Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Coastal Areas: A Study on Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
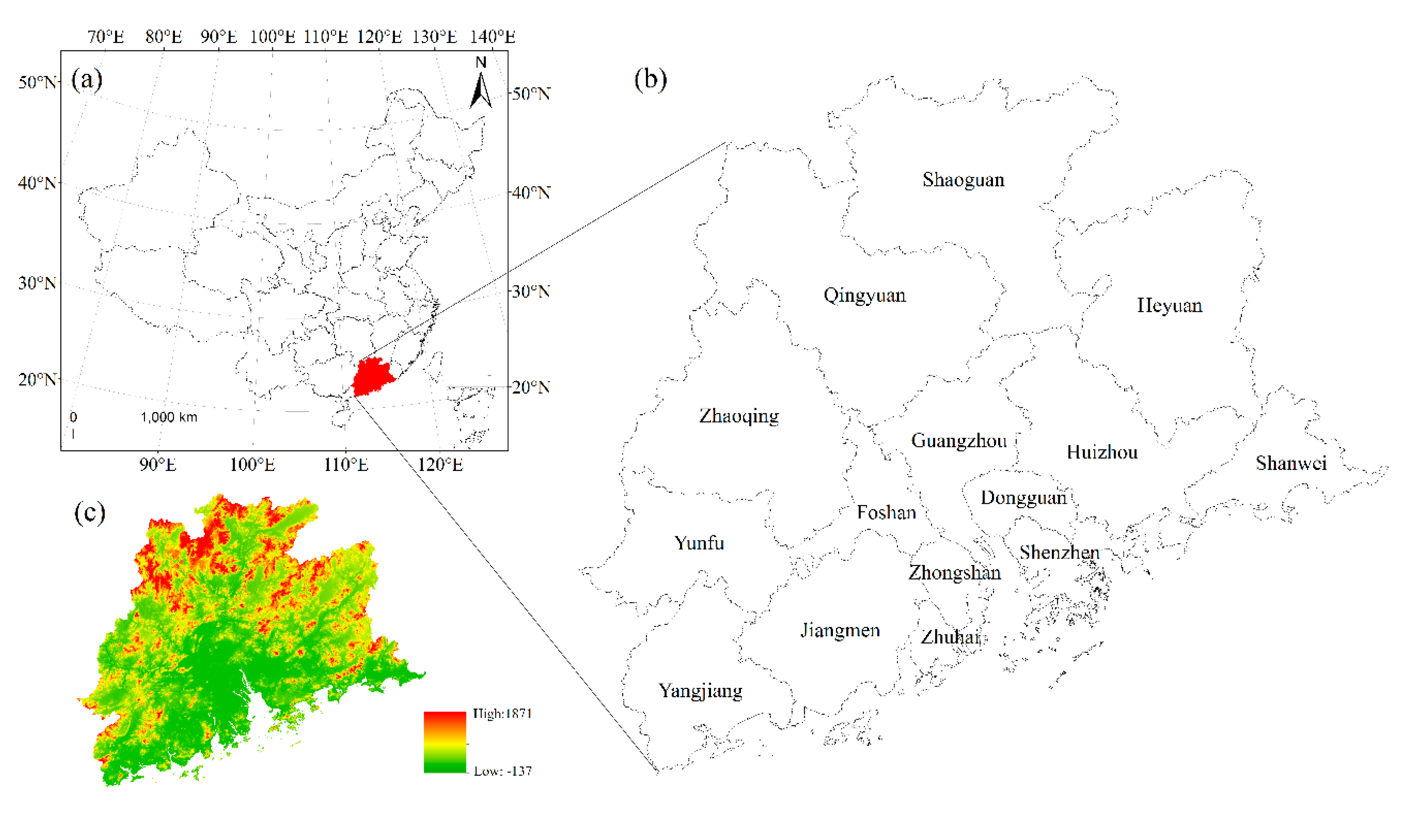
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
3. Methods
3.1. Spatial Pattern Indicators
3.1.1. Urban-Land Expansion Intensity Index
3.1.2. Urban-Land Expansion Difference Index
3.1.3. Fractal Dimension
3.2. Driving Force Analysis—Geographical Detector
| Nonlinear-weaken: p(M∩N) < Min(p(M), p(N)) Uni-enhance/weaken: Min(p(M), p(N)) < p(M∩N) < Max(p(M), p(N)) Bi-enhance: Max(p(M), p(N)) < p(M∩N) < (p(M) + p(N)) Independent: p(M∩N) = p(M) + p(N) Nonlinear-enhance: p(M∩N) > (p(M) + p(N)) |
3.3. Driving Factors Selection
4. Results
4.1. Spatial Pattern of Urban Land Expansion
4.2. Results of Driving-Forces Analysis
4.2.1. Factor and Risk Detector
4.2.2. Interaction Detector
5. Discussion: Implications of Political Effects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scialabba, N. Integrated Coastal Area Management and Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Food and Agriculture Org.: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C. Exploring the dynamics of migration to mega-delta cities in Asia and Africa: Contemporary drivers and future scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, S94–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Woodroffe, C.D.; Hanson, S.; Hinkel, J.; Kebede, A.S.; Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T. Sea-Level Rise Impacts and Responses: A Global Perspective; Finkl, C.W., Ed.; Coastal Hazards; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 117–149. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A Meta-Analysis of Global Urban Land Expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y. Urbanization impact on landscape patterns in Beijing City, China: A spatial heterogeneity perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guetté, A.; Gaüzère, P.; Devictor, V.; Jiguet, F.; Godet, L. Measuring the synanthropy of species and communities to monitor the effects of urbanization on biodiversity. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 79, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; McDowell, W.H.; Wollheim, W.M. Tracking evolution of urban biogeochemical cycles: Past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.A.; Stewart, I.; Facchini, A.; Cersosimo, I.; Mele, R.; Chen, B.; Uda, M.; Kansal, A.; Chiu, A.; Kim, K.-G.; et al. Energy and material flows of megacities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5985–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGranahan, G.; Balk, D.; Anderson, B. The rising tide: Assessing the risks of climate change and human settlements in low elevation coastal zones. Environ. Urban 2007, 19, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Hay, G.J.; Weng, Q.; Resch, B. Collective Sensing: Integrating Geospatial Technologies to Understand Urban Systems—An Overview. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1743–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Tian, J.; Shi, P.; Hu, D. Simulation of the spatial stress due to urban expansion on the wetlands in Beijing, China using a GIS-based assessment model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Scepan, J.; Clarke, K.C. The Use of Remote Sensing and Landscape Metrics to Describe Structures and Changes in Urban Land Uses. