Evaluation of the SEdiment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sediment Delivery Ratio (SDR)
1.2. Spatial Discretization
1.3. Study Objectives
- The main focus of this study was on the advancement of the soil erosion research in the Shihmen Reservoir watershed to include determination of the watershed-specific coefficient, β, using known SDRw values, and developing the SDRi relationship and SEDD model for the watershed, applying the findings to the assessment of the sediment yield (SY) by sheet and rill erosion in the watershed.
- In this study, the non-point source sheet and rill erosion calculated by the USLE is the main target land degradation process. Landslides, gully erosion, and channel type erosions are not considered.
- The datasets employed are assumed to be from the same period and are the most recent available data for this study area.
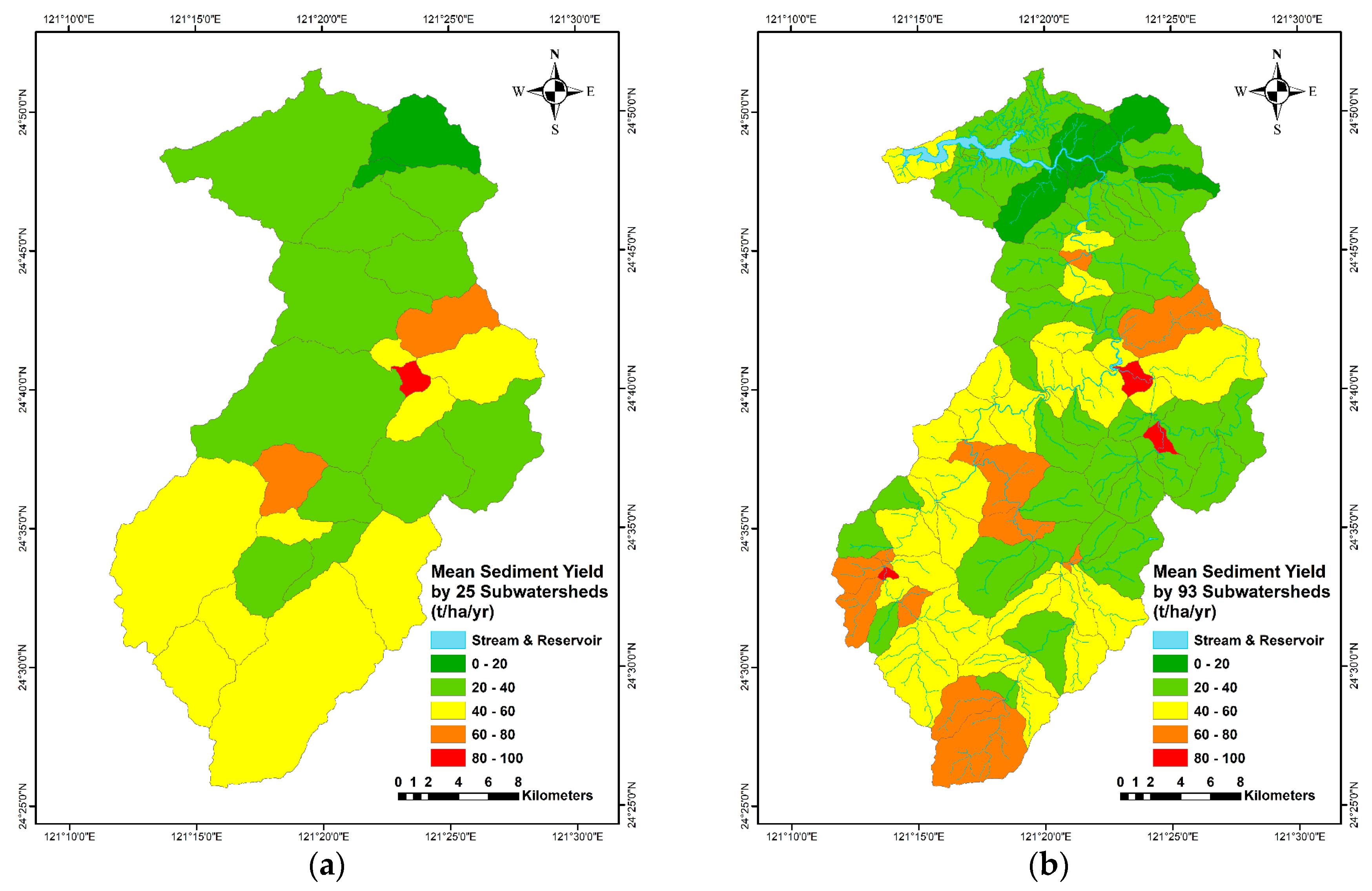
- This study, additionally, explores the statistical properties of the SDR, SL, and SY of the watershed using two sub-watershed discretizations (25 and 93) of the Shihmen Reservoir watershed and compares the results.
