfolios are formed twice a year. Related studies applied several cut-offs [28,29]. We also used alternative cut-offs (10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and 50%), which allowed us to evaluate different SRI demand levels. For instance, at the 10% cut-off level, the high-rated portfolio included 10% government bonds from countries with the highest ESG scores, whereas the low-rated portfolio included 10% government bonds from countries with the lowest ESG scores. We formed equally-weighted portfolios rather than value-weighted ones to improve diversification. Drut [9] showed that highly socially responsible government bond portfolios could be formed without significant loss of diversification. Nonetheless, given the process involved informing a value-weighted portfolio, the standard deviation may have been affected, since this type of portfolio is less diversified. Statman and Glushkov [30], for instance, found that a value-weighted portfolio (top–bottom portfolio) had a higher standard deviation than an equally-weighted one.
Table 1 provides descriptive statistics for the high- and low-rated portfolios at different cut-offs. The high-rated portfolios showed higher average returns than the low-rated ones at any cut-off. As for standard deviation, the high-ranked government bonds showed lower variability in terms of returns. This evidence suggests that risk affected low-rated portfolios to a larger extent than high-rated ones. Descriptive statistics allowed us to identify what the financial outcomes of ESG screening processes on government bonds may be. However, an extensive evaluation using risk-adjusted measures is advisable.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the high- and low-rated portfolios at the 10% (10), 20% (20), 30% (30), 40% (40) and 50% (50) cut-offs. Mean (SD) is the average return (standard deviation) of portfolios. Difference is the mean (SD) difference between high and low portfolios. The full sample period was from June 2006 to December 2017.
4.2. Ledoit and Wolf Approach
To estimate statistical financial performance differences between high and low portfolios, we followed the Ledoit and Wolf (LW) [31] approach. Accordingly, the Sharpe ratio [32]—the ratio of excess return to standard deviation—was used to compare the performance of alternative investment strategies. From two investment portfolios, i and j, whose excess returns over the risk-free rate at time t were and , respectively, a total of T return pairs (, ), …, (, ) were observed. The difference between two Sharpe ratios is given by , where and are the sample mean and standard deviation, respectively. To run statistical inference between the two Sharpe values, prior studies [33,34] used the Jobson and Korkie [35] test and the correction proposed by Memmel [36]. However, this test is not valid if the returns distribution is non-normal, or if the observations are correlated over time, both phenomena being quite common in financial returns time series data. LW [31] proposed a studentized time series bootstrap approach that works asymptotically and has satisfactory properties in finite samples. The literature [37,38] shows the enhanced inference accuracy of the studentized bootstrap over standard inference based on asymptotic normality. LW proposed testing by inverting a bootstrap confidence interval. A two-sided bootstrap confidence interval with nominal level 1−α for (true difference between the Sharpe ratios) was constructed and if zero was not contained in the interval, then was rejected at nominal level α. Specifically, LW proposed constructing a symmetric studentized time series bootstrap confidence interval. To do this, the two-sided distribution function of the studentized statistic is approximated through the bootstrap by , where is the true difference between the Sharpe ratios, is the estimated difference computed from the original data, is a standard error for (also calculated from the original data), is the estimated difference computed from bootstrap data and is a standard error for (also calculated from bootstrap data). Letting be a quantile of , a bootstrap 1α confident interval for is given by . LW noted that with heavy-tailed data or data of a time series nature, this quantile will typically be somewhat larger than its standard normal counterpart (used in the traditional tests) in small to moderate samples, resulting in more conservative inferences. To generate the bootstrap data, we used the circular block bootstrap of Politis and Romano [39], resampling blocks of pairs from the observed pairs (, ), t = 1, …, T, with a replacement. Applying the studentized circular block bootstrap requires a choice of the block size b and LW proposed using the calibration procedure of Loh [40], suggesting that M = 5000 bootstrap sequences is sufficient for reliable inference. The standard error is calculated using kernel estimation, specifically the pre-whitened quadratic spectral kernel of Andrews and Monahan [41]. The standard error is the natural standard error calculated from the bootstrap data, making use of a special block dependence structure. The bootstrap p-values are computed as , where , the original studentized test statistic, , denotes the centered studentized statistic computed from the mth bootstrap sample by d*,m, m = 1, …, M and M is the number of bootstrap resamples.
