Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Industrial Agglomeration and Spatial Effect
2.2. Location Theory and Location Factors
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Moran’s I
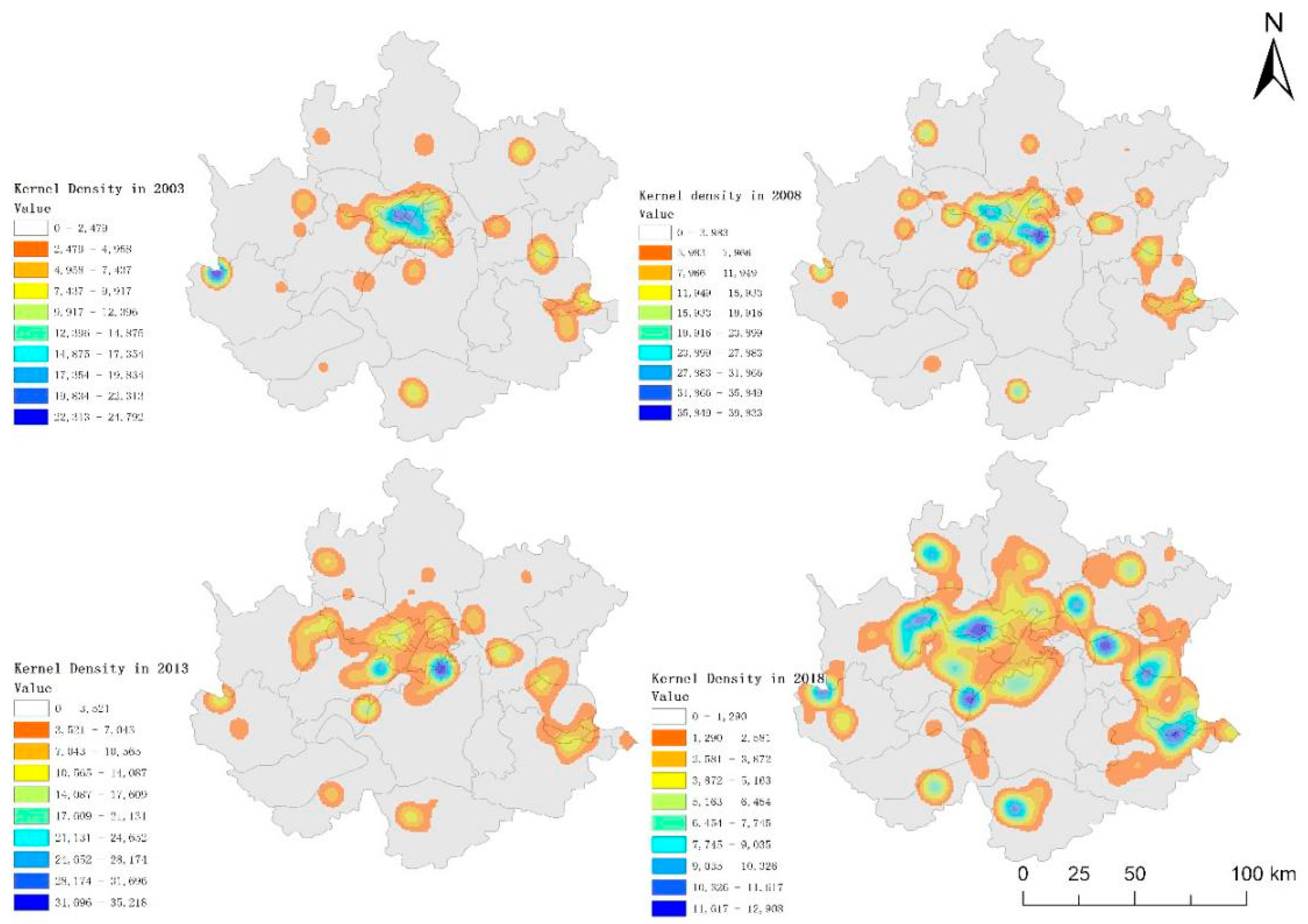
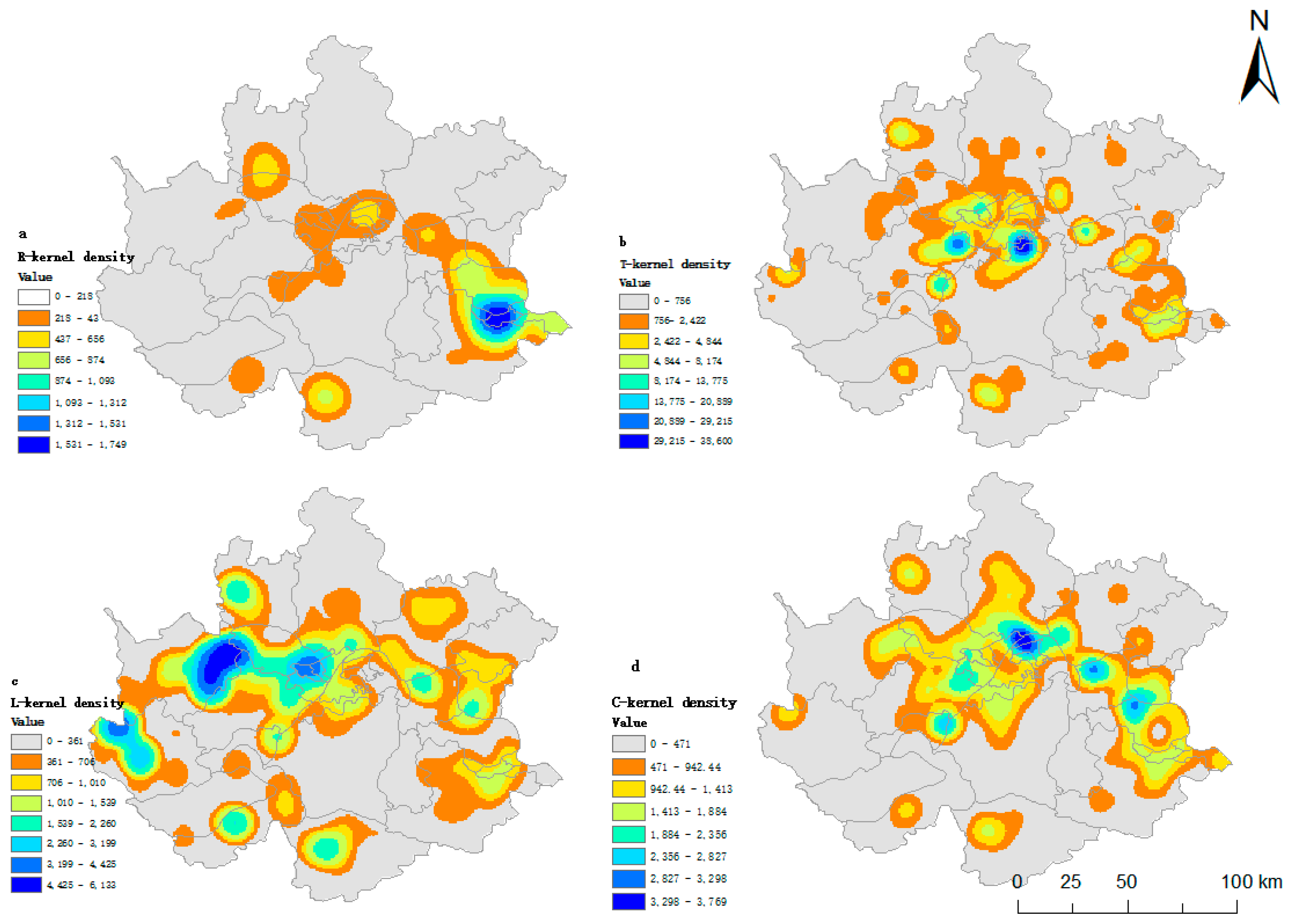
3.3.2. Kernel Density
3.3.3. Variables
3.3.4. Model
4. Results
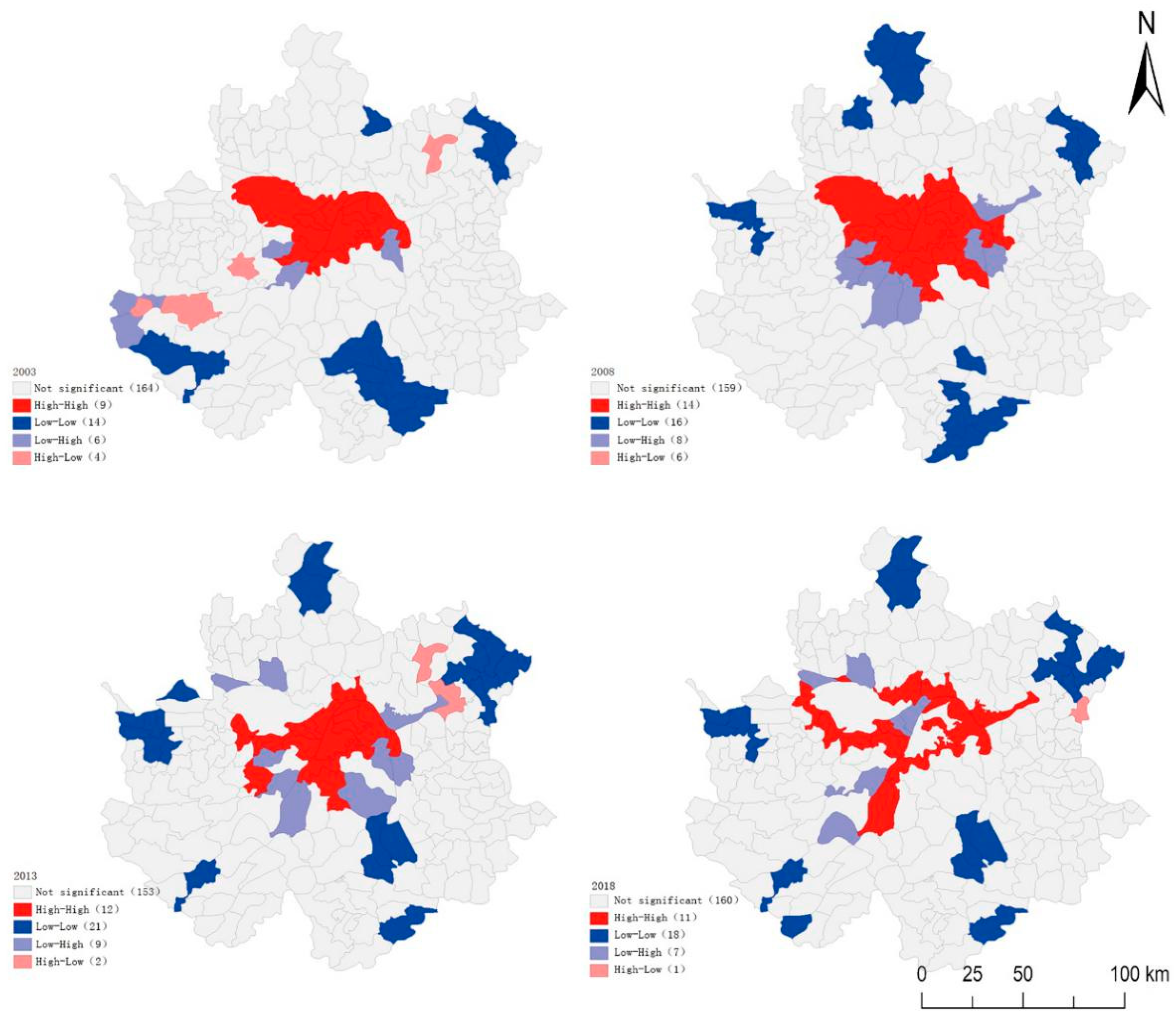
4.1. Temporal Evolution of Manufacturing Agglomeration
4.2. Manufacturing Suburban Agglomeration and Reconstruction is Significant
4.3. Analysis of Factors Influencing Manufacturing Agglomeration
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Classification Due to Factor Intensive | Manufacturing Industries |
|---|---|
| Labor-intensive Industry (L) | Processing of food from agricultural products (C13), manufacture of food (C14), manufacture of beverages (C15), manufacture of textiles (C17), manufacture of textiles and apparel (C18), manufacture of leather, furs, feathers, and related products (C19), manufacture of furniture (C21), manufacture of paper and paper products (C22), printing and reproducing of recording media (C23), manufacture of articles for culture, education, and sport activities (C24), other manufacturing (C41). |
| Capital-intensive Industry (C) | Processing of petroleum, coking, and nuclear fuel (C25), manufacture of rubber and plastic (C29), manufacture of non-metallic mineral products (C30), manufacture of metallic products (C33). |
| Technology-intensive industry (T) | Manufacture of raw chemical materials and chemical products (C26), manufacture of medicines (C27), manufacture of general purpose machinery (C34), manufacture of special purpose machinery (C35), manufacture of automobile (C36), manufacture of railway, vessel, aerospace, and transport equipment (C37), manufacture of electrical machinery and equipment (C38), manufacture of computers and communications equipment (C39),manufacture of instruments (C40), comprehensive utilization of waste resources (C42), metal products, machinery, and equipment maintenance industry (C43). |
| Resource-intensive industry (R) | Manufacture of tobacco (C16), processing of timber and manufacture of wood, bamboo, rattan, palm, and straw products (C20), manufacture of chemical fibers (C28), smelting and pressing of ferrous metals (C31), smelting and pressing of non-ferrous metals (C32). |
Appendix B
| Mi | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | −0.002 | 0.009 | −0.26 | 0.794 | −0.02 | 0.015 | |
| FTZ | −0.003 | 0.01 | −0.34 | 0.733 | −0.023 | 0.016 | |
| Airport | 0.017 | 0.01 | 1.76 | 0.078 | −0.002 | 0.036 | * |
| Railway | −0.022 | 0.013 | −1.66 | 0.097 | −0.049 | 0.004 | * |
| Port | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.09 | 0.926 | −0.021 | 0.023 | |
| Land price | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.83 | 0.407 | −0.003 | 0.001 | |
| Wage | −0.002 | 0.004 | −0.18 | 0.86 | −0.013 | 0.017 | |
| Development zone | 0.5 | 0.112 | 4.46 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.719 | *** |
| Innovation | 0.03 | 0.019 | 1.55 | 0.12 | −0.008 | 0.068 | |
| Fin | 0.016 | 0.004 | 4.07 | 0 | 0.008 | 0.024 | *** |
| Service platform | −0.192 | 0.064 | −3.02 | 0.003 | −0.317 | −0.067 | *** |
| Leading | −0.131 | 0.074 | −1.78 | 0.076 | −0.276 | 0.014 | * |
| Facilities | 0.001 | 0 | 2.53 | 0.012 | 0 | 0.002 | ** |
| Goods | −0.003 | 0.002 | −1.67 | 0.095 | −0.007 | 0.001 | * |
| PM20.5 | −0.024 | 0.036 | −0.65 | 0.514 | −0.095 | 0.047 | |
| PM10 | −0.047 | 0.026 | −1.79 | 0.073 | −0.098 | 0.004 | * |
| Constant | 8.763 | 3.386 | 2.59 | 0.01 | 2.127 | 15.399 | *** |
| Mean dependent var | 22.223 | SD dependent var | 35.488 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.427 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 876.750 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 4336.904 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 4399.285 | ||||
| Variables | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | p1 | p99 | Skew. | Kurt. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mi | 197 | 22.223 | 35.488 | 0 | 238 | 0 | 234 | 3.757 | 20.644 |
