Creative Enough to Become an Entrepreneur: A Multi-Wave Study of Creative Personality, Education, Entrepreneurial Identity, and Innovation
Abstract
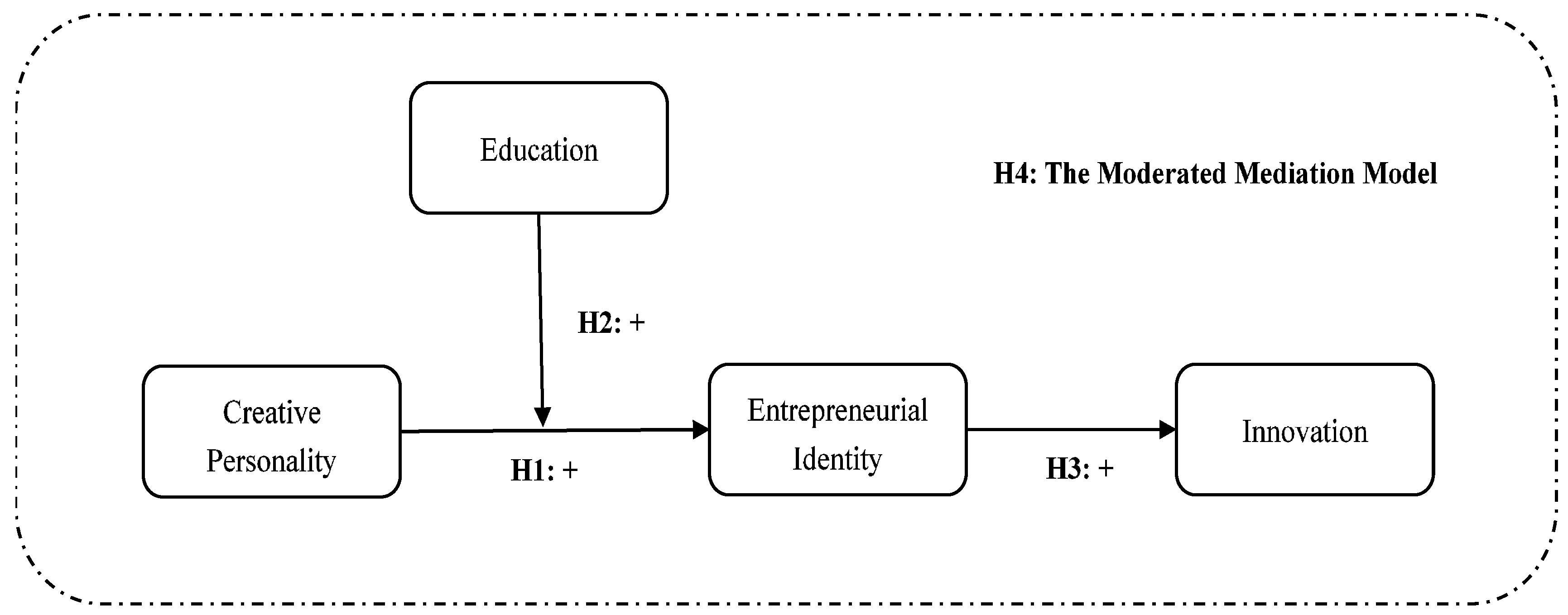
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses
2.1. Creative Personality and Entrepreneurial Identity
2.2. The Moderating Role of Education
2.3. Outcome: Innovation
2.4. Complete Theoretical Model
3. Methods
3.1. Sample Descriptions
3.2. Measures
3.3. Analytical Strategy and Results
3.4. Additional Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Contributions
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Directions
4.4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Down, S.; Warren, L. Constructing narratives of enterprise: Clichés and entrepreneurial self-identity. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2008, 14, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnieks, C.Y.; Mosakowski, E. Who am I? Looking inside the ‘entrepreneurial identity’. Front. Entrep. Res. 2007, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, D.A.; Haynie, J.M. Family business, identity Conflict, and an Expedited Entrepreneurial Process: A Process of Resolving Identity Conflict. Entrep. Theory Pr. 2009, 33, 1245–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navis, C.; Glynn, M.A. Legitimate distinctiveness and the entrepreneurial identity: Influence on investor judgments of new venture plausibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2011, 36, 479–499. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.; Holt, R. The Mature Entrepreneur: A Narrative Approach to Entrepreneurial Goals. J. Manag. Inq. 2009, 19, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.E.; Roberts, J.A. Self-Employment and Job Satisfaction: Investigating the Role of Self-Efficacy, Depression, and Seniority. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2004, 42, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, M.A.; Maw-Der, F.; Zhaoli, S. Joint effects of prior start-up experience and coping strategies on entrepreneurs’ psychological well-being. J. Bus. Ventur. 2013, 28, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.; Nicolaou, N. Creative personality, opportunity recognition and the tendency to start businesses: A study of their genetic predispositions. J. Bus. Ventur. 2015, 30, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, H.Y.; Foo, S.L. Moderating effects of tolerance for ambiguity and risktaking propensity on the role conflict-perceived performance relationship: Evidence from Singaporean entrepreneurs. J. Bus. Ventur. 1997, 12, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Burtscher, J.; Vallaster, C.; Angerer, M. Sustainable Entrepreneurship Orientation: A Reflection on Status-Quo Research on Factors Facilitating Responsible Managerial Practices. Sustainability 2018, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.-L.; González-Torres, T.; Montero-Navarro, A.; Gallego-Losada, R. Investing Time and Resources for Work–Life Balance: The Effect on Talent Retention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.-L.; Montero-Navarro, A.; Gallego-Losada, R. The Opportunity Presented by Technological Innovation to Attract Valuable Human Resources. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashforth, B.E.; Mael, F. Social identity theory and the organization. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyserman, D.; Coon, H.M.; Kemmelmeier, M. Rethinking individualism and collectivism: Evaluation of theoretical assumptions and meta-analyses. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 3–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromkin, H.L.; Snyder, C.R. The Search for Uniqueness and Valuation of Scarcity. In Social Exchange; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, M.A. Institutions and identity theory. In Handbook of Institutional Theory; Greenwood, R., Oliver, C., Suddaby, R., Sahlin-Andersson, K., Eds.; Sage: Addison, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alvesson, M.; Ashcraft, K.L.; Thomas, R. Identity Matters: Reflections on the Construction of Identity Scholarship in Organization Studies. Organization 2008, 15, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.M. Ideal Selves as Resources for the Situated Practice of Identity. Manag. Commun. Q. 2010, 24, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, S.M.; Yao, X.; Kung-Mcintyre, K. The Behavioral Impact of Entrepreneur Identity Aspiration and Prior Entrepreneurial Experience. Entrep. Theory Pr. 2009, 35, 245–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Larson, G.S. Making the ideal (local) entrepreneur: Place and the regional development of high-tech entrepreneurial identity. Hum. Relat. 