Strategic Aspects of Asset Management: An Overview of Current Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Data
2.1. Designing the Search Request
2.2. Bibliometric Analysis
- On the first step, the software extracted terms with a condition “both from title and abstract” (in order to ensure the inclusion of all relevant terms as we already filtered articles by title).
- On the second step, we chose the condition “use full counting of terms” (it allows to count any appearance of the term, not only its mere presence or absence as in condition “binary count”); thus, more than 13,000 terms were extracted.
- On the third step, we chose the condition “minimum 5 occurrences of a term” (in order to reduce superfluous terms and ensure that only relevant terms are taken into account); as a result, the number of terms was reduced to 875.
- Finally, we manually reduced this number to the 161 most relevant terms that present direct interest for the aims of our study.
2.3. Systematic Literature Review—Epistemological Orientations
2.4. Systematic Literature Review—Contextualization of Strategy
- Corporate level: How to gain advantage from managing a set of businesses?
- Business/competitive level: How to gain and sustain a competitive advantage for a single line of business?
- Functional level: How to manage a particular activity within a business in ways that support the business strategy?
3. Results
3.1. Exploring the Importance of Strategic Asset Management Research in the Field of Asset Management
- Asset (physical, engineering, fleet, infrastructure)
- Asset-intensive business
- Facilities management (excluding real estate)
- Asset management vs. maintenance
- Corporate and enterprise asset management
- Strategic asset management and asset management strategy
- Maintenance (including performance measurement)
- Asset life-cycle management
- (1) “Operational level decision making” with a clear focus on maintenance, decision making and system reliability;
- (2) “Asset life cycle management” with a clear focus on managing asset life cycles and risk with information technology support;
- (3) “Strategic asset management” with a clear focus on strategy, efficiency, enterprise level decision making;
- (4) “Organizational aspects of asset management” with a clear focus on change, culture, and human factor;
- (5) “Asset information management” with a clear focus on the role of information technology in supporting decision making and continuous improvement.
- Cluster (1) through terms “asset management strategy,” “condition,” (in (1) asset condition is described e.g., through “ageing” and “deterioration”), “decision making” (“decision support tool” in (3)), “effective manager” (partially related to “effectiveness” in (3)), “maintenance” (different variations of terms related to maintenance in both clusters), “performance” (“performance measurement” in (3));
- Cluster (2) through terms “long term” (we presume that long term orientation implies a strategic view), “life cycle,” “performance measurement,” “cost” (both clusters contain terms connected with cost);
- Cluster (4) through terms “sustainability” (“sustainable management” in (3)), “maintenance” (both terms in different variations), “manager” (in (1) “asset manager”), and “effectiveness” (in (2) “effective asset manager”);
- Cluster (5) through terms “historical data” (we presume that data management and information management are related fields), “human resource” (“maintenance manager,” “manager” in cluster” (1)), “continuous improvement” (implicitly related to sustainability), “decision support” (“decision support tool” in (3)).
3.2. Exploring the Nature of Strategic Asset Management Research
3.3. Exploring the Possibility to Align Asset Management Strategies With Different Levels of Organizational Strategy
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Further Interpretation of Results Within Strategic Management Literature
4.3. Implications, Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| # | Snowballing Stages | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Start set: 20 articles | [1,2,9,10,15,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115] |
| 2 | 1st iteration (backward snowballing): 21 articles | [28,29,30,34,42,44,45,48,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128] |
| 3 | 2nd iteration (forward snowballing): 26 articles | [4,11,13,14,33,35,68,78,117,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144] |
| 4 | Second loop: 8 articles | [36,108,145,146,147,148,149,150] |
Appendix B
| Articles | Corporate | Competitive | Functional | Operational | |
| Unit of Analysis | Contextualization of AM strategy | ||||
| Alegre, H. (2010) [49] | + (global context, stakeholders’ expectations) | + (tactical planning) | + (implementation of plans) | ||
| Anderson, Keleher & Smith (2008) [50] | + | ||||
| Bakir & Raine (2018) [37] | + (key performance indicators, strategic asset management program) | + (field staff) | |||
| Baum & Vlok (2013) [38] | + (senior sponsorship, motivation, supportive culture) | + (decision networks, information network for maintenance planning) | |||
| Beitelmal et al. (2017) [51] | + (influence of external environment, long-term planning, stakeholders’ satisfaction) | + (KPIs, asset management policy and culture, organizational support, organizational structure) | + (asset management processes) | ||
| Brown et al. (2014) [78] | + (vision, mission & values, corporate governance, policy, objectives & strategy, external context, multi-agencies cooperation, sustainability management, allocation and prioritization of limited financial resources, leadership & change management) | + (industry & market structure) | + (asset life-cycle management, AM policy, objectives & strategy, evaluation of asset performance) | + (service delivery, operational planning) | |
| Caradot et al. (2017) [52] | + | ||||
| Clements & Mancarella (2018) [46] | + | ||||
| El-Akruti, Dwight & Zhang (2013) [39] | + (product cost and price, quality and quantity, business performance and profit margin, competitive position, maintenance as key to competitive advantage) | + (asset life cycle & supporting activities) | + (asset performance) | ||
| El-Akruti, Kiridena & Dwight (2018) [3] | + (corporate mission & goals, organizational change on response to external pressures) | + (competitive demands & priorities) | + (asset-related supporting activities) | + (asset performance) | |
| Geiss & Guder (2017, December) [53] | + | ||||
| Godau & McGeoch (2016) [69] | + (CEO and key stakeholders’ involvement, communication & continuous improvement) | + (asset management objectives, roles, functions & documentation, asset management maturity, asset life cycle, standardization) | + (asset criticality & hierarchy, asset data) | ||
