Abstract
Land use/cover change (LUCC) is one of the causes of global climate and environmental change. Understanding rapid LUCC in urbanized areas is vital for natural resources management for sustainable development. This study primarily considered Vientiane, the capital of Laos, which experienced rapid LUCC due to both natural and anthropogenic factors. The study used geographical information system (GIS) combined with ERDAS and TerrSet technologies to objectively process the ground surveyed and remotely obtained data in order to investigate the historical LUCC as well as predict future LUCC in the study area during the periods of 1995–2018 and 2030–2050, respectively. A comprehensive list of assessment factors comprised of both natural and anthropogenic factors was used for analysis using the cellular automata–Markov (CA–Markov) model. The results show a historical loss of intact forest of 24.36% and of bare land of 1.01%. There were also tremendous increases in degraded forest (11.36%), agricultural land (8.91%), built-up areas (4.49%) and water bodies (1.16%). Finally, the LUCC prediction results indicate the conversion of land use from one type to another, particularly from natural to anthropogenic use, in the near future. These changes demonstrate that the losses associated with ecosystem services will destructively impact human wellbeing in the city and other areas of the country. The study results provide the basic scientific knowledge for LUCC planners, urban designers and natural resources managers. They serve as a decision-making support tool for the establishment of sustainable land resource utilization policies in Vientiane and other cities of similar conditions.
1. Introduction
Human socioeconomic activities, the associated human population increase and general urbanization trend have caused remarkable changes in the expansion of cities around the world, threatening the sustainability of land use/cover change (LUCC) of an area [1]. The United Nations predicts that the world’s population will increase about 60% by 2050 [1,2]. To date, population growth in urban areas has been found in almost all countries around the world, and it has been among the major reasons for rapid changes of land use/land cover (LULC) [3]. Various natural land covers are being converted and replaced with urban construction for residential and other human use [3,4,5]. Land conversion from its original use into another land use type is called LUCC, which is a consequence of complex connections between human activity and the physical environment [6]. LUCC is the key to changing the global environment, which has a huge impact on ecosystem alterations, biological cycles and biodiversity [7,8]. These changes directly cause landscape degradation and affect land surface, leading to the emission of greenhouse gases, loss of biodiversity, soil resources degradation and global climate change [9,10,11,12]. In this case, it is critical to identify the factors responsible for these changes to simulate future LUCC [13,14]. To comprehend the process of LUCC and its changes in the future in urbanized areas, LUCC modeling is very important [14]. Several models used for LUCC analysis and predictions focus on the analysis of the causes and consequences of LUCC, such as analytical equation-based models, statistical models, evolutionary models, cellular models, Markov models, hybrid models, expert system models and multiagent models [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In Guanting Reservoir Basin, China, a study of land use/land cover dynamics through scenario-based simulations using the cellular automata–Markov (CA–Markov) model was performed by Ruben et al. [14]. A study to monitor and predict LUCC using remote sensing and GIS techniques was performed in the hilly area of Jiangle, China. by Chen et al. [23]. Simulated LUCC detection and prediction was performed in the Kathmandu District of Nepal by Wang et al. [24]. Khawaldah investigated and simulated LUCC in the Amman area of Jordan using a GIS-based Markov model and remote sensing [25]. Hamad et al. [9] predicted LUCC under two different scenarios in 2023. Despite the availability of various studies that analyze and predict LUCC, only two studies of this kind for Vientiane, Laos, are available. The current study focused on mapping LUCC based on different classification methods in the study area [26]. Praseuth et al. [27] mapped multi-temporal composite Landsat 8 images in the Vientiane urbanized area of Laos. Wah Hue et al. [28] mapped LUCC in the Vientiane area using object-oriented classification on multitemporal Landsat data. In this study, we significantly investigated the LUCC causes, processes and consequences, emphasizing the economic development in the region [14,24].
Vientiane, which is the center of Laos’s socioeconomic and political development, is currently the only developed city in the country [29]. The city is challenged by rapid population growth and a high rate of urbanization mainly due to rural–urban migration, as the city is hoped to offer a good living standard. In this case, most migrants permanently settle in the city, adding to the total population of the area [29]. As a result, there has been a hasty change in the originally agricultural and/or forest lands to residential areas and other urban settings [29,30]. Due to the lack of proper management of the available land, there are serious concerns about the future LUCC. This will affect the quality of life and may lead to natural disasters such as floods due to uncontrolled settlements with unreliable sewage systems, and fires due to blocked street roads, etc. This study provides the basic scientific knowledge to aid decision-making and future environmental protection in the region with specific attention to Vientiane city, the capital of Laos and the main developed city of the country. The main objectives of this study were therefore to investigate and analyze the spatiotemporal data of historical LUCC information (for 2013 and 2018) and predict the LUCC for 2030, 2040 and 2050.
Therefore, this study is the first to spatiotemporally analyze the LUCC based on the historical changes of urban areas using Vientiane as a case study. This simulated the complex spatial variations in LUCC in historical situations and used relevant information to predict the future LUCC in the area. Thus, this study investigated the subject matter for a period of about 55 years (1995–2050) using the CA–Markov model.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Location
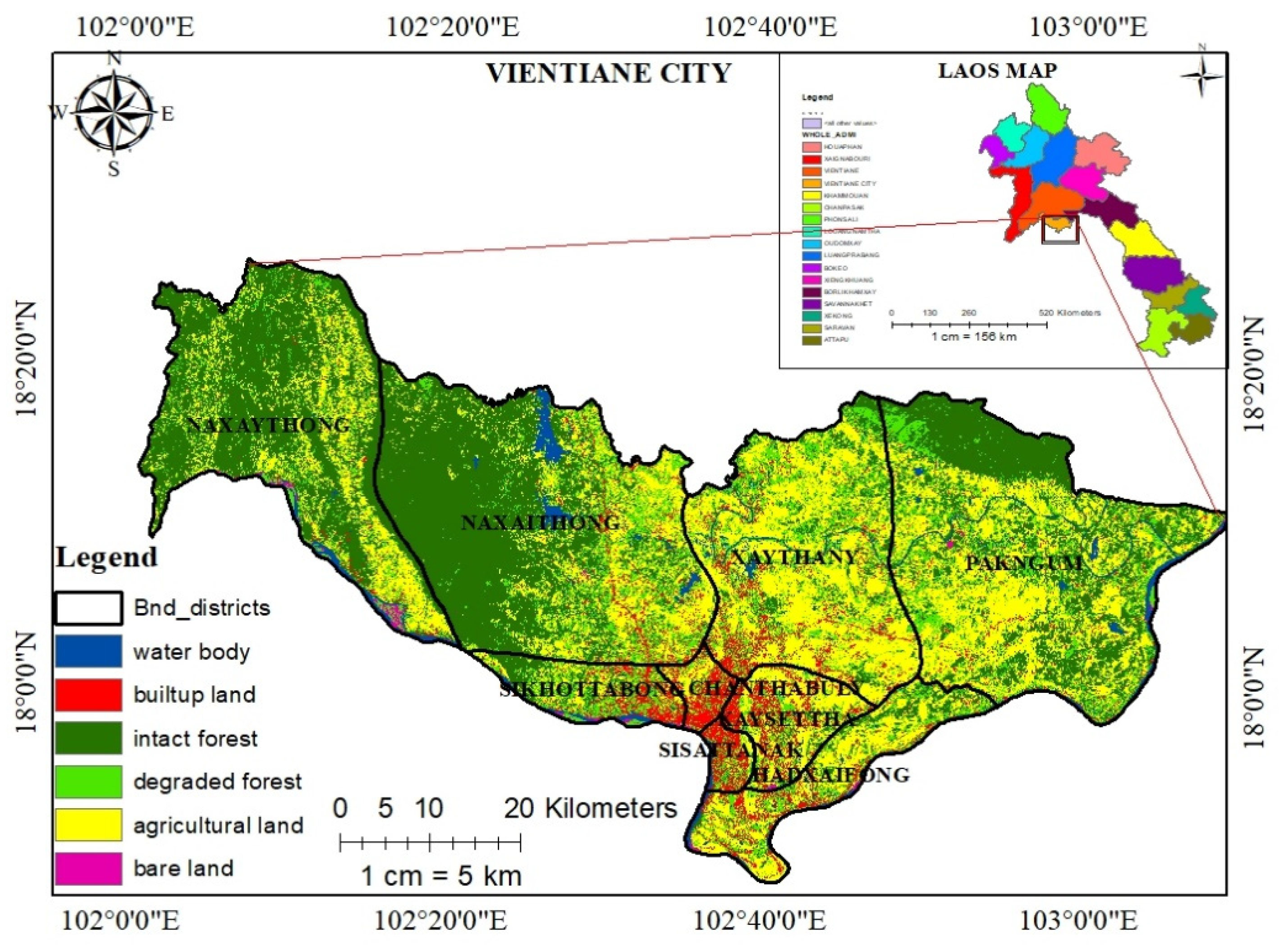
Vientiane is the capital city of Laos PDR and is located in the northwest of the country, on the Laos–Thailand border at 17.9757° N, 102.6331° E, while Laos is located within 17°-58′–29.4780″ N and 102°-37′–51.1212″ E [27]. As displayed in Figure 1, Vientiane is politically divided into nine administrative districts: Hatsayfong, Saysettha, Chanthabouly, Xaythany, Parkngum, Sangthong, Sikhotabong, Naxaythong and Sisattanack. The city population grew from 30,800 in 1950 to approximately 820,940 in 2015 [31]. The city has a tropical monsoon climate with an average temperature of over 80 °F (27 °C) and an average annual precipitation of 1300–2100 mm, mainly during the five months from May to September. The dry season is from October to April [27]. The geography of Vientiane is mostly a mixture of mountainous and small-scale flat areas, with the elevation ranging from 70 to 950 m above sea level. Figure 1 presents the map of the study area.
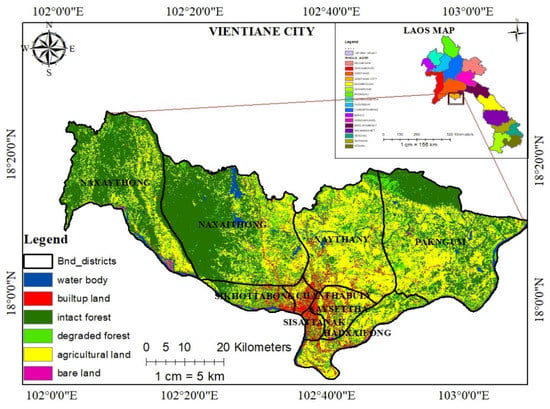
Figure 1.
Map of the study area Vientiane’s 2018, Lao PDR.