| Mi | Coef. | St. Err. | z | p > |z| | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.35 | 0.727 | −0.018 | 0.026 | |
| FTZ | −0.009 | 0.009 | −1.02 | 0.308 | −0.027 | 0.008 | |
| Airport | 0.011 | 0.009 | 1.18 | 0.24 | −0.007 | 0.029 | |
| Railway | −0.015 | 0.012 | −1.25 | 0.213 | −0.04 | 0.009 | |
| Port | −0.002 | 0.013 | −0.15 | 0.88 | −0.027 | 0.023 | |
| Land price | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.43 | 0.665 | −0.002 | 0.003 | |
| Wage | −0.062 | 0.011 | −0.66 | 0.511 | −0.012 | 00.06 | |
| Development zone | 0.597 | 0.159 | 3.76 | 0 | 0.286 | 0.909 | *** |
| Innovation | 0.092 | 0.049 | 1.86 | 0.063 | −0.005 | 0.188 | * |
| Fin | 0.012 | 0.012 | 1.01 | 0.311 | −0.011 | 0.034 | |
| Service platform | −0.415 | 0.136 | −3.06 | 0.002 | −0.681 | −0.149 | *** |
| Leading | −0.298 | 0.116 | −2.58 | 0.01 | −0.524 | −0.071 | *** |
| Facilities | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.47 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | *** |
| Goods | −0.002 | 0.003 | −0.85 | 0.394 | −0.008 | 0.003 | |
| PM20.5 | −0.1 | 0.047 | −2.14 | 0.032 | −0.192 | −0.008 | ** |
| PM10 | −0.025 | 0.024 | −1.07 | 0.285 | −0.072 | 0.021 | |
| Constant | 11.08 | 3.85 | 2.88 | 0.004 | 3.535 | 18.625 | *** |
| lnalpha | 0.026 | 0.102 | .b | .b | −0.173 | 0.226 | |
| Mean dependent var | 22.223 | SD dependent var | 35.488 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.056 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 90.408 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 1551.113 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 1616.777 | ||||
| Ti | Coef. | St. Err. | z | p > |z| | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | 0.019 | 0.014 | 10.42 | 0.155 | −0.007 | 0.046 | |
| FTZ | −0.024 | 0.011 | −2.23 | 0.026 | −0.046 | −0.003 | ** |
| Airport | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.27 | 0.785 | −0.018 | 0.024 | |
| Railway | −0.027 | 0.015 | −1.82 | 0.068 | −0.057 | 0.002 | * |
| Port | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.97 | 0.331 | −0.015 | 0.043 | |
| Land price | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1.07 | 0.286 | −0.001 | 0.005 | |
| Wage | −0.078 | 0.019 | −0.44 | 0.663 | −0.017 | 0.021 | |
| Development zone | 0.804 | 0.197 | 4.07 | 0 | 0.417 | 1.191 | *** |
| Innovation | 0.171 | 0.064 | 2.66 | 0.008 | 0.045 | 0.298 | *** |
| Fin | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.78 | 0.434 | −0.017 | 0.039 | |
| Service platform | −0.708 | 0.177 | −4.01 | 0 | −1.054 | −0.362 | *** |
| Leading | −0.539 | 0.146 | −3.68 | 0 | −0.826 | −0.252 | *** |
| Facilities | 0.003 | 0.001 | 4.60 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.004 | *** |
| Goods | −0.003 | 0.004 | −0.91 | 0.364 | −0.01 | 0.004 | |
| PM20.5 | −0.156 | 0.056 | −2.80 | 0.005 | −0.266 | −0.047 | *** |
| PM10 | −0.015 | 0.028 | −0.52 | 0.6 | −0.07 | 0.041 | |
| Constant | 11.671 | 4.472 | 2.61 | 0.009 | 2.907 | 2.435 | *** |
| lnalpha | 0.282 | 0.127 | .b | .b | 0.033 | 0.532 | |
| Mean dependent var | 8.802 | SD dependent var | 22.745 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.102 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 119.163 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 1088.771 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 1154.435 | ||||
| Li | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | −0.005 | 0.012 | −0.42 | 0.676 | −0.029 | 0.019 | |
| FTZ | −0.003 | 0.01 | −0.36 | 0.722 | −0.022 | 0.015 | |
| Airport | 0.007 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 0.505 | −0.013 | 0.027 | |
| Railway | −0.013 | 0.014 | −0.90 | 0.369 | −0.04 | 0.015 | |
| Port | 0.01 | 0.014 | 0.71 | 0.478 | −0.017 | 0.036 | |
| Land price | 0 | 0.001 | −0.03 | 0.976 | −0.002 | 0.002 | |
| Wage | −0.107 | 0.121 | −1.47 | 0.141 | −023 | 0.029 | ** |
| Development zone | 0.515 | 0.17 | 3.03 | 0.002 | 0.182 | 0.848 | *** |
| Innovation | 0.076 | 0.042 | 1.78 | 0.074 | −0.007 | 0.159 | * |
| Fin | 0 | 0.011 | −0.03 | 0.979 | −0.021 | 0.021 | |
