Abstract
Research on sound-absorbing materials made of natural fibers is an emerging area in sustainable materials. In this communication, the use of raw esparto grass as an environmentally friendly sound-absorbing material is explored. Measurements of the normal-incidence sound-absorption coefficient and airflow resistivity of three different types of esparto from different countries are presented. In addition, the best-fit coefficients for reasonable prediction of the sound-absorption performance by means of simple empirical formulae are reported. These formulae require only knowledge of the airflow resistivity of the fibrous material. The results presented in this paper are an addition to the characterization of available natural fibers to be used as alternatives to synthetic ones in the manufacturing of sound-absorbing materials.
1. Introduction
The use of sound-absorbing materials is one of the main engineering approaches used to control environmental noise [1]. Sound-absorbing materials are usually porous and are being used increasingly in the reduction of reverberant noise in buildings and as constituents of commercially available noise-isolation composites in several applications. Since the use of asbestos fiber was prohibited in the 1970s [2], the main materials employed for noise control have been made of glass and mineral fibers. However, the disposal of these kinds of fibrous materials in landfills has become an environmental challenge. They are difficult to recycle, their burning causes toxic fumes emission, and their industrial production requires large amounts of energy, which increases the emission of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere. Thus, several countries have included the concept of green building materials in their legislation in order to favor the use of environmentally friendly materials, less contaminating processes, and recycled products [3].
The development of acoustical materials based on renewable resources as viable alternatives to mineral wool, fiberglass, and other synthetic fibers has received much attention, in particular in automotive applications [4]. Recent research has been devoted to the use of natural fibers for manufacturing sound-absorbing eco-materials, including vegetal and animal fibers [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. In general, natural fibers are biodegradable and their processing can be made more economical and environmentally friendly. Natural fibers have also proven to be safer to human health compared with most mineral synthetic fibers since they do not require handling precautions.
Studies of the use of natural fibers to manufacture sound-absorption materials can be divided into two types: those that explore the use of raw fibers and those that consider the effect of adding fibers to polymer matrices to produce sound-absorbing composite materials. The latter are usually called biocomposites and these have been comprehensively reviewed by several authors [5,6].
Asdrubali et al. [7] have presented a review of the research developed on acoustical materials made of natural fibers and recyclable materials. Berardi and Iannace [8] have also reviewed the literature regarding the sound-absorption properties of some natural fibers, including kenaf, wood, hemp, coconut, cork, cane, cardboard, and sheep wool. Acoustic properties of bio luffa samples have been evaluated by Koruk and Genk [9]. Tea leaf waste has also been used to make a sound-absorbing material with a low carbon footprint [10]. The sound-absorption properties of environmentally friendly panels made of coir fiber from coconut husk bonded with adhesive have been studied both experimentally and theoretically by Fouladi et al. [11,12]. Coconut husk and palm leaf have also been investigated by other authors [13,14].
Several other natural fibers suitable as bases for sound-absorption materials have been reported in the literature, such as sisal [15], ramie [16], corn husk [17], broom fibers [18], kenaf [19], bamboo [20], bagasse [21], fique [22], straw and cane [23], oil palm empty bunch [24], coir and date palm [25], pineapple leaf [26], coffee waste [27], flax [28], and chicken feathers [29], among others. These researchers have reported the acoustic performance of different combinations of densities and thicknesses of both the fibers and the resulting bulk materials. The effects produced by the addition of an air space behind the samples have also been noted. Most of these natural materials exhibited very good sound-absorption properties in the middle- and high-frequency range (above 500–1000 Hz), and their sound-absorption values are comparable with commercial materials made of mineral fibers.
Empirical Model for Fibrous Sound-Absorbing Materials
Fibrous materials are composed of an assembly of continuous strands that trap air between them, resulting in a porous material. When such a material is exposed to an incident sound wave, sound energy is converted into heat due to thermal and viscous losses of air molecules at the walls of the interior pores in the material. In fibrous materials, much of the energy can also be absorbed by scattering among the fibers and by the vibration caused in the individual fibers [1,2]. The fibers of the material rub together under the influence of the sound waves and lose energy due to work done by frictional forces.