2.2. Data Sources
Satellite imagery acquisition was performed giving the special consideration of the cloud cover, seasonality, and the phonological effects. In this study, Landsat images from 1995 and 2004 were collected from Landsat Thematic Mapper TM 5, and images from 2013 and 2018 were obtained from Landsat 8- OLI with a ground resolution of 30 × 30 m [32]. The track numbers of 128/47, 128/48 were acquired as shown in Table 1. Using Google Earth at 15 m resolution, The LUCC classification was connected with ERDAS software, which enabled us to obtain the position where the images from remote sensing were visible. The road data system is a critical factor derived from OpenStreetMap [33], which is processed by QGIS software and used as a conversion format file for future LUCC prediction by the CA–Markov model in TerrSet software.

Table 1.
Satellite imagery data used for land use/cover change (LUCC) analysis.
2.3. Image Processing and Data Analysis
To ensure the accuracy of the identification of spatiotemporal changes and the geometric compatibility with other sources’ information, previous studies have used different pre-processing techniques such as ArcGIS, ENVI, ERDAS, QGIS, or other software capable of handling land use classification. Thus, in this study, the images from 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018 were classified using ERDAS IMAGINE 2014 and ArcGIS 10.3 by combined classification. The combined classification included both supervised classification and unsupervised classification methods, which are broadly used in land cover classification. The maximum likelihood algorithm (MLC) is the most commonly used method in supervised classification with remotely sensed image data [3], which computes the posterior possibility of a pixel fitting into the corresponding class based on the Bayes theorem [34]. The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) map coordinate system, Zone 48 North, and Datum Arc 1984 (WGS_1984_UTM_ZONE_48N) were used in these images. Google Earth Pro was used to interpret images in ERDAS 2014, which can visualize the real visible images from different years. After both supervised and unsupervised classification, the LUCCs were successfully interpreted and classified in the study area [27]. This study classified LUCCs into six classes, water bodies (WB), built-up land (BUL), intact forest (IF), degraded forest (DF), agricultural land (AL), and bare land (BL) as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Definition of land use and land cover classification types.
The Kappa index and overall accuracy were assessed; if the accuracy of each image is over 85%, this is considered acceptable for LUCC prediction [25,40]. The algorithm of the Kappa coefficient (K) for the LUCC classification accuracy assessment is shown in Equation (1):
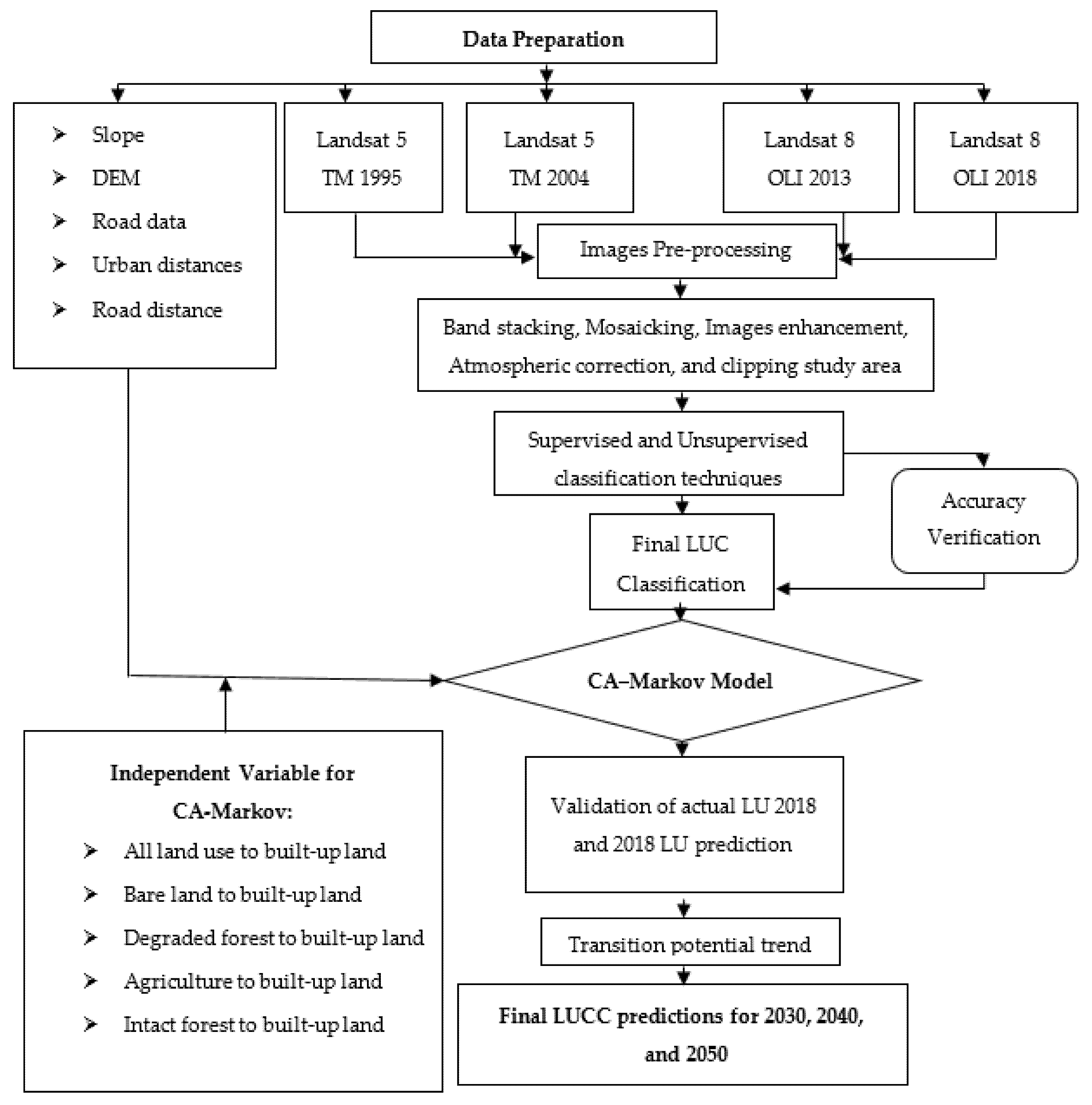
where K is the kappa coefficient, N is the total number of sites in the matrix, r is the number of rows in the matrix, is the number in rows i and columns i, is the total for row i, and is the total for the column. The flowchart of the methodology (Figure 2) presents the study procedures from data sources/preparation to the final LULC classification and prediction.
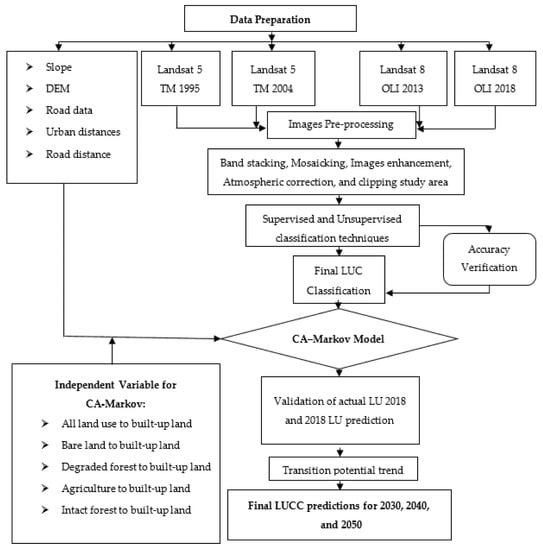
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the methodology.
2.4. Future Prediction of LUCC Dynamic
Markov chain analysis has recently been used in various studies of future land use prediction [41]. It can determine the probability of trends from the early images to the last images to identify the transition tendency of the future LUCC probability according to the specific years [42]. The main processing of the Markov chain generates a transfer matrix and probability transfer matrix for the prediction of future land use/cover change trends. The Markov chain model can be summarized as a set of state . In this study, the recent state is , and it transforms to state in the next stage, with the possibility indicated by transition probabilities . Therefore, state in the system could be identified by former stage . in the Markov chain; see Equation (2) [24]:
where P stands for the probability matrix in the Markov model, and Pij is the probability of converting from current state i to state j in the next period. S is the land use status, and t; t+1 are the time point—see Equation (3) [25]. A low transition probability will be near 0 and a higher transition probability will be near 1. In the Markov model, the land use/cover change prediction takes 2004 as the base () and the 2013 LUCC map as the later ) image. Based on the transition matrix between the two periods from 2004 to 2013 and from 2013 to 2018, we can predict the LUCC in 2030, 2040 and 2050.
Cellular automata (CA) is a bottom-up dynamic model that integrates the spatiotemporal dimension and thus adds a modeling direction. It simulates the time–space complexity even though space–time and state are discrete [20]. The CA ability is very important for land use and cover change to demonstrate and simulate the spatial and dynamic processes in LUCC prediction research. The cellular automata (CA) model mainly contains cells, cell space, neighbors, rules, and time. The neighbors are identified by the filter of the CA model. The closer the distance between the central cell and its neighbor, the greater the weight factor [24]:
Here, S represents the set of states of the finite cells; t and t+1 are the early year and the later year; N is the neighborhood of cells, and f is the conversion rule of local space.
The CA–Markov model is a mixture between cellular automata and Markov chain, used to predict the transition possibility matrix in a cross-presentation of two different images so that it can stipulate a strong method for spatial-temporal dynamic modeling [43]. The CA–Markov model processes raster data in the land change modeler (LCM) by using TerrSet Clark lab software based on geotiff or tiff format data processing in ArcGIS. The transition probabilities matrix of the Markov chain model is the inputs of the CA model [44]. These are some of the procedures in the CA–Markov prediction: (1) creating a suitability atlas in multi-criteria evaluation MCE, (2) generating a state transition probability matrix and transfer matrix in the Markov model, and (3) future land use prediction using the CA model [45].
The kappa values of the CA–Markov model for LUCC simulation ranged from −1 to 1, where positive values are a sign of agreement, and negative values illustrate of a lack of agreement Kappa ≤ 0.5 shows high agreement, 0.5 ≤ Kappa ≤ 0.75 marks a moderate level of agreement, and 0.75 ≤ Kappa < 1 [14,46] indicates a high level of agreement. Equations (5) and (7) for the summary statistics are:
where no information is N(n), medium grid cell-level information is M(m), and perfect grid cell-level information across the landscape is P(p).
