Analysis on Decoupling between Urbanization Level and Urbanization Quality in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Data
2.1. Measurement of Urbanization Level
2.1.1. Evaluation of Urbanization Quality
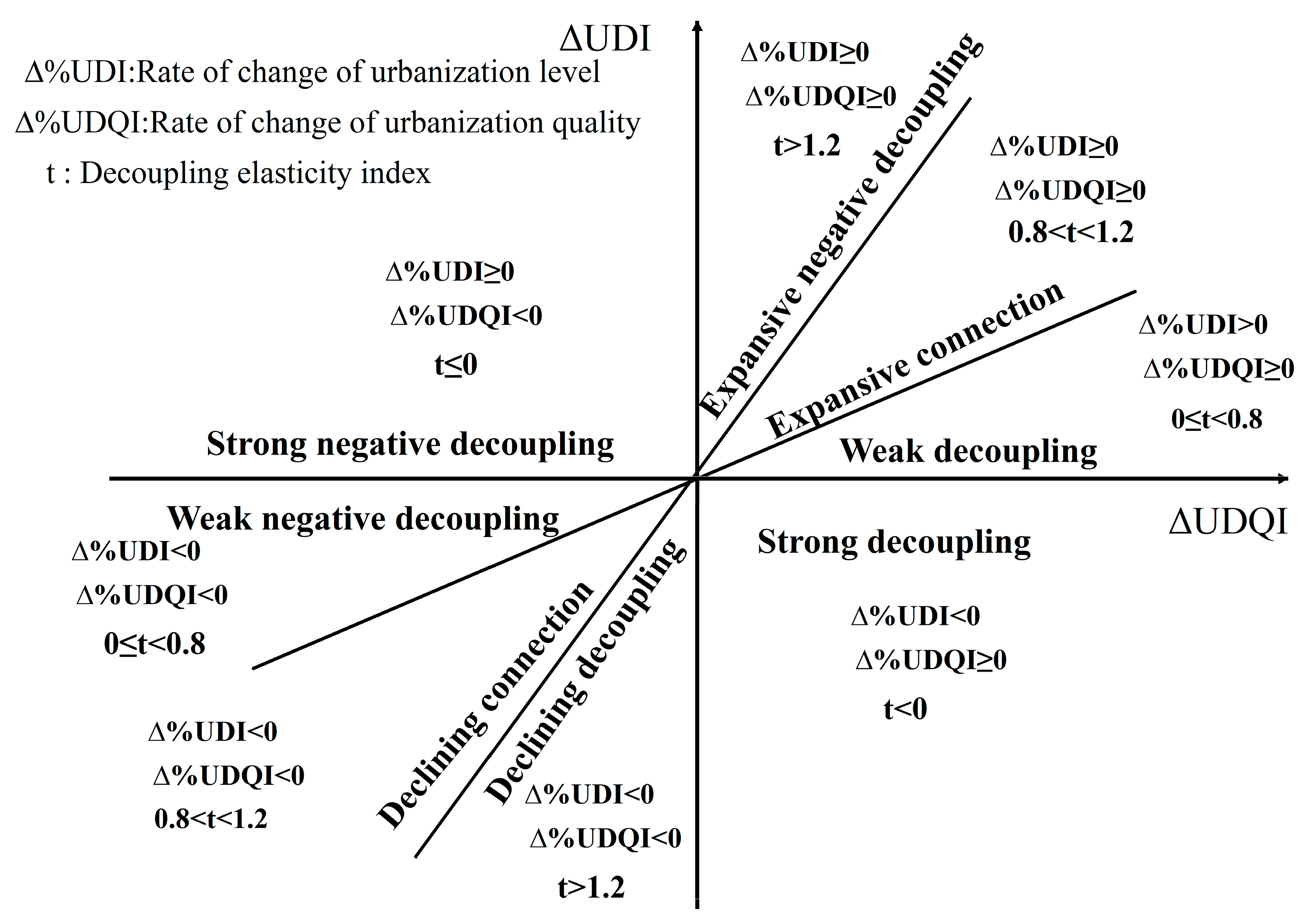
2.1.2. Decoupling Analysis
2.2. Data Source
3. Results
3.1. Changes of Urbanization Level in China
