Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Nexus between Energy Consumption and Financial Development
2.2. Empirical Evidence from Preceding Studies
3. Materials and Methods
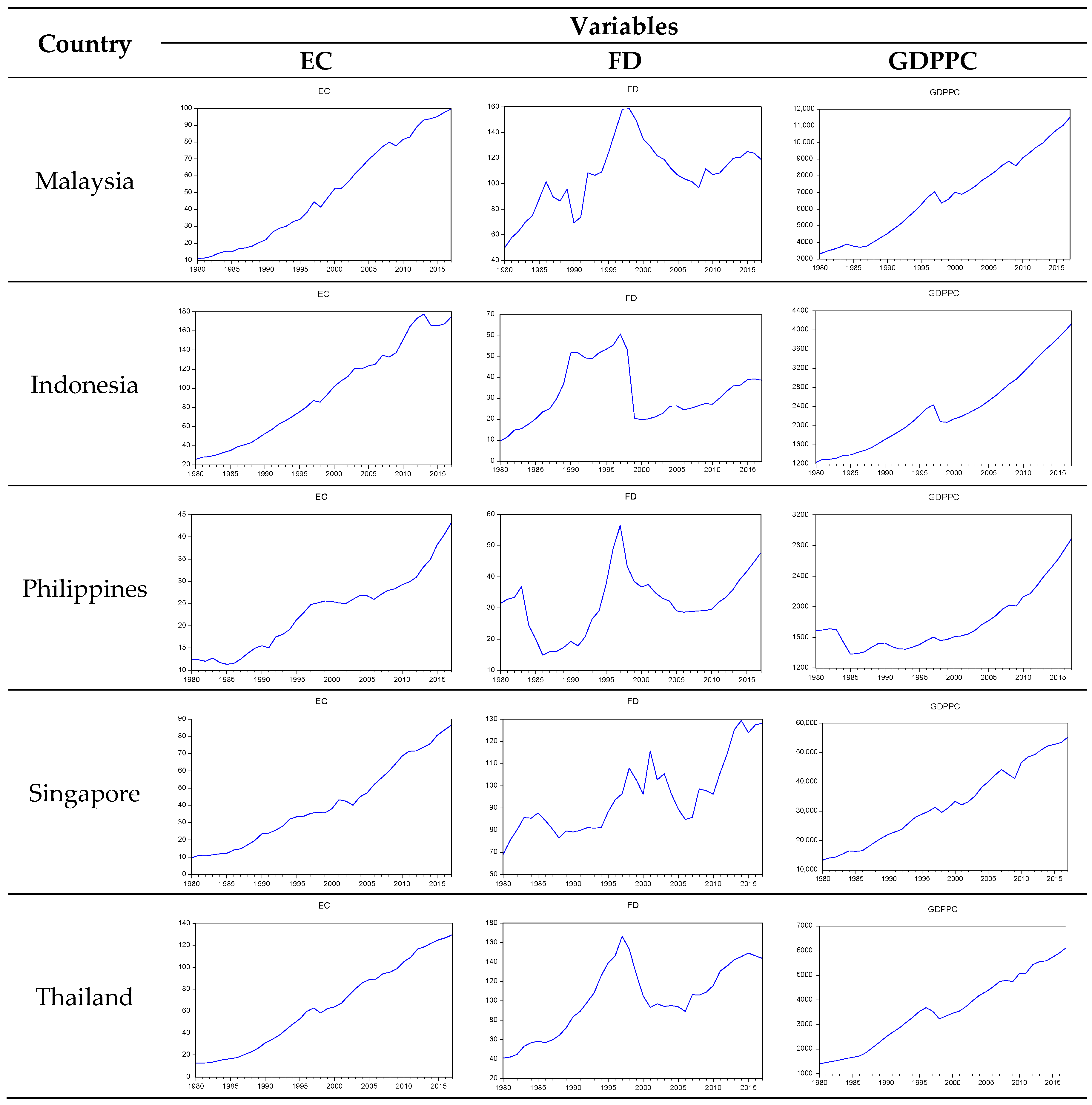
3.1. Data and Variables
3.2. Test of the Stationarity of Data
3.3. Test of the Effect of a Structural Break in Cointegration
3.4. Test of Cointegration—ARDL Bounds Test Approach
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.-C.; Chang, C.-P. Energy consumption and economic growth in Asian economies: A more comprehensive analysis using panel data. Resour. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantama, Y.U.; Abdullahi, Y.Z.; Inuwa, N. Energy consumption-economic growth nexus in Nigeria: An empirical assessment based on ARDL bound test approach. Eur. Sci. J. 2012, 8, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Jumbe, C.B. Cointegration and causality between electricity consumption and GDP: Empirical evidence from Malawi. Energy Econ. 2004, 26, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I. Financial Development And Economic Growth: Evidence From Turkey. Appl. Econom. Int. Dev. 2008, 8, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Furuoka, F. Financial development and energy consumption: Evidence from a heterogeneous panel of Asian countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T. Financial development and economic growth: An empirical research for China. Econ. Sci. 2001, 3, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sadorsky, P. The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2528–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Shahbaz, M.; Ahmed, A.U.; Alam, M.M. Financial development and energy consumption nexus in Malaysia: A multivariate time series analysis. Econ. Model. 2013, 30, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbaz, M.; Lean, H.H. Does financial development increase energy consumption? The role of industrialization and urbanization in Tunisia. Energy Policy 2012, 40, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-mulali, U.; Sab, C.N.B.C. The impact of energy consumption and CO2 emission on the economic and financial development in 19 selected countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4365–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U.; Sab, C.N.B.C. The impact of energy consumption and CO2 emission on the economic growth and financial development in the Sub Saharan African countries. Energy 2012, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Hye, Q.M.A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Leitão, N.C. Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadorsky, P. Financial development and energy consumption in Central and Eastern European frontier economies. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Islam, F.; Butt, M.S. Finance–growth–energy nexus and the role of agriculture and modern sectors: Evidence from ARDL bounds test approach to cointegration in Pakistan. Glob. Bus. Rev. 2016, 17, 1037–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roubaud, D.; Shahbaz, M. Financial development, economic growth, and electricity demand: A sector analysis of an emerging economy. J. Energy Dev. 2017, 43, 47–98. [Google Scholar]
- Karanfil, F. How many times again will we examine the energy-income nexus using a limited range of traditional econometric tools? Energy Policy 2009, 37, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minier, J. Opening a stock exchange. J. Dev. Econ. 2009, 90, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A. Contribution of Financial development in electricity-growth nexus in Pakistan. Acta Univ. Danub. Œconomica 2015, 11, 223–240. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, M. A reassessment of finance-growth nexus for Pakistan: Under the investigation of FMOLS and DOLS techniques. IUP J. Appl. Econ. 2009, 8, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Komal, R.; Abbas, F. Linking financial development, economic growth and energy consumption in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-S.; Sonn, Y.-H. Productive energy consumption and economic growth: An endogenous growth model and its empirical application. Resour. Energy Econ. 1996, 18, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielnik, O.; Goldemberg, J. Foreign direct investment and decoupling between energy and gross domestic product in developing countries. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A.; Kahouli, B. Causal relationships between energy consumption, foreign direct investment and economic growth: Fresh evidence from dynamic simultaneous-equations models. Energy Policy 2014, 67, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glasure, Y.U.; Lee, A.-R. Cointegration, error-correction, and the relationship between GDP and energy: The case of South Korea and Singapore. Resour. Energy Econ. 1998, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafindadi, A.A.; Ozturk, I. Effects of financial development, economic growth and trade on electricity consumption: Evidence from post-Fukushima Japan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartleet, M.; Gounder, R. Energy consumption and economic growth in New Zealand: Results of trivariate and multivariate models. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 3508–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, H.H.; Smyth, R. Multivariate Granger causality between electricity generation, exports, prices and GDP in Malaysia. Energy 2010, 35, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B.K. Multivariate cointegration tests and the law of one price in international wheat markets. Rev. Agric. Econ. 1992, 14, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-C. Effects of financial developments and income on energy consumption. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2015, 35, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çoban, S.; Topcu, M. The nexus between financial development and energy consumption in the EU: A dynamic panel data analysis. Energy Econ. 2013, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Li, P. On the nexus of financial development, economic growth, and energy consumption in China: New perspective from a GMM panel VAR approach. Energy Econ. 2018, 71, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.B. Economic development, pollutant emissions and energy consumption in Malaysia. J. Policy Model. 2008, 30, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Smith, R. Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J. Econom. 1995, 68, 79–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, B.; Sulaiman, J. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries: A cointegration approach. Energy 2013, 55, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.; Chen, S. An empirical analysis of financial development and energy demand: Establishing the role of globalization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24326–24337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durusu-Ciftci, D.; Ispir, M.S.; Yetkiner, H. Financial development and economic growth: Some theory and more evidence. J. Policy Model. 2017, 39, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, J.; Perera, N.; Verma, R. Unit Root Tests and Structural Breaks: A Survey with Applications. J. Quant. Methods Econ. Bus. Adm. 2007, 3, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, M.; Ciarreta, A.; Zarraga, A. Linear and nonlinear causality between energy consumption and economic growth: The case of Mexico 1965–2014. Energies 2018, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, I. Unit Root Tests and Structural Breaks in the Swedish Electricity Price. Master’s Thesis, Lulea University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, J.P.; Perman, R. Unit roots and structural breaks: A survey of the literature. In Cointegration for the Applied Economist; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Harvie, C.; Pahlavani, M.; Saleh, A.S. Identifying structural breaks in the Lebanese economy 1970–2003: An application of the Zivot and Andrews test. Middle East Bus. Econ. Rev. 2006, 18, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, A.W.; Hansen, B.E. Residual-based tests for cointegration in models with regime shifts. J. Econom. 1996, 70, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, A.; Diaconeasa, M.C.; Brad, L.; Lădaru, G.-R.; Ioanăș, C. Factors Influencing Energy Consumption in the Context of Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosetti, V.; Carraro, C.; Massetti, E.; Sgobbi, A.; Tavoni, M. Optimal energy investment and R&D strategies to stabilize atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations. Resour. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Saud, S.; Baloch, M.A.; Lodhi, R.N. The nexus between energy consumption and financial development: Estimating the role of globalization in Next-11 countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18651–18661. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalik, M.K.; Babu, M.S.; Loganathan, N.; Shahbaz, M. Does financial development intensify energy consumption in Saudi Arabia? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutabba, M.A. The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: Evidence from the Indian economy. Econ. Model. 2014, 40, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhani, S.; Solarin, S.A. Financial development and energy demand in the United States: New evidence from combined cointegration and asymmetric causality tests. Energy 2017, 134, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtioui, S. Does economic growth and financial development spur energy consumption in Tunisia? J. Econ. Int. Financ. 2012, 4, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, M.; Rodríguez, J.C. Energy Consumption and Financial Development in NAFTA Countries, 1971–2015. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, K.-Y.; Sun, R.-J.; Li, H.; Jiang, H.-D. A review of China’s energy consumption structure and outlook based on a long-range energy alternatives modeling tool. Pet. Sci. 2017, 14, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, V.; Smyth, R.; Sharma, S. The energy-GDP nexus: Evidence from a panel of Pacific Island countries. Resour. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoong, S.W.; Phoong, S.Y.; Moghavvemi, S.; Phoong, K.H. Multiple Breakpoint Test on Crude Oil Price. Found. Manag. 2019, 11, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phoong, S.Y.; Phoong, S.W. Modelling the economic cycle between GDP and government spending on technological innovation. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Hum. 2017, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zivot, E.; Andrews, D.W.K. Further evidence on the great crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.; Alam, T.; Ghauri, S.P. Structural Breaks and Unit Root: Evidence from Pakistani Macroeconomic Time Series; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M. Three Essays on More Powerful Unit Root Tests with Non-Normal Errors; University of Alabama Libraries: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlavani, M.; Wilson, E.; Worthington, A. Trade-GDP nexus in Iran: An application of the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 2, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perron, P. The great crash, the oil price shock, and the unit root hypothesis. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1989, 57, 1361–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitomo, N. Tests of unit roots and cointegration hypotheses in econometric models. Jpn. Econ. Rev. 1996, 47, 79–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.M. Chow Test Analysis on Structural Change in New Zealand Housing Price During Global Subprime Financial Crisis. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Pacific-Rim Real Estate Society Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 15–18 Janurary 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, G.T.E.; Kiesha, O. Structural reforms in ASEAN-5 economies: Past successes and future challenges. Policy 2016, 8, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, K.; Honda, K. Impacts of Financial Crisis on Asian Energy Supply and Demand and Outlook; Institute of Energy Economics: Tokyo, Japan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, B. Chow Test for Structural Stability. Univ. Bath. 2006. Available online: http://people.bath.ac.uk/bm232/EC50161/Chow%20Test.doc (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Ozturk, I.; Acaravci, A. Electricity consumption and real GDP causality nexus: Evidence from ARDL bounds testing approach for 11 MENA countries. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.; Samudram, M.; Vaithilingam, S. Malaysian money demand function revisited: The ARDL approach. J. Asia Pac. Bus. 2008, 9, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, R.H. Dealing with bank system failure: Indonesia, 1997–2003. Bull. Indones. Econ. Stud. 2004, 40, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasri, R. Explaining the Twin Crises in Indonesia; Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Indonesia: Depok, Indonesia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.D. The Indonesian financial crisis: From banking crisis to financial sector reforms, 1997–2000. Indonesia 2001, 71, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jian, J.; Fan, X.; He, P.; Xiong, H.; Shen, H. The Effects of Energy Consumption, Economic Growth and Financial Development on CO2 Emissions in China: A VECM Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, M.; Lee, J.; Payne, J.E. RALS-LM unit root test with trend breaks and non-normal errors: Application to the Prebisch-Singer hypothesis. Stud. Nonlinear Dyn. Econom. 2017, 21, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Yu, B.; Greenwood-Nimmo, M. Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. In Festschrift in Honor of Peter Schmidt; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 281–314. [Google Scholar]