2.5. Determined Driver Factors for LUCC Prediction in the CA–Markov Model
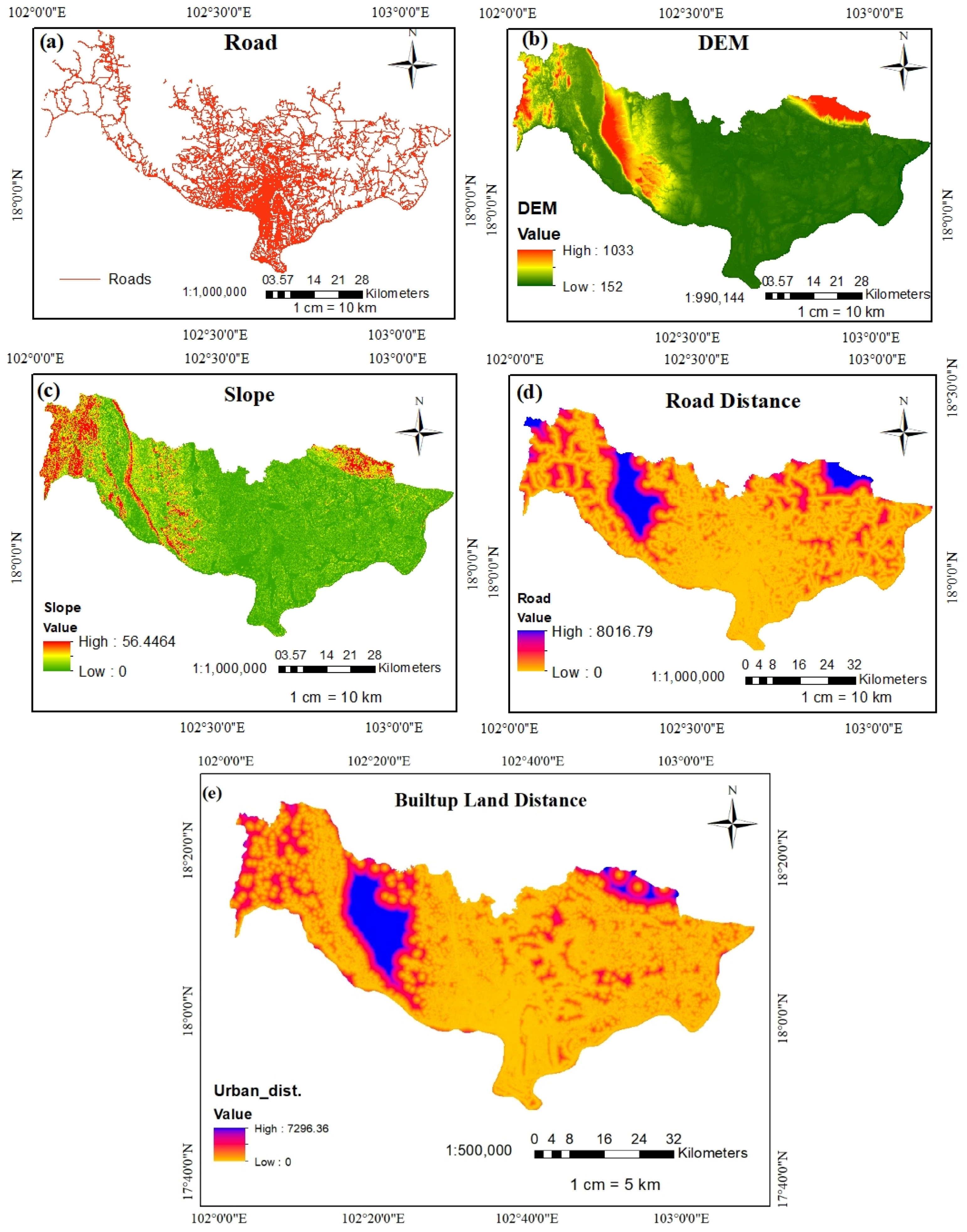
There are multiple factors that drive changes in land types in the study area. The digital elevation model (DEM), slope map, road data, the distance from the road, and the distance from built-up land have been taken into considered as driver factors, see Figure 3, and processed in ArcGIS and QGIS software for the LUCC prediction in the TerrSet Clark labs software.
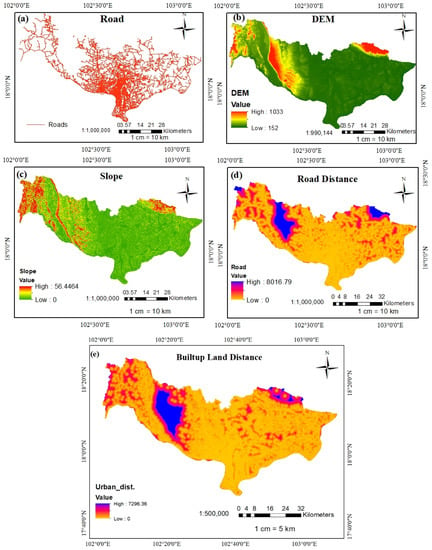
Figure 3.
Driving factors for the CA–Markov model: (a) road data; (b) digital elevation model (DEM); (c) slope; (d) road distance; and (e) built-up land distance.
2.6. Predicted LUCC Class Direction of Transition Potential
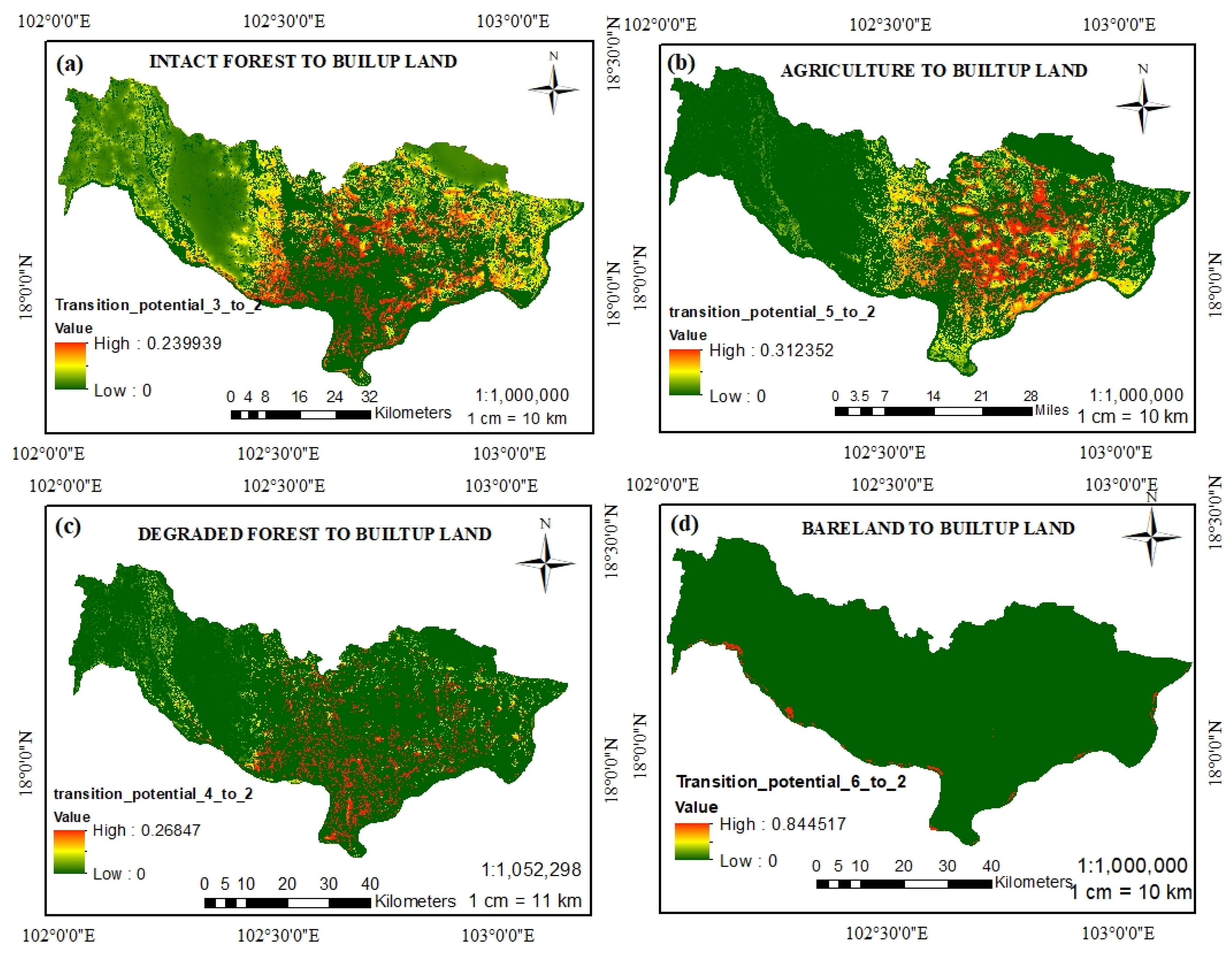
The system will process drivers in a run transition sub model (RTSM) using an multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network in Terrset Clark lab software. In this study, 1358 samples per class were processed in the machine learning window. According to the results obtained, predictions of the transition potential in LUCC were made for four main districts: (1) Xaythany District, (2) Parkngum, (3) Hatsayfong, and (4) Sikhotabong; the current city expansion in 2018 is still located in three main districts, Chanthabouly (1), Sisaktanack (2), and Xaysetha (3), see Figure 1. The largest land use/cover type changes in future predictions are (1) agricultural land, (2) intact forest, and (3) degraded forest, and there is a slight change for bare land (see the future potential transition in Figure 4). After we finalized the potential transition of the model processing, the LUCC prediction was able to continuously run the process to predict the specific time, provided by the software.
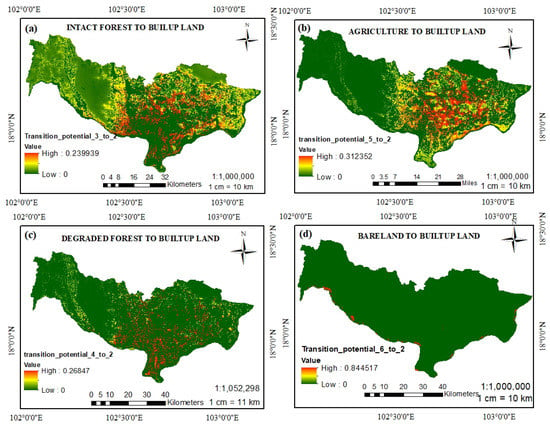
Figure 4.
Direction predicted of each land use and cover transition potential: (a) transition potential from intact forest to built-up land; (b) transition potential from agriculture to built-up land; (c) transition potential from degraded forest to built-up land; and (d) transition potential from bare land to built-up land.
2.7. Land Use/Cover Change Prediction and Validation
In this study, the LUCC classification in ArcGIS software from 2004 to 2013 and from 2013 to 2018 were processed using the CA–Markov model in Terrset software 18.31. The data processing in Terrset software based on the land change modeler (LCM). Firstly, input data in change analysis included the earlier land cover images of 2004 and the later land cover images of 2013. Then, the transition potential was used to run driver factors in the machine learning window. After we finished the machine learning processing, the land use prediction in 2018 was carried out via change prediction tools with validation data for a comparison between the actual land use in 2018 and the predicted land use in 2018. Finally, when the Kappa index was more than 80%, it meant that it was suitable for the LUCC predictions for 2030, 2040 and 2050 for 12, 10 and 10 year intervals, respectively, based on the data obtained in 2004 and 2018 that were used for the CA–Markov model integrated with Terrset software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Classification Accuracy Verification
An important pre-requisite in the classification, detection, and prediction of LUCC studies is the accuracy and validation of the classification model [25]. The kappa statistic is a general metric applied for calculating the classification accuracy of both models as well as the user of the classification model [47]. The value of the kappa coefficient indicates the accuracy of the reference data and LUCC value in the image classification; the values of kappa are from −1 to +1 [48]. A kappa coefficient of < 0 means no agreement, 0–0.2 means slight agreement, 0.2–0.41 means fair agreement, 0.41–0.60 means moderate agreement, 0.60–0.80 means substantial agreement, and 0.81–1.0 means perfect agreement [49].
