Overview of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning as a Sustainability Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
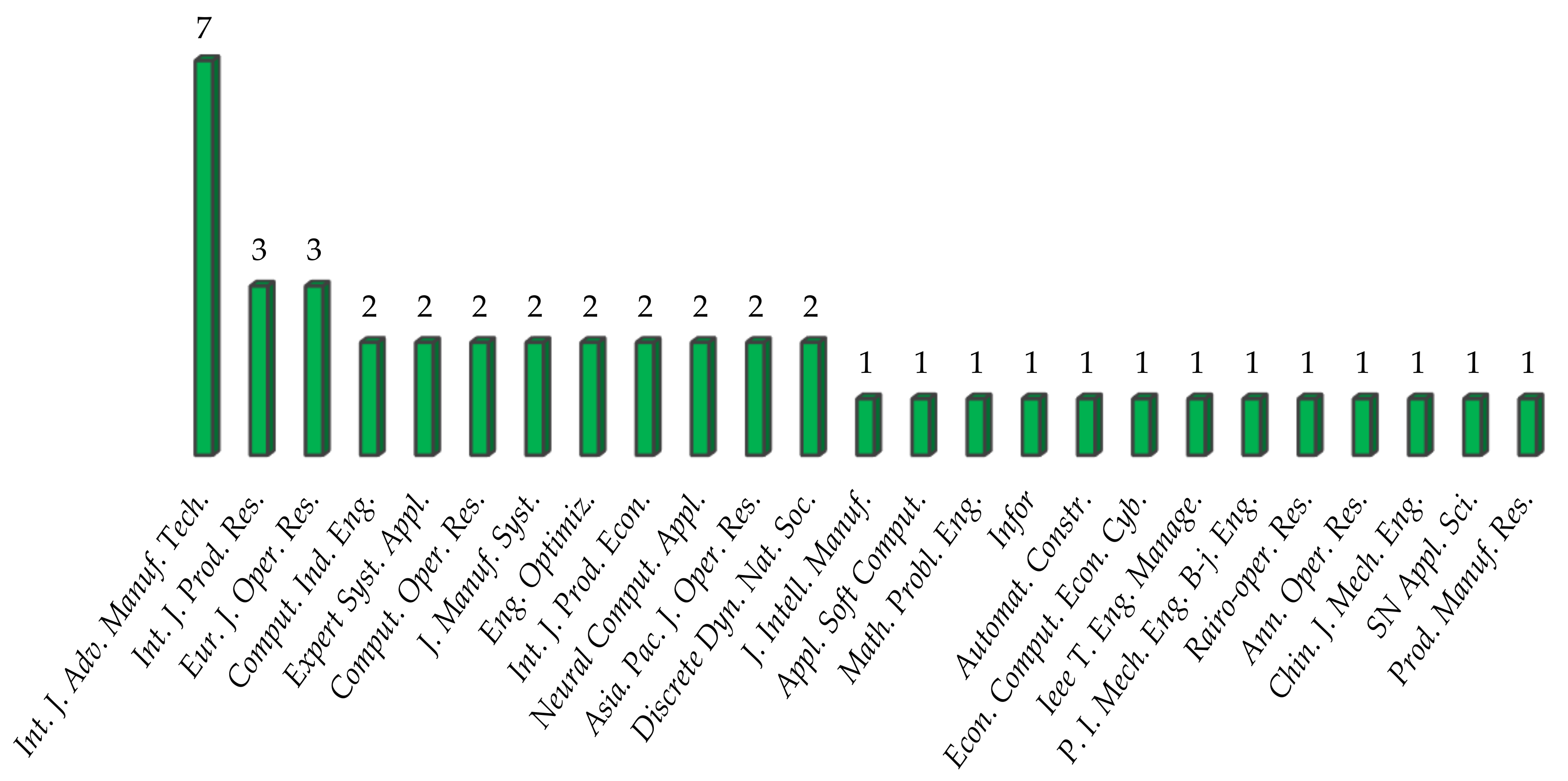
2. Review Methodology
3. Current Trends in the DFLP Formulation
4. Current Trends in the Mathematical Modeling of the DFLP
5. Contributions of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning to Supply Chain Sustainability
6. Guidelines for Future Research
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tari, F.G.; Neghabi, H. A new linear adjacency approach for facility layout problem with unequal area departments. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 37, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirkhah, A.S.; Navidi, H.; Bidgoli, M.M. Dynamic Facility Layout Problem: A New Bilevel Formulation and Some Metaheuristic Solution Methods. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2015, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntas, S.; Selim, H. Facility layout using weighted association rule-based data mining algorithms: Evaluation with simulation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.-Y.; Hu, M.H.; Wang, M.-J. Simulated annealing based parallel genetic algorithm for facility layout problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navidi, H.; Bashiri, M.; Bidgoli, M.M. A heuristic approach on the facility layout problem based on game theory. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 1512–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Nasab, H.; Fereidouni, S.; Ghomi, S.M.T.F.; Fakhrzad, M.B. Classification of facility layout problems: A review study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 94, 957–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Rogers, D.S. A framework of sustainable supply chain management: Moving toward new theory. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2008, 38, 360–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Washispack, S. Mapping the Path Forward for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Review of Reviews. J. Bus. Logist. 2018, 39, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.; Schoenherr, T.; Charan, P. The thematic landscape of literature in sustainable supply chain management (SSCM). Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 1091–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Póvoa, A.P.F.D.; Da Silva, C.; Carvalho, A. Opportunities and challenges in sustainable supply chain: An operations research perspective. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 268, 399–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.; Evans, S.; Taticchi, P. Industrial sustainability: Challenges, perspectives, actions. Int. J. Bus. Innov. Res. 2013, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Flores, R.B.; Cruz-Sotelo, S.E.; Ojeda-Benítez, S.; Ramírez-Barreto, M.E. Sustainable Supply Chain Management—A Literature Review on Emerging Economies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.; Despeisse, M. Additive manufacturing and sustainability: An exploratory study of the advantages and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Sustainable Industry 4.0 framework: A systematic literature review identifying the current trends and future perspectives. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, J.; Saldanha, T.J.V.; Mithas, S.; Sambamurthy, V. Information Technology and Sustainability: Evidence from an Emerging Economy. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2018, 27, 756–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Das, M.; Ali, S.M.; Raihan, A.S.; Paul, S.K.; Kabir, G. Evaluating strategies for environmental sustainability in a supply chain of an emerging economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, D.O.; Silvestre, B.S. Advancing social sustainability in supply chain management: Lessons from multiple case studies in an emerging economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stindt, D. A generic planning approach for sustainable supply chain management —How to integrate concepts and methods to address the issues of sustainability? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemipour, G.; Lee, T.S.; Loong, Y.T. Performance Analysis of Intelligent Robust Facility Layout Design. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Nookabadi, A.S. Managing a new multi-objective model for the dynamic facility layout problem. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hawarneh, A.; Bendak, S.; Ghanim, F. Dynamic facilities planning model for large scale construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2019, 98, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaderi, N.; Ghezavati, V.; Mozafari, M. Developing a mathematical model for the dynamic facility layout problem considering material handling system and optimizing it using cloud theory-based simulated annealing algorithm. Sn. Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turanoğlu, B.; Akkaya, G. A new hybrid heuristic algorithm based on bacterial foraging optimization for the dynamic facility layout problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 98, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemipour, G.; Lee, T.S.; Rilling, D. A review of intelligent approaches for designing dynamic and robust layouts in flexible manufacturing systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, L.; Bigliardi, B.; Bottani, E. Sustainable Supply Chain and Innovation: A Review of the Recent Literature. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Islam, S.; Karia, N.; Fauzi, F.A.; Afrin, S. A literature review on green supply chain management: Trends and future challenges. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boar, A.; Bastida, R.; Marimon, F. A Systematic Literature Review. Relationships between the Sharing Economy, Sustainability and Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D. Producing a systematic review. In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2009; pp. 671–689. [Google Scholar]
- Novais, L.R.; Maqueira, J.M.; Ortiz, A. A systematic literature review of cloud computing use in supply chain integration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 129, 296–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, D.; Day, S.; Godsell, J. Supply Chain Configurations in the Circular Economy: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zavala-Alcívar, A.; Verdecho, M.J.; Alfaro-Saiz, J.-J. A Conceptual Framework to Manage Resilience and Increase Sustainability in the Supply Chain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rollins, J.; Yan, E. Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997–2017: A selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulturel-Konak, S.; Konak, A. A large-scale hybrid simulated annealing algorithm for cyclic facility layout problems. Eng. Optim. 2014, 47, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, V.M.; Hunagund, I.; Krishnan, K. Design of robust layout for Dynamic Plant Layout Problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2011, 61, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zeng, T.; Fan, L.; Han, Y.; Xia, B. An Improved Genetic Algorithm Based Robust Approach for Stochastic Dynamic Facility Layout Problem. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKendall, A.R.; Hakobyan, A. Heuristics for the dynamic facility layout problem with unequal-area departments. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 201, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-L.; Chuang, S.-P.; Hsu, T.-S. A genetic algorithm for dynamic facility planning in job shop manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 52, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedzadeh, M.; Mazinani, M.; Moradinasab, N.; Roghanian, E. Parallel variable neighborhood search for solving fuzzy multi-objective dynamic facility layout problem. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 65, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Dai, X.; Qiu, B.; Li, J. A revised electromagnetism-like mechanism for layout design of reconfigurable manufacturing system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 63, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolai, F.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Taghipour, M. A multi-objective particle swarm optimisation algorithm for unequal sized dynamic facility layout problem with pickup/drop-off locations. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 4279–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, R.; Baboli, A.; Javadian, N.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Kazemi, M.; Khorrami, J. Solving a group layout design model of a dynamic cellular manufacturing system with alternative process routings, lot splitting and flexible reconfiguration by simulated annealing. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 2642–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendall, A.; Liu, W.-H. New Tabu search heuristics for the dynamic facility layout problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, P.; Saberi, E. An efficient hybrid algorithm for dynamic facility layout problem using simulation technique and PSO. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. Res. 2013, 47, 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini-Nasab, H.; Emami, L. A hybrid particle swarm optimisation for dynamic facility layout problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, M.; Dalfard, V.M.; Amiri, S. A new intelligent algorithm for dynamic facility layout problem in state of fuzzy constraints. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 24, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, R.; Javadian, N.; Paydar, M.M.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M. A Simulated Annealing for Intra-Cell Layout Design of Dynamic Cellular Manufacturing Systems With Route Selection, Purchasing Machines And Cell Reconfiguration. Asia Pac. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 30, 1350004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazinani, M.; Abedzadeh, M.; Mohebali, N. Dynamic facility layout problem based on flexible bay structure and solving by genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 65, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandi, H.; Taabayan, P.; Behroozi, M. Metaheuristics for fuzzy dynamic facility layout problem with unequal area constraints and closeness ratings. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 2701–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.-H. A new data structure of solution representation in hybrid ant colony optimization for large dynamic facility layout problems. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 142, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgi, N.; Abedzadeh, M.; Zeinali, M. Tabu search heuristic for efficiency of dynamic facility layout problem. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 77, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.-H.; Lo, J.-C. Dynamic Facility Layout with Multi-Objectives. Asia Pac. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 31, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Al Khaled, A.; Vadlamani, S. Hybrid imperialist competitive algorithm, variable neighborhood search, and simulated annealing for dynamic facility layout problem. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 1871–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, R.; Khaksar-Haghani, F.; Javadian, N.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. Solving a multi-floor layout design model of a dynamic cellular manufacturing system by an efficient genetic algorithm. J. Manuf. Syst. 2014, 33, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematian, J. A robust single row facility layout problem with fuzzy random variables. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourvaziri, H.; Naderi, B. A hybrid multi-population genetic algorithm for the dynamic facility layout problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 24, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, A.D.; Wong, K.Y. Solving unequal-area static and dynamic facility layout problems using modified particle swarm optimization. J. Intell. Manuf. 2015, 28, 1317–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Ma, H.; Tang, Y. An Optimization Method for the Remanufacturing Dynamic Facility Layout Problem with Uncertainties. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulutas, B.; Islier, A.A. Dynamic facility layout problem in footwear industry. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 36, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlelahi, F.Z.; Pournader, M.; Gharakhani, M.; Sadjadi, S.J. A robust approach to design a single facility layout plan in dynamic manufacturing environments using a permutation-based genetic algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 230, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Seifbarghy, M. A novel meta-heuristic algorithm for multi-objective dynamic facility layout problem. Rairo Oper. Res. 2016, 50, 869–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourvaziri, H.; Pierreval, H. Dynamic facility layout problem based on open queuing network theory. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 259, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, A.; Singh, S.P. Integrating big data analytic and hybrid firefly-chaotic simulated annealing approach for facility layout problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 2016, 270, 489–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.P. A similarity score-based two-phase heuristic approach to solve the dynamic cellular facility layout for manufacturing systems. Eng. Optim. 2017, 49, 1848–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, D.; He, K.; Xue, Y. Combining Wang–Landau sampling algorithm and heuristics for solving the unequal-area dynamic facility layout problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitayasak, S.; Pongcharoen, P.; Hicks, C. A tool for solving stochastic dynamic facility layout problems with stochastic demand using either a Genetic Algorithm or modified Backtracking Search Algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 190, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Kulturel-Konak, S.; Konak, A. A problem evolution algorithm with linear programming for the dynamic facility layout problem—A general layout formulation. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 88, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulturel-Konak, S. The zone-based dynamic facility layout proble. INFOR 2019, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tan, X.; Li, J. Research on Dynamic Facility Layout Problem of Manufacturing Unit Considering Human Factors. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitayasak, S.; Pongcharoen, P. Performance improvement of Teaching-Learning-Based Optimisation for robust machine layout design. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 98, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yuan, S.; Ye, Y. Optimizing facility layout planning for reconfigurable manufacturing system based on chaos genetic algorithm. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2019, 7, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulturel-Konak, S. Approaches to uncertainties in facility layout problems: Perspectives at the beginning of the 21st Century. J. Intell. Manuf. 2007, 18, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muther, R. Systematic Layout Planning; Industrial Education Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Singhal, S. Implementation of fuzzy TOPSIS methodology in selection of procedural approach for facility layout planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 88, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukchin, Y.; Tzur, M. A new MILP approach for the facility process-layout design problem with rectangular and L/T shape departments. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 7339–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, R.D.; Kirkizoglu, Z.; Chen, W. A new optimization model to support a bottom-up approach to facility design. Comput. Oper. Res. 2010, 37, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Che, A. Novel integer linear programming models for the facility layout problem with fixed-size rectangular departments. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 95, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, M.Z.; Azab, A. Mathematical modeling and multi-start search simulated annealing for unequal-area facility layout problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Jokar, M.R.A. A survey on multi-floor facility layout problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 107, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drira, A.; Pierreval, H.; Hajri-Gabouj, S. Facility layout problems: A survey. Annu. Rev. Control. 2007, 31, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelny, J.; Michalski, R. A novel version of simulated annealing based on linguistic patterns for solving facility layout problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 124, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathhorn, J.; Sisikoglu, E.; Sir, M.Y. A multi-objective mixed-integer programming model for a multi-floor facility layout. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 4223–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, J.A.; White, J.A.; Bozer, Y.A.; Tanchoco, J.M.A. Facilities Planning, 4th ed.; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
| References | Problem Type | Planning Phase | Planning Approach | Number of Facilities | Number of Floors | Number of Dept. (n) | Space Consideration | Dept. Shape | Dept. Dimensions | Dept. Area | Material Handling Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kheirkhah et al. [2] | G | B | F | S | S | 5 ≤ n ≤ 60 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Moslemipour et al. [19] | G | B | R | S | S | 2 ≤ n ≤ 9 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Emami and Nookabadi [20] | G | B | F | S | S | 4 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Al Hawarneh et al. [21] | G | B | F | M | S | n = 25 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Pournaderi et al. [22] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Turanoğlu and Akkaya [23] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6,15,30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Kulturel-Konak and Konak [34] | G | B | C | S | S | n = 6,12,15 | B | R | V | U | OFLP |
| Pillai et at. [35] | G | B | R | S | S | n = 5,15,30 | B | R | F | E | OFLP |
| Peng et al. [36] | G | B | R | S | S | 8 ≤ n ≤ 125 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| McKendall and Hakobyan [37] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 125 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| Yang et al. [38] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 10 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Abedzadeh et al. [39] | G | B | F | S | S | 4 ≤ n ≤ 12 | B | R | V | U | MRLP |
| Guan et al. [40] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 10,20,25 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Jolai et al. [41] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6,12 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| Kia et al. [42] | G | B,D | F | S | S | 4 ≤ n ≤ 10 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| McKendall and Liu [43] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Azimi and Saberi [44] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6,15,30 | B | R | F | U | MRLP |
| Hosseini-Nasab and Emami [45] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6,15,30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Kaveh et al. [46] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Kia et al. [47] | G | D | F | S | S | n = 8,10,12 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Mazinani et al. [48] | G | B | F | S | S | 10 ≤ n ≤ 20 | B | R | F,V | U | MRLP |
| Samarghandi et al. [49] | G | B | F | S | S | 10 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | U | MRLP |