| Hanski et al. (2016) [70] | + (stakeholders’ expectations, sustainability issues, external environment) | + (customer-driven approach to business) | + (ISO 55000 guidelines adoption, AM risks, roles & responsibilities) | + (asset data on criticality & failure, asset information management) | |
| Herder & Wijnia, (2012) [15] | + (resource allocation, external change & adaptation, public interests) | + (systems approach, creating value from assets, asset design, risk management, agent-based modelling, optimization of AM process) | + | ||
| Hogan et al. (2011) [71] | + (resource allocation, organizational change) | + (higher quality and lower operational costs) | + (maintenance planning & strategy from tactical point of view) | ||
| Jolicoeur & Barrett (2005) [31] | + (budget constraints, investment decisions, stakeholder involvement, long term planning) | + (cost-effectiveness, market positioning) | + (asset management planning & performance of assets, asset life cycle) | + (service delivery, asset rationalization) | |
| Joseph et al. (2018) [72] | + (policies form regulators & investors, organizational culture and support) | + (new product introduction to provide added value) | + (choice of optimal asset management strategy, asset displacement decisions) | + (asset utilization) | |
| Kannapiran et al. (2008) [54] | + | ||||
| Kauer & Sacher (2004) [55] | + (acceptance of senior management) | + (economic efficiency/cost-effectiveness) | + (asset risk management, asset life cycle) | + (asset inspection & servicing) | |
| Khasnabis, Bartus & Ellis (2004) [56] | + (limited funds distribution, long-term fleet planning) | + (replacement vs. rebuilding programs) | + (fleet data) | ||
| Komonen, Kortelainen & Räikkonen (2006) [36] | + (scenarios of strategic development, green-field, expansion & replacement investment decisions, strategic change & long-term perspective) | + (market & industry structure, portfolio of competitive advantage: effectiveness/flexibility) | + (asset life cycle management, maintaining and optimizing asset value, improving profit-making capability, choice of maintenance strategy, asset risk management) | + (system and equipment level objectives & constraints) | |
| Komonen, Kortelainen, & Räikkönen (2012) [1] | + (resource allocation & investment decisions, stakeholders’ expectations, external pressures, shareholders’ demands, values, visions, long-term objectives & strategy, portfolio management, decisions on mergers, disposals, outsourcing & production cooperation) | + (competitive advantage & changing demand, industry structure, barriers to entry & sources of differentiation, resources & competencies development) | + (asset life cycle management & optimization, optimal capacity, equipment effectiveness, reliability & flexibility, lower maintenance costs, asset criticality, improvement, replacement & maintenance programs) | + (operation and maintenance) | |
| Kortelainen, Happonen & Kinnunen (2016) [68] | + (capital investment decisions, business objectives & performance, in-house or outsourcing decisions, co-operation with service providers, stakeholder management, requirements for sustainability & safety) | + (asset life cycle management, asset portfolio, KPI) | + (operational success factors) | ||
| Laue et al. (2014) [14] | + (corporate governance, policy & strategy, stakeholder management, risk & sustainability, inter-organizational collaboration, regulatory pressures) | + (asset governance, AM policy, strategy & plans, performance measurement & audit, AM capability & maturity) | + (operations & maintenance, condition monitoring) | ||
| Liyanage (2012) [10] | + (influence of stakeholders & external demands) | + (resources & capabilities, creation of value, business climate) | + (asset information management, integration of systems & interoperability of solutions, AM excellence & multidisciplinary approach, asset life cycle) | + (provision of service) | |
| Maletič et al. (2018) [13] | + (sustainable development goals: economic, environmental, employee-related social performance, stakeholders’ expectations) | + (gaining competitive advantage, resources & capabilities) | + (AM policy& strategy, risk management, performance assessment, lifecycle management, optimizing cost, performance & risk, continuous improvement) | ||
| Martin et al. (2015) [61] | + (stakeholders’ expectations, mobilization of limited resources, legislative & regulatory requirements) | + (industry influence) | + (AM plans, practices, policy and strategy, forecasting & modelling, proactive risk management) | + (service level) | |
| Mathieu et al. (2017, December) [62] | + (regulatory pressures) | + (high quality/low cost) | + (balancing performance, risk and costs, asset life cycle, KPIs, asset manager as a tactical layer of decision-making) | + (operational excellence, provision of services) | |
| Matthews, Piratla & Koo (2016) [59] | + (leadership, resources allocation, climate and risk, environmental pressures) | + (reactive/proactive strategies) | + (active condition assessment) | ||
| Ngo, Shah & Mishra (2018) [58] | + (limited resources allocation) | + (cost-effectiveness) | + (decisions on purchase, replacement & rehabilitation of fleet) | + (operations & maintenance to increase service life) | |
| Ossai, Boswell & Davies (2014) [60] | + (stakeholders’ expectations) | + (plant management, initiation of sustainable asset management programs, compliance with KPIs) | + (operations & maintenance) | ||
| Park, S., Park, S.I., & Lee (2016) [63] | + (regulatory pressures & limited budget allocation) | + (AM policies, strategies, plans, register, life cycle assessment) | + (operations, asset utilization) | ||
| Patidar, Soni, V.K., & Soni, P.K. (2017) [33] | + (senior management support & continuous improvement) | + (maintenance function, performances & manufacturing performance) | |||
| Pidwerbesky, Hunt & Douglas (2007) [64] | + (outsourcing vs. in-house, current and new business opportunities) | + (client expectations) | + (regional asset management network, communications, relationship management & procurement) | + (regional maintenance managers) | |
| Pinjala, Pintelon & Vereecke (2006) [44] | + (in-house or outsourcing, organizational structure & design) | + (competitive priorities/basis for competition: cost, quality, flexibility) | + (maintenance strategy, maintenance policy & strategy, maintenance as a separate part of the primary activities within the value chain, performance measurement) | ||
| Posavljak, Tighe & Godin (2013) [40] | + (resource allocation, long-term planning of investments) | + (minimal cost to the public) | + (maximization of network performance, choice between routine maintenance, preservation & rehabilitation, life cycle cost analysis) | + (maintenance) | |
| Roshani & Filion (2014) [47] | + (budget limitations) | + (optimization of rehabilitation, optimal allocation of limited financial resources, choice of asset management strategy) | |||