According to the historical LUCC classification results, Land-sat TM and Land-sat OLI have randomly selected 108 points for each LULC class to assess the classification accuracy by manual checking in Google Earth Pro [24]. The overall LULC classification accuracy for the years 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018 is 92.59%, 92.59%, 87.04% and 91.67%, respectively, with the overall kappa statistics of 0.9111, 0.9111, 0.8444, and 0.9000, respectively (Table 3 and Table 4).

Table 3.
The results of the classification accuracy for 1995 and 2004. LU, land use; WB, water bodies; BUL, built-up land; IF, intact forest; DF, degraded forest; AL, agricultural land; BL, bare land.

Table 4.
The results of the classification accuracy for 2013 and 2018. LU, land use; WB, water bodies; BUL, built-up land; IF, intact forest; DF, degraded forest; AL, agricultural land; BL, bare land.
3.2. Analysis of Land Use/Cover Change from 1995 to 2018
Rapid population growth, migration from rural to urban areas, the reclassification of rural areas as urban areas, lack of evaluation of ecological services, poverty, ignorance of biophysical limitations, and the use of ecologically incompatible technologies are the main reasons behind LUCC [50]. Land use/cover changes during 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018 were analyzed using supervised and unsupervised classification based on ERDAS and GIS software. The total area and percentage of each LUCC class were compared. According to Table 5, there is strong evidence of landscape patterns changing throughout the last two and a half decades in Vientiane.

Table 5.
Statistics of LUCC classification for 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018.
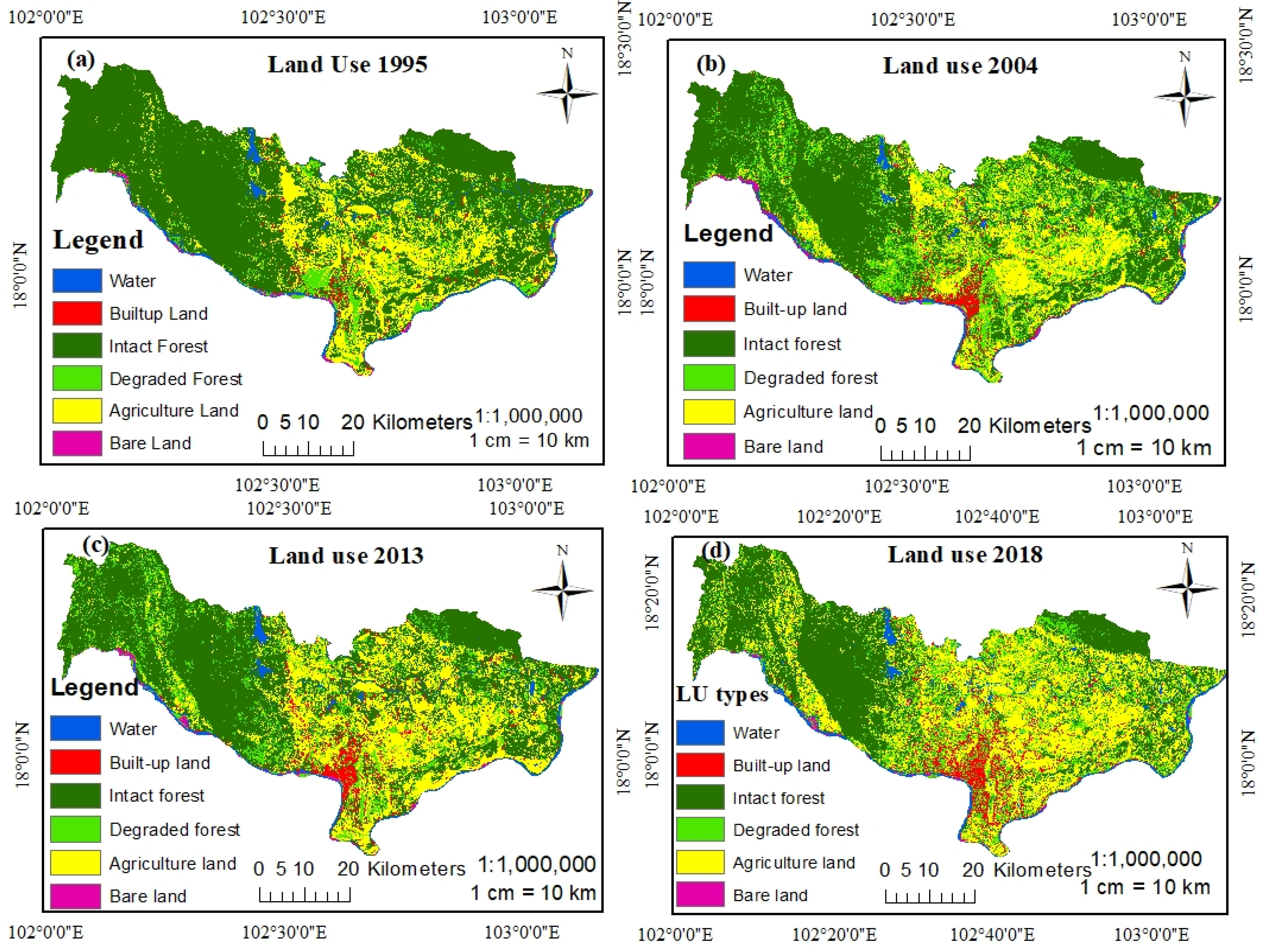
In 1995, intact forest was the largest land cover class in the study area, with the initial coverage of 63.83% (which equated to an area of 2339.56 km2 slowly decreasing to 39.47% in 2018, as shown in Table 5). Agricultural land was the next largest land use/cover change class, with an area of 811.40 km2 (22.14%), while degraded forest was 260.36 km2 (7.10%). Other LUCC classes accounted for smaller proportions of the study site: built-up land covered 101.60 km2 (2.77%), water bodies covered 98.40 km2 (2.68%), and bare land covered 53.77 km2 (1.47%). Intact forest was located in higher elevation areas above about 277 m in the Phu-Phanang National biodiversity area, (see Figure 5). Due to human activity, the forest degraded very quickly, losing natural balance, and biodiversity and undergoing temperature changes. Since 1990, agricultural activity has become the dominant source of income in the study area, by producing 56% of the gross domestic product (GDP) [27]; this indicates that agriculture has taken over a large area since 1995. Agricultural land increased continually from 1995 to 2018 reaching an expansion of 31.05% (1137.04 km2) in 2018, versus 1013.42, 843.87 and 811.40 km2 in 2013, 2004 and 2005, respectively. Built-up land was the fourth largest land cover class, covering only 7.10%, due to GDP growth and population migration. Two reasons for the lower built-up land expansion are the GDP and population growth. In 1995 the GDP of Laos was USD 1764 billion compared with USD 2.366 billion in 2004; by 2013, it had increased to USD 11.94 billion and by 2018 it reached to USD 17.95 billion [51]; meanwhile, the population of Laos was 4846 million people in 1995; and increased to 7062 million by 2018, such that the mean population increased rapidly over those 23 years. The results indicate that, from 1995 to 2018, according to the Landsat image classification, the built-up area increased quickly from 101.60 km2 to 266.00 km2. Water bodies area increased, while bare land decreased. Most of the water was found in reservoirs, with the Mekong River in the southwest to northwest and Namngum River in the southeast to northeast of the study area. The decrease in bare land was due to a transition from built-up land and other land. At riversides, soil erosion was significant every year due to natural disasters, heavy rainfall, and heavy wind. However, sand excavation for construction must decrease.
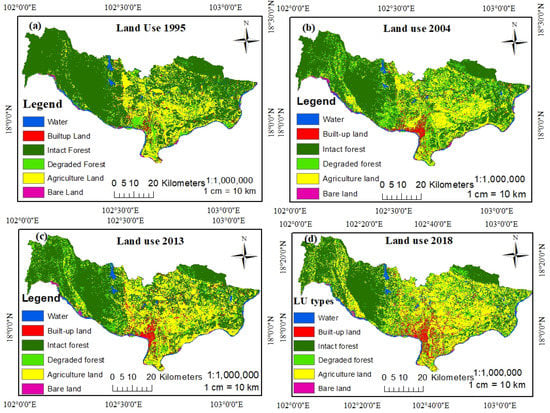
Figure 5.
Land use and cover change classification from 1995 to 2018: (a) 1995, (b) 2004, (c) 2013 and (d) 2018.
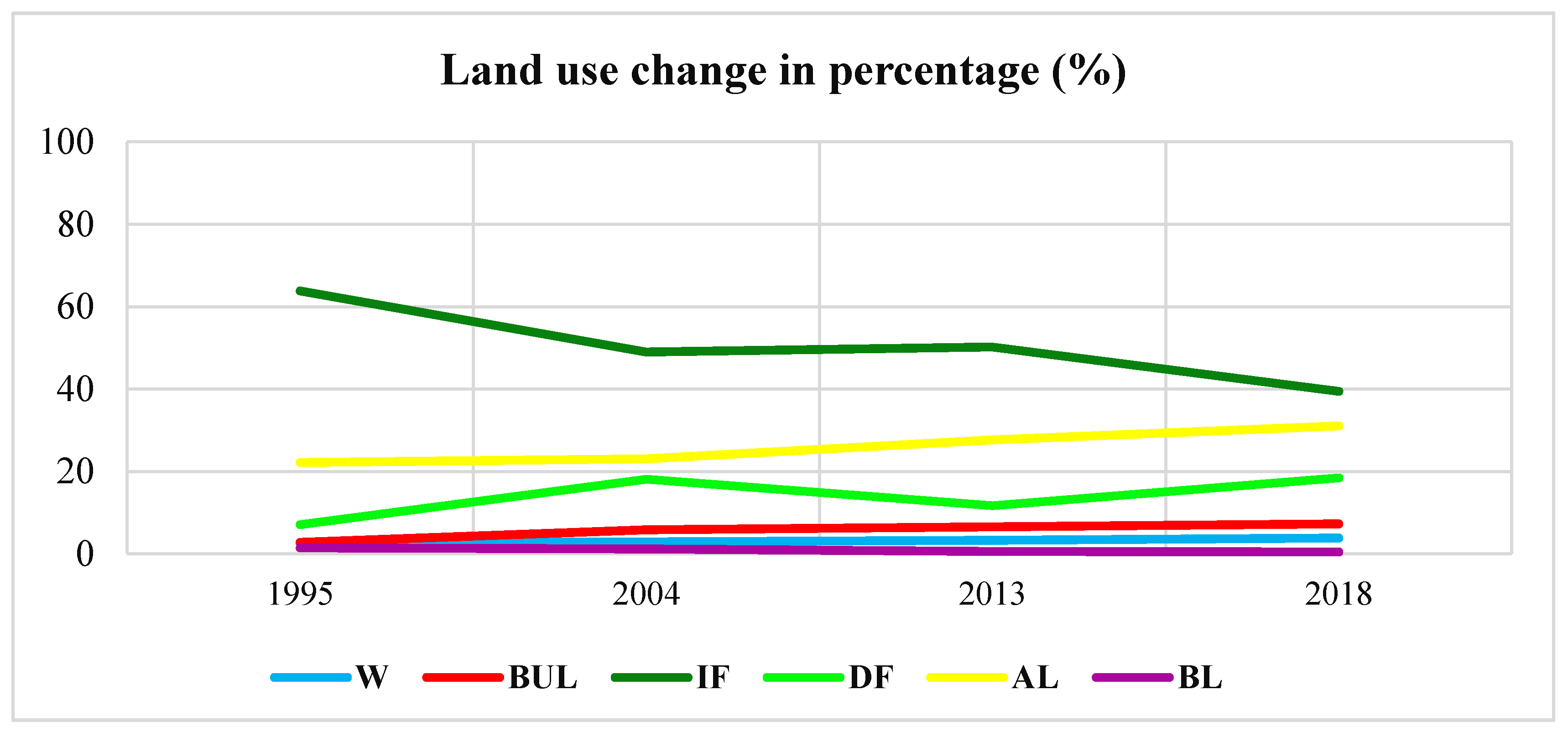
According to the increases and decreases shown in Table 5 and Figure 6, from 1995 to 2004, and from 2013 to 2018, human activity, which includes built-up land distribution and farming activity, decreased intact forest by 545.37 km2 (23%) and 392.87 km2 (21%), respectively. In contrast, intact forest increased between 2004 and 2013 to reach 44.12 km2. Built-up land increased from 1995 to 2004 to 110%, accounting for 111.94 km2.
