Leaching Characteristics of Low Concentration Rare Earth Elements in Korean (Samcheok) CFBC Bottom Ash Samples
Abstract
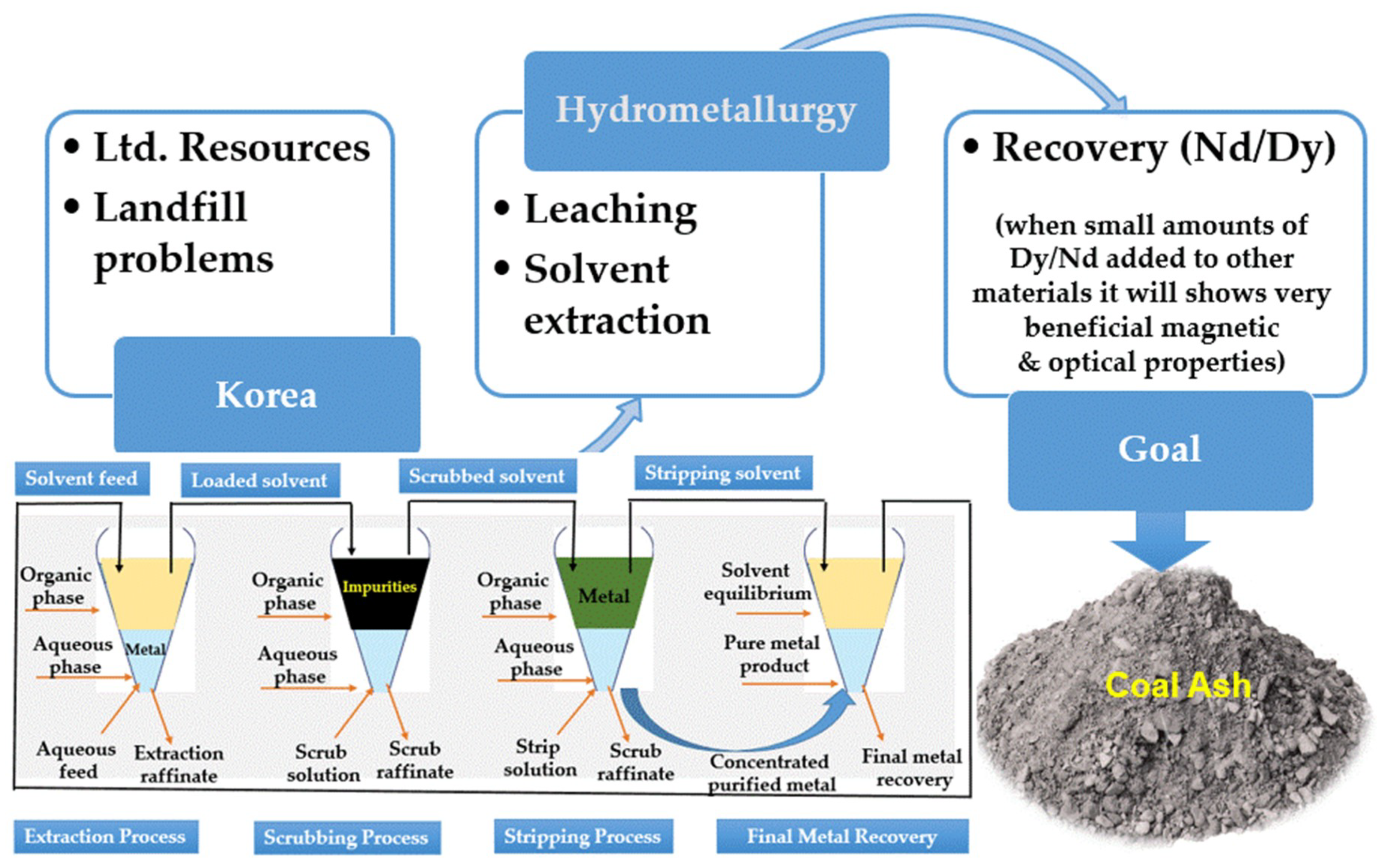
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
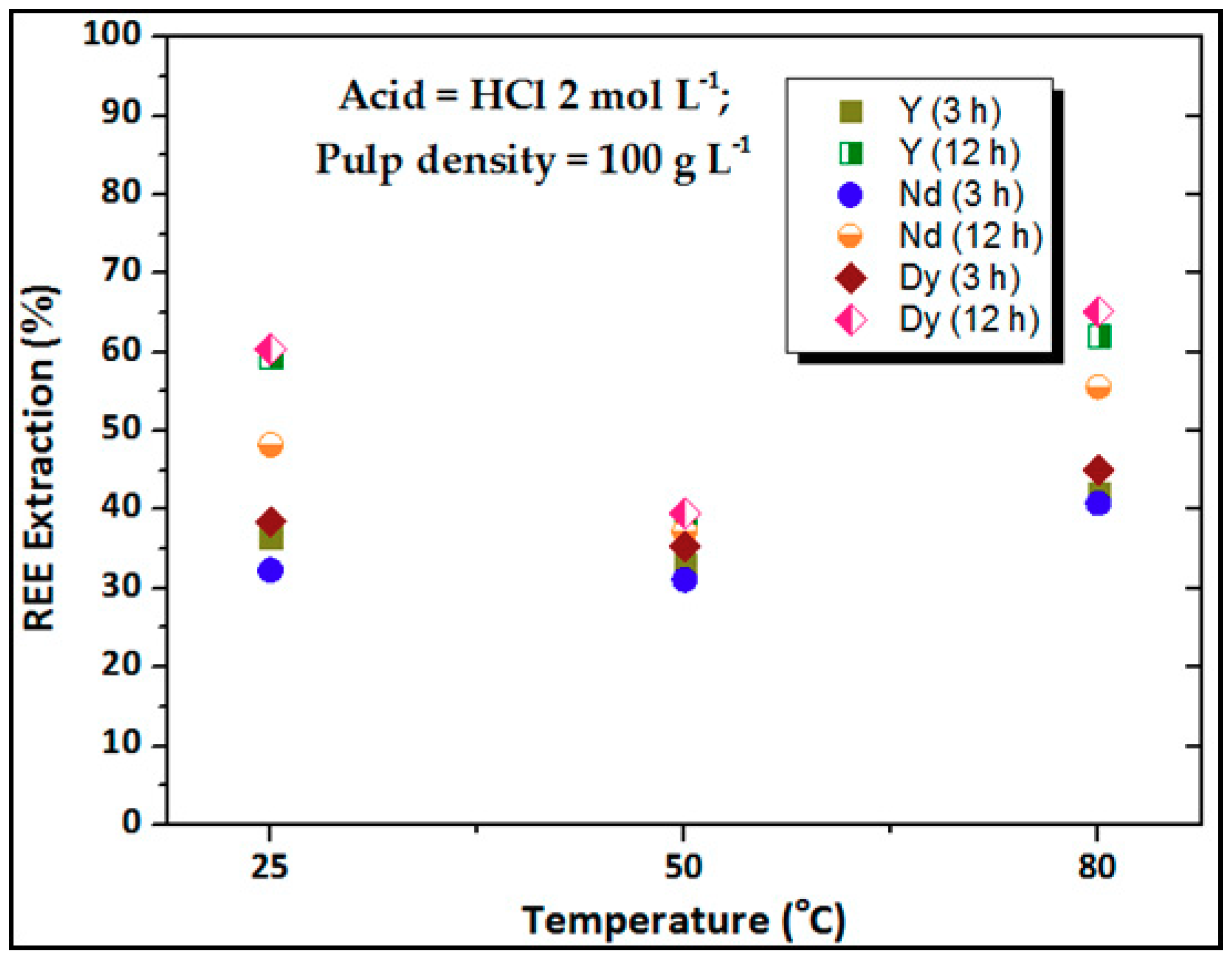
3.1. Effect of Temperature
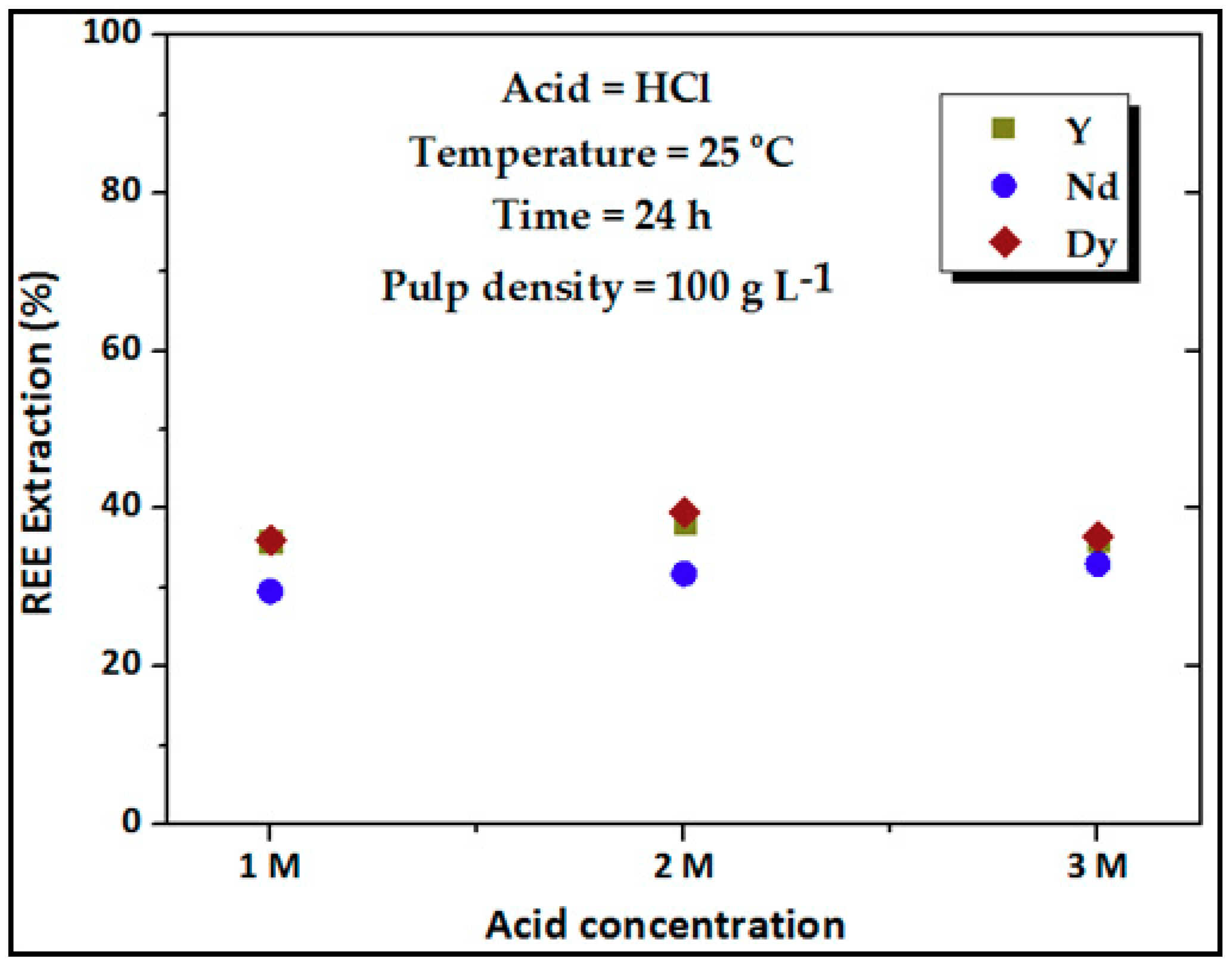
3.2. Effect of Acid Concentration
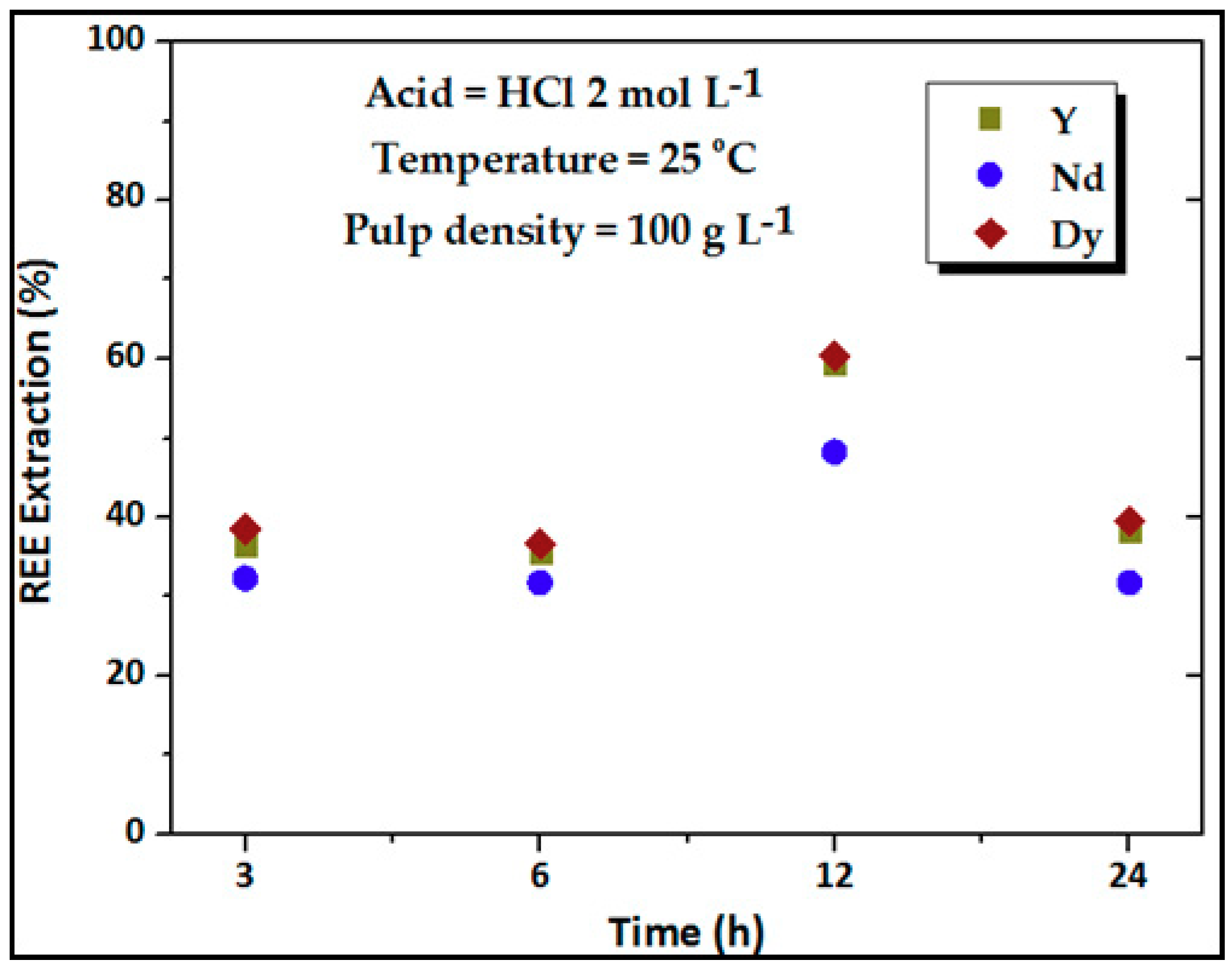
3.3. Effect of Leaching Time
3.4. Estimation of Percentage (%) of REE Extraction at Optimal Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, S. Critical Materials Strategy; US Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/piprod/documents/cms_dec_17_full_web.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2017).
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Gerven, T.V.; Yongxiang, Y.; Allan Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, M. Rare Earth Elements: The Global Supply Chain Congressional Research Service. 2013. Available online: https://fas.org/sgp/crs/natsec/R41347.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2017).
- European Commission. Report on Critical Raw Materials for the EU; DG Enterprise & Industry: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; Available online: http://www.catalysiscluster.eu/wp/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/2014_Critical-raw-materials-for-the-EU-2014.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2014).
- Goonan, T.G. Rare Earth Elements: End Use and Recyclability; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; p. 15. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2011/5094/pdf/sir2011-5094.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2012).
