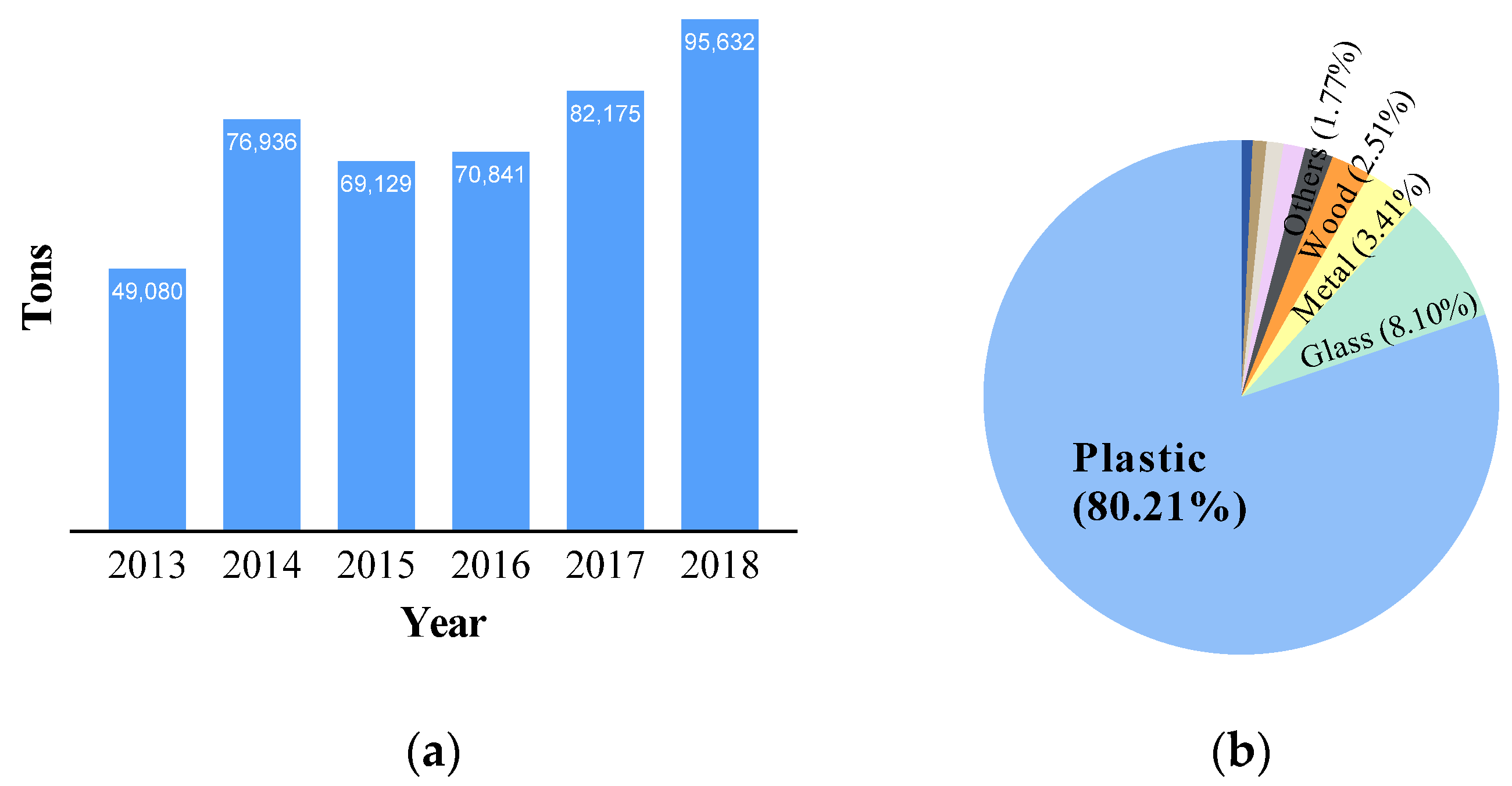Abstract
This study summarizes existing studies on plastic recycling to determine whether ocean plastics with high pollution degrees could be used for cement-based materials. In particular, the methods to recycle plastic waste, the effects of recycled plastic on the physical and mechanical properties of cement-based materials, and their effective usage were investigated. Workability, density, compressive strength, split tensile strength, and flexural strength of cement-based materials with recycled plastics were reviewed and divided into recycled aggregates and fibers. Based on the previous investigation, the direction of research necessary to recycle marine plastics is suggested. As the amount of recycled plastic aggregate increased, the mechanical strength of cement-based materials decreased. The recycled plastic aggregate lowered the density and increased porosity of the cement-based material. Meanwhile, recycled plastic fibers reduced the compressive strength but improved the tensile strength; to effectively improve tensile strength, a volume content of less than 1.5% should be added to prevent balling fibers. Furthermore, an appropriate aspect ratio should be determined based on the type of plastic to be used.
1. Introduction
Ocean waste is an environmental problem that continues to receive social attention because it damages the marine environment, ecosystem, and marine landscape [1]. Plastics are widely found in marine waste because of their low density, high strength, and durability compared to their weight, formability, and low price; they are a significant source of ocean pollution [1,2]. The amount of plastic waste discharged to the ocean worldwide has been estimated to be 4,800,000 to 12,700,000 tons, and 1,600,000 km2 of waste was formed in the North Pacific region [2,3]. To solve this problem, South Korea is conducting a project to collect waste accumulated in the ocean; as of 2018, ~95,632 tons have been collected, as shown in Figure 1a [4]. Figure 1b indicates that ~80% of this waste is made of plastic; however, landfill or incineration methods are employed to discard this waste instead of recycling [5]. Therefore, some researchers have suggested developing and using biodegradable plastic as a solution [6,7,8]. Although this method can solve the long-term plastic waste problem, it cannot resolve the issue of recycling ocean plastic waste. To recycle plastic waste, products are re-produced through washing, sorting, crushing, melting, etc. [9]. Waste sorted and collected on land can be sufficiently recycled; however, ocean waste contains salts, which makes it difficult to wash, and sorting this waste is difficult. There are several types of ocean plastic waste, including fishing nets, buoys, ropes, plastic boxes used in fisheries and aquaculture, beverage bottles used on land, food packaging containers, plastic bags, etc.
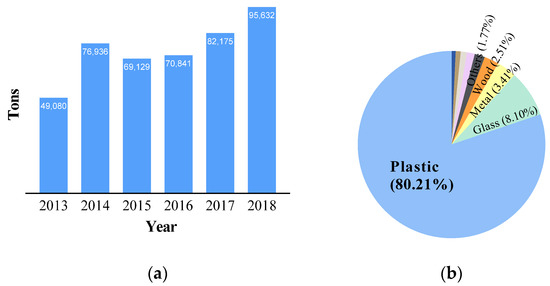
Figure 1.
Waste collection project in South Korea: (a) amount of collected ocean waste; (b) types of collected ocean waste, based on [4].
The main components of these plastics include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), nylon 6, polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) [9]. To recycle and upcycle ocean waste, the European Union organized the Circular Ocean project that aims to inspire communities to realize the hidden economic opportunities of waste fishing nets and ropes in the Northern Periphery and Arctic region [10]. It uses ocean waste to produce textiles that can be used for manufacturing clothing and fashion accessories; it is currently producing products through practical use. However, it targets waste fishing nets based on nylon 6. Furthermore, a high degree of pretreatment is required because these clothes and miscellaneous goods have considerable direct contact with the human body. Moreover, the amount of waste used is not substantial. Therefore, many studies have investigated the use of plastics based on PET, PS, and HDPE as recycled aggregates or reinforcements in cement-based materials [11,12,13,14]. However, this has not yet been put into practical use. If ocean plastics are used in construction projects, a larger amount of ocean plastics can be processed than when used in clothing or fashion accessories. Since there is no direct human contact, it is expected that they can be used with less pretreatment. Therefore, in this study, the authors review research conducted on recycling plastics for use in cement-based materials to confirm the (1) recycling methods, (2) characteristics of cement-based materials with recycled plastics, and (3) the appropriate usage.