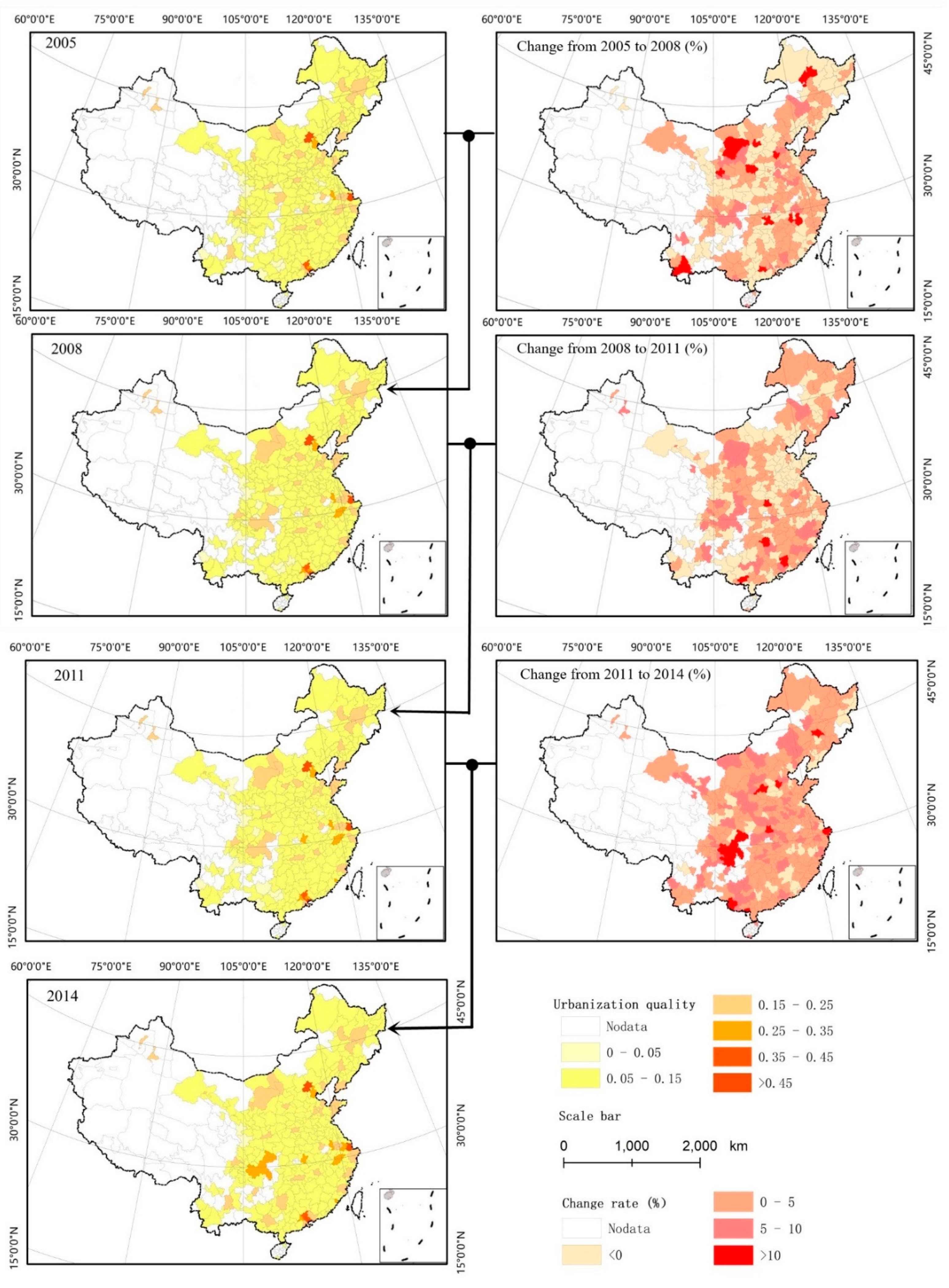
3.2. Change of Urbanization Quality
3.3. Decoupling States
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duffin, E. Degree of Urbanization (Percentage of Urban Population in Total Population) by Continent in 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/270860/urbanization-by-continent/ (accessed on 26 April 2019).