| Chen [50] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 6,15,30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Bozorgi et al. [51] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | E | SRLP |
| Chen and Lo [52] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 20 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Hosseini et al. [53] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Kia et al. [54] | G,R | B | F | S | M | 10 ≤ n ≤ 80 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Nematian [55] | G | B | R | S | S | 4 ≤ n ≤ 15 | B | R | F | U | SRLP |
| Pourvaziri and Naderi [56] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 30 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Derakhshan and Wong [57] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 8,11,20 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| Li et al. [58] | G,R | B | F | S | S | n = 27 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Ulutas and Islier [59] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 54 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Zarea et al. [60] | G | B | R | S | S | n = 9 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Hosseini and Seifbarghy [61] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 15 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Pourvaziri and Pierreval [62] | G | B | F | S | S | n = 8 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Tayal and Singh [63] | G | D | F | S | S | n = 12 | B | R | F | E | SRLP |
| Kumar and Singh [64] | G | B, D | F | S | S | n = 5,7,8 | B | R | F | E | MRLP |
| Liu et al. [65] | G | B | F | S | S | 6 ≤ n ≤ 20 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| Vitayasak et al. [66] | G | B | F | S | S | 10 ≤ n ≤ 50 | B | R | F | U | MRLP |
| Xiao et al. [67] | G | B | F | S | S | 10 ≤ n ≤ 35 | B | R, I | V | U | OFLP |
| Kulturel-Konak [68] | G | B | F | S | S | 12 ≤ n ≤ 25 | B | R | V | U | OFLP |
| Li et al. [69] | G | D | F | S | S | n = 12 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| Vitayasak and Pongcharoen [70] | G | D | F | S | S | 10 ≤ n ≤ 50 | B | R | F | U | MRLP |
| Wei et al. [71] | G | D | F | S | S | n = 10 | B | R | F | U | OFLP |
| References | Type of Model 1 | Type of Objective Function | Objective Function 2 | Constraints 3 | Demand | Type of Data | Distance Metric | Solution Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kheirkhah et al. [2] | BLPM | MO | a,b,g | 2,6,15 | C | D | R | A |
| Moslemipour et al. [19] | QAP | SO | a | 2 | U | D | R | E,A |
| Emami and Nookabadi [20] | QAP | MO | a,b,L | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Al Hawarneh et al. [21] | LIP | SO | a,b | 2,6 | C | D | E | A |
| Pournaderi et al. [22] | QAP | MO | a,b | 1,15 | C | D | R | A |
| Turanoğlu and Akkaya [23] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Kulturel-Konak and Konak [34] | MINLP | SO | a,b | 2,6 | C | D | R | M |
| Pillai et at. [35] | QAP | MO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Peng et al. [36] | QAP | SO | a,b | 15 | U | N | R | A,S |
| McKendall and Hakobyan [37] | MILP | SO | a,b | 2,6,9 | C | D | R | A |
| Yang et al. [38] | MILP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Abedzadeh et al. [39] | MILP | MO | a,b,f,L | 2,6,8 | C | D | R | A |
| Guan et al. [40] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | FD | A |
| Jolai et al. [41] | MINLP | MO | a,b,L,M | 2,6,7,9 | C | D | R | A |
| Kia et al. [42] | MINLP | SO | a,b,h | 2,3 | C | D | R | E,A |
| McKendall and Liu [43] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Azimi and Saberi [44] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Hosseini-Nasab and Emami [45] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Kaveh et al. [46] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | U | D,N | R | A,S |
| Kia et al. [47] | MINLP | SO | a,b,h | 2,3,12,13 | C | D | R | E,A |
| Mazinani et al. [48] | MILP | SO | a,b | 2,6,8,9 | C | D | R | A |
| Samarghandi et al. [49] | NLP | MO | a,b,L | 2 | U | D,N | R | A |
| Chen [50] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Bozorgi et al. [51] | QAP | MO | a,b,L,M | 2 | C | D | E | A |
| Chen and Lo [52] | QAP | MO | a,b,L | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Hosseini et al. [53] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Kia et al. [54] | MILP | SO | a,b,h | 2,3,11,12,13,14 | C | D | R | A |
| Nematian [55] | FSPM | SO | a | 2,6,10 | C | N | R | H |
| Pourvaziri and Naderi [56] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Derakhshan and Wong [57] | MINLP | SO | a,b | 2,6 | C | D | R | A |
| Li et al. [58] | MINLP | SO | a,b | 1,2 | C | D | R | A |
| Ulutas and Islier [59] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | C | D | R | A |
| Zarea et al. [60] | QAP | SO | a,b | 2 | U | D | R | A |
| Hosseini and Seifbarghy [61] | NLP | MO | a,b,g | 2,15,18 | C | D | R | A |
| Pourvaziri and Pierreval [62] | QAP | MO | a,b,g,e | 2,4,7,15 | U | D,N | R | A |
| Tayal and Singh [63] | QAP | MO | a,b,d,i,L | 2 | U | N | R | A |