2. Types of Recycled Materials in the Construction Industry
Recycled materials used in the construction industry are largely used as aggregates and as fibers to enhance the tensile strength of cement-based materials. To replace conventional aggregates, it is typical to use recycled PET as the coarse aggregate of concrete, fine aggregate of concrete and mortar, and recycled PS as the lightweight aggregates of lightweight concrete materials, and recycled PET, nylon 6, and HDPE as fibers of fiber-reinforced cementitious composites. To date, very few studies have investigated the use of plastics collected from the ocean in the construction industry. Therefore, this study aims to investigate all studies that recycled plastics collected from the ocean and land.
2.1. Aggregates
Methods for recycling plastics and using them as aggregates are largely divided into two categories: replacement of coarse aggregates for concrete or lightweight concrete with plastic flakes crushed to 3–16 mm. One method is replacing the fine aggregates of concrete and mortar with plastic powder crushed to a size of less than 2 mm. Table 1 summarizes the examples of recycling plastics and using them as aggregates. Although plastics such as PET, HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, and PP are used in concrete, most of the plastics used tend to be recycled PET bottles. The types of plastics used in lightweight concrete were expanded polystyrene (EPS), PS, polyurethane (PUR), and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), and studies mainly recycled EPS foam and used it as a lightweight aggregate.

Table 1.
Type of plastic aggregate and target materials in the literature.
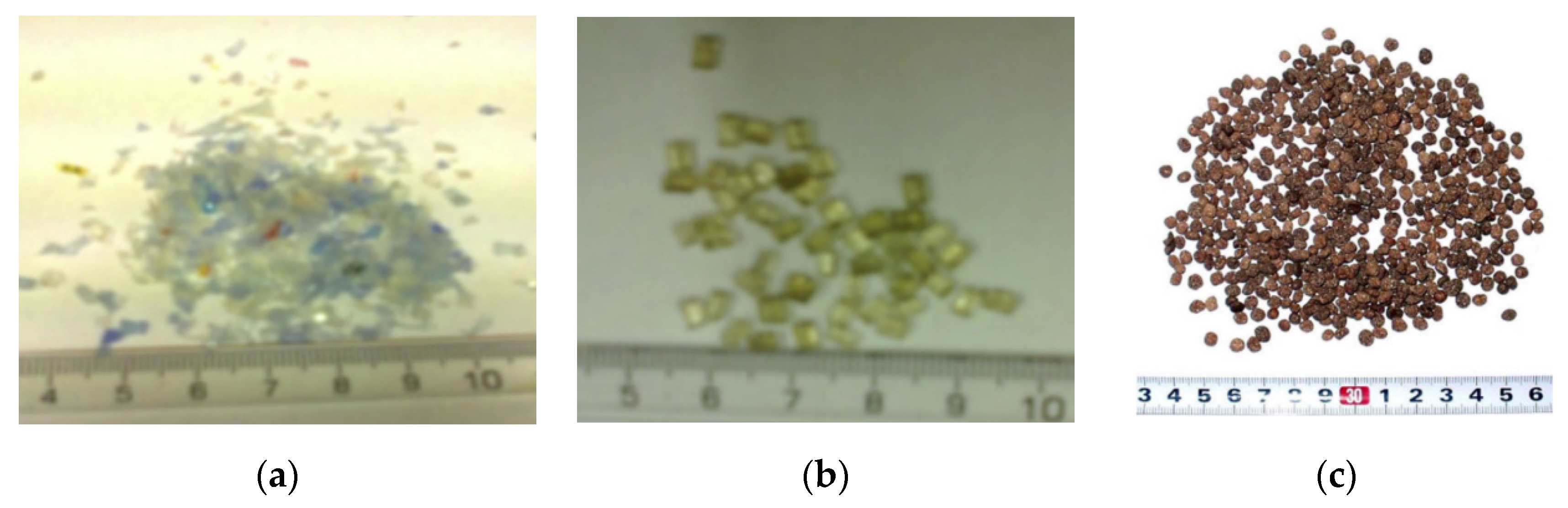
Figure 2 shows the shape of the recycled plastic. The main method used to convert plastic into an aggregate is pulverizing using a shredder. In some studies, pellets manufactured to a certain size through melting were used [36,38,41]. Furthermore, there are studies that employed grinding and crushing; however, these methods are not considerably different from grinding and, therefore, they were employed as methods to control the size of the recycled product. Choi et al. [25] produced waste PET lightweight aggregate (WPLA) with PET bottles mixed with river sand powder, as shown in Figure 2c. Alqahtani et al. [45] produced a solid sheet via compression and heating by mixing LLDPE and a red dune sand filler at a ratio of 30:70 and then produced the aggregate by crushing. Therefore, the use of plastic as an aggregate in cement-based materials was carried out through washing and grinding.
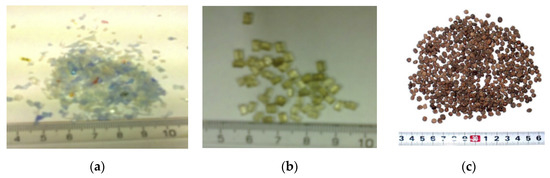
Figure 2.
Shape of recycled plastic aggregates: (a) Shredded PET [41]; (b) PET pellets [41]; (c) waste PET lightweight aggregate (WPLA) [25].
2.2. Fiber
Table 2 lists studies that recycled plastic as a reinforcing fiber for cement-based materials. Similar to aggregates, the most common plastic type was PET, followed by nylon 6, PP, HDPE, and glass fiber-reinforced plastic (GFRP).

Table 2.
Types of plastic fibers in the literature.