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Day, J.; Ellis, P. Urbanization for Everyone: Benefits of Urbanization in Indonesia’s Rural Regions. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2014, 140, 04014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T. Southern Appalachia’s Nineteenth-Century Bright Tobacco Boom: Industrialization, Urbanization, and the Culture of Tobacco. Agric. Hist. 2014, 88, 175–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z. Research on the Investigation of Current Situation of the Sports Culture of the Square under the Trend of Rural Urbanization in Shandong Province. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2017, 28, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaraman, R.; Nolan, L.; Shitole, T.; Sawant, K.; Shitole, S.; Sood, K.; Nanarkar, M.; Ghannam, J.; Betancourt, T.S.; Bloom, D.E.; et al. The psychological toll of slum living in Mumbai, India: A mixed methods study. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 119, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, M.; Routray, P.; Torondel, B.; Clasen, T. Neighbour-shared versus communal latrines in urban slums: A cross-sectional study in Orissa, India exploring household demographics, accessibility, privacy, use and cleanliness. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. A time series analysis of urbanization induced land use and land cover change and its impact on land surface temperature with Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, W.; Gu, H.-H.; Li, F. Progress in the Remote Sensing Monitoring of the Ecological Environment in Mining Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, J.; Eitelberg, D.A.; Verburg, P.H. A global analysis of land take in cropland areas and production displacement from urbanization. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 43, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, P.; Saxena, A.; Singh, D.S.; Verma, D. Impact of Rapid Urbanization on Water Quality Index in Groundwater Fed Gomati River, Lucknow, India. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Li, L. Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: A case of fine particles (PM 2.5) in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, M.F.J.; La Sorte, F.A.; Nilon, C.H.; Katti, M.; Goddard, M.A.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Warren, P.S.; Williams, N.S.G.; Cilliers, S.; Clarkson, B.; et al. A global analysis of the impacts of urbanization on bird and plant diversity reveals key anthropogenic drivers. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20133330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Yanxu, L.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.-L.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, Z. Assessing urbanization quality using structure and function analyses: A case study of the urban agglomeration around Hangzhou Bay (UAHB), China. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.Y. Spatial-temporal characteristics and determinants of land urbanization quality in China: Evidence from 285 prefecture-level cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, B.J.L. Urbanization. In Urban Ecology: An International Perspective on the Interaction Between Humans and Nature; Marzluff, J.M., Shulenberger, E., Endlicher, W., Alberti, M., Bradley, G., Ryan, C., Simon, U., ZumBrunnen, C., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K. The Urbanization of the Human Population. Sci. Am. 1965, 213, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Kahn, J.R.; Ofek, H. City Size, Quality of Life, and the Urbanization Deflator of the GNP: 1910–1984. South. Econ. J. 1988, 54, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Feng, K. Coupling analysis of urbanization and energy-environment efficiency: Evidence from Guangdong province. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnahan, D.; Gove, W.; Galle, O.R. Urbanization, Population Density, and Overcrowding: Trends in the Quality of Life in Urban America. Soc. Forces 1974, 53, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barles, S.; Lestel, L. The Nitrogen Question. J. Urban Hist. 2007, 33, 794–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D. The causal relationship between land urbanization quality and economic growth: Evidence from capital cities in China. Qual. Quant. 2016, 51, 2707–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Pijanowski, B.C. The effects of China’s cultivated land balance program on potential land productivity at a national scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Tayyebi, A. Urban expansion and its consumption of high-quality farmland in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 54, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Song, W. Determinants of cropland abandonment at the parcel, household and village levels in mountain areas of China: A multi-level analysis. Land Use Policy 2014, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Klobodu, E.K.M. Urbanization, democracy, bureaucratic quality, and environmental degradation. J. Policy Model. 2017, 39, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Dai, Q.; Su, H. Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: Achievements, challenges and reflections. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P.J. An index of rurality for England and Wales. Reg. Stud. 1977, 11, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P.; Edwards, G. Rurality in England and Wales 1981: A replication of the 1971 index. Reg. Stud. 1986, 20, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, P.J. Changing patterns of urbanisation in rural areas of England and Wales, 1961–1971. Reg. Stud. 1978, 12, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, N. An assessment of rurality in Italian farms using a quantitative approach. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 25, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Centre for Human Settlements. The State of the World’s Cities; UN-HABITAT: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Habitat, U.N. State of the World’s Cities 2012/2013: Prosperity of Cities; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, F.L.; Noor, Z.Z.; Figueroa, M.J. Review of urban sustainability indicators assessment—Case study between Asian countries. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.; Bosch, P.; Airaksinen, M. Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for Smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when? Cities 2019, 89, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, W. Research on the evaluation model of the modernization level of urban construction in Jiangsu Province, China. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2510–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sheng, J. New evaluation system for the modernization level of a province or a city based on an improved entropy method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongyu, L.; Peiyu, Y. In A Review on Leisure City Evaluation Index Systems and Model. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Social Science and Higher Education (ICSSHE in Xiamen, China, on 23 August 2019); Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M. A novel assessment of urbanization quality and its applications. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 508, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D.; Chen, H.; Ye, C. Progress of China’s new-type urbanization construction since 2014: A preliminary assessment. Cities 2018, 78, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, S. Research on the Quality and Level of Urbanization in the Baoshan District, Shanghai. In Building Resilient Cities in China: The Nexus between Planning and Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B. A Novel Coordination Model of Urbanization Speed and Quality based on Multidimensional Economic Data. Rev. Tec. Fac. Univ. Zulia 2016, 39, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Indicators to Measure Decoupling of Environmental Pressure from Economic Growth. Available online: http://www.olis.oecd.org/olis/2002doc.nsf/LinkTo/sg-sd2002 (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Akizu-Gardoki, O.; Bueno, G.; Wiedmann, T.; Lopez-Guede, J.M.; Arto, I.; Hernandez, P.; Moran, D. Decoupling between human development and energy consumption within footprint accounts. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, N.; Zhao, D. Empirical Research on Decoupling Relationship between Energy-Related Carbon Emission and Economic Growth in Guangdong Province Based on Extended Kaya Identity. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, B. Decoupling analysis of world economic growth and CO2 emissions: A study comparing developed and developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shan, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; Yu, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. Decoupling of economic growth and emissions in China’s cities: A case study of the Central Plains urban agglomeration. Appl. Energy 2019, 244, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Fu, S.; Yang, D. Decoupling of Land Use Intensity and Ecological Environment in Gansu Province, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Bureau of Statistics. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).



| Classification | Index | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Land urbanization quality | Per capita built-up area (m2/person) | Total urban population/built-up area |
| GDP output value per unit area (10,000 yuan/km2) | Urban GDP/urban built-up area | |
| Per capita public green space area (m2/person) | Urban public green space area/urban non-agricultural population | |
| Urban road area per capita (m2) | Area of urban roads/total urban population | |
| Economic urbanization quality | Employed population in secondary and tertiary industries (10,000 person) | Population engaged in secondary and tertiary industries |
| Proportion of tertiary industry population (%) | Population engaged in tertiary industry/total population | |
| Proportion of secondary industry output value (%) | Added value of secondary industry/GDP | |
| Proportion of tertiary industry output value (%) | Added value of tertiary industry/GDP | |
| Total industrial output value (10,000 yuan) | Revenue from principal business of the current period + cost price of goods in stock at the end of the period − cost price of goods in stock at the beginning of the period | |
