Abstract
This work presents a multi-course project-based learning (MPL) approach implemented using two electrical engineering (EE) interdisciplinary undergraduate courses at Qatar University. Implementing an MPL approach helps in the development of critical thinking and collaborative decision-making skills. The attainment of these skills is also the outcome of education for sustainable development (ESD); the skills help students acquire the knowledge, attitudes, and values necessary to shape a sustainable future. The participating students’ worked on a design project, which was used to assess the fulfillment of a set of student learning outcomes (SLOs), focusing on engineering soft skills and project management skills. The skills include the ability to communicate effectively, to work collaboratively in a team, to think both critically and creatively, and to manage projects efficiently with realistic constraints and standards. The challenges of implementing the MPL method are the organization of pedagogical activities that are planned for each of the courses involved, the coordination of the materials delivered by each course, and the supervision of around 90 students per year performing the MPL method. The experience of MPL deployment in the EE program was rated using student surveys. It was assumed that the MPL approach would be beneficial to the students based on the instructors’ and students’ feedback from the same courses in previous years. This was verified using chi-square statistics of the survey results. The implementation of the MPL also helped in increasing the average marks scored by the students in the design project. Some interesting feedback, statistical analyses, and improvement actions are reported for future upgrades. This work also contributes to the MPL pragmatic body of knowledge by exploring a successful initiative and its outcomes, which can help in attaining the skills needed for ESD.
1. Introduction
Conscious societies should use technology, innovations, and cooperation to change development trends towards sustainable growth, which is respectful of the environment. This requires a broad set of skills, such as creative problem solving and collaborative decision-making. [1,2]. There is a huge demand for electrical engineering graduates to incorporate the outcomes of such education for sustainable development (ESD). This can help them to be efficient in using their knowledge from courses to solve complicated problems, and will guide them in self-directed, lifelong learning processes [3]. There is a need to modify traditional education methods and incorporate innovative teaching methods where the students are no longer passive participants and they are equipped with the ESD skill sets and knowledge that the market demands [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Recent similar work, where the authors emphasized modifications to incorporate ESD in curricula, is taken as a reference for the work presented in this paper [10].
Two junior-level courses were used to assess the design and problem-solving skills of undergraduate electrical engineering students at Qatar University. The first course is titled “Electronics Engineering” (ELEC 333), and the second “Sensors and Instrumentation” (ELEC 371). The content, as well as the educational strategy of the courses, were modified in order to incorporate ESD, fulfill the requirements set by the industry, and to increase the students’ levels of interest toward design, problem-solving, and independent learning. In the study, the students were asked to work on a multi-course project, i.e., a single project that is used in the assessments of multiple courses. The guidelines were designed in such a way that the students could work on a project that involved the concepts studied in the courses and develop the skills required for a sustainable future. The project-grading rubric was also designed to evaluate whether the course-learning outcomes of both courses were met. This study was carried out in the fall semester of 2015, spanning September 2015 to January 2016.
Previously, there were two different projects for the courses; this was overwhelming for the students. Student-learning outcomes for both courses could be assessed within a single project based on the instructors’ requirements and feedback from the student. Students are motivated when they believe that the learning outcomes are meaningful, under their control, and can help in solving problems faced in real life [3,4]. Theoretical concepts were taught in the courses “Electronics Engineering” and “Sensors and Instrumentation”, while experiments were done in the “Electronics Engineering Lab” course and the embedded lab of the “Sensors and Instrumentation ” course. The majority of the students assumed that the best form of skills would be learnt from the labs and practical projects. However, different projects in different courses did not provide motivation because the projects were overwhelming for the students, and they could not develop an effective working prototype using the concepts presented in each course; this is why the multi-course project strategy was implemented [11].
A multi-course, project-based learning (MPL) experience was shared with a group from Montana Tech of the University of Montana [12]. It described the implementation of MPL in a software development task in their Computer Science department courses that they argued was an integral part of ESD. There was also recent work done by the Nanjing Institute of Technology where researchers emphasized the notion that multi-course practical lessons in project form can help to promote student understanding and consciousness of the application of professional knowledge to an engineering project [13]. An interesting approach was carried out by the Virginia Military Institute, where the authors tried to work on a multi-semester project [14]. The authors described the implementation of the project and showed how it addressed skill set deficits in conventional curricula. However, none of the stated works provided details on how the projects were designed and implemented, and did not present a detailed statistical analysis regarding the effectiveness of the approach. This paper provides a detailed description of how the authors implemented a multi-course project in a sequence of steps (Figure 1), which will be discussed in detail later. One of the major motivations of this case study, besides changing the traditional curriculum to incorporate ESD, was to confirm the effectiveness of a multi-course project in achieving student learning outcomes and assisting project-based learning (PBL). PBL helps in the development of inquiry processes when learning real-world topics, and is also attractive to students [15].
