Human Health, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Systems for a Large, Mixed-Use Urban Building
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Treatment System Design
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory Development
2.3. Water Use Scenarios
2.4. QMRA
- DR(...) is a dose-response function for the reference pathogen,
- Vi is the volume of water ingested per day for use i,
- ni is the number of days of exposure over a year for use i,
- C is the pathogen concentration in the untreated source water, and
- TP is the treatment performance expressed as a log10 reduction in the total treatment processes (e.g., TP = TPMBR + TPdisinfection).
2.5. LCCA
- NPV (2016 $) = net present value of all costs and revenues necessary to construct and operate the wastewater treatment facility,
- Costx = cost in future year x,
- i (%) = real discount rate, and
- x = number of years in the future.
2.6. LCA
2.7. Multiple Indicator Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. QMRA
3.2. LCCA
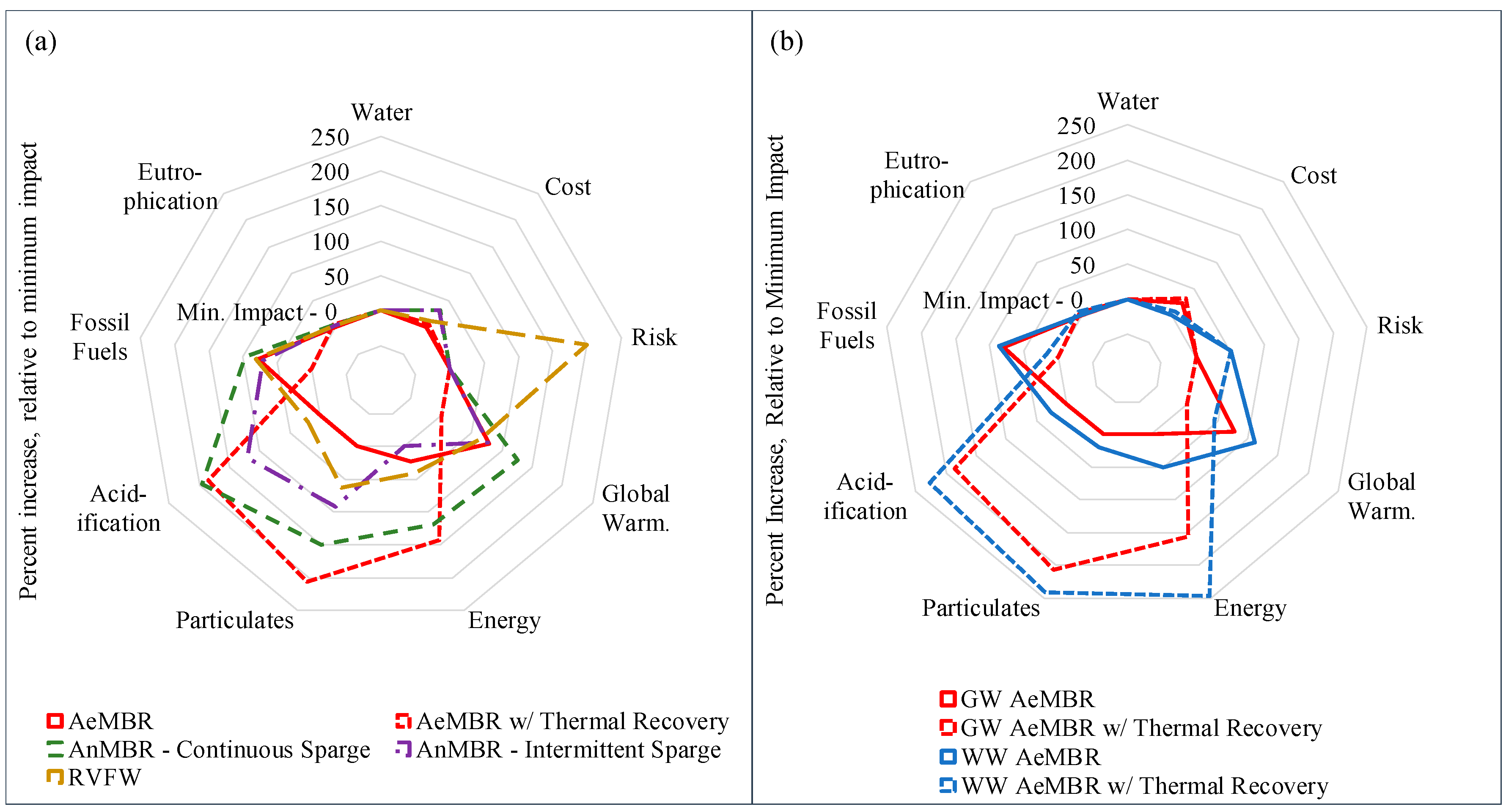
3.3. LCA
3.4. Integrated Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Decision Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Disclaimer
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. EPA Water Reuse Action Plan; EPA-820-R-20-001; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Morelli, B.; Cashman, S.; Ma, X.; Garland, J.; Bless, D.; Jahne, M. Life Cycle Assessment and Cost Analysis of Distributed Mixed Wastewater and Graywater Treatment for Water Recycling in the Context of an Urban Case Study (No. EPA/600/R-18/280); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2019.