| GDP (10,000 yuan) | Gross Domestic Product | |
| Per capita GDP (yuan) | Total output (total GDP, i.e., total output of social goods and services)/total population | |
| GDP growth rate (%) | The proportion of the increase within a certain period of time in the market value of all final products produced by the use of production factors over the previous period | |
| Social urbanization quality | Public financial revenue per capita (yuan) | Total financial revenue/national population |
| Per capita public financial expenditure (yuan) | Total financial expenditure/national population | |
| Per capita deposit in RMB (yuan) | Residents deposit in RMB in domestic banking financial institutions and the central bank/total population | |
| Average wage of employees in service (yuan) | The average amount of monetary wage per employee in a certain period of time | |
| Number of public library books per 100 person (book/volume) | Number of books in public library (volume)/urban population (100 person) | |
| Number of college students per 10,000 person (person) | College students (person)/urban population (10,000 person) | |
| Number of buses owned per 10,000 person (unit) | All kinds of buses in urban area (unit)/population in urban area (10,000 person) | |
| Bed number owned per 10,000 person (beds) | Total number of beds in urban area/population in urban area (10,000) | |
| Number of doctors owned per 10,000 person (person) | Number of urban doctors/urban population (10,000 person) | |
| Ecological urbanization quality | Green area of built-up area (%) | Total green land area in urban built-up area/total land area in urban built-up area |
| Ratio of general industrial solid wastes utilized (%) | Industrial solid waste comprehensive utilization/industrial solid waste production | |
| Centralized treatment rate of sewage treatment plant (%) | Removal amount of pollution factors in sewage/total amount of sewage | |
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste (%) | Quantity of waste handled by harmless treatment/total domestic waste |
| Decoupling State | Growth Rate of Urbanization Level | Growth Rate of Urbanization Quality | Elasticity T | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative decoupling | Weak negative decoupling | <0 | <0 | 0 ≤ t < 0.8 |
| Strong negative decoupling | ≥0 | <0 | t ≤ 0 | |
| Expansive negative decoupling | ≥0 | ≥0 | t > 1.2 | |
| Decoupling | Declining decoupling | <0 | <0 | t > 1.2 |
| Strong decoupling | <0 | ≥0 | t < 0 | |
| Weak decoupling | >0 | ≥0 | 0 ≤ t < 0.8 | |
| Connection | Declining connection | <0 | <0 | 0.8 < t < 1.2 |
| Expansive connection | ≥0 | ≥0 | 0.8 < t < 1.2 | |
| Urbanization Rate | Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |
| 10%~20% | 7 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20%~30% | 47 | 42 | 30 | 15 | 14 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| 30%~40% | 91 | 95 | 91 | 95 | 88 | 67 | 60 | 50 | 39 | 32 |
| 40%~50% | 63 | 66 | 75 | 77 | 77 | 74 | 93 | 89 | 91 | 92 |
| 50%~60% | 40 | 35 | 34 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 50 | 62 | 69 | 71 |
| 60%~70% | 15 | 24 | 30 | 32 | 37 | 45 | 43 | 45 | 47 | 49 |
| 70%~80% | 11 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 19 |
| 80%~90% | 9 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 90%~100% | 3 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Decoupling State | Weak Negative Decoupling | Strong Negative Decoupling | Expansive Negative Decoupling | Declining Decoupling | Strong Decoupling | Weak Decoupling | Declining Connection | Expansive Connection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 14 | 181 | 53 | 24 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 2 |
| 2007 | 9 | 71 | 114 | 2 | 18 | 53 | 1 | 17 |
| 2008 | 12 | 165 | 72 | 19 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 2009 | 9 | 41 | 129 | 4 | 14 | 61 | 0 | 27 |
| 2010 | 29 | 178 | 21 | 46 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 2011 | 8 | 82 | 125 | 10 | 28 | 23 | 0 | 9 |
| 2012 | 11 | 74 | 145 | 10 | 13 | 26 | 0 | 6 |
| 2013 | 11 | 117 | 94 | 5 | 17 | 25 | 1 | 15 |
| 2014 | 8 | 74 | 106 | 2 | 7 | 60 | 1 | 27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Wen, B.; Yang, D.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Y. Analysis on Decoupling between Urbanization Level and Urbanization Quality in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176835
Zhang X, Song W, Wang J, Wen B, Yang D, Jiang S, Wu Y. Analysis on Decoupling between Urbanization Level and Urbanization Quality in China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176835
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xueru, Wei Song, Jingtao Wang, Bo Wen, Dazhi Yang, Shiliang Jiang, and Yanbin Wu. 2020. "Analysis on Decoupling between Urbanization Level and Urbanization Quality in China" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176835
APA StyleZhang, X., Song, W., Wang, J., Wen, B., Yang, D., Jiang, S., & Wu, Y. (2020). Analysis on Decoupling between Urbanization Level and Urbanization Quality in China. Sustainability, 12(17), 6835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176835