2013, 67, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Down, S.; Reveley, J. Generational Encounters and the Social Formation of Entrepreneurial Identity: ‘Young Guns’ and ‘Old Farts’. Organization 2004, 11, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnellon, A.; Ollila, S.; Middleton, K.W. Constructing entrepreneurial identity in entrepreneurship education. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2014, 12, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, H. Provisional selves: Experimenting with image and identity in professional adaptation. Adm. Sci. Q. 1999, 44, 764–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montiel, C.H.; Alejandro, M.R.; Gerardo, H.A.; Marcela, P.C.Y. Relationship between creativity, personality and entrepreneurship: An exploratory study. Int. Bus. Res. 2015, 8, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalley, C.E.; Hitt, M.A.; Zhou, J. Introduction: Integrating creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship to enhance the organization’s capability to navigate in the new competitive landscape. In The Oxford Handbook of Creativity, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shalley, C.E.; Zhou, J.; Oldham, G.R. The Effects of Personal and Contextual Characteristics on Creativity: Where Should We Go from Here? J. Manag. 2004, 30, 933–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, N.; Potočnik, K.; Zhou, J. Innovation and Creativity in Organizations. J. Manag. 2014, 40, 1297–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Shalley, C.E. Deepening our understanding of creativity in the workplace: A review of different approaches to creativity research. In APA Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 275–302. [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt, J.; Shane, S.A. Opportunities and Entrepreneurship. J. Manag. 2003, 29, 333–349. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, M.B.; Gardner, W. Who is this “We”? Levels of collective identity and self representations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 71, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, H.; Barbulescu, R. Identity as narrative: Prevalence, effectiveness, and consequences of narrative identity work in macro work role transitions. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2010, 35, 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Oldham, G.R. Enhancing Creative Performance: Effects of Expected Developmental Assessment Strategies and Creative Personality. J. Creat. Behav. 2001, 35, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalley, C.E.; Oldham, G.R. Competition and Creative Performance: Effects of Competitor Presence and Visibility. Creat. Res. J. 1997, 10, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, E.C.; Shaw, E.J.; Houtz, J.C. The Creative Personality. Gift. Child Q. 2005, 49, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillis, I.; Rentschler, R. The role of creativity in entrepreneurship. J. Enterprising Cult. 2010, 18, 49–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.; Venkataraman, S. The Promise of Entrepreneurship as a Field of Research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2000, 25, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markus, H.; Kunda, Z. Stability and malleability of the self-concept. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriez, B.; Soenens, B.; Beyers, W. Personality, identity styles, and religiosity: An integrative study among late adolescents in Flanders Belgium. J. Pers. 2004, 72, 877–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.; Wurf, E. The dynamic self-concept: A social psychological perspective. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1987, 38, 299–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.E.; Lord, R.G. Implicit effects of justice on self-identity. J. Appl. Psychol. 2010, 95, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, E.H. Identity: Youth and Crisis; Norton & Compan: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.T.; Mirvis, P.H. The New Career Contract: Developing the Whole Person at Midlife and Beyond. J. Vocat. Behav. 