| Stimie & Vlok (2016) [32] | + (strategic direction, organizational design, communication, change management) | + (sustainable competitive advantage) | + (AM systems, processes, practices, commitment) | ||
| Suryani et al. (2015, March) [41] | + (long-term financing decisions) | + (maintenance and renewal strategies, network reliability) | + (periodical maintenance and inspections) | ||
| Swanson (2001) [48] | + (business performance, quality & productivity, cost reduction) | + (choice of maintenance strategy, asset design, monitoring & analysis) | |||
| Szasz & MacDonald (2012) [65] | + (reinvestment cycle) | + (revenue generation, competitive pressure, expectation of business and financial performance) | + (reliability and availability plans and risks, asset life cycle) | + (condition monitoring, failure reporting) | |
| Tafazzoli (2017, October) [66] | + (resource allocation, decisions on infrastructure expansion, environmental pressures) | + (revenue risks) | + (policies and practices, balancing resources across assets, upgrading assets, continuous improvement, extending service-life) | + (maintaining and operating, data collection) | |
| Tranfield, Denyer & Burr (2004) [45] | + (planning for capital investment, stakeholder’s engagement, business objectives, capital investment, decisions on in-house/outsourcing) | + (asset strategy, knowledge & monitoring, balancing risks, costs and performance throughout the life cycle of assets) | + (service delivery) | ||
| Tsang (1998) [28] | + (strategic objectives, budget constraints & resource allocation) | + (business performance & core competence) | + (maximizing asset utilization in terms of costs and outputs, performance measurement) | + (service delivery & maintenance operation) | |
| Tsang (2002) [30] | + (organizational design & contracts) | + (customer orientation, business performance) | + (maintenance support, integration with operations, focus on performance, asset life cycle) | ||
| Tsang, Jardine & Kolodny (1999) [29] | + (mission & strategic objectives, in-house or outsourcing decisions) | + (competitive environment & business performance) | + (KPI, business process reengineering) | + (operational efficiency) | |
| Velmurugan & Dhingra (2015) [35] | + (vision of the organization, adaptability to changes on the environment) | + (business targets, customer needs, availability of resources for reaching strategic objectives) | + (maintenance function, maintenance strategy selection and optimization) | + (operating systems, maintenance performance measurement) | |
| Wenzler (2005) [42] | + (regulatory pressures, limited resource allocation) | + (higher quality with lower costs, business capabilities, market structure & competition, commercial goals) | + (keeping assets healthy and operational, replacement decisions, asset design, financial returns on assets, failure modelling) | + (operation and maintenance, asset information quality, quality of service) | |
| White, Too, E., & Too, L. (2010) [8] | + (limited funding, globalization, stakeholder demands, overall performance, long term organizational goals, values, strategy & structure) | + (returns to scale, monopolistic & regulated markets, added value, customer needs, competencies & capabilities for sustaining competitive advantage, focus on customers and accountability of results) | + (performance of assets, optimal allocation of scarce resources, asset portfolio, AM goals, roles & responsibilities) | + (operation) | |
| Wijnia & de Croon (2019) [11] | + (long-term development of asset base in terms of costs, performance and risk) | + (life-cycle optimization, failure modelling, optimal strategy choice) | + (asset risk and age profiles, asset data) | ||
| Yahaya et al. (2018) [43] | + | ||||
| Yeung, Chu & NG (2015) [67] | + (communications with stakeholders, authority, long term strategic plan & goals, change management, decisions on outsourcing) | + (balancing risk & performance, optimizing life cycle cost in long term perspective, continuous improvement of AM system, AM practices, plans & policies, risk management) | + (maintenance, asset database, operational procedures, control activities) | ||
| Yiu (2008) [34] | + (make-or-buy decision, outsourcing/insourcing/co-sourcing) | + (benchmarking) | + (facilities management as market-firm decisions) | ||
References
- Komonen, K.; Kortelainen, H.; Räikkönen, M. Corporate asset management for industrial companies: An integrated business-driven approach. In Asset Management: The State of the Art in Europe from a Life Cycle Perspective; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 47–63. ISBN 9789400727243. [Google Scholar]
- Schraven, D.F.J.; Hartmann, A.; Dewulf, G.P.M.R. Research orientations towards the ‘management’ of infrastructure assets: An intellectual structure approach. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 11, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akruti, K.; Kiridena, S.; Dwight, R. Contextualist-retroductive case study design for strategic asset management research. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantakos, P.C.; Chountalas, P.T.; Magoutas, A.I. The contemporary landscape of asset management systems. Qual. Access Success 2019, 20, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bulita, H. Fundamentals of Real Property Administration; BOMI Institute: Arnold, MD, USA, 1994; ISBN 1573900001. [Google Scholar]
- White, E.N. Terotechnology (Physical Asset Management). Min. Technol. 1975, 57, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, N.A.J. Physical Asset Management; Springer: Quensland, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- White, A.D.; Too, E.; Too, L. Strategic infrastructure asset management: A conceptual framework to identify capabilities. J. Corp. Real Estate 2010, 12, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi-Echendu, J.E.; Willett, R.; Brown, K.; Hope, T.; Lee, J.; Mathew, J.; Vyas, N.; Yang, B.S. What is engineering asset management? In Definitions, Concepts and Scope of Engineering Asset Management; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 3–16. ISBN 9781849961776. [Google Scholar]
- Liyanage, J.P. Smart engineering assets through strategic integration: Seeing beyond the convention. In Asset Management: The State of the Art in Europe from a Life Cycle Perspective; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 11–28. ISBN 9789400727243. [Google Scholar]
- Wijnia, Y.; de Croon, J. Strategic asset planning: Balancing cost, performance and risk in an ageing asset base. In Asset Intelligence through Integration and Interoperability and Contemporary Vibration Engineering Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenburg, R.J.; Braaksma, J.J.J.; Van Dongen, L.A.M. Asset life cycle plans: Twelve steps to assist strategic decision-making in asset life cycle management. In Optimum Decision Making in Asset Management; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 259–287. ISBN 9781522506522. [Google Scholar]