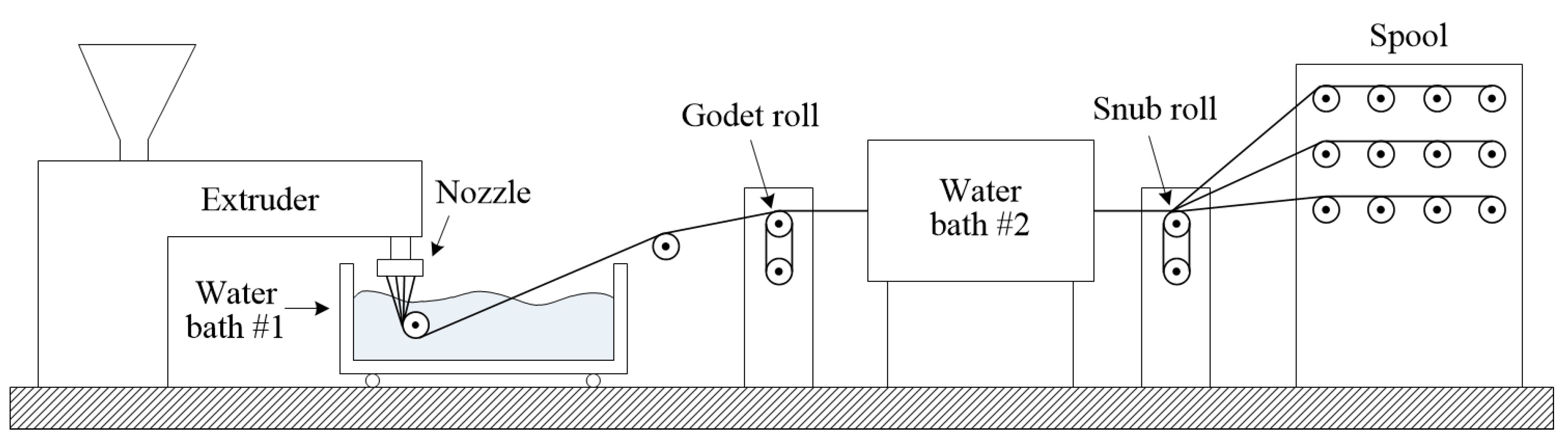
Most methods for converting plastic into reinforcing fibers employed cutting, and in some studies, fibers were extruded using recycled PET pellets [49,50,55,56,59]. In some cases, PET was melted to produce recycled sheets and then slit to produce fibers [51,53]. The basic method of manufacturing fibers from plastic is extrusion, as shown in Figure 3. However, to produce fibers through extrusion from plastic waste, it must first be melted to produce pellets. Furthermore, plastics must be classified as one type to proceed with this process, and some plastics showed decreasing strength during this process [66]. PET bottles are made from similar grades of plastic; as a result, they are suitable for both the bottle manufacturing process and for reprocessing into fibers [9,66]. However, to use other plastics, it is possible to minimize the reduction in the strength of recycled plastics by cutting them. However, the process of cutting plastic sheets into fibers has not been automated yet and, therefore, it has a limitation in that it must be done manually [65]. Attempts to automate this process are currently underway; however, information on this process is very limited [67].
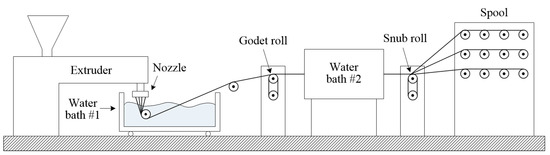
Figure 3.
Extrusion apparatus, based on [50].
For fibers used to enhance the tensile strength of cement-based materials, tensile strength, aspect ratio, and fiber geometry are important properties that need to be studied [68,69,70]. Table 3 lists the properties of the recycled fibers used in the existing literature. Among the recycled fibers, the PET fibers showed the highest tensile strength; smaller diameters tended to have lower strength. In addition, the aspect ratio was the highest when using the extrusion process; furthermore, it can change fiber geometry. When the fiber is manufactured by cutting plastic, the fiber diameter cannot be changed and, therefore, the aspect ratio cannot be changed beyond a certain value. The geometry of the raw material, which generates a mechanical bond when the fiber is pulled out in the cement-based materials, should be considered.

Table 3.
Properties of recycled plastic fiber in the literature.
2.3. Others
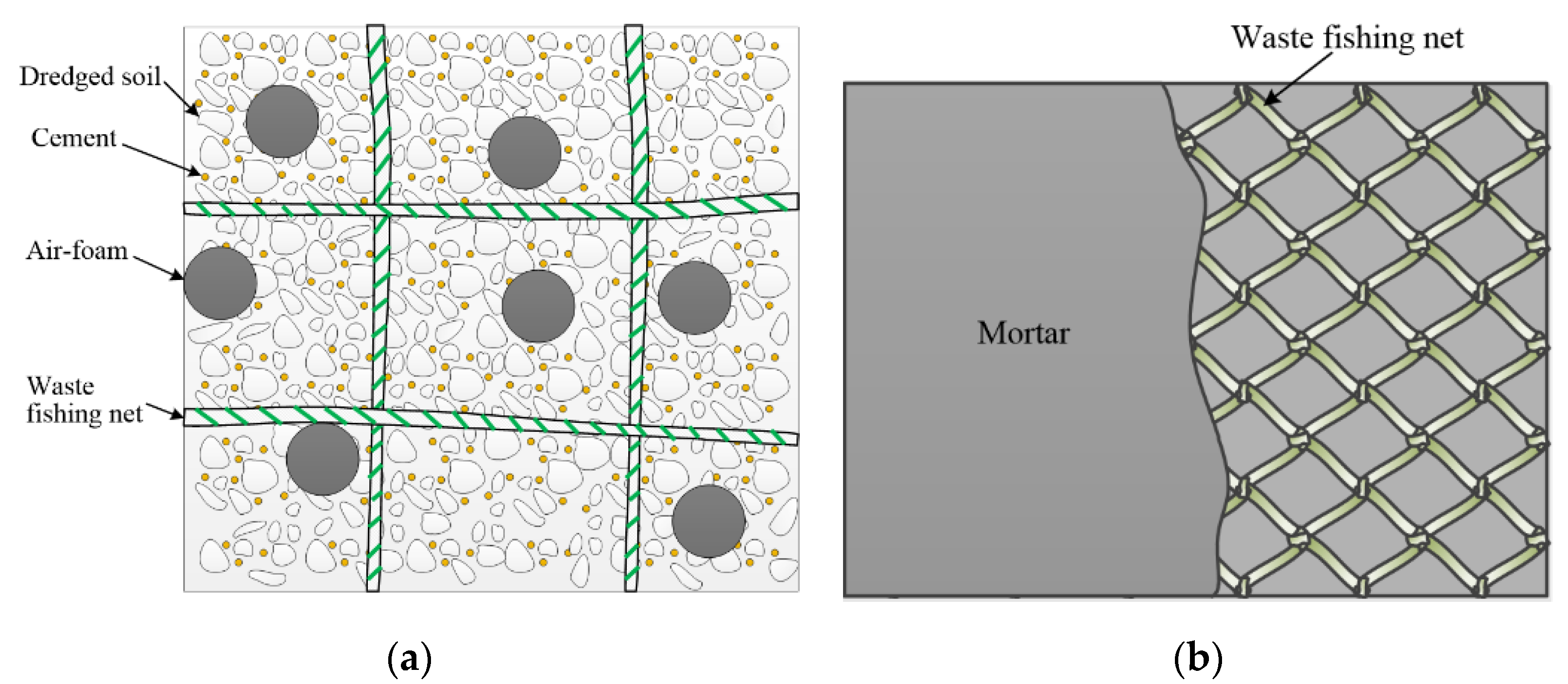
In addition to the use of recycling plastics as aggregates and fibers, studies on the use of recycling plastic waste in construction projects are summarized in Table 4. In the surveyed studies, textiles and reinforcing bars that reinforce lightweight soil, mortar, and concrete used in the construction industry were produced from waste fishing nets. In the case of textiles, the waste fishing net is cut to a certain size and used as a reinforcing material to improve the tensile strength of lightweight soil and mortar (Figure 4) [71,72]. Bertelsen et al. [73] and Sigvardsen [74] produced a waste fishing net in a bar shape and used it as a near-surface mounted (NSM) reinforcement. This method is still being tested in a limited way and, therefore, there are only a few studies on this topic.

Table 4.
Types of recycled plastic products used in the construction industry.
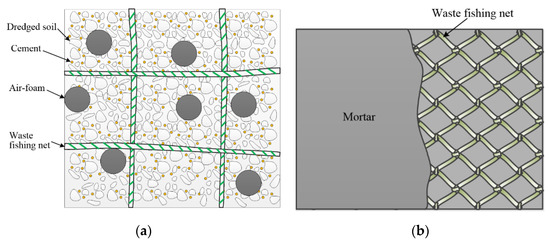
Figure 4.
