New Production Route of Magnesium Hydroxide and Related Environmental Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substances Used in the Research
- -
- magnesium sulphate(VI), production technology of Arkop, Ltd. (Kolejowa 34A, 32-332 Bukowno, Poland),
- -
- sodium hydroxide, p.a., produced by Avator,
- -
- 25% ammonia solution, produced by Avator,
- -
- acetone technical grade, produced by Avator.
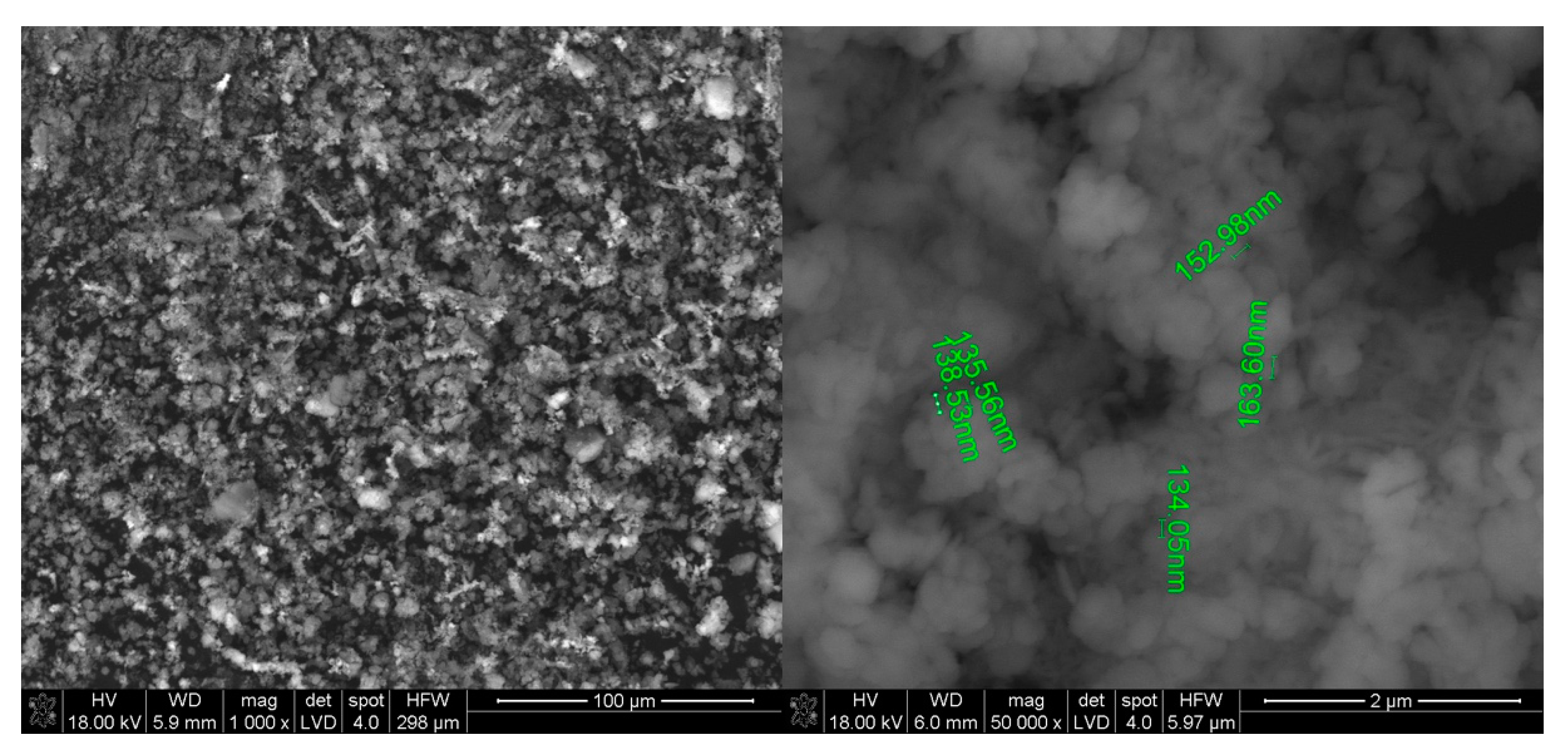
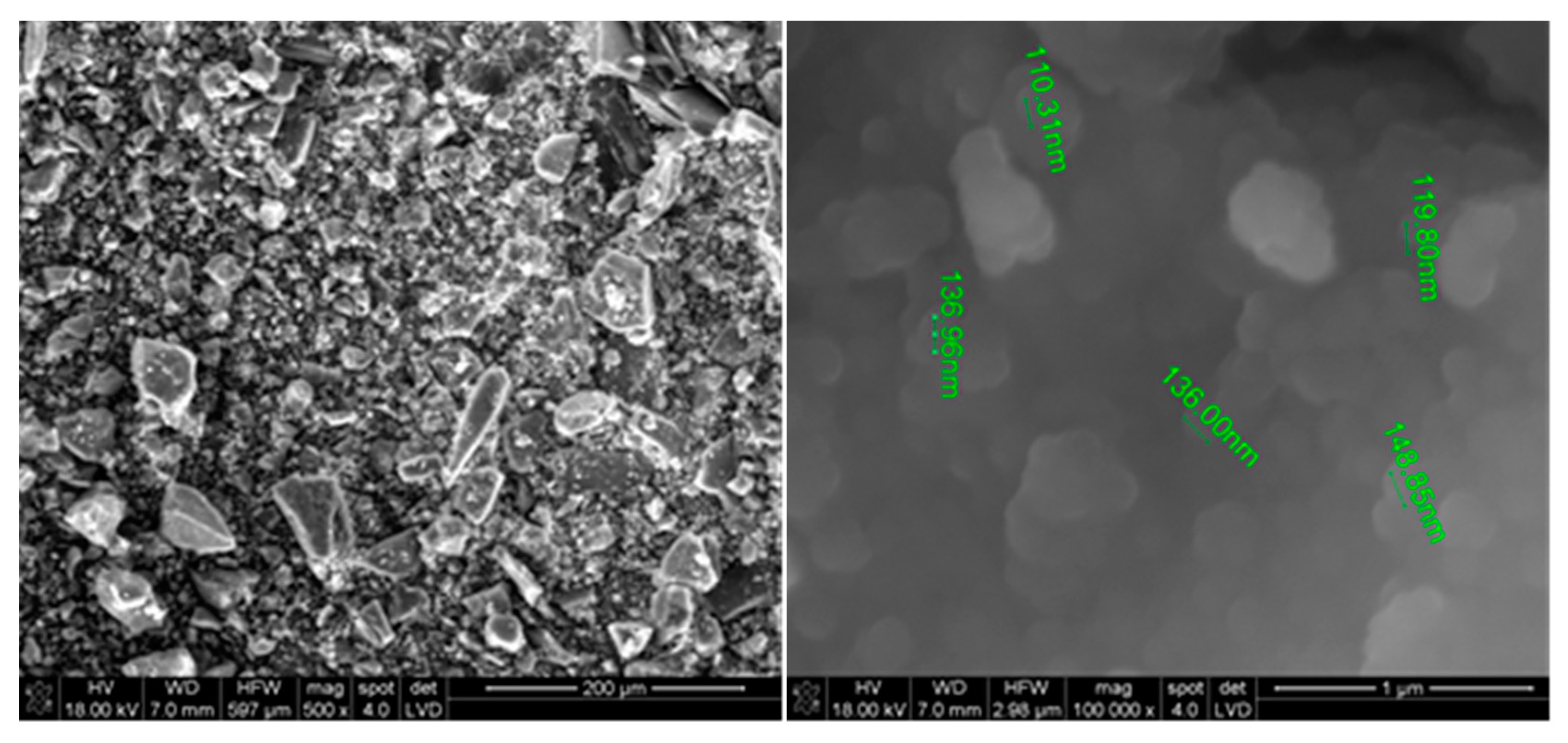
2.2. Experimental
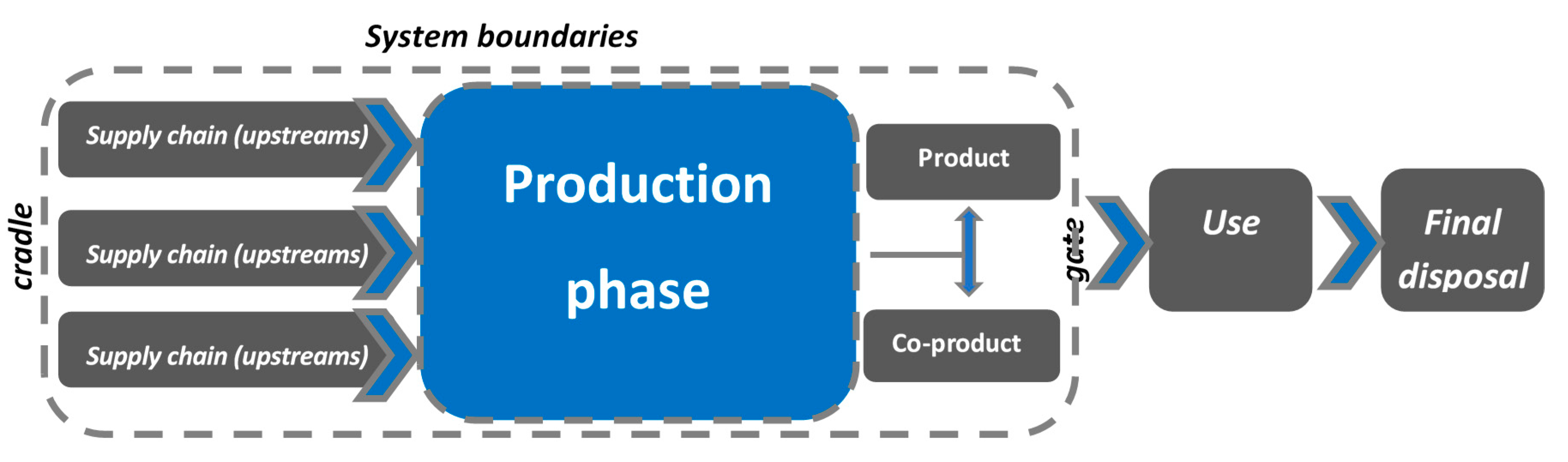
2.3. Environmental Analysis—Purpose and Scope
2.4. LCI—Life Cycle Inventory
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Production of Polymers. Available online: https://eippcb.jrc.ec.europa.eu/reference/production-polymers (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Klepki, T. Nowoczesne Materiały Polimerowe i ich Przetwórstwo—Część 1; Politechnika Lubelska: Lublin, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, X.; Ao, M.; Guo, X.; Xue, D. Environment-friendly, flame retardant thermoplastic elastomer–magnesium hydroxide composites. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2017, 10, 1750042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.Z. Tensile and flexural properties of polypropylene composites filled with highly effective flame retardant magnesium hydroxide. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Shao, C.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, H. Preparation and characterization of ethylene–vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA)–magnesium hydroxide (MH)–hexaphenoxycyclotriphosphazene (HPCTP) composite flame-retardant materials. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, M.; Dai, J.; Bai, J.; Xue, B.; Song, Y.; Peng, Y. Flame-retarded polyethylene terephthalate with carbon microspheres/magnesium hydroxide compound flame retardant. Fire Mater. 2018, 42, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, M.; Park, S.H.; Suhara, F.; Law, S. Flame retardant and mechanical properties of natural fibre-PP composites containing magnesium hydroxide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 83, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Su, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D. Influence of magnesium source on the crystalization behaviors of magnesium hydroxide. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 3771–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, P.; Jarosiński, A.; Wzorek, Z. Porównanie metod oczyszczania technicznego siarczanu(VI) magnezu do specjalnego zastosowania. Przemysł Chemiczny 2014, 93, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Casetta, M.; Michaux, G.; Ohl, B.; Duquesne, S.; Bourbigot, S. Key role of magnesium hydroxide surface treatment in the flame retardancy of glass fiber reinforced polyamide 6 Polymer. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 148, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, X.; Maa, C.; Zhaoa, J.; Lib, Z.; Xub, Z.; Liua, Y. Preparation of magnesium hydroxide nanoplates using a bubbling setup. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, P.; Yin, X.; Yang, X.; Han, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, N.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Functionalized magnesium hydroxide fluids/acrylate-coated hybrid cotton fabric with enhanced mechanical, flame retardant and shape-memory properties. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Shi, R.; Ma, X.; Tan, L.; Ji, Q.; Xia, Y. Enhanced flame-retardant properties of cellulose fibers by incorporation of acid-resistant magnesium-oxide microcapsules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apparatus and Method for Producing Magnesium from Seawater, Orville Lee Maddan. U.S. Patent 6,267,854, 31 July 2001.