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.; Sun, Y.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodolfo, M.R. Extraction of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud) by dry digestion followed by water leaching. Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating rare earth element availability: A case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. Global potential of rare earth resources and rare earth demand from clean technologies. Minerals 2017, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrer, M.; Sykes, J. The Statistics of the Rare Earths Industry; Royal Statistical Society: London, UK, 2013; Volume 10, pp. 12–16. Available online: https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2013.00645.x (accessed on 13 April 2013).
- Lee, J.C.; Wen, Z. Pathways for greening the supply of rare earth elements in China. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, J.A. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2018. US Geological Survey, 2018. Available online: https://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/mcs/2018/mcs2018.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2018).
- Erickson, B.E. From Coal, a New Source of Rare Earths: U.S. Efforts to Extract Valuable Elements from Coal Waste Surge. Available online: https://cen.acs.org/materials/inorganic-chemistry/coal-new-source-rare-earths/96/i28 (accessed on 8 July 2018).
- Mayfield, D.; Lewis, A. Coal Ash Recycling: A Rare Opportunity. Available online: https://waste-management-world.com/a/coal-ash-recycling-a-rare-opportunity (accessed on 14 October 2013).
- Joshi Prakash, B.; Preda Dorin, V.; Skyler David, A.; Tsinberg, A.; David Green, B.; Marinelli William, J. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements and Compounds from Coal Ash. U.S. Patent No. 8,968,688, 3 March 2015. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US8968688B2/en (accessed on 17 April 2012).
- Barakos, G.; Mischo, H.; Gutzmer, J. An Outlook on the Rare Earth Elements Mining Industry. Available online: https://www.ausimmbulletin.com/feature/an-outlook-on-the-rare-earth-elements-mining-industry/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Dai, S.; Finkelman, R.B. Coal as a promising source of critical elements: Progress and future prospects. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 186, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D. Metallurgical processes for the recovery and recycling of lanthanum from various resources—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Uchimiya, M.; Kwon, E.E.; Jeon, B.H.; Deep, A.; Yun, S.T. Global demand for rare earth resources and strategies for green mining. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhuang, Z.; Huang, F.; Wu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Lin, Z. Recycling rare earth elements from industrial wastewater with flowerlike nano-Mg(OH)2. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2013, 5, 9719–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud). Min. Eng. 2015, 76, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I. Selective leaching of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud), using a functionalized hydrophobic ionic liquid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Tam, J.; Yang, M.; Azimi, G. Technospheric mining of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud): Process optimization, kinetic investigation, and microwave pretreatment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademaker, J.H.; Kleijn, R.; Yang, Y. Recycling as a strategy against rare earth element criticality: A systemic evaluation of the potential yield of NdFeB magnet recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10129–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, J.; Uemura, R. Rare Earth Extraction from NdFeB Magnet Using a Closed-Loop Acid Process. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Kubota, F.; Baba, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Selective extraction and recovery of rare earth metals from phosphor powders in waste fluorescent lamps using an ionic liquid system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hower, J.C.; Granite, E.J.; Mayfield, D.B.; Lewis, A.S.; Finkelman, R.B. Notes on Contributions to the Science of Rare Earth Element Enrichment in Coal and Coal Combustion Byproducts. Minerals 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, V.M. Rare elements in coal ashes. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1935, 27, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Dai, S.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhao, L.; Kostova, I.J.; Silva, L.F.; Mardon, S.M.; Gurdal, G. A note on the occurrence of yttrium and rare earth elements in coal combustion products. Coal Combust. Gasif. Product. 2013, 5, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, C.; Tang, M.; Cao, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, N.; Wen, M.; Luo, Y.; Hu, T.; Ji, W. Study on the modes of occurrence of rare earth elements in coal fly ash by statistics and a sequential chemical extraction procedure. Fuel 2019, 237, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, W.; Wiatros-Motyka, M.M.; Wdowin, M. Coal fly ash as a resource for rare earth elements. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2015, 22, 9464–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mardon, S.M.; Hower, J.C. Impact of coal properties on coal combustion by-product quality: Examples from a Kentucky power plant. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S. Coal deposits as potential alternative sources for lanthanides and yttrium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwakura, S.; Kumagai, Y.; Kubo, H.; Wagatsuma, K. Dissolution of rare earth elements from coal fly ash particles in a dilute H2SO4 solvent. Open J. Phys. Chem. 2013, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Kim, K.; Powell, M.A.; Equeenuddin, S.M. Recovery of metals and other beneficial products from coal fly ash: A sustainable approach for fly ash management. Int. J. Coal Sci. Tecnol. 2016, 3, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Multinational Oil and Gas Company. BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2018. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/en/corporate/pdf/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2018-full-report.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2018).