A fibrous sound-absorbing material has a solid phase (skeleton) and a fluid phase (usually air). It is convenient to consider the fluid and solid phases as decoupled. Thus, the solid phase can be assumed to be rigid and motionless. Under these assumptions, approaches to describing the acoustic behavior of fibrous materials have been developed, which can be divided into empirical, analytical, and semi-phenomenological models [30]. Although they must be used carefully, simple empirical equivalent-fluid expressions have been presented to describe the acoustic behavior of fibrous materials where only the airflow resistivity is needed. The most commonly employed of these models is the one used by Delany and Bazley [31]. They performed an analysis of sound-absorbing materials that included highly porous fiberglass and rockwool materials. They carried out measurements of airflow resistivity and characteristic impedance using an impedance tube in the frequency range 250–4000 Hz. Using regression analysis from approximately 200 data points, they determined power–law relationships between the variables to predict the sound-absorption coefficient. Their model has the advantage that only the determination of the resistance experienced by the air when it passes through open pores in the material is required, i.e., the airflow resistivity (σ) of the porous material. A good fit of the Delany and Bazley relationships are, in MKS units [32],
where zc is the characteristic wave impedance, kc is the characteristic sound propagation constant, ρ is the air density, c is the speed of sound, ω is the angular frequency (ω = 2πf), f is the frequency, Ci (i = 1, …, 8) are eight numerical coefficients, and the dimensionless parameter χ = ρf/σ. These empirical expressions yield accurate results in the range 0.01 < χ < 1.0 [30].
The surface impedance (zs) is
where d is the thickness of the material. Consequently, the normal-incidence sound-absorption coefficient (α) is determined by
Although some researchers have reported further improvements to the Delany and Bazley model [33,34], their original expressions are widely used in most practical cases. Since each material has its own microstructure, the eight coefficients in Equations (1) and (2) should be unique to each type of porous material. In addition, Attenborough [35] has pointed out that empirical relationships of the form of Equations (1) and (2) should be valid for fibrous porous materials as well as non-fibrous ones. Therefore, the Delany and Bazley model has been successfully applied to different sound-absorbing materials [36,37,38], including those made of natural fibers [39,40]. One such study was recently presented by Berardi and Iannace [32]. They determined the eight best-fit coefficients in Equations (1) and (2) for samples of nine natural fibers. For the calculations, they used an inverse method based on minimization of the errors between the measured and predicted values [13,38].
In this work, the sound-absorption properties of raw esparto grass fiber are examined as an environmentally friendly material. Sound-absorption coefficients and airflow resistivities are measured for three different types of esparto from different countries. Using these results, the best-fit coefficients for reasonable prediction of the sound-absorption performance by means of simple empirical formulae are reported. Although some authors have recently explored the inclusion of esparto in biocomposites [41] and reported measurements of its sound-absorbing performance [42], to the best of the authors’ knowledge, a sound absorption empirical prediction model for this kind of fiber has not been previously presented.
2. Materials and Methods
Esparto, also known as alfa grass, comes from two different species of perennial grasses scientifically known as Stipa tenacissima and Lygeum spartum. Esparto grass is a gramineous plant endemic to the Western Mediterranean and is also grown in the northern areas of North African countries. Esparto plants require small amounts of water and virtually no chemicals during their growth [43]. Therefore, their production involves a low carbon footprint and no chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) emissions. Although esparto’s use as a building material has not been widely explored, its strong raw fibers have been used for centuries, mainly in the manufacture of ropes, mats, baskets, and decorative elements. Esparto is also commercially cultivated for industrial paper pulp production [44]. Esparto fibers are short and wide at the basal level and longer and thinner above the leaf [45]. After manual removal of their blades, the esparto leaves are left to dry in the sun. The resulting material is then combed to produce what is called raw esparto. Subsequent processing may include soaking in distilled water pools for two to four weeks to make the fiber more resistant and to facilitate its crushing and weaving.