- U.S. EPA Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Research. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/water-research/onsite-non-potable-water-reuse-research#:~:text=Onsite%20non%2Dpotable%20water%20reuse%20systems%20(ONWS)%20capture%20and,stormwater%2C%20or%20roof%20collected%20rainwater (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- NBRC. Making the Utility Case for Onsite Non-potable Water Systems; National Blue Ribbon Commission for Onsite Non-potable Water Systems, 2018; Available online: http://uswateralliance.org/sites/uswateralliance.org/files/publications/NBRC_Utility%20Case%20for%20ONWS_032818.pdf.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Kehoe, P.; Chang, T. Public Health and Utility Leaders Collaborate to Advance Onsite Reuse 2019. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual WateReuse Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 10 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- SFPUC. San Francisco’s Non-Potable Water System Projects; San Francisco Public Utilities Commission: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- WJW Foundation. Non-potable Water Reuse Practice Guide; William J. Worthen Foundation: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- City of San Francisco. Article 12C: Alternate Water Sources for Non-Potable Application; San Francisco Health Code: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- NSF/ANSI. NSF/ANSI 350-2017 Onsite Residential and Commercial Water Reuse Treatment Systems; NSF International: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schoen, M.E.; Jahne, M.A.; Garland, J. Human health impact of non-potable reuse of distributed wastewater and greywater treated by membrane bioreactors. Microb. Risk Anal. 2018, 9, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SFPUC. Non-potable Water Program Guidebook: A Guide for Implementing On-Site Non-Potable Water Systems in San Francisco; San Francisco Public Utilities Commission: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Sharvelle, S.; Ashbolt, N.; Clerico, E.; Hultquist, R.; Leverenz, H.; Olivieri, A. Risk-Based Framework for the Development of Public Health Guidance for Decentralized Non-Potable Water Systems; Water Environment and Reuse Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-941242-83-4. [Google Scholar]
- Schoen, M.E.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Jahne, M.A.; Garland, J. Risk-based enteric pathogen reduction targets for non-potable and direct potable use of roof runoff, stormwater, and greywater. Microb. Risk Anal. 2017, 5, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, D.R.; Moglia, M.; Cook, S.; Beale, D.J. Towards sustainable urban water management: A critical reassessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 7150–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, V.G. Applying Integrated Urban Water Management Concepts: A Review of Australian Experience. Environ. Manag. 2006, 37, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, J.C.; Hester, E.T.; Carey, C.C. Assessing and Enhancing Environmental Sustainability: A Conceptual Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6830–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Xue, X.; Gonzalez-Mejia, A.; Garland, J.; Cashdollar, J. Sustainable Water Systems for the City of Tomorrow-A Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12071–12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, X.; Schoen, M.E.; Ma, X.; Hawkins, T.R.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Cashdollar, J.; Garland, J. Critical insights for a sustainability framework to address integrated community water services: Technical metrics and approaches. Water Res. 2015, 77, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Sharvelle, S.; Fourness, D.; Grigg, N.; Roesner, L.; Haukaas, J. Centralized and Decentralized Strategies for Dual Water Supply: Case Study. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 05017017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Sharvelle, S.; Grigg, N.; Pivo, G.; Haukaas, J. Collaborative, Risk-Informed, Triple Bottom Line, Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Planning Framework for Integrated Urban Water Management. Water 2018, 10, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonasson, O.J.; Kandasamy, J. Decentralised water reuse in Sydney, Australia: Drivers for implementation and energy consumption. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 13, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, M.E.; Xue, X.; Wood, A.; Hawkins, T.R.; Garland, J.; Ashbolt, N.J. Cost, energy, global warming, eutrophication and local human health impacts of community water and sanitation service options. Water Res. 2017, 109, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, T.P.; Nguyen, M.T.; Sukardi, M.; Miot, A.; Horvath, A.; Nelson, K.L. Life-Cycle Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of a Building-Scale Wastewater Treatment and Nonpotable Reuse System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10303–10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavvada, O.; Nelson, K.L.; Horvath, A. Spatial optimization for decentralized non-potable water reuse. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvada, O.; Horvath, A.; Stokes-Draut, J.R.; Hendrickson, T.P.; Eisenstein, W.A.; Nelson, K.L. Assessing Location and Scale of Urban Nonpotable Water Reuse Systems for Life-Cycle Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13184–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, S.; Ma, X.; Mosley, J.; Garland, J.; Crone, B.; Xue, X. Energy and greenhouse gas life cycle assessment and cost analysis of aerobic and anaerobic membrane bioreactor systems: Influence of scale, population density, climate, and methane recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Flores, L.; Ferrer, I. Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high rate algal ponds. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Davies, E.G.R.; Liu, Y. Life cycle assessment of decentralized greywater treatment systems with reuse at different scales in cold regions. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Callegari, A.; Hlavínek, P.; Capodaglio, A.G. Membrane bioreactors for sustainable, fit-for-purpose greywater treatment: A critical review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X. Constructed wetlands for greywater recycle and reuse: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharvelle, S.; Roesner, L.; Glenn, R. Treatment, Public Health, and Regulatory Issues Associated with Graywater Reuse: Guidance Document; WateReuse Research Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Guidelines for Water Reuse; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 643.