| Service platform | −0.307 | 0.121 | −2.53 | 0.011 | −0.545 | −0.069 | ** |
| Leading | −0.098 | 0.109 | −0.90 | 0.368 | −0.313 | 0.116 | |
| Facilities | 0.001 | 0.001 | 1.59 | 0.112 | 0 | 0.002 | |
| Goods | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.77 | 0.439 | −0.004 | 0.008 | |
| PM20.5 | 0.081 | 0.049 | 1.65 | 0.099 | −0.015 | 0.177 | * |
| PM10 | −0.045 | 0.026 | −1.72 | 0.086 | −0.095 | 0.006 | * |
| Constant | 1.461 | 4.046 | 0.36 | 0.718 | −6.469 | 9.391 | |
| lnalpha | 0.099 | 0.123 | .b | .b | −0.142 | 0.34 | |
| Mean dependent var | 5.929 | SD dependent var | 9.134 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.044 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 49.140 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 1105.194 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 1170.858 | ||||
| Ci | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | −0.026 | 0.022 | −1.18 | 0.24 | −0.068 | 0.017 | |
| FTZ | −0.009 | 0.016 | −0.58 | 0.562 | −0.041 | 0.022 | |
| Airport | 0.053 | 0.019 | 2.80 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.09 | *** |
| Railway | 0.006 | 0.021 | 0.27 | 0.79 | −0.036 | 0.047 | |
| Port | −0.028 | 0.021 | −1.33 | 0.182 | −0.07 | 0.013 | |
| Land price | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.25 | 0.799 | −0.004 | 0.005 | |
| Wage | −0.056 | 0.045 | −0.17 | 0.862 | −0.034 | 0.015 | |
| Development zone | 0.265 | 0.235 | 1.13 | 0.259 | −0.195 | 0.724 | |
| Innovation | 0.015 | 0.039 | 0.38 | 0.705 | −0.062 | 0.091 | |
| Fin | 0.02 | 0.015 | 1.38 | 0.168 | −0.009 | 0.049 | |
| Service platform | −0.229 | 0.153 | −1.50 | 0.134 | −0.528 | 0.071 | |
| Leading | −0.241 | 0.179 | −1.35 | 0.178 | −0.593 | 0.11 | |
| Facilities | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.29 | 0.022 | 0 | 0.003 | ** |
| Goods | −0.009 | 0.004 | −2.05 | 0.041 | −0.018 | 0 | ** |
| PM20.5 | −0.146 | 0.078 | −1.88 | 0.06 | −0.298 | 0.006 | * |
| PM10 | −0.02 | 0.041 | −0.48 | 0.63 | −0.1 | 0.061 | |
| Constant | 9.797 | 6.142 | 1.60 | 0.111 | −2.241 | 21.834 | |
| lnalpha | 0.717 | 0.185 | .b | .b | 0.354 | 1.08 | |
| Mean dependent var | 1.518 | SD dependent var | 3.033 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.057 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 35.204 | Prob > chi2 | 0.009 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 626.305 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 691.969 | ||||
| Ri | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | (95% Conf | Interval) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.56 | 0.575 | −0.019 | 0.034 | |
| FTZ | −0.017 | 0.012 | −1.50 | 0.135 | −0.04 | 0.005 | |
| Airport | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.47 | 0.636 | −0.017 | 0.028 | |
| Railway | −0.01 | 0.016 | −0.63 | 0.527 | −0.04 | 0.021 | |
| Port | −0.005 | 0.015 | −0.30 | 0.765 | −0.034 | 0.025 | |
| Land price | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1.01 | 0.313 | −0.001 | 0.005 | |
| Wage | −0.007 | 0.001 | −0.15 | 0.884 | −0.021 | 0.024 | |
| Development zone | 0.661 | 0.19 | 3.48 | 0 | 0.289 | 1.033 | *** |
| Innovation | 0.032 | 0.049 | 0.64 | 0.519 | −0.065 | 0.128 | |
| Fin | 0.015 | 0.013 | 1.22 | 0.223 | −0.009 | 0.04 | |
| Service platform | −0.289 | 0.134 | −2.16 | 0.031 | −0.552 | −0.027 | ** |
| Leading | −0.354 | 0.131 | −2.71 | 0.007 | −0.611 | −0.098 | *** |
| Facilities | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.30 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | *** |
| Goods | −0.008 | 0.003 | −2.46 | 0.014 | −0.015 | −0.002 | ** |
| PM20.5 | −0.161 | 0.057 | −2.81 | 0.005 | −0.273 | −0.049 | *** |
| PM10 | −0.014 | 0.03 | −0.48 | 0.634 | −0.074 | 0.045 | |
| Constant | 13.48 | 4.65 | 2.90 | 0.004 | 4.367 | 22.594 | *** |
| lnalpha | 0.299 | 0.141 | .b | .b | 0.022 | 0.576 | |
| Mean dependent var | 4.832 | SD dependent var | 7.571 | ||||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.065 | Number of obs | 197.000 | ||||