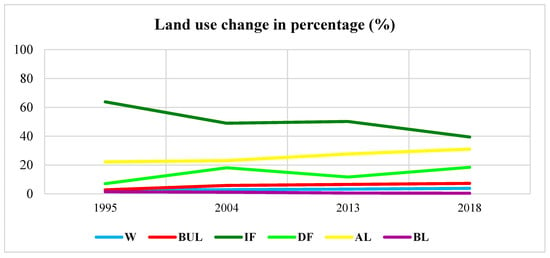
Figure 6.
Changes in percentages of land use/cover in 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018.
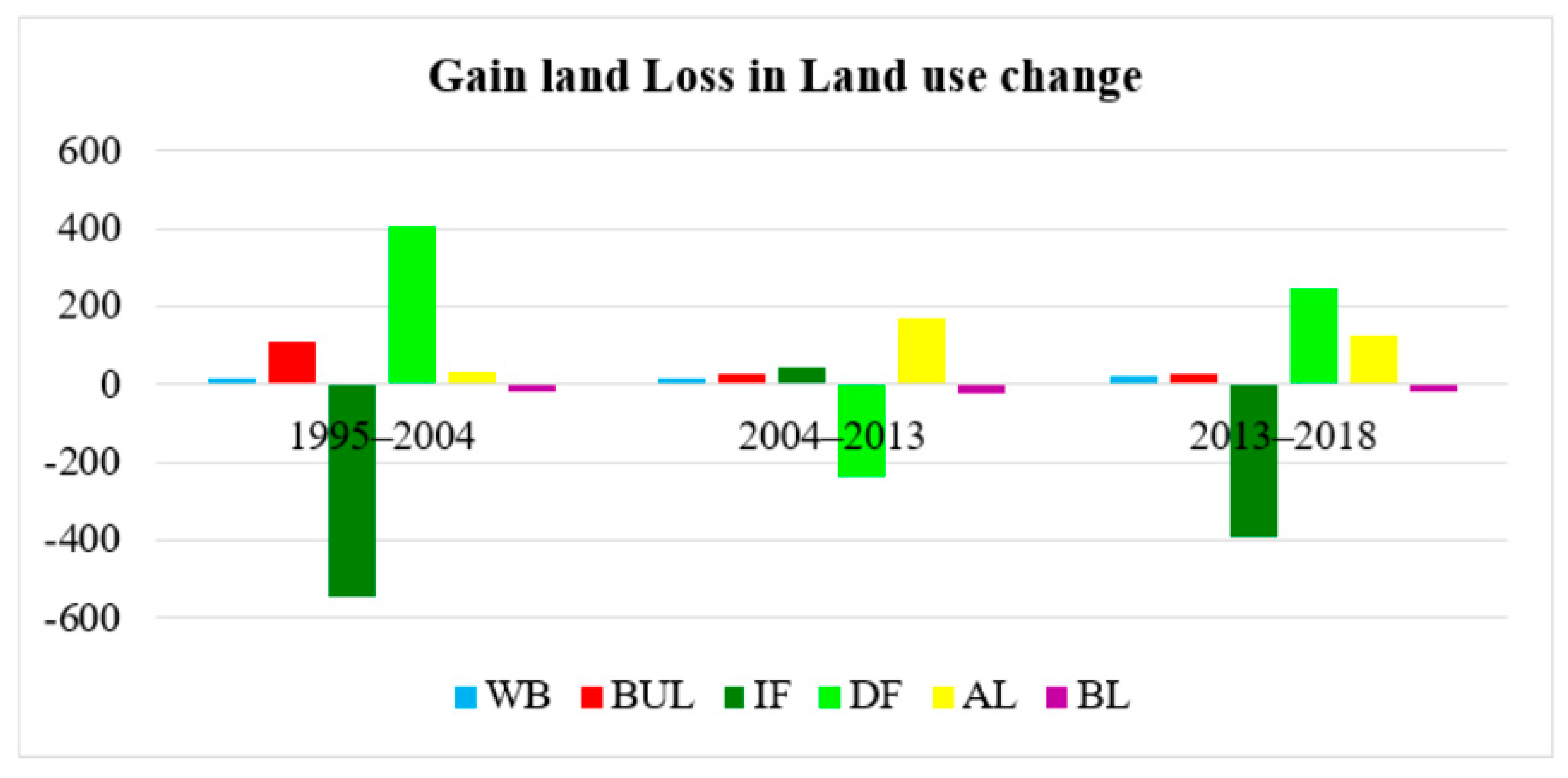
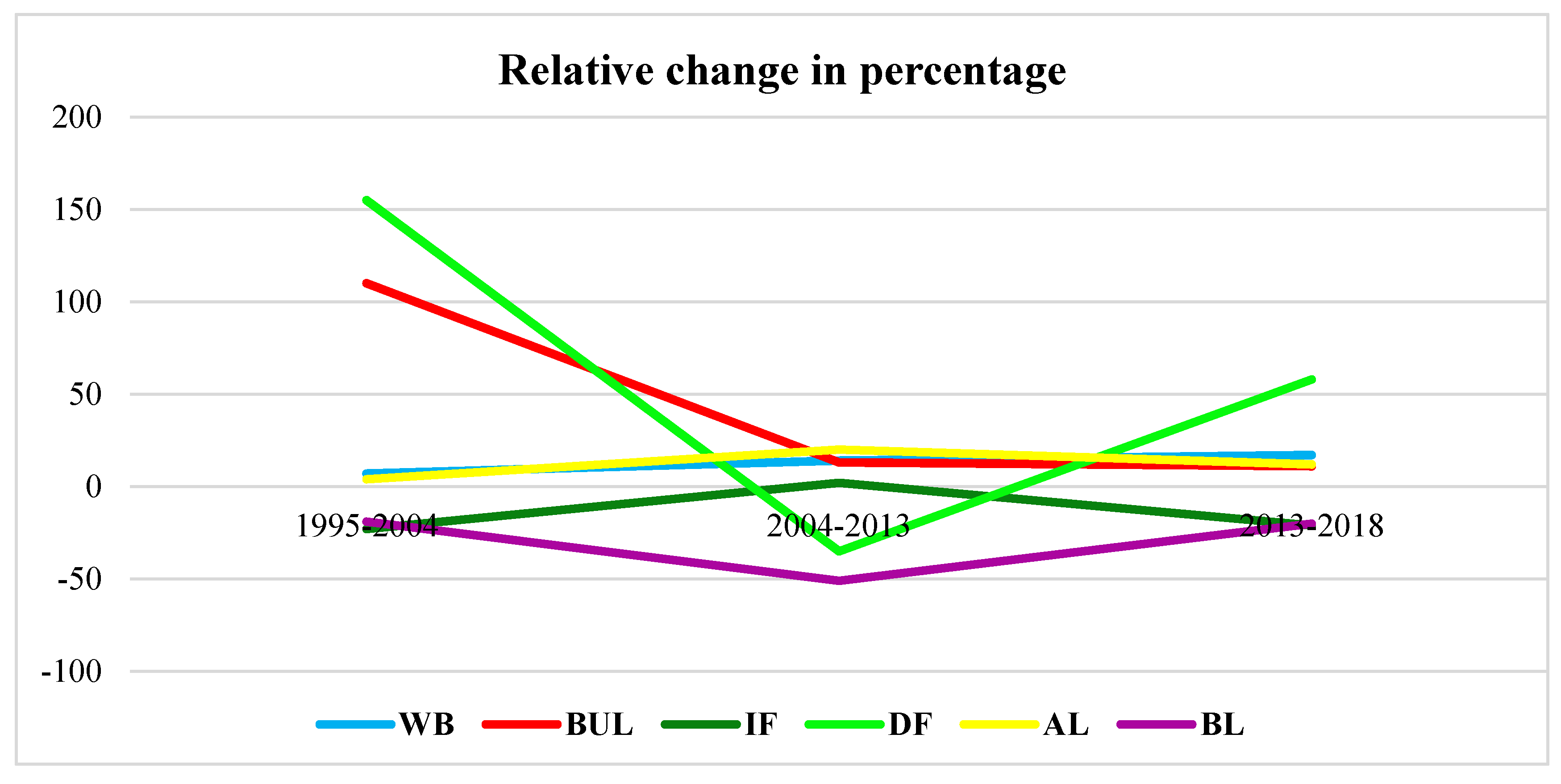
The net increases in agricultural land between 1995 and 2004, between 2004 and 2013 and between 2013 and 2018 were 32.48, 169.55 and 123.62 km2, accounting for 4%, 20%, and 12%, respectively, as shown in Table 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8. From 2004 to 2013, degraded forest decreased relatively little, to 235.98 km2, accounting for 35% of the total area, due to the transferring 20% compared to an increase of only 4% the previous period. The area of water bodies slightly increased due to the human need for fishponds and other small reservoirs in the area to support agricultural activities. The increase in water bodies among the three periods from 1995 to 2004, from 2004 to 2013, and from 2013 to 2018 were 7%, 14% and 17%, accounting for 6.69, 14.89 and 20.74 km2, respectively.

Table 6.
Relative changes of LUCC in the area during the periods of 1992–2003, 2003–2014 and 1992–2014.