- Henrist, C.; Mathieu, J.P.; Vogels, C.; Rulmont, A.; Cloots, R. Morphological study of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles precipitated in dilute aqueous solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 249, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarosiński, A.; Madejska, L.; Natanek, W. Wstępna ocena możliwości przeróbki odpadów magnezowych na nawozowy siarczan magnezu. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi 2001, 17, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Guan, S.; Gao, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. In Situ preparation and surface modification of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 348, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.A. Magnesium Compounds. In U.S Geological Survey Mineral Yearbook; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Savage, E. Magnesium Hydroxide Market and Hydroxide Markets; Blendom Information Services: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Smakowski, T.; Ney, R.; Glos, K. Minerals Yearbook of Poland 2013; IGSMiE PAN: Krakow, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Zheng, H.; Yin, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Li, B. Mg(OH)2 Complex Nanostructures with Superhydrophobicity and Flame Retardant Effects. J. Phys. Chem 2010, 114, 17362–17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosiński, A.; Kozak, A.; Zelazny, S. Utilization of solutions obtained after magnesium removal from sphalerite concentrates with spent electrolyte derived from winning of cathode zinc. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi 2013, 29, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarosiński, A.; Mączka, W. Technologiczne aspekty wykorzystania błota pochromowego. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi 2001, 17, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Niedworok, E.; Wardas, M.; Stec, M.; Adamek, E.; Maciejewska-Paszek, I. Rola wybranych makroelementów na przykładzie jonów magnezu w żywieniu człowieka. Nowiny Lekarskie 2002, 6, 292–294. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrera, M.P.; Volpe, S.L.; Mao, J.J. Therapeutic uses of magnesium. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 80, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, B.A.; Uhl, F.M.; Townsend, D. The impact of high surface area magnesium hydroxide on the stability of vinylidene chloride copolymers. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 357–358, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelek, L.; Kulczycka, J.; Lewandowska, A.; Zarebska, J. Life cycle assessment of energy generation in Poland. Int. J. LCA 2016, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Consumption of Fuel, Electricity and Heat | Value [Unit] | |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity (mixing of incoming solutions) | 0.176 [kWh] | |
| Electricity (sedimentation) | 0.102 [kWh] | |
| Electricity (drying) | 0.01 [kWh] | |
| Consumption of materials | ||
| NaOH (dry) | 14.40 [g] | |
| MgSO4 (dry) | 20.64 [g] | |
| Water (sedimentation) | 1.2 [dm3] | |
| Water (ammonia recovery) | 0.045 [dm3] | |
| 25% ammonia solution | 5 1 | 20 2 [kg] |
| Acetone (liquid) | 100 1 | 800 2 [g] |
| Emissions to water/soil | ||
| Industrial waste water—all water in the process is re-used | ||
| Co-products | ||
| Na2SO4 | 23.45 | g |
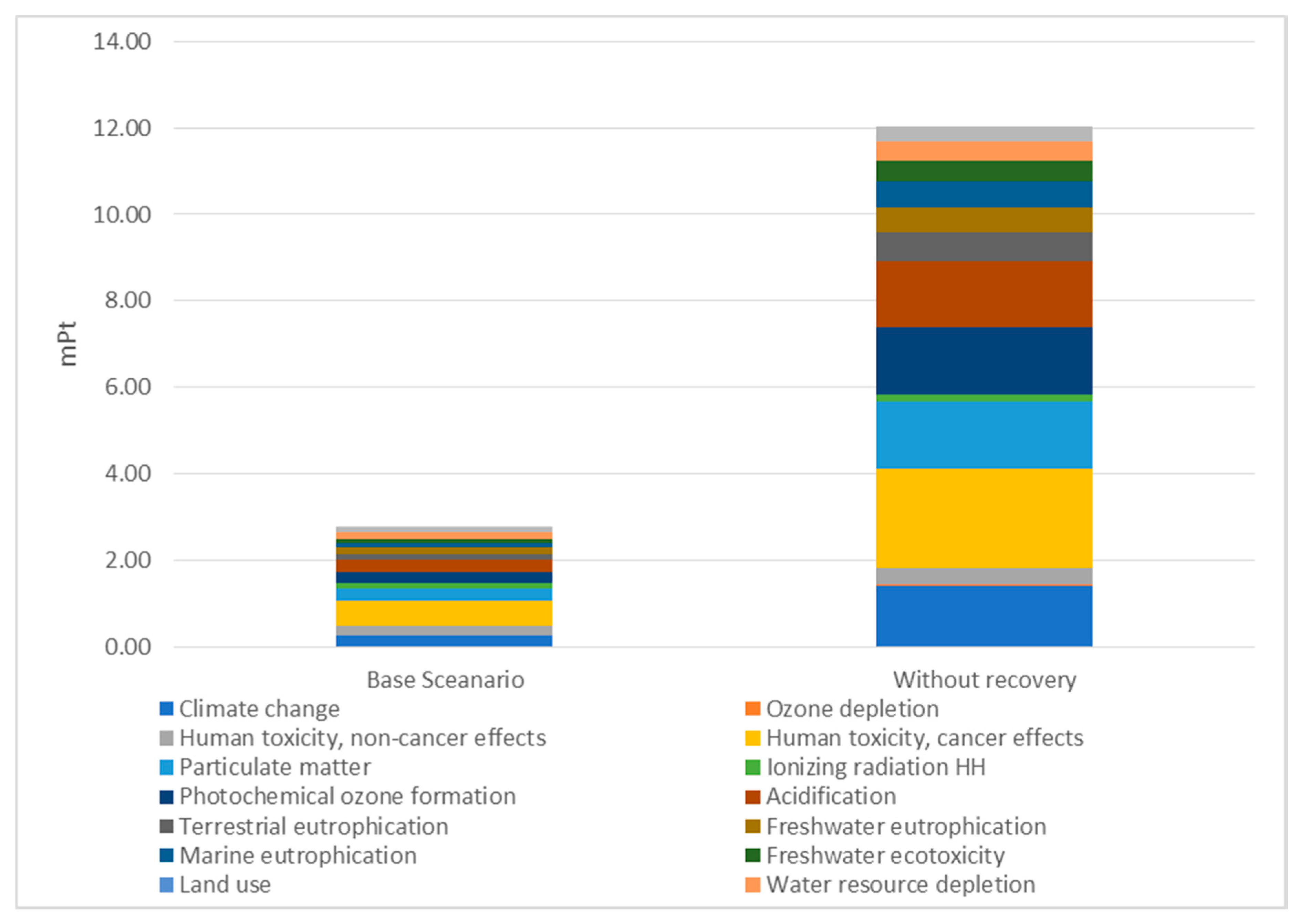
| Impact Categories | Eco-Indicator mPt | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Scenario | None Recovery Scenario | Difference | |
| Climate change | 0.26 | 1.42 | 1.16 |
| Ozone depletion | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Human toxicity, cancer effects | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.18 |
| Human toxicity, non-cancer effects | 0.57 | 2.28 | 1.70 |
| Particulate matter | 0.29 | 1.57 | 1.27 |
| Ionising radiation HH (human health) | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| Photochemical ozone formation | 0.25 | 1.57 | 1.32 |
| Acidification | 0.28 | 1.53 | 1.25 |
| Terrestrial eutrophication | 0.13 | 0.66 | 0.53 |
| Freshwater eutrophication | 0.14 | 0.57 | 0.43 |
| Marine eutrophication | 0.11 | 0.61 | 0.50 |
| Freshwater ecotoxicity | 0.09 | 0.47 | 0.39 |
| Land use | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Water resource depletion | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.30 |
| Mineral, fossil resource depletion | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
| Total environmental burden [mPt] | 2.79 | 12.02 | 9.23 |
| Product | Dominant Emissions/Resources Affecting the Environment in a Given Impact Category | Share in the General Indicator of a Given Impact Category [%] |
|---|---|---|
| Base scenario | Climate change | |
| Emissions to air: CO2 | 84.7 | |
| Emissions to air: CH4 | 13.3 | |