1995, 47, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratt, M.G. The Good, the Bad, and the Ambivalent: Managing Identification among Amway Distributors. Adm. Sci. Q. 2000, 45, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.B. The Social Self: On Being the Same and Different at the Same Time. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 17, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.R.; Kitayama, S. Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1991, 98, 224–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisrich, R.D. Entrepreneurship/intrapreneurship. Am. Psychol. 1990, 45, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, J.S.; Shepherd, D.A. Entrepreneurial action and the role of uncertainty in the theory of the entrepreneur. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2006, 31, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Seibert, S.E.; Lumpkin, G. The Relationship of Personality to Entrepreneurial Intentions and Performance: A Meta-Analytic Review. J. Manag. 2009, 36, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.; Hmieleski, K.; Siegel, D.S.; Ensley, M.D. The Role of Human Capital in Technological Entrepreneurship. Entrep. Theory Pr. 2007, 31, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.S. Human Capital; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Ployhart, R.E.; Moliterno, T.P. Emergence of the Human Capital Resource: A Multilevel Model. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2011, 36, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, J.M.; Rauch, A.; Frese, M.; Rosenbusch, N. Human capital and entrepreneurial success: A meta-analytical review. J. Bus. Ventur. 2011, 26, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquis, C.; Tilcsik, A. Imprinting: Toward a multilevel theory. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2013, 7, 195–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, J.; Folta, T.B.; Cooper, A.C.; Woo, C.Y. Survival of the Fittest? Entrepreneurial Human Capital and the Persistence of Underperforming Firms. Adm. Sci. Q. 1997, 42, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, K.; Freeman, D.; Reed, A.; Lim, V.K.G.; Felps, W. Testing a social-cognitive model of moral behavior: The interactive influence of situations and moral identity centrality. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 97, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon, M.; Wincent, J.; Singh, J.; Drnovsek, M. The nature and experience of entrepreneurial passion. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2009, 34, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, H.; Gimeno, J. Becoming a founder: How founder role identity affects entrepreneurial transitions and persistence in founding. J. Bus. Ventur. 2010, 25, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasvathy, S.; Venkataraman, S. Made, as well as Found: Researching Entrepreneurship as a Science of the Artificial; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Perry-Smith, J.E.; Mannucci, P.V. From Creativity to Innovation: The Social Network Drivers of the Four Phases of the Idea Journey. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2017, 42, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Cognitive Theory: An Agentic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosling, S.D.; Rentfrow, P.J.; Swann, W.B.; Swann, W.B., Jr. A very brief measure of the Big-Five personality domains. J. Res. Pers. 2003, 37, 504–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, K.; Americus, R., II. The self-importance of moral identity. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2002, 83, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokhin, S.; Schulze, W.S. Entrepreneurship, innovation, and corruption. J. Bus. Ventur. 2009, 24, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMartino, R.; Barbato, R. Differences between women and men MBA entrepreneurs: Exploring family flexibility and wealth creation as career motivators. J. Bus. Ventur. 2003, 18, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Price, B. Regression Analysis by Example, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Muthén, L.K.; Muthén, B.O. Mplus User’s Guide, 7nd ed.; Muthén & Muthén: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1998–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zyphur, M.; Narayanan, J.; Arvey, R.D.; Chaturvedi, S.; Avolio, B.J.; Lichtenstein, P.; Larsson, G. The genetic basis of entrepreneurship: Effects of gender and personality. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2009, 110, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Mackenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. Cultural Consequences: International Differences in Work-Related Values; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | Mean | SD | N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Age | 17.90 | 2.31 | 12,686 | |||||||||||
