Acoustic Emission Wave Velocity Attenuation of Concrete and Its Application in Crack Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
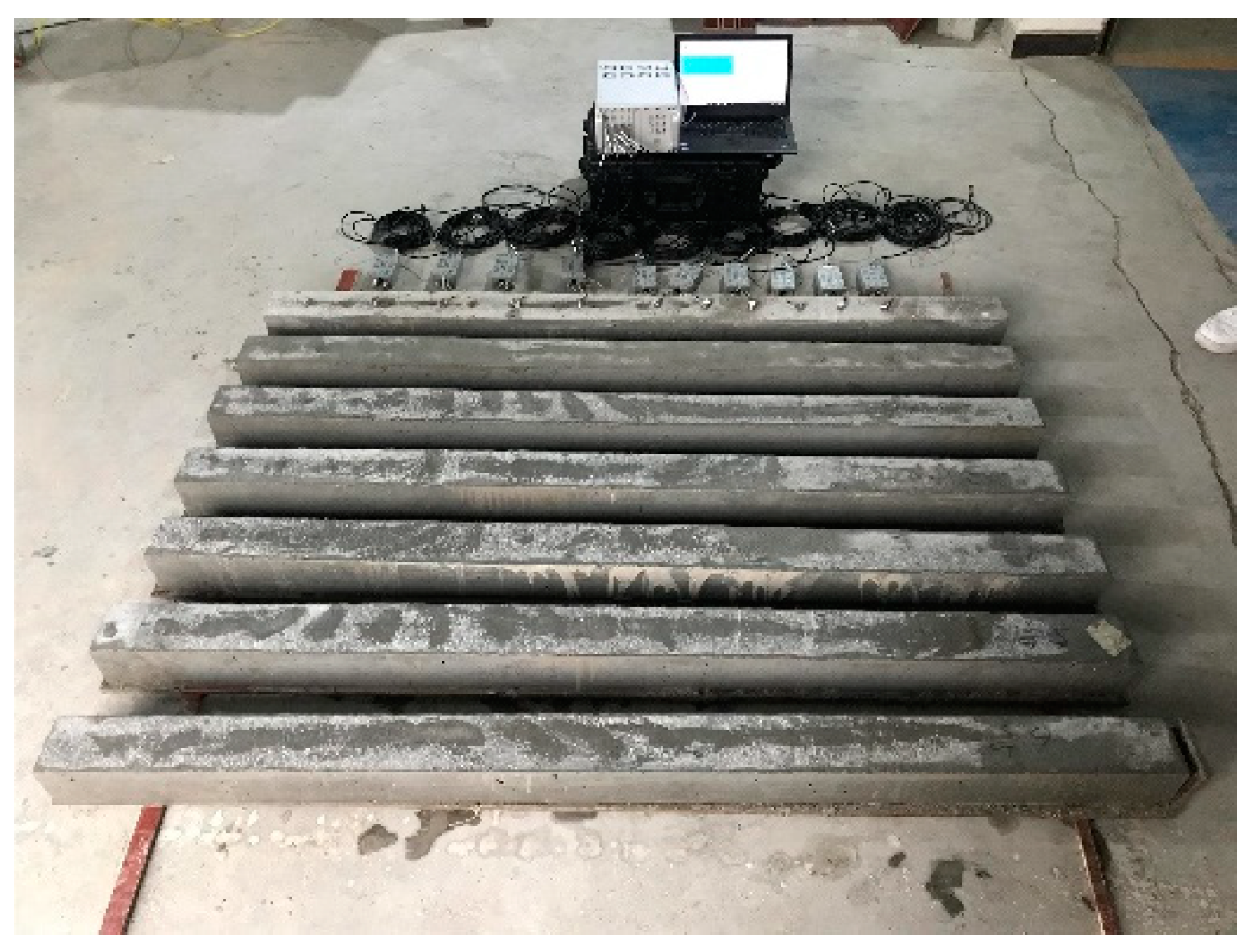
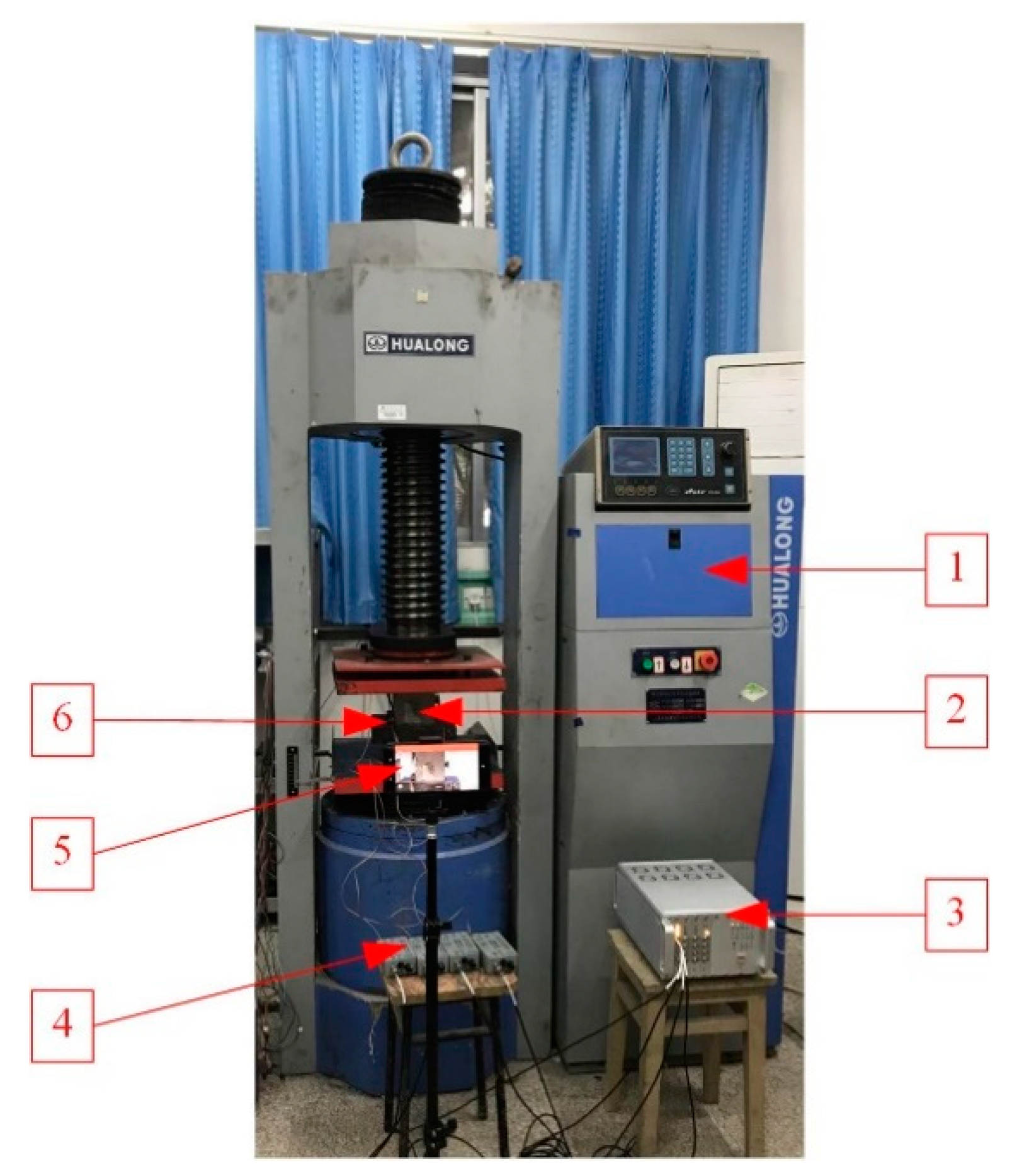
2.2. Test System
2.3. TEST SCHEME
- (1)
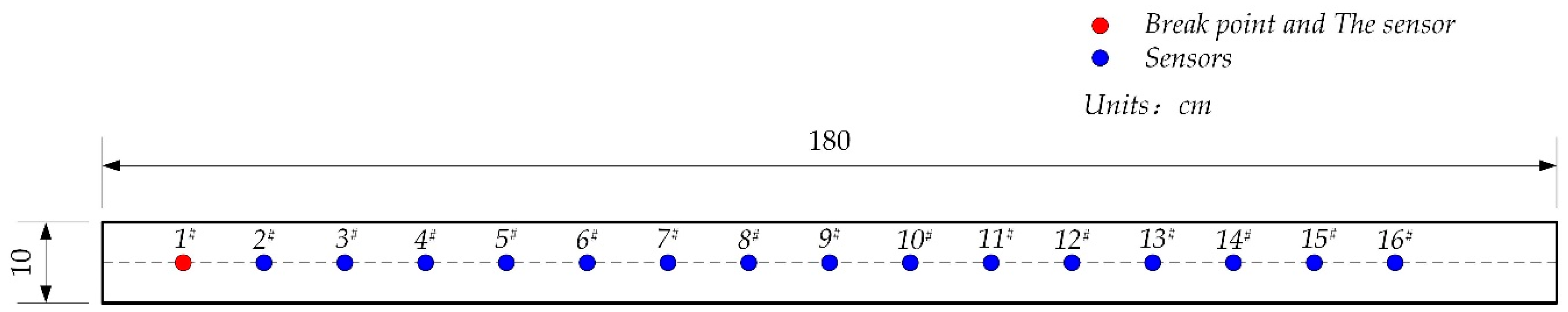
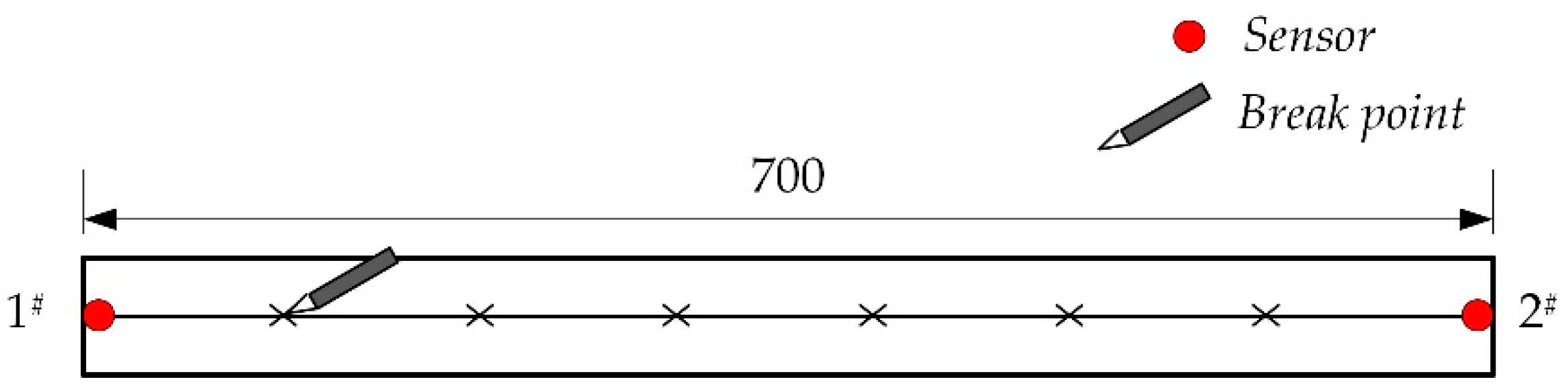
- Sensor installation. First, a coupling agent was applied to the receiving surface of the sensor, and then adhered to the surface of the concrete sample; the sensor is installed at an equal spacing of 10 cm. The PLB point and the sensor’ locations are exhibited in Figure 3.
- (2)
- Sensor debugging. Three PLB pre-tests were conducted near the break point of each sensor to verify their accuracy.
- (3)
- PLB testing. Five PLB tests were performed at 2 s intervals at the break point to emulate five AE sources. Seventeen sensors were used to record the signal.
- (4)
- Signal arrival time extraction. Waveform information was analyzed, and the transmission time was extracted.
- (5)
- Wave velocity calculation. Using the signal arrival time to Sensor #1 as the origin of the PLB signal and the signal arrival time to Sensors #2–16 as the receiving time, the AE wave velocities were calculated for the propagation distances of 100, 200, 300, …, and 1500 mm.