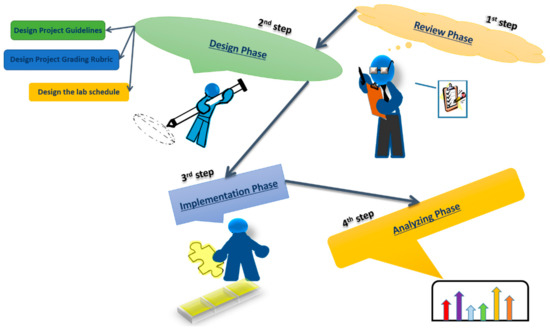
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the MPL case study.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents an overview of the implemented multi-course project learning strategy which is suitable for these courses. The implementation of this study, starting from the review phase, is presented in Section 3; this section also provides the details of the project guidelines, the project-grading rubric, and the lab schedule, and gives details of the conducted survey. Section 4 provides the survey results and an evaluation of the performance of the MPL study in terms of improving students’ grades, along with a discussion of the results. Finally, Section 5 presents conclusions and suggestions from the authors for improvements based on instructor and student feedback.
2. Educational Strategy in PBL
One of the most important building blocks of MPL is project-based learning (PBL), which is also one of the most popular teaching models that help students in applying the competencies they have acquired during the course on real-life problems. PBL relies on an active, integrated, and constructive process in learning, influenced by social and contextual factors, which is very important in developing competencies in students for an enhanced sustainable future [16,17,18]. The PBL teaching approach should include the following characteristics: student-centered learning, small student groups learning, teacher as a mentor or guide, encountering authentic problems before any preparation, problems used as a tool to achieve the required knowledge, and self-directed learning to acquire new knowledge [9,18]. The successful implementation of PBL into engineering education done in Aalborg University, Denmark can be taken as a reference [18,19,20].
According to the authors, clear and precise project guidelines stating the deliverables and grading rubric is needed for a multi-course project; this is to avoid any confusion in the students on how they should present the project and highlight the requirements of each course. It is also imperative that the project-grading rubric should be in line with the course learning outcomes that the project assessment is aiming to meet. The MPL incorporates PBL and thus requires clear and precise guidelines, involving teamwork and adapting the students’ prior knowledge [21]. PBL believes in collaboratively working in groups to solve problems, with the teacher only being a facilitator of collaborative learning [16,17,18,22]. In addition, students are equipped with critical thinking and creative skills [17,22]. These approaches help the students to be prepared for the demanding market, which longs for sustainability and students who are more communicative in delivering their knowledge in their professional careers [23]. Studies involving surveys to see the effect of PBL in teaching ESD in European higher education institutions were conducted in [24], which helped to update the theoretical framework and provided a more precise perspective on how sustainability competencies can be better developed in class. There was a similar study done on a large scale in [25] where the impact of PBL on the engineering students at a technical university in Malaysia was investigated and it was found that lab-based courses with hands-on experimental studies had a more positive effect. Similar studies were done for Germany and Vietnam in [26] and [27], respectively.
3. Research Method
The study evaluates a multi-course project-based learning paradigm in comparison to an independent course project-based learning paradigm, which was carried out in four phases: a review phase, a design phase, an implementation phase, and an observation and reflection phase (Figure 1). The first action-planning or review phase involves the teacher planning the actions to be taken in the study, in the form of linking the learning strategies to the tasks that will be given to the students. In the second phase, the design of the project and its evaluation plan is completed. In the third phase, the action implementation is carried out according to what was planned. The fourth phase is an observation and reflection phase, where activities are recorded throughout the study. The reflection phase is done at the end with the data obtained during the study to critique the approach and suggest improvement [28].
3.1. Study Participants
This research was conducted at Electrical Engineering Department, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar. The subjects of this research were students of ELEC333 (Electronic Engineering) and ELEC371 (Sensors and Instrumentation) in the fall semester of the 2015/2016 academic year with 90 students, consisting of 54 male students and 36 female students.