| Chi-square | 65.508 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | ||||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 984.929 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 1050.593 | ||||
References
- Henderson, J.V. Marshall’s scale economies. J. Urban Econ. 2003, 53, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Scott, A.J. Industrial agglomeration and development: A survey of spatial economic issues in East Asia and statistical analysis of Chinese regions. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 79, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Yuan, F. Growth type and functional trajectories: An empirical study of urban expansion in Nanjing, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elif, A.; Geoffrey, J.D. Hewings. The determinants of agglomeration for the manufacturing sector in the Istanbul metropolitan area. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2012, 48, 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.-G.; Liu, W.-D.; Liu, Z.-G. The Quantitative Study on Inter-Regional Industry Transfer. China Ind. Econ. 2011, 6, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wong, C.; Duan, X. Urban growth and spatial restructuring patterns: The case of Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Environ. Plan. B 2016, 43, 515–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, C. Shifts in China’s economic geography studies in an era of industrial restructuring. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 865–879. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, M. Assessment and analysis of regional economic collaborative development within an urban agglomeration: Yangtze River Delta as a case study. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J. Globalization and the Rise of City-regions. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2001, 9, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Storper, M. Regions, Globalization, Development. Reg. Stud. 2003, 37, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, G. New Regionalism Reconsidered: Globalization and the Remaking of Political Economic Space. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2001, 25, 804–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, K.; Gao, X. Manufacturing industry agglomeration and spatial clustering: Evidence from Hebei Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 2941–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Michael, R. Spatial agglomeration and location determinants: Evidence from the US communications equipment manufacturing industry. Urban Stud. 2015, 53, 2154–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Goetz, S.J. Technology intensity and agglomeration economies. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, Y. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution of manufacturing geographical agglomeration and influencing factors of old industrial base: A case of Jilin Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Hwang, S.; Lee, M. Agglomeration economies and location choice of Korean manufacturers within the United States. Appl. Econ. 2012, 44, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Hwang, S. Regional Characteristics, Industry Agglomeration and Location Choice: Evidence from Japanese Manufacturing Investments in Korea. J. Asian Econ. 2016, 30, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Sun, J. Agglomeration economies and the match between manufacturing industries and cities in China. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2014, 6, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. Agglomeration and relocation: Manufacturing plant relocation in Korea. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2014, 93, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzoglou, K.; Tsekeris, T. Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in Greece: Sectoral Patterns and Determinants. Econ. Plan. Stud. 2013, 21, 1853–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J. Industry classification considering spatial distribution of manufacturing activities. Area 2014, 46, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hao, X. The Agglomeration of Manufacturing Industry, Innovation and Haze Pollution in China: Theory and Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Cai, Y. Co-location of manufacturing and producer services in Nanjing, China. Cities 2017, 63, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, J. Regional and sectoral differences in the spatial restructuring of Chinese manufacturing industries during the post-WTO period. GeoJournal 2012, 77, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. The characteristics of industrial agglomeration based on micro-geographic data. Geogr. Res. 2019, 35, 95–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Liu, W.; Michael, D. State land policy, land markets and geographies of manufacturing: The case of Beijing, China. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Zhao, X. Land market, land development and urban spatial structure in Beijing. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Increasing returns and economic geography. J. Political Econ. 1991, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P. The new economic geography: Past, present and the future. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2004, 83, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Smith, T.E. On the spatial scale of industrial agglomerations. J. Urban Econ. 2015, 89, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Klaesson, J.; Larsson, J.P. How local are spatial density externalities? Neighbourhood effects in agglomeration economies. Reg. Stud. 2016, 50, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P.; Venables, A. The Spatial Economy: Cities, Regions and International Trade; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, R.E.; Krugman, P. Agglomeration, Integration and Tax Harmonization. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2004, 48, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A. Theory of the Location of Industries; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Losch, A. The Economics of Location; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, L.N. Location and the Theory of Production. Q. J. Econ. 1958, 72, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, J.B. Productivity Growth, Convergence, and Welfare: What the Long-Run Data Show. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnovskikh, S. Industrial clusters in Russia: The development of special economic zones and industrial parks. Russ. J. Econ. 2017, 3, 174–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.; Rocha, R. Labor pooling as an agglomeration factor: Evidence from the Brazilian Northeast in the 2002–2014 period. EconomiA 2018, 19, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, G.; Langella, M. Local agglomeration, entrepreneurship and the 2008 recession: Evidence from Italian industrial districts. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2016, 58, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cainelli, G.; Ganau, R.; Giunta, A. Spatial agglomeration, Global Value Chains, and productivity. Micro-evidence from Italy and Spain. Econ Lett. 2018, 169, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Xie, S. Can industrial agglomeration promote pollution agglomeration? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Jin, H. Industrial agglomeration and CO2 emissions: Evidence from 187 Chinese prefecture-level cities over 2005–2013. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Analysis of China’s Manufacturing Industry Carbon Lock-In and Its Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Does industrial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Nadvi, K. Industrial clusters and industrial ecology: Building ‘eco-collective efficiency’in a South Korean cluster. Geoforum 2018, 90, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.Y.; Shen, Z.C. The temporal and spatial evolution of population & industrial agglomeration and environmental pollution and the relevance analysis. J. Arid. Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, e8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.L.; Wang, Q. How China achieved its 11th Five-Year Plan emissions reduction target: A structural decomposition analysis of industrial SO2 and chemical oxygen demand. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 574, 110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, R. Determinants of Firm Failure: Empirical Evidence form China. Growth Change 2016, 47, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhu, S. Evolutionary Economic Geography in China; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.J.; Liang, W. Local Government Competition Aects the Spatial Mismatch of Regional Industrial Transfer—Based on Game Theory Model. Rev. Ind. Organ. 2018, 12, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Li, Y.; Miao, C.; Li, J.; Lv, K. Debates and research trends of local embeddedness of transferred enterprises. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 844–852. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Lv, Y. Employment centers and polycentric spatial development in Chinese cities: A multi-scale analysis. Cities 2020, 99, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Sun, L.; Pu, W. Research on the influence of manufacturing agglomeration modes on regional carbon emission and spatial effect in China. Econ. Model. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Kang, Y.; Lee, S. A study on the impact of soft location factors in the relocation of service and manufacturing firms. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2014, 18, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anet, W. What Makes Firms Leave the Neighbourhood? Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 1613–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of manufacturing enterprises in Yangtze River Delta: Scale effects and dynamic evolution. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 1236–1252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lu, L.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X. The spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of hotel industry in the metropolitan area: An empirical study based on China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Sang, D.; Li, X. Metropolitan area boundary define and research method discussion: A case study of Chongqing metropolitan area plan-making. Urb. Dev. Stud. 2015, 1, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Xie, B. Study on the Method of Metropolitan Area Delimitation Based on Multidata: A Case Study of Wuhan. Urban Stud. 2017, 2, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association: LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wang, W.; Sun, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, X. Ecological Pressure of Carbon Footprint in Passenger Transport: Spatio-Temporal Changes and Regional Disparities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Lu, C.P.; Ren, W.X. POI-based Spatial Correlation of the Residences and Retail Industry in Shenyang City. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 442–449. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Wei, Y.H.D. Intra-metropolitan location of foreign direct investment in Wuhan, China: Institution, urban structure, and accessibility. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 47, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use: Toward a General Theory of Land Rent; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F. Intra-metropolitan FDI firm location in Guangzhou, China: A Poisson and negative binomial analysis. Ann. Reg. Sci. 1999, 33, 535–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yang, W.; Du, D. The Scientific Cooperation Network of Chinese Scientists and Its Proximity Mechanism. Sustainability 2020, 12, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, J. Industrial Policy and Innovation Capability of Strategic Emerging Industries: Empirical Evidence from Chinese New Energy Vehicle Industry. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Evolving spatial distribution of manufacturing industries in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 435–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, L.