- Korea Energy Economics Institute. 2017 Energy Info. Korea. Available online: http://www.keei.re.kr/keei/download/EnergyInfo2017.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Proctor, D. South Korean Plant Finds Flexibility with Advanced CFB Technology. Power, 2018. Available online: https://www.powermag.com/south-korean-plant-finds-flexibility-with-advanced-cfb-technology (accessed on 8 January 2018).
- Blackman, S. South Korean Power Production: A Nation’s Clean Coal Goal. Power Technology; Sarah Blackman: Houston, TX, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.power-technology.com/features/featurefocus-south-korean-power-clean-coal-goal/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- James, U.; Robert, G. Samcheok Leads the Way in Advanced Ultra Supercritical CFB. Modern Power Systems. Available online: https://www.modernpowersystems.com/features/featuresamcheok-leads-way-in-advanced-ultrasupercritical-cfb-4927714/ (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Baek, C.; Seo, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, J.; Ahn, J.; Cho, K. Utilization of CFBC Fly ash as a binder to produce in-Furnace Desulfurization Sorbent. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Park, J.Y. Development of a leaching assessment framework for the utilization of coal ash at South Korean mine reclamation sites. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, B.K.; Cantoni, B.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Wiesner, M.R. Application of nanofiltration for Rare Earth Elements recovery from coal fly ash leachate: Performance and cost evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.; Heinrichs, M.; Gadkari, V.V.; Taha, R.; Winecki, S.; Argumedo, D. Acid Digestion Processes for Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal Byproducts. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20170356067A1/en (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- US Department of Energy. Report on Rare Earth Elements from Coal and Coal Byproducts. Report to Congress. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2018/01/f47/EXEC-2014-000442%20-%20for%20Conrad%20Regis%202.2.17.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2019).
- Lin, R.; Howard, B.H.; Roth, E.A.; Bank, T.L.; Granite, E.J.; Soong, Y. Enrichment of rare earth elements from coal and coal by-products by physical separations. Fuel 2017, 200, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.D.; Shin, S.M.; Kim, S.H. Leaching kinetics of lanthanum in sulfuric acid from rare earth element (REE) slag. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiravi, M.; Ackah, L.; Guru, R.; Mohaty, M.; Liu, K.; Xu, B.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L. Chemical extraction of rare earth elements from coal ash. Min. Met. Proc. 2017, 34, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. Principles of Extractive Metallurgy; Routledge 1 Edition, 2 December 2017; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers S. A.: Hohenrain, Switzerland, 1986; ISBN 2-88124-041-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Composition (wt %) | Samcheok | Yeosu | Shin Seocheon | Taean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 44.04 | 33.45 | 1.08 | 4.29 |
| SiO2 | 22.34 | 41.84 | 53.77 | 57.84 |
| Fe2O3 | 8.51 | 3.85 | 6.49 | 9.11 |
| Al2O3 | 6.49 | 4.61 | 30.08 | 20.77 |
| MgO | 6.23 | 2.69 | 0.9 | 1.32 |
| K2O | 0.91 | 0.62 | 3.74 | 1.08 |
| Na2O | 0.6 | 1.12 | 0.36 | 0.92 |