Recycled waste fishing net textile reinforcement: (a) for lightweight soil; (b) for mortar, based on [71,72].
3. Properties of Construction Materials Containing Recycled Plastics
To summarize the existing studies and confirm the effect of plastic recycling on the properties of cement-based materials, the relative properties were calculated as
Relative property = Test results with plastic / Test results without plastic
Physical and mechanical properties were investigated, including workability, fresh density, hardened density, compressive strength, split tensile strength, and flexural strength. Recycled plastic aggregate was added by replacing the existing aggregate with a volume content or weight ratio, while recycled plastic fibers were added as a volume content of the test specimen.
3.1. Physical Properties
3.1.1. Effect of Recycled Plastic Aggregate
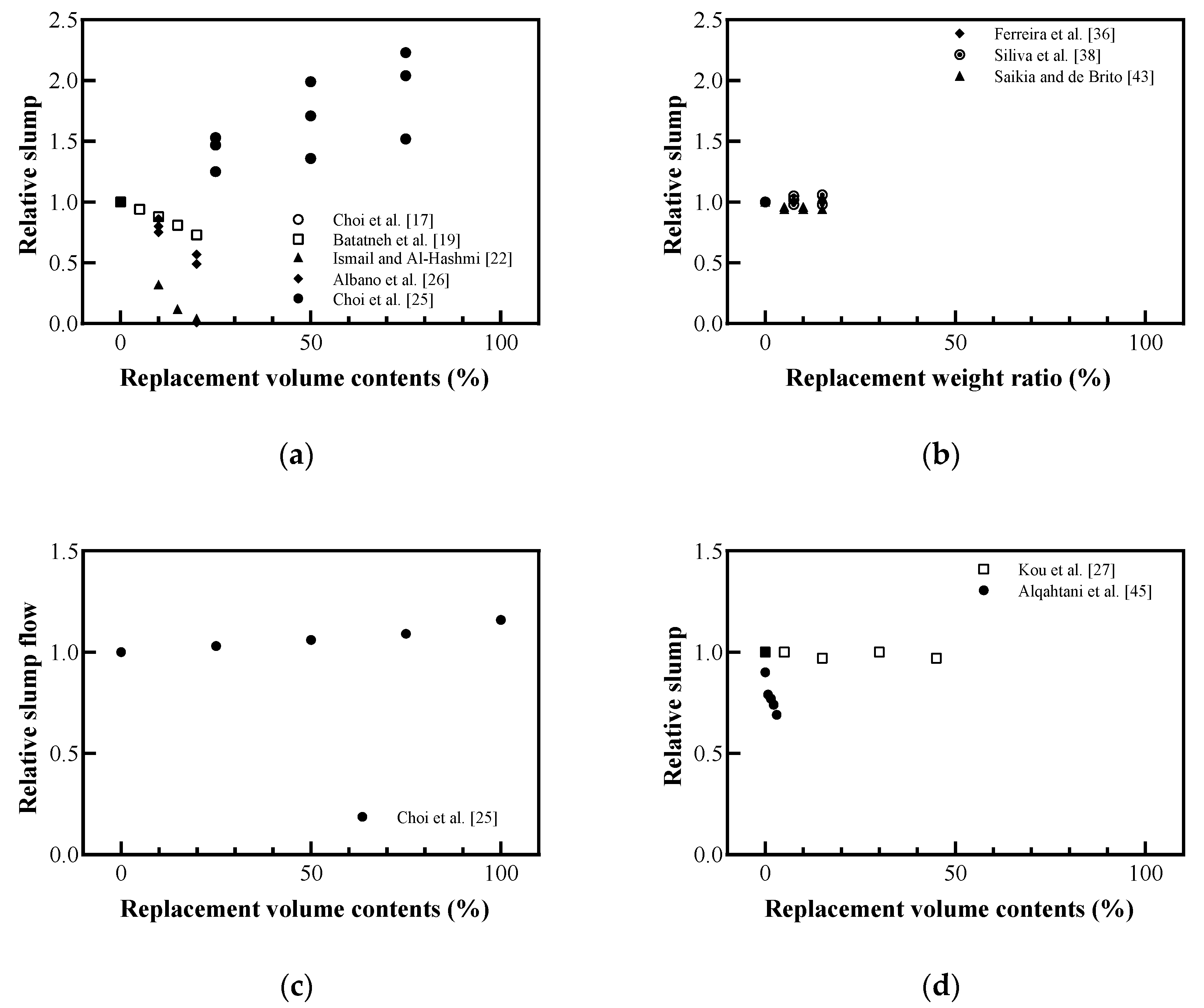
Figure 5 shows the relative slump and slump flow of concrete, mortar, and lightweight concrete based on the plastic aggregate replacement ratio. The slump and slump flow indicate the workability of cement-based materials. Most results (except Choi et al. [17] and Choi et al. [25]) show that workability decreases as the amount of plastic aggregate increases. Albano et al. [26] attributed this tendency to the low water absorption of the plastic aggregate, which is 0.1% compared to 1.83% for the cement aggregate. Because there is scope to reduce the water content in the mixture, the remaining water that did not react with the cement increased its porosity, thereby reducing the workability of the mixture. Further, Saikia and de Brito [43] prepared plastic waste in fine, coarse, and pellet shapes; they found that workability decreased for the irregularly shaped aggregates made by crushing or shredding, regardless of their size. However, workability increased for the pellet-shaped plastic that had a smooth surface. Choi et al. [25] reported that mixing plastic and river sand filler to produce a smooth and round aggregate reduced friction, which resulted in a tendency to increase workability. Thus, the shape of the plastic aggregate is an important factor to improve the workability of cement-based materials replaced with plastic aggregates.
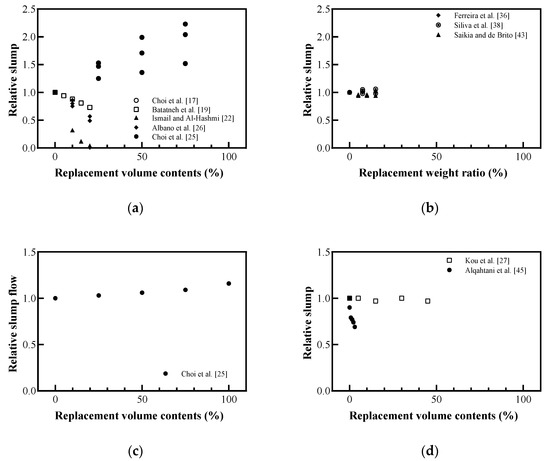
Figure 5.
Relative workability with plastic aggregates: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in mortar; (d) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Choi et al. [17], Batayneh et al. [19], Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22], Choi et al. [25], Albano et al. [26], Kou et al. [27], Ferreira et al. [36], Silva et al. [38], Saikia and de Brito [43], Alqahtani et al. [45]).