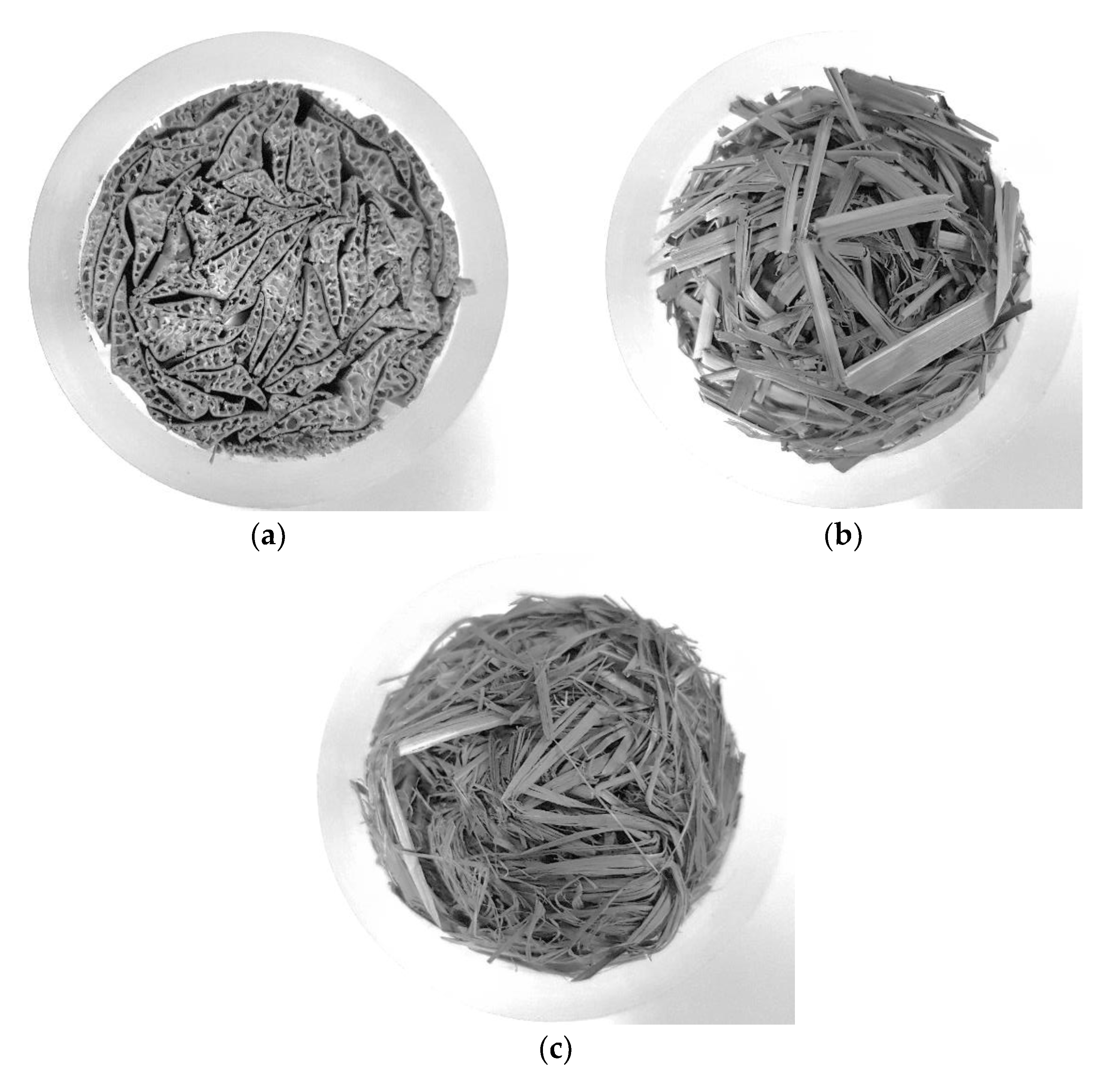
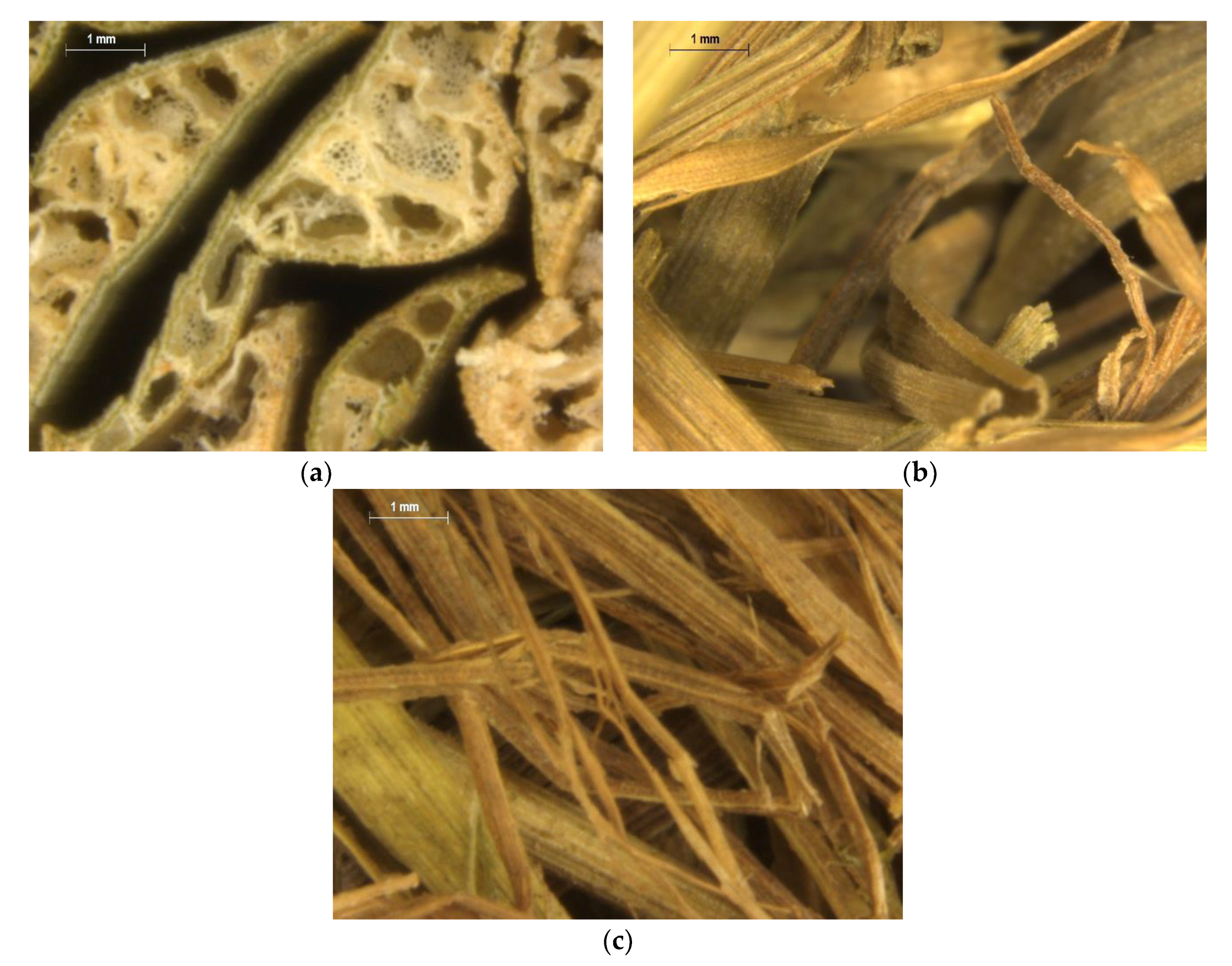
Three different types of pure, raw, dry esparto were obtained from an industrial supplier (Espartos Albarracin S.L., Murcia, Spain). The types of esparto were labeled as Type 1 (originating from Pakistan), Type 2 (originating from Tunisia), and Type 3 (originating from Egypt). The material was handled as received, and no chemicals or binders were added. Since the fibers of Type 1 were thicker than those of the other types and exhibited visible inner channels, they were cut to fixed lengths and packed in a cylindrical sample of a diameter of 40 mm so that samples could be arranged with channels parallel to the tube impedance axis. This arrangement is similar to that used previously to test cardboard samples [8,32]. The samples were weighted to estimate their mean density. Esparto samples of Types 2 and 3 were cold compressed by a mechanical press into a mold to produce equivalent cylindrical samples. The pressing force was varied to produce samples of approximately equal nominal length to that of Type 1. For each type of esparto, nominal lengths of 30, 50, 70, and 90 mm were considered in the experiments. Extreme care was taken to ensure that the volume was filled homogeneously so as to minimize the effects of air cavities in the back of the samples. Figure 1 shows photographs of representative samples of each material. Figure 2 shows enlarged photographs to display some of the features of each esparto fiber. We note the high inhomogeneity of the fibrous material, which is usual in most natural materials.