- This study determines the watershed prioritization of soil conservation using the SY determined by the SEDD.
2. Study Area
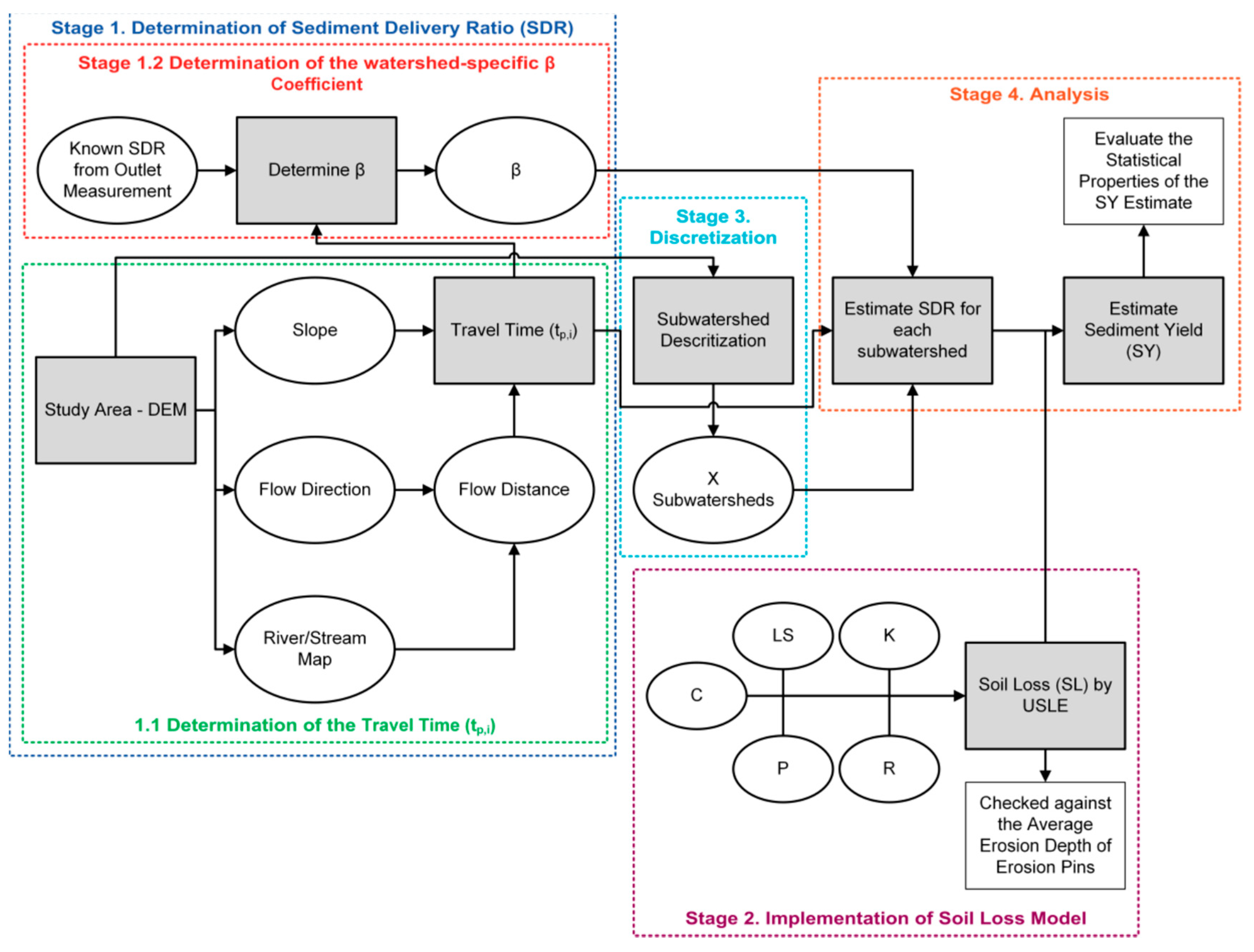
3. Methodology
- Stage 1 (1.1):
- 1.