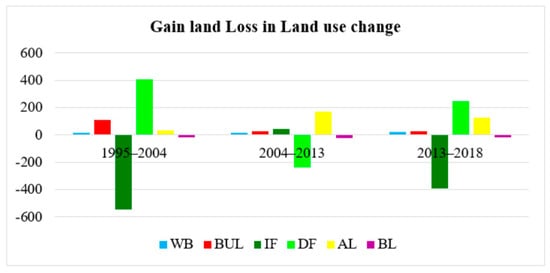
Figure 7.
Gain and loss of area in LUCC between 1995 and 2004, between 2004 and 2013 and between 2013 and 2018.
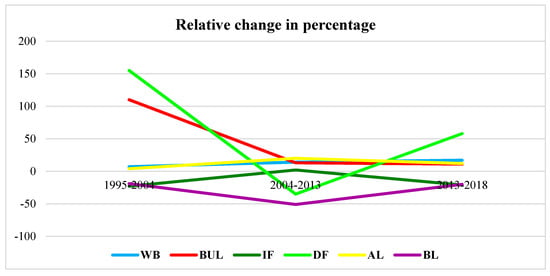
Figure 8.
Relative changes in percentage between 1995 and 2004, between 2004 and 2013 and between 2013 and 2018.
The significant conversions of intact forest directly increased the areas of agricultural land, degraded forest, built-up land, water, and bare land by 76.14, 49.79, 12.70, 2.66 and 0.91 km2, respectively. However, the total degraded forest at that point was 288.99 km2; in contrast, the land converted in 2004 represented more than double the previous land use conversions of 1995, including 409.3 km2 agricultural land, 215.3 km2 intact forest, 24.14 km2 built-up land, 3.13 km2 bare land, and 1.95 km2 water bodies. The land use types that were less converted were water bodies and bare land.
3.3. LUCC Detection Matrix from 1995 to 2004 and 2013 to 2018
Significant conversions of intact forest accounted for 2465.23 km2 in 1995, converting 458.64 km2 to degraded forest, 215.31 km2 to agricultural land, 49.48 km2 to built-up land, 5.58 km2 to water bodies and 2.22 km2 to bare land. Built-up land is the land use type that increased year after year; of the total land converted to built-up land in 2004, 32.94 km2 was from agricultural land, 19.05 km2 was from degraded forest, 49.48 km2 was from intact forest, 14.83 km2 was from built-up land, and other bare land and water contributed 0.73 km2 and 0.83 km2, respectively, as shown in Table 6. The total area of each land use conversion in 1995 from water, built-up land, degraded forest, agricultural land, and bare land was 92.04, 76.06, 288.99, 715.58 and 25.77 km2, respectively. The total land use converted in 2004 was larger, accounting for 1876.2, 781.8, 759.82, 96 and 31.36 km2 from intact forest, degraded forest, agricultural land, water and bare land, respectively, as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
LUCC detection matrix, during the period 1995–2004. LU, land use; WB, water bodies; BUL, built-up land; IF, intact forest; DF, degraded forest; AL, agricultural land; BL, bare land.
According to Table 8, the total LULC conversions from water bodies, built-up land, intact forest, degraded forest, agricultural land, and bare land in 2013 were 112.43, 157.18, 1956.96, 468.52, 945.60 and 20.50 km2, respectively, and in 2018 were 140.1, 245.97, 1440.90, 676.09, 1141.31 and 16.92 km2, respectively. In 2013, about 87.19 km2 of agricultural land and 59.46 km2 of intact forest represented the main transfers in the land use area which were converted into built-up land. Water bodies increased due to other land use transitions, and bare land decreased in the study area.

Table 8.
LUCC detection matrix, during the period 2013–2018. LU, land use; WB, water bodies; BUL, built-up land; IF, intact forest; DF, degraded forest; AL, agricultural land; BL, bare land.
3.4. Future Land Use/Cover Change Simulations
3.4.1. Model Validation of Predicted Land Use/Cover Change in 2018
The area transition matrix and area transition possibility matrix were created by using two land use types in 2004 and 2013; the results are shown in Table 5 [24]. Machine learning was run by the CA–Markov model in TerrSet software. Finally, a predicted map for 2018 was produced (see Figure 9). The predictions for 2018 had a relatively high Kappa coefficient for quantity and location [9]. The validation target, kappa index of agreement (KIA) was used for the 2018 LUCC predictions, which were acceptable according to both the actual 2018 LUCC and the predicted 2018 LUCC comparison. The kappa statistics were as follows: is 0.8873, is 0.8782, is 0.8782, and is 0.8430, as shown in Table 9. All the kappa results showed an acceptable standard greater than 80% which confirmed that the accuracy was reasonable for future land use prediction. The results obtained in terms of both actual 2018 LUCC and predicted 2018 LUCC showed different percentages for the increase in bare land (16.86%), intact forest (15.99%), and built-up land (7.81%), while other land uses degraded forest (15.74%), water bodies (13.93%), and agricultural land (10.71%), as shown in Table 10. The corrected percentage for each type of land use and land cover was over 85%, so the model was acceptable for making predictions for 2030, 2040 and 2050.
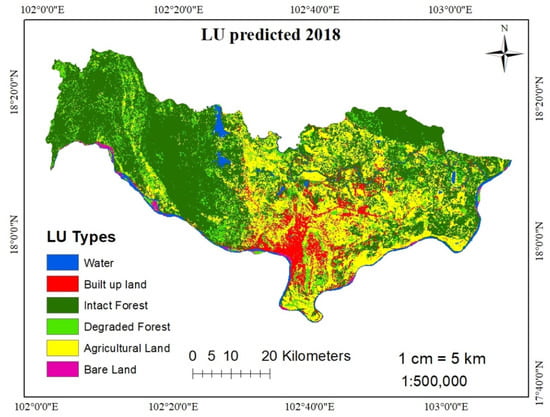
Figure 9.
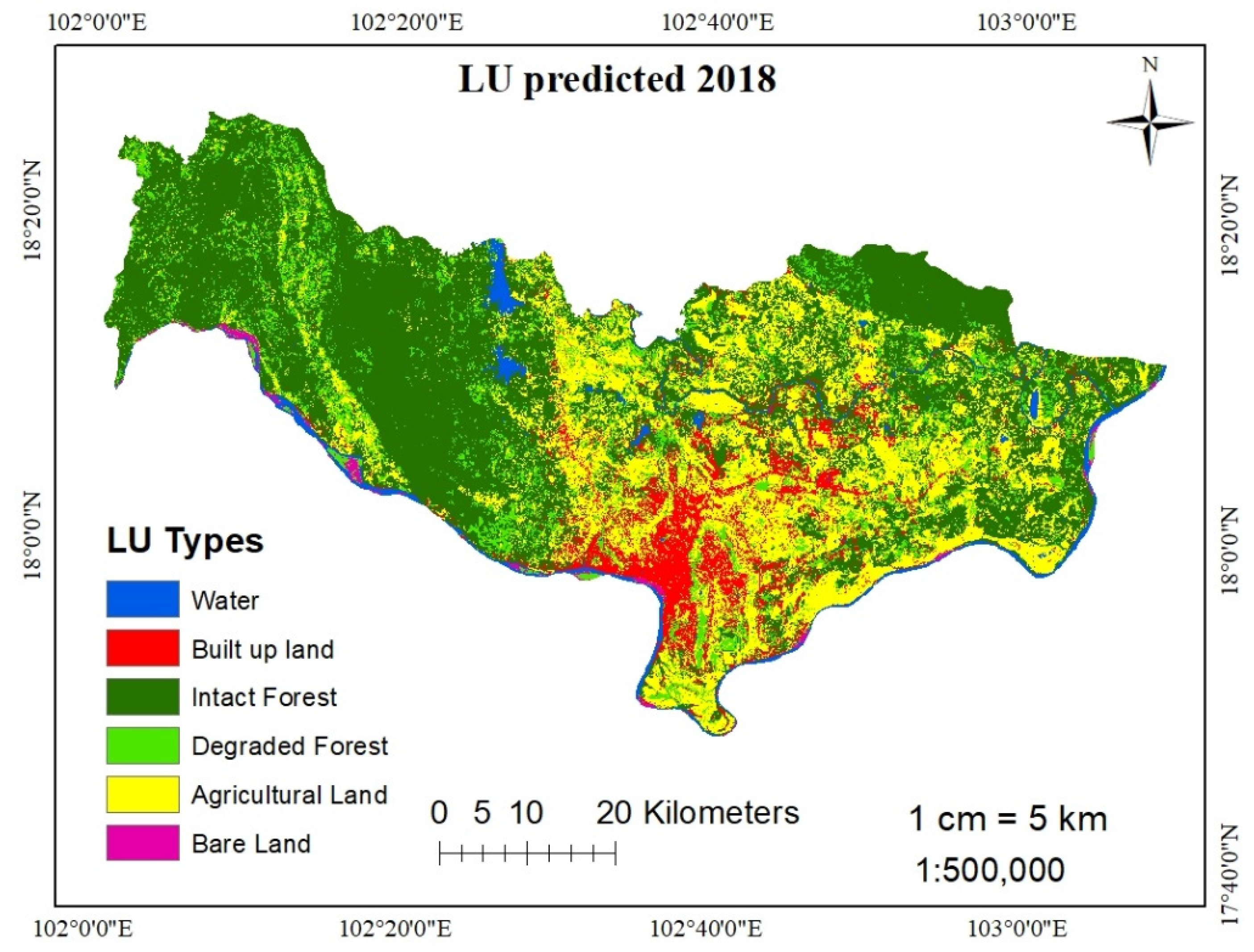
Predicted LUCC for 2018.

Table 9.
Kappa coefficient (index of agreement) of LUCC predicted for 2018.

Table 10.
The difference in area between the actual and predicted LUCC in 2018 (km2).
