Study on Runoff Simulation of the Source Region of the Yellow River and the Inland Arid Source Region Based on the Variable Infiltration Capacity Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Source Area of the Yellow River
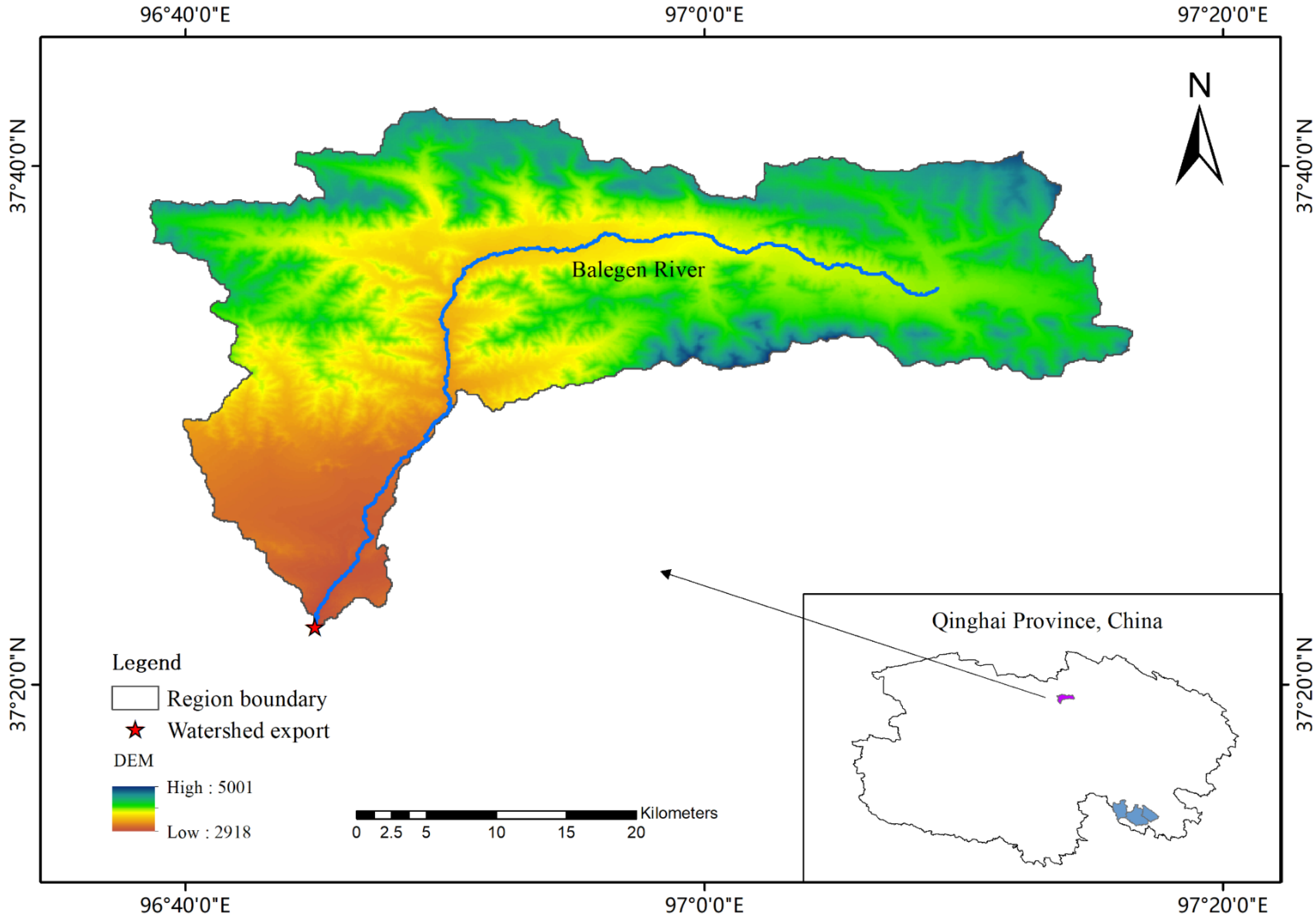
2.2. Inland Arid Source Area
3. Methods and Data
3.1. VIC Model
3.2. Data
3.2.1. DEM Data
3.2.2. Vegetation Data
3.2.3. Soil Data
3.2.4. Meteorological Data
3.2.5. Control File
3.2.6. Actual Measured Runoff
4. Model Results and Analysis
5. Runoff Analysis in Climate Perturbation Experiments
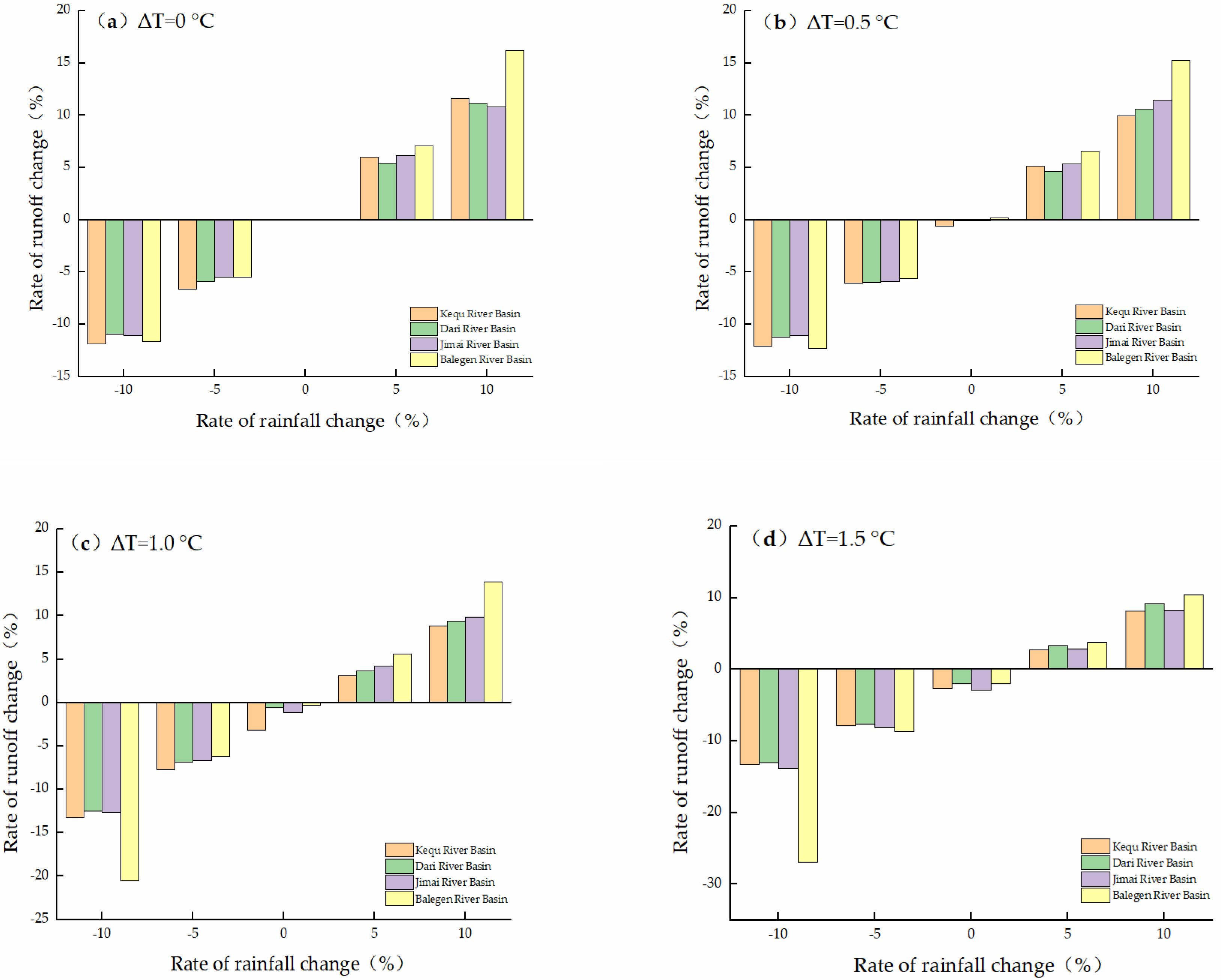
5.1. Assumptions of Climate Perturbation Experiments
5.2. Analysis of Runoff Change
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, L. Human impacts on runoff regime of middle and lower Yellow River. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Fu, J. Changes in intra-annual runoff and its response to climate change and human activities in the headstream areas of the Tarim River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chang, J.; Leng, G.; Huang, Q. Integrated index for drought assessment based on variable fuzzy set theory: A case study in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-J. Trend of Annual Runoff for Major Rivers in China under Climate Change. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Sohl, T.L.; Young, C.J. Projecting the land cover change and its environmental impacts in the Cedar River Basin in the Midwestern United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kang, T.; Bu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016. Water 2020, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, F. Changes and Influencing Factors of Surface Water Resources in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 3, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, P.; Yang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, G. Analysis on the variation trend and cause of precipitation and runoff in Chengbihe Basin over the past 50 years. J. Guangxi Univ. ( Nat. Sci. Ed) 2019, 44, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Huang, L.; Li, H. Evaluation on Study of Mathematical Modeling of Hydrology. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2004, 4, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, L. Progress on studies and applications of the Distributed Hydrological Models. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 41, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Chang, J.; Chen, L. Runoff change in upper reach of Yellow River under future climate change based on VIC model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 35, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chang, J. Application of VIC model based standardized drought index in the Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Jin, J.; Huang, A.; Zhan, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, C. Typical hydro-meteorological changes and runoff process simulation in Yellow River basin. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. A land-surface hydrology parameterization with subgrid variability for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res 1994, 99, 14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Surface soil moisture parameterization of the VIC-2L model: Evaluation and modification. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1996, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Liang, X. Streamflow simulation for continental-scale river basins. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xie, Z. A new surface runoff parameterization with subgrid-scale soil heterogeneity for land surface models. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, F. Distributed Hydrological Simulaton in the Lhasa River Basin Based on VIC Model. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 48, 524–529. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xia, D.; Liu, Y. An Analysis of Land Use Change Dynamics and Its Impacts on Hydrological Processes in the Jialing River Basin. Water 2014, 6, 3758–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.H.; Su, F.G.; Liang, X.; Zeng, Q.C.; Hao, Z.C.; Guo, Y.F. Applications of a surface runoff model with Horton and Dunne runoff for VIC. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, D.; NolteHolube, R.; Raschke, E. A large-scale horizontal routing model to be coupled to land surface parametrization schemes. Tellus Ser. A-Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanol. 1996, 48, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, D.; Raschke, E.; Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Regional scale hydrology: I. Formulation of the VIC-2L model coupled to a routing model. Hydrol. Sci. J. -J. Sci. Hydrol. 1998, 43, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, D.; Raschke, E.; Nijssen, B.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Regional scale hydrology: II. Application of the VIC-2L model to the Weser River, Germany. Hydrol. Sci. J. -J. Sci. Hydrol. 1998, 43, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z. Analysis of Hydrological Variables Based on the VIC-3L Model in Headwater Catchment of the Tarim River Basin. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2010, 46, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.C.; Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Sohlberg, R. Global land cover classification at 1km spatial resolution using a classification tree approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.G.; Xie, Z.H. A model for assessing effects of climate change on runoff in China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2003, 13, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.A.; Jackson, T.J.; Rawls, W.J. Estimating soil water-holding capacities by linking the Food and Agriculture Organization soil map of the world with global pedon databases and continuous pedotransfer functions. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Application Reaearch on Vic Model in Chinese Humid Area. Master’s Thesis, HoHai University, NanJing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H. Study on Rainfall-Runoff Simulation and Driving Factorsin Typical Watershed of the Three-River Headwaters. Master’s Thesis, Qinghai University, XiNing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Xie, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, J. Evaluation of Hourly Precipitation Fusion Dataset CMPA V1.0 in Typical Basins of Loess Plateau. Water Resour. Power 2019, 37, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q. An Application of Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) Macro Scale Land Surface Hydrological Model in China. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University, ChangSha, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tuo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tuo, Z.; Qiao, Y. Analysis of Yellow River Regional Representative Hydrological Station. In Proceedings of the Transformation of Economic Development Mode and Independent Innovation—The 12th Annual Conference of China Science and Technology Association, Fuzhou, China; 2010; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, L. Application of Rainfall Runoff Model in Annual Runoff Reduction Calculation. Heilongjiang Sci. Technol. Water Conserv. 2003, 3, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D. Natural runoff reduction and correction method. Henan Water Resour. South North Water Divers. 2013, 14, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhu, D. Research on Calculation Model of Natural Runoff Reduction on the Moon Scale. Zhi Huai 2018, 4, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. 2018: Summary for Policymakers. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty, Masson-Delmotte, V.P., Zhai, H.-O., Pörtner, D., Roberts, J., Skea, P.R., Shukla, A., Pirani, W., Moufouma-Okia, C., Péan, R., Pidcock, S., et al., Eds.; in Press.