3.2. Review Phase
The course instructors first reviewed the course learning outcomes and checked if there was any possibility of developing a project that could be used to assess some of the learning outcomes of the courses. Figure 2 and Figure 3 shows the mapping of the respective course learning outcome (CLO) with the student learning outcome (SLO) of a program which has Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET) accreditation. The Electrical Engineering Department of Qatar University is an ABET-accredited higher education unit.
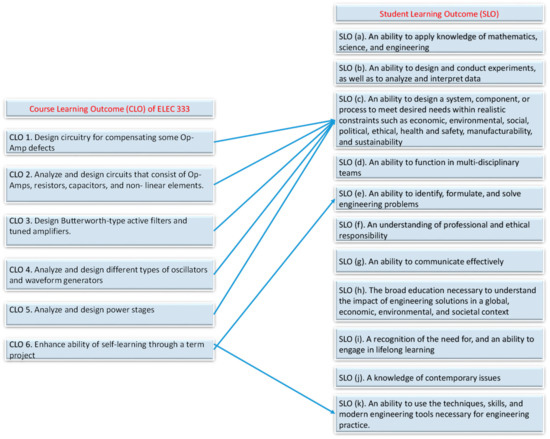
Figure 2.
Mapping of the course learning outcome (CLO) of the ELEC 333 (Electronic Engineering) course with the student learning outcome (SLO).
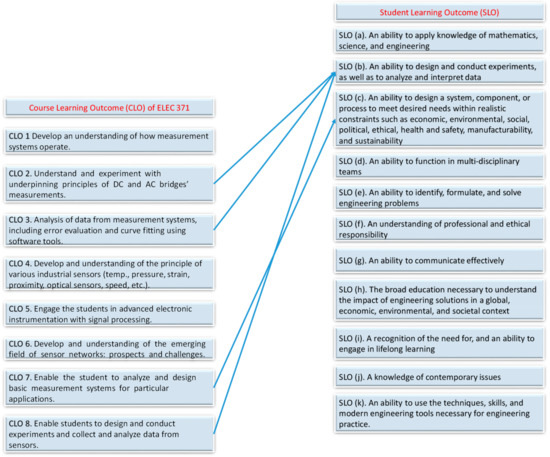
Figure 3.
Mapping of CLO of the ELEC 371 (Sensors and Instrumentation) course with the SLO.
After careful review of CLOs with the SLOs for these courses, the authors confirmed that a multi-course project could be very effective as an assessment tool for most of the course learning outcomes for these courses (ELEC 333 and 371). A design term project was assigned to assess the combined CLOs for these courses.
3.3. Design Phase
Based on the results of the discussion of the research team, design phase planning was carried out for designing the study. Learning, according to MPL, starts with the determination of project guidelines, project-grading rubric, planning projects, and arranging schedules. Figure 1 shows the steps of activity involved in the implementation of the multicourse project.
• Design Project Guidelines
It was made sure that the students were informed of the specific learning outcomes of each course that would be assessed using this study and that the project complemented the materials students were learning in the course and the labs via self-learning. Moreover, it was confirmed that the MPL study was to assess the course learning outcomes without repetition of the assessment.
• Design Project Grading Rubric
The three forms of GroupWise evaluation of the MPL were designed: experimental skills were to be evaluated by the experimental demonstration, scientific writing skill was to be evaluated through report writing and professional communication, and presentation skills were to be evaluated using oral presentation followed by a question and answer session. Project grading rubrics and weightages were set according to the course-learning outcome of the different courses. Project guidelines (Figure A1), project grading rubric (Figure A2) for ELEC 333 and 371 and the lab schedules (Figure A3) for the courses can be found in the Appendix A.
• Design the lab schedule
Dedicated lab sessions were scheduled to provide hands-on training on some of the concepts needed for the project. It was made sure that the flow of the lab schedule helped in the timely progress of the project.
3.4. Implementation Phase
This phase of the study is involved in monitoring and evaluating the study progress throughout the project, and ends with the completion of project assignments. Finally, using the detailed lab schedule, the students are assisted in implementing their project. The authors also placed deadlines before the actual due date to check the progress of the student and provide useful feedback to help them proceed.
• Project Management
Projects are meant to improve the creativity of the students. It can also enhance the students’ conceptual understanding of electronics, sensors, and instrumentation and their application in daily life, especially in relation to measurement. It also helps students to learn, more than what was covered in the lectures, using self-learning techniques. In this learning, four or five students form a group with different levels of understanding and ability to work together. This simple multi-course project begins with the project design stage followed by verifying the design in the simulation phase, and finally testing it with a real prototype.