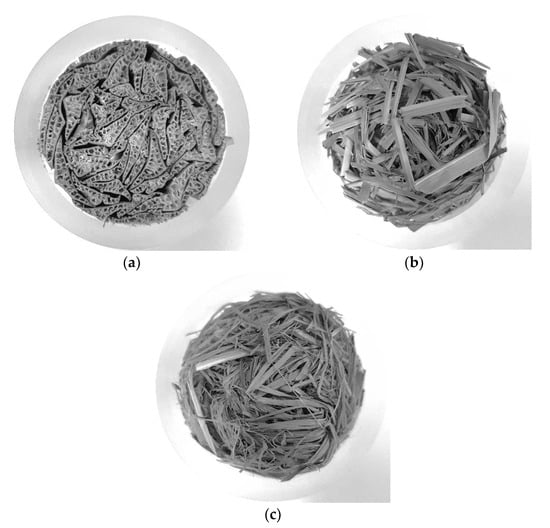

Figure 1.
Photographs of the three different esparto samples studied in this paper: (a) Type 1 (Pakistan), (b) Type 2 (Tunisia), and (c) Type 3 (Egypt).
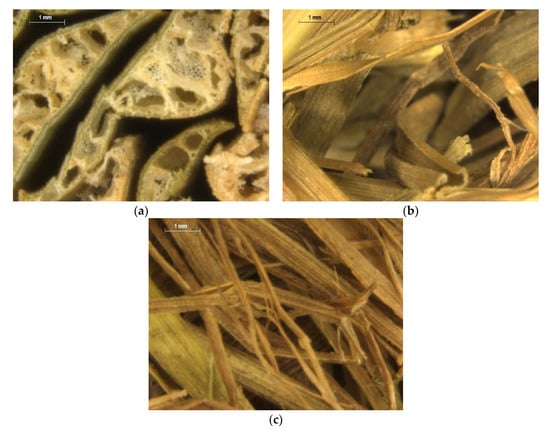

Figure 2.
Features of each esparto fiber: (a) Type 1 (Pakistan), (b) Type 2 (Tunisia), and (c) Type 3 (Egypt).
The normal-incidence sound-absorption coefficient of each sample was experimentally obtained using the transfer-function method in an impedance tube designed to follow the ISO 10534-2 standard [46]. The impedance tube had a wall thickness of 5 mm, an inner diameter of 40 mm, and a length of 1.35 m. Two ½-inch laboratory-grade microphones (Bruel & Kjaer 4189), connected to their respective preamplifiers (Bruel & Kjaer ZC0032), were mounted flush with the tube walls. The distances between the microphones were selected so as to allow a valid measurement in the frequency range 200 to 3150 Hz. One extreme of the tube was closed with a loudspeaker (Beyma CP800TI), and the opposite end was closed with a sample holder with a rigid termination. The microphone signals were processed in real time by an FFT signal analyzer (Bruel & Kjaer Pulse C3560-C), which also provided a broadband random signal as input to the loudspeaker. The measurement system was controlled by a notebook.
Since we were interested in characterizing only the effects of the raw fiber material, no air space was used behind the samples. The samples were also carefully sealed to avoid gaps between the sample and the tube walls. The microphones were previously calibrated with an acoustic calibrator (Bruel & Kjaer 4231), and each measurement was repeated with the position of the microphones inverted so as to correct the measurement errors caused by their phase mismatch.
