Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Toxic Epiphytic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.2. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.3. Culture, DNA Extraction, and PCR Amplification
2.4. Design of Species-Specific Primers
2.5. qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions
3.2. Collected Macroalgae Species and Attachment Rates
3.3. Morphological Features of Ostreopsis cf. ovata
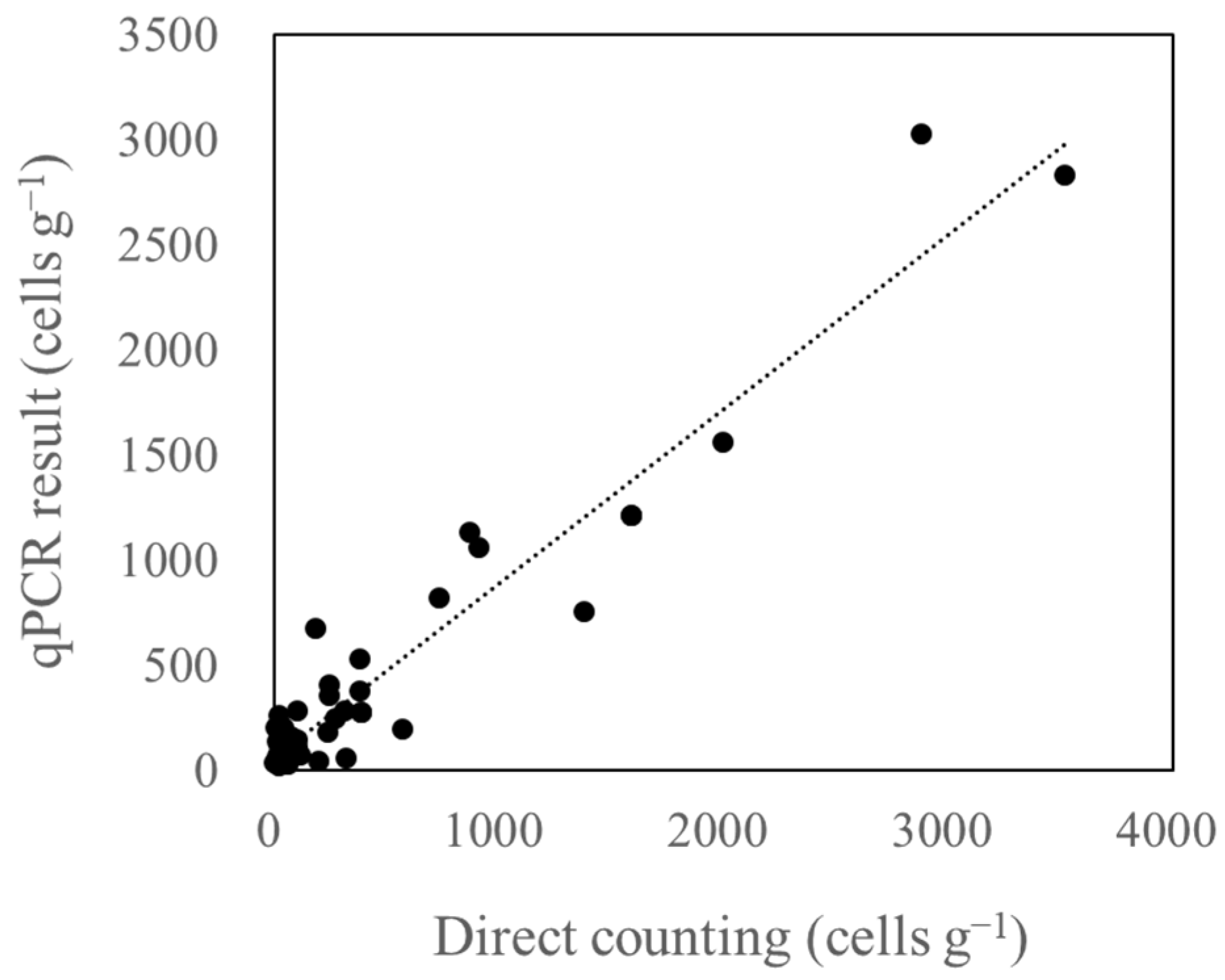
3.4. Relationship between Microscopic Analysis and qPCR Results
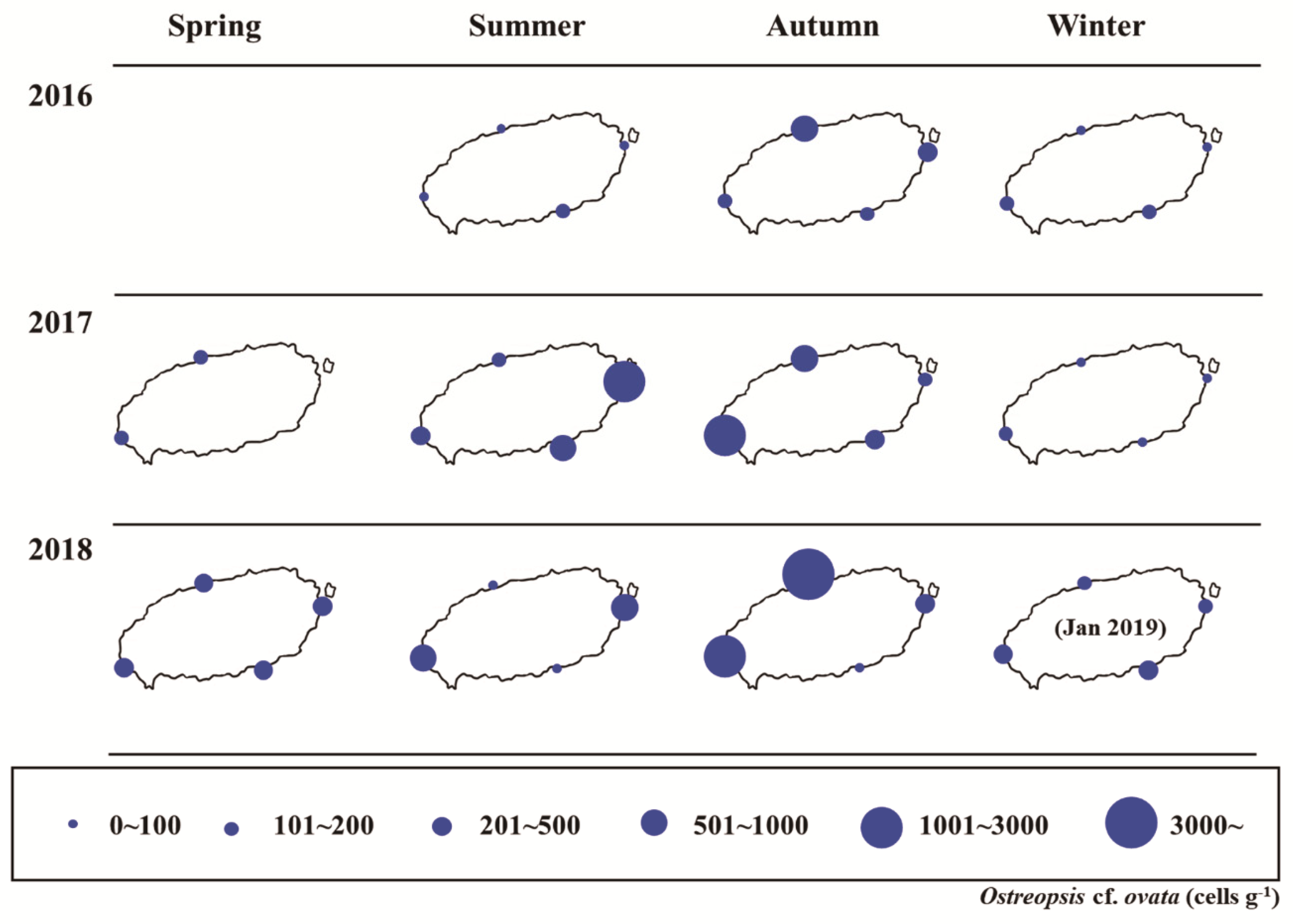
3.5. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Ostreopsis cf. ovata
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsons, M.L.; Aligizaki, K.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Fraga, S.; Morton, S.L.; Penna, A.; Rhodes, L. Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis: Reassessment of the state of knowledge of their taxonomy, geography, ecophysiology, and toxicology. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accoroni, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Penna, A.; Capellacci, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Abboud–Abi Saab, M.; Giussani, V.; Asnaghi, V. Ostreopsis fattorussoi sp. nov.(Dinophyceae), a new benthic toxic Ostreopsis species from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 1064–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gémin, M.-P.; Réveillon, D.; Hervé, F.; Pavaux, A.-S.; Tharaud, M.; Séchet, V.; Bertrand, S.; Lemée, R.; Amzil, Z. Toxin content of Ostreopsis cf. ovata depends on bloom phases, depth and macroalgal substrate in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Seino, N.; Murakami, Y.; Murata, M. Toxins produced by benthic dinoflagellates. Biol. Bull. 1987, 172, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukena, T.; Satake, M.; Usami, M.; OSHiMA, Y.; Naoki, H.; Fujita, T.; Kan, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structure elucidation of ostreocin D, a palytoxin analog isolated from the dinoflagellate Ostreopsis siamensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2585–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichadou, L.; Glaizal, M.; Armengaud, A.; Grossel, H.; Lemée, R.; Kantin, R.; Lasalle, J.-L.; Drouet, G.; Rambaud, L.; Malfait, P. Health impact of unicellular algae of the Ostreopsis genus blooms in the Mediterranean Sea: Experience of the French Mediterranean coast surveillance network from 2006 to 2009. Clin. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Fleming, L.E.; Gowen, R.; Davidson, K.; Hess, P.; Backer, L.C.; Moore, S.K.; Hoagland, P.; Enevoldsen, H. Marine harmful algal blooms, human health and wellbeing: Challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2016, 96, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibiriçá, C.E.J.; Leite, I.P.; Batista, T.V.; Fernandes, L.F.; Chomérat, N.; Herve, F.; Hess, P.; Mafra, L.L. Ostreopsis cf. ovata Bloom in Currais, Brazil: Phylogeny, Toxin Profile and Contamination of Mussels and Marine Plastic Litter. Toxins 2019, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Kana, T.M. Recent insights about relationships between nutrient availability, forms, and stoichiometry, and the distribution, ecophysiology, and food web effects of pelagic and benthic Prorocentrum species. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Feller, A.; Riccardi, M.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M. Comparative growth and toxin profile of cultured Ostreopsis ovata from the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Seas. Toxicon 2010, 55, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, K.; Capper, A.; Sparrow, L. Ocean surface warming: Impact on toxic benthic dinoflagellates causing ciguatera. ELS 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Battocchi, C.; Crinelli, R.; Carloni, E.; Magnani, M. Unique toxin profile of a Mediterranean Ostreopsis cf. ovata strain: HR LC-MS n characterization of ovatoxin-f, a new palytoxin congener. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.S.; Yoon, E.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Yih, W.; Park, J.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Rho, J.-R. Ostreol A: A new cytotoxic compound isolated from the epiphytic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata from the coastal waters of Jeju Island, Korea. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3023–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selina, M.S.; Orlova, T.Y. First occurrence of the genus Ostreopsis (Dinophyceae) in the Sea of Japan. Bot. Mar. 2010, 53, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, G.S.; Tartaglione, L.; Grillo, C.; Melchiorre, N. The Genoa 2005 Outbreak. Determination of Putative Palytoxin in Mediterranean Ostreopsis o vata by a New Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialajo, L.; Bertolotto, R.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Chiantore, M.; Grillo, C.; Lemee, R.; Melchiorre, N.; Moretto, P.; Povero, P.; Ruggieri, N. The toxic benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata: Quantification of proliferation along the coastline of Genoa, Italy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Nau, A.W.; Holland, W.C.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Tester, P.A. Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Chomerat, N.; Grossel, H.; Marco-Miralles, F.; Lemee, R.; Nezan, E.; Sechet, V. Ovatoxin-a and palytoxin accumulation in seafood in relation to Ostreopsis cf. ovata blooms on the French Mediterranean coast. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Munday, R.; Suda, S.; Molenaar, S.; Hallegraeff, G. Dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum identified as the causative organism of pinnatoxins in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Phycologia 2011, 50, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohu, S.; Thibaut, T.; Mangialajo, L.; Labat, J.-P.; Passafiume, O.; Blanfuné, A.; Simon, N.; Cottalorda, J.-M.; Lemée, R. Occurrence of the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in relation with environmental factors in Monaco (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohu, S.; Mangialajo, L.; Thibaut, T.; Blanfuné, A.; Marro, S.; Lemée, R. Proliferation of the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in relation to depth, biotic substrate and environmental factors in the North West Mediterranean Sea. Harmful Algae 2013, 24, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totti, C.; Accoroni, S.; Cerino, F.; Cucchiari, E.; Romagnoli, T. Ostreopsis ovata bloom along the Conero Riviera (northern Adriatic Sea): Relationships with environmental conditions and substrata. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistocchi, R.; Pezzolesi, L.; Guerrini, F.; Vanucci, S.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E. A review on the effects of environmental conditions on growth and toxin production of Ostreopsis ovata. Toxicon 2011, 57, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accoroni, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Pichierri, S.; Colombo, F.; Totti, C. Morphometric analysis of Ostreopsis cf. ovata cells in relation to environmental conditions and bloom phases. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accoroni, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Iacovo, E.D.; Pichierri, S.; Marini, M.; Campanelli, A.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Totti, C. Influence of environmental factors on the toxin production of Ostreopsis cf. ovata during bloom events. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Shah, M. In HAN 46: Harmful Algae News No. 46 (05/09/12). Available online: http://hab.ioc-unesco.org/index.php?option=com_oe&task=viewDocumentRecord&docID=9439 (accessed on 18 May 2012).
- Kang, N.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lim, A.S.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.S.; Yih, W. Morphology and molecular characterization of the epiphytic benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the temperate waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yih, W.; Kim, J.H.; Myung, G.; Jeong, H.J. Abundance of epiphytic dinoflagellates from coastal waters off Jeju Island, Korea During Autumn 2009. Ocean Sci. J. 2011, 46, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- David, L.B.; Thomas, R.T.; Ana, T.B. Population dynamics and toxicity of natural populations of benthic dinoflagellates in southwestern Puerto Rico. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1988, 119, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Vila, M.; Camp, J.; Garcés, E.; Masó, M.; Delgado, M. High resolution spatio-temporal detection of potentially harmful dinoflagellates in confined waters of the NW Mediterranean. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Garces, E.; Maso, M. Potentially toxic epiphytic dinoflagellate assemblages on macroalgae in the NW Mediterranean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 26, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoni, G.; Borghini, B.; Camici, G.; Casotti, M.; Righini, P.; Rustighi, C. Fioriture algali di Ostreopsis ovata (Gonyaulacales: Dinophyceae): Un problema emergente. Biol. Ambient. 2003, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.L.; Preskitt, L.B. A survey of epiphytic dinoflagellates from the coastal waters of the island of Hawai. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, S. Distribution of toxic dinoflagellates along the leaves of seagrass Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa from the Gulf of Tunis. Cah. de Biol. Mar. 2005, 46, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, G.; Lechuga-Devéze, C.H.; Popowski, G.; Troccoli, L.; Salinas, C.A. Epiphytic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera in the northwestern coast of Cuba. Rev. de Biol. Trop. 2006, 54, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachani, M.A.; Dhib, A.; Fathalli, A.; Ziadi, B. Harmful epiphytic dinoflagellate on Tyrrhenian Sea reefs. Harmful Algae 2003, 24, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shears, N.T.; Ross, P.M. Blooms of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Ostreopsis; an increasing and ecologically important phenomenon on temperate reefs in New Zealand and worldwide. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolodkov, Y.B.; Campos-Bautista, G.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; González-González, J.A.G.; Hoppenrath, M.; Arenas, V. Seasonal changes of benthic and epiphytic dinoflagellates in the Veracruz reef zone, Gulf of Mexico. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 47, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selina, M.S.; Morozova, T.V.; Vyshkvartsev, D.I.; Orlova, T.Y. Seasonal dynamics and spatial distribution of epiphytic dinoflagellates in Peter the Great Bay (Sea of Japan) with special emphasis on Ostreopsis species. Harmful Algae 2014, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illoul, H.; Hernández, F.R.; Vila, M.; Adjas, N.; Bournissa, M.; Koroghli, A.; Marouf, N.; Rabia, S.; Ameur, F.L.K. The genus Ostreopsis along the Algerian coastal waters (SW Mediterranean Sea) associated with a human respiratory intoxication episode. Cryptogam. Algol. 2012, 33, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Jelena, G.; Daniela, M.P.; Ljiljana, I.; Petar, K.; Patrizia, C.; Carmela, D.A.; Emma, D.I.; Ernesto, F.; Martino, F.; et al. Toxin-producing Ostreopsis cf. ovata are likely to bloom undetected along coastal areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5574–5582. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.; Oliveira, P.B.; Moita, M.T.; David, H.; Caeiro, M.F.; Zingone, A.; Amorim, A.; Silva, A. Ocurrence of Ostreopsis in two temperate coastal bays (SW iberia): Insights from the plankton. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, V.; Asnaghi, V.; Pedroncini, A.; Chiantore, M.J.H.A. Management of harmful benthic dinoflagellates requires targeted sampling methods and alarm thresholds. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Park, M.G. Genetic Analyses of the rbcL and psaA Genes From Single Cells Demonstrate a Rhodophyte Origin of the Prey in the Toxic Benthic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, L.; Chiantore, M.; Petrillo, M.; Asnaghi, V. Habitat effects on Ostreopsis cf. ovata bloom dynamics. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.P. Marine Algae of Jeju; Academic Press: Seoul, Korea, 2009; p. 477. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H. First report for appearance and distribution patterns of the epiphytic dinoflagellates in the korean peninsula. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 30, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Kurashima, A. Occurrence of the toxic benthic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus in Ago Bay, central part of Japan. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2010, 74, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nelles, L.; Fang, B.