Review of Emergy Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment: Coupling Development Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Study on the Coupling of LCA and EMA
2.1. EMA Theory and Application
2.2. LCA Theory and Application
2.3. Sensitivity Analysis and Uncertainty Analysis
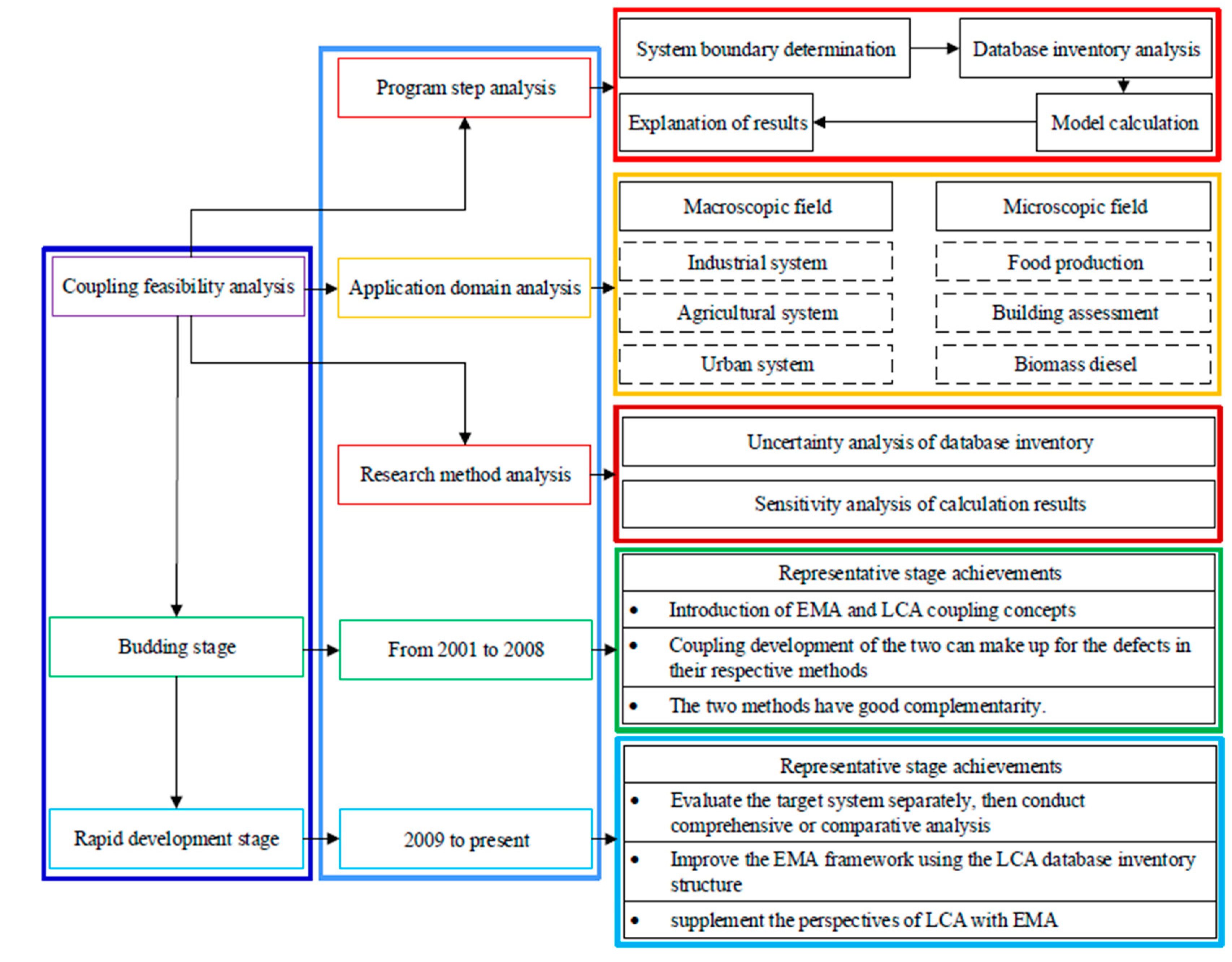
3. Coupling Development Process
4. Coupling Development Prospect
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lou, B.; Qiu, Y.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy-based indicators of regional environmental sustainability: A case study in Shanwei, Guangdong, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy-based indices and ratios to evaluate sustainability: Monitoring economies and technology toward environmentally sound innovation. Ecol. Eng. 1997, 9, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, P.; Paoli, C.; Fabiano, M. Emergy required for the complete treatment of municipal wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Ries, R. Complementary life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment plants: An integrated approach to comprehensive upstream and downstream impact assessments and its extension to building-level wastewater generation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustead, I. Resource implications with particular reference to energy requirements for glass and plastic milk bottles. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1974, 27, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raugei, M.; Rugani, B.; Benetto, E.; Ingwersen, W.W. Integrating emergy into LCA: Potential added value and lingering obstacles. Ecol. Model. 2014, 271, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, J.L.; Bakshi, B.R. Promise and problems of emergy analysis. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.J. An exploration of reliable methods of estimating emergy requirements at the regional scale: Traditional emergy analysis, regional thermodynamic input-output analysis, or the conservation rule-implicit method. Ecol. Model. 2013, 251, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Herendeen, R.A. Embodied energy analysis and EMERGY analysis: A comparative view. Ecol. Econ. 1996, 19, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T.; Doherty, S.J.; Scatena, F.N.; Kharecha, P.A. Emergy evaluation of reforestation alternatives in Puerto Rico. For. Sci. 2000, 46, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.P.; Chen, B. Embodied energy and emergy evaluation of a typical biodiesel production chain in China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Giannetti, B.F.; Wang, J.J.; Casazza, M. Donor-side evaluation of coastal and marine ecosystem services. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Sarkis, J.; Ulgiati, S.; Zhang, P. Measuring China’s circular economy. Science 2013, 339, 1526–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.M.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.C.; Xia, X.H.; Zhou, S.Y.; Zhou, J.B. Ecological Economic Evaluation Based on Emergy as Embodied Cosmic Exergy: A Historical Study for the Beijing Urban Ecosystem 1978–2004. Entropy 2010, 12, 1696–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Mansson, B.A.; McGlade, J.M. Ecology, thermodynamics and H.T. Odum’s conjectures. Oecologia 1993, 93, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.J.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Stern, D.I. Aggregation and the role of energy in the economy. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Campbell, D.E.; Franzese, P.P.; Ulgiati, S. The geobiosphere emergy baseline: A synthesis. Ecol. Model. 2016, 339, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, E. On the Second-Law inconsistency of Emergy Analysis. Energy 2010, 35, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvuglia, A.; Benetto, E.; Rios, G.; Rugani, B. SCALE: Software for CAL culating Emergy based on life cycle inventories. Ecol. Model. 2013, 248, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Ulgiati, S. Updated evaluation of exergy and emergy driving the geobiosphere: A review and refinement of the emergy baseline. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wei, Y.; Pan, H.Y.; Xiao, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.Z. The comparison of performances of a sewage treatment system before and after implementing the cleaner production measure. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy evaluations and environmental loading of electricity production systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2002, 10, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Duan, H.B. Sustainability evaluation of an e-waste treatment enterprise based on emergy analysis in China. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.F.; Campbell, D.E.; Li, Z.A.; Ren, H. Emergy synthesis of an agro-forest restoration system in lower subtropical China. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, P.; Wan, S.W.; Qin, P.; Du, J.J.; Wang, H. A comparison of the sustainability of original and constructed wetlands in Yancheng Biosphere Reserve, China: Implications from emergy evaluation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.I.; Xiang, P.A. Emergy analysis of paddy farming in Hunan Province, China: A new perspective on sustainable development of agriculture. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D. Emergy Evaluation of Korean Agriculture. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2017, 26, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Han, J.C.; Wu, F.Q. Emergy and benefit evaluation of “pig-methane-pomegranate” recycling agriculture in Guanzhong Plain. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2017, 35, 199–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.; Yang, D.G.; Huo, J.W.; Xia, F.Q.; Zhang, Z.P. Evaluation of Oasis Sustainability Based on Emergy and Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Feng, X. New emergy evaluating indices for industrial systems. Energy Source Part B 2008, 3, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liang, H.; Dong, L.; Sun, L.; Gao, Z.Q. Design for sustainability of industrial symbiosis based on emergy and multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, H.; Dong, L.; Fang, K.; Ren, J.Z.; Geng, Y.; Fujii, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z. Eco-benefits assessment on urban industrial symbiosis based on material flows analysis and emergy evaluation approach: A case of Liuzhou city, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 119, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Deng, X.Z.; Chu, X.; Zhao, C.H.; Zhang, F. Emergy analysis on urban metabolism by counties in Beijing. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 101, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Giannetti, B.F.; Zhang, Y.; Gasazza, M. Emergy-based comparative analysis of urban metabolic efficiency and sustainability in the case of big and data scarce medium-sized cities, A case study for Jing-Jin-Ji Region (China). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keena, N.; Raugei, M.; Etman, M.A.; Ruan, D.; Dyson, A. Clark’s Crow: A design plugin to support emergy analysis decision making towards sustainable urban ecologies. Ecol. Model. 2018, 367, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Tan, K.M.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.X. Emergy-based analysis of grain production and trade in China during 2000–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Guan, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, C. Emergy analysis of Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) for waste heat power generation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Tang, S.J.; Hao, Y.; Pang, M.Y. Integrated emergy and economic evaluation of a case tidal power plant in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.Y.; Zhang, F.; Chu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. Ecosystem services assessment based on emergy accounting in Chongming Island, Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, C.H.; Zhang, C.X.; Ma, M.D.; Rao, W.Z.; Li, W.Y.; He, K.; Gao, M.D. Developing the ecological compensation criterion of industrial solid waste based on emergy for sustainable development. Energy 2018, 157, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.D.; Shui, W.; Deng, S.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lin, L.; Xiao, Y.L.; et al. Investigating impact of waste reuse on the sustainability of municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration industry using emergy approach: A case study from Sichuan province, China. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranghi, S.; Parisi, M.L.; Basosi, R.; Sinicropi, A. Environmental Profile of the Manufacturing Process of Perovskite Photovoltaics: Harmonization of Life Cycle Assessment Studies. Energies 2019, 12, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.N.; Lee, C.K.M.; Chen, C.H. Review of life cycle assessment towards sustainable product development. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Huang, Y.Q.; Yuan, H.Y.; Yin, X.L.; Wu, C.Z. Life cycle assessment of biofuels in China: Status and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Standards Organization. ISO 14040:2006 Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Guidelines; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- The International Standards Organization. ISO 14044:2006 Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, S.P.; Egilmez, G.; Kucukvar, M. Emergy and end-point impact assessment of agricultural and food production in the United States: A supply chain-linked Ecologically-based Life Cycle Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetto, R.; Danielle, M.D.S.; Bo, P.W.; Jane, B.; Bhavik, B.; Blane, G.; John, M.J.; Ana, L.R.P.; Xin, Y.L.; Alexis, L.; et al. Towards integrating the ecosystem services cascade framework within the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) cause-effect methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1284–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Buranakarn, V. Emergy indices and ratios for sustainable material cycles and recycle options. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccubbin, N. Paper versus polystyrene: Environmental impact. Science 1991, 252, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, M.B. Paper versus polystyrene: A complex choice. Science 1991, 251, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelic, D.; Budak, I.; Tadic, B.; Simunobic, G.; Kljajic, V.; Agarski, B. Multi-criteria decision-making and life cycle assessment model for optimal product selection: Case study of knee support. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas, A.; Uriarte, L.; Gandía, L.M. Application of Eco-Design and Life Cycle Assessment Standards for Environmental Impact Reduction of an Industrial Product. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royne, F.; Hackl, R.; Ringstrom, E.; Berlin, J. Environmental Evaluation of Industry Cluster Strategies with a Life Cycle Perspective: Replacing Fossil Feedstock with Forest-Based Feedstock and Increasing Thermal Energy Integration. J. Ind. Ecol. 2018, 22, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.L.H.; Lo, I.M.C.; Woon, K.S.; Yan, D.Y.S. Life cycle assessment of waste treatment strategy for sewage sludge and food waste in Macau: Perspectives on environmental and energy production performance. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.; Hong, T.; Park, J. Development of the life-cycle economic and environmental assessment model for establishing the optimal implementation strategy of the rooftop photovoltaic system. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 24, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccherini, A.; Baldassarre, A.; Donini, L.; Lepore, G.O.; Caneschi, A.; De, L.A.; Innocenti, M.; Montegrossi, G.; Giuseppe, C.; Oberhauser, W.; et al. Sustainable synthesis of quaternary sulphides: The problem of the uptake of zinc in CZTS. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 775, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.L.; Tang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.S.; Zuo, J.; Song, Z.L. Environmental and economic impacts assessment of concrete pavement brick and permeable brick production process—A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.S.; Liu, W.; Yuan, X.L.; Tang, H.R.; Tang, Y.Z.; Wang, M.S.; Zuo, J.; Song, Z.L.; Sun, J. Environmental Impact Analysis and Process Optimization of Batteries Based on Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.T.; Ye, L.P.; Qi, C.C.; Yang, D.L.; Shen, X.X.; Hong, J.L. Life cycle assessment and water footprint evaluation of crude steel production: A case study in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.D.; Hoeve, M.T.; Nielsen, S.; Scheutz, C. Life cycle assessment comparing the treatment of surplus activated sludge in a sludge treatment reed bed system with mechanical treatment on centrifuge. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welfle, A.; Gilbert, P.; Thornley, P.; Stephenson, A. Generating low-carbon heat from biomass: Life cycle assessment of bioenergy scenarios. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, N.; Pirog, R.; Rasmussen, R. Comparative life cycle environmental impacts of three beef production strategies in the Upper Midwestern United States. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Mathys, A.; Knoch, A.; Heinz, V. Meat alternatives: Life cycle assessment of most known meat substitutes. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Zhang, X.P.; Jia, L.; He, Y.F.; Huang, L. Life Cycle Assessment of Centrifugal Chiller on Environment Impacts and Its Key Influence Factors’. J. Referig. 2016, 37, 58–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, H.Q.; Shu, H.P.; Zhao, W.D.; Yan, T.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, X. A Robust Eco-Design Approach Based on New Sensitivity Coefficients by Considering the Uncertainty of LCI. J. Adv. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 16, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulgiati, S.; Raugei, M.; Bargigli, S. Overcoming the inadequacy of single-criterion approaches to Life Cycle Assessment. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W.; Ren, J.Z.; Dong, L. Is the hydrogen production from biomass technology really sustainable? Answer by Life Cycle Emergy Analysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 10507–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Griffin, W.M.; Matthews, H.S. Representing and visualizing data uncertainty in input-output life cycle assessment models. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnemann, G.W.; Schuhmacher, M.; Castells, F. Uncertainty assessment by a Monte Carlo simulation in a life cycle inventory of electricity produced by a waste incinerator. J. Clean. Prod. 2003, 11, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, M.L.; Ferrara, N.; Torsello, L.; Basosi, R. Life cycle assessment of atmospheric emission profiles of the Italian geothermal power plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Mutel, C.; Lesage, P.; Samson, R. Effects of Distribution Choice on the Modeling of Life Cycle Inventory Uncertainty: An Assessment on the Ecoinvent v2.2 Database. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 22, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.L.; Shake, S.; Rosenbaum, R.K.; Jolliet, O. Analytical uncertainty propagation in life cycle inventory and impact assessment: Application to an automobile front panel. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.L. Uncertainty propagation in life cycle assessment of biodiesel versus diesel: Global warming and non-renewable energy. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, X.; Li, X.Z. Life cycle assessment of corn- and cassava-based ethylene production. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 67, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, E.A.; Heijungs, R.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; de Boer, I.J.M. Methods for uncertainty propagation in life cycle assessment. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.P.; Martins, N.; Gouveia, J.B. A review of emergy theory, its application and latest developments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwersen, W.W. Uncertainty characterization for emergy values. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, B.; Laura, V.; Alberto, C.; Ulgiati, S. Integrating life cycle assessment and emergy synthesis for the evaluation of a dry steam geothermal power plant in Italy. Energy 2015, 86, 476–487. [Google Scholar]
- Ingwersen, W.W. Emergy as a Life Cycle Impact Assessment Indicator. Ind. Ecol. 2011, 15, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, B.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. A fuzzy-based approach for characterization of uncertainties in emergy synthesis: An example of paved road system. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Zou, W. The marine ecosystem services values for China based on the emergy analysis method. J. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 161, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, A.L.R.; Ometto, A.R. Ecosystem Services in Life Cycle Assessment: A novel conceptual framework for soil. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 643, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Martinez, M.M.; Noguerol, R.; Casales, B.I.; Lois, R.; Soto, B. Evaluation of environmental impact of two ready-to-eat canned meat products using Life Cycle Assessment. J. Food Eng. 2018, 237, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardon, L.; Hélias, A.; Sialve, B.; Steyer, J.P.; Bernard, O. Life-cycle assessment of biodiesel production from microalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladini, F.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Bastianoni, S.; Bakshi, B.R. Synergies between industry and nature—An emergy evaluation of a biodiesel production system integrated with ecological systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulselli, R.M.; Simoncini, E.; Pulselli, F.M.; Bastianoni, S. Emergy analysis of building manufacturing, maintenance and use: Em-building indices to evaluate housing sustainability. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Ekvall, T.; Guinee, J.; Heijungs, R.; Hellweg, S.; Koehler, A.; Pennington, D.; Suh, S. Recent developments in Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukidwe, N.U.; Bakshi, B.R. Industrial and ecological cumulative exergy consumption of the United States via the 1997 input-output benchmark model. Energy 2007, 32, 1560–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzigallo, A.C.I.; Granai, C.; Borsa, S. The joint use of LCA and emergy evaluation for the analysis of two Italian wine farms. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.S.; Ingwersen, W.; Trucco, C.; Ries, R.; Campbell, D. Comparison of energy-based indicators used in life cycle assessment tools for buildings. Build. Environ. 2014, 79, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, R.S. Hybrid Emergy-LCA (HEML) based metabolic evaluation of urban residential areas: The case of Beijing, China. Ecol. Complex. 2009, 6, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.X.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.J.; Yang, X.L.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y.Q. Integrated assessment of economic and environmental consequences of shifting cropping systemfrom wheat-maize to monocropped maize in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Raugei, M.; Ulgiati, S. On boundaries and ‘investments’ in Emergy Synthesis and LCA: A case study on thermal vs. photovoltaic electricity. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, B.; Benetto, E. Improvements to Emergy Evaluations by Using Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, B.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. Emergy-based life cycle assessment (Em-LCA) for sustainability appraisal of infrastructure systems: A case study on paved roads. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Liu, X.D.; Dai, J.; Lin, C.; Xia, X.H.; Gao, R.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Yang, J.; Qi, J. Evaluating the environmental impacts of an urban wetland park based on emergy accounting and life cycle assessment: A case study in Beijing. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, B.; Benetto, E.; Arbault, D.; Tiruta-Barna, L. Emergy-based mid-point valuation of ecosystem goods and services for life cycle impact assessment. Int. J. Metall. 2013, 10, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, A.B.; Raugei, M.; Ripa, M.; Ulgiati, S. Dealing with waste products and flows in life cycle assessment and emergy accounting: Methodological overview and synergies. Ecol. Model. 2015, 315, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Hao, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Ulgiati, S. An emergy-LCA analysis of municipal solid waste management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursun, B.; Bakshi, B.R.; Mahata, M.; Martin, J.F. Life cycle and emergy based design of energy system in developing countries: Centralized and localized options. Ecol. Model. 2015, 305, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Zhang, K.L.; Zou, W.; Wang, Z.Y. Study on regional system of man-sea relationship and its synergetic development in the coastal regions of China. Geogr. Res. 2015, 4, 1824–1838. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Item | Advantages | Disadvantages | Complementarities |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMA | Convert different kinds of resources into a single unit Donor-side perspective | Environmental effect assessment | Application area: Both macroscopic and microscopic systems Application purpose: Natural ecosystem sustainability analysis Analysis procedures: Similar four phases Research methodology: Uncertainty analysis and sensitivity analysis |
| Standardization issues | |||
| Accuracy problems | |||
| Unclear conceptual terms | |||
| LCA | Environmental impact assessment User-side perspective | Lack environmental impact of ecosystem services | |
| System boundary determination problems | |||
| Basic data lag problems | |||
| Single standard approach |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, M. Review of Emergy Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment: Coupling Development Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010367
Wang Q, Xiao H, Ma Q, Yuan X, Zuo J, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang M. Review of Emergy Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment: Coupling Development Perspective. Sustainability. 2020; 12(1):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010367
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qingsong, Hongkun Xiao, Qiao Ma, Xueliang Yuan, Jian Zuo, Jian Zhang, Shuguang Wang, and Mansen Wang. 2020. "Review of Emergy Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment: Coupling Development Perspective" Sustainability 12, no. 1: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010367
APA StyleWang, Q., Xiao, H., Ma, Q., Yuan, X., Zuo, J., Zhang, J., Wang, S., & Wang, M. (2020). Review of Emergy Analysis and Life Cycle Assessment: Coupling Development Perspective. Sustainability, 12(1), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010367







