Analysis of Urban Morphological Effect on the Microclimate of the Urban Residential Area of Kampung Baru in Kuala Lumpur Using a Geospatial Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
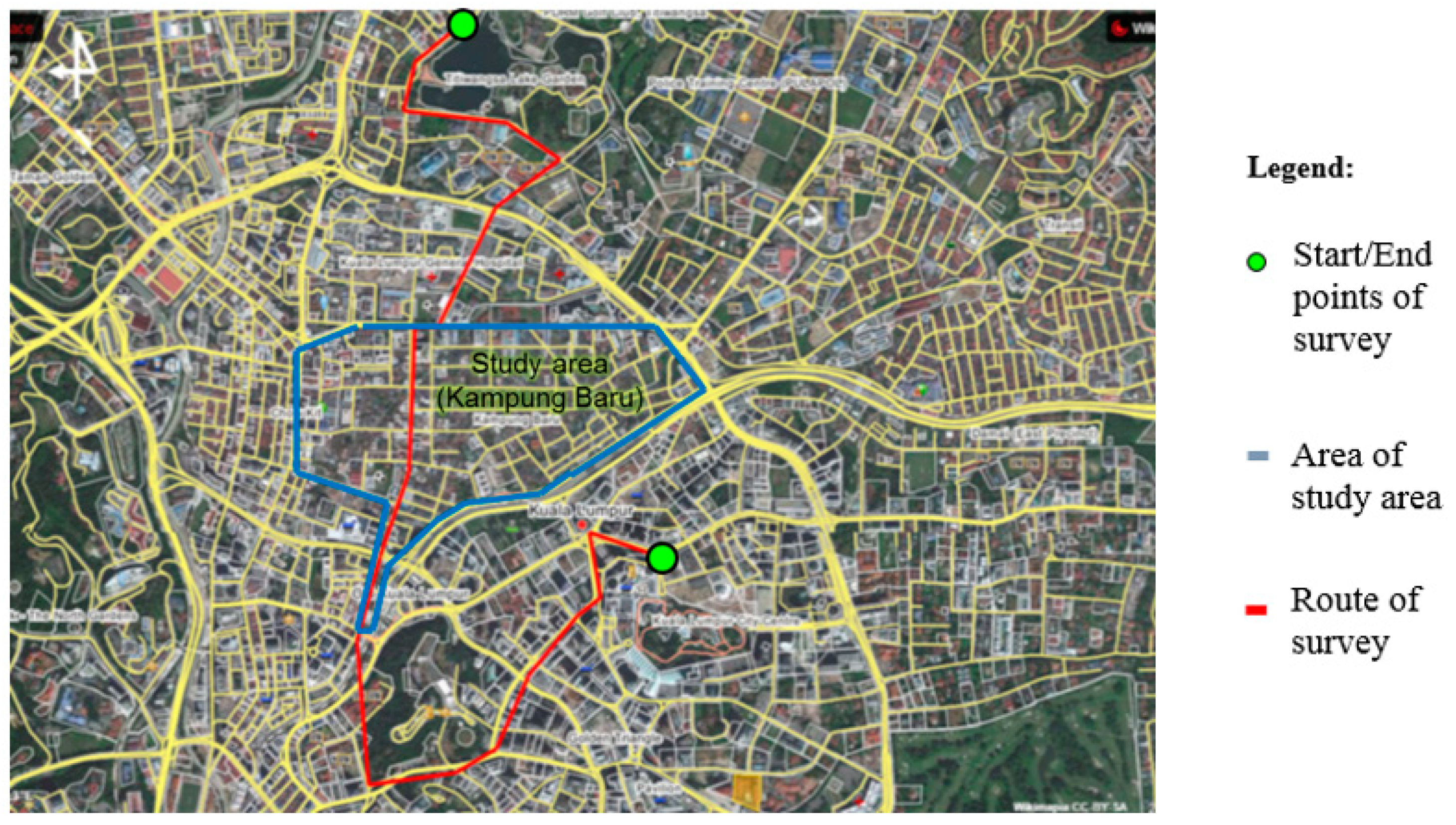
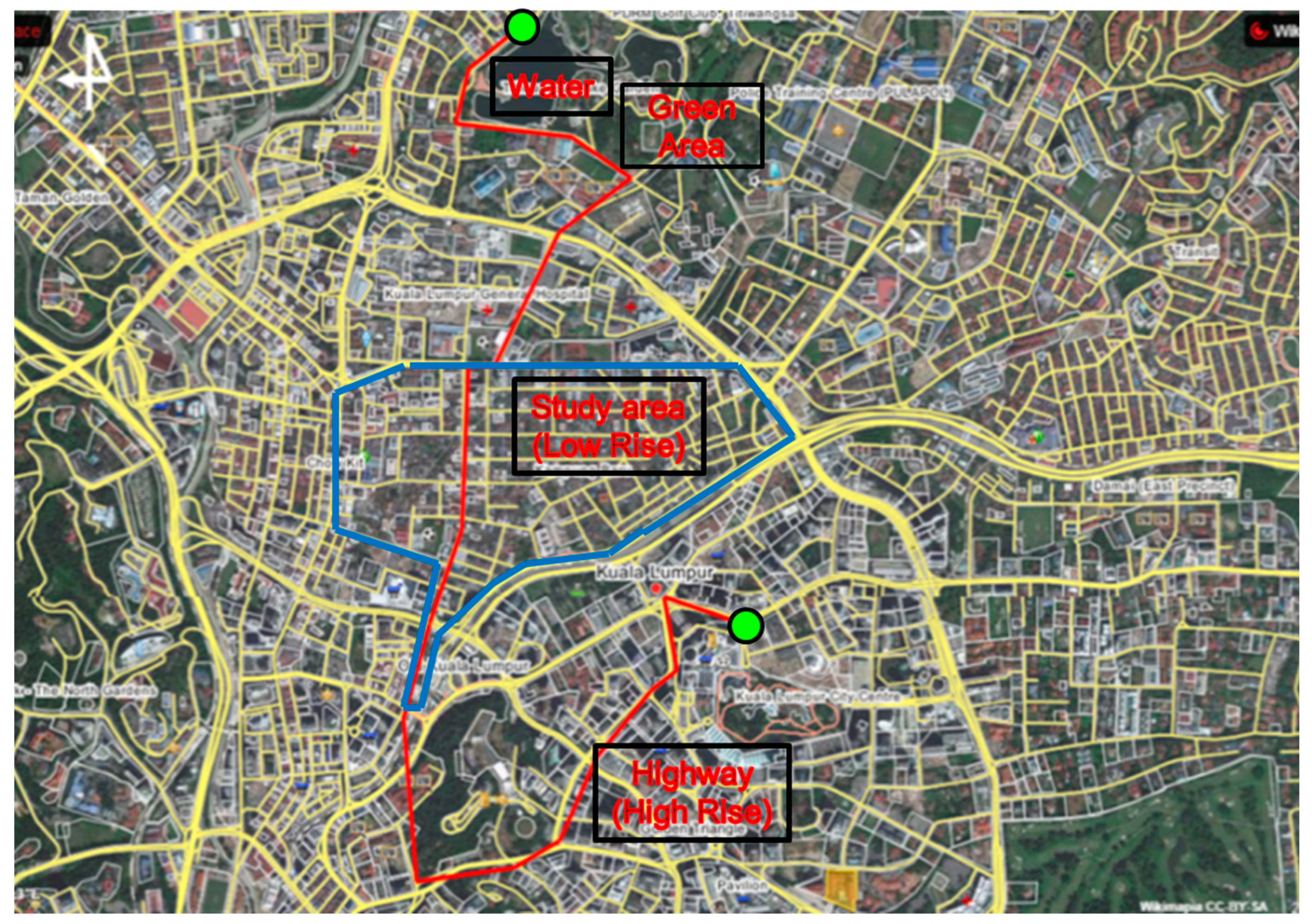
2.1. Study Area
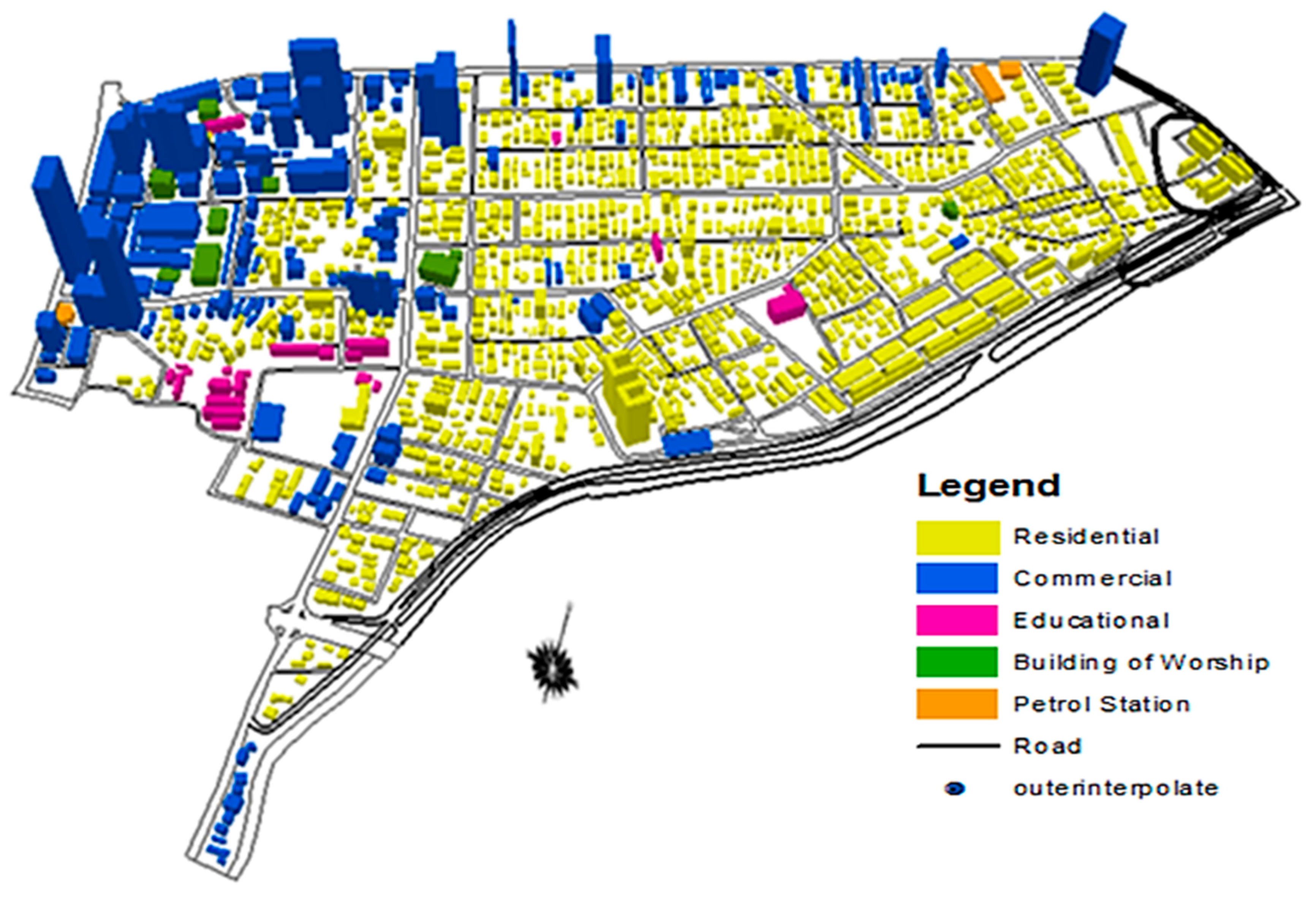
2.2. Building Morphology
2.3. Field Measurement
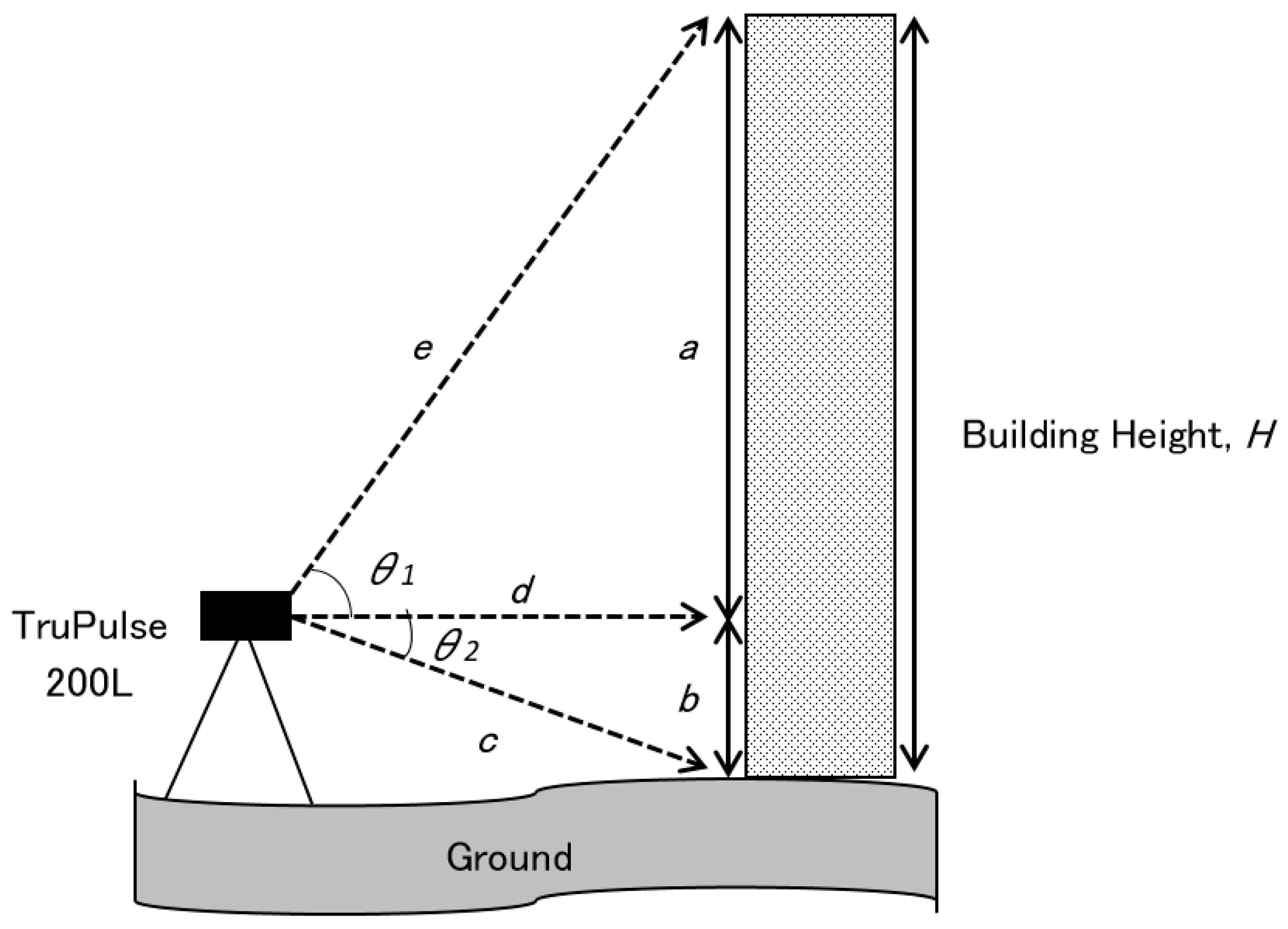
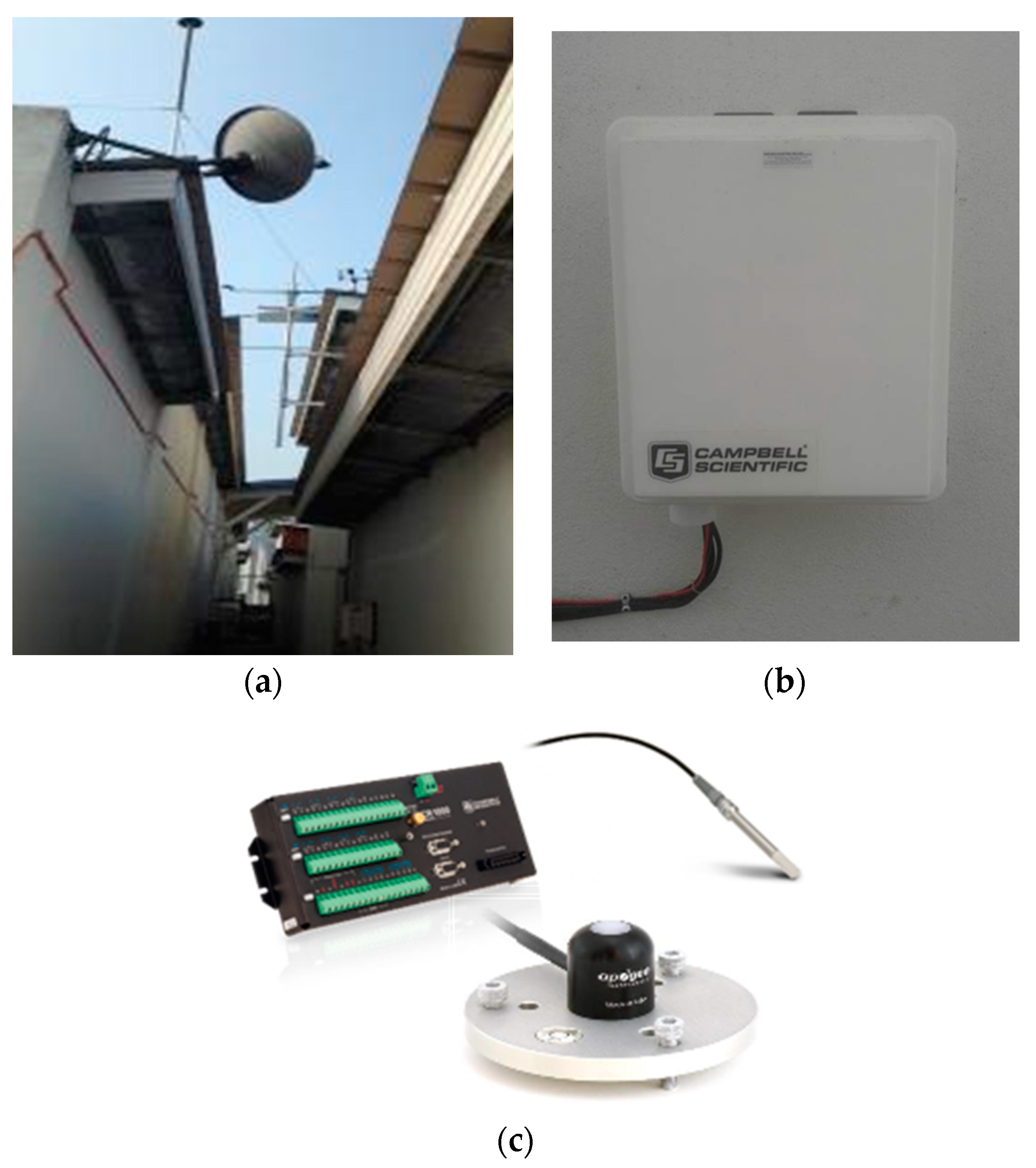
2.3.1. Instrumentation
2.3.2. Site Selection
2.3.3. Fixed Measurement
2.3.4. Mobile Measurement
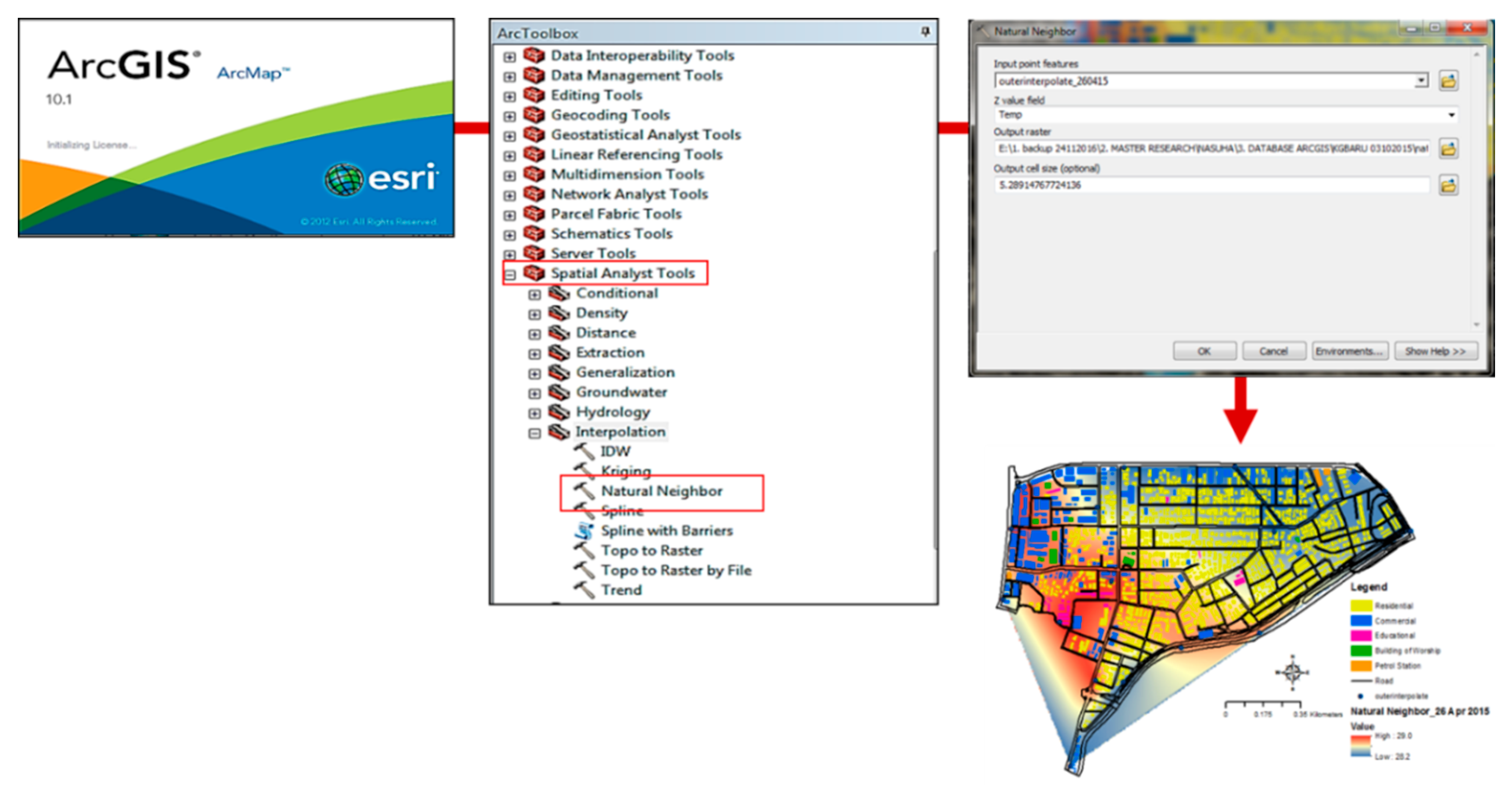
2.4. Geospatial GIS Data
3. Results and Discussion
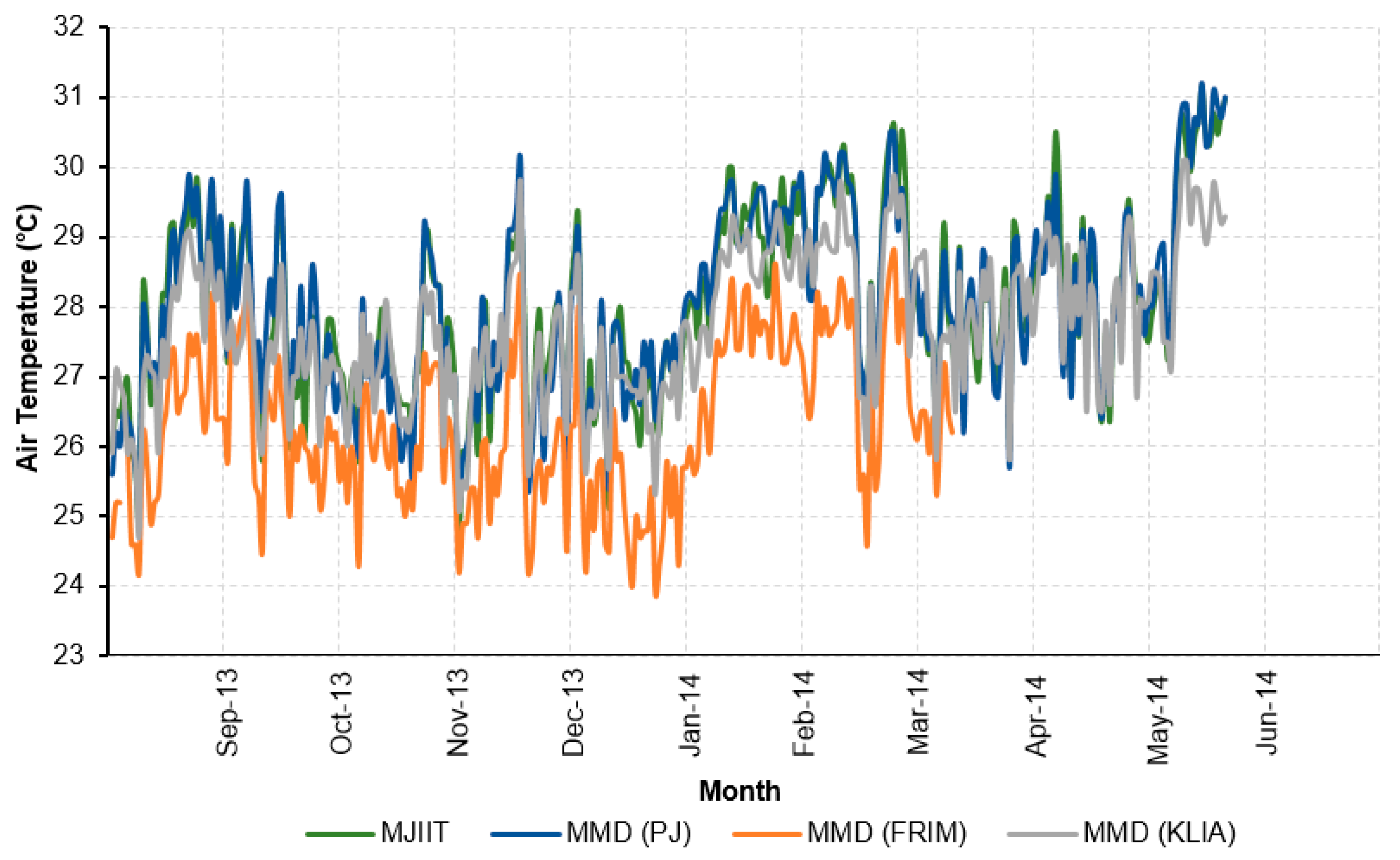
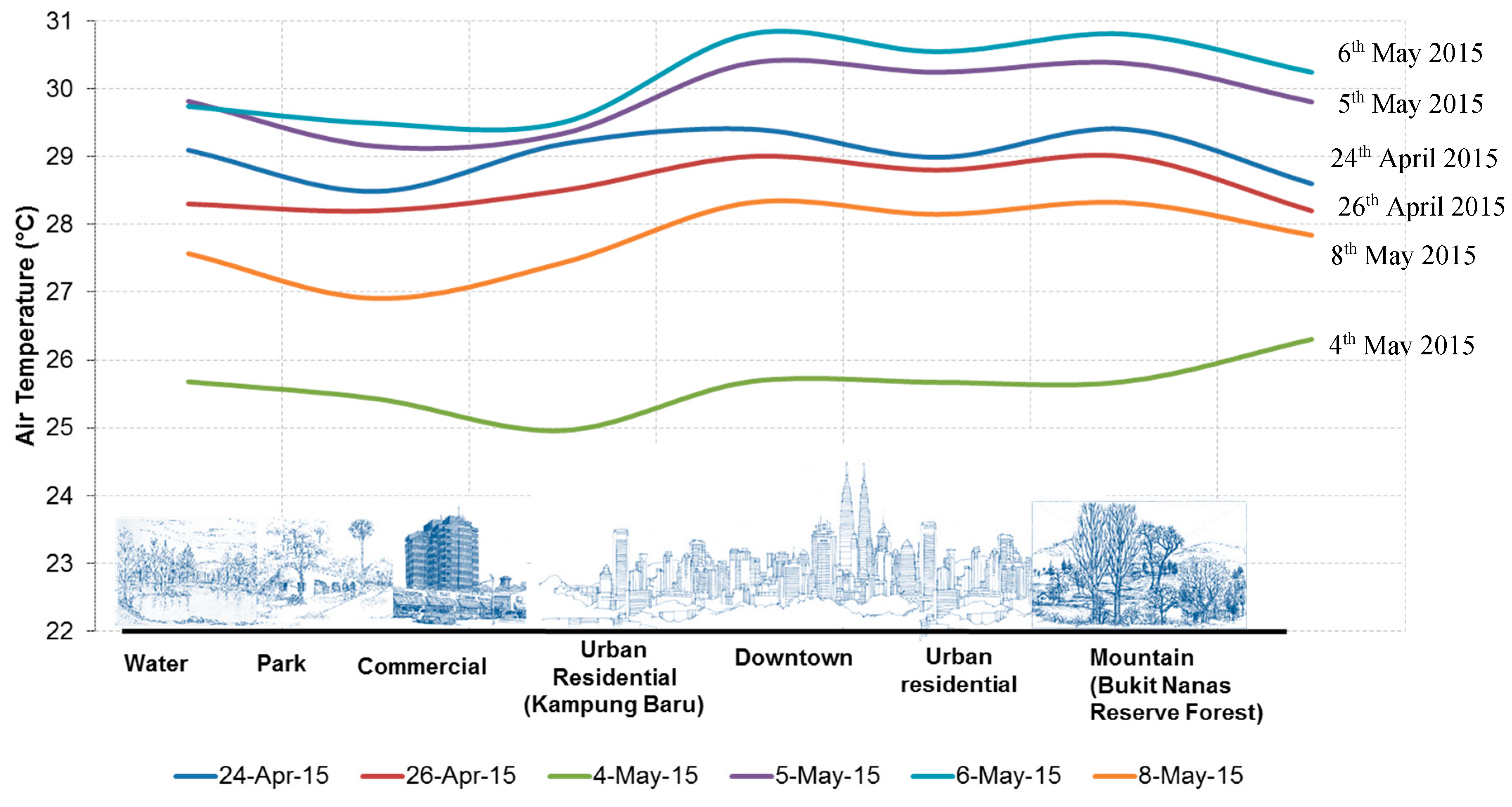
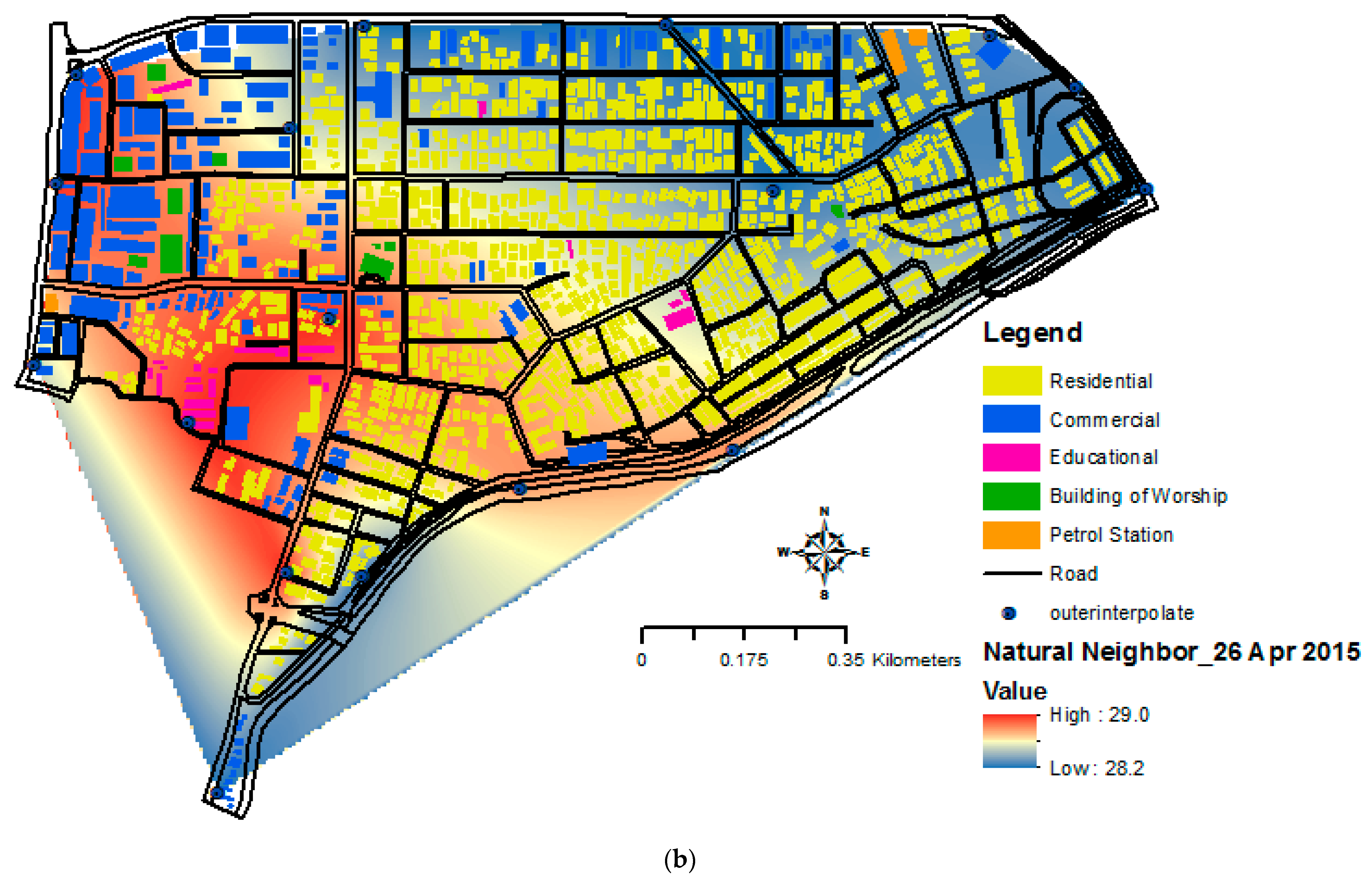
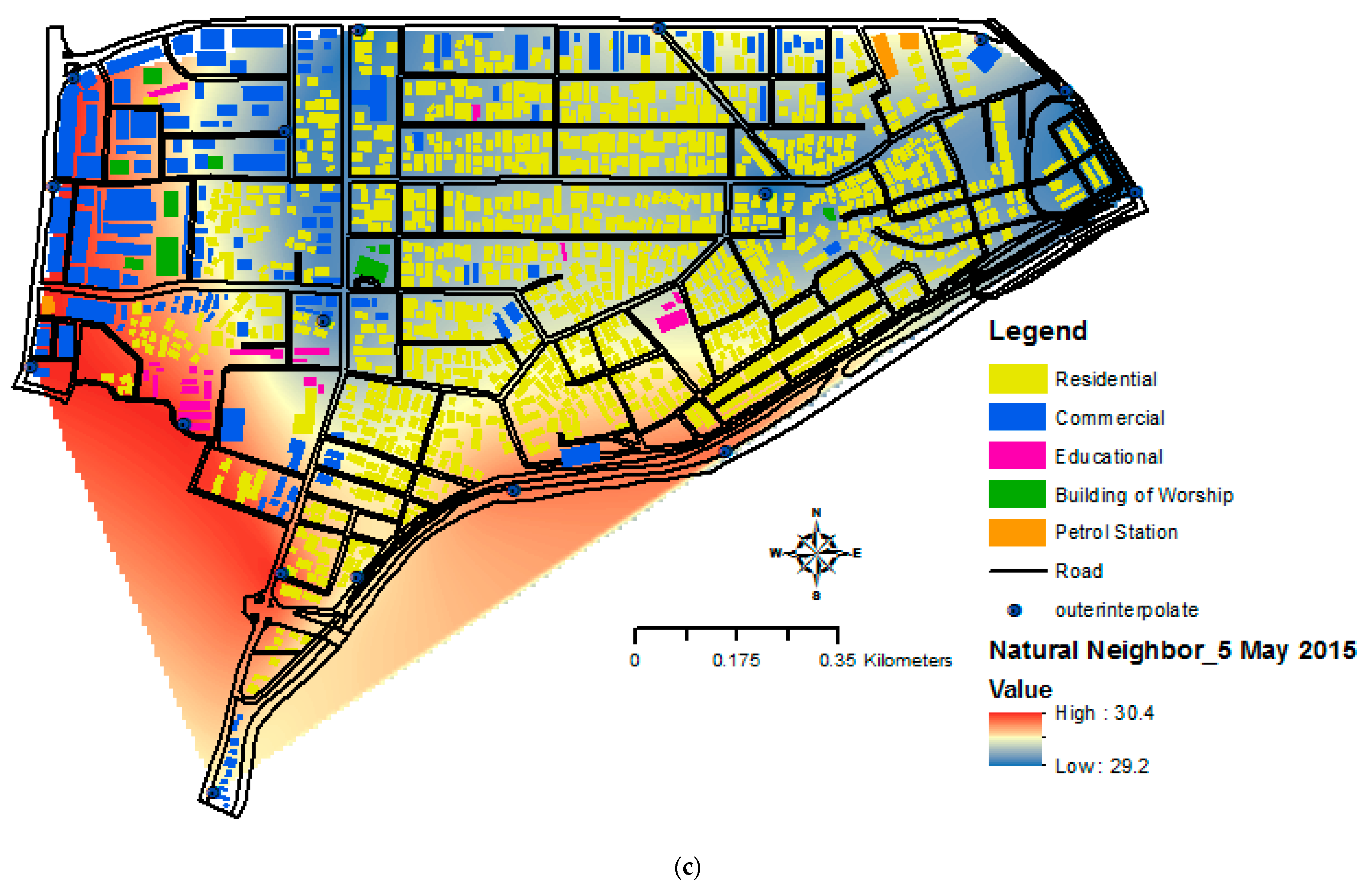
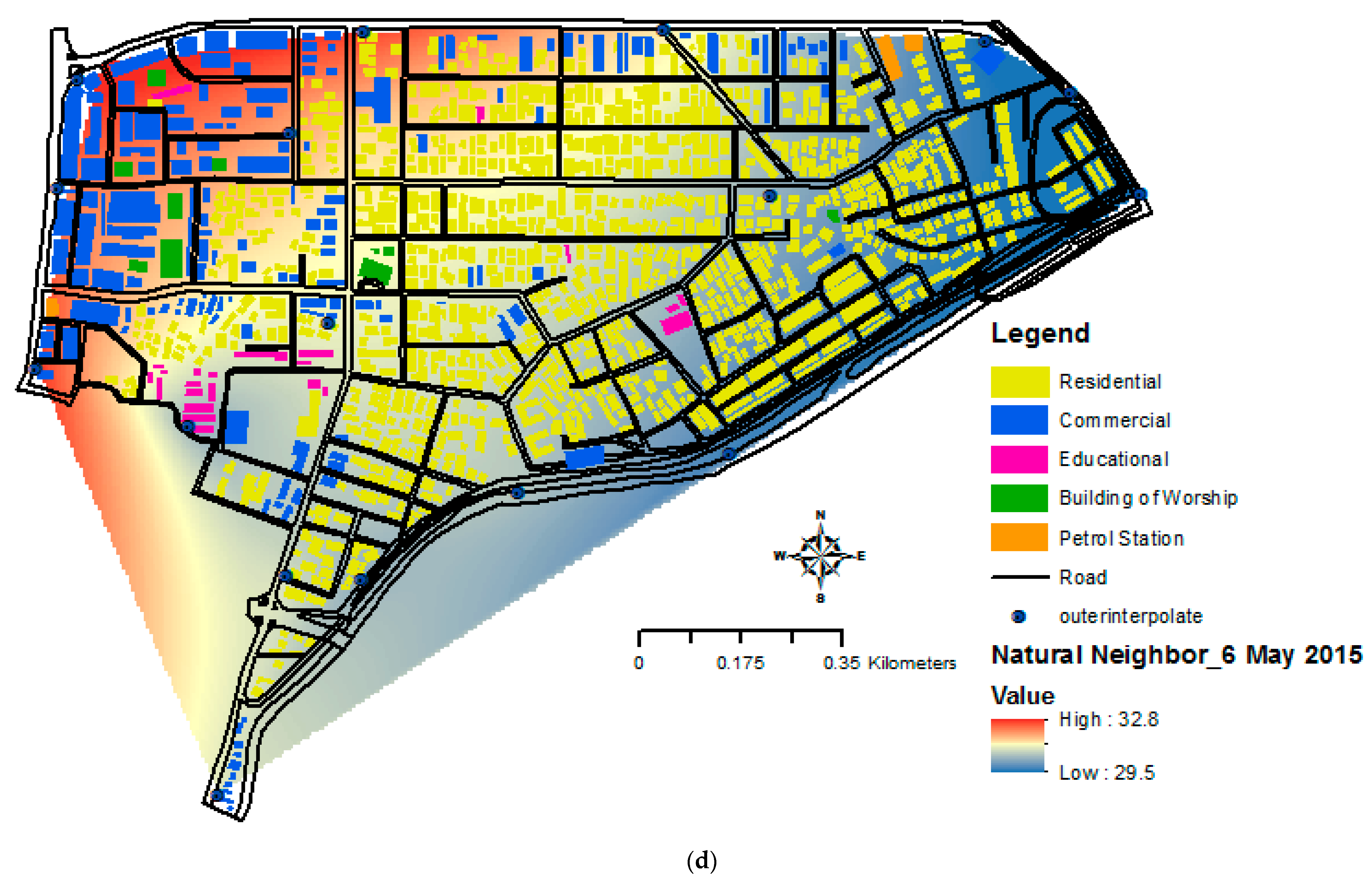
3.1. Temporal Analysis of Urban Temperatures
3.2. Temperature Variation under Different Environmental Settings
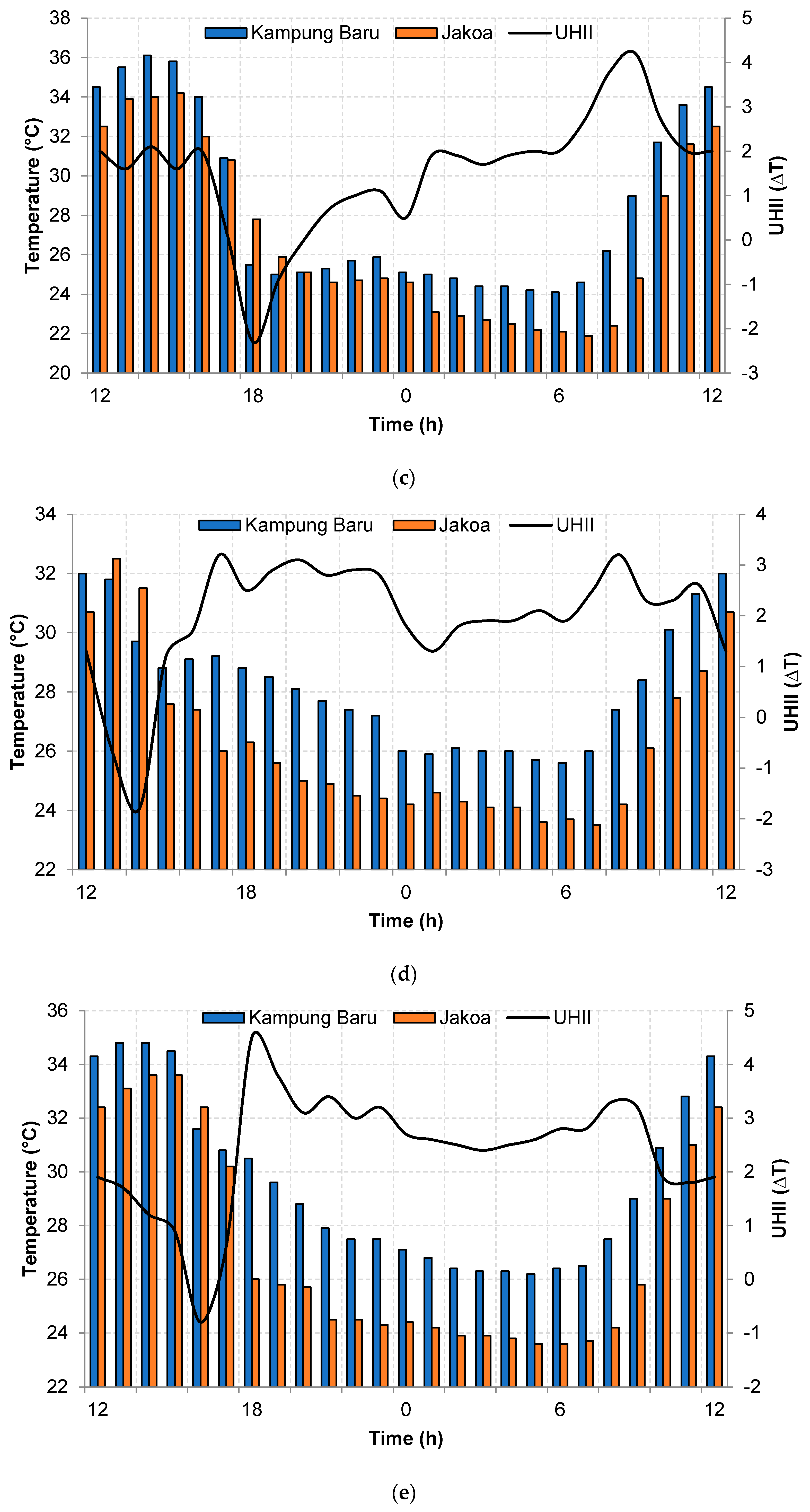
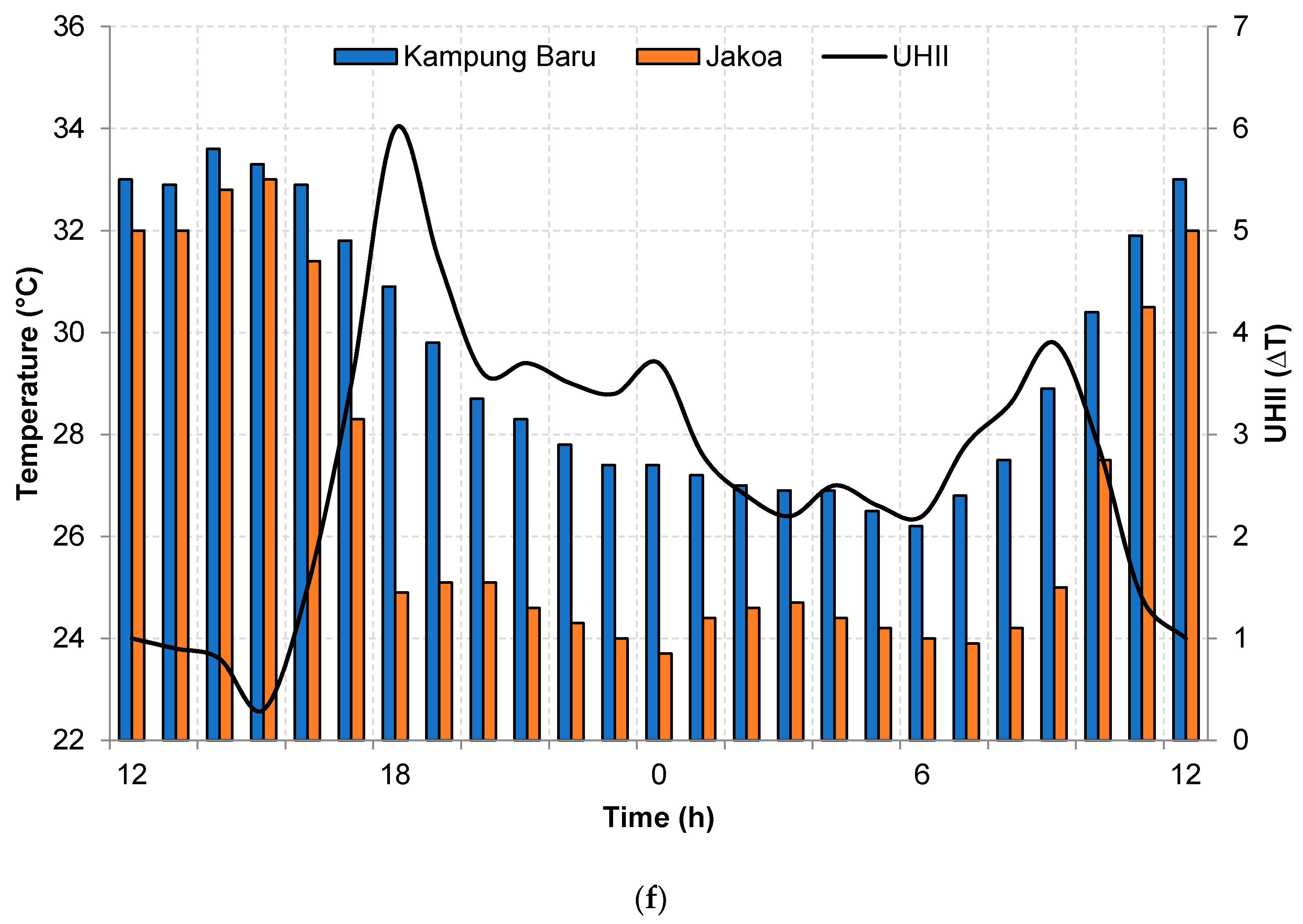
3.3. Temporal Analysis of UHI Intensity (UHII)
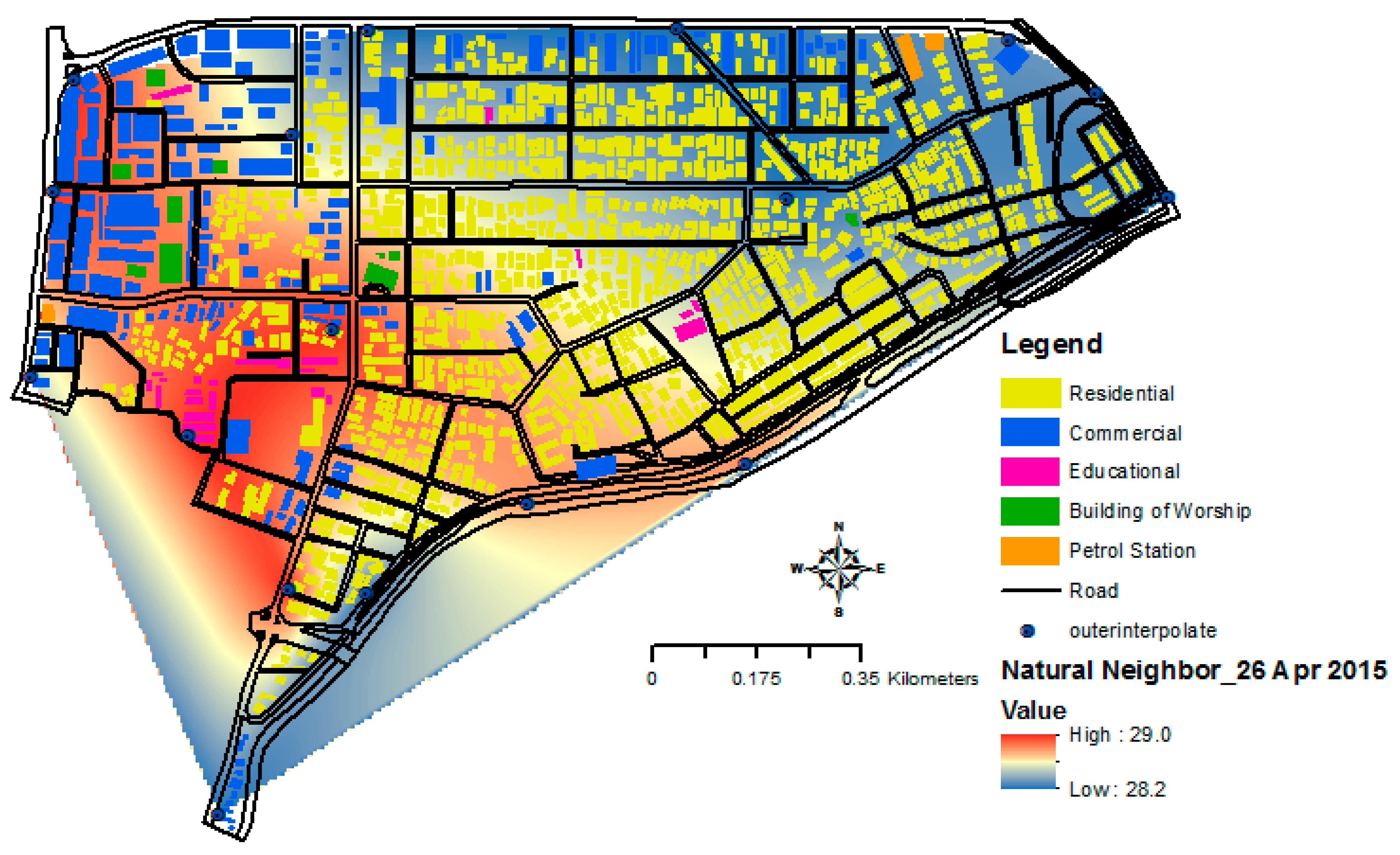
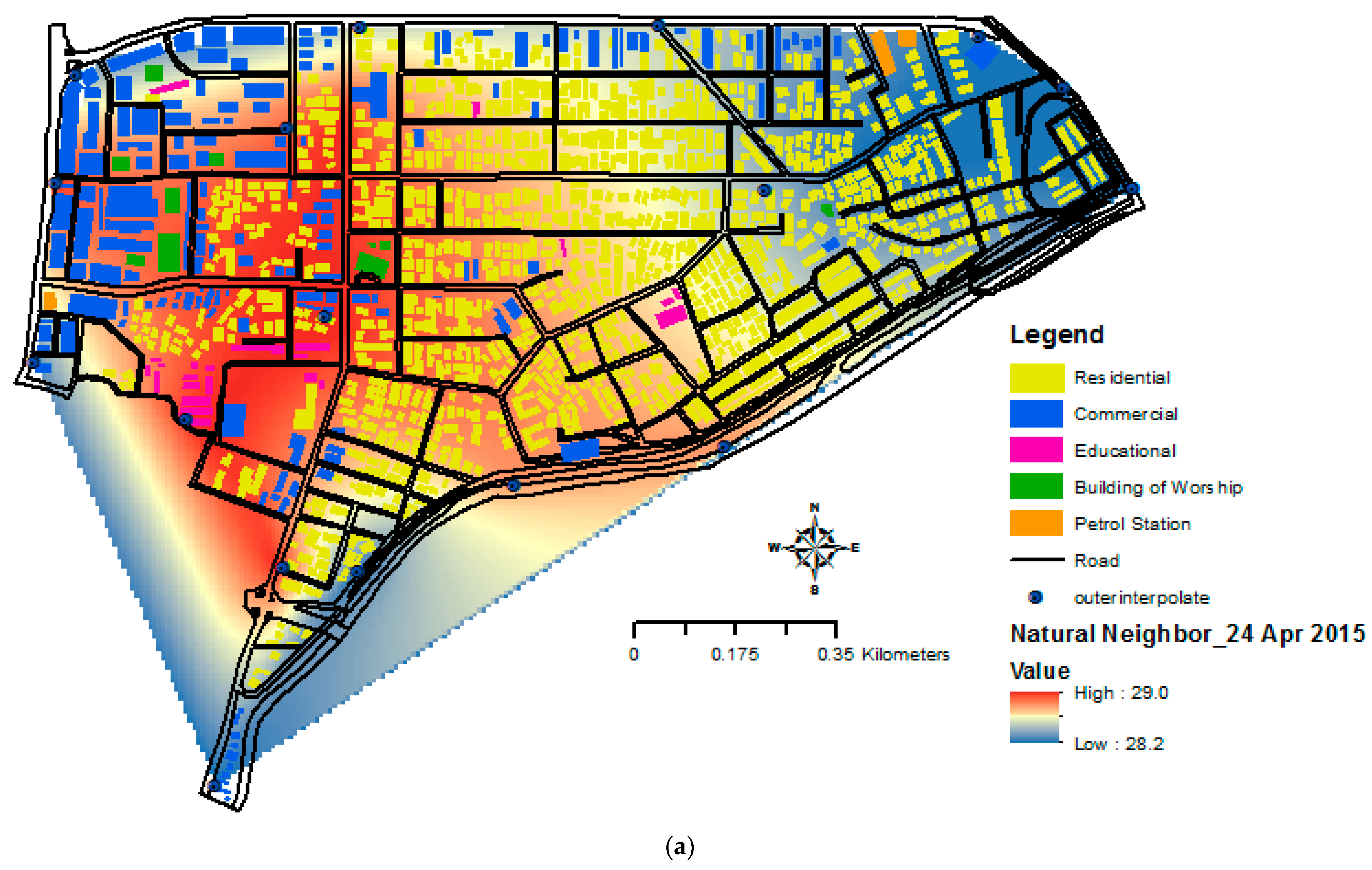
3.4. Relationship between Urban Heat Island (UHI) and Building Morphology in GIS Interface