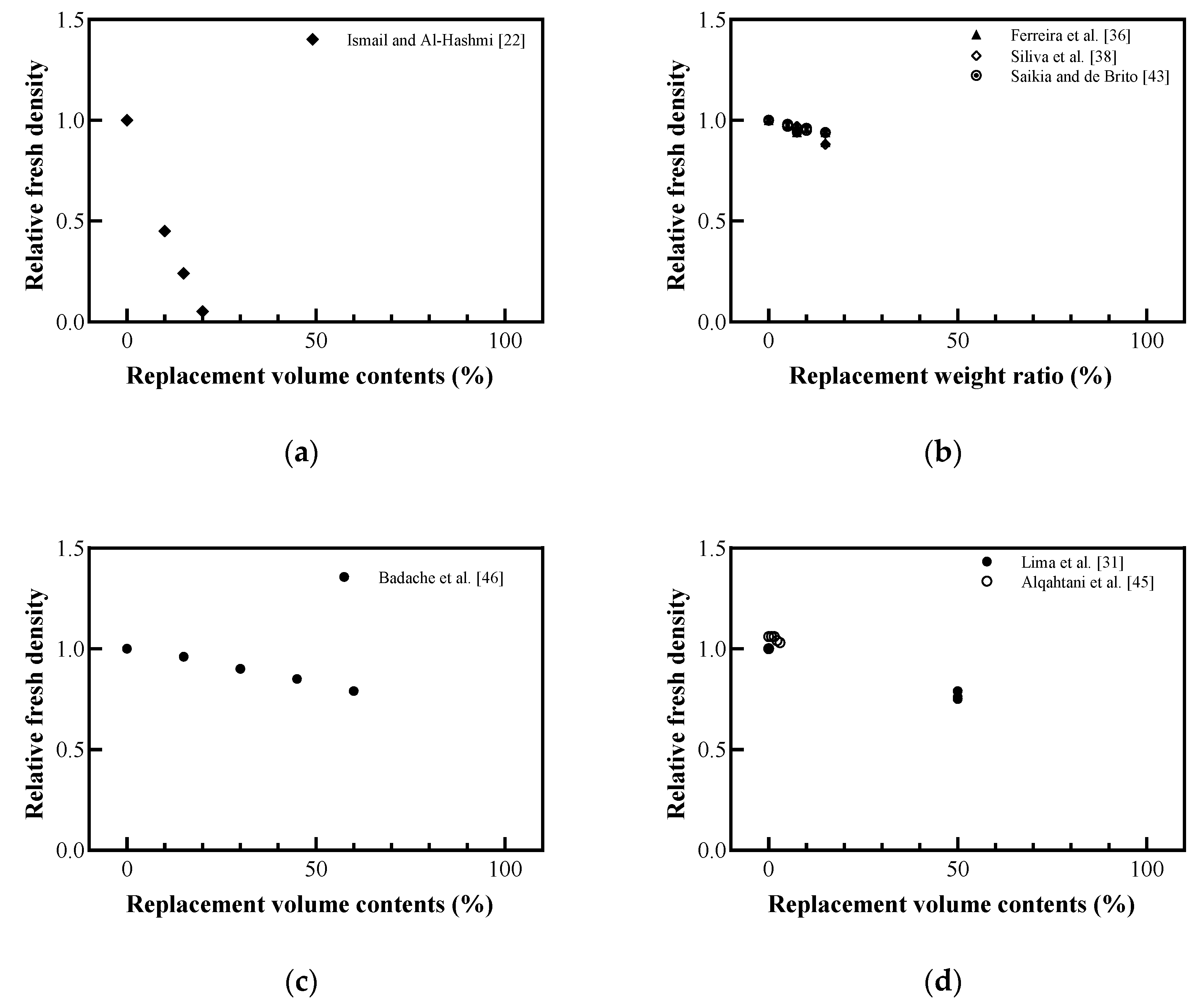
Figure 6 shows the effect of plastic aggregate replacement on the fresh density of concrete. As the replacement contents of plastic aggregates increased, the fresh density decreased, and there was a difference in the amount of reduction depending on the replacement target. Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22] reported that, when PE aggregates with a density of 386.7 kg/m3 replaced fine aggregates with a density of 1688 kg/m3, it caused a reduction in the fresh density of concrete by ~93%. When the fine aggregate was replaced by weight ratio, the decrease in fresh density was relatively less than when substituted by the volume ratio. Badache et al. [46] observed a relatively small decrease compared to the results of Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22] using HDPE with a density of 922 kg/m3 as a fine aggregate. As shown in Figure 6d, lightweight concrete replaced with a coarse aggregate showed a smaller reduction in fresh density than that with a fine aggregate. In particular, Alqahtani et al. [45] reported the tendency of a slight increase in the fresh density caused by substituting a lightweight aggregate with a density of 1410 kg/m3 with an aggregate made of a plastic material with a density of 1540 kg/m3.
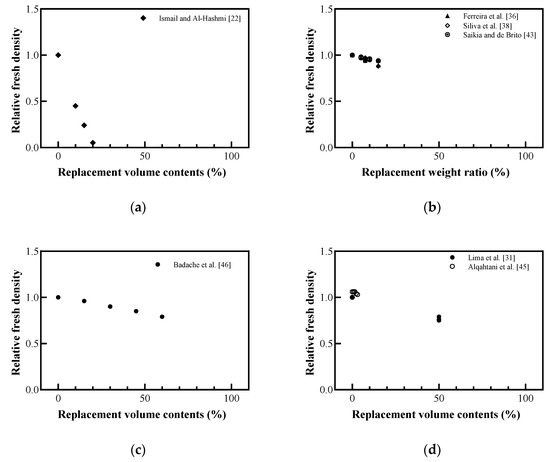
Figure 6.
Relative fresh density with plastic aggregates: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in mortar; (d) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22], Lima et al. [31], Ferreira et al. [36], Silva et al. [38], Saikia and de Brito [43], Alqahtani et al. [45], Badache et al. [46]).
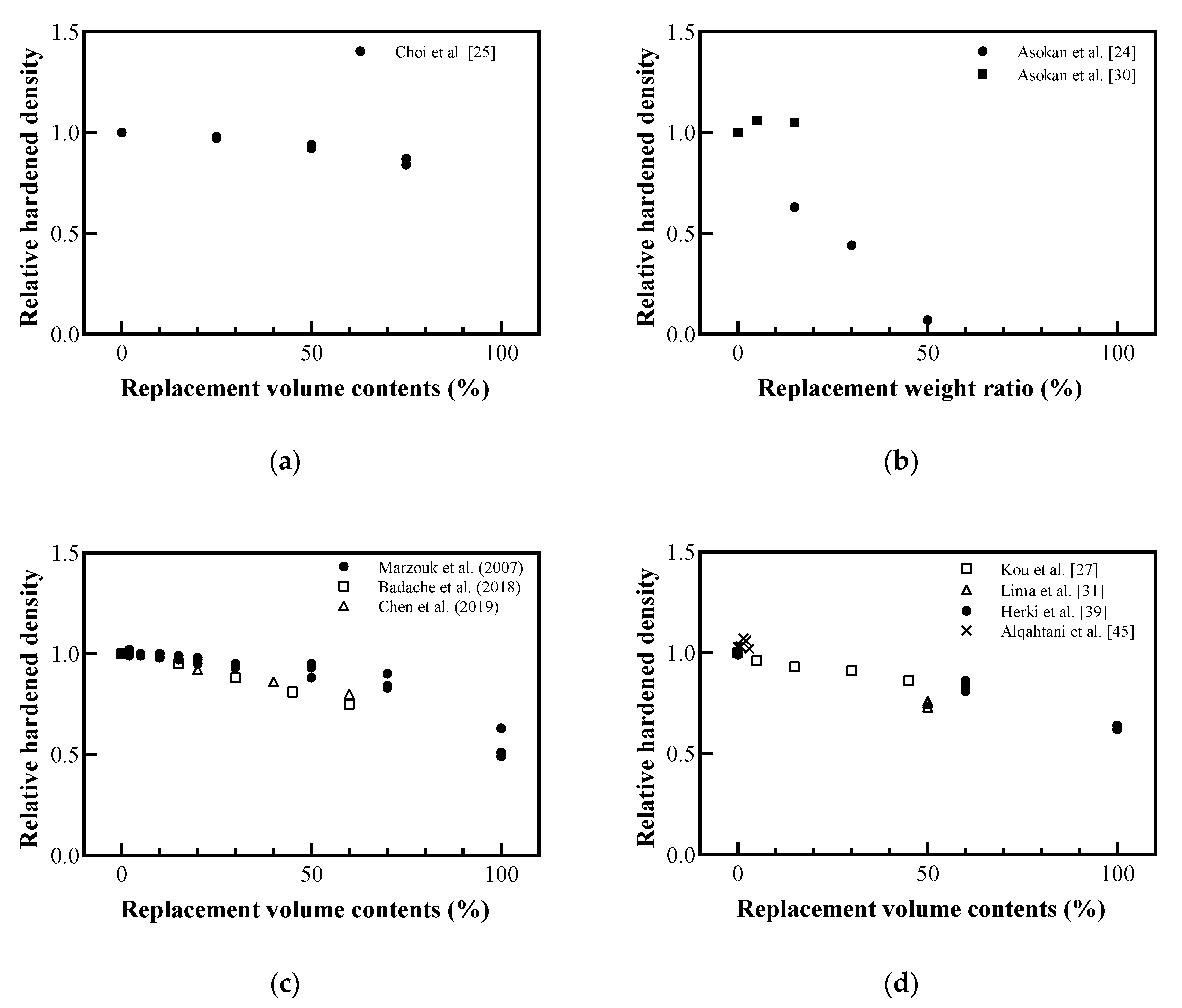
In addition, hardened density, as shown in Figure 7, also differed based on the difference between the densities of the plastic aggregate and the replaced aggregate. Asokan et al. [24] reported that recycled GFRP powder, which has a lower density than cement and aggregate, caused the largest reduction in hardened density. Overall, the density of the recycled plastic aggregates decreased the fresh density and hardened density, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Among recycled plastic materials, PET recycled aggregates showed a relatively small reduction, and recycled aggregates produced by mixing plastics with sand fillers showed the least reduction.