• Project Assessment
Two sets of information (survey-based and evidence-based) were used in this study to evaluate which technique is more suitable: MPL or single course PBL. At the end of the course, an anonymous survey was carried out among students enrolled in the program. The anonymous survey was tailored based on [15]. Instructions were given to the participants that the study was to see the feedback of the students about the effectiveness of multi-course projects in the mentioned courses in electrical engineering. The questionnaire was prepared carefully so that there were no repetitive questions and used the authors’ expertise in preparing surveys that provide results that can be analyzed for meaningful conclusions [29]. Extreme care was taken to maintain the anonymity of the study and confidentiality of responses by preventing the identification of data obtained from the participants. Furthermore, the identification of participants was prevented by analyzing and reporting the data in a cumulative manner. Table 1 shows the survey questionnaire conducted to gather the student’s feedback and the questionnaire. From the previous experience of the authors, who were the instructors of these courses, and feedback from students who took the course previously, a positive and efficient learning experience was expected from the project approach.

Table 1.
Survey questionnaires.
At the end of the semester, to evaluate whether the estimation complies with the findings or not, students’ and instructors’ written feedback, project grades of the students in the previous semester and the current semester where the multi-course project was implemented, were recorded. The students’ multicourse project grades were used for assessment. Male and female students were evaluated to see whether the performance of MPL vs. single course PBL is generally effective in a particular student group or both groups.
3.5. Observation and Reflection Phase
This study targets the following effects of MPL on the students’ grades and observations, which were reflected from students’ grades and feedback from the survey.
• Effect on Students’ Project Grades
The project grades after the MPL implementation were compared with other semesters where MPL was not implemented. These results can be helpful in deciding whether the MPL approach is better than the PBL approach or not.
• Overall Observations
This study was designed to observe several key issues in sustainable learning outcomes in engineering education. The key factors, which were evaluated as a part of this study and reported in the result section, are (i) the overall effect on students’ learning outcomes; (ii) creative thinking skill improvement; and (iii) constraints in the implementation of actions.
4. Analysis
Data analysis were carried in this study in several ways: (i) analyzing the evidence-based indicator, i.e., the grade of the project, (ii) chi-square statistics of the survey study, and (iii) the creative-way-of-thinking indicator.
• Evidence-Based Indicator
The project grades of the students in the previous semester and the 2015 fall semester, where the multi-course project was implemented, were compared as evidence-based indicators. Course-wise, average project grades from different semesters were compared and male- and female-group grades were compared as well.
• Chi-Square Statistics
A Chi-Square (χ2) statistic is a test that measures how expectations compare to actual observed data (or model results). The data used in calculating a chi-square statistic must be random, raw, mutually exclusive, drawn from independent variables, and drawn from a large enough sample.
The formula for a chi-square (χ2) statistic is
where, c is degrees of freedom, O is the observed value(s), and E is the expected value(s).
The survey questions were designed in such a way so that the answers help in analyzing the assumptions of whether MPL is actually a helpful approach for the students. From the feedback from the instructors of the same course in the earlier semesters, it is assumed that it would be a very helpful approach. This was evaluated by using chi-square distribution [30] as chi-square analysis is the most efficient way of evaluating survey results with different expected results [31]. All the questions in the survey were asked and the authors expected positive results for the questions, i.e., the authors’ prediction. Analysis was done to check the effectiveness of the MPL based on the results obtained from the survey and conducting chi-square analysis considering alpha level (α) = 5%, the degree of freedom (c) = 4 (i.e., number of categories−1, as there were five categories—Strongly agree, Agree, Neutral, Disagree, Strongly Disagree). The authors assumed that the students would respond positively (Strongly Agree, Agree) for all the questions and this assumption was analyzed with the observed response and chi-square analysis was conducted to confirm if the assumption should be accepted or rejected.
• The Creative-Way-of-Thinking Indicator
Innovation in system design, user-interface, and presentation with minimal help from the instructor was considered a creative way of thinking. The indicator of this was calculated by the scores obtained by students in each aspect. The indicator of success in this action research is if the ability of students to think creatively in each aspect reaches above 60%.