The airflow resistivity of each sample was determined in the laboratory using the method presented by Ingar and Dear [47]. This method has been shown to be a good alternative to the ISO standardized method [48]. The same equipment used to measure sound absorption was used to implement this method. In this method, the material sample is placed in the middle of the impedance tube. Sound pressures are measured by a microphone located in front of the sample and near the rigid termination. The airflow resistivity is indirectly determined from the difference between these sound pressures, as described in [47]. Further details of the experiments can be found in [49]. The tests were repeated three times on three different samples of each type of esparto to determine the average values of the sound-absorption coefficient and airflow resistivity.
To determine the best-fit coefficients Ci (i = 1, …, 8) in Equations (1) and (2), an iterative numerical process was implemented in a Matlab computer code to minimize the quadratic error function
where N is the total number of tested frequencies, αi is the measured sound-absorption coefficient at the i-th frequency, and is the corresponding value estimated from Equations (1)–(4). The nonlinear optimization was performed using the Nelder–Mead simplex method [50,51]. In this work, the direct fminsearch Matlab implementation of the Nelder–Mead method was used. This implementation allows one to find a minimum of an unconstrained multivariable function using a derivative-free approach as described by Lagarias et al. [52]. The coefficients obtained by Arenas et al. [39] for cellulose samples were used as initial input values to the numerical process. These values ensured fast convergence and small errors in the prediction.
3. Results and Discussion
The results of the measurement of airflow resistivity for each material are shown in Table 1. The best-fitting coefficients calculated through the optimization process described in Section 2 for each material are shown in Table 2.

Table 1.
Average and standard deviation results for samples of different types of esparto.

Table 2.
Best-fitting coefficients in Equations (1) and (2) determined for samples of different types of esparto. The coefficients of the Delany and Bazley formula are shown for comparison.
Figure 3 shows the average experimental results of normal-incidence sound-absorption coefficient as a function of frequency, the corresponding numerical results using the best-fitting coefficients of Table 1.
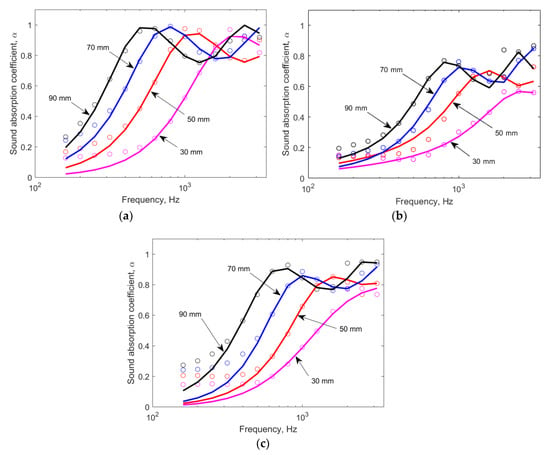
Figure 3.
Sound-absorption coefficients for the three different esparto samples of different thicknesses studied in this paper: (a) Type 1 (Pakistan), (b) Type 2 (Tunisia), and (c) Type 3 (Egypt). Results are shown for the experimental results (circles) and those determined from the empirical formulae using the best-fitting coefficients of Table 2.
The three materials display the characteristic behavior of a bulk fibrous sound-absorbing material, where the sound-absorption coefficient increases with frequency up to a maximum value. Increased low-frequency sound absorption is also observed for increased material thickness. It is observed that, out of the three types, esparto Type 1 with a thickness of 90 mm exhibited the best sound-absorbing performance, with a first sound-absorption peak value near unity at 500 Hz. This is related to its airflow resistivity, which is about four and two times larger than the airflow resistivity of Type 2 and Type 3, respectively (see Table 1). The effect of the inner channels of this type of esparto adds more acoustic resistance to the resulting material, which improves the sound absorption. Sound-absorption results for esparto Types 2 and 3 show sound-absorption peaks occurring at about the same frequencies for each thickness, although esparto Type 3 exhibits higher sound-absorption coefficients than esparto Type 2. These results are comparable to those obtained with traditional fiberglass materials of equivalent thickness [29].
Due to the particular characteristics of each inhomogeneous natural fibrous material, their properties are not all described by the variation in airflow resistivity, and consequently their coefficients should be peculiar to each material. Therefore, it is not surprising that the formulae with the original Delany and Bazley coefficients [31] cannot appropriately predict the characteristic wave impedance and the characteristic sound propagation constant of the esparto.