- Determine the study area and input the DEM.
- 2.
- Determine the slope, flow direction, and river/stream map from a derived depression-less DEM.
- 3.
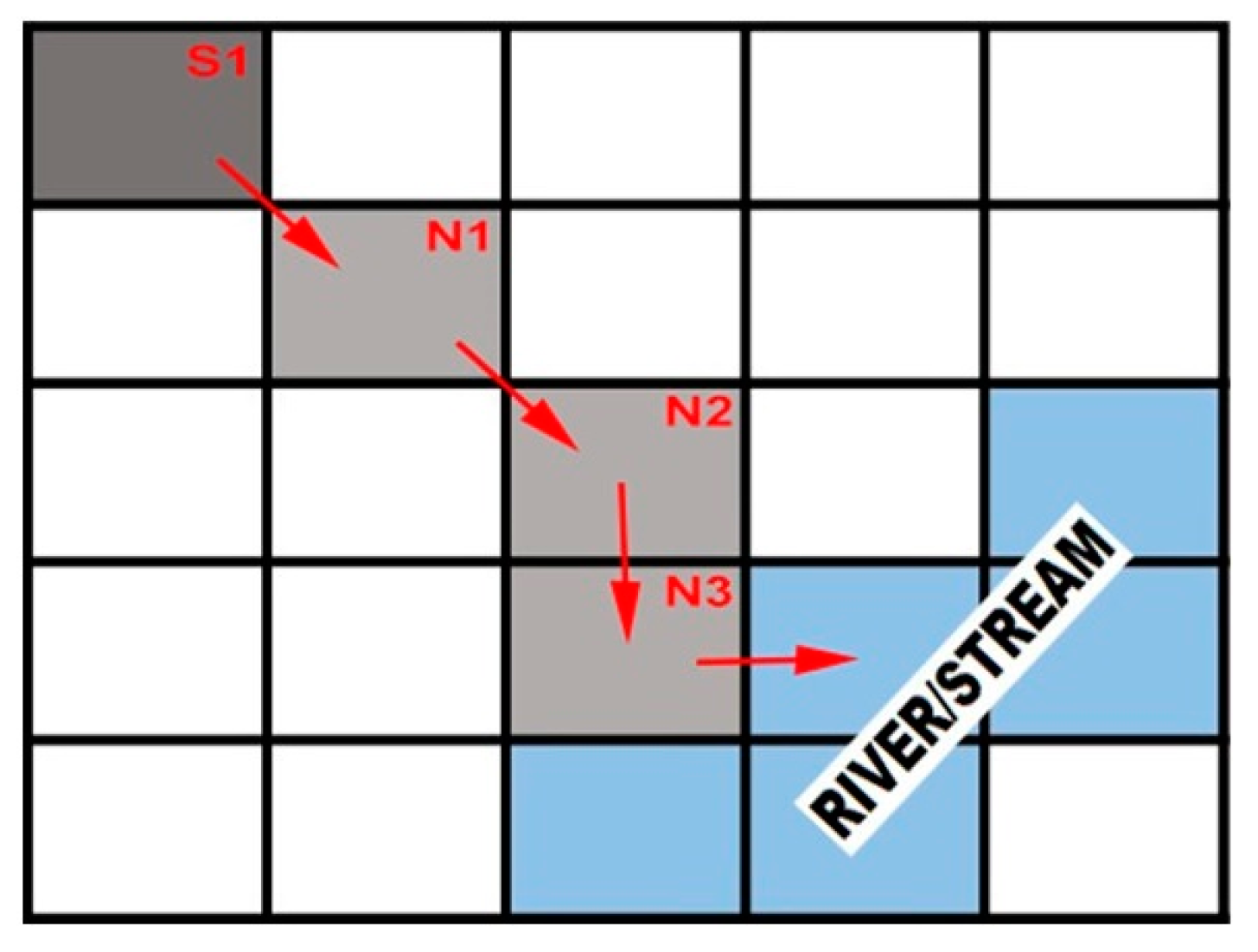
- Use the flow direction and river/stream map as input to determine the flow distance, which is then used with the slope to determine the travel time.
