The Influence of the Air Cargo Network on the Regional Economy under the Impact of High-Speed Rail in China
Abstract
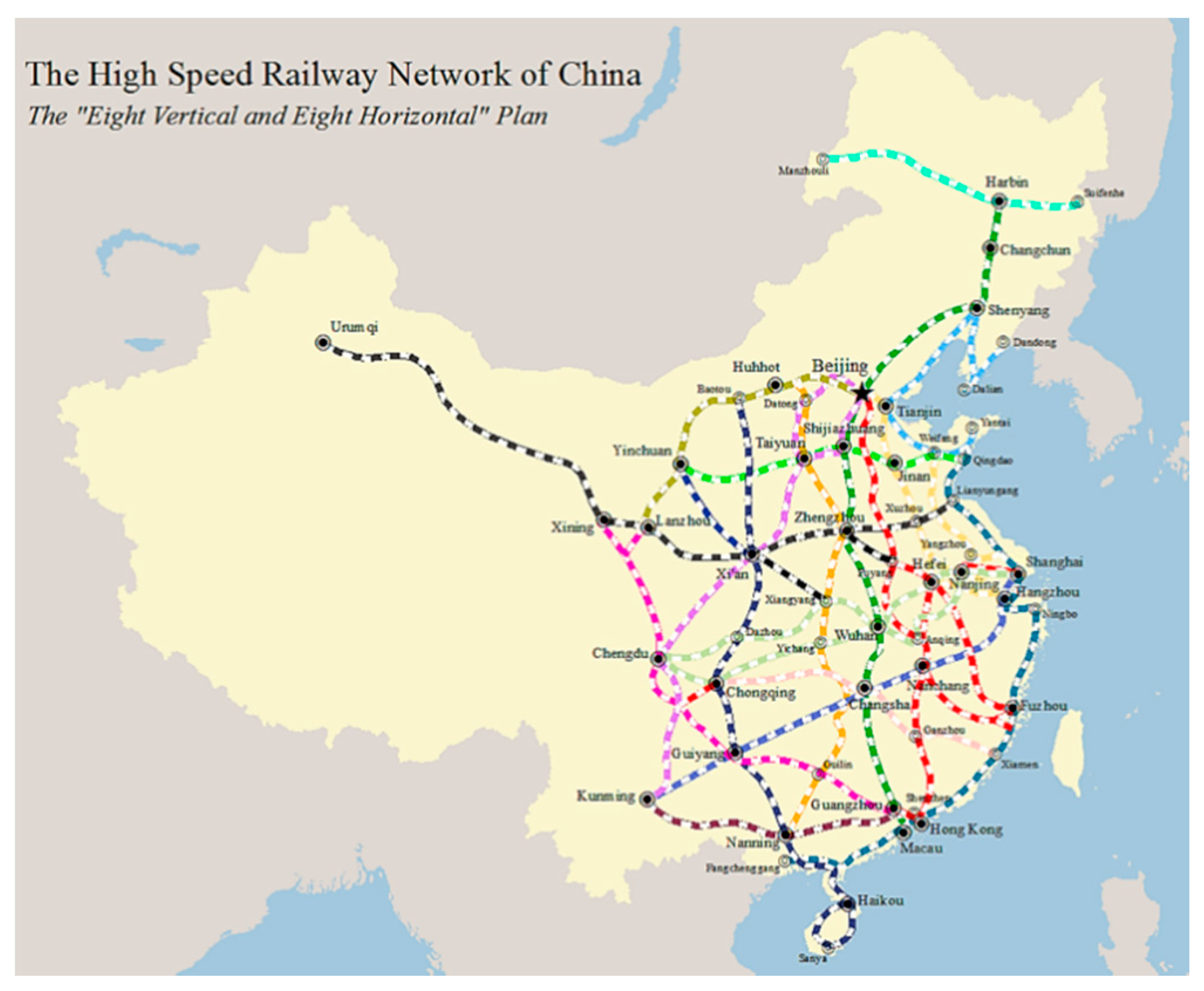
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Analytical Framework
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. HSR and Air Transport
2.1.2. Air Transport and Regional Economy
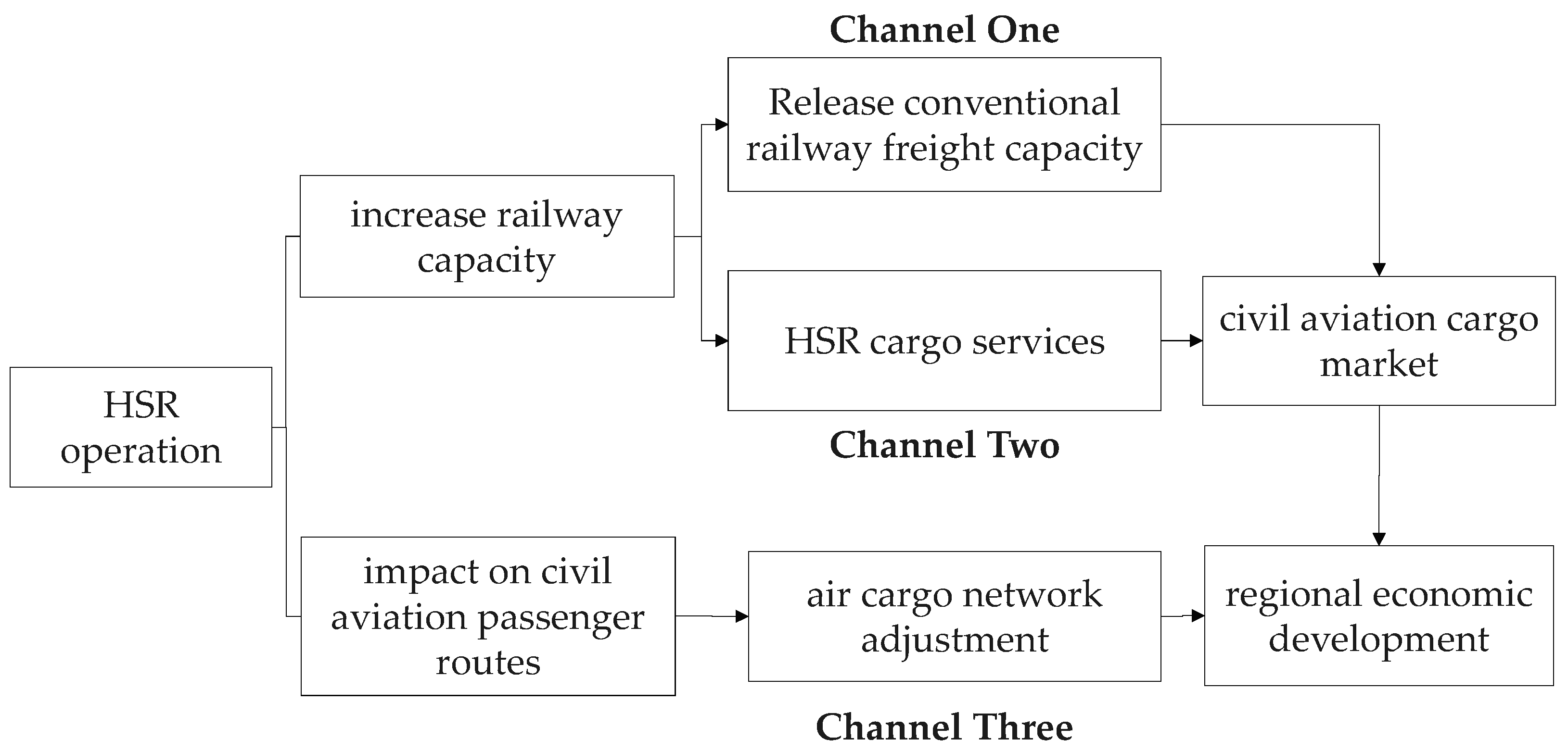
2.2. Analytical Framework
2.2.1. Channel One: Conventional Railway Capacity Release and Regional Economic Development
2.2.2. Channel Two: HSR Cargo Service and Regional Economic Development
2.2.3. Channel Three: Air Cargo Network Adjustment and Regional Economic Development
3. The Model
3.1. Model Construction
3.1.1. Air Cargo Network and Regional Economy
3.1.2. HSR, Air Cargo Network and Regional Economy
3.2. Variable Definitions and Sensitivity Analysis
3.2.1. Variable Definitions
- (1)
- : in order to measure the development of the regional economy, in reference to the common practices in Chinese and non-Chinese research, this study uses the real GDP per capita for city i at year .