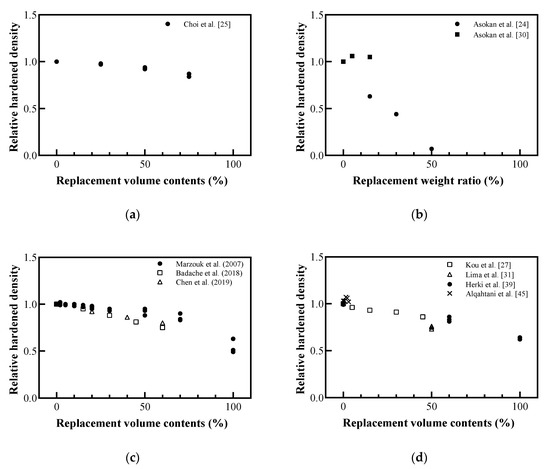
Figure 7.
Relative hardened density with plastic aggregates: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in mortar; (d) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Marzouk et al. [20], Asokan et al. [24], Choi et al. [25], Kou et al. [27], Asokan et al. [30], Lima et al. [31], Herki et al. [39], Alqahtani et al. [45], Badache et al. [46], Chen [47]).
When recycled plastic is used as a fiber, workability and density are reduced similarly to when used as an aggregate. However, the advantage of the fiber geometry is that the resistance to shrinkage is improved. In general, the concrete using recycled plastic aggregate shows a higher shrinkage than that of concrete using natural aggregate, which is reported to decrease resistance to shrinkage owing to the low stiffness of the plastic aggregate [29,33,75]. However, it has been reported that the shrinkage generally decreases when the fiber form is used [48,76]. The shape of the fiber is reduced by the interfacial shear resistance between the fiber and the matrix resisting the tensile force caused by the shrinkage [77]. Besides, the crack width and total crack area, owing to the plastic shrinkage, decrease as the volume ratio of recycled fibers increases [51,76,78,79,80]. Kim et al. [51] reported that fiber geometry affected the ability to control plastic shrinkage cracking due to the difference in bond strength. In contrast, they also reported that a sufficient number of fibers, when the fiber volume ratio exceeds 0.5%, were incorporated to control plastic shrinkage cracking; hence, the fiber geometry had no further effect [51].
3.1.2. Effect of Recycled Plastic Fibers
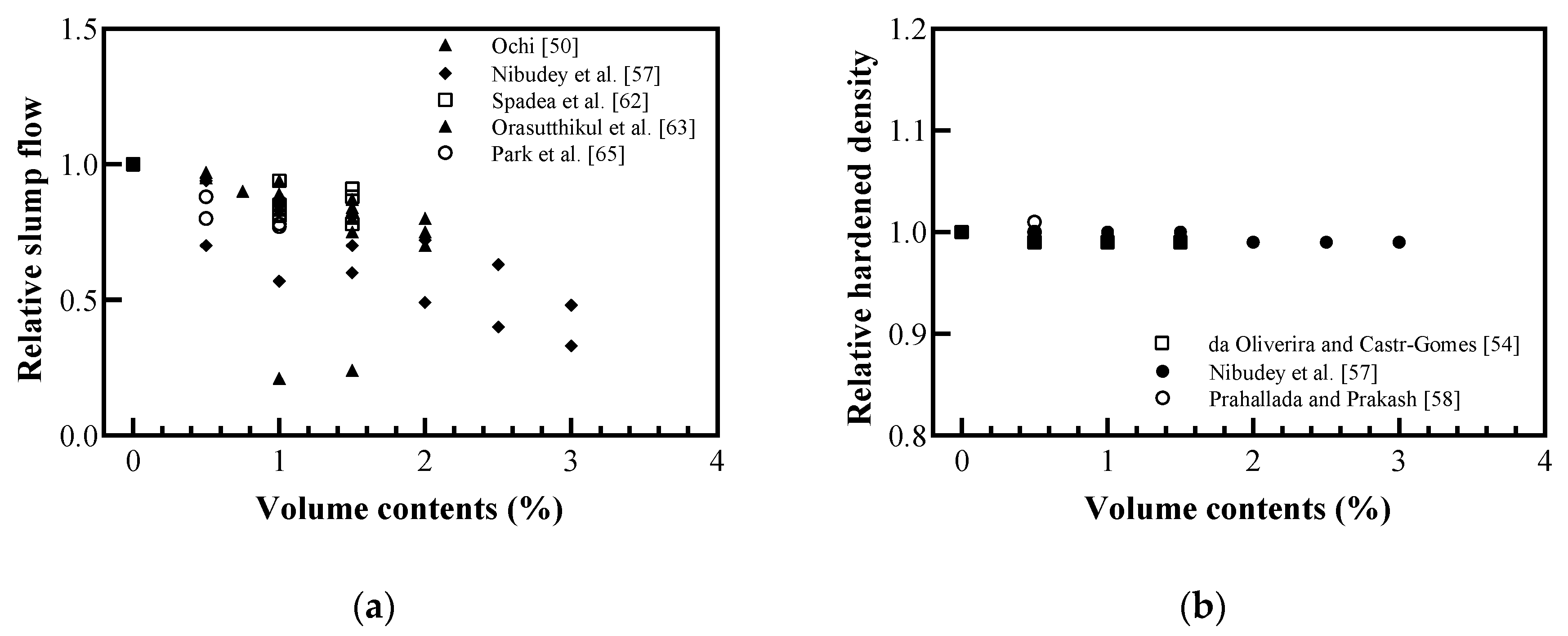
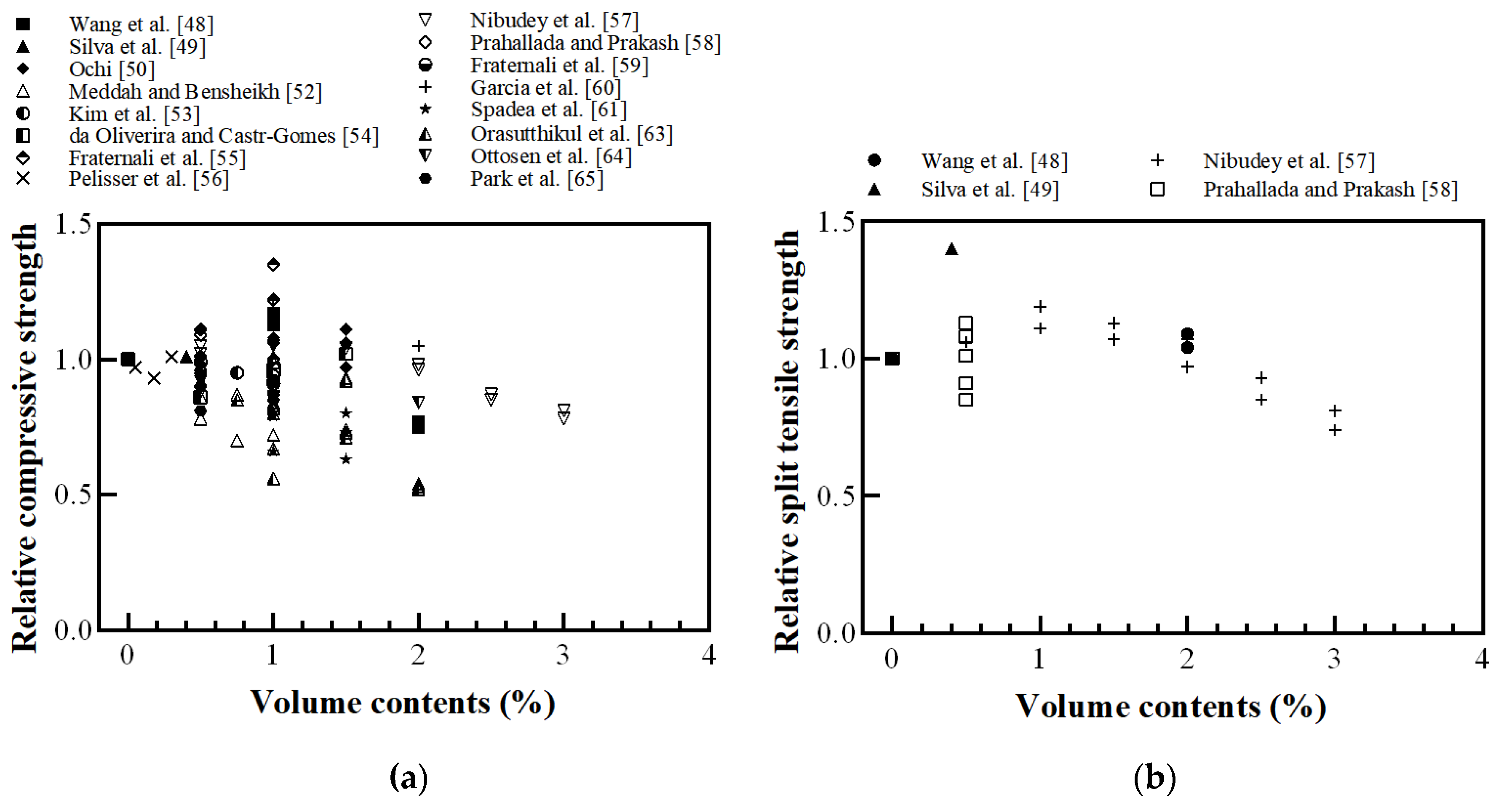