| Kumar and Singh [64] | QAP | SO | a,b | 16 | C | D | R | A |
| Liu et al. [65] | MINLP | SO | a,b | 2,6 | C | D | R | H |
| Vitayasak et al. [66] | LIP | SO | a,b | 2,6,10 | U | D,N | R | A |
| Xiao et al. [67] | MILP | SO | a,b | 2,5,6,17 | C | D | R | A |
| Kulturel-Konak [68] | MINLP | SO | a,b | 2,5,6,7 | C | D | R | M |
| Li et al. [69] | NLP | MO | a,b,j,k,N | 1,2,6 | C | D | R | A |
| Vitayasak and Pongcharoen [70] | LIP | SO | c | 2,6 | U | D | R | A |
| Wei et al. [71] | NLP | MO | a,b,N | 2,6,10 | C | D | R | A |
| References | i | ii | iii | iv | v | vi | vii | viii | ix | x | xi | xii | xiii | xiv | xv | xvi | xvii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kheirkhah et al. [2] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Moslemipour et al. [19] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Emami and Nookabadi [20] | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| Pournaderi et al. [22] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Turanoğlu and Akkaya [23] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Kulturel-Konak and Konak [34] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Pillai et at. [35] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Peng et al. [36] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| McKendall and Hakobyan [37] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Yang et al. [38] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Abedzadeh et al. [39] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Guan et al. [40] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Jolai et al. [41] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Kia et al. [42] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| McKendall and Liu [43] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Azimi and Saberi [44] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hosseini-Nasab and Emami [45] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Kaveh et al. [46] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Kia et al. [47] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Mazinani et al. [48] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Samarghandi et al. [49] | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||
| Chen [50] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Bozorgi et al. [51] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Chen and Lo [52] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hosseini et al. [53] | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| Kia et al. [54] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Pourvaziri and Naderi [56] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Derakhshan and Wong [57] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Li et al. [58] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Ulutas and Islier [59] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Zarea et al. [60] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hosseini and Seifbarghy [61] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Pourvaziri and Pierreval [62] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Tayal and Singh [63] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Vitayasak et al. [66] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Xiao et al. [67] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Kulturel-Konak [68] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Li et al. [69] | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitayasak and Pongcharoen [70] | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| Wei et al. [71] | √ |
| References | E | S | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kheirkhah et al. [2] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Minimization of the need for new material handling devices during peak demand periods. (3) Minimization of the number of idle material handling devices during low demand periods. | |
| Moslemipour et al. [19] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs. | |
| Emami and Nookabadi [20] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Al Hawarneh et al. [21] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Pournaderi et al. [22] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Reduction in the number of material handling devices needed. (3) Consideration of budget limitations when planning the layout design. | |
| Turanoğlu and Akkaya [23] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Kulturel-Konak and Konak [34] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Pillai et at. [35] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Peng et al. [36] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Reduction in the number of material handling devices needed. | |
| McKendall and Hakobyan [37] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Yang et al. [38] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Abedzadeh et al. [39] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Guan et al. [40] | √ | (1) Minimization of the materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Jolai et al. [41] | √ | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Maximization of distance requests among departments to avoid exposing workers to occupational health/safety risk factors like noise, heat or vibration. |