- Maletič, D.; Maletič, M.; Al-Najjar, B.; Gomišček, B. Development of a model linking physical asset management to sustainability performance: An empirical research. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laue, M.; Brown, K.; Scherrer, P.; Keast, R. Integrated strategic asset management: Frameworks and dimensions. In Infranomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Herder, P.M.; Wijnia, Y. A systems view on infrastructure asset management. In Asset Management: The State of the Art in Europe from a Life Cycle Perspective; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 31–46. ISBN 9789400727243. [Google Scholar]
- Hodkiewicz, M.R. The development of ISO 55000 series standards. In Engineering Asset Management-Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 427–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, London, UK, 13–14 May 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, R.; Tunger, D. Science indicators revisited—Science citation index versus SCOPUS: A bibliometric comparison of both citation databases. Inf. Serv. Use 2006, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.; Wang, J. Coverage and overlap of the new social sciences and humanities journal lists. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gomes, L.A.V.; Facin, A.L.F.; Salerno, M.S.; Ikenami, R.K. Unpacking the innovation ecosystem construct: Evolution, gaps and trends. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Peacock, R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: Audit of primary sources. Br. Med. J. 2005, 331, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Procedures for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; Keele University & Durham University: Durham, UK, 2007; ISBN 1353-7776. [Google Scholar]
- Van Raan, A.F. Advances in bibliometric analysis: Research performance assessment and science mapping. In Bibliometrics: Use and Abuse in the Review of Research Performance; Portland Press Ltd.: London, UK, 2014; pp. 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L.; Dekker, R.; Van Den Berg, J. A comparison of two techniques for bibliometric mapping: Multidimensional scaling and VOS. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bakker, F.G.A.; Groenewegen, P.; Den Hond, F. A bibliometric analysis of 30 years of research and theory on corporate social responsibility and corporate social performance. Bus. Soc. 2005, 44, 283–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R.T. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Q. 2002, 26, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Peteraf, M.; Gamble, J.; Strickland III, A.J.; Jain, A.K. Crafting & Executing Strategy: The Quest for Competitive Advantage: Concepts and Cases; McGraw-Hill Education: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 0078029503. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, A.H. A strategic approach to managing maintenance performance. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 1998, 4, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.H.C.; Jardine, A.K.S.; Kolodny, H. Measuring maintenance performance: A holistic approach. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1999, 19, 691–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A.H. Strategic dimensions of maintenance management. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2002, 8, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolicoeur, P.W.; Barrett, J.T. Coming of age: Strategic asset management in the municipal sector. J. Facil. Manag. 2005, 3, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimie, J.E.; Vlok, P.J. A mechanism for the early detection and management of physical asset management strategy execution failure. South African J. Ind. Eng. 2016, 27, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, L.; Soni, V.K.; Soni, P.K. Maintenance strategies and their combine impact on manufacturing performance. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 7, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yiu, C.Y. A conceptual link among facilities management, strategic management and project management. Facilities 2008, 26, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, R.S.; Dhingra, T. Maintenance strategy selection and its impact in maintenance function: A conceptual framework. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2015, 35, 1622–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komonen, K.; Kortelainen, H.; Räikkonen, M. An asset management framework to improve longer term returns on investments in the capital intensive industries. In Proceedings of the 1st World Congress on Engineering Asset Management, WCEAM 2006, Gold Coast, Australia, 11–14 July 2006; pp. 418–432. [Google Scholar]
- Bakir, P.; Raine, C. Engaging field staff in strategic asset management. J. Water, Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2018, 8, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.; Vlok, P.J. Mapping primary constraints in physical asset management strategy execution, using social network analysis. South African J. Ind. Eng. 2013, 24, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Akruti, K.; Dwight, R.; Zhang, T. The strategic role of Engineering Asset Management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posavljak, M.; Tighe, S.L.; Godin, J.W. Strategic total highway asset management integration. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2354, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryani, E.; Hendrawan, R.A.; Faster, E.A.P.; Dewi, L.P. A simulation model for strategic planning in asset management of electricity distribution network. In Proceedings of the Communications in Computer and Information Science, Bali, Indonesia, 11–14 March 2015; pp. 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzler, I. Development of an asset management strategy for a network utility company: Lessons from a dynamic business simulation approach. Simul. Gaming 2005, 36, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, M.S.; Azis, N.; Selva, A.M.; Kadir, M.Z.A.A.; Jasni, J.; Hairi, M.H.; Ghazali, Y.Z.Y.; Talib, M.A. Effect of pre-determined maintenance repair rates on the health index state distribution and performance condition curve based on the Markov Prediction Model for sustainable transformers asset management strategies. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinjala, S.K.; Pintelon, L.; Vereecke, A. An empirical investigation on the relationship between business and maintenance strategies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2006, 104, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Burr, M. A framework for the strategic management of long-term assets (SMoLTA). Manag. Decis. 