- (2)
- : the availability of HSR is set as a dummy variable for city i at year . The data period is from 2008 to 2017. A value of 1 or 0 is assigned as the dummy variable of HSR availability during the study period. The cities with HSR are classified under the treatment group, and the assigned value is set as 1; cities without HSR fall under the control group, and the assigned value is set as 0.
- (3)
- : for city i at year , when the HSR is put into operation, the years after the HSR’s opening are set as 1 and 0 otherwise.
- (4)
- : the actual amount of foreign investments in city i at year , which measures the level of trade development in the city concerned.
- (5)
- : the proportion of the secondary industry production value to the overall GDP for city i at year . This variable indicates that industrial structure and freight transportation are closely related to the development of secondary industry, which is the main source of the derived freight demand.
- (6)
- : the number of employees for city i at year which can measure the actual human resources engaged in production and business activities.
- (7)
- the actual fixed asset investment for city i at year , which can measure the level of city investment.
- (8)
- : the direct research and development investment for city i at year , which can measure the technological inputs.
- (9)
- : this variable measures the clustering coefficient of the air cargo network for the airport of city i at year . In our study, all of the Chinese airports, particularly airports with air cargo exchanges during the 10 year period from 2008 to 2017, are considered (as shown in Table 1). Each airport’s clustering coefficient is calculated to reflect its air cargo network characteristics. In other words, each airport is regarded as a hub for its air cargo network.
3.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. The Data
3.3.1. Data Sources
3.3.2. Description of Data
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Empirical Results with the OLS Method
4.1.1. Impacts of the Air Cargo Network on All of China and Different Regions
4.1.2. Impacts of the Air Cargo Network on Cities of Different Scales
4.2. Empirical Results with the DID Method
4.2.1. Impacts of the Air Cargo Network on China Overall and the Different Regions
4.2.2. Impacts of the Air Cargo Network on Cities of Different Scales
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Givoni, M. Development and impact of the modern high-speed train: A review. Transp. Rev. 2006, 26, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jack, S.; Shun, H.; Li, L. Do high-speed railways lead to urban economic growth in China-a panel data study of China’s cities. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2018, 69, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Enlightenment and research of tourism impact on high-speed rail. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Alan, A.L. Mechanism and HSR effect of spatial structure of regional tourist flow: Case study of Beijing-Shanghai HSR in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 214–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Huang, J.; Wen, Y. Impact of high-speed railway on spatial pattern of Chinese cities’ accessibility. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, N.; Pels, E.; Nash, C. High-speed rail and air transport competition: Game engineering as tool for cost-benefit analysis. Transp. Res. Part B 2010, 44, 812–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobruszkes, F.; Dehon, C.; Givoni, M. Does European high-speed rail affect the current level of air services? An EU-wide analysis. Transp. Res. Pol. Pract. 2014, 69, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Strauss, J.; Lu, L. The impact of high-speed rail on civil aviation in China. Transp. Policy 2019, 74, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, Y. Transportation policy for high-speed rail competing with airlines. Transp. Res. Pol. Pract. 2018, 116, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, R. High speed trains and the development and regeneration of cities. Greengauge 2006, 21, 5–126. [Google Scholar]