| 2. Gender | 0.50 | 0.50 | 12,686 | 0.01 | ||||||||||
| 3. Race 1 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 12,686 | −0.05 *** | 0.00 | |||||||||
| 4. Race 2 | 0.25 | 0.43 | 12,686 | −0.04 *** | 0.00 | −0.25 *** | ||||||||
| 5. Mother Education | 10.87 | 3.17 | 11,878 | 0.04 *** | −0.02 * | −0.40 *** | −0.01 | |||||||
| 6. Father Education | 10.95 | 3.93 | 10,880 | 0.03 ** | −0.01 | −0.29 *** | −0.09 *** | 0.65 *** | ||||||
| 7. Poverty Status | 0.19 | 0.40 | 9891 | −0.09 *** | 0.05 *** | 0.05 *** | 0.21 *** | −0.23 *** | −0.21*** | |||||
| 8. Marital Status | 0.80 | 0.40 | 12,686 | 0.03 ** | 0.10 *** | 0.03 *** | −0.15 *** | 0.01 | 0.00 | −0.08 *** | ||||
| 9. Creative Personality | 4.68 | 1.93 | 6943 | −0.01 | −0.02 | −0.04 *** | 0.00 | 0.08 *** | 0.06 *** | −0.02 | 0.02 | |||
| 10. Education | 13.24 | 2.63 | 7057 | 0.00 | 0.06 *** | −0.16 *** | −0.08 *** | 0.40 *** | 0.41 *** | −0.18 *** | 0.08 *** | 0.09 *** | ||
| 11. Entrepreneurial Identity | 0.19 | 0.39 | 7891 | 0.00 | −0.15 *** | −0.05 *** | 0.08 *** | 0.05 *** | 0.05 *** | 0.02 | 0.03 * | 0.06 *** | 0.05 *** | |
| 12. Innovation | 0.01 | 0.11 | 7988 | 0.01 | −0.05 *** | −0.03 ** | −0.03 * | 0.07 *** | 0.06 *** | −0.02 | 0.04 ** | 0.03 * | 0.09 *** | 0.08 *** |
| Criteria | Entrepreneur Identity | Innovation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | |
| Control Variables | ||||||
| Age | 0.01 (0.02) | 0.01 (0.02) | 0.01 (0.02) | −0.02 (0.05) | −0.01 (0.05) | −0.01 (0.06) |
| Gender | −0.80 (0.07) *** | −0.79 (0.08) *** | −0.79 (0.08) *** | −1.21 (0.27) *** | −1.14 (0.28) *** | −1.02 (0.28) *** |
| Race 1 | 0.02 (0.11) | 0.05 (0.12) | 0.04 (0.12) | −0.38 (0.42) | −0.41 (0.46) | 0.40 (0.46) |
| Race 2 | 0.37 (0.09) *** | 0.33 (0.10) ** | 0.33 (0.10) ** | −0.52 (0.36) | −0.47 (0.36) | −0.52 (0.37) |
| Mother Education | 0.03 (0.02) * | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.14 (0.06) | 0.07 (0.06) | 0.07 (0.06) |
| Father Education | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.05 (0.04) | 0.02 (0.04) | 0.01 (0.04) |
| Poverty Status | 0.13 (0.10) | 0.17 (0.11) | 0.17 (0.11) | −0.38 (0.48) | −0.43 (0.53) | −0.45 (0.53) |
| Marital Status | 0.38 (0.12) ** | 0.38 (0.13) ** | 0.38 (0.13) ** | 1.25 (0.60) * | 1.01 (0.60) | 0.94 (0.60) |
| Predictors | ||||||
| Creative Personality | 0.09 (0.02) *** | 0.09 (0.02) *** | 0.09 (0.09) | 0.07 (0.09) | ||
| Education | 0.03 (0.02) * | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.21 (0.05) ** | 0.21 (0.05) *** | ||
| Interactions | ||||||
| Creative * Education | 0.02 (0.01 ) ** | 0.00 (0.01) | −0.00 (0.03) | |||
| Mediator | ||||||
| Entrepreneurial Identity | 0.76 (0.27) ** | |||||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| Predictor | Moderator | Mediator | Criterion | Indirect Effect | SE | Z | p Value (Two-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creative Personality | Education Low (−1 SD) | Entrepreneurial Identity | Innovation | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.78 | 0.43 |
| Education High (+1 SD) | 0.12 * | 0.05 | 2.47 | 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Creative Enough to Become an Entrepreneur: A Multi-Wave Study of Creative Personality, Education, Entrepreneurial Identity, and Innovation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104043
Zhou J, Xu X, Li Y, Liu C. Creative Enough to Become an Entrepreneur: A Multi-Wave Study of Creative Personality, Education, Entrepreneurial Identity, and Innovation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(10):4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104043
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jinyi, Xingzi Xu, Yawen Li, and Chengcheng Liu. 2020. "Creative Enough to Become an Entrepreneur: A Multi-Wave Study of Creative Personality, Education, Entrepreneurial Identity, and Innovation" Sustainability 12, no. 10: 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104043
APA StyleZhou, J., Xu, X., Li, Y., & Liu, C. (2020). Creative Enough to Become an Entrepreneur: A Multi-Wave Study of Creative Personality, Education, Entrepreneurial Identity, and Innovation. Sustainability, 12(10), 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104043