Table 2 shows the results of applying the Sharpe ratio and the LW procedure to estimate the statistical significance of the difference between the Sharpe ratio in high- and low-rated portfolios. We found that high-rated portfolios outperformed low-rated ones with any cut-off. Nonetheless, the LW t-statistic indicated that differences were not statistically significant. These results were in line with most previous studies, which reported that SRI performed similarly to conventional investments. Derwall and Koedijk [4] found that U.S. SRI fixed-income funds performed similarly to conventional funds. Leite and Cortez [5] found similar results for German and French SRI fixed-income funds. Nonetheless, these studies included the performance of corporate bonds in their investigations. While significant differences were not found using different cut-offs, we found that the biggest difference between the Sharpe value of the high- and low-portfolios appeared at the most demanding SRI level, the 10% cut-off. This evidence suggested that government bonds from countries with the best ESG practices performed substantially better than those with the worst practices. Hence, investors driving funds to, for example, countries with a stable institutional framework, high regulatory quality, no environmental vulnerabilities, or nonexistent social conflicts, not only reduced the risks associated with investments, but also achieved financial performance similar to conventional investments. The superior financial performance of the high-rated portfolios could be seen as a reward for recognizing that countries with outstanding ESG policies should do better than less responsible ones.

Table 2.
Portfolio performance of the high- and low-rated portfolios at the 10% (10), 20% (20), 30% (30), 40% (40), and 50% (50) cut-offs based on the Sharpe ratio and the Ledoit and Wolf (LW) significant tests.
4.3. Robustness Checks
To test the robustness of our findings, we considered three additional financial performance evaluation measures. We used the adaptation proposed by Ferruz and Sarto (FS) [42] regarding the Sharpe ratio used previously by some studies [43,44]. FS [42] noted that the Sharpe ratio assumes positive portfolio excess returns. However, they determined that this was not always the case. Consequently, when this happens, the Sharpe ratio can produce anomalous results. In this context, FS [42] proposed a correction to the Sharpe ratio as follows: , where is the portfolio p return at time t, is the risk-free return at time t and is the standard deviation of the portfolio p at time t. We also used the Sortino ratio [45,46] to evaluate performance on the basis of the lower partial moments (LPM). According to the Sortino ratio, risk is measured by the negative deviations of returns in relation to a minimum acceptable return (e.g., zero, the risk-free rate, or the average return). We used a rolling interest rate based on the evolution of the risk-free monthly interest rate. The Sortino specification is , where is the portfolio p return at time t and is the target return or minimum acceptable return. This measure has been used previously [29,47,48].
We also computed alpha values from a multi-factor model, including some fiscal and economic variables as controls. Previous related literature [7,8] controlled for gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate, inflation, fiscal condition (debt/GDP and Primary Balance (PB)/GDP), current account, liquidity ratio, country openness and sovereign credit ratings. For a more extensive discussion and understanding of the effects of each variable, see, for instance Capelle-Blancard et al. [7]. To start, we considered these variables and assessed their significance as determinants of international government bond returns (Appendix B). To this end, we estimated a fixed effects panel data model, as a Hausman test was conducted and showed that a fixed effects model was required instead of a random effects model. This approach was often used to address this concern in previous research. As data on control variables are annual, we used a cubic spline interpolation to generate monthly data. Our results showed that, except for GDP growth rate and debt/GDP, variables were significant and thereby had an impact on government bond returns (data available on request). We consequently left these two variables out of the analysis. We also performed the analysis using the eight control variables and the results were unaltered. The next step to evaluate the financial performance by computing alphas was to include control variables in the multi-factor model. Since we handled six variables for 24 countries, we employed principal component analysis (PCA) to determine the main dimensions. The principal components thus represented a vector of variables capturing fiscal and economic conditions. To end, we formed a long-short portfolio, a difference portfolio, which was formed by subtracting the low-rated portfolio returns from the returns on the high-rated portfolio. The resulting alpha was the estimated financial portfolio performance. This approach was commonly used in previous related studies [49,50]. A challenge in the evaluation of financial performance is the need for controlling alternative explanations. On a corporate side, Dang et al. [51] studied the use of firm size measures in the literature and found that it is a key variable in this area since affects the independent and dependent variables simultaneously. In this regard, country size measures could affect the financial performance evaluation of bond portfolios. We addressed that point including in the multi-factor model several control variables which could be associated with the size of countries, such as GDP growth rate and current account. In addition, since according to the World Bank country classifications by income level (2018–2019), the countries assessed belong to the leading group, except China and Turkey, which belong to the upper-middle-income economies, our samples mainly focused on developed countries with homogeneous characteristics from a wealth point of view, thereby restricting country SIZE effects on the financial performance of our bond portfolios.