2004, 42, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.; Mancarella, P. Systemic modelling and integrated assessment of asset management strategies and staff constraints on distribution network reliability. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 155, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani, E.; Filion, Y.R. Event-based approach to optimize the timing of water main rehabilitation with asset management strategies. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 04014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, L. Linking maintenance strategies to performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 70, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, H. Is strategic asset management applicable to small and medium utilities? Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Keleher, P.; Smith, P. Towards an assessment tool for the strategic management of asset criticality. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2008, 5, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitelmal, W.; Molenaar, K.R.; Javernick-Will, A.; Pellicer, E. Challenges and barriers to establishing infrastructure asset management A comparative study between Libya and the USA. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2017, 24, 1184–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradot, N.; Sonnenberg, H.; Kropp, I.; Ringe, A.; Denhez, S.; Hartmann, A.; Rouault, P. The relevance of sewer deterioration modelling to support asset management strategies. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, C.; Guder, S. Reliability-centered asset management of wind turbines—A holistic approach for a sustainable and cost-optimal maintenance strategy. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on System Reliability and Safety, ICSRS 2017, Milan, Italy, 20–22 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kannapiran, A.; Chanan, A.; Singh, G.; Tambosis, P.; Jeyakumaran, J.; Kandasamy, J. Strategic asset management planning of stormwater drainage systems. Water Pract. Technol. 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, R.; Sacher, H. Asset Management and Cost Saving Maintenance Strategy Based on Risk-Informed Decision Making. In Proceedings of the Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management, Basle, Switzerland, 14–18 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khasnabis, S.; Bartus, J.; Ellis, R.D. Asset management strategy to meet long-term transit fleet needs of state departments of transportation. Transp. Res. Rec. 2004, 1887, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.Y.; Yip, T.L. Strategic asset management for campus facilities: Balanced scorecard. In Engineering Asset Management—Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1695–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, H.H.; Shah, R.; Mishra, S. Optimal asset management strategies for mixed transit fleet. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 117, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.C.; Piratla, K.; Koo, D.D. Sustainability Evaluation of Pipe Asset Management Strategies. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering, 2016, Tempre, AZ, USA, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Ossai, C.I.; Boswell, B.; Davies, I.J. Sustainable asset integrity management: Strategic imperatives for economic renewable energy generation. Renew. Energy 2014, 67, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; Poon, E.; Chung, Y.W.; Lai, K.C.; Wong, C.L. Development of a total asset management strategy for the operations and maintenance branch of the drainage services department, the government of the Hong Kong special administrative region. In Engineering Asset Management—Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 929–943. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, A.; Rennotte, C.; Romain, F.; Vosse, B.; Al Shehri, S. Strategic asset management implementation (SAMI) at National Grid, Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the 2017 Saudi Arabia Smart Grid Conference, SASG 2017, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 12–14 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Park, S.I.; Lee, S.H. Strategy on sustainable infrastructure asset management: Focus on Korea’s future policy directivity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidwerbesky, B.; Hunt, S.; Douglas, R.A. Asset management strategy for unsealed low-volume roads in New Zealand. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 1989, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szasz, R.; MacDonald, M.L. Asset management strategies for battery and rectifier systems. In Proceedings of the INTELEC, International Telecommunications Energy Conference (Proceedings), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 30 September–4 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tafazzoli, M. Strategizing sustainable infrastructure asset management in developing countries. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure 2017: Policy, Finance, and Education, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 October 2017; pp. 375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, M.K.F.; Chu, G.W.Y.; Ng, K.Y. Strategic asset management approach for sewage treatment facilities in drainage services department, the government of Hong Kong special administrative region. In Engineering Asset Management—Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 901–920. [Google Scholar]
- Kortelainen, H.; Happonen, A.; Kinnunen, S.K. Fleet service generation—challenges in corporate asset management. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Godau, R.; McGeoch, M. Use of generational models for asset management strategies in an Australian metro rail organisation. In Proceedings of the 10th World Congress on Engineering Asset Management (WCEAM 2015); Springer: London, UK, 2016; pp. 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hanski, J.; Valkokari, P.; Kortelainen, H.; Kinnunen, S.-K.; Ylä-Kujala, A.; Herala, A.; Marttonen-Arola, S.; Kärri, T. Knowledge Intensive Service Concepts for Fleet Asset Management; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, J.; Hardiman, F.; Naughton, M.D. Asset management: A review of contemporary & individualised strategies. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 2011, WCE 2011, London, UK, 6–8 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, T.; Ugalde-Loo, C.E.; Liang, J.; Coventry, P.F. Asset management strategies for power electronic converters in transmission networks: Application to Hvdc and FACTS devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Creating and sustaining superior performance. Compet. Advant. 1985, 167, 167–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M. Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors; Free Press: Camden, ME, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wernerfelt, B. A resource-based view of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. The Resource-Based Theory of Competitive Advantage: Implications for Strategy Formulation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1991, 33, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Hamel, G. The core competence of the corporation. In Strategische Unternehmungsplanung—Strategische Unternehmungsführung; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.; Laue, M.; Tafur, J.; Mahmood, M.N.; Scherrer, P.; Keast, R. An integrated approach to strategic asset management. Infranomics 2014, 24, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W.R. Institutions and Organizations: Ideas, Interests and Identities; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781452242224. [Google Scholar]