3.4.2. Future LUCC Simulations for 2030, 2040 and 2050
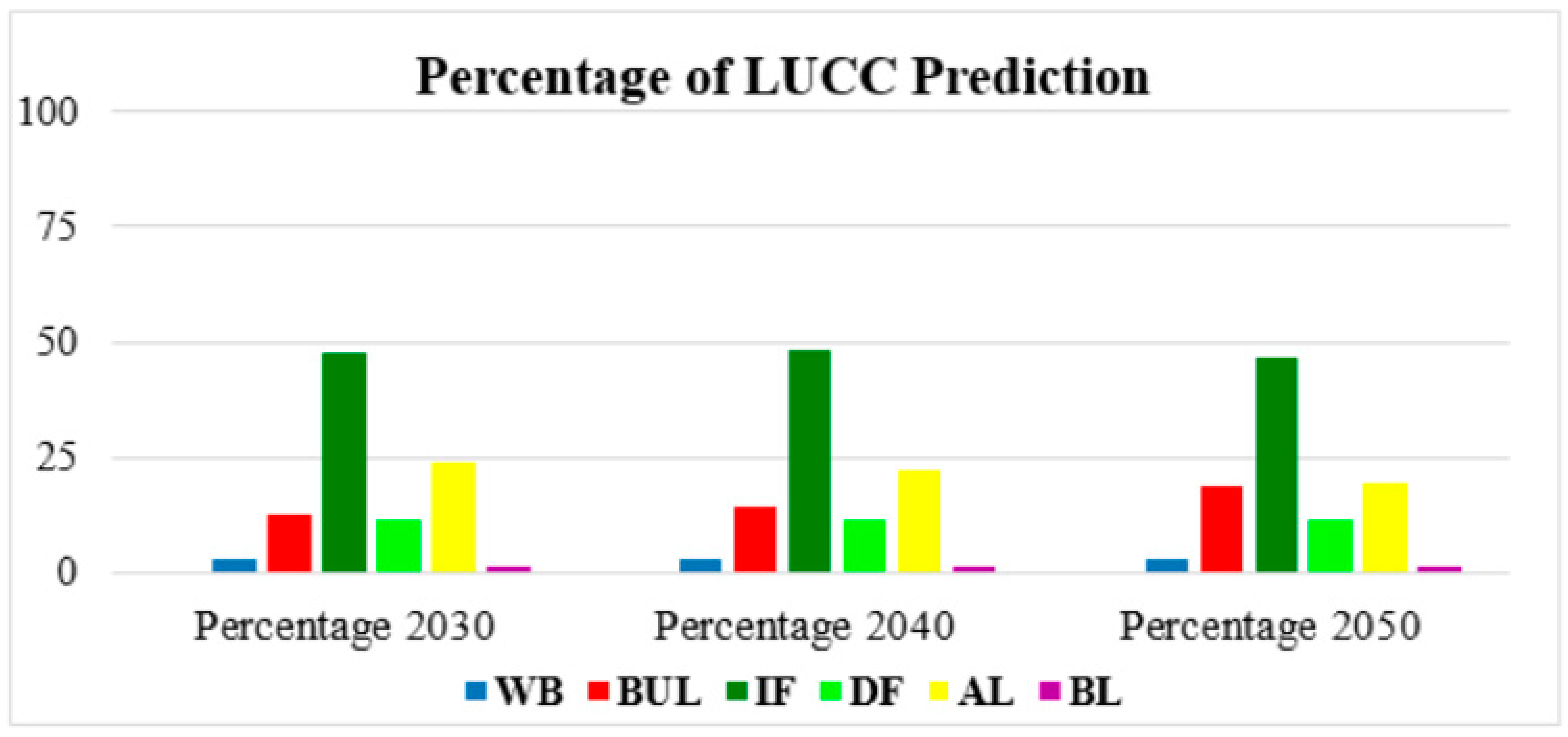
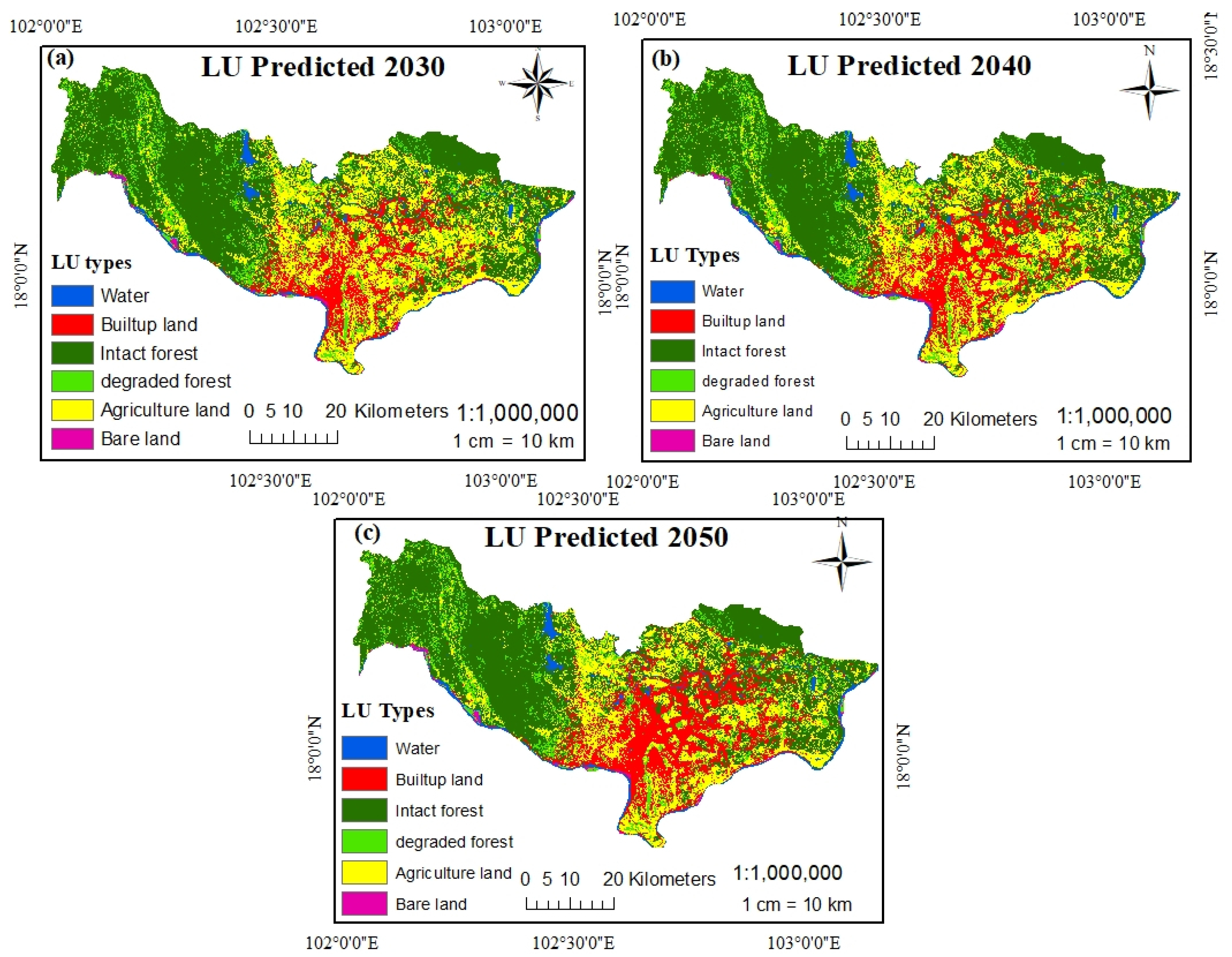
The future LUCC prediction for 2030, 2040 and 2050 in Vientiane were obtained, which followed by the same method used for the prediction of LUCC for 2018. The time surveyed of prediction was accounting for 32 years from 2018 to 2050, with time intervals for land use and cover change prediction of 12, 10, and 10 years, respectively. In this study, the future prediction focused on built-up land changes. According to Table 11 and Figure 10, built-up land greatly increased in 2030, 2040 and 2050, accounting for 457.41 km2 (12.48%), 533.71 km2 (14.56%), and 689.44 km2 (18.81%), respectively. Due to the fast-growing population in Vientiane mainly caused by rural–urban migration for education, jobs, and good life, the future scenarios need to take into account economic development and technologies as reasons for the rapid growth of built-up land. However, other land use types were gradually reducing by being converted into built-up land. These are for instance intact forest which the simulation showed will increase slightly in 2040 but be reduced again in 2050 by 1764.95 km2 (48.16%) and 1717.24 km2 (46.85%), respectively, Likewise, the degraded forest and agricultural land decreased significantly. The final LUCC maps prediction of 2030, 2040, ad 2050 were presented in Figure 11, which obviously indicates that almost all agricultural land diminished by the city expansion; the expansion was noted to extend mostly along the southeast aspect, where the major street is located.

Table 11.
Area coverage of LUCC prediction for 2030, 2040 and 2050 (km2).
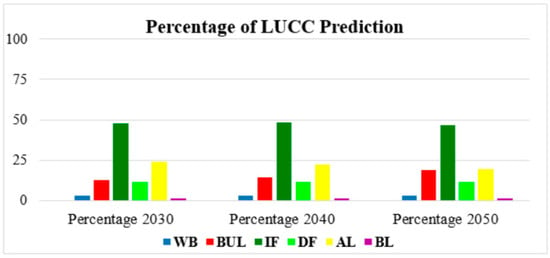
Figure 10.
Percentage changes in LUCC predicted for 2030, 2040 and 2050.
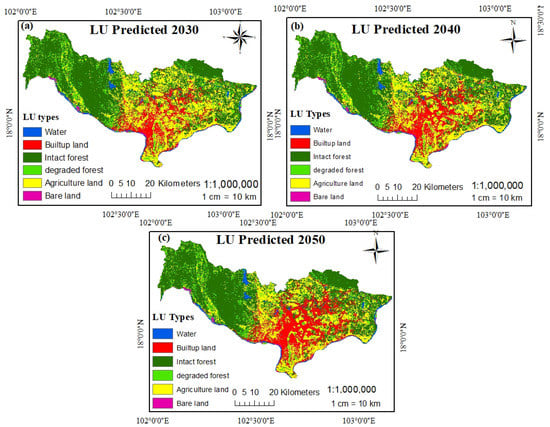
Figure 11.
Land use and land cover prediction maps for 2030 (a), 2040 (b) and 2050 (c).
4. Conclusions
This study applied satellite imagery from the period 1995–2004 from Landsat5 TM and that of 2013 and 2018 from Landsat8 OLI images to classify historical land use/cover changes in Vientiane, Laos. This used a geographic information system (ArcGIS 10.3) and ERDAS IMAGE 2014 technologies for LUCC classification. The application of machine learning in the CA–Markov model in TerrSet software predicted spatial and temporal changes in future LUCC by using the land change modeler (LCM) in TerrSet Clark Lab software. To process the CA–Markov model, a total of five drivers of urban sprawl arising from both natural and anthropogenic factors were collected. These are road network, digital elevation model (DEM), slope aspects, distance from road, and distance from urban areas. Another five independent variables were used to support the LCM analysis such as the conversion from all land uses to built-up land, conversion from bare land to built-up land, conversion from degraded forest to built-up land, conversion from agricultural lands to built-up land, and conversion from intact forest to built-up land.
The overall coefficients of historical LUCC classification for 1995, 2004, 2013 and 2018 were above 87%, as shown in Table 3 and Table 4, which indicates a high accuracy rate. The classification results illustrated that built-up land was the type of land use increasing the fastest in the area, due to the growth in the population of the city to 528,109 in 1995; 698,318 in 2005, and 820,940 in 2015 [52]. Other land use type such as agricultural land, water bodies, and degraded forest also increased year by year; in contrast, intact forest experienced a reduction in area due to the lack of strict policies, which provide the guidelines to prohibit land expansion and deforestation in Vientiane city. The kappa index of agreement for 2018 predicting land use indicated an accuracy of above 84%; as shown in Table 9, which showed the suitability of its use for future predictions with the CA–Markov model. The statistical results of the future of the predicted LUCC illustrate that urban built-up land continued to increase rapidly, leading to the conversions of other land use types such as agricultural land, degraded forest, intact forest, etc. Other land uses like bare land and water bodies were stable, because water bodies (rivers, reservoirs and drainage) cannot be converted to urban built-up lands, while bare land is mainly located by the Mekong River and due to the need for sand for construction, is gradually but significantly reduced. The assessment of agricultural land and degraded forest led to concerns about these land use types disappearing in the near future due to farming activities and urban sprawl. Due to the urban sprawl in Vientiane, the hotspot areas may change. However, the scale of urban sprawl in the four major districts, Xaythany, Parkngum, Hatsayfong, and Sikhotabong is likely to be large, whereas the other five districts may be gradually reduced in scale over time.