-L.; Volckaert, G.; Vandenberghe, A.; Wachter, R.D. Nucleotide sequence of a crustacean 18S ribosomal RNA gene and secondary structure of eukaryotic small subunit ribosoraal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 8749–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seo, H. Distribution and Molecular Phylogeny of the Toxic Benthic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis sp. in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Sea 2019, 24, 236–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, B.S.; Yoon, E.Y.; Jeong, E.J.; Park, J.; Kim, E.-H.; Rho, J.-R. Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Polyhydroxy Compound Ostreol B Isolated from the Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, D.R.; Morton, S.L. Community dynamics and physiology of epiphytic/bentic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera. Nato Asi Ser. G Ecol. Sci. 1998, 41, 293–314. [Google Scholar]
- Tawong, W.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Adachi, M. Effects of temperature, salinity and their interaction on growth of benthic dinoflagellates Ostreopsis spp. from Thailand. Harmful Algae 2015, 44, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Kang, H.; Oh, Y.H.; Park, S.R.; Kim, G. Green tide development associated with submarine groundwater discharge in a coastal harbor, Jeju, Korea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauzein, C.; Couet, D.; Blasco, T.; Lemée, R. Uptake of dissolved inorganic and organic nitrogen by the benthic toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. Harmful Algae 2017, 65, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-W.; Kim, G. Linking groundwater-borne nutrients and dinoflagellate red-tide outbreaks in the southern sea of Korea using a Ra tracer. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Date | Species | Origin | Abundance (Cells L−1) | Abundance (Cells g−1) | Temperature (°C) | Salinity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 October | Ostreopsis lenticularis | Caribbean Sea, Puerto Rico | 16,000 | >28 | [29] | ||
| 1995 | Ostreopsis sp. | Mediterranean, Catalan Sea | 78,000 | [30] | |||
| 1997 July | Ostreopsis sp. | Mediterranean, Catalan Sea | 596,000 | 24–26 | 37.2–38.1 | [31] | |
| 1998 August | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Ligurian Sea | 50,000 | 25 | [32] | ||
| 2001 July | Ostreopsis ovata | Islands of Hawaii | 7346 | 25.4 | 26.7 | [33] | |
| 2001 August–September | Ostreopsis siamensis | Gulf of Tunis, Tunisia | 3600 | 20–27 | 37 | [34] | |
| 2001 November | Ostreopsis sp. | Islands of Hawaii | 18,194 | 27.6 | 30.8 | [33] | |
| 2001–2002 | Ostreopsis lenticularis | northernwestern Cuba | <1000 | [35] | |||
| 2002 August | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Tyrrhenian Sea | 10,550 | [36] | |||
| 2004 February | Ostreopsis siamensis | New Zealand | 1,406,000 (±385,500) | 20 | [37] | ||
| 2005 May–December | Ostreopsis heptagona | Gulf of Mexico | 1202 | 29.5 | 31 | [38] | |
| 2006 July | Ostreopsis ovata | Mediterranean, Ligurian Sea | 87,000 (±27,000) | 2,541,000 (±588,000) | >26 | 38.0–38.2 | [16] |
| 2007 October | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Adriatic Sea | 25,200 | 1,700,000 | 16.8–21.8 | [22] | |