Figure 8 shows the relative slump flow and hardened density based on the volume contents of the recycled plastic fibers. As shown in Figure 8a, slump flow decreases as the plastic fiber content increases. Nibudey et al. [57] concluded that the workability property of fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) was affected by the resistance offered by the fibers to the movement of aggregates. Orasutthikul et al. [63] reported that fiber geometry affected the slump flow because of fiber balling, which resulted in fiber–mortar separation. Thus, the addition of recycled plastic reduced the workability. If the fiber geometry, which is prone to the agglomeration of fibers, was used, it showed a higher slump flow for the same content than that using well-dispersed fibers because of the fiber–mortar separation. As shown in Figure 8b, the hardened density of the FRC decreased as the fiber volume of the plastic fiber volume content increased; furthermore, there was no significant reduction in the hardened density of the plastic FRC compared to the density of conventional concrete (without plastic fibers). The small reduction compared to that for the plastic recycled aggregate is because the fiber had a minimal volume content (0.5–3%).
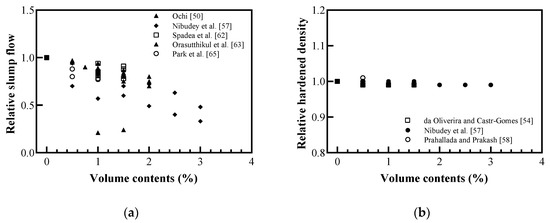
Figure 8.
Relative physical properties of fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) with recycled plastic fiber: (a) slump flow; (b) hardened density (redrawn using Ochi [50], de Oliveira and Castro-Gomes [54], Nibudey et al. [57], Prahallada and Prakash [58], Spadea et al. [62], Orasutthikul et al. [63], Park et al. [65]).
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.2.1. Effect of Recycled Plastic Aggregate
Figure 9 shows the effect of using recycled plastic aggregate on compressive strength. In most studies, as the substitution rate of plastic recycled aggregate increased, the compressive strength decreased.
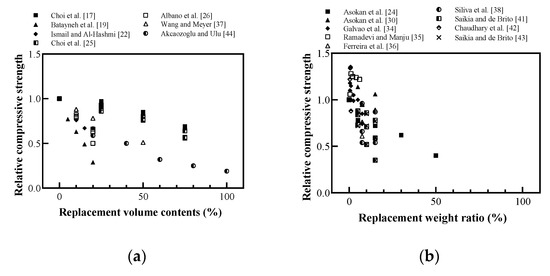
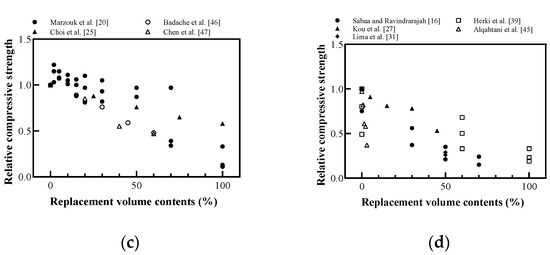
Figure 9.