3. Fundamental Concepts
3.1. Datum AE Velocity
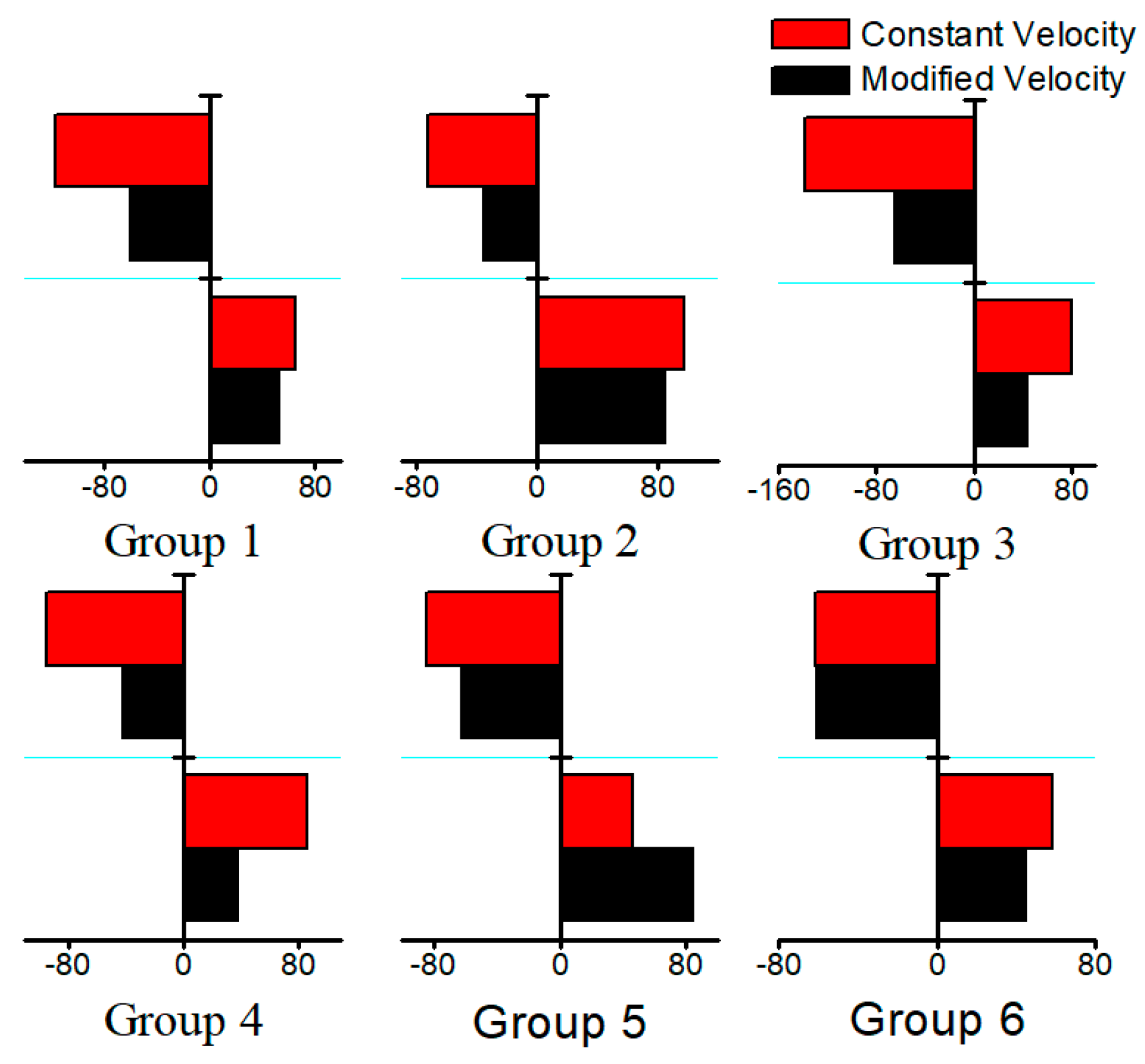
3.2. Attenuation Rate of AE Wave Velocity
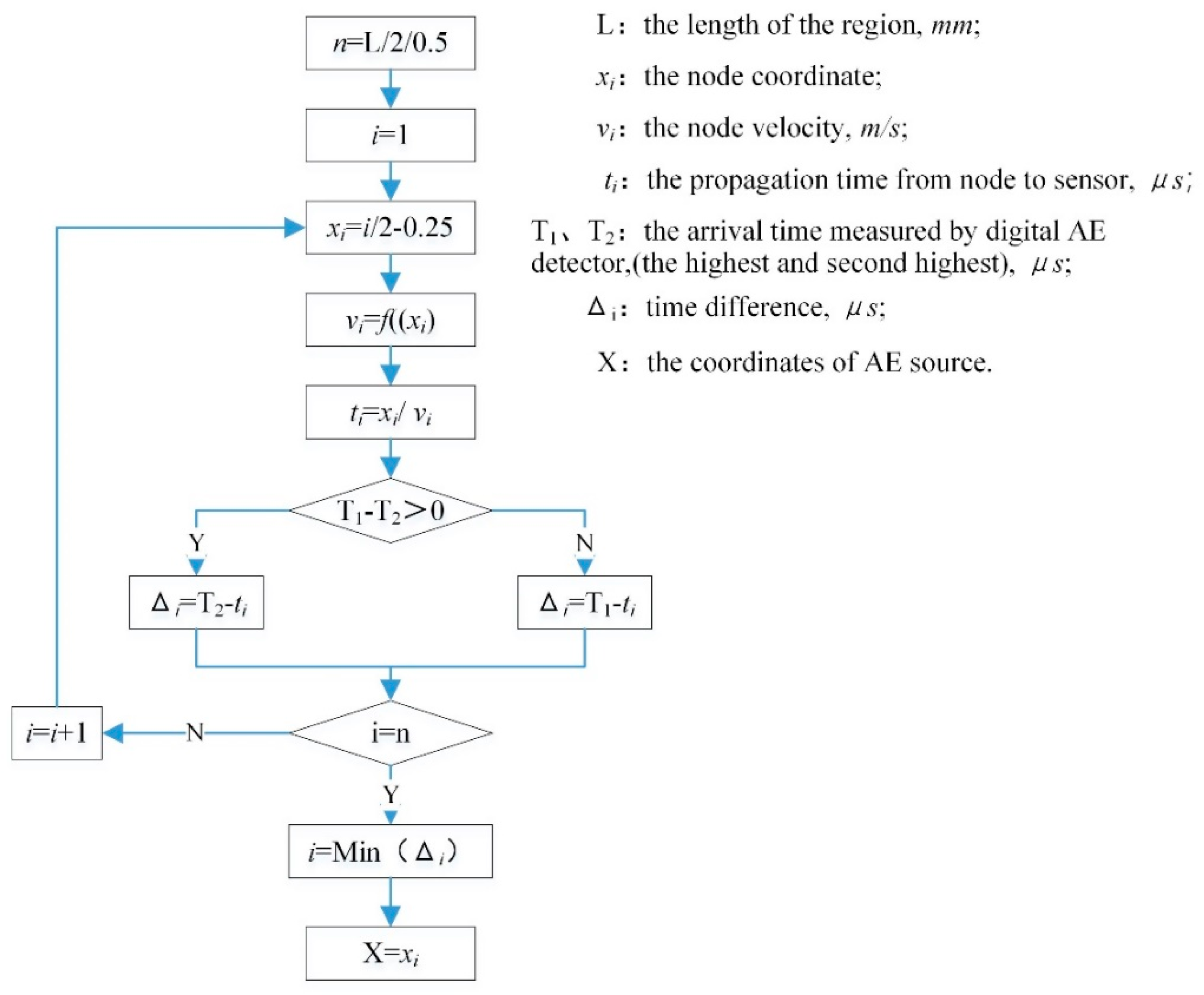
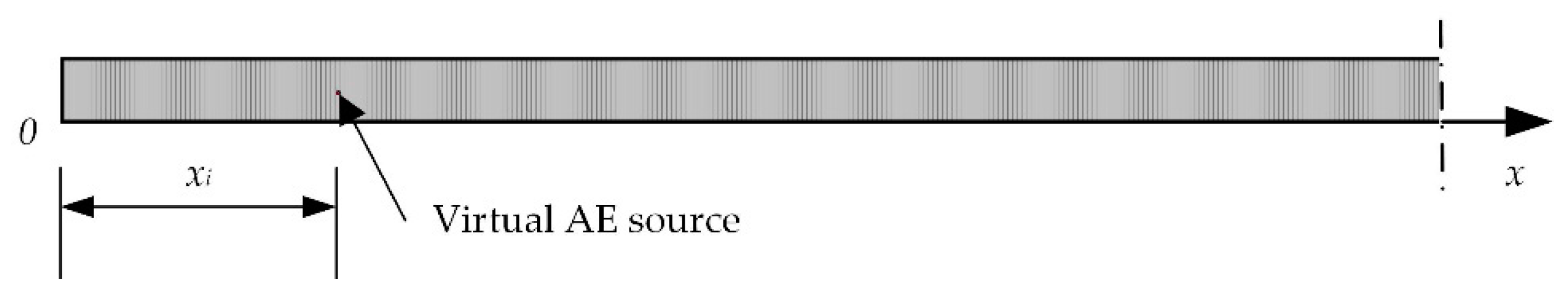
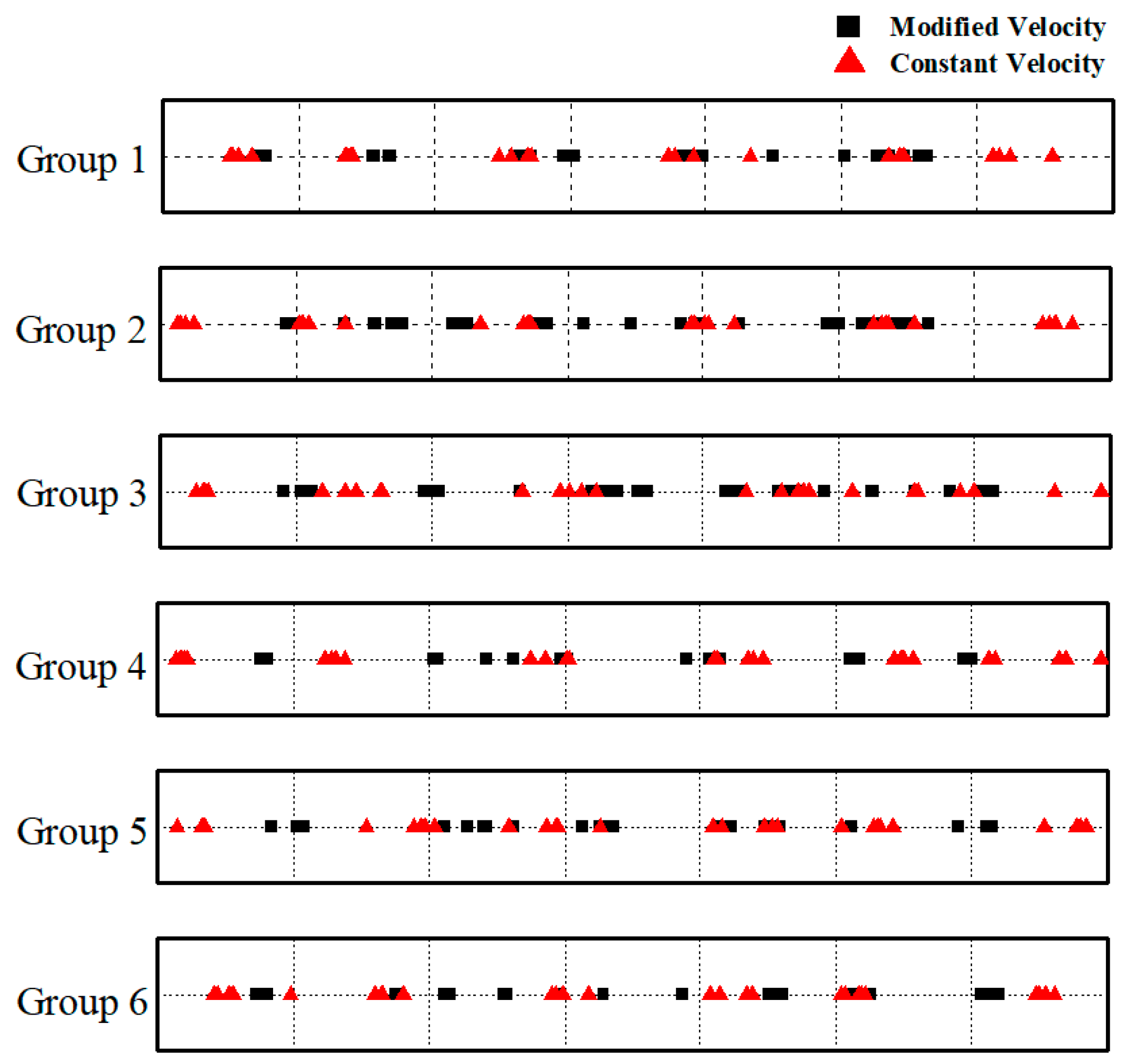
3.3. Region Exhaustive Localization Method Based on the Modified Wave Velocity
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Waveform and Parameters of PLB
4.2. Effect of Material Composition
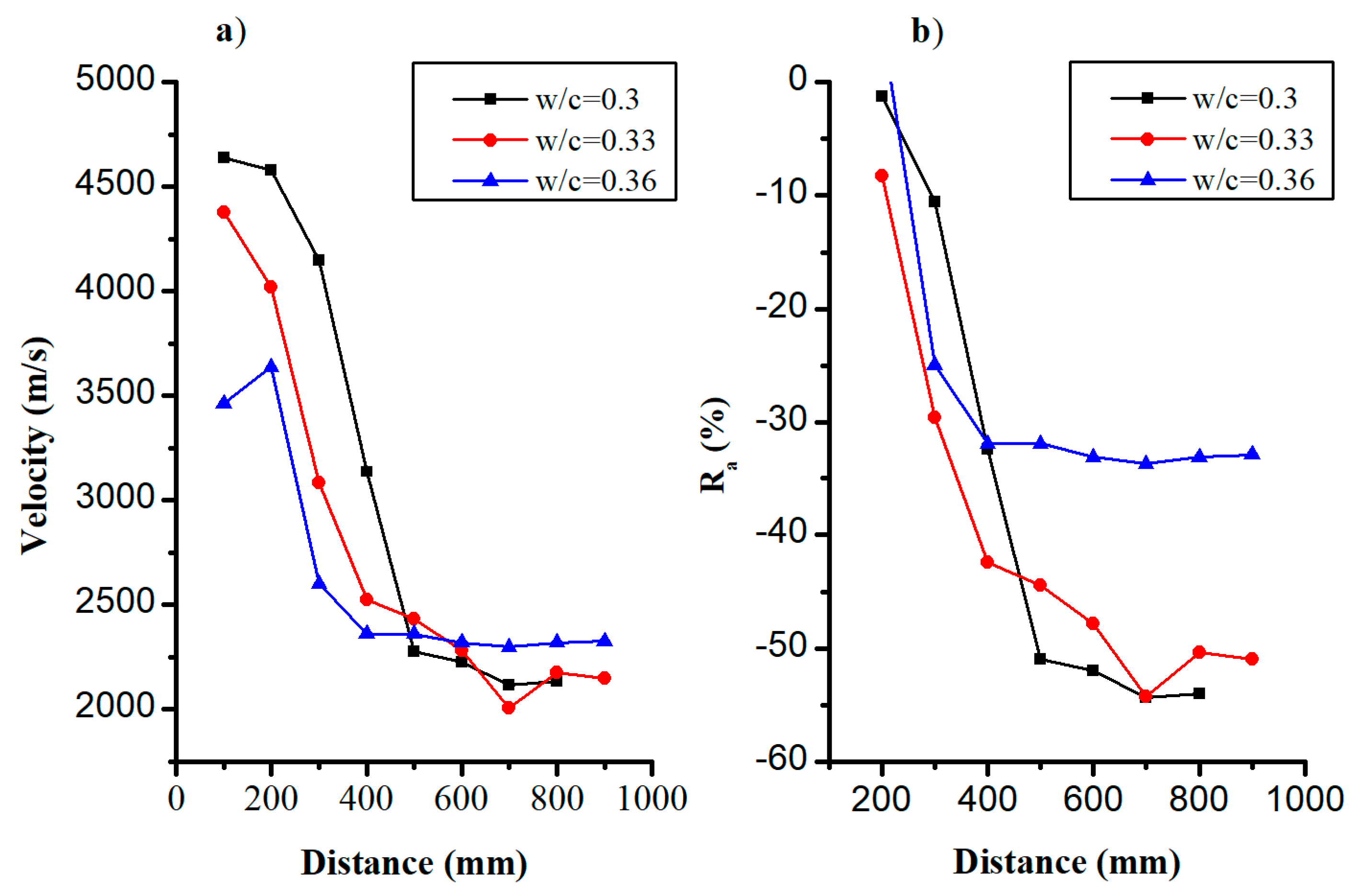
4.2.1. Water-Cement Ratio (w/c)
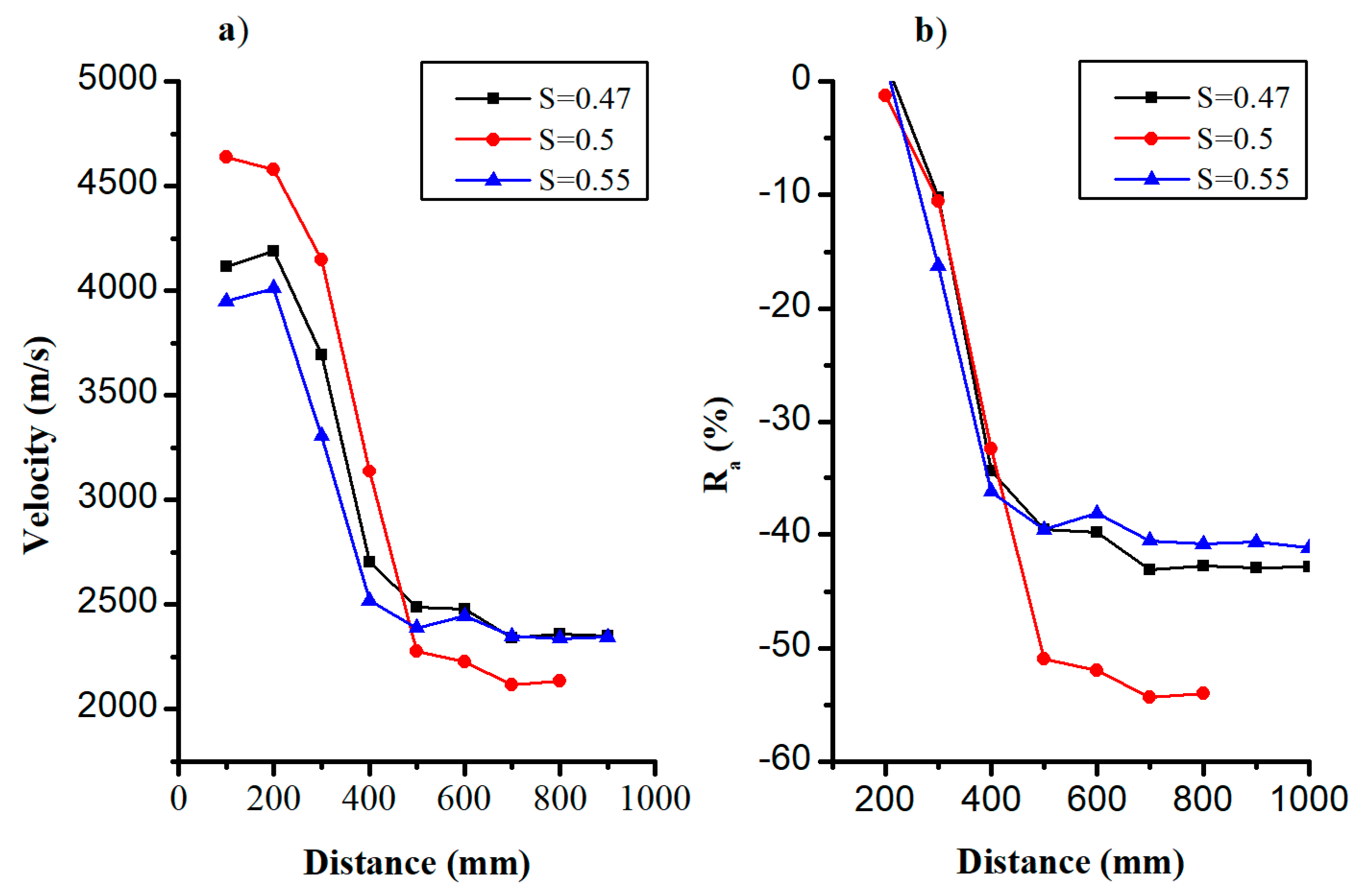
4.2.2. Sand Ratio
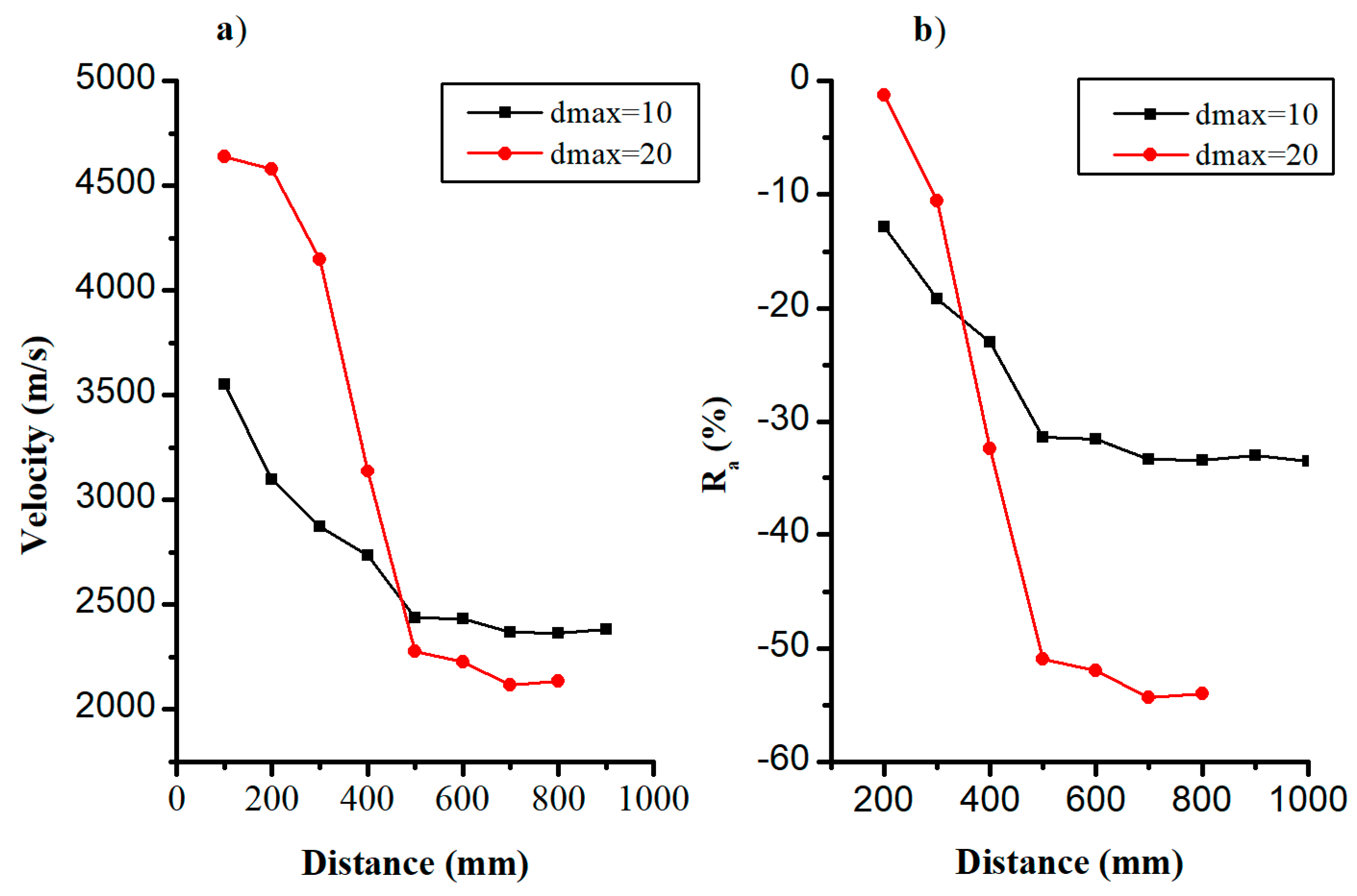
4.2.3. Maximum Aggregate Size
4.3. Wave Velocity Correction Model
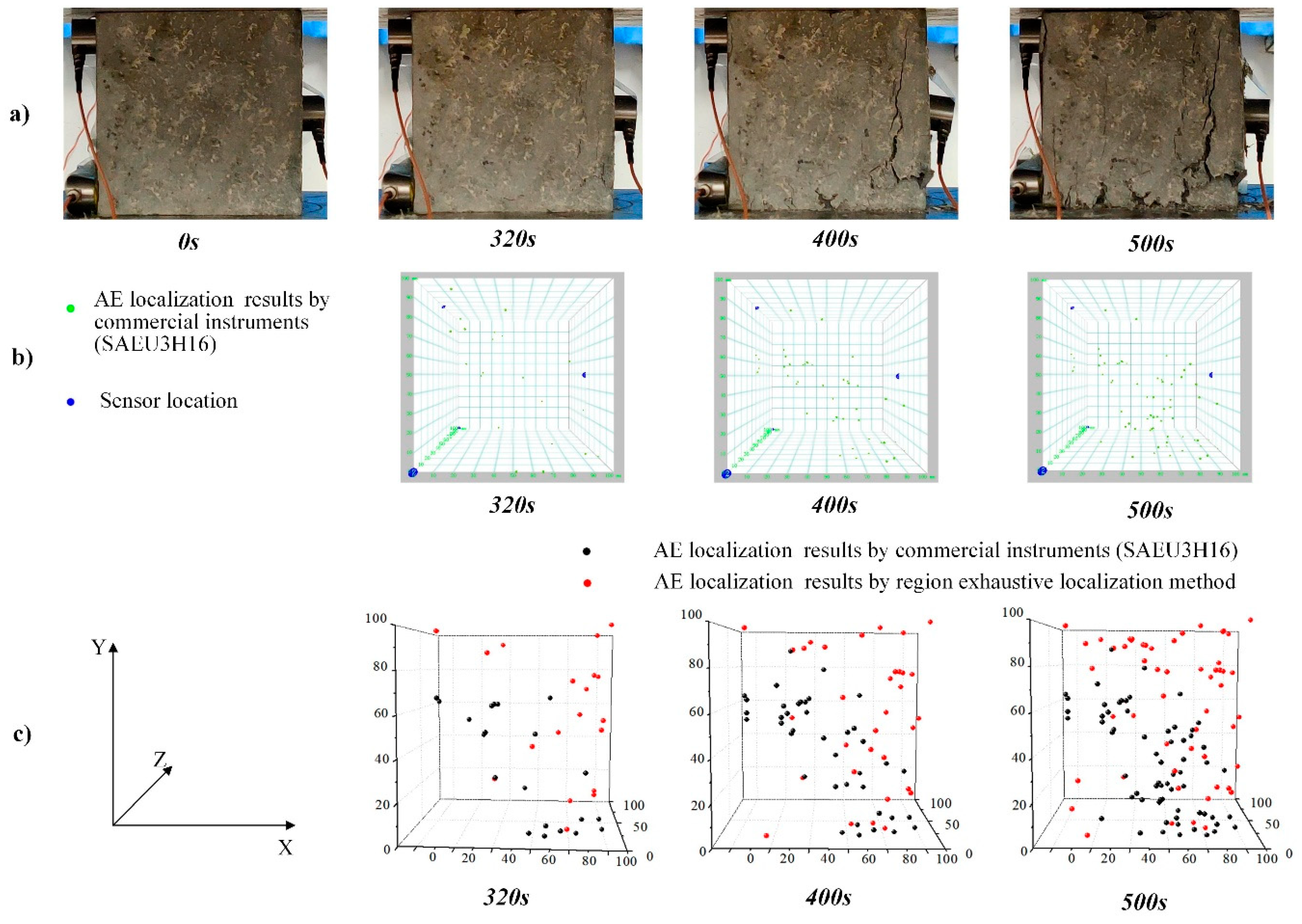
5. Localization Examples
5.1. Test Scheme
5.2. Material and Wave Velocity
5.3. Localization Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Ohtsu, M. Prospective applications of AE measurements to infradock of concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, D.; He, M.; He, D. A new method to classify railway vehicle axle fatigue crack AE signal. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 131, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorsuhada, M.N. An overview on fatigue damage assessment of reinforced concrete structures with the aid of acoustic emission technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.C.; Pirskawetz, S.; Van Zijl, G.P.A.G.; Schmidt, W. Acoustic emission for characterising the crack propagation in strain-hardening cement-based composites (SHCC). Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 69, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinteri, A.; Xu, J.; Lacidogna, G. Reliable onset time determination and source location of acoustic emissions in concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, L. Signal-based acoustic emission monitoring on mortar using cement-based piezoelectric sensors. ACI Mater. J. 2011, 108, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulioti, D.; Barkoula, N.M.; Paipetis, A.; Matikas, T.E.; Shiotani, T.; Aggelis, D.G. Acoustic emission behavior of steel fibre reinforced concrete under bending. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3532–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Lu, F.; Huang, S.; Cheng, X. Investigation of acoustic emission source localization performance on the plate structure using piezoelectric fiber composites. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 282, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, V.; Vargas, Y.; Ruzzante, J.; Gaete, L. Localization algorithm for acoustic emission. Phys. Procedia 2010, 3, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.D.; Choi, W.C.; Seo, S.Y. Acoustic emission activities and damage evaluation of reinforced concrete beams strengthened with CFRP sheets. NDT E Int. 2010, 43, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marec, A.; Omas, J.H.; Guerjouma, R.E. Damage characterization of polymer-based composite materials: Multivariable analysis and wavelet transform for clustering acoustic emission data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2008, 22, 1441–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, T. Acoustic source localization. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, A. Acoustic emission source location in two dimensions by an array of three sensors. Nondestruct. Test. 1976, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yuan, S.; Liu, M. Distributed coordination algorithm for impact location of preciseness and real-time on composite structures. Measurement 2013, 46, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, T.; Das, S.; Martin, S.A.; Jata, K.V. Locating point of impact in anisotropic fiber reinforced composite plates. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barricelli, N.A. Symbiogenetic evolution processes realized by artificial methods. Methods 1957, 143–182. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, A.; Burnell, D. Computer Models in Genetics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1970; ISBN 0-07-021904-4. [Google Scholar]
- McLaskey, G.C.; Glaser, S.D.; Grosse, C.U. Beamforming array techniques for acoustic emission monitoring of large concrete structures. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, D. Near-field beamforming analysis for acoustic emission source localization. Ultrasonics 2012, 52, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, H.M.; Lanza di Scalea, F. Macro-fiber composite piezoelectric rosettes for acoustic source location in complex structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, S.; Bartoli, I.; di Leo, P.; Lanza di Scalea, F.; Ajovalasit, A.; D’Acquisto, L.; Rhymer, J.; Kim, H. High-velocity impact location on aircraft panels using macro-fiber composite piezoelectric rosettes. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, S.; Bartoli, I.; Rhymer, J.; di Scalea, F.L.; Kim, H. Validation of the Piezoelectric Rosette Technique for Locating Impacts in Complex Aerospace Panels. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/7984/79841E/Validation-of-the-piezoelectric-rosette-technique-for-locating-impacts-in/10.1117/12.880293.short?SSO=1 (accessed on 31 March 2011).