- Christiaan, B.; Eric, P. Intermodal competition in the London-Paris passenger market: High-speed rail and air transport. J. Urban Econ. 2012, 71, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu, T. The history and future of high-speed railways in Japan. Jpn. Railw. Transp. Rev. 2007, 8, 6–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F. A study on network of domestic air passenger flow in China. Geogr. Res. 2011, 20, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Sun, C. Performance evaluation of China’s air routes based on network data envelopment analysis approach. Air Transp. Manag. 2016, 55, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Zheng, Y. Global transpark: New competitiveness for Hong Kong and South China based on air logistics. Urban Plan. Int. 2007, 22, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Alkaabi, K.A.; Debbage, K.G. The geography of air freight: Connections to U.S. metropolitan economies. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Meng, C. Analysis on structure of air cargo network of China based on economy. J. Civ. Aviat. Univ. China 2012, 30, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Lectical analysis of high-speed railway and civil aviation. Traffic Transp. 2011, 12, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, J. Substitution opportunities of high-speed train for air transport. Transp. Bus. 2008, 7, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Boardman, A.E.; Gillen, D.; Waters II, W.G. Towards Estimating the Social and Environmental Costs of Transportation in Canada; Research Report for Transport Canada; Transport Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2004.
- Tan, X. The development of high-speed railway in China and its impacts on the industry of civil aviation transportation. Money China 2011, 6, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yonghwa, P.; Hun, K.H. Analysis of the impact of high-speed rail road service on air transport demand. Transp. Res. Part E 2006, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, C.; Raquel, E.; Juan, C.M. Competition of high-speed train with air transport: The case of Madrid-Barcelona. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2007, 13, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luan, W.; Cai, Q. Research on the competition between high-speed rail and air transport. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. Soc. Sci. 2011, 32, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H. Analysis on factors of high-speed railway traffic demand. Railw. Econ. Res. 1996, 1, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jing, Y.; Yang, H. Impacts of high-speed rail on China’s domestic air transportation. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda, J.D. From airport city to aerotropolis. Airpt. World 2001, 4, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H. Research on mechanism and path of spillover effect of aviation economy on regional economy. J. Zhengzhou Univ. Aeronaut. 2016, 34, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Huddleston, P. Regional and local economic impacts of transportation investment. Transp. Q. 1990, 44, 579–594. [Google Scholar]