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Urban innovation, regional externalities of foreign direct investment and industrial agglomeration: Evidence from Chinese cities. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Lang, W.; Li, X. Does Institutional Embeddedness Promote Regional Enterprises’ Migration? An Empirical Analysis Based on the “Double Transfer” Strategy in Guangdong, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.D.; Leung, C.K.; Li, W.; Pan, R. Institutions, location, and networks of multinational enterprises in China: A case study of Hangzhou. Urban Geogr. 2008, 29, 639–661. [Google Scholar]
- Drucker, J.; Feser, E. Regional industrial structure and agglomeration economies: An analysis of productivity in three manufacturing industries. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. The spatial correlation and interaction between manufacturing agglomeration and environmental pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H. The Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Haze Pollution in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xiang, Q. Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: Based on an extended CDM model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 3, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.J.; Wang, M.F.; Li, J.; Ning, Y.M. Agglomeration and suburbanization: A study on the spatial distribution of software industry and its evolution in Metropolitan Shanghai. Acta Geogra. Sinica 2011, 66, 1682–1694. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Sun, L. Manufacture restructuring and main determinants in Beijing Metropolitan Area. Acta Geogra. Sinica 2012, 67, 1308–1316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Forstall, R.L.; Greene, R.P. Defining job concentrations: The Los Angeles case. Urban Geogr. 1997, 18, 705–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivo, G. A taxonomy of suburban office clusters: The case of Toronto. Urban Stud. 1993, 30, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Areas | Districts |
|---|---|
| Cental | Jiang’an, Jianghan, Qiaokou, Hanyang, Wuchang, Qinshan, Hongshan |
| Outer | Dongxihu, Hannan, Caidian, Jiangxia, Huangpi, Xinzhou |
| Suburbs | Xiaonan, Hanchuan, Part of Xiantao, Part of Honghu, Jiayu, Xian’an, Daye, Liangzihu, Tieshan, Huangshigang, Xisaishan, Huangzhou, Tuanfeng, Huarong, Xialu, Echeng |
| Type | Variable | Sub-Variables | Definition | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market | Accessibility | CBD | Distance to CBD | GIS spatial analysis tools were used to calculate Euclidean distance (this study) |
| FTZ | Distance to East Lake Free Trade Zone | |||
| Airport | Distance to Tianhe Airport | |||
| Railway | Distance to Wuhan Railway Station | |||
| Port | Distance to Yangluo Port | |||
| Labor cost | Wage | Average salary of employees | National Bureau of Statistics | |
| Land market | Land price | Industrial land price | http://www.whtdsc.com/ | |
| Government policy | Innovation and entrepreneurial environment | Innovation | Number of universities and scientific research laboratories | http://kjt.hubei.gov.cn/ |
| Service Platform | Number of technical service platforms | http://www.hbsccloud.com/ | ||
| Institution | Development zone | Number of national, provincial and municipal industrial parks | http://jxt.hubei.gov.cn/ | |
| Investment | Fin | Loans margin of financial institutions | National Bureau of Statistics | |
| Leading effect | Leading | Number of enterprises with annual turnover exceeding RMB 10 billion | National Bureau of Statistics | |
| Urban environment | Convenience | Facilities | Number of shopping, dining, entertainment, accommodation, hospitals, elementary schools | Point of interest |
| Prosperity | Goods | Total social consumer goods | National Bureau of Statistics | |
| Air quality | PM2.5 | Annual average | Atmospheric monitoring stations | |
| PM10 | Annual average |