From the analysis of previous and future land use and land cover change, the change has obviously been slow in past years, but the speed increased up to 2018, mainly due to the fast development of the city. Nevertheless, when compared to relative land use variation in other countries with more rapidly increasing populations, the impact in Vientiane is still under lower change.
The approach, technologies, and model used in this study obtained a high kappa coefficient, which demonstrates that the model can produce high-quality simulated results and can be used as a reference in other research and other study areas. The recommendations of this paper can be applied to any urbanized expansion analysis in a CA–Markov model based on the existing drivers in the selected study area.
Finally, this study recommends to urban designers and policymakers who take responsibility for city planning to consider adopting an ecosystem-based approach to socioeconomic and ecological problems in the city. Such approaches can be implemented in short-term and long-term development plans. On the top of that, the urban development plans must provide policies and financial support for implementing smart interventions such as ecosystem conservation, farming zones and water conservation. They must also manage settlement expansion, restore and protect water sources and watersheds, increase the forest cover area through the afforestation mechanism (green city approach) and pass regulations that restrict unplanned settlement for sustainable urban development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.F. and Z.T.; methodology, C.F., Z.T. and J.Z.; software, C.F. and E.K.; validation, C.F., E.K. and K.U.; formal analysis, C.F., K.U. and X.L; investigation, C.F.; resources, C.F.,Z.T., J.Z. and X.L.; data curation, C.F., E.K. and Z.T.; writing, C.F.; writing—review and editing, Z.T., E.K., B.A.-S. and X.L.; visualization, C.F., Z.T. and J.Z.; supervision, C.F.; project administration, C.F.; and funding acquisition, C.F., J.Z., Z.T. and X.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Funding No. 41371495) and the National Major Program of Water Pollution Control and Treatment Technology of China (No. 2014ZX07201-011-002).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for Landsat5 TM, Landsat8 OLI images, and ASTER DEM images. The authors greatly appreciate the reviewers and editors for their critical feedback and valuable suggestions that greatly helped in improving the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, P. Urbanization and the New Phase of Growth in China. In Urbanization and Its Impact in Contemporary China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. A Systematic Review Analyzing the Prevalence and Circulation of Influenza Viruses in Swine Population Worldwide. Pathogens 2020, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, J.; Kumar, M. Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, H.-Q.; Wang, R.-S.; Paulussen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, B.-H.; Wang, Z. Monitoring and predicting land use change in Beijing using remote sensing and GIS. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Li, H.; Inohae, T.; Su, W.; Nagaie, T.; Hokao, K. Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, J.; Baysal, G.; Bulley, H.N.; Fürst, C. Assessing driving forces of land use and land cover change by a mixed-method approach in north-eastern Ghana, West Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 411–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, C.R.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Michalak, A.M.; Fisher, J.B.; Biondi, F.; Koch, G.; Litvak, M.; Ogle, K.; Shaw, J.D.; Wolf, A.; et al. Global patterns of drought recovery. Nature 2017, 548, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmy, M.W.A.; Gessler, P.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Salem, B. Land use/land cover change detection and prediction in the north-western coastal desert of Egypt using Markov-CA. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a CA-Markov Model under Two Different Scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgu, K. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Land Use Patterns and Biodiversity in Relation to Farm Productivity at Multiple Scales in Tigray, Ethiopia; Wageningen Universiteit: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rahel, H.; Kamal, K.; Heiko, B. Land Cover Changes Induced by Demining Operations in Halgurd-Sakran National Park in the Kurdistan Region. of Iraq. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, Y.; Hashimoto, S. Integrated assessment of land-use/coverage changes and their impacts on ecosystem services in Gansu Province, northwest China: Implications for sustainable development goals. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 15, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Defourny, P.; Shrestha, S. Land cover characterization and mapping of continental Southeast Asia using multi-resolution satellite sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4181–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, G.B.; Zhang, K.; Dong, Z.; Jun, X. Analysis and Projection of Land-Use/Land-Cover Dynamics through Scenario-Based Simulations Using the CA-Markov Model: A Case Study in Guanting Reservoir Basin, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.F. Integrating Linear Programming and Analytical Hierarchical Processing in Raster-GIS to Optimize Land Use Pattern at Watershed Level. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2010, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyandye, C.; Mandara, C.G.; Safari, J. GIS and Logit Regression Model Applications in Land Use/Land Cover Change and Distribution in Usangu Catchment. Am. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 3, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkenhead, M.; Aalders, I. Predicting land cover using GIS, Bayesian and evolutionary algorithm methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Mustak, S.; Srivastava, P.K.; Szabó, S.; Islam, T. Predicting Spatial and Decadal LULC Changes Through Cellular Automata Markov Chain Models Using Earth Observation Datasets and Geo-information. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, X.; Lv, L.-N. A spatiotemporal model of land use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. Ecol. Model. 2012, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, P.; Subedi, K.; Thapa, B. Application of a Hybrid Cellular Automaton–Markov (CA-Markov) Model in Land-Use Change Prediction: A Case Study of Saddle Creek Drainage Basin, Florida. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, W.L.; Ramsey, M.S.; Christensen, P.R. Monitoring urban land cover change: An expert system approach to land cover classification of semiarid to arid urban centers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; De Nijs, T.C.; Van Eck, J.R.; Visser, H.; De Jong, K. A method to analyse neighbourhood characteristics of land use patterns. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2004, 28, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yujun, S.; Saeed, S. Monitoring and predicting land use and land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS techniques—A case study of a hilly area, Jiangle, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Gebru, B.M.; Lamchin, M.; Kayastha, R.; Lee, W.-K. Land Use and Land Cover Change Detection and Prediction in the Kathmandu District of Nepal Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaldah, H.A. A Prediction of Future Land Use/Land Cover in Amman Area Using GIS-Based Markov Model and Remote Sensing. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, S.-W.; Korom, A.; Seng, Y.-W.; Sihapanya, V.; Phimmavong, S.; Phua, M.-H. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Vientiane Area, Lao PDR Using Object-Oriented Classification on Multi-Temporal Landsat Data. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 11340–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shiferraw, H.; Bewket, W.; Alamirew, T.; Zeleke, G.; Teketay, D.; Bekele, K.; Schaffner, U.; Eckert, S. Implication of lad use/land cover dynamics and Prosopis invasion on ecosystem service values in Afar Region, Ethiopia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 675, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praseuth, S.; Tuan, D.P.; Duc, C.M.; Quang, H.B.; Nhat, T.N.T. Mapping land cover types in Vientiane, Laos using multi-temporal composite Landsat 8 images. In Proceedings of the 6th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 12–13 December 2019; pp. 563–568. [Google Scholar]
- Pholsena, V. Mobility, familiarity and prejudice: Living together in a multiethnic town in southern Laos. Ethn. Racial Stud. 2018, 43, 1872–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, K.K.; Maynard, S.; Pearson, J.; Dobriyal, P.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. Recognising the role of local and Indigenous communities in managing natural resources for the greater public benefit: Case studies from Asia and Oceania region. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Population, C. The population of the provinces of Laos according to census results and latest official projections. Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/laos/cities/ (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- USGS. Earth Explorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 28 August 2016).
- OpenStreetMap© Online Mapping Project Database. Available online: http://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 11 December 2011).
- Chilagane, N.A.; Kashaigili, J.J.; Mutayoba, E. Historical and Future Spatial and Temporal Changes in Land Use and Land Cover in the Little Ruaha River Catchment, Tanzania. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 76–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, F.; Xi, J.; Xie, P.; Li, C. A Multitarget Land Use Change Simulation Model Based on Cellular Automata and Its Application. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Yaroshenko, A.; Turubanova, S.; Dubinin, M.; Laestadius, L.; Thies, C.; Aksenov, D.; Egorov, A.; Yesipova, Y.; Glushkov, I.; et al. Mapping the World’s Intact Forest Landscapes by Remote Sensing. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Evans, T.; Venter, O.; Williams, B.; Tulloch, A.I.; Stewart, C.; Thompson, I.; Ray, J.C.; Murray, K.A.; Salazar, Á.; et al. The exceptional value of intact forest ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, Y.; Gardner, T.A.; Goldsmith, G.R.; Silman, M.R.; Zelazowski, P. Tropical Forests in the Anthropocene. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2014, 39, 125–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.G. Degraded forest, degraded land and the development of industrial tree plantations in Laos. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2014, 35, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-C. Applying the Grey prediction model to the global integrated circuit industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2003, 70, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, S.; Zhang, J.; Vittal, V. Finite state Markov chain model for wind generation forecast: A data-driven spatiotemporal approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 16–20 January 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Sharma, N.; Garg, P.; Kappas, M. Statistical independence test and validation of CA Markov land use land cover (LULC) prediction results. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2016, 19, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelat, S.; Daamen, W.; Kaag, B.; Duives, D.; Hoogendoorn, S. A Markov-chain Activity-based Model for Pedestrians in Office Buildings. Collect. Dyn. 2020, 5, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.-C.; Kuang, L.-H.; Zhao, X.-M.; Guo, X. Scenario-based simulation of land use in Yingtan (Jiangxi Province, China) using an integrated genetic algorithm-cellular automata-Markov model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.Q.; Ahamad, M.S.S.; Hussin, W.M.A.W.; Samat, N.; Ahmad, S.Z. Markov CA, Multi Regression, and Multiple Decision Making for Modeling Historical Changes in Kirkuk City, Iraq. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2013, 42, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, A.K. Land Use Land Cover Changes in Detection of Water Quality: A Study Based on Remote Sensing and Multivariate Statistics. J. Environ. Public Health 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. Accuracy assessment and validation of remotely sensed and other spatial information. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2001, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patekar, P.; Unhale, P. Remote Sensing and GIS application in change detection study using Multi Temporal Satellite. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2013, 2, 374–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mallupattu, P.K.; Reddy, J.R.S. Analysis of Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using Remote Sensing Data and GIS at an Urban Area, Tirupati, India. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 268623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asia Pacific Parliamentary Forum. 17th Annual Meeting of The Asia-Pacific Parliamentary Forum (APPF). Vientiane Capital, Lao PDR, 11–15 January 2009. Available online: http://www.na.gov.la/files/appf17/population.html (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- Population, C. Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Available online: http://www.citypopulation.de/en/laos/cities/ (accessed on 8 June 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).