5. Result and Discussion
5.1. Description of Evidence-Based Indicator
Based on the results of project groups in their term project performance, evidence-based evaluation was carried out. Since MPL involved planning projects, arranging schedules, monitoring, and evaluating throughout the project, and ended with the completion of project assignments, the assessment of outcome was done in three steps: demonstration, presentation, and report evaluation. In addition to being a means of enhancing student creativity, this project was expected to have an impact on increasing students’ conceptual understanding of amplifiers, sensors, instrumentation, and their application in daily life.
As evident from Figure 4, the MPL has definitely helped in increasing the male average project grades (out of 100) from 77 and 77 to 87 and 85, respectively (Figure 4E) for ELEC 333 and ELEC 371; a similar increase is also seen for the female group, i.e., from 82 and 83 to 84 and 86 (Figure 4F). The number of students doing well in the project, i.e., getting project grades in the range 80 and above, has also increased. Many projects in the earlier semesters helped talented students but there were also many students who did not achieve the desired learning outcomes and received poor grades with less understanding of the project. With the new approach, only 2% of the students did not do well and received scores less than 60 out of the total score 100, as seen in Figure 4.
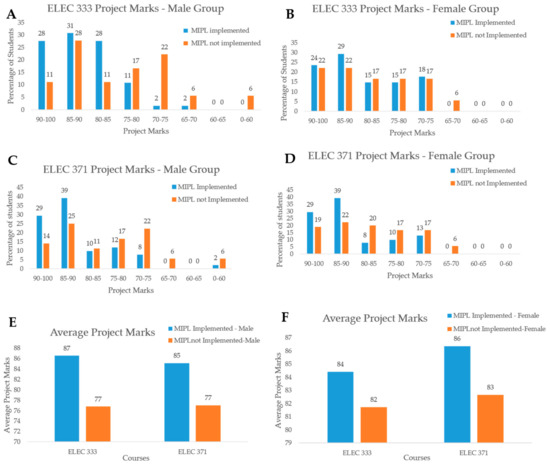
Figure 4.
Comparison of the project grades of ELEC 333 ((A): male group, (B): female group), ELEC 371 ((C): male group, (D): female group), and average project grades ((E): male group, (F): female group).
Once the project is assigned, the students are asked to study more about the problem proposed in the project and come up with a solution using the concepts learned during the course. The students came up with the design of the solution, followed by simulating it in a simulation tool and finally implementing it practically. Students in groups also discussed the selection of tools and components used in the design so that students understand the components and their functionality. This is done to equip students with creative thinking skills. During the implementation of the designed system, students also discuss and present related successes and failures of the trial design and try to reflect on its successes and failures. For groups that have failed to achieve success, their overall score reflected the fact. Every activity carried out by students is always followed by an observation of their creative thinking skills. Figure 5 presents a sample design project prototype with the marks achieved using the project grading rubric.
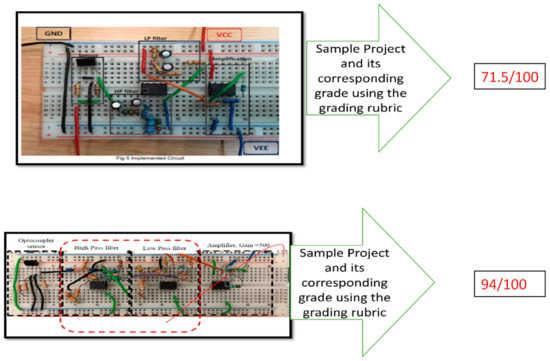
Figure 5.
Sample projects and their corresponding grades, which were graded using the designed rubric.
5.2. Description of Chi-Square Statistics
The survey results were as per the assumptions, giving very positive feedback regarding the MPL implementation. Chi-square statistical analysis was done on the survey results to validate the assumption that MPL is an effective pedagogical approach and is preferred by the students. Chi-square analysis is done on the students’ responses, as shown in Table 2. In addition, chi-square analysis was done separately based on male and female (36 and 54, respectively) responses in order to confirm the results. It was found that the results were similar (Table 2).

Table 2.
Chi-square statistics results on the answers to the survey questions.
A histogram of the overall students’ responses representing the answers to the survey questions is presented in Figure 6a–o. In Figure 6a–h, it is evident that both the male and female students have answered positively for the questions. Similar positive feedback can also be seen in Figure 6k,l,o. These all give a positive impression regarding the MPL implementation done, whereas Figure 6i,j,m,n had some negative feedback and should be considered as suggestions for improvement.