- DiMaggio, P.J.; Powell, W.W. The Iron Cage Revisited: Institutional Isomorphism and Collective Rationality in Organizational Fields. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1983, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C. Strategic responses to institutional processes. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1991, 16, 145–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, A.G.M.; Vermeulen, P.A.M.; Meeus, M.T.H.; Zietsma, C. I need time! Exploring pathways to compliance under institutional complexity. Acad. Manag. J. 2015, 58, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, D.J.; Montgomery, C.A. Corporate Strategy: A Resource-Based Approach; McGraw Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ansoff, H.I. Strategies for Diversification.: University of Warwick eResources. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1957, 35, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tushman, M.L.; O’Reilly, C.A. Ambidextrous organizations: Managing evolutionary and revolutionary change. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1996, 38, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, S.; Birkinshaw, J.; Probst, G.; Tushman, M.L. Organizational ambidexterity: Balancing exploitation and exploration for sustained performance. Organ. Sci. 2009, 20, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, D.; Tushman, M. Strategic Organization Design; Scott, Foresman and Company: Glenview, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Men, L.R. Why Leadership Matters to Internal Communication: Linking Transformational Leadership, Symmetrical Communication, and Employee Outcomes. J. Public Relations Res. 2014, 26, 256–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.F.Y.; Wong, C.S. Transformational leadership, leader support, and employee creativity. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2011, 32, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenkov, D.S.; Manev, I.M. Top management leadership and influence on innovation: The role of sociocultural context. J. Manag. 2005, 31, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Johnston, H.H. Evaluating the impacts of operating strategies on efficiency in the US airline industry. In Data Envelopment Analysis: Theory, Methodology, and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 97–128. [Google Scholar]
- Parnell, J.A. Generic strategies after two decades: A reconceptualization of competitive strategy. Manag. Decis. 2006, 44, 1139–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.G. Understanding dynamic capabilities. Strateg. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzberg, H. The fall and rise of strategic planning. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1994, 72, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, R. Strategy as practice. Long Range Plann. 1996, 29, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzabkowski, P. Strategy as practice: Recursiveness, adaptation, and practices-in-use. Organ. Stud. 2004, 25, 529–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R. Completing the practice turn in strategy research. Organ. Stud. 2006, 27, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Strategic planning in a turbulent environment: Evidence from the oil majors. Strateg. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 491–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantere, S. Strategic practices as enablers and disablers of championing activity. Strateg. Organ. 2005, 3, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronios, A.; Nastasie, D.; Chanana, V.; Haider, A. Integration through standards—An overview of international standards for engineering asset management. In Proceedings of the 2nd World Congress on Engineering Asset Management and the Fourth International Conference on Condition Monitoring (WCEAM 2007), Harrogate, UK, 11–14 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, U.; Galar, D.; Parida, A.; Stenström, C.; Berges, L. Maintenance performance metrics: A state-of-the-art review. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2013, 19, 233–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, J.P.; Kumar, U. Towards a value-based view on operations and maintenance performance management. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2003, 9, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.B.; Sarasoja, A.L.; Galamba, K.R. Sustainability in facilities management: An overview of current research. Facilities 2016, 34, 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.; Kumar, U.; Galar, D.; Stenström, C. Performance measurement and management for maintenance: A literature review. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2015, 21, 2–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyatrapoomi, N.; Kumar, A.; Setunge, S. Framework for investment decision-making under risk and uncertainty for infrastructure asset management. Res. Transp. Econ. 2004, 8, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schneider, J.; Gaul, A.J.; Neumann, C.; Hogräfer, J.; Wellßow, W.; Schwan, M.; Schnettler, A. Asset management techniques. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2006, 28, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, J.M.; Gomes, C.F.; Yasin, M.M. A literature review of maintenance performance measurement: A conceptual framework and directions for future research. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2011, 17, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, E.G. A framework for strategic infrastructure asset management. In Definitions, Concepts and Scope of Engineering Asset Management; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 31–62. ISBN 9781849961776. [Google Scholar]