Finally, a common impediment to understanding the true relationship between different aspects of empirical finance is the endogeneity problem; variables are sometimes endogenous and causality relations are complicated [52]. Examples of endogeneity problem in our scenery include that bonds which expect to outperform would use SRI, or something not captured in credit rating could affect SRI and performance simultaneously. We evaluate the causality relation between ESG scores and bond performance for each country using the Granger—causality test. Scholtens [53] is an example of a study that applies this test in a CSR context. We find unidirectional causality from ESG scores to bond performance. In addition, following Li [52], to deal with a possible endogeneity problem, we include the lagged dependent variable in our multi-factor model used to evaluate financial performance. Our findings do not change significantly. Given that we rank government bonds at t according to countries’ ESG scores available at t–1, the ESG scores used are lagged. Capelle-Blancard et al. [7], who use lagged ESG scores, suggest that lagging ESG scores helps to avoid the endogeneity problems and simultaneity bias that may arise as a result of a contemporaneous bidirectional causality existing between ESG aspects and bond performance.
Table 3 and Table 4 display the results of applying the additional portfolio financial performance measures. By using the FS [42] ratio, we found that the results were in line with our previous results. The values of high-rated portfolios were higher than those of the low-rated counterparts at any cut-off. The findings using the Sortino specification were also similar. High-rated portfolios outperformed low-rated ones under any cut-off. Results about these measures were limited to a descriptive comment since processes, such as Ledoit and Wolf [31], to evaluate statistical significance differences were not available. Finally, we found positive alphas in the long-short portfolios, meaning that high-ranked government bonds outperformed low-ranked ones, although alphas were not significant. These robustness checks supported our previous findings.

Table 3.
Financial performance of the high- and low-rated portfolios at the 10% (10), 20% (20), 30% (30), 40% (40), and 50% (50) cut-offs using the Ferruz and Sarto (FS) ratio and the Sortino ratio.

Table 4.
Financial performance of the long-short portfolios at the 10% (10), 20% (20), 30% (30), 40% (40) and 50% (50) cut-offs using the multi-factor model.
5. Conclusions
The expansion of SRI has led to extensive research on its financial consequences. Previous research has mainly focused on the financial benefit or the cost of ESG screening processes on investments related to corporate firms. Both mutual funds and stock portfolios have been evaluated from an SRI investment approach. However, despite the growing interest of portfolio investors in applying SRI criteria to government bonds, to the best of our knowledge, no previous studies have investigated the financial outcomes of SRI screenings on government bond portfolios.
Our main objective in this study was to evaluate the financial performance of government bond portfolios formed according to ESG criteria. We opened a discussion on financial performance of SRI for an asset other than firms. Using RobecoSAM information to classify the government bonds according to ESG performance, we assessed financial differences between high- and low-ranked government bonds. Using several portfolio financial performance measures, our results showed that high-rated portfolios outperform low-rated ones under any SRI level (cut-off), although differences were not significant. These findings are in line with most previous studies that reported that SRI performs similarly to conventional investments. Most empirical studies on the performance of SRI mutual funds across different geographical areas found no significant differences between their performance and that of conventional funds [5,50]. Likewise, many empirical studies evaluating differences between high and low-ranked firms, according to their CSR scores, also found that the differences are not significant [2,28]. Therefore, the absence of significant differences is considered a relevant finding in most previous research.