- Stage 2:
- 4.
- Find the six parameters of the USLE equation and estimate SL.
- 5.
- Determine the SDR using measured outlet SY and estimated SL.
- Back to stage 1.2:
- 6.
- Determine β from the SDR, SL, and the travel time found.
- Stage 3:
- 7.
- Return to the DEM and discretize the study area into sub-watersheds/hydrological units or any other applicable unit of analysis.
- Stage 4:
- 8.
- Re-estimate the SDR for the parent watershed and each sub-watershed.
- 9.
- Estimate the sediment yield (SY) and perform any further analysis necessary.
3.1. Sediment Distributed Delivery Model (SEDD)
3.2. Sediment Yield Determination
4. Results
4.1. The β Coefficient
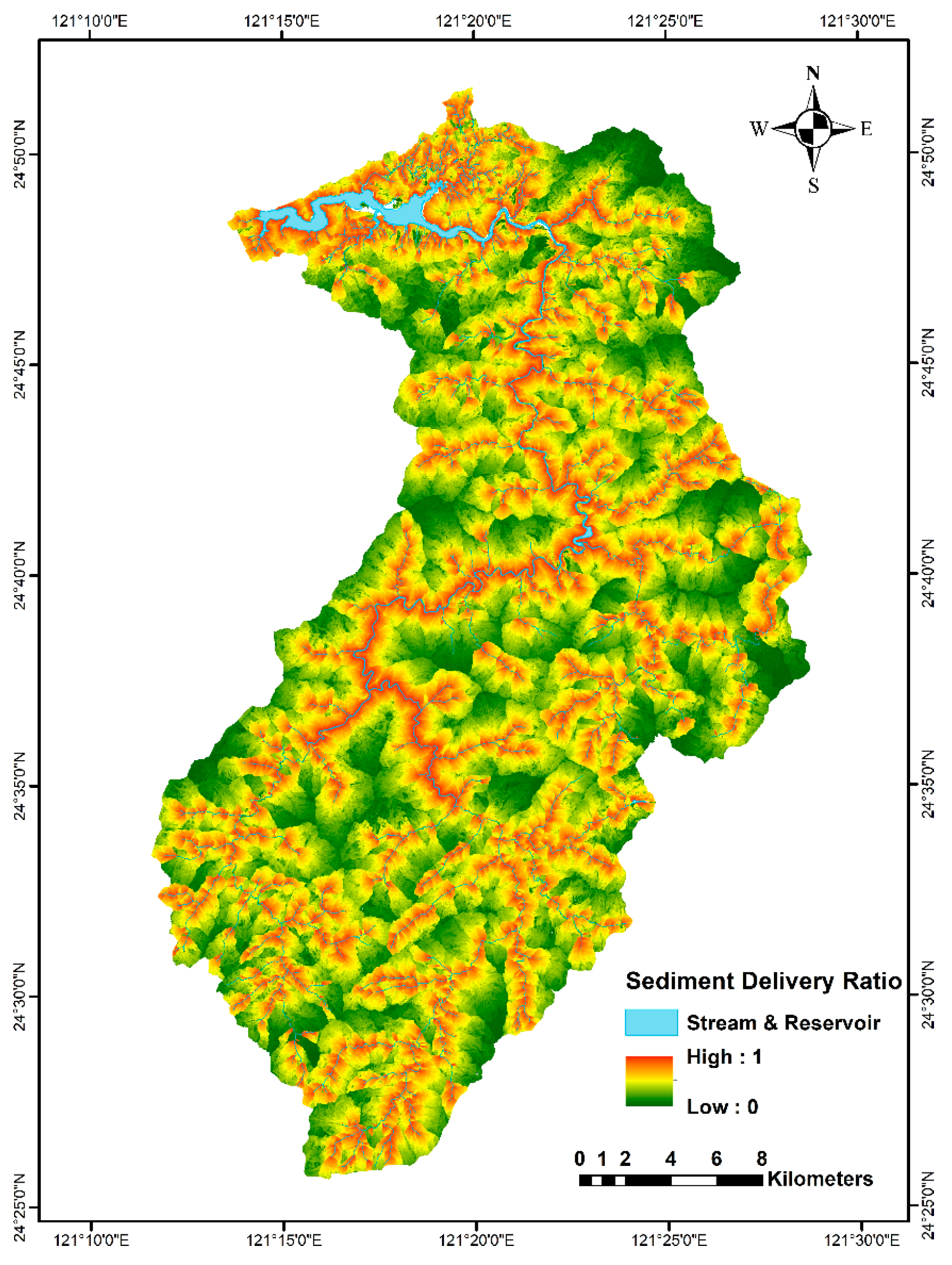
4.2. Grid-Based Travel Time, SDR, SL, and SY
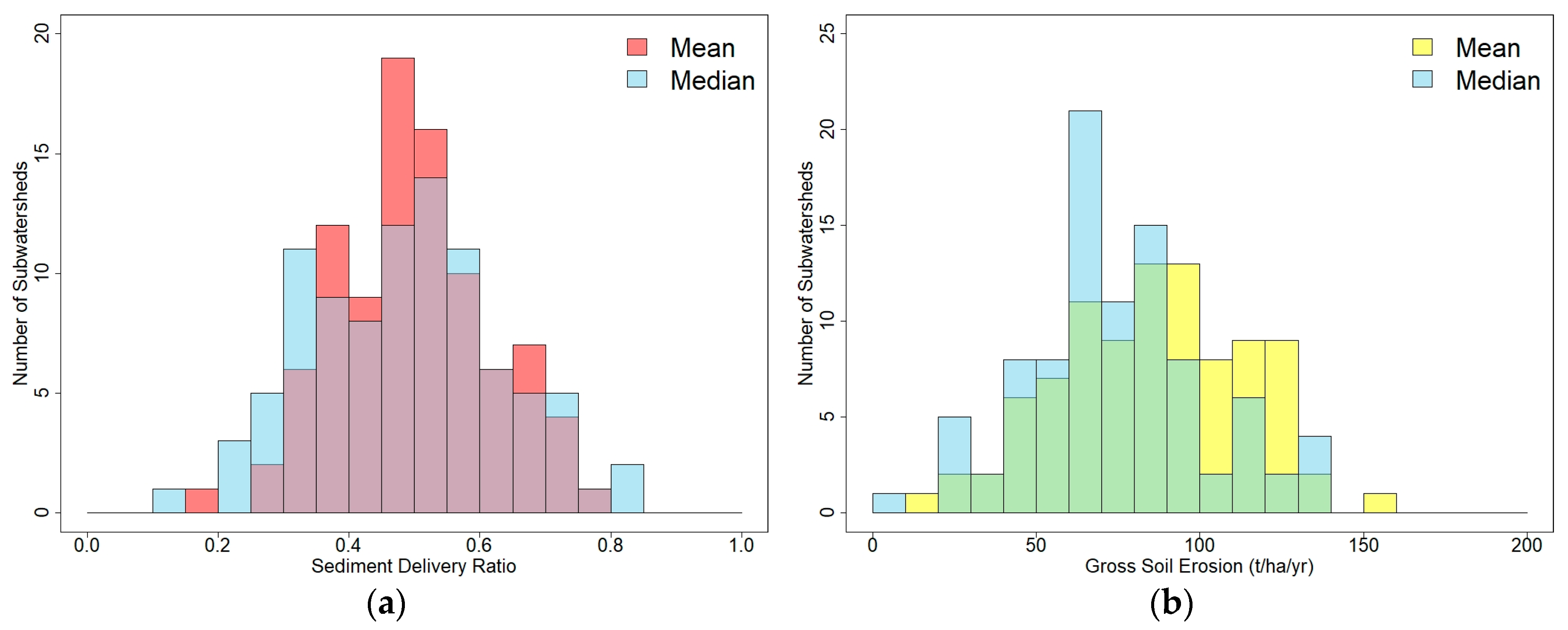
4.3. Comparison by Sub-Watershed Discretization on SDR, SL, and SY
5. Discussion
5.1. The Importance of SDR
5.2. The β Coefficient in the Model
5.3. SEDD Model Using the Grid–Cell-Based Analysis
5.4. Mean, Median, and Mode of 25/93 Sub-Watersheds
5.5. Sub-Watershed Prioritization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, A. Land Degradation in South Asia: Its Severity, Causes and Effects upon the People; Final Report for the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, United Nations Development Programme, and United Nations Environment Programme: Rome, Italy, 1993; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/v4360e/V4360E00.htm (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- IPCC. 2007: Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report; Pachauri, R.K., Reisinger, A., Eds.; Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; 104p. [Google Scholar]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; de Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; Molenaar, C.; de Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-related sustainable development goals: Four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, C.Y.; Lin, B.S.; Chen, C.K.; Chang, D.W. Application of Airborne Lidar Technology in Analyzing Sediment-Related Disasters and Effectiveness of Conservation Management in Shihmen Watershed. J. Geoengin. 2014, 9, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Kondolf, M.; Tullos, D.; Kuo, W.C. Sediment Management in Taiwan’s Reservoirs and Barriers to Implementation. Water 2018, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, C.; Wu, J.Q.; McCool, D.K.; Stöckle, C.O. Estimating Water Erosion and Sediment Yield with GIS, RUSLE, and SEDD. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 58, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.-Y. Research Progress on the Watershed Sediment Delivery Ratio. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 75, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-H. Analyzing Soil Erosion of Shihmen Reservoir Watershed Using Slope Units. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Z.X.; You, G.J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.J. Use of a Total Station to Monitor Post-Failure Sediment Yields in Landslide Sites of the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed, Taiwan. Geomorphology 2012, 139, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Z.X.; You, G.J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.J. Modeling the Sediment Yield from Landslides in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed, Taiwan. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathurst, J.C.; Burton, A.; Ward, T.J. Debris Flow Run-out and Landslide Sediment Delivery Model Tests. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-L.; Feng, M.-C.; Tu, Y.-T. Applying AGNPS to Investigate Sediment Delivery Ratio for Different Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 38, 373–386. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Soil and Water Conservation Bureau (SWCB). Evaluation on Sediment Environment Change and Soil and Water Conservation Plan for Shihmen Reservoir Watershed; SWCB Report; Soil and Water Conservation Bureau (SWCB): Taipei, Taiwan, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Shen, C.W.; Chiu, Y.J. Dynamic Modeling of Sediment Budget in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-Y.; Wang, T.-L.; Yu, J.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yuan, Y. Modeling sediment yields and stream stability due to sediment-related disaster in Shihmen reservoir watershed in Taiwan. Water 2019, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, D.H.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.S.; Seeboonruang, U.; Tsai, F. Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.-S.; Seeboonruang, U.; Thomas, K. Predicting Sheet and Rill Erosion of Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Taiwan Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.-S.; Seeboonruang, U. Using Machine Learning-Based Algorithms to Analyze Erosion Rates of a Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.-Z.; Wang, G.-H.; Tan, Z.-L.; Dong, X.-M.; Jia, C.-L. Delineation of Hydrological Response Unit Based on Remote Sensing Data. DEStech Trans. Eng. Technol. Res. 2017, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, E.F.; Sivapalan, M.; Beven, K.; Band, L. Effects of Spatial Variability and Scale with Implications to Hydrologic Modeling. J. Hydrol. 1988, 102, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Soil Sci. 1975, 120, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savvidou, E. A Study of Alternative Hydrological Response Units (HRU) Configurations in the Context of Geographical Information Systems (GIS)—Based Distributed Hydrological Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Cyprus University of Technology, Limassol, Cyprus, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. CHAPTER 1—SWAT Input Data: Overview. In SWAT Input/Output File Doc, Version 2012; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, V.; Minacapilli, M. Sediment Delivery Processes at Basin Scale. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1995, 40, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferro, V.; Porto, P.; Tusa, G. Testing a Distributed Approach for Modelling Sediment Delivery. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1998, 43, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, V.; Porto, P. Sediment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Kothyari, U.C. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield Using GIS. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2000, 45, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, G.; Chen, S.; McCool, D.K. Modeling the Impacts of No-till Practice on Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield with RUSLE, SEDD, and ArcView GIS. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 85, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Navas, A. Relating Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield to Geomorphic Features and Erosion Processes at the Catchment Scale in the Spanish Pre-Pyrenees. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V. Assessing Sediment Connectivity in Dendritic and Parallel Calanchi Systems. Catena 2019, 172, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-S.; Chen, C.-K.; Thomas, K.; Hsu, C.-K.; Ho, H.-C. Improvement of the K-Factor of USLE and Soil Erosion Estimation in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Sustainability 2019, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2 Book. Media 2009, 35, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Meyer, D.; Dimitriadou, E.; Hornik, K.; Weingessel, A.; Leisch, F.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group (Formerly: E1071), TU Wien; rdrr.io: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R Package Version 3.0-12. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Jhan, Y.-K. The Analysis of Soil Erosion of Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.-J. Terrain Factor Analysis of Soil Erosion in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-H. Analysis of Soil Erosion of Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Taiwan and Lam Phra Ploeng Basin in Thailand. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains; Agriculture Handbook No. 282; Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; USDA Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Ferro, V.; Di Stefano, C.; Minacapilli, M.; Santoro, M. Calibrating the SEDD Model for Sicilian Ungauged Basins. IAHS-AISH Publ. 2003, 279, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.E. Use of Caesium-137 Measurements and Long-Term Records of Sediment Load to Calibrate the Sediment Delivery Component of the SEDD Model and Explore Scale Effect: Examples from Southern Italy. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V.; Porto, P.; Rizzo, S. Testing a Spatially Distributed Sediment Delivery Model (SEDD) in a Forested Basin by Cesium-137 Technique. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Burguet, M.; Taguas, E.V.; Gómez, J.A. Exploring Calibration Strategies of the SEDD Model in Two Olive Orchard Catchments. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Lana-Renault, N.; García-Ruiz, J.M.; Navas, A. Assessing the Potential Effect of Different Land Cover Management Practices on Sediment Yield from an Abandoned Farmland Catchment in the Spanish Pyrenees. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 1440–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoni, V.A. Sedimentation Engineering, Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice; No. 54; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; He, X. Assessing Effects of Landscape Pattern on Sediment Yield Using Sediment Delivery Distributed Model and a Landscape Indicator. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 22, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.-H. Evaluation of Sediment Delivery Ratio and Completeness Ratio of the Reservoir Watershed. Ph.D. Thesis, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Haan, C.T.; Barfield, B.J.; Hayes, J.C. Design Hydrology and Sedimentology for Small Catchments; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jhan, Y.-K.; Shen, Z.-P.; Chen, W.W.; Tsai, F. Analysis of soil erosion of Shihmen reservoir watershed. In Proceedings of the 34th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing 2013, ACRS, Bali, Indonesia, 20–24 October 2013; pp. 3034–3039. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.H.; Yang, K.J.; Tsai, F.; Seeboonruang, U. Identifying and Comparing Relatively High Soil Erosion Sites with Four DEMs. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, K.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.-S.; Seeboonruang, U. Evaluation of the SEdiment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6221. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156221
Thomas K, Chen W, Lin B-S, Seeboonruang U. Evaluation of the SEdiment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Sustainability. 2020; 12(15):6221. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156221
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Kent, Walter Chen, Bor-Shiun Lin, and Uma Seeboonruang. 2020. "Evaluation of the SEdiment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed" Sustainability 12, no. 15: 6221. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156221
APA StyleThomas, K., Chen, W., Lin, B.-S., & Seeboonruang, U. (2020). Evaluation of the SEdiment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model in the Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Sustainability, 12(15), 6221. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156221