- Zuashkiani, A.; Rahmandad, H.; Jardine, A.K.S. Mapping the dynamics of overall equipment effectiveness to enhance asset management practices. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2011, 17, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi-Echendu, J.E. Managing physical assets is a paradigm shift from maintenance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Engineering Management Conference, 2004, Singapore, 18–21 October 2004; pp. 1156–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.E.; Spare, J.H. Asset management, risk, and distribution system planning. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, New York, NY, USA, 10–13 October 2004; pp. 1681–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.E.; Humphrey, B.G. Asset management for transmission and distribution. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2005, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfawy, M.R. Integration of municipal infrastructure asset management processes: Challenges and solutions. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2008, 22, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronios, A.; Lin, S.; Gao, J. A data quality model for asset management in engineering organisations. In Engineering Asset Management; Springer: London, UK, 2006; pp. 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Dwight, R. Searching for real maintenance performance measures. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 1999, 5, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akruti, K.; Dwight, R. A framework for the engineering asset management system. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2013, 19, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.; Mengel, D.; Bandara, W.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L. Building an ontology and process architecture for engineering asset management. In Engineering Asset Lifecycle Management; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 86–97. ISBN 9781849960021. [Google Scholar]
- Halfawy, M.M.R.; Newton, L.A.; Vanier, D.J. Review of commercial municipal infrastructure asset management systems. Electron. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2006, 11, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Komonen, K. A cost model of industrial maintenance for profitability analysis and benchmarking. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2002, 79, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertani, M.Z.; Parlikad, A.K.; McFarlane, D. Towards an approach to select an asset information management strategy. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2008, 5, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, A.; Kumar, U. Maintenance performance measurement (MPM): Issues and challenges. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2006, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintelon, L.; Parodi-Herz, A. Maintenance: An Evolutionary Perspective. In Complex System Maintenance Handbook; Springer: London, UK, 2008; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Schuman, C.A.; Brent, A.C. Asset life cycle management: Towards improving physical asset performance in the process industry. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2005, 25, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, E. Infrastructure asset: Developing maintenance management capability. Facilities 2012, 30, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, D.J.D. Why industry needs asset management tools. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2001, 15, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, B.; Alsyouf, I. Improving effectiveness of manufacturing systems using total quality maintenance. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2000, 11, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskarada, S.; Gao, J.; Koronios, A. Agile maturity model approach to assessing and enhancing the quality of asset information in engineering asset management information systems. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Proceedings—Series of the Gesellschaft fur Informatik (GI), Klagenfurt, Austria, 31 May–2 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Bai, Q. Optimization in decision making in infrastructure asset management: A review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akruti, K.; Dwight, R.; Zhang, T.; Al-Marsumi, M. The role of life cycle cost in engineering asset management. In Engineering Asset Management-Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, K.; Hvolby, H.H.; Watanabe, C. A review of the three most popular maintenance systems: How well is the energy sector represented? Int. J. Glob. Energy Issues 2011, 35, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Asgarpoor, S. Reliability and maintainability improvement of substations with aging infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletič, D.; Maletič, M.; Al-Najjar, B.; Gotzamani, K.; Gianni, M.; Kalinowski, T.B.; Gomišček, B. Contingency factors influencing implementation of physical asset management practices. Organizacija 2017, 50, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Osama, A. Fuzzy-based methodology for integrated infrastructure asset management. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2017, 10, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, C.B.H.; Jooste, W.J.L. A technologically-driven asset management approach to managing physical assets—A literature review and research agenda for ‘smart’ asset management. South Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2016, 27, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pärn, E.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Sing, M.C.P. The building information modelling trajectory in facilities management: A review. Autom. Constr. 2017, 75, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchrompo, S.; Parlikad, A.K. A review of asset management literature on multi-asset systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 181, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, I.; Parlikad, A.K.; Macchi, M.; Garetti, M. A framework for implementing value-based approach in asset management. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist, T.; Laakso, K.; Reunanen, M. Value-driven maintenance planning for a production plant. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraven, D.; Hartmann, A.; Dewulf, G. Effectiveness of infrastructure asset management: Challenges for public agencies. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2011, 1, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Parlikad, A.K. An Approach to Value-Based Infrastructure Asset Management. In Value Based and Intelligent Asset Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wiewiora, A.; Brown, K.; Dhakal, S.P.; Mahmood, M.N. Managing Knowledge for Asset Management: Shifting from Process to Relational Frames. In Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Engineering Asset Management (WCEAM 2012); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 625–635. [Google Scholar]