- Betz, D.C.; Thursby, G.; Culshaw, B.; Staszewski, W. Structural damage location with fiber Bragg grating rosettes and lamb waves. Struct. Health Monit. 2007, 6, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; He, C.; Wu, B.; Fei, R.; Wang, X. Application of wavelet transform on modal acoustic emission source location in thin plates with one sensor. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2004, 81, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgeon, M.; Wevers, M. One sensor linear location of acoustic emission events using plate wave theories. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 265, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, N.; Koo, J.H.; Oishi, R.; Enoki, M.; Kishi, T. Two-dimensional AE source location with two sensors in thin CFRP plates. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1823–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, M.R. AE source orientation by plate wave analysis. J. Acoust. Emiss. 1991, 9, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G. Acoustic BASIS; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Li, B.; Zhou, L. Three-dimensional analytical solution of acoustic emission source location for cuboid monitoring network without pre-measured wave velocity. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, L. Study on Acoustic Emission Localization of Concrete Using Modified Velocity. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. Tests for AE Wave Propagation Characteristic in RC Slabs. J. Vib. Shock 2019, 38, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, A.; Qu, J.M. Experimental Research on Size Effect of Acoustic Emission Location Accuracy. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2016, 35, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



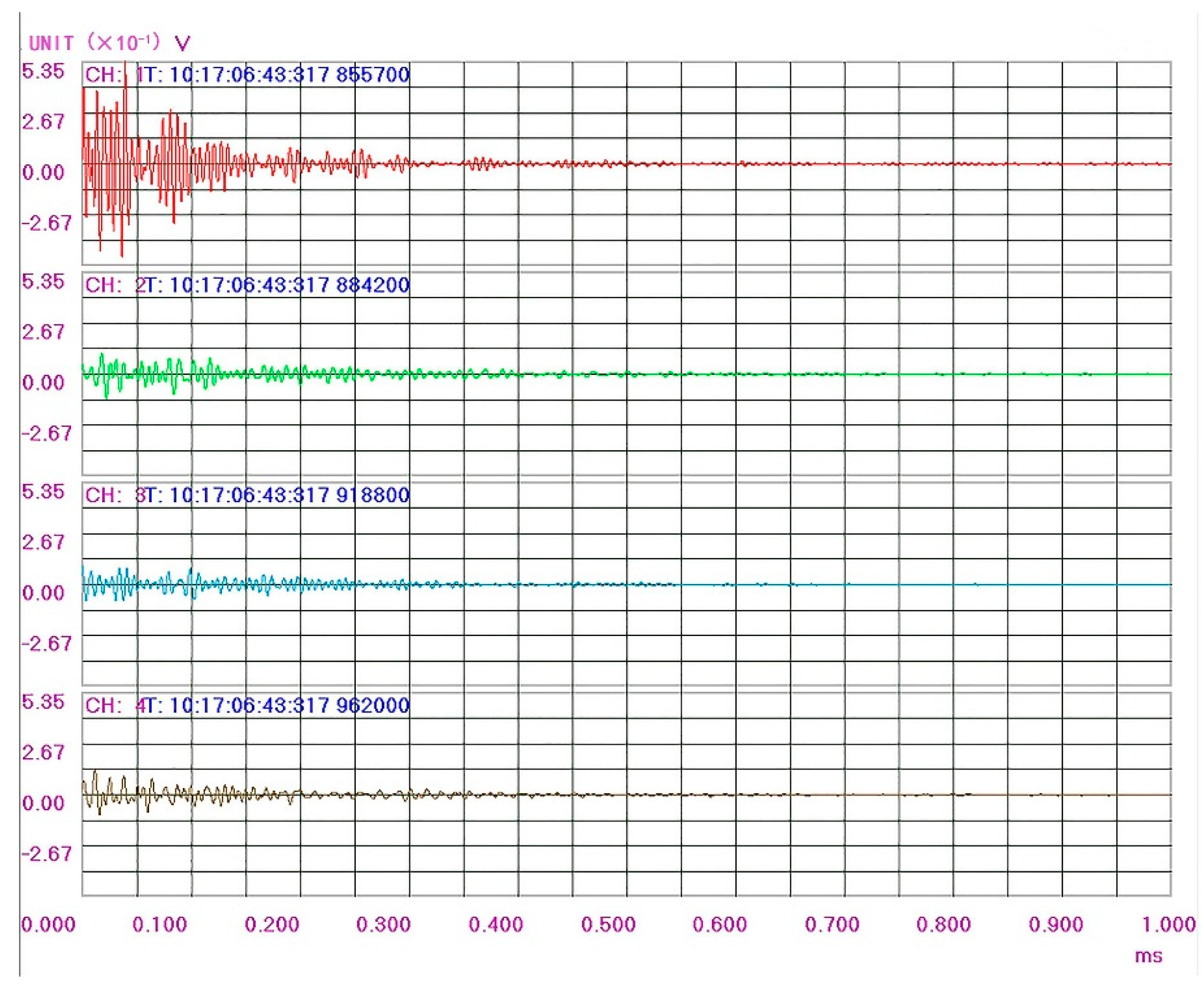

| Channel | AE Amplitude | AE Count | AE Duration | AE Energy | AE Arrival Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97.1 | 198 | 1481 | 5.952 | 10:17:06:43:316:855700 |
| 2 | 81.3 | 148 | 1388 | 0.190 | 10:17:06:43:316:884200 |
| 3 | 73.6 | 145 | 1325 | 0.044 | 10:17:06:43:316:918600 |
| 4 | 68.7 | 127 | 1352 | 0.035 | 10:17:06:43:316:962000 |
| 5 | 56.9 | 52 | 1060 | 0.003 | 10:17:06:43:317:027200 |
| 6 | 57.8 | 31 | 992 | 0.002 | 10:17:06:43:317:068600 |
| 7 | 59.9 | 24 | 961 | 0.002 | 10:17:06:43:317:106700 |
| 9 | 53.9 | 17 | 960 | 0.001 | 10:17:06:43:317:192400 |
| 10 | 51.3 | 12 | 941 | 0.001 | 10:17:06:43:317:232300 |
| 11 | 50.9 | 9 | 983 | 0.001 | 10:17:06:43:317:273500 |
| 13 | 45.9 | 2 | 22 | 0 | 10:17:06:43:317:361600 |
| Group | w/c | S | dmax [mm] | Mixture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 10 | 1:0.3:1.47:1.47 |
| 2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 20 | 1:0.3:1.47:1.47 |
| 3 | 0.3 | 0.47 | 20 | 1:0.3:1.4:1.56 |
| 4 | 0.3 | 0.55 | 20 | 1:0.3:1.61:1.32 |
| 5 | 0.33 | 0.5 | 20 | 1:0.33:1.66:1.66 |
| 6 | 0.36 | 0.5 | 20 | 1:0.36:1.86:1.86 |
| Coordinate of Break Point [mm] | Constant Velocity [m/s] | Modified Velocity [m/s] |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2659 | 2797–6706 |
| 200 | 2706 | 2640–8580 |
| 300 | 2906 | 3158–10,224 |
| 400 | 2797 | 3021–9302 |
| 500 | 2782 | 2980–11,397 |
| 600 | 2631 | 2742–7441 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Yang, K.; He, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Acoustic Emission Wave Velocity Attenuation of Concrete and Its Application in Crack Localization. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187405
Li D, Yang K, He Z, Zhou H, Li J. Acoustic Emission Wave Velocity Attenuation of Concrete and Its Application in Crack Localization. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187405
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongxue, Kang Yang, Zhaoyi He, Hanlin Zhou, and Jiaqi Li. 2020. "Acoustic Emission Wave Velocity Attenuation of Concrete and Its Application in Crack Localization" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187405
APA StyleLi, D., Yang, K., He, Z., Zhou, H., & Li, J. (2020). Acoustic Emission Wave Velocity Attenuation of Concrete and Its Application in Crack Localization. Sustainability, 12(18), 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187405