| Kia et al. [42] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Minimization of machinery operations costs. | |
| McKendall and Liu [43] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Azimi and Saberi [44] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Hosseini-Nasab and Emami [45] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Kaveh et al. [46] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Kia et al. [47] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Minimization of machinery operations costs. | |
| Mazinani et al. [48] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Samarghandi et al. [49] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Chen [50] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Bozorgi et al. [51] | √ | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Maximization of distance requests among departments to avoid exposing workers to occupational health/safety risk factors like noise or vibration. |
| Chen and Lo [52] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Hosseini et al. [53] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Kia et al. [54] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Minimization of machinery operations costs. | |
| Nematian [55] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs. | |
| Pourvaziri and Naderi [56] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Derakhshan and Wong [57] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Li et al. [58] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. (2) Consideration of budget limitations when planning the layout design. | |
| Ulutas and Islier [59] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Zarea et al. [60] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Hosseini and Seifbarghy [61] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs, the machines rearrangement costs, and the fixed costs related to the material handling equipment. | |
| Pourvaziri and Pierreval [62] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs (including costs generated by the transportation devices while traveling empty) and machines rearrangement costs. (2) Minimization of work in process. | |
| Tayal and Singh [63] | √ | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs, machines rearrangement costs and transport time. (2) Minimization of the risk level associated with hazardous materials and waste paths. |
| Kumar and Singh [64] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and the rearrangement costs. (2) Reduction in the number of machines per department. | |
| Liu et al. [65] | √ | (1) Minimization of the materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Vitayasak et al. [66] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Xiao et al. [67] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Kulturel-Konak [68] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and facility rearrangement costs. | |
| Li et al. [69] | √ | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs, facility rearrangement costs (including relocation and setup costs), and lost opportunity costs during the relocation time. (2) Consideration of budget limitations when planning the layout design. (3) Maximization of the area utilization ratio in the production facility. (4) Implementation of the safe and comfort human-machine interaction. (5) Minimization of the risk of workers’ physical and mental damage. |
| Vitayasak and Pongcharoen [70] | √ | (1) Minimization of the flow distance, which has a significant impact on materials handling costs. | |
| Wei et al. [71] | √ | (1) Minimization of materials handling costs and the equipment replacement cost. (2) Maximization of the area utilization ratio in the production facility. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Gosende, P.; Mula, J.; Díaz-Madroñero, M. Overview of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning as a Sustainability Strategy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8277. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198277
Pérez-Gosende P, Mula J, Díaz-Madroñero M. Overview of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning as a Sustainability Strategy. Sustainability. 2020; 12(19):8277. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198277
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Gosende, Pablo, Josefa Mula, and Manuel Díaz-Madroñero. 2020. "Overview of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning as a Sustainability Strategy" Sustainability 12, no. 19: 8277. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198277
APA StylePérez-Gosende, P., Mula, J., & Díaz-Madroñero, M. (2020). Overview of Dynamic Facility Layout Planning as a Sustainability Strategy. Sustainability, 12(19), 8277. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198277