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2002, 34, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Urban growth and environmental impacts in Jing-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze, River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L. Urban transformation and institutional policies: Case study of mega-region development in China’s Pearl River Delta. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2013, 139, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Important progress and future direction of studies on China’s urban agglomerations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, J.-A.; Wei, C.-F.; Xie, D.-T. An insight on drivers of land use change at regional scale. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Gertner, G.Z.; Sun, Z.; Anderson, A.A. The impact of interactions in spatial simulation of the dynamics of urban sprawl. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 73, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Driving forces and their interactions of built-up land expansion based on the geographical detector—A case study of Beijing, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S. A 2010 update of National Land Use/Cover Database of China at 1:100,000 scale using medium spatial resolution satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, J. Understanding the Fractal Dimensions of Urban Forms through Spatial Entropy. Entropy 2017, 19, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, S. Multi-dimensional analysis of urban expansion patterns and their driving forces based on the center of gravity-GTWR model: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 1076–1092. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chen, L. Spatiotemporal variation analysis of driving forces of urban land spatial expansion using logistic regression: A case study of port towns in Taicang City, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braimoh, A.K.; Onishi, T. Spatial determinants of urban land use change in Lagos, Nigeria. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, R. Remote sensing monitoring and driving force analysis of urban expansion in Guangzhou City, China. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Ouyang, Z. Forty years of urban expansion in Beijing: What is the relative importance of physical, socioeconomic, and neighborhood factors? Appl. Geogr. 2013, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, H. Land use dynamics, built-up land expansion patterns, and driving forces analysis of the fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, eastern China (1978–2008). Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Liu, X.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Assessing local determinants of neural tube defects in the Heshun Region, Shanxi Province, China. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Yu, N.; Wu, S.; et al. Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China during the early 21st century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Category | Variable | Abbreviation | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical factors | Elevation | ELE | m |