| Number | Vegetation Classification | Albedo | Minimum Stomatal Impedance (s/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Water | / | / |
| 1 | Evergreen needleleaf forest | 0.12 | 250 |
| 2 | Evergreen broadleaf forest | 0.12 | 250 |
| 3 | Deciduous needleleaf forest | 0.18 | 150 |
| 4 | Deciduous broadleaf forest | 0.18 | 150 |
| 5 | Mixed forest | 0.18 | 200 |
| 6 | Woodland | 0.18 | 200 |
| 7 | Wooded grasslands | 0.19 | 125 |
| 8 | Closed shrublands | 0.19 | 135 |
| 9 | Open shrublands | 0.19 | 135 |
| 10 | Grasslands | 0.20 | 120 |
| 11 | Crop land | 0.10 | 120 |
| 12 | Bare ground | / | / |
| 13 | Urban and built-up | / | / |
| Number | Soil Classification | Porosity (m3/m3) | Saturated Soil Water Potential (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | No data/ocean | / | / |
| 1 | Sand | 0.445 | 0.069 |
| 2 | Loamy sand | 0.434 | 0.036 |
| 3 | Sandy loam | 0.415 | 0.141 |
| 4 | Silt loam | 0.471 | 0.759 |
| 5 | Silt | 0.523 | 0.759 |
| 6 | Loam | 0.445 | 0.355 |
| 7 | Sandy clay loam | 0.404 | 0.135 |
| 8 | Silty clay loam | 0.486 | 0.617 |
| 9 | Clay loam | 0.467 | 0.263 |
| 10 | Sandy clay | 0.415 | 0.098 |
| 11 | Silty clay | 0.497 | 0.324 |
| 12 | Clay | 0.482 | 0.468 |
| 13 | Salt flats | / | / |
| 14 | Inland water | / | / |
| 15 | Rock debris or desert detritus | / | / |
| 16 | Glaciers | / | / |
| Study Areas | NSE | RE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The source region of the Yellow River | Kequ River basin | 0.74 | 6.01 |
| Dari River basin | 0.93 | 5.66 | |
| Jimai River basin | 0.75 | 4.59 | |
| The inland arid source region | Balegen River basin | 0.71 | 6.50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Xie, H.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J. Study on Runoff Simulation of the Source Region of the Yellow River and the Inland Arid Source Region Based on the Variable Infiltration Capacity Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177041
Wang Y, Zheng W, Xie H, Liu Q, Wei J. Study on Runoff Simulation of the Source Region of the Yellow River and the Inland Arid Source Region Based on the Variable Infiltration Capacity Model. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuan, Wengang Zheng, Hongwei Xie, Qi Liu, and Jiahua Wei. 2020. "Study on Runoff Simulation of the Source Region of the Yellow River and the Inland Arid Source Region Based on the Variable Infiltration Capacity Model" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177041
APA StyleWang, Y., Zheng, W., Xie, H., Liu, Q., & Wei, J. (2020). Study on Runoff Simulation of the Source Region of the Yellow River and the Inland Arid Source Region Based on the Variable Infiltration Capacity Model. Sustainability, 12(17), 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177041