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oke, T.R. Boundary Layer Climates, 2nd ed.; Methuen Co.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.Q.; Ossen, D.R.; Jamei, E.; Manaf, N.A.; Said, I.; Ahmad, M.H. Urban surface temperature behaviour and heat island effect in a tropical planned city. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Solecki, W.D.; Parshall, L.; Chopping, M.; Pope, G.; Goldberg, R. Characterizing the urban heat island effect in current and future climates in urban New Jersey. Environ. Hazards 2005, 6, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; White, M.; Ding, W. An urban form experiment on urban heat island effect in high density area. Procedia Eng. 2016, 169, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolis, L. The Urban Heat Island Effect in Windsor, ON: An Assessment of Vulnerability and Mitigation Strategies; City of Windsor: Windsor, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Kim, Y.; Sung, H.C.; Jieun, R.; Seong, W.J. Trend Analysis of urban heat island intensity according to urban area change in Asian mega cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, N.; Curtis, J.; Wendler, G. The urban heat island effect at Fairbanks, Alaska. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1999, 64, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Yu, C. Study of green areas and urban heat island in a tropical city. Habitat Int. 2005, 29, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Cui, P.; Wong, N.H.; Marcel Ignatius, M. Assessing the effects of urban morphology parameters on microclimate in Singapore to control the urban heat island effect. Sustainability 2018, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, S.; Wong, N.H. Temporal variation in the impact of urban morphology on outdoor air temperature in the tropics: A campus case study. Build. Environ. 2020, 181, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwolt, S. The urban microclimate of Singapore. J. Trop. Geogr. 1966, 22, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuel, R. Assessment of impact of land cover changes on urban bioclimate: The case of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2003, 46, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, S. Observations on the effect of a city’s form and function on temperature patterns: A case of Kuala Lumpur. J. Trop. Geogr. 1973, 36, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, I.S. Mitigation of urban heat island of the city of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 11, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Zakiah, S.M. The Influence of Urban Heat towards Pedestrian Comfort and the Potential Use of Plants and Water as Heat