| slope | SLP | ° | |
| Distance to rivers | D_RV | km | |
| Distance to coastline | D_CL | km | |
| Socioeconomic factors | Permanent population | P_POP | thousand persons |
| Gross domestic product | GDP | billion RMB | |
| Proportion of secondary and tertiary industries in GDP | ST_GDP | % | |
| Total investment in fixed assets | T_FAI | billion RMB | |
| Distance to main roads | D_RD | km | |
| Distance to Guangzhou and Shenzhen | D_GS | km |
| City | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2015 | 2000–2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | 0.141 | 0.036 | 0.019 | 0.080 |
| Shenzhen | 0.040 | 0.026 | 0.015 | 0.030 |
| Foshan | 0.057 | 0.015 | 0.001 | 0.026 |
| Dongguan | 0.037 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.023 |
| Zhuhai | 0.187 | 0.046 | 0.014 | 0.103 |
| Zhongshan | 0.031 | 0.048 | 0.028 | 0.042 |
| Zhaoqing | 0.023 | 0.022 | 0.045 | 0.034 |
| Yunfu | 0.086 | 0.075 | 0.023 | 0.079 |
| Yangjiang | 0.039 | 0.010 | 0.021 | 0.026 |
| Shaoguan | 0.065 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.037 |
| Shanwei | 0.068 | 0.022 | 0.075 | 0.069 |
| Qingyuan | 0.155 | 0.011 | 0.038 | 0.081 |
| Huizhou | 1.304 | 0.044 | 0.008 | 0.571 |
| Heyuan | 0.415 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.193 |
| Jiangmen | 0.087 | 0.027 | 0.142 | 0.119 |
| PRDUA | 0.153 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.081 |
| City | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | 1.1687 | 1.2002 | 1.2057 | 1.2070 | 0.0383 |
| Shenzhen | 1.1926 | 1.2282 | 1.2328 | 1.2464 | 0.0538 |
| Foshan | 1.2005 | 1.2068 | 1.1837 | 1.1862 | −0.0143 |
| Dongguan | 1.2131 | 1.2444 | 1.2392 | 1.2417 | 0.0286 |
| Zhuhai | 1.1643 | 1.1672 | 1.1701 | 1.1660 | 0.0017 |
| Zhongshan | 1.1518 | 1.2209 | 1.2098 | 1.2056 | 0.0538 |
| Zhaoqing | 1.1436 | 1.1485 | 1.1525 | 1.1595 | 0.0159 |
| Yunfu | 1.1491 | 1.1561 | 1.1539 | 1.1762 | 0.0271 |
| Yangjiang | 1.1879 | 1.2042 | 1.2062 | 1.2060 | 0.0181 |
| Shaoguan | 1.1204 | 1.1366 | 1.1471 | 1.1480 | 0.0276 |
| Shanwei | 1.1029 | 1.1330 | 1.1392 | 1.1387 | 0.0358 |
| Qingyuan | 1.1118 | 1.1404 | 1.1421 | 1.1433 | 0.0315 |
| Huizhou | 1.1369 | 1.1890 | 1.1757 | 1.1830 | 0.0461 |
| Heyuan | 1.1766 | 1.2118 | 1.2133 | 1.2159 | 0.0393 |
| Jiangmen | 1.1878 | 1.1980 | 1.2058 | 1.2042 | 0.0164 |
| Driving Factor | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P_POP | 44.83% | 10.58% | 2.39% |
| T_FAI | 32.55% | 8.51% | 2.63% |
| GDP | 29.94% | 27.42% | 5.40% |
| D_GS | 22.14% | 25.18% | 6.93% |
| D_CL | 9.04% | 3.57% | 3.31% |
| ST_GDP | 6.16% | 19.52% | 5.67% |
| ELE | 5.21% | 15.28% | 5.26% |
| SLP | 4.83% | 16.95% | 4.75% |
| D_RV | 3.96% | 7.47% | 3.95% |
| D_RD | 2.96% | 4.98% | 2.25% |
| Factors | P_POP | GDP | ST_GDP | T_FAI | D_GS | D_RD | ELE | SLP | D_RV | D_CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_POP | 0.4483 | |||||||||
| GDP | 0.4988 | 0.2994 | ||||||||
| ST_GDP | 0.4983 | 0.4910 * | 0.0616 | |||||||
| T_FAI | 0.5022 | 0.3332 | 0.5076 * | 0.3255 | ||||||