- Brueckner, J.K. Economic contribution of the aviation sector to HongKong: A value-added approach. Chin. Econ. 2006, 39, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda, J.D.; Jonathan, D. Green air cargo as an economic development engine: A note on opportunities and constraints. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2005, 11, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, G.D. Air transportation and urban-economic restructuring: Competitive advantage in the US Carolinas. J. Air Transp. Manag. 1999, 5, 21–221. [Google Scholar]
- David, G.; Ashish, L. The new economy and opportunities for airports. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2002, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y. The function of hub airport on the region economic development. Econ. Geogr. 2001, 21, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Mo, H. Geography of air transportation: Retrospect and prospect. Prog. Geogr. 2011, 30, 670–680. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, R.; Barabas, I.A.L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, K. The impact of air transportation and airport on regional economic development. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2006, 26, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R. Empirical analysis on the structure of domestic air cargo network in China. Enterp. Econ. 2011, 3, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, H.E. Spatial productivity spillovers from public infrastructure: Evidence from state highways. Int. Tax Public Financ. 1995, 2, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, T.; Yu, T.H.E.; Cho, S.H.; Jensen, K.; Ugrate, D.D.L.T. Evaluating the spatial spillover effect of transportation infrastructure on agriculture output across the United States. Transp. Geogr. 2013, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R. Developing trend of difference-in-difference and its application in public policy evaluation. Financ. Minds 2018, 3, 84–111. [Google Scholar]
- Imbensand, G.W.; Wooldridge, J.M. Recent developments in the econometrics of program evaluation. J. Econ. Lit. 2009, 47, 5–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenfelter, O. Estimating the effect of training programs on earning. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1978, 60, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, Y. The policy effect of tax-and-fees reforms in rural China: A difference-in-differences estimation. Econ. Res. J. 2005, 8, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ network. Nature 1998, 393, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Wang, R.; Su, H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, J.S.; Li, W.; Cai, X. Structural Properties of US Flight Network. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2003, 20, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cai, X. Statistical analysis of airport network of China. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, M.; Maria, F. Topology of the Italian airport network: A scale-free small-world network with a fractal structure? Chaos Soitions Fractals 2007, 31, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Fu, X.; Xiao, Y. International trade drivers and freight network analysis-The case of the Chinese air cargo sector. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 71, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Jin, F.; Liu, W. Roles of accessibility, connectivity and spatial interdependence in realizing the economic impact of high-speed rail: Evidence from China. Transp. Policy 2020, 91, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Graham, D. Air transport and economic growth: A review of the impact mechanism and causal relationships. Transp. Rev. 2020, 40, 506–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wan, Y.; Yang, H. Impacts of high-speed rail on airlines, airports and regional economies: A survey of recent research. Transp. Policy 2019, 81, A1–A19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.; Renelt, D. A sensitivity analysis of cross-country growth regressions. Am. Econ. Rev. 1992, 82, 942–963. [Google Scholar]
- Sala-i-Martin, X. i just ran two million regressions. Am. Econ. Rev. 1997, 87, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Baizhu, C.; Phillips, K.L. China’s Regional Economic Growth: Panel Data Sensitivity Analysis; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, R.; Hansman, R. Impact of Air Transportation on Regional Economic and Social Connectivity in the United States; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, L.; Klink, H.; Pol, P. Airports as centres of economic growth. Transp. Rev. 1996, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, R.; Fik, T.J.; Malecki, E.J. Changes in air service connectivity and employment. Environ. Plan. A 1995, 27, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, K.; Lall, S.; Stough, R. High-technology employment and hub airports. J. Air Transp. Manag. 1999, 5, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, K.; Taylor, S. International air transportation and economic development. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2000, 6, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.D.; Kasarda, J.D. Air passenger linkages and employment growth in U.S. metropolitan areas. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1991, 56, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerman, R. High-speed rail in Europe: Experience and issues for future development. Ann. Reg. Sci. 1997, 31, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Domestic | International | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Airport Number | Number of Airports with Air Cargo Activity | Domestic Air Cargo Routes Number | Total Airport Number | Number of Airports with Air Cargo Activity | International Air Cargo Route Number | |
| 2008 | 150 | 67 | 961 | 104 | 93 | 6027 |
| 2009 | 163 | 72 | 1094 | 93 | 87 | 4644 |
| 2010 | 172 | 75 | 1211 | 110 | 90 | 5185 |
| 2011 | 175 | 62 | 1121 | 126 | 114 | 6147 |
| 2012 | 178 | 63 | 1063 | 121 | 118 | 7035 |
| 2013 | 188 | 64 | 905 | 118 | 118 | 7281 |
| 2014 | 198 | 50 | 540 | 123 | 121 | 7482 |
| 2015 | 204 | 52 | 475 | 137 | 126 | 7739 |
| 2016 | 212 | 57 | 663 | 146 | 137 | 8199 |
| 2017 | 224 | 56 | 737 | 158 | 151 | 8840 |
| Variable | The Proportion of Times When the Regression Coefficient is Significant | Significant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | 95% | 99% | ||
| C1 | 0% | 50% | 33% | ** |
| C2 | 17% | 32% | 0% | * |
| FDI | 13% | 0% | 0% | - |
| SEC | 17% | 25% | 25% | ** |
| LAB | 0% | 0% | 92% | *** |
| K | 0% | 0% | 67% | *** |
| R&D | 11% | 0% | 89% | *** |
| Variable | Obs. | Mean | S.d. | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 760 | 0.00072 | 0.00096 | 0 | 0.00733 |
| C2 | 760 | 0.01209 | 0.01508 | 0 | 0.0748 |
| FDI | 760 | 0.02792 | 0.03722 | 0.00004 | 0.78891 |
| SEC | 760 | 45.98 | 11.21 | 14.95 | 85.08 |
| LAB | 760 | 434,162 | 1,096,637 | 94,980 | 9,868,700 |
| K | 760 | 217,000 | 214,000 | 10,579 | 1,720,000 |
| R&D | 760 | 1,132,261 | 1,683,187 | 13,277 | 13,300,000 |