We observe that the calculated best-fitting coefficients can accurately predict the sound-absorption values for the types of esparto studied in this paper at frequencies higher than 400 Hz, in particular for thicker samples. The calculated coefficients are also able to correctly predict the succession of peaks and troughs in the curves of the sound-absorption coefficient versus frequency. The predicted quadratic error values according to Equation (5) for esparto Types 1, 2, and 3 are 0.0395, 0.0300, and 0.0383, respectively (see Table 2). Therefore, the average error for all data was less than 4%. We notice, however, that the empirical model underestimates the sound absorption at low frequencies, which is known as a limitation of this empirical approach [33].
It should be noted that the sound-absorption results shown above do not include the effect of an air gap behind the material. It is well-known that the introduction of an air cavity between the material and the rigid backing surface can increase the sound-absorption performance at low frequencies [1,30]. Although this air gap reduces the total stiffness reactance, it increases the thickness of the combination and may also increase the influence of antiresonances [30].
Although the structural integrity of the samples made in this study is not assured, practical and sustainable sound-absorbing panels based on esparto fiber may be constructed by inserting the esparto fiber into acoustically transparent bags, such as jute bags, as suggested by Berardi and Iannace for similar natural fibers [8].
Future work should also include analysis of the effects of adding fire retardant or insect repellent, improving durability, and other considerations for practical purposes.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the work presented in this communication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by CONICYT-FONDECYT, grant number 1171110.
Acknowledgments
The authors are deeply grateful to Juan Merino for his support in providing the natural fiber samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Crocker, M.J.; Arenas, J.P. Use of sound-absorbing materials. In Handbook of Noise and Vibrations; Crocker, M.J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 696–713. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Crocker, M.J. Recent trend in porous sound-absorbing materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Asdrubali, F. Eco-materials with noise reduction properties. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martinez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3031–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P. Applications of Acoustic Textiles in Automotive/Transportation. In Acoustic Textiles; Padhye, R., Nayak, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Efendy, M.G.A.; Le, T.M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Schiavoni, S.; Horshenkov, K. A review of sustainable materials for acoustic applications. Build. Acoust. 2012, 19, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruk, H.; Genc, G. Investigation of the acoustic properties of bio luffa fiber and composite materials. Mater. Lett. 2015, 157, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, S.; Küçük, H. Investigation of industrial tea-leaf-fibre waste material for its sound absorption properties. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.H.; Nor, M.J.M.; Ayub, M.; Leman, Z.A. Utilization of coir fiber in multilayer acoustic absorption panel. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.H.; Ayub, M.; Nor, M.J.M. Analysis of coir fiber acoustical characteristics. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramis, J.; del Rey, R.; Alba, J.; Godinho, L.; Carbajo, J. A model for acoustic absorbent materials derived from coconut fiber. Mater. Constr. 2014, 64, e008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.A.; Raja, R.I.; Rahman, R.A. Experimental study on natural fibers for green acoustic absorption materials. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 10, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Oldham, D.J.; Egan, C.A.; Cookson, R.D. Sustainable acoustic absorbers from the biomass. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Li, Y. Sound absorption performance of natural fibers and their composites. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 2278–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Yan, X. Corn husk for noise reduction: Robust acoustic absorption and reduced thickness. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 134, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G.; Di Gabriele, M. The acoustic characterization of broom fibers. J. Nat. Fibers 2017, 14, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Z.Y.; Putra, A.; Nor, M.J.M.; Yaakob, M.Y. Sound absorption performance of natural kenaf fibres. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 130, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, T.; Tsujiuchi, N.; Adachi, A. The development of sound absorbing materials using natural bamboo fibers. High performance structures and composites. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2002, 59, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Malawade, U.A.; Jadhav, M.G. Investigation of the acoustic performance of bagasse. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, T.S.; Navacerrada, M.A.; Diaz, C.; Fernandez-Morales, P. Fique fibres as a sustainable material for thermoacoustic conditioning. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, C.; Taktak, M.; Zein, A.; Hentati, T.; Elnady, T.; Fakhfakh, T.; Haddar, M. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the acoustic performance of sugarcane wastes-based material. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 109, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Or, K.H.; Putra, A.; Selamat, M.Z. Oil palm empty fruit bunch fibres as sustainable acoustic absorber. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 119, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taban, E.; Khavanin, A.; Faridan, M.; Samaei, S.E.; Samimi, K.; Rashidi, R. Comparison of acoustic absorption characteristics of coir and date palm fibers: Experimental and analytical study of green composites. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Or, K.H.; Selamat, M.Z.; Nor, M.J.M.; Hassan, M.H.; Prasetiyo, I. Sound absorption of extracted pineapple-leaf fibres. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 136, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.Y.; Cho, H.M.; Kim, Y.U.; Lee, S.C.; Berardi, U.; Kim, S. Circular reutilization of coffee waste for sound absorbing panels: A perspective on material recycling. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, Y. Sound Absorption Characterization of Natural Materials and Sandwich Structure Composites. Aerospace 2018, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusno, A.; Sakagami, K.; Okuzono, T.; Toyoda, M.; Otsuru, T.; Mulyadi, R.; Kamil, K. A pilot study on the sound absorption characteristics of chicken feathers as an alternative sustainable acoustical material. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.F.; Atalla, N. Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Delany, M.; Bazley, E. Acoustical properties of fibrous absorbent materials. Appl. Acoust. 1970, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Predicting the sound absorption of natural materials: Best-fit inverse laws for the acoustic impedance and the propagation constant. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 115, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechel, F. Eine Modelltheorie zum Faserabsorber Teil I: Regulare Faserordnung. Acustica 1976, 36, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Miki, Y. Acoustical properties of porous materials—Modifications of Delany-Bazley models. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. E 1990, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenborough, K. Acoustical characteristics of porous materials. Phys. Rep. 1982, 82, 179–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, I.P.; Davern, W.A. Calculation of acoustic impedance of multi-layer absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 1986, 19, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, M.; Pompoli, F. A simple empirical model of polyester fibre materials for acoustical applications. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rey, R.; Alba, J.; Arenas, J.P.; Sanchis, V. An empirical modelling of porous sound absorbing materials made of recycled foam. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 604–609. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Rebolledo, J.; del Rey, R.; Alba, J. Sound absorption properties of unbleached cellulose loose-fill insulation material. Bioresources 2014, 9, 6227–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.C.B.; Terashima, F.J.H.; Barbieri, N.; de Lima, K.F. Sound absorption coefficient assessment of sisal, coconut husk and sugar cane fibers for low frequencies based on three different methods. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 156, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sair, S.; Mansouri, S.; Tanane, O.; Abboud, Y.; El Bouari, A. Alfa fiber-polyurethane composite as a thermal and acoustic insulation material for building applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousshine, S.; Boubel, A.; Garoum, M.; Ammar, A. Sound absorption measurements of bio-sourced esparto-fibres: Effect of the compression. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Maghchiche, A.; Haouam, A.; Immirzi, B. Extraction and characterization of Algerian alfa grass short fibers (Stipa Tenacissima). Chem. Chem. Technol. 2013, 7, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadji, H.; Diouf, P.N.; Benaboura, A.; Bedard, Y.; Riedl, B.; Stevanovic, T. Comparative study of lignins isolated from Alfa grass (Stipa tenacissima L.). Biores Technol. 2009, 100, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, S.; Koubaa, A.; Khadhri, A.; Ksontini, M.; Smiti, S. Variations in the morphological characteristics of Stipa tenacissima fiber: The case of Tunisia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10534-2. Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes—Part 2: Transfer-Function Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneve, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ingard, K.U.; Dear, T.A. Measurement of acoustic flow resistance. J. Sound Vib. 1985, 403, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9053. Acoustics—Determination of Airflow Resistance—Part 1: Static Airflow Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- del Rey, R.; Alba, J.; Arenas, J.P.; Ramis, J. Evaluation of two alternative procedures for measuring airflow resistance of sound absorbing materials. Arch. Acoust. 2013, 38, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comp. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias, J.C.; Reeds, J.A.; Wright, M.H.; Wright, P.E. Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead simplex method in low dimensions. SIAM J. Optimiz. 1998, 9, 112–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).