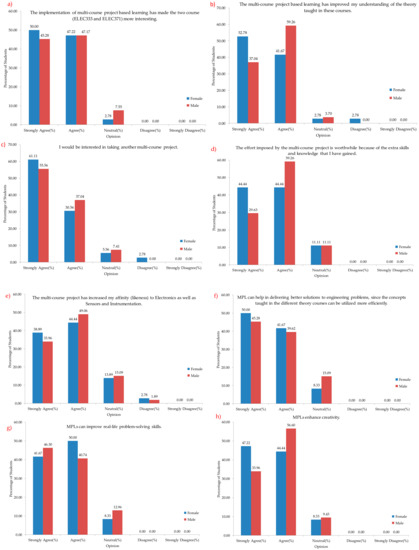
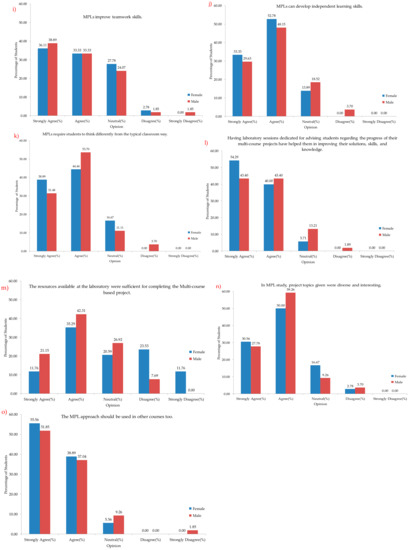
Figure 6.
Statistics of the answers to the survey questions 1–15 (a–o).
5.3. Students’ Creative Way of Thinking
Creative thinking is the imperative skill required for raising awareness amongst students regarding sustainable solutions. Increasing student creativity with the application of multi-project-based learning models also had a positive response verified from the students’ responses and project grades. The results of the student reflection questionnaire (97% and 92%; Figure 6a), stated that the experience made the courses interesting, which is motivated by the application of this model (91% and 92%; Figure 6c), and helped in making learning more effective and understandable (94% and 96%; Figure 6b), respectively, for male and female. Eighty-seven percent of male students and 91% of female students feel that this approach also helped them to enhance their creative thinking skills by utilizing the concepts they received in classroom learning (Figure 6h). Seventy-eight percent of male students and 86% of female students also advocated that the approach helped them in self-learning, which helps them to be aware of the topics themselves in addition to what is taught in the lecture.
5.4. Constraints in the Implementation of Actions
The study was designed to motivate students to look for sustainable solutions with the help of competencies developed during the course of the project. This study certainly did not run smoothly; there were some obstacles that the authors as instructors and students who involved in the experiment have faced. The limitations in the process involved some students who could not manage to enhance their understanding by assuming that the learning is too difficult and it involves additional tasks. Some students also had issues regarding working in teams or groups, with some students not contributing at all to the projects, and some students contributing too much and intimidating other team members. This can cause students with low abilities to feel insecure in presentations and practices [15]. These are issues that already exist in project work and, thus, are also seen in MPL. In order to deal with the issues of increasing the motivation of such students, the instructor should be innovative. Instructors must be able to solve problems, especially in dealing with students with low abilities, lack of motivation, and lack of focus, to improve teacher–student relations [15]. Moreover, there were certain feedback from students that suggested measures to be taken to improve the experience. Based on the students’ responses, several modifications have to be made in future studies to improve the MPL experience.
- (a)
- The multi-course project topics should be more diverse and interesting.
- (b)
- Resources available at the laboratory should be sufficient for completing the multi-course projects.
- (c)
- The lab schedule should be modified to teach students to develop their independent learning skills.
- (d)
- More emphasis should be put on the teamwork experience, and laboratory experiments should be modified to have sessions on team-building exercises.
In summary, the outcomes of this MPL study contributes more than similar works done in PBL-based studies [32,33,34,35] in the following manner:
- This paper discusses the step-by-step implementation of MPL which can help attain the competencies required for ESD.
- This paper has analyzed the effects of MPL implementation for two undergraduate-level courses in terms of student performance and also student perception through a survey.
- This paper has also highlighted some of the improvements that can be made in order to make the acquisition of ESD competencies more effective.
- The authors believe that implementing MPL for undergraduate levels is more effective for training and making students aware of always trying to work towards a sustainable future.