Overall, our evidence indicates that an investor can satisfy ESG concerns without sacrificing financial performance by investing in government bonds. In this regard, as SRI investor claims have led firms to be more concerned with their corporate social responsibility strategies [2,10], for instance, Li et al. [55] found that SRI mutual funds had a positive effect on firm’s future CSR, investors screening government bonds according to their sustainability scores could influence countries in terms of ESG guiding principles. Our results suggest that SRI can be used as a tool to enhance the ESG policies of countries. Currently, many countries are shifting toward a sustainable economy. For instance, the Paris Agreement aims to strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change in the context of sustainable development and efforts to eradicate poverty. To this end, it recommends that financial resources flow toward climate-resilient development and the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Global capital markets are one of the most powerful tools in the fight against climate change and to develop sustainable economies. However, they are often overlooked by governments. If governments are aware that social responsibility issues may influence investment decisions and that investors can satisfy their social concerns and simultaneously produce similar financial performance as conventional investments, then they should improve ESG standards and display this information to attract new investments. Since SRI investors drive their funds toward investments with high levels of sustainability [2], governments could use the ESG information as a tool to attract an increasing number of investors concerned with SRI issues. Aiming to make the country’s interests related to socially responsible concerns visible for investors—in line with the European initiative [56], whose objective is that large firms disclose both financial and non-financial information—it might be beneficial for governments to publish official reports about their achievements in socially responsible policies, strategies and activities to help SRI investors make well-informed investment decisions. Socially responsible policies and strategies may positively affect bond performance through different channels. Environmental challenges are a potential risk for investors, as environmental externalities can result in significant economic losses, while repairing environmental damage such as air and water pollution can generate considerable fiscal costs. Adequate investments towards preventing environmental problems limit such potential liabilities. Likewise, a weak social climate dominated by labor unrest, extreme inequality or other social tensions is another potential investment risk. Social policies providing a strong social cohesion support orderly conflict resolution and facilitate the implementation of necessary reforms, thus contributing to sustainable economic development.
We consider that further research would be worthwhile to broaden the knowledge in this field, for instance, to evaluate the particular effect of each ESG dimension on the financial performance of SRI government bond portfolios, in line with previous studies on stock portfolios [24]. Evaluating specific channels through which mutual funds could affect their holding bonds’ social performance [55]. Different maturities of government bonds could be considered to form portfolios, as well as include more countries, especially developing countries and evaluate a longer sample period. In addition, since previous research on SRI investment funds and SRI stock portfolios found that different market states (e.g., expansion and recession) affect the financial performance of SRI [57,58], researchers could evaluate this concern about SRI government bond portfolios. Specific SRI issues assessed previously on firms could be analyzed from now on in this context.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in all aspects of this study.
Funding
This research was funded by the ECO2015-66240P project and the financial support of the Government of Aragón and of the European Social Fund under grant (reference G/17030/5423/440030/11101 and 17030/5423/440030/91101) and the project Gespublica S56_17R.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Max Schieler, Executive Director of RobecoSAM AG, for providing us with the Country Sustainability Ranking.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. RobecoSAM Information about ESG Dimensions
Environmental dimension: Environmental challenges pose a potential risk for investors, as environmental externalities can result in significant economic losses, whereas repairing environmental damage, such as air and water pollution, can generate considerable fiscal costs. Adequate investments in preventing environmental problems limit such potential liabilities. Another important risk is related to the country’s exposure to natural hazards, such as floods, hurricanes, or typhoons. In addition to evaluating a country’s environmental vulnerabilities and policies, RobecoSAM examines its energy dependency and energy policies. Countries that rely heavily on fossil fuel imports are vulnerable to abrupt and/or sharp external price movements or supply shortages. In addition to assessing the risks themselves, RobecoSAM specifically looks for evidence that policies for mitigating such risks have been implemented.
Social dimension: A weak social climate dominated by labor unrest, extreme inequality, or other social tensions is another potential investment risk. A delicate social climate can easily result in violent turmoil, disrupting important economic activity, such as manufacturing or trade and/or paralyze policymaking. Strong social cohesion, conversely, supports orderly conflict resolution and facilitates the implementation of necessary reforms, thus contributing to sustainable economic development.
Governance dimension: RobecoSAM examines a broad range of data that considers a country’s institutional framework, regulatory quality, rule of law, government efficiency, central bank independence and political stability, among other factors. Civil liberties, internal conflicts and corruption also reflect a country’s governance profile. The corruption level, for instance, shows the extent to which public power is exercised to protect the interests of a small group at the expense of the economy and society at large. A study by Robeco demonstrated the added value of considering political risk when taking investment decisions for government bonds, over a time period of 25 years.
Appendix B. Description of Control Variables
GDP growth rate: ΔGDP/GDP; annual percentages of constant-price GDP changes; source: International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Inflation: ΔP/P; annual percentages of average consumer price changes; source: IMF.
Fiscal Condition: Debt/GDP; all liabilities that require payment or payments of interest and/or principal by the debtor to the creditor at a date or dates in the future; source: IMF.
Primary Balance (PB): PB/GDP; primary net lending/borrowing plus net interest payable/paid; source: IMF.
Current Account (CA): CA/GDP; all transactions other than those in financial and capital items; source: IMF.
Liquidity ratio: Reserves/Imports; total reserves comprise holdings of monetary gold, special drawing rights and holdings of foreign exchange under the control of monetary authorities; source: WB.