- National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine Using Graywater and Stormwater to Enhance Local Water Supplies: An Assessment of Risks, Costs, and Benefits; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-309-38835-1.
- DeOreo, W.B.; Mayer, P.; Dziegielewski, B.; Kiefer, J. Residential end Uses of Water; Version 2 (Executive Report); Water Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dziegielewski, B.; Kiefer, J.C.; Opitz, E.M.; Porter, G.A.; Lantz, G.L.; DeOreo, W.B.; Mayer, P.W.; Nelson, J.O. Commercial and Institutional End Uses of Water; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2000; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, C.N.; Rose, J.B.; Gerba, C.P. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-471-18397-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pecson, B.M.; Triolo, S.C.; Olivieri, S.; Chen, E.C.; Pisarenko, A.N.; Yang, C.-C.; Olivieri, A.; Haas, C.N.; Trussell, R.S.; Trussell, R.R. Reliability of pathogen control in direct potable reuse: Performance evaluation and QMRA of a full-scale 1 MGD advanced treatment train. Water Res. 2017, 122, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soller, J.A.; Parker, A.M.; Salveson, A. Public Health Implications of Short Duration, Off-Specification Conditions at Potable Reuse Water Treatment Facilities. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, S.K.; Petersen, S.R. Life-Cycle Costing Manual for the Federal Energy Management Program; National Instititute of Standards and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Lavappa, P.D.; Kneifel, J.D.; O’Rear, E. Energy Price Indices and Discount Factors for Life-Cycle Cost Analysis—2017 Annual Supplement to NIST Handbook 135; National Instititute of Standards and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- CWB (California Water Boards). Financial Assistance Funding—Grants and Loans—Clean Water State Revolving Fund (CWSRF); California Water Boards: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 14044: 2006 Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines; ISO 14044; The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 14040: Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework; The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, P.J.; Parameswaran, P.; Lim, K.; Bae, J.; Shin, C.; Ho, J.; McCarty, P.L. A comparative pilot-scale evaluation of gas-sparged and granular activated carbon-fluidized anaerobic membrane bioreactors for domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 120949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.; Evans, P.J.; Parameswaran, P. Long-Term Performance of a Pilot-Scale Gas-Sparged Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor under Ambient Temperatures for Holistic Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7347–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaitidak, D.M.; Yadav, K.D. Characteristics and treatment of greywater—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wichmann, K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkowicz, S.; Collins, K. A Review of Multiple Criteria Analysis for Water Resource Planning and Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, M.; Arora, M.; Malano, H.; Moglia, M.; Sharma, A.; George, B.; Pamminger, F. An Integrated Framework for Assessment of Hybrid Water Supply Systems. Water 2016, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Reuse Type | Wastewater Type | Log Reduction Targeta | ||
| Enteric Viruses | Parasitic Protozoa | Enteric Bacteria | ||
| Indoor Use | Mixed wastewater | 8.5 | 7 | 6 |
| Graywater | 6 | 4.5 | 3.5 | |
| Unrestricted Irrigation | Mixed wastewater | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Graywater | 5.5 | 4.5 | 3.5 | |
| Treatment System | Wastewater Type | Log Reduction Valuesb | ||
| Enteric Viruses | Parasitic Protozoa | Enteric Bacteria | ||
| AeMBR and AnMBRc | Mixed wastewater | 9 | 9 | 11 |
| Graywater | 9 | 9 | 11 | |
| RVFW | Mixed wastewater | 9.5 | 7 | 12.8 |
| Graywater | 6.5 | 5 | 8.8 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arden, S.; Morelli, B.; Schoen, M.; Cashman, S.; Jahne, M.; Ma, X.; Garland, J. Human Health, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Systems for a Large, Mixed-Use Urban Building. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135459
Arden S, Morelli B, Schoen M, Cashman S, Jahne M, Ma X, Garland J. Human Health, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Systems for a Large, Mixed-Use Urban Building. Sustainability. 2020; 12(13):5459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135459
Chicago/Turabian StyleArden, Sam, Ben Morelli, Mary Schoen, Sarah Cashman, Michael Jahne, Xin (Cissy) Ma, and Jay Garland. 2020. "Human Health, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Systems for a Large, Mixed-Use Urban Building" Sustainability 12, no. 13: 5459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135459
APA StyleArden, S., Morelli, B., Schoen, M., Cashman, S., Jahne, M., Ma, X., & Garland, J. (2020). Human Health, Economic and Environmental Assessment of Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse Systems for a Large, Mixed-Use Urban Building. Sustainability, 12(13), 5459. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135459