| TiO2 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 1.83 | 1.13 |
| MnO | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.1 |
| P2O5 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.31 |
| Ig loss | 2.74 | 3.77 | 1.49 | 3.44 |
| (a) | |
| Sample Name | Composition (wt %) |
| Samcheok samples | Anhydrite (CaSO4), oldhamite (CaS), portlandite (Ca(OH)2), Calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H), quartz (SiO2), lime (CaO), periclase(MgO), and aluminum trioxide (Al2O3) |
| (b) | |
| Sample Name | Composition (wt %) |
| Shin Seocheon samples | Mullite (Al6Si2O13), quartz (SiO2), sillimanite (Al2SiO5), portlandite (Ca(OH)2), Calcium aluminum trioxide (CaAl2O3) |
| Sample Name | Composition (wt %) |
|---|---|
| Samcheok leaching residue | Anhydrite (CaSO4), Calcite (CaCO3), and quartz (SiO2) |
| Element | Samcheok | Yeosu | Shin Seocheon | Taean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 13.6 | 9.22 | 59.7 | 60.5 |
| La | 11.4 | 9.64 | 86.5 | 55.6 |
| Ce | 21.7 | 20.1 | 16.12 | 115 |
| Pr | 2.5 | 2.34 | 18.5 | 13.3 |
| Nd | 10.9 | 8.82 | 63.2 | 50.1 |
| Sm | 1.69 | 1.68 | 12.6 | 10.6 |
| Eu | 0.47 | 0.46 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
| Gd | 2.11 | 1.8 | 12.8 | 11 |
| Tb | 0.36 | 0.26 | 2.06 | 1.8 |
| Dy | 2.07 | 1.52 | 10.6 | 9.94 |
| Ho | 0.43 | 0.32 | 2.18 | 2.18 |
| Er | 1.22 | 0.86 | 5.72 | 6.24 |
| Tm | <0.20 | 0.2 | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| Yb | 1.28 | 0.8 | 5.38 | 5.88 |
| Lu | 0.59 | 0.2 | 0.82 | 0.94 |
| Th | 5.79 | 3.78 | 36.7 | 19.5 |
| U | 2.09 | 1.78 | 10.1 | 6.02 |
| total | 78.4 | 63.78 | 346.34 | 371.84 |
| Test # | Test Conditions | % REE Extraction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Conc. (mol L−1) | Temp (°C) | Time (h) | Y (%) | Nd (%) | Dy (%) | |
| 1 | 1 | 25 | 24 | 35.8 | 29.5 | 35.7 |
| 2 | 2 | 25 | 24 | 38.2 | 31.7 | 39.1 |
| 3 | 3 | 25 | 24 | 36.0 | 33.0 | 36.2 |
| 4 | 2 | 25 | 3 | 36.5 | 32.2 | 38.1 |
| 5 | 2 | 25 | 6 | 35.5 | 31.7 | 36.2 |
| 6 | 2 | 25 | 12 | 59.4 | 48.2 | 60.3 |
| 7 | 2 | 50 | 3 | 33.0 | 31.1 | 35.2 |
| 8 | 2 | 50 | 6 | 38.0 | 36.6 | 41.0 |
| 9 | 2 | 50 | 12 | 38.3 | 37.2 | 39.1 |
| 10 | 2 | 80 | 3 | 42.0 | 40.8 | 44.9 |
| 11 | 2 | 80 | 6 | 48.4 | 45.9 | 50.7 |
| 12 | 2 | 80 | 12 | 62.1 | 55.5 | 65.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuan, L.Q.; Thenepalli, T.; Chilakala, R.; Vu, H.H.T.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, J. Leaching Characteristics of Low Concentration Rare Earth Elements in Korean (Samcheok) CFBC Bottom Ash Samples. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092562
Tuan LQ, Thenepalli T, Chilakala R, Vu HHT, Ahn JW, Kim J. Leaching Characteristics of Low Concentration Rare Earth Elements in Korean (Samcheok) CFBC Bottom Ash Samples. Sustainability. 2019; 11(9):2562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092562
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuan, Lai Quang, Thriveni Thenepalli, Ramakrishna Chilakala, Hong Ha Thi Vu, Ji Whan Ahn, and Jeongyun Kim. 2019. "Leaching Characteristics of Low Concentration Rare Earth Elements in Korean (Samcheok) CFBC Bottom Ash Samples" Sustainability 11, no. 9: 2562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092562
APA StyleTuan, L. Q., Thenepalli, T., Chilakala, R., Vu, H. H. T., Ahn, J. W., & Kim, J. (2019). Leaching Characteristics of Low Concentration Rare Earth Elements in Korean (Samcheok) CFBC Bottom Ash Samples. Sustainability, 11(9), 2562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092562