| 2008 June–August | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Balearic Sea | 1000 | 60,000 | 23–27.5 | [21] | |
| 2008 July | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Ligurian Sea | 213,000 | 600,000 | 22.5 | [20] | |
| 2008 September | Ostreopsis spp. | Northwestern Sea of Japan | 4213 | 17–22.2 | [39] | ||
| 2009 October | Ostreopsis spp. | Jeju Island, Korea | 8660 | 21.0–23.6 | 28.9–32.5 | [28] | |
| 2010 July–August | Ostreopsis spp. | Mediterranean, Tyrrhenian Sea | 21,680 | 79,000 | 19.8–25.8 | 36.5–37.9 | [40] |
| 2010 September–October | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Adriatic Sea | 42,600 | 334,306 | [41] | ||
| 2013 September | Ostreopsis spp. | Lagos Bay, Atlantic Ocean | 17,000 | 115,831 | 24 | [42] | |
| 2015 July | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Ligurian Sea | 51,719 | 2,289,100 | 25.9 | [43] | |
| 2016 October | Ostreopsis spp. | Lagos Bay, Atlantic Ocean | 640 | 45,251 | 20 | [42] | |
| 2017 July | Ostreopsis sp. | Korea (Pohang) | 1588 | 20–25 | 29.1–32.1 | [44] | |
| 2017 June–July | Ostreopsis cf. ovata | Mediterranean, Ligurian Sea | 81,380 | 890,528 | >25 | [45] |
| Year | Month | Jeju (N) | Gosan (W) | Wimi (S) | Seongsan (E) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. (°C) | Salinity | Temp. (°C) | Salinity | Temp. (°C) | Salinity | Temp. (°C) | Salinity | ||
| 2016 | July | 17.6 | 33.9 | 18.6 | 32.4 | 19.8 | 24.4 | 18.9 | 33.1 |
| October | 19.5 | 26.4 | 22.5 | 34.5 | 22.3 | 28.8 | 21.7 | 32.7 | |
| December | 16.9 | 32.0 | 17.5 | 34.9 | 18.6 | 33.5 | 18.2 | 35.2 | |
| 2017 | March | 15.5 | 28.1 | 15.9 | 36.1 | 15.8 | 33.1 | 14.4 | 35.0 |
| July | 24.3 | 22.7 | 23.3 | 32.7 | 20.8 | 23.5 | 25.5 | 31.9 | |
| October | 20.0 | 27.1 | 21.9 | 33.1 | 21.9 | 30.4 | 21.2 | 32.8 | |
| 2018 | January | 12.1 | 29.6 | 11.3 | 34.4 | 14.0 | 29.6 | 12.9 | 34.3 |
| March | 16.0 | 28.7 | 17.0 | 34.3 | 16.2 | 28.2 | 14.6 | 34.1 | |
| July | 23.8 | 24.8 | 24.5 | 32.5 | 22.8 | 27.7 | 23.6 | 32.0 | |
| September | 24.4 | 33.2 | 26.3 | 32.6 | 24.2 | 26.4 | 24.3 | 32.4 | |
| 2019 | January | 12.7 | 32.2 | 14.2 | 34.4 | 16.9 | 34.2 | 14.8 | 34.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Hwang, J.; Hyung, J.-H.; Yoon, E.Y. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Toxic Epiphytic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5864. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145864
Park J, Hwang J, Hyung J-H, Yoon EY. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Toxic Epiphytic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Sustainability. 2020; 12(14):5864. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145864
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jaeyeon, Jinik Hwang, Jun-Ho Hyung, and Eun Young Yoon. 2020. "Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Toxic Epiphytic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5864. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145864
APA StylePark, J., Hwang, J., Hyung, J.-H., & Yoon, E. Y. (2020). Temporal and Spatial Distribution of the Toxic Epiphytic Dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata in the Coastal Waters off Jeju Island, Korea. Sustainability, 12(14), 5864. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145864