Ameliorator in Kuala Lumpur City Centre Area. Master’s Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Seri Kembangan, Selangor, Malaysia, November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Giridharan, R.; Lau, S.S.Y.; Ganesan, S. Nocturnal heat island effect in urban residential developments of Hong Kong. Energy Build. 2005, 37, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Lima, E.D.; Lopes, A. The urban heat island effect and the role of vegetation to address the negative impacts of local climate changes in a small Brazilian city. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Aktas, Y.D.; Stocker, J. Urban heat island modelling of a tropical city: Case of Kuala Lumpur. Geosci. Lett. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambri Harun, Z.; Reda, E.; Abdulrazzaq, A.; Abbas, A.A.; Yusri Yusup, Y.; Zaki, S.A. Urban heat island in the modern tropical Kuala Lumpur: Comparative weight of the different parameters. Alex. Eng. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givoni, B. Climate Considerations in Building and Urban Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, S.A.; Othman, N.E.; Syahidah, S.W.; Yakub, F.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; Shahidan, M.F.; Mohd Saudi, A.S. Effects of urban morphology on microclimate parameters in an urban university campus. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.A.; Syahidah, S.W.; Shahidan, M.F.; Ahmad, M.I.; Yakub, F.; Hassan, M.Z.; Md Daud, M.Y. Assessment of outdoor air temperature with different shaded area within an urban university campus in hot-humid climate. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icaza, L.E.; Dobbelsteen, A.V.D.; Hoeven, F.V.D. Integrating urban heat assessment in urban plans. Sustainability 2016, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite remote sensing of surface urban heat islands: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Irakulis, I. A methodology for comparing the surface urban heat island in selected urban agglomerations around the world from Sentinel-3 SLSTR Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, K.A.M. Kampung Baru: Organizational Study of an Urban Malay Settlement. Ph.D. Thesis, International Islamic University Malaysia, Jalan Gombak, Selangor, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sabatino, S.; Leo, L.S.; Cataldo, R.; Ratti, C.; Britter, R.E. Construction of digital elevation models for a southern European city and a comparative morphological analysis with respect to Northern European and North American cities. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taket, N.D.; Howarth, S.M.; Burge, R.E. A model for the imaging of urban areas by synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, S.J.; Brown, M.J.; Linger, S.P. Morphological Analyses Using 3D Building Databases: Los Angeles, California; Rep. LA-UR-02; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2002; p. 781. [Google Scholar]







| Data Logger | Model | Climatic Variables | Accuracy | T.I. | H.A.G. (m) | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campbell Scientific CR1000 | CSL 215-L Temp/RH Probe | Air Temp. | ±0.3 °C | 10.0 min | ~68.0 | March 2014–February 2015 |
| Relative Humidity | ±4.0% | |||||
| SP 110-L Apogee Silicon Pyranometer | Solar Radiation | ±5.0% for daily total radiation |
| Instruments Model | Climatic Variables | Measurement Range | Instruments Accuracy | Response Time in Airflow of 1 m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hobo pro-V2 data logger | Air temperature | −40° to 70 °C (−40° to 158 °F) | ±0.21 °C from 0° to 50 °C (±0.38 °F from 32° to 122 °F) | 5 min in air moving at 1 m/s |
| Relative humidity | 0% to 95% RH | ±2.5% from 10% to 90% RH (typical), to a maximum of ±3.5% | 5 min in air moving at 1 m/s with protective cap |
| No. | Element | Location Picture | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Water/pond |  | Titiwangsa Lake Gardens |
| 2. | Park |  | Titiwangsa Lake Gardens |