Country openness: (X + M)/GDP; the sum of exports and imports of goods and services measured as a share of gross domestic product; source WB.
Standard & Poor’s (S&P) sovereign credit ratings: numerical variable assigning 1 to CCC, 2 to CCC+ and so on through 18 to AAA; source: Thomson Reuters.
References
- Global Sustainable Investment Review. 2016. Available online: https://www.gsi-alliance.org (accessed on 10 July 2018).
- Mollet, J.C.; Ziegler, A. Socially Responsible Investing and Stock Performance: New Empirical Evidence for the US and European Stock Markets. Rev. Financ. Econ. 2014, 23, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Sustainable Investment Forum—EUROSIF. European SRI Study. 2016. Available online: https://www.eurosif.org (accessed on 13 March 2018).
- Derwall, J.; Koedijk, K. Socially Responsible fixed-income Funds. J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2009, 36, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, P.; Cortez, M.C. The Performance of European Socially Responsible Fixed-Income Funds. 2016. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2726094 (accessed on 25 May 2018).
- Revelli, C.; Viviani, J.L. Financial Performance of Socially Responsible Investing (SRI): What have we Learned? A meta-analysis. Bus. Ethics Eur. Rev. 2015, 24, 158–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelle-Blancard, G.; Crifo, P.; Diaye, M.A.; Scholtens, B.; Oueghlissi, R. Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Performance and Sovereign Bond Spreads: An Empirical Analysis of OECD Countries. 2016. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2874262 (accessed on 11 June 2018).
- Hoepner, A.G.; Neher, A. Sovereign Debt and Sustainable Development Culture. 2013. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2295688 (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Drut, B. Sovereign Bonds and Socially Responsible Investment. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 92, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.A. Data in Search of a Theory: A Critical Examination of the Relationships among Social Performance, Social Disclosure, and Economic Performance of US Firms. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1985, 10, 540–557. [Google Scholar]
- Osthoff, P. What Matters to SRI Investors. In The Routledge Hand Book of Responsible Investment, 1st ed.; Hebb, T., Hawley, J.P., Hoepner, A.G., Neher, A.L., Wood, D., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 705–724. [Google Scholar]
- Kreander, N.; Gray, R.H.; Power, D.M.; Sinclair, C.D. Evaluating the Performance of Ethical and non-ethical Funds: A Matched Pair Analysis. J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2005, 32, 1465–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.; Whittaker, J. Performance and Performance Persistence of ‘ethical’ unit Trusts in the UK. J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2007, 34, 1327–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utz, S.; Wimmer, M. Are they any Good at all? A Financial and Ethical Analysis of Socially Responsible Mutual Funds. J. Asset Manag. 2014, 15, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldreyer, E.F.; Diltz, J.D. The Performance of Socially Responsible Mutual Funds: Incorporating Socio political Information in Portfolio Selection. Manag. Financ. 1999, 25, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, S.; Brooks, C.; Pavelin, S. Corporate Social Performance and Stock Returns: UK Evidence from Disaggregate Measures. Financ. Manag. 2006, 35, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, A.; Osthoff, P. The Effect of Socially Responsible Investing on Portfolio Performance. Eur. Financ. Manag. 2007, 13, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.E.; Warren, G.J.; Boon, J. What is Different about Socially Responsible Funds? A Holdings-Based Analysis. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 138, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statman, M.; Glushkov, D. Classifying and Measuring the Performance of Socially Responsible Mutual Funds. J. Portf. Manag. 2016, 42, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, E.; Vermeir, W.; Corten, F. Corporate Social Responsibility and Financial Performance. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2005, 5, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galema, R.; Plantinga, A.; Scholtens, B. The Stocks at Stake: Return and Risk in Socially Responsible Investment. J. Bank. Financ. 2008, 32, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwall, J.; Guenster, N.; Bauer, R.; Koedijk, K. The Eco-Efficiency Premium Puzzle. Financ. Anal. J. 2005, 61, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.G.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The Impact of Corporate Sustainability on Organizational Processes and Performance. Manag. Sci. 2014, 60, 2835–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, B.R.; Schuhmacher, F. Do Socially (Ir)Responsible Investments Pay? New Evidence from International ESG Data. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2016, 59, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, R.G.; Serafeim, G.; Krzus, M.P. Market Interest in Nonfinancial Information. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 2011, 23, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.C.; Silva, F.; Areal, N. Socially Responsible Investing in the Global Market: The Performance of US and European Funds. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 17, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörisch, J.; Ortas, E.; Schaltegger, S.; Álvarez, I. Environmental Effects of Sustainability Management Tools: An Empirical Analysis of Large Companies. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbritter, G.; Dorfleitner, G. The Wages of Social responsibility—where are they? A Critical Review of ESG Investing. Rev. Financ. Econ. 2015, 26, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, B.R. Do Socially Responsible Investment Policies Add or Destroy European Stock Portfolio Value? J. Bus. Ethics. 2016, 135, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statman, M.; Glushkov, D. The Wages of Social Responsibility. Financ. Anal. J. 2009, 65, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoit, O.; Wolf, M. Robust Performance Hypothesis Testing with the Sharpe Ratio. J. Empir. Financ. 2008, 15, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, W.F. Mutual Fund Performance. J. Bus. 1966, 39, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiguel, V.; Nogales, F.J. Portfolio Selection with Robust Estimation. Oper. Res. 2009, 57, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbarro, D.; Wong, W.-K.; Kenton Zumwalt, J. Stochastic Dominance Analysis of iShares. Eur. J. Financ. 2007, 13, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, J.D.; Korkie, B.M. Performance Hypothesis Testing with the Sharpe and Treynor Measures. J. Financ. 1981, 36, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmel, C. Performance Hypothesis Testing with the Sharpe Ratio. Financ. Lett. 2003, 1, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, P. The Bootstrap and Edgeworth Expansion; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, S.N. Resampling Methods for Dependent Data; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, D.N.; Romano, J.P. A Circular Block-Resampling Procedure for Stationary Data. In Exploring the Limits of Bootstrap; LePage, R., Billard, L., Eds.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, W.-Y. Calibrating Confidence Coefficients. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.K.; Monahan, J.C. An Improved Heteroskedasticity and Autocorrelation Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimator. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1992, 60, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruz, L.; Sarto, J.L. An Analysis of Spanish Investment Fund Performance: Some Considerations Concerning Sharpe’s Ratio. Omega 2004, 32, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, H. Refinements to the Sharpe Ratio: Comparing Alternatives for Bear Markets. J. Asset Manag. 2007, 7, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Seco, L.; Wu, L.L.B. Portfolio Optimization in Hedge Funds by OGARCH and Markov Switching Model. Omega 2015, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, F.A.; Price, L.N. Performance Measurement in a Downside Risk Framework. J. Investig. 1994, 3, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sortino, F.A.; Van Der Meer, R. Downside Risk. J. Portf. Manag. 1991, 17, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, K.B.; Lien, D. An Empirical Examination of the Effectiveness of Dollar-Cost Averaging using Downside Risk Performance Measures. J. Econ. Financ. 2003, 27, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meligkotsidou, L.; Vrontos, I.D.; Vrontos, S.D. Quantile Regression Analysis of Hedge Fund Strategies. J. Empir. Financ. 2009, 16, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.E.; Lee, D.D.; Shen, Y. Does it Cost to be Sustainable? J. Corp. Financ. 2012, 18, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.; Cortez, M.C.; Silva, F.; Adcock, C. The Performance of Socially Responsible Equity Mutual Funds: Evidence from Sweden. Bus. Ethics Eur. Rev. 2018, 27, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Li, Z.F.; Yang, C. Measuring firm size in empirical corporate finance. J. Bank. Financ. 2018, 86, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Endogeneity in CEO power: A survey and experiment. Investig. Anal. J. 2016, 45, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtens, B. A note on the interaction between corporate social responsibility and financial performance. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 68, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newey, W.K.; West, K.D. Simple, Positive Semi-Definite, Heteroskedasticity and Autocorrelation consistent Covariance Matrix. Econometrica 1986, 55, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Patel, S.; Ramani, S. The Role of Mutual Funds in Corporate Social Responsibility. 2019. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3366100 (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Directive2014/95/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 October 2014 Amending Directive 2013/34/EU as Regards Disclosure of Non-Financial and Diversity Information by Certain Large Undertakings and Groups. Available online: http://www.europarl.europa.eu (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Leite, P.; Cortez, M.C. Performance of European Socially Responsible Funds during Market Crises: Evidence from France. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2015, 40, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Bezares, F.; Przychodzen, W.; Przychodzen, J. Corporate sustainability and share holder wealth—Evidence from British companies and lessons from the crisis. Sustainability 2016, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).