| Human toxicity, cancer effects | ||
| Emissions to water: Chromium (VI) | 61.7 | |
| Emissions to soil: Chromium (VI) | 22.8 | |
| Emissions to air: Chromium (VI) | 8.13 | |
| Particulate matter | ||
| Emissions to air: Particulates <2.5 μm | 53.6 | |
| Emissions to air: SO2 | 42 | |
| Photochemical ozone formation | ||
| Emissions to air: NOX | 59.8 | |
| Emissions to air: NMVOC | 30.9 | |
| Acidification | ||
| Emissions to air: SO2 | 69.9 | |
| Emissions to air: NOx | 26.2 | |
| Impact Category | Unit | Base Scenario | Non-Recovery Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate change | kg CO2 eq | 2.64 × 10−6 | 195.9025 |
| Ozone depletion | kg CFC-11 eq | 1.66 × 10−6 | 3.42 × 10−6 |
| Human toxicity, cancer effects | CTUh | 3.17 × 10−7 | 3.13 × 10−6 |
| Human toxicity, non-cancer effects | CTUh | 0.02 | 126 × 10−6 |
| Particulate matter | kg PM2.5 eq | 2.46 | 0.08921 |
| Ionising radiation HH | kBq U235 eq | 0.12 | 2.64411 |
| Photochemical ozone formation | kg NMVOC eq | 0.20 | 0.747045 |
| Acidification | molc H+ eq | 0.34 | 1.087174 |
| Terrestrial eutrophication | molc N eq | 3.09 × 10−3 | 1.73 |
| Freshwater eutrophication | kg P eq | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Marine eutrophication | kg N eq | 11.39 | 0.16 |
| Freshwater ecotoxicity | CTUe | 12.26 | 61.87 |
| Land use | kg C deficit | 0.19 | 19.33 |
| Water resource depletion | m3 water eq | 2.12 × 10−4 | 0.55 |
| Mineral, fossil resource depletion | kg Sb eq | 2.64 × 10−6 | 4.89 × 10−4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarosinski, A.; Radomski, P.; Lelek, L.; Kulczycka, J. New Production Route of Magnesium Hydroxide and Related Environmental Impact. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218822
Jarosinski A, Radomski P, Lelek L, Kulczycka J. New Production Route of Magnesium Hydroxide and Related Environmental Impact. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218822
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarosinski, Andrzej, Piotr Radomski, Lukasz Lelek, and Joanna Kulczycka. 2020. "New Production Route of Magnesium Hydroxide and Related Environmental Impact" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218822
APA StyleJarosinski, A., Radomski, P., Lelek, L., & Kulczycka, J. (2020). New Production Route of Magnesium Hydroxide and Related Environmental Impact. Sustainability, 12(21), 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12218822