| 3. | Highway |  | Along Jalan Tun Razak |
| 4. | Urban Residential |  | Kampung Baru |
| 5. | Downtown |  | Kuala Lumpur City Center |
| 6. | Mountain/rural |  | Bukit Nenas Reserve Forest |
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Date | 24–26 April 2015, 4–8 May 2015 |
| Time | Night time (20:30–22:30) |
| Vehicle | Motorcycle |
| Speed of vehicle | 20–30 km/h |
| Instruments | Hobo temperature/RH mini data logger with radiation shield |
| Intervals | 1 s |
| Instrument’s height | 1.4 m |
| Code | Category |
|---|---|
| A | Aeronautical |
| B | Built Environment |
| D | Demarcation |
| G | Geology |
| H | Hydrography |
| S | Soil |
| T | Transportation |
| U | Utility |
| V | Vegetation |
| X | Special Use (Dataset-specific) |
| Z | General |
| Date | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| 14 October 2015 | −0.7 | 4.4 |
| 15 October 2015 | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| 16 October 2015 | −2.3 | 4.2 |
| 17 October 2015 | −1.8 | 3.2 |
| 18 October 2015 | −0.8 | 4.5 |
| 19 October 2015 | 0.3 | 6.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaki, S.A.; Azid, N.S.; Shahidan, M.F.; Hassan, M.Z.; Md Daud, M.Y.; Abu Bakar, N.A.; Mat Ali, M.S.; Yakub, F. Analysis of Urban Morphological Effect on the Microclimate of the Urban Residential Area of Kampung Baru in Kuala Lumpur Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7301. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187301
Zaki SA, Azid NS, Shahidan MF, Hassan MZ, Md Daud MY, Abu Bakar NA, Mat Ali MS, Yakub F. Analysis of Urban Morphological Effect on the Microclimate of the Urban Residential Area of Kampung Baru in Kuala Lumpur Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7301. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187301
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaki, Sheikh Ahmad, Nor Suhada Azid, Mohd Fairuz Shahidan, Mohamad Zaki Hassan, Mohd Yusof Md Daud, Nor Azlina Abu Bakar, Mohamed Sukri Mat Ali, and Fitri Yakub. 2020. "Analysis of Urban Morphological Effect on the Microclimate of the Urban Residential Area of Kampung Baru in Kuala Lumpur Using a Geospatial Approach" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7301. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187301
APA StyleZaki, S. A., Azid, N. S., Shahidan, M. F., Hassan, M. Z., Md Daud, M. Y., Abu Bakar, N. A., Mat Ali, M. S., & Yakub, F. (2020). Analysis of Urban Morphological Effect on the Microclimate of the Urban Residential Area of Kampung Baru in Kuala Lumpur Using a Geospatial Approach. Sustainability, 12(18), 7301. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187301