| Variable | Overall | Eastern China | Central China | Western China | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | |
| C1 | 0.030 (6.51) *** | 0.029 (6.34) *** | 0.033 (6.11) *** | 0.032 (6.08) *** | 0.026 (3.35) ** | 0.024 (3.08) ** | 0.018 (2.06) | 0.017 (1.95) | ||||
| C2 | 0.015 (2.28) | 0.012 (1.78) | 0.006 (0.75) | 0.002 (0.28) | 0.019 (2.39) | 0.017 (1.99) | 0.016 (1.40) | 0.015 (1.24) | ||||
| FDI | −0.033 (−4.79) *** | −0.031 (−4.52) *** | −0.020 (−2.89) ** | −0.014 (−1.53) | −0.014 (−1.49) | 0.004 (0.46) | −0.028 (−2.17) | −0.028 (−2.17) | −0.015 (−1.20) | −0.050 (−4.13) *** | −0.045 (−3.87) *** | −0.046 (−3.78) ** |
| SEC | −0.050 (−3.58) *** | −0.051 (−3.67) *** | −0.065 (−4.62) *** | −0.067 (−3.55) *** | −0.066 (−3.54) *** | −0.089 (−4.60) *** | 0.004 (0.18) | 0.007 (0.30) | 0.002 (0.07) | −0.019 (−0.79) | −0.025 (−1.01) | −0.025 (−0.99) |
| LAB | −0.019 (−1.39) | −0.020 (−1.39) | −0.015 (−1.06) | −0.026 (−1.12) | −0.024 (−1.04) | −0.012 (−0.49) | 0.001 (0.04) | 0.011 (0.33) | −0.003 (−0.07) | −0.024 (−1.30) | −0.027 (−1.50) | −0.026 (−1.39) |
| K | −0.107 (−1.83) | −0.110 (−1.87) | −0.124 (−2.04) | −0.899 (−5.65) *** | −0.909 (−5.74) *** | −1.032 (−6.24) *** | −0.934 (−4.52) *** | −1.054 (−5.13) *** | −1.203 (−6.00) *** | 0.069 (1.05) | 0.071 (1.07) | 0.070 (1.05) |
| R&D | 0.204 (7.68) *** | 0.203 (7.64) *** | 0.214 (7.85) *** | −0.007 (−0.54) | −0.008 (−0.61) | −0.008 (−0.59) | 0.832 (6.86) *** | 0.913 (6.56) *** | −0.035 (7.29) *** | 0.585 (8.63) *** | 0.585 (8.61) *** | 0.580 (8.49) *** |
| R2 | 0.802 | 0.800 | 0.790 | 0.827 | 0.827 | 0.809 | 0.919 | 0.914 | 0.909 | 0.800 | 0.799 | 0.797 |
| Variable | Overall | Super-Large Cities | Other Cities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| C1 | 0.030 (6.514) *** | 0.029 (6.34) *** | −0.436 (−5.05) *** | −0.447 (−5.41) *** | 0.026 (6.40) *** | 0.026 (6.30) *** | |||
| C2 | 0.015 (2.28) | 0.012 (1.78) | −0.063 (−0.49) | −0.241 (−1.77) | 0.021 (3.80) *** | 0.021 (3.63) *** | |||
| FDI | −0.033 (−4.79) *** | −0.031 (−4.52) *** | −0.020 (−2.89) ** | 0.150 (2.26) | 0.155 (2.37) | −0.106 (−2.26) | −0.028 (−4.21) *** | −0.026 (−3.80) *** | −0.016 (−2.41) |
| SEC | −0.050 (−3.58) *** | −0.051 (−3.67) *** | −0.065 (−4.62) *** | −0.244 (−2.99) ** | −0.251 (−3.14) ** | 0.058 (0.95) | −0.038 (−2.43) | −0.038 (−2.45) | −0.052 (−3.26) ** |
| LAB | −0.019 (−1.39) | −0.020 (−1.39) | −0.015 (−1.06) | 0.067 (1.86) | 0.065 (1.84) | 0.053 (1.35) | −0.010 (−0.79) | −0.011 (−0.84) | −0.004 (−0.31) |
| K | −0.107 (−1.83) | −0.110 (−1.87) | −0.124 (−2.04) | −0.015 (−0.05) | −0.029 (−0.10) | −0.639 (−2.24) | −0.017 (−0.31) | −0.026 (−0.46) | −0.032 (−0.54) |
| R&D | 0.204 (7.68) *** | 0.203 (7.64) *** | 0.214 (7.85) *** | 0.040 (1.68) | 0.041 (1.73) | 0.048 (1.84) | 0.586 (11.58) *** | 0.583 (11.40) *** | 0.625 (12.03) *** |
| R2 | 0.802 | 0.800 | 0.790 | 0.852 | 0.852 | 0.818 | 0.834 | 0.829 | 0.821 |
| Variable | Overall | Eastern China | Central China | Western China | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | |
| T∗P | 0.11 (0.036) *** | 0.076 (0.031) | 0.066 (0.028) | 0.139 (0.049) *** | 0.101 (0.040) | 0.062 (0.040) | 0.003 (0.048) | 0.020 (0.038) | −0.027 (0.036) | −0.031 (0.083) | −0.047 (0.075) | 0.074 (0.059) |
| T∗P∗C1 | 0.01 (0.004) | 0.013 (0.003) *** | 0.017 (0.005) | 0.020 (0.005) *** | 0.007 (0.005) | 0.006 (0.005) | −0.017 (0.010) | −0.009 (0.009) | ||||
| T∗P∗C2 | 0.016 (0.006) * | 0.021 (0.006) *** | 0.014 (0.009) * | 0.023 (0.009) ** | −0.002 (0.008) | −0.003 (0.008) | 0.029 (0.014) | 0.016 (0.012) | ||||
| FDI | 0.003 (0.007) | 0.004 (0.007) | 0.004 (0.007) | −0.016 (0.012) | −0.014 (0.124) | −0.016 (0.013) | 0.012 (0.014) | 0.012 (0.013) | 0.012 (0.013) | 0.005 (0.010) | 0.003 (0.010) | 0.004 (0.010) |
