A Volunteered Geographic Information-Based Environmental Decision Support System for Waste Management and Decision Making
Abstract
:1. Introduction
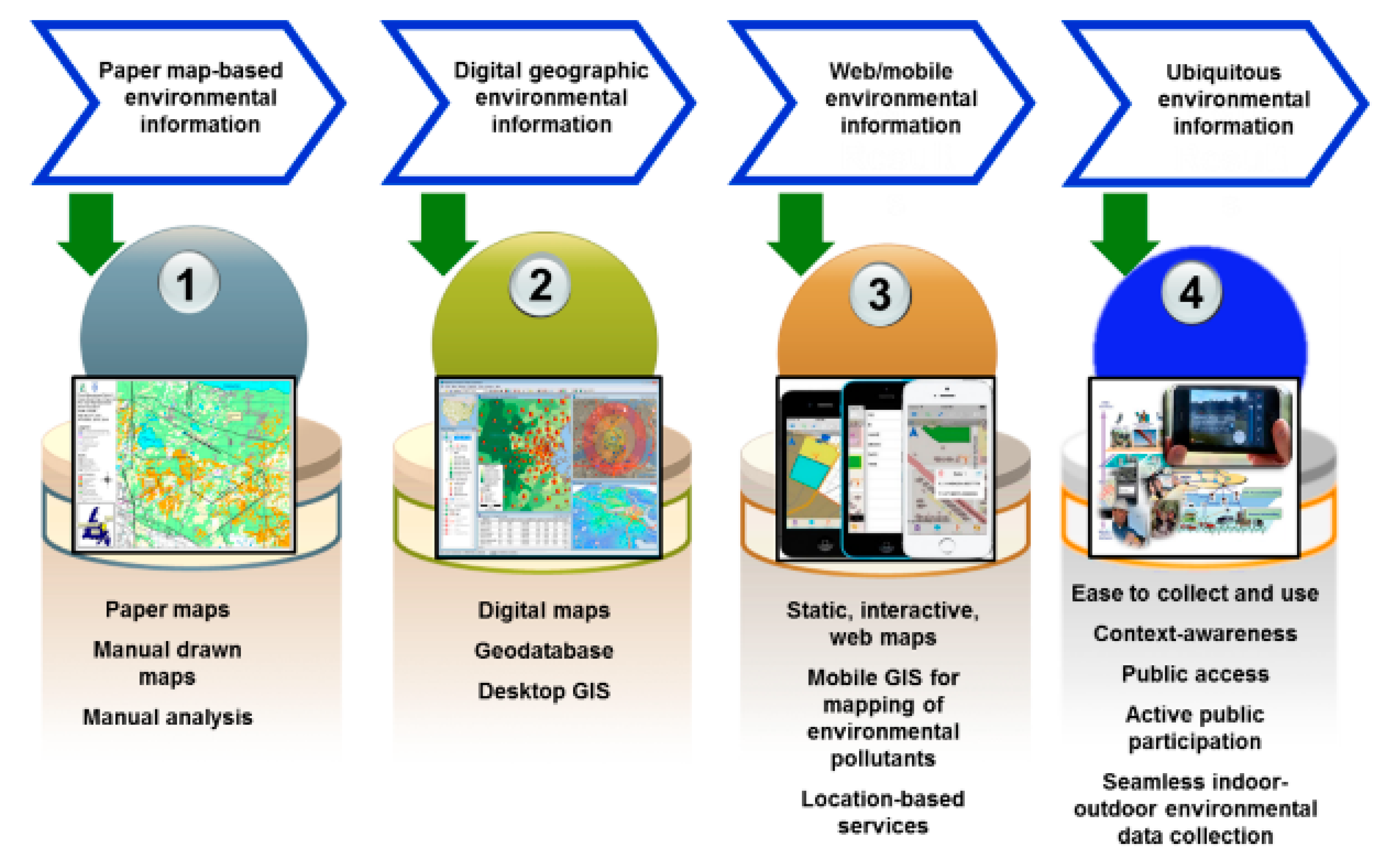
2. Environmental Geographic Information Trends
3. VGI-Based Environmental Decision Support System
3.1. Geo-Referencing of VGI
3.2. Spatial Analysis
3.3. GIS-MCDA Tools
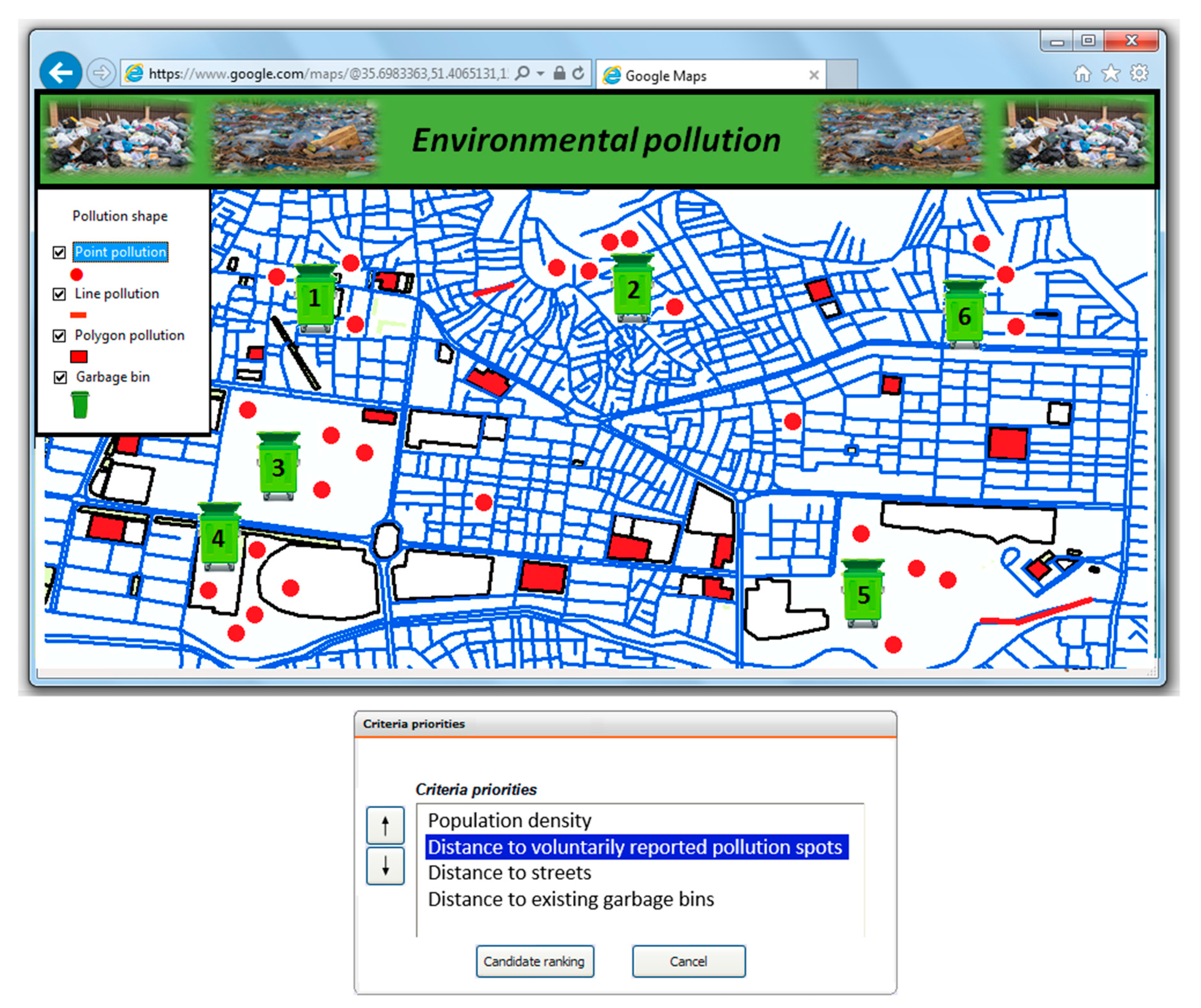
4. Prototype Implementation of VGI-Based Environmental Decision Support Tools
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdi, A.; Yazdanpanah, Q.; Javadi, Z. Dust Crises and its Regional Geopolitical and Security Impact in West Asia. Pollution 2020, 6, 453–468. [Google Scholar]
- Fatehian, S.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Kakroodi, A.A.; Dero, Q.Y.; Samany, N.N. A volunteered geographic information system for managing environmental pollution of coastal zones: A case study in Nowshahr, Iran. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 163, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Fonseca, A.; Câmara, A.; Ferreira, F. Promoting the use of environmental data collected by concerned citizens through information and communication technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah Dero, Q.; Yari, E.; Charrahy, Z. Global warming, environmental security and its geo-economic dimensions case study: Caspian Sea level changes on the balance of transit channels. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.S.; Jamil, M.A.; Mazhar, A.; Ikram, A.; Ahmed, A.; Munawar, U. Smart environment monitoring system by employing wireless sensor networks on vehicles for pollution free smart cities. Procedia Eng. 2015, 107, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizel, F.; Etzion, Y.; Shafran-Nathan, R.; Levy, I.; Fishbain, B.; Bartonova, A.; Broday, D.M. Node-to-node field calibration of wireless distributed air pollution sensor network. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M. Citizens as sensors: The world of volunteered geography. GeoJournal 2007, 69, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haklay, M.M.; Servedio, V.D.P. Citizen Science, Participatory Sensing and Social Computation. In Participatory Sensing, Opinions and Collective Awareness; Loreto, V., Haklay, M., Hotho, A., Servedio, V.C., Stumme, G., Theunis, J., Tria, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.A.; Sieber, R.E. Situating the Adoption of VGI by Government Crowdsourcing Geographic Knowledge; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, V. Volunteer monitoring: A brief history. Volunt. Monit. 1994, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, V.W.; Shen, L.; Yau, R.M.; Tam, C.M. On using a communication-mapping model for environmental management (CMEM) to improve environmental performance in project development processes. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3093–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulos, E.; Honicky, R.; Hooker, B. Citizen science: Enabling participatory urbanism. In Handbook of Research on Urban Informatics: The Practice and Promise of the Real-Time City; Foth, M., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 414–436. [Google Scholar]
- Rinner, C.; Kumari, J.; Mavedati, S. A Geospatial Web Application to Map Observations and Opinions in Environmental Planning; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Castell, N.; Kobernus, M.; Liu, H.-Y.; Schneider, P.; Lahoz, W.; Berre, A.J.; Noll, J. Mobile technologies and services for environmental monitoring: The Citi-Sense-MOB approach. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.P.; Lei, S.; Kelly, M. Citizen science in the age of neogeography: Utilizing volunteered geographic information for environmental monitoring. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2012, 102, 1267–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkel, A. Visualizing the perceived environment using crowdsourced photo geodata. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Kobernus, M.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. A conceptual approach to a citizens’ observatory—Supporting community-based environmental governance. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forrester, G.; Baily, P.; Conetta, D.; Forrester, L.; Kintzing, E.; Jarecki, L. Comparing monitoring data collected by volunteers and professionals shows that citizen scientists can detect long-term change on coral reefs. J. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiker, G.A.; Bridges, T.S.; Varghese, A.; Seager, T.P.; Linkov, I. Application of multicriteria decision analysis in environmental decision making. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsevski, P.V.; Donevska, K.R.; Mitrovski, C.D.; Frizado, J.P. Integrating multi-criteria evaluation techniques with geographic information systems for landfill site selection: A case study using ordered weighted average. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Malczewski, J. Decision complexity and consensus in Web-based spatial decision making: A case study of site selection problem using GIS and multicriteria analysis. Cities 2015, 45, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.M. Semantic interoperability of GIS and MCDA tools for environmental assessment and decision making. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 100, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Dhar, A.; Kar, A. Environmental vulnerability assessment using Grey Analytic Hierarchy Process based model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 56, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorabeh, S.N.; Firozjaei, M.K.; Nematollahi, O.; Firozjaei, H.K.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. A risk-based multi-criteria spatial decision analysis for solar power plant site selection in different climates: A case study in Iran. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, H.E.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; do Valle Junior, R.F.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L. A multi criteria analog model for assessing the vulnerability of rural catchments to road spills of hazardous substances. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 64, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, A.; Hewage, K.; Reza, B.; Sadiq, R. Multiple stakeholders in multi-criteria decision-making in the context of Municipal Solid Waste Management: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanolya, N.M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. The use of subjective–Objective weights in GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis for flood hazard assessment: A case study in Mazandaran, Iran. GeoJournal 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J.; Rinner, C. Multicriteria Decision Analysis in Geographic Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Masoumi, Z.; Van Genderen, J.; Sadeghi Niaraki, A. An improved ant colony optimization-based algorithm for user-centric multi-objective path planning for ubiquitous environments. Geocarto Int. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Kim, K.; Varshosaz, M. Multi-criteria decision-based model for road network process. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 573–582. [Google Scholar]