6. Conclusions
The paper has provided a detailed description of the implementation of MPL study for junior-level electrical engineering courses at Qatar University. An MPL study is imperative for incorporating competencies that are required for sustainable development, such as creative and critical thinking. These approaches help the students to be prepared for the demanding market, which longs for sustainability. The authors have tried to incorporate MPL in their courses to equip the students with these competencies and to make them aware of the ESD during the process. The authors have tried to provide systematic instructions on how such an approach could be implemented for electrical engineering courses at programs following ABET accreditation, where it is very important to ensure that the student learning outcomes are met. The survey conducted at the end of the semester provided positive feedback on this approach. There were some suggestions that are useful for improving the approach. This case study would be useful for motivating more of such approaches for engineering programs. The approach has been useful in advocating the fundamental principles of PBL. The implementation results of the MPL model make learners more creative, and thus, it becomes easier for the learners to understand the study material presented by the teacher. Moreover, MPL is also able to provide opportunities for students to apply knowledge in a real context because their teacher has already delivered certain topics related to the material. Furthermore, the implementation of this multi-project based learning can be a solution, making learning more productive and fun while reducing the overload of individual project-based learning schemes.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, A.K., M.E.H.C. and F.T.; Investigation, A.K., M.E.H.C., A.J.S.P.G. and F.T.; Methodology, A.K., M.E.H.C., A.J.S.P.G. and F.T.; Writing—original draft, A.K. and M.E.H.C.; Writing—review & editing, A.K., M.E.H.C., N.A.E. and M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding The APC was funded by Qatar National Library.
Acknowledgments
The publication of this article was funded by the Qatar National Library. The authors would like to thank the initial guidance provided by Mohieddine Benammar.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Figure A1.
Project Guidelines.
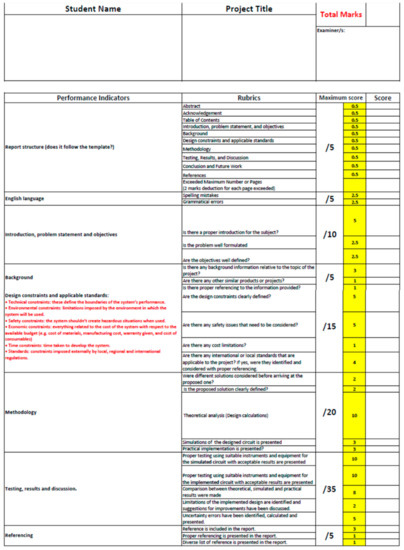
Figure A2.
Project Report Grading Rubric.
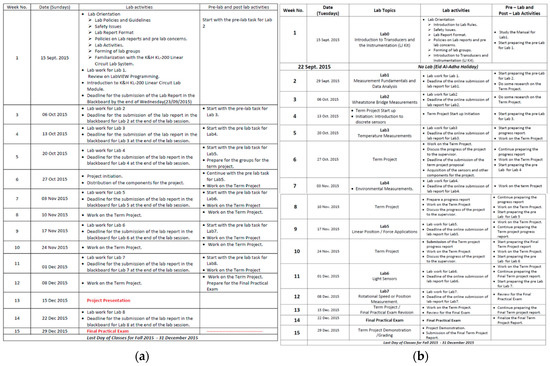
Figure A3.
Lab Schedule for (a) Electronics Engineering, (b) Sensors and Instrumentation.