| SEC | 0.319 (0.033) *** | 0.313 (0.033) *** | 0.308 (0.032) *** | 0.319 (0.109) *** | 0.649 (0.109) | 0.704 (0.111) *** | 0.895 (0.133) *** | 0.904 (0.131) *** | 0.832 (0.119) *** | 0.246 (0.040) *** | 0.249 (0.040) *** | 0.274 (0.037) *** |
| LAB | 0.002 (0.003) | 0.002 (0.003) | 0.002 (0.004) | 0.002 (0.005) | −0.003 (0.006) | −0.002 (0.006) | 0.004 (0.005) | 0.005 (0.005) | 0.006 (0.005) | −0.002 (0.008) | −0.001 (0.008) | −0.001 (0.008) |
| K | 0.100 (0.017) *** | 0.095 (0.017) *** | 0.100 (0.017) *** | 0.039 (0.025) | 0.033 (0.024) | 0.039 (0.025) | −0.124 (0.037) *** | −0.116 (0.034) *** | −0.131 (0.035) *** | 0.178 (0.028) *** | 0.177 (0.028) *** | 0.177 (0.028) *** |
| R&D | 0.084 (0.027) ** | 0.084 (0.027) ** | 0.083 (0.027) ** | 0.174 (0.047) *** | 0.171 (0.047) *** | 0.182 (0.048) *** | −0.035 (0.030) | −0.034 (0.030) | −0.035 (0.030) | 0.037 (0.044) | 0.047 (0.044) | 0.041 (0.044) |
| R2 | 0.953 | 0.952 | 0.952 | 0.953 | 0.953 | 0.952 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.950 | 0.950 | 0.949 |
| Variable | Overall | Super-Large Cities | Other Cities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| T∗P | 0.11 (0.036) *** | 0.076 (0.031) | 0.066 (0.028) | −0.354 (1.853) | 0.413 (0.345) | −0.354 (1.853) | 0.100 (0.036) ** | 0.049 (0.031) | 0.040 (0.036) ** |
| T∗P∗C1 | 0.01 (0.004) | 0.013 (0.003) *** | 0.052 (0.059) | 0.058 (0.057) | 0.009 (0.004) | 0.013 (0.004) *** | |||
| T∗P∗C2 | 0.016 (0.006) * | 0.021 (0.006) *** | −0.054 (0.203) | 0.051 (0.203) | 0.014 (0.006) | 0.020 (0.006) *** | |||
| FDI | 0.003 (0.007) | 0.004 (0.007) | 0.004 (0.007) | 0.043 (0.028) | 0.041 (0.027) | 0.037 (0.028) | 0.0004 (0.007) | 0.001 (0.007) | 0.001 (0.007) |
| SEC | 0.319 (0.033) *** | 0.313 (0.033) *** | 0.308 (0.032) *** | 0.375 (0.248) | 0.371 (0.246) | 0.338 (0.248) | 0.327 (0.032) *** | 0.318 (0.032) *** | 0.312 (0.032) *** |
| LAB | 0.002 (0.003) | 0.002 (0.003) | 0.002 (0.004) | −0.0001 (0.010) | −0.0002 (0.010) | 0.002 (0.010) | 0.002 (0.004) | 0.002 (0.004) | 0.002 (0.004) |
| K | 0.100 (0.017) *** | 0.095 (0.017) *** | 0.100 (0.017) *** | 0.068 (0.063) | 0.069 (0.062) | 0.066 (0.063) | 0.122 (0.018) *** | 0.112 (0.018) *** | 0.118 (0.018) *** |
| R&D | 0.084 (0.027) ** | 0.084 (0.027) ** | 0.083 (0.027) ** | 0.031 (0.066) | 0.031 (0.066) | 0.038 (0.066) | 0.109 (0.030) *** | 0.107 (0.030) *** | 0.107 (0.030) *** |
| R2 | 0.953 | 0.952 | 0.952 | 0.944 | 0.930 | 0.929 | 0.957 | 0.956 | 0.956 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Strauss, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, X. The Influence of the Air Cargo Network on the Regional Economy under the Impact of High-Speed Rail in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198120
Hao L, Zhang N, Li H, Strauss J, Liu X, Guo X. The Influence of the Air Cargo Network on the Regional Economy under the Impact of High-Speed Rail in China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(19):8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198120
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Lulu, Na Zhang, Hongchang Li, Jack Strauss, Xuejie Liu, and Xuemeng Guo. 2020. "The Influence of the Air Cargo Network on the Regional Economy under the Impact of High-Speed Rail in China" Sustainability 12, no. 19: 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198120
APA StyleHao, L., Zhang, N., Li, H., Strauss, J., Liu, X., & Guo, X. (2020). The Influence of the Air Cargo Network on the Regional Economy under the Impact of High-Speed Rail in China. Sustainability, 12(19), 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198120