- Sahelgozin, M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Dareshiri, S. Proposing a multi-criteria path optimization method in order to provide a Ubiquitous Pedestrian Wayfinding Service. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, N.-B.; Parvathinathan, G.; Breeden, J.B. Combining GIS with fuzzy multicriteria decision-making for landfill siting in a fast-growing urban region. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Thompson, R.G. Application of boolean logic and GIS for determining suitable locations for Temporary Disaster Waste Management Sites. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 20, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, M.; Homaee, M.; Mahmodi, S. An integrated multi criteria approach for landfill siting in a conflicting environmental, economical and socio-cultural area. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo, G.D.; Gisi, S.D. Using MCDA and GIS for hazardous waste landfill siting considering land scarcity for waste disposal. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-C.; Wu, J.; Li, P. Assessment of health-care waste disposal methods using a VIKOR-based fuzzy multi-criteria decision making method. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2744–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeinaddini, M.; Khorasani, N.; Danehkar, A.; Darvishsefat, A.A. Siting MSW landfill using weighted linear combination and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) methodology in GIS environment (case study: Karaj). Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nas, B.; Cay, T.; Iscan, F.; Berktay, A. Selection of MSW landfill site for Konya, Turkey using GIS and multi-criteria evaluation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, M.; Hadidi, M.; Vessali, E.; Mosstafakhani, P.; Taheri, K.; Shahoie, S.; Khodamoradpour, M. Integrating multi-criteria decision analysis for a GIS-based hazardous waste landfill sitting in Kurdistan Province, western Iran. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2740–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Jang, S.-G. Ubiquitous Geographic Information Springer Handbook of Geographic Information; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Fustes, D.; Cantorna, D.; Dafonte, C.; Arcay, B.; Iglesias, A.; Manteiga, M. A cloud-integrated web platform for marine monitoring using GIS and remote sensing. Application to oil spill detection through SAR images. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2014, 34, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawiak, M.; Prospathopoulos, A.; Perivoliotis, L.; łuba, M.; Kioroglou, S.; Stepnowski, A. Interactive visualization of marine pollution monitoring and forecasting data via a Web-based GIS. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Shen, D.; Khalid, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. GIS-based emergency response system for sudden water pollution accidents. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 79, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapati, S. Using Geographic Information Systems to Increase Citizen Engagement; BM Center for The Business of Government: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karnatak, H.C.; Shukla, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Murthy, Y.V.S.; Bhanumurthy, V. Spatial mashup technology and real time data integration in geo-web application using open source GIS—A case study for disaster management. Geocarto Int. 2012, 27, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudreau, P.; Johnson, P.A.; Sieber, R. Creating and testing a portable template for municipal-level adoption of the Geospatial Web 2.0. In Proceedings of the Spatial Knowledge and Information—Canada, Fernie, BC, Canada, 3–6 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maisonneuve, N.; Stevens, M.; Niessen, M.E.; Steels, L. NoiseTube: Measuring and mapping noise pollution with mobile phones. In Information Technologies in Environmental Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoody Vanolya, N.M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Toomanian, A. Validation of spatial multicriteria decision analysis results using public participation GIS. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 112, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feick, R.; Hall, G.B. Balancing consensus and conflict with a GIS-based multi-participant, multi-criteria decision support tool. GeoJournal 2001, 53, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. The Roles and Challenges of National Geospatial Data Infrastructure for Data Sharing and Openness in Big Data Era. Mag. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2013, 61, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Hajiloo, F.; Samany, N.N. A web-based public participation GIS for assessing the age-friendliness of cities: A case study in Tehran, Iran. Cities 2019, 95, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. Collaborative spatial multicriteria evaluation: A review and directions for future research. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroushaki, S. ParticipatoryGIS: A Web-Based Collaborative GIS and Multicriteria Decision Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. Web 2.0-Based Collaborative Multicriteria Spatial Decision Support System: A Case Study of Human-Computer Interaction Patterns. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.; Goonetilleke, A.; Campbell, D. A new fuzzy multicriteria evaluation method for group site selection in GIS. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2003, 12, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowski, P.; Nyerges, T. Geographic Information Systems for Group Decision-Making: Towards A Participatory, Geographic Information Science; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kyem, P.A.K. An application of a choice heuristic algorithm for managing land resource allocation problems involving multiple parties and conflicting interests. Trans. Gis 2001, 5, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, M.; Minowa, M. A GIS-based multi-criteria decision making approach to forest conservation planning at a landscape scale: A case study in the Kinabalu Area, Sabah, Malaysia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, A.; Densham, P.J.; Haklay, M. Web-based GIS for collaborative planning and public participation: An application to the strategic planning of wind farm sites. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsevski, P.V.; Cathcart, S.C.; Mirzaei, G.; Jamali, M.M.; Ye, X.; Gomezdelcampo, E. A group-based spatial decision support system for wind farm site selection in Northwest Ohio. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidipoor, M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Moeinmehr, A.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Choi, S.-M. A GIS-based decision support system for facilitating participatory urban renewal process. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, J. Mathematical derivation of an election system. Isis 1781, 44, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.T.; Johnson, P.A. Citizen and government co-production of data: Analyzing the challenges to government adoption of VGI. Can. Geogr. 2020, (in press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F.; Li, L. Assuring the quality of volunteered geographic information. Spat. Stat. 2012, 1, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feick, R.; Roche, S. Understanding the Value of VGI. Crowdsourcing Geographic Knowledge; Sui, D., Elwood, S., Goodchild, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Horita, F.E.; Albuquerque, J. An approach to support decision-making in disaster management based on volunteer geographic information (VGI) and spatial decision support systems (SDSS). In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Systems for Crisis Response and Management, Baden-Baden, Germany, 1 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Elwood, S.; Goodchild, M.F.; Sui, D.Z. Researching Volunteered Geographic Information: Spatial Data, Geographic Research, and New Social Practice. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2012, 102, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, F.O.; Spinsanti, L. A conceptual workflow for automatically assessing the quality of volunteered geographic information for crisis management. In Proceedings of the AGILE, Frank O. Ostermann, Laura Spinsanti, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 18–22 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- See, L.; Comber, A.; Salk, C.; Fritz, S.; van der Velde, M.; Perger, C.; Schill, C.; McCallum, I.; Kraxner, F.; Obersteiner, M. Comparing the quality of crowdsourced data contributed by expert and non-experts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upton, V.; Ryan, M.; O’Donoghue, C.; Dhubhain, A.N. Combining conventional and volunteered geographic information to identify and model forest recreational resources. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 60, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagin, A.J.; Metzger, M.J. The credibility of volunteered geographic information. GeoJournal 2008, 72, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haklay, M. How good is volunteered geographical information? A comparative study of OpenStreetMap and Ordnance Survey datasets. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2010, 37, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koukoletsos, T. A Framework for Quality Evaluation of VGI Linear Datasets; University College London: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Omidipoor, M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Samany, N.N. A Web-based geo-marketing decision support system for land selection: A case study of Tehran, Iran. Ann. Gis 2019, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granell, C.; Havlik, D.; Schade, S.; Sabeur, Z.; Delaney, C.; Pielorz, J. Future Internet technologies for environmental applications. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Putnik, G.D.; Lopes, N.; Lopes, A.; Cruz-Cunha, M.M. A Cloud and Ubiquitous Architecture for Effective Environmental Sensing and Monitoring. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 64, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasani, S.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M. Spatial data integration using ontology-based approach. The International Archives of Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Malczewski, J. A web 3.0-driven collaborative multicriteria spatial decision support system. Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2012, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Malczewski, J. A user-centered multicriteria spatial decision analysis model for participatory decision making: An ontology-based approach. In Proceedings of the Global Geospatial Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 14–17 May 2012. [Google Scholar]









| 0 | 2 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 3 | 0 | |
| Alternative’s Borda score | 3 | 5 | 1 |
| Group rankings of alternatives | 2 | 1 | 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Choi, S.-M. A Volunteered Geographic Information-Based Environmental Decision Support System for Waste Management and Decision Making. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156012
Sadeghi-Niaraki A, Jelokhani-Niaraki M, Choi S-M. A Volunteered Geographic Information-Based Environmental Decision Support System for Waste Management and Decision Making. Sustainability. 2020; 12(15):6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadeghi-Niaraki, Abolghasem, Mohammadreza Jelokhani-Niaraki, and Soo-Mi Choi. 2020. "A Volunteered Geographic Information-Based Environmental Decision Support System for Waste Management and Decision Making" Sustainability 12, no. 15: 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156012
APA StyleSadeghi-Niaraki, A., Jelokhani-Niaraki, M., & Choi, S.-M. (2020). A Volunteered Geographic Information-Based Environmental Decision Support System for Waste Management and Decision Making. Sustainability, 12(15), 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156012