| Country | Variables EC | FD | GDPPC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malaysia | 36.5653 *** | 25.45166 *** | 17.04503 *** |
| Indonesia | 32.57413 *** | 29.58952 *** | 14.50024 *** |
| Philippines | 46.67442 *** | 14.14112 *** | 71.78095 *** |
| Singapore | 5.675828 *** | 2.469036 * | 9.513005 *** |
| Thailand | 49.66331 *** | 4.515376 *** | 24.24333 *** |
| Levin, Lin and Chu | ADF Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null: Unit root (Assumes Common Unit Root Process) | Null: Unit root (Assumes Individual Unit Root Process) | |||
| Test Statistics | Probability | Test Statistics | Probability | |
| Malaysia | −3.10953 | 0.0009 | 11.3337 | 0.0786 |
| Indonesia | −2.70441 | 0.0034 | 10.3520 | 0.1106 |
| Philippines | 3.22481 | 0.9994 | 2.07530 | 0.9126 |
| Singapore | −2.38512 | 0.0085 | 4.09117 | 0.6643 |
| Thailand | −3.23710 | 0.0006 | 9.20032 | 0.1626 |
| Country | Variables | Test Statistics | Order of Integration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaysia | EC | Level | −3.538905 | I (1) |
| First difference | −8.066572 ** | |||
| FD | Level | −4.487476 | I (1) | |
| First difference | −3.946545 *** | |||
| GDPPC | Level | −2.735251 | I (1) | |
| First difference | −7.503437 *** | |||
| Indonesia | EC | Level | −4.924191 | I (1) |
| First difference | −4.859985 *** | |||
| FD | Level | −7.681760 *** | I (0) | |
| First difference | −5.122355 | |||
| GDPPC | Level | −3.089788 *** | I (0) | |
| First difference | −6.420811 | |||
| Philippines | EC | Level | −2.522312 | I (1) |
| First difference | −5.759279 *** | |||
| FD | Level | −2.987915 | I (1) | |
| First difference | −7.296979 *** | |||
| GDPPC | Level | −1.635966 | I (1) | |
| First difference | −7.807071 * | |||
| Singapore | EC | Level | −3.832414 ** | I (0) |
| First difference | −5.806963 | |||
| FD | Level | −3.792653 *** | I (0) | |
| First difference | 0.083147 | |||
| GDPPC | Level | −4.975770 ** | I (0) | |
| First difference | −6.545626 | |||
| Thailand | EC | Level | −3.860627 | I (1) |
| First difference | −6.135177 *** | |||
| FD | Level | 0.000112 *** | I (0) | |
| First difference | −5.576288 | |||
| GDPPC | Level | −2.777161 | I (1) | |
| First difference | −5.494244 ** |
| Country | Model | Test Statistics | Critical Value | Reject H0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 5% | ||||
| Malaysia | C | −3.88 | −5.44 | −4.92 | No |
| C/T | −4.29 | −5.80 | −5.29 | ||
| C/S | −3.99 | −5.97 | −5.50 | ||
| Indonesia | C | −3.36 | −5.44 | −4.92 | No |
| C/T | −5.20 | −5.80 | −5.29 | ||
| C/S | −4.68 | −5.97 | −5.50 | ||
| Philippines | C | −3.42 | −5.44 | −4.92 | No |
| C/T | −3.85 | −5.80 | −5.29 | ||
| C/S | −3.83 | −5.97 | −5.50 | ||
| Singapore | C | −4.99 | −5.44 | −4.92 | No |
| C/T | −4.43 | −5.80 | −5.29 | ||
| C/S | −5.27 | −5.97 | −5.50 | ||
| Thailand | C | −3.13 | −5.44 | −4.92 | No |
| C/T | −3.92 | −5.80 | −5.29 | ||
| C/S | −5.67 | −5.97 | −5.50 | ||
| Countries | Models | F | DW Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malaysia | (1,0,1) | 3.6167 | 1.79 |
| Indonesia | (4,0,2) | 2.1368 | 2.16 |
| Philippines | (1,3,1) | 7.2371 | 1.99 |
| Singapore | (4,4,3) | 7.5909 | 1.94 |
| Thailand | (4,4,4) | 5.2977 | 2.25 |
| I (0) | I (1) | ||
| Critical Value at 1% | 4.13 | 4.38 | |
| Critical Value at 5% | 3.1 | 3.87 | |
| Critical Value at 10% | 2.63 | 3.35 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahi, M.; Phoong, S.W.; Ismail, I.; Isa, C.R. Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010005
Mahi M, Phoong SW, Ismail I, Isa CR. Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach. Sustainability. 2020; 12(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahi, Masnun, Seuk Wai Phoong, Izlin Ismail, and Che Ruhana Isa. 2020. "Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach" Sustainability 12, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010005
APA StyleMahi, M., Phoong, S. W., Ismail, I., & Isa, C. R. (2020). Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach. Sustainability, 12(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010005