- Woodall, P.; Gao, J.; Parlikad, A.; Koronios, A. Classifying data quality problems in asset management. In Engineering Asset Management-Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 321–334. [Google Scholar]
- Alhazmi, N. A theoretical framework for physical asset management practices. Facilities 2018, 36, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, B. Total quality maintenance: An approach for continuous reduction in costs of quality products. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 1996, 2, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsyouf, I. Measuring maintenance performance using a balanced scorecard approach. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2006, 12, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brous, P.; Janssen, M.; Schraven, D.; Spiegeler, J.; Duzgun, B.C. Factors influencing adoption of IoT for data-driven decision making in asset management organizations. In Proceedings of the IoTBDS 2017—2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security, 2017, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghanian, P.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M.; Bagheri-Shouraki, S.; Razi Kazemi, A.A. Critical component identification in reliability centered asset management of power distribution systems via fuzzy AHP. IEEE Syst. J. 2012, 6, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.; Ma, L.; Sun, Y.; Bandara, W. Identifying core functions of asset management. In Definitions, Concepts and Scope of Engineering Asset Management; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 19–30. ISBN 9781849961776. [Google Scholar]
- Roda, I.; Macchi, M. A framework to embed Asset Management in production companies. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2018, 232, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

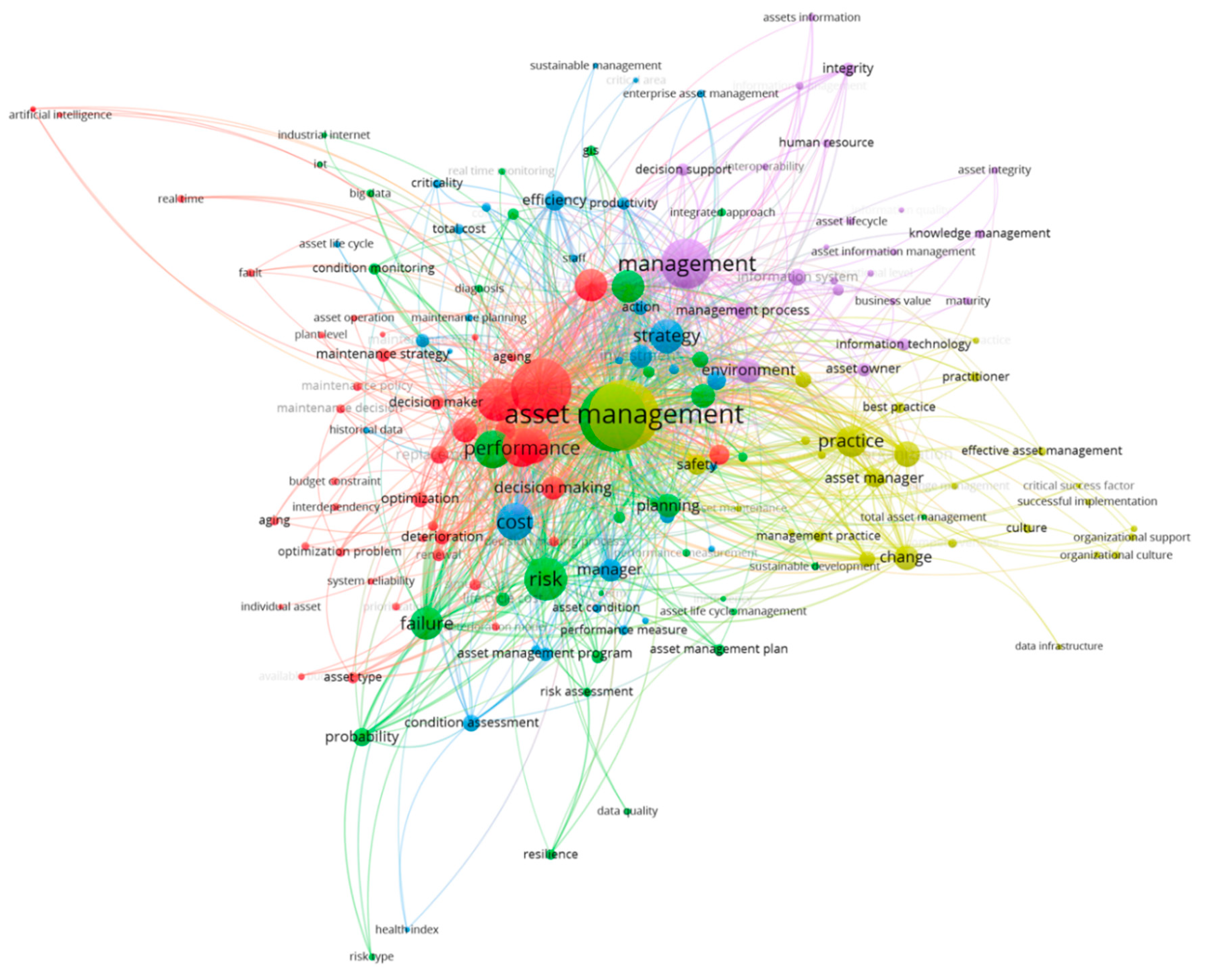
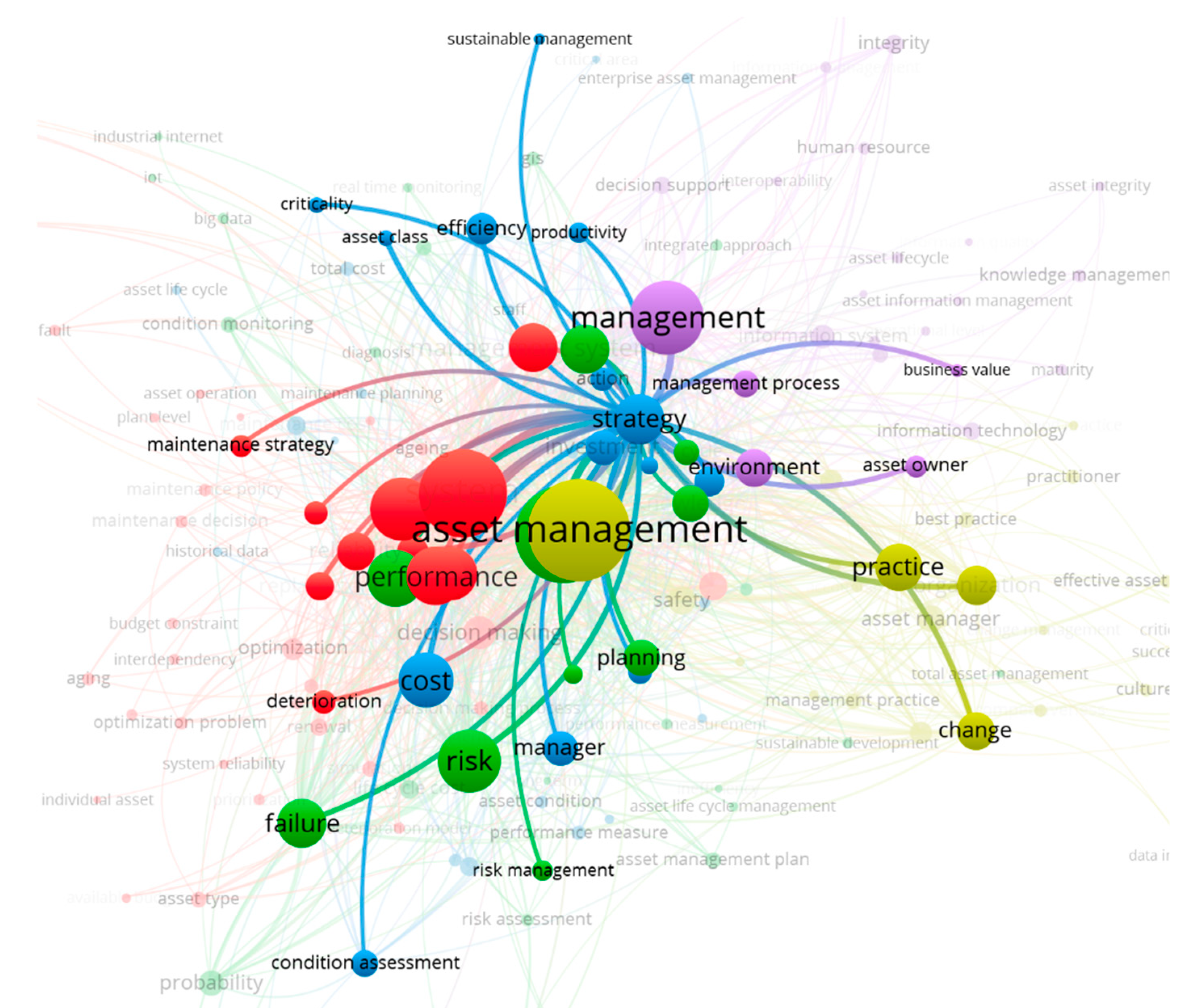

| # | Cluster | Key Terms | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | “Operational level decision making” (40 items) | Ageing, aging, artificial intelligence, asset management strategy, asset operation, asset type, available budget, budget constraint, customer satisfaction, decision, decision maker, decision making, decision making process, deterioration, deterioration model, effective management, failure rate, fault, flexibility, individual asset, integrated control, integrated control, interdependency, maintenance, maintenance decision, maintenance policy, maintenance strategy, management system, optimization, optimization problem, performance, plant level, prioritization, real time, reliability, renewal, replacement, simulation, stakeholder, system, system reliability | Focus on system reliability, maintenance, modelling risk, failure and renewal/replacement within budget constraints, control and plant level decision making |
| 2 | “Asset life cycle management” (36 items) | Asset, asset life cycle management, asset management plan, asset performance, big data, complexity, condition, condition data, condition monitoring, coordination, data quality, diagnosis, failure, GIS (geographic information system), industrial internet, inefficiency, integrated approach, IoT, knowledge, life cycle, life cycle cost, life cycle management, long term, performance measurement, planning, probability, real time monitoring, resilience, risk, risk assessment, risk management, risk type, short term, sustainable development, technology, total asset management | Managing individual assets/group of assets over their life cycles with a focus on information technology and risk management |
| 3 | “Strategic asset management” (32 items) | Action, asset class, asset condition, asset lifecycle, asset management program, asset management tool, condition assessment, cost, critical area, criticality, decision support tool, effectiveness, efficiency, enterprise asset management, health index, historical data, investment, life cycle cost analysis, maintenance cost, maintenance manager, maintenance planning, maintenance process, maintenance requirement, manager, performance measurement, productivity, resource allocation, staff, strategic asset management, strategy, sustainable management, total cost | Focus on enterprise level asset management, technical/economic efficiency, managerial decision making and strategy |
| 4 | “Organizational aspects of asset management” (28 items) | Accountability, asset maintenance, asset management, asset management framework, asset management organization, asset management practice, asset manager, best practice, change, change management, competitiveness, critical success factor, culture, data infrastructure, effective asset manager, good practice, key success factor, management practice, organization, organizational change, organizational culture, organizational support, practice, practitioner, profitability, safety, successful implementation, sustainability | Focus on change management, organizational culture and managerial practice |
| 5 | “Asset information management” (25 items) | Asset information, asset information management, asset integrity, asset lifecycle, asset owner, assets information, business value, continuous improvement, decision support, environment, human resource, information management, information quality, information system, information technology, integrity, interoperability, knowledge management, lifecycle, management, management process, maturity, operational level, performance evaluation, risk analysis | Focus on information technology and knowledge management |
| Contribution of Papers | References | |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical (n = 24) | Conceptual (10) | [1,8,14,15,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Exploratory (10) | [11,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] | |
| Predictive (4) | [13,46,47,48] | |
| Prescriptive (n = 11) | Instrumental (9) | [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58] |
| Normative (2) | [59,60] | |
| Descriptive (n = 18) | Descriptive (18) | [3,10,14,28,29,30,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrikova, E.; Volkova, I.; Burda, Y. Strategic Aspects of Asset Management: An Overview of Current Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155955
Gavrikova E, Volkova I, Burda Y. Strategic Aspects of Asset Management: An Overview of Current Research. Sustainability. 2020; 12(15):5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155955
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrikova, Elizaveta, Irina Volkova, and Yegor Burda. 2020. "Strategic Aspects of Asset Management: An Overview of Current Research" Sustainability 12, no. 15: 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155955
APA StyleGavrikova, E., Volkova, I., & Burda, Y. (2020). Strategic Aspects of Asset Management: An Overview of Current Research. Sustainability, 12(15), 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12155955