| Stats | Max | Min | Mean | SD | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mi | 238 | 0 | 22.22 | 35.49 | 197 |
| CBD | 126 | 6.1 | 62.24 | 29.34 | 197 |
| FTZ | 139.9 | 17.55 | 76.82 | 29.02 | 197 |
| Airport | 159.7 | 27.76 | 87.03 | 31.42 | 197 |
| Railway | 160.6 | 11 | 96.21 | 29.97 | 197 |
| Port | 179.1 | 36 | 113.4 | 31.88 | 197 |
| Land price | 1391 | 195.8 | 459.6 | 178.8 | 197 |
| Wage | 111,987 | 39,623 | 57,054 | 13,109 | 197 |
| Development zone | 10 | 0 | 0.35 | 1.171 | 197 |
| Innovation | 409 | 0 | 5.096 | 32.55 | 197 |
| Fin | 194 | 0 | 2.569 | 18.08 | 197 |
| Service Platform | 58 | 0 | 1.03 | 6.027 | 197 |
| Leading | 16 | 0 | 0.249 | 1.53 | 197 |
| Facilities | 23,325 | 8.05 | 655 | 2201 | 197 |
| Goods | 1100 | 0.75 | 39 | 135.2 | 197 |
| PM2.5 | 71.35 | 59.61 | 65.73 | 3.077 | 197 |
| PM10 | 96.58 | 72.66 | 82.53 | 4.145 | 197 |
| Year | 2003 | 2008 | 2013 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.342 | 0.401 | 0.208 | 0.120 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mi | Ti | Li | Ci | Ri | |
| CBD | 0.004 | 0.019 | −0.005 | −0.026 | 0.008 |
| (0.011) | (0.014) | (0.012) | (0.022) | (0.014) | |
| FTZ | −0.009 | −0.024 ** | −0.003 | −0.009 | −0.017 |
| (0.009) | (0.011) | (0.010) | (0.016) | (0.012) | |
| Airport | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.053 *** | 0.005 |
| (0.009) | (0.011) | (0.010) | (0.019) | (0.012) | |
| Railway | −0.015 | −0.027 * | −0.013 | 0.006 | −0.010 |
| (0.012) | (0.015) | (0.014) | (0.021) | (0.016) | |
| Port | −0.002 | 0.014 | 0.011 | −0.028 | −0.005 |
| (0.013) | (0.015) | (0.014) | (0.021) | (0.015) | |
| Wage | −0.062 | −0.078 | −0.107 ** | −0.056 | −0.007 |
| (0.011) | (0.019) | (0.121) | (0.045) | (0.001) | |
| Land price | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.002) | |
| Innovation | 0.092 * | 0.171 *** | 0.076 * | 0.015 | 0.032 |
| (0.049) | (0.064) | (0.042) | (0.039) | (0.049) | |
| Service platform | −0.415 *** | −0.708 *** | −0.307 * | −0.229 | −0.289 ** |
| (0.136) | (0.177) | (0.121) | (0.153) | (0.134) | |
| Development zone | 0.597 *** | 0.804 *** | 0.515 *** | 0.265 | 0.661 *** |
| (0.159) | (0.197) | (0.17) | (0.235) | (0.19) | |
| Fin | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.020 | 0.015 |
| (0.012) | (0.014) | (0.011) | (0.015) | (0.013) | |
| Leading | −0.298 *** | −0.539 *** | −0.098 | −0.241 | −0.354 *** |
| (0.116) | (0.146) | (0.109) | (0.179) | (0.131) | |
| Facilities | 0.002 *** | 0.003 *** | 0.001 | 0.002 ** | 0.002 ** |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| Goods | −0.002 | −0.003 | 0.002 | −0.009 ** | −0.008 ** |
| (0.003) | (0.004) | (0.003) | (0.004) | (0.003) | |
| PM2.5 | −0.110 ** | −0.156 *** | 0.081 * | −0.146 * | −0.161 * |
| (0.047) | (0.056) | (0.049) | (0.078) | (0.057) | |
| PM10 | −0.025 | −0.015 | −0.045* | −0.020 | −0.014 |
| (0.024) | (0.028) | (0.026) | (0.041) | (0.030) | |
| Constant | 11.08 *** | 11.671 *** | 1.461 | 9.797 | 13.48 *** |
| (3.85) | (4.472) | (4.046) | (6.142) | (4.65) | |
| lnalpha | 0.026 | 0.282 ** | 0.099 | 0.717 *** | 0.299 ** |
| (0.102) | (0.127) | (0.123) | (0.185) | (0.141) | |
| Observations | 197 | 197 | 197 | 197 | 197 |
| r2_p | 0.056 | 0.102 | 0.044 | 0.057 | 0.065 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Zheng, Z.; Luo, J.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198005
Luo L, Zheng Z, Luo J, Jia Y, Zhang Q, Wu C, Zhang Y, Sun J. Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants. Sustainability. 2020; 12(19):8005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Lei, Zhenhua Zheng, Jing Luo, Yuqiu Jia, Qi Zhang, Chun Wu, Yifeng Zhang, and Jia Sun. 2020. "Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants" Sustainability 12, no. 19: 8005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198005
APA StyleLuo, L., Zheng, Z., Luo, J., Jia, Y., Zhang, Q., Wu, C., Zhang, Y., & Sun, J. (2020). Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area: An Analysis of Sectoral Patterns and Determinants. Sustainability, 12(19), 8005. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198005