References
- Wiek, A.; Withycombe, L.; Redman, C.L. Key competencies in sustainability: A reference framework for academic program development. Sustain. Sci. 2011, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Leeuw, S.; Wiek, A.; Harlow, J.; Buizer, J. How much time do we have? Urgency and rhetoric in sustainability science. Sustain. Sci. 2012, 7, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dochy, F.; Segers, M.; Van den Bossche, P.; Gijbels, D. Effects of problem-based learning: A meta-analysis. Learn. Instr. 2003, 13, 533–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, M. Teaching electric drives control course: Incorporation of active learning into the classroom. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2013, 56, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafinia, A.; Ping, H.W.; Uddin, M.N.; Amindoust, A. Teaching of simulation an adjustable speed drive of induction motor using MATLAB/Simulink in advanced electrical machine laboratory. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 103, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anuchin, A.; Vagapov, Y.; Belloc, C. Development of curriculum for a postgraduate course on Electric Drives and Motion Control. In Proceedings of the 50th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Stoke-on-Trent, UK, 1–4 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, C.; Radulescu, M.M.; Enikö, S.; Melinda, R.K.; Jakab, Z.L. Embedded motor drive prototype platform for testing control algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Electricity (ICATE), Craiova, Romania, 23–25 October 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Martin, D.; Alonso-Martinez, J.; Carrasco, J.E.-G.; Arnaltes, S. Problem-based learning in wind energy using virtual and real setups. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2012, 55, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.E.; Canavan, B.; Smith, J. Problem-based learning in communication systems: Student perceptions and achievement. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2010, 53, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuskanen, T.; Vehkamäki, H.; Riuttanen, L.; Lauri, A. An Exploratory Study of the Learning of Transferable Skills in a Research-Oriented Intensive Course in Atmospheric Sciences. Sustainability 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, K. A multi-course collaborative project: Using technology to learn. J. Fam. Consum. Sci. 2008, 100, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Schahczenski, C.; Ackerman, F. A successful multi-course project. J. Comput. Sci. Coll. 2017, 33, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Baochun, X.; Yunlong, S.; Jingqiu, W.; Wei, C. Design and Implementation of Teaching for the Training Project of Multi-course. China Mod. Educ. Equip. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.A.; Hardin, J.-M. The Can Crusher Project: A Multi-Semester Design Project to Enhance Retention of Engineering Skill Sets. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2–5 August 2015; ASME American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Two Park Avenue, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayati, N.; Sumarni, W.; Supanti, S. Improving Student Creative Thinking Skills Through Project Based Learning. Kne Soc. Sci. 2019, 2019, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrows, H.S. Problem-based learning in medicine and beyond: A brief overview. New Dir. Teach. Learn. 1996, 1996, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijselaers, W.H. Connecting problem-based practices with educational theory. New Dir. Teach. Learn. 1996, 1996, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekola, J.; Messo, T. Application of problem-based learning method for a course on modeling and control of electric drives. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017-43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barge, S. Principles of Problem and Project Based Learning: The Aalborg PBL Model; Aalborg University Press: Aalborg, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmos, A.; Fink, F.K.; Krogh, L. The Aalborg PBL Model: Progress, Diversity and Challenges; Aalborg University Press: Aalborg, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jonassen, D.H.; Hung, W. All problems are not equal: Implications for problem-based learning. In Essential Readings in Problem-Based Learning; Purdue University Press: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2015; pp. 7–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hmelo-Silver, C.E. Problem-based learning: What and how do students learn? Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 16, 235–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, D.; Dochy, F.; Van den Bossche, P.; Segers, M. Effects of problem-based learning: A meta-analysis from the angle of assessment. Rev. Educ. Res. 2005, 75, 27–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Barreiro-Gen, M.; Lozano, F.J.; Sammalisto, K. Teaching Sustainability in European Higher Education Institutions: Assessing the Connections between Competences and Pedagogical Approaches. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabarullah, N.H.; Hussain, H.I. The effectiveness of problem-based learning in technical and vocational education in Malaysia. In Education+ Training; Emrald Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Brodowski, M.; Brock, A.; Etzkorn, N.; Otte, I. Monitoring of education for sustainable development in Germany–insights from early childhood education, school and higher education. Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 25, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P. Searching for education for sustainable development in Vietnam. Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.A.; Sharma, R.S. An experiment in blended learning: Learning without lectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on E-Learning, E-Management and E-Services (IC3e), Kuching, Malaysia, 16–17 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khandakar, A.; Chowdhury, M.E.; Ahmed, R.; Dhib, A.; Mohammed, M.; Al-Emadi, N.A.; Michelson, D. Portable system for monitoring and controlling driver behavior and the use of a mobile phone while driving. Sensors 2019, 19, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, H.O.; Seneta, E. Chi-square distribution. Encycl. Biostat. 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Scott, A. On simple adjustments to chi-square tests with sample survey data. Ann. Stat. 1987, 15, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.P.; Safai, N.M. Board 101: Project Based Learning for a Mechanical Engineering Major Student: The Sustainability of Internal Combustion Engines (Student Poster). In Proceedings of the 2019 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Tampa, FL, USA, 18 June 2019; ASEE: Washington, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-C. Revisiting the effects of project-based learning on students’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis investigating moderators. Educ. Res. Rev. 2019, 26, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teff-Seker, Y.; Portman, M.E.; Kaplan-Mintz, K. Project-Based Learning in Education for Sustainable Development: A Case Study of Graduate Planning Students. Case Stud. Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Bogner, F.X. How freshmen perceive Environmental Education (EE) and Education for Sustainable Development (ESD). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).