| D_GS | 0.5201 | 0.3348 | 0.2869 * | 0.3424 | 0.2214 | |||||
| D_RD | 0.4551 | 0.3054 | 0.0952 * | 0.3401 | 0.2338 | 0.0296 | ||||
| ELE | 0.4660 | 0.3169 | 0.1091 | 0.3489 | 0.2351 | 0.0823 | 0.0521 | |||
| SLP | 0.4707 | 0.3229 | 0.0990 | 0.3733 | 0.2489 | 0.0754 | 0.0672 | 0.0483 | ||
| D_RV | 0.4646 | 0.3144 | 0.1219 * | 0.3830 * | 0.2540 | 0.0699 | 0.0968 * | 0.0974 * | 0.0396 | |
| D_CL | 0.4970 | 0.4508 | 0.1243 | 0.4023 | 0.2842 | 0.1689 * | 0.1139 | 0.1230 | 0.2308 * | 0.0904 |
| Factors | P_POP | GDP | ST_GDP | T_FAI | D_GS | D_RD | ELE | SLP | D_RV | D_CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_POP | 0.1058 | |||||||||
| GDP | 0.3150 | 0.2742 | ||||||||
| ST_GDP | 0.3270 * | 0.3104 | 0.1952 | |||||||
| T_FAI | 0.1469 | 0.2965 | 0.3244 * | 0.0851 | ||||||
| D_GS | 0.4042 * | 0.3326 | 0.3468 | 0.2645 | 0.2518 | |||||
| D_RD | 0.1475 | 0.2873 | 0.2262 | 0.1273 | 0.2755 | 0.0498 | ||||
| ELE | 0.2163 | 0.3438 | 0.2535 | 0.2156 | 0.3086 | 0.1829 | 0.1528 | |||
| SLP | 0.2321 | 0.3699 | 0.2880 | 0.2327 | 0.3522 | 0.1929 | 0.2020 | 0.1695 | ||
| D_RV | 0.1841 * | 0.3684 * | 0.3549 * | 0.2068 * | 0.3602 * | 0.1267 * | 0.2138 | 0.2369 | 0.0747 | |
| D_CL | 0.1216 | 0.2912 | 0.2123 | 0.1531 * | 0.2777 | 0.1065 * | 0.1703 | 0.1962 | 0.1984 * | 0.0358 |
| Factor | P_POP | GDP | ST_GDP | T_FAI | D_GS | D_RD | ELE | SLP | D_RV | D_CL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_POP | 0.0239 | |||||||||
| GDP | 0.0887 * | 0.0540 | ||||||||
| ST_GDP | 0.0753 | 0.1004 | 0.0567 | |||||||
| T_FAI | 0.0415 | 0.0854 * | 0.0680 | 0.0263 | ||||||
| D_GS | 0.1078 * | 0.0838 | 0.0988 | 0.1095 * | 0.0693 | |||||
| D_RD | 0.0438 | 0.0710 | 0.0746 | 0.0495 | 0.0859 | 0.0225 | ||||
| ELE | 0.0686 | 0.0815 | 0.0870 | 0.0746 | 0.0922 | 0.0722 | 0.0526 | |||
| SLP | 0.0770 * | 0.0839 | 0.0946 | 0.0675 | 0.0996 | 0.0645 | 0.0688 | 0.0475 | ||
| D_RV | 0.0776 * | 0.1066 * | 0.0993 * | 0.0797 * | 0.1125 * | 0.0639 * | 0.0894 | 0.0894 * | 0.0395 | |
| D_CL | 0.0702 * | 0.0777 | 0.0833 | 0.0669 * | 0.0954 | 0.0760 * | 0.0615 | 0.0676 | 0.0967 * | 0.0331 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Ju, H.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, W. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Coastal Areas: A Study on Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010191
Yan Y, Ju H, Zhang S, Jiang W. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Coastal Areas: A Study on Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(1):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010191
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yichen, Hongrun Ju, Shengrui Zhang, and Wei Jiang. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Coastal Areas: A Study on Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta, China" Sustainability 12, no. 1: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010191
APA StyleYan, Y., Ju, H., Zhang, S., & Jiang, W. (2020). Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Urban Expansion in Coastal Areas: A Study on Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability, 12(1), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010191