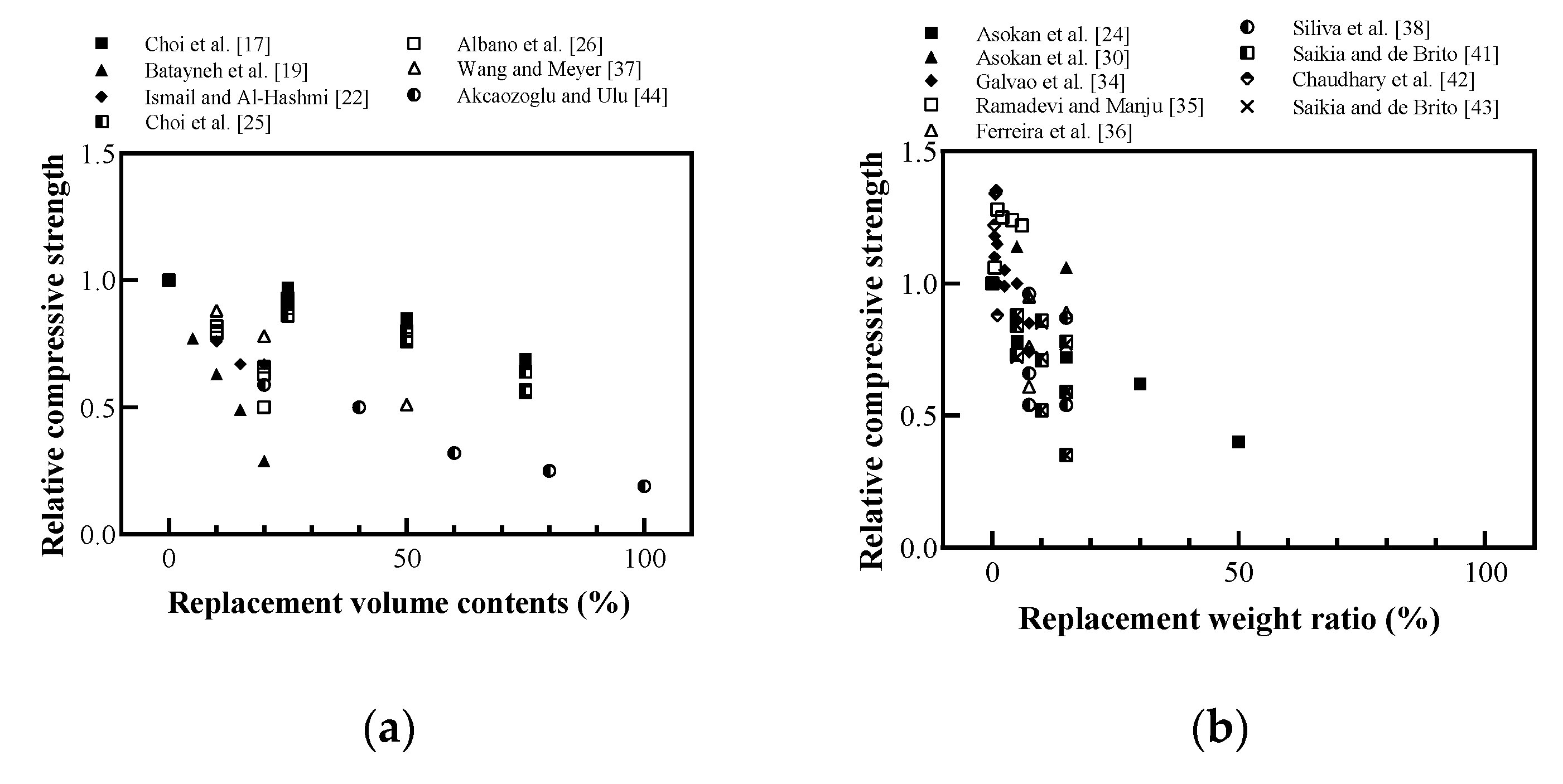
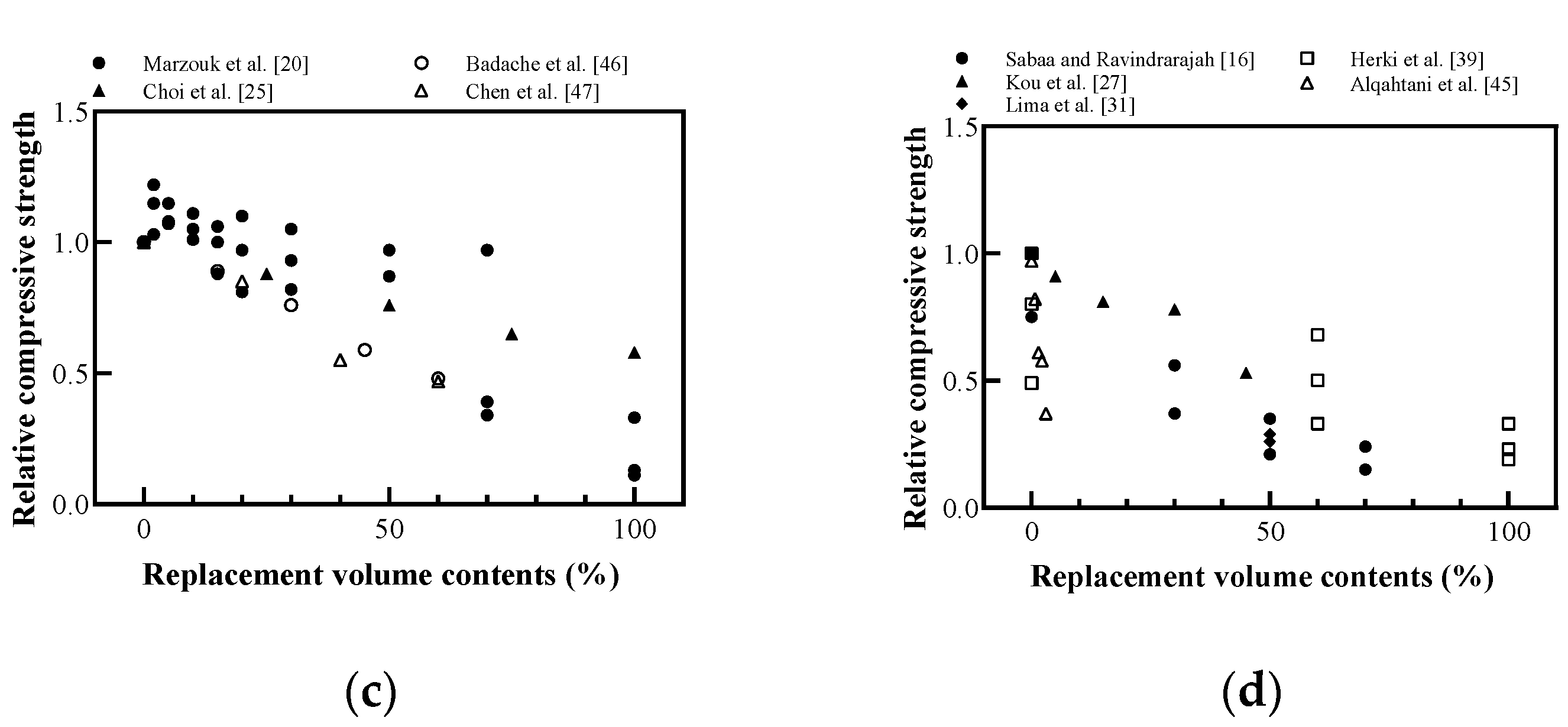
Relative compressive strength of cement-based materials with recycled plastic aggregate: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in mortar; (d) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Sabaa and Ravindrarajah [16], Choi et al. [17], Batayneh et al. [19], Marzouk et al. [20], Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22], Asokan et al. [24], Choi et al. [25], Albano et al. [26], Kou et al. [27], Asokan et al. [30], Lima et al. [31], Galvão et al. [34], Ramadevi and Manju [35], Ferreira et al. [36], Wang and Meyer [37], Silva et al. [38], Herki et al. [39], Saikia and de Brito [41], Chaudhary et al. [42], Saikia and de Brito [43], Akçaözoğlu and Ulu [44], Alqahtani et al. [45], Badache et al. [46], Chen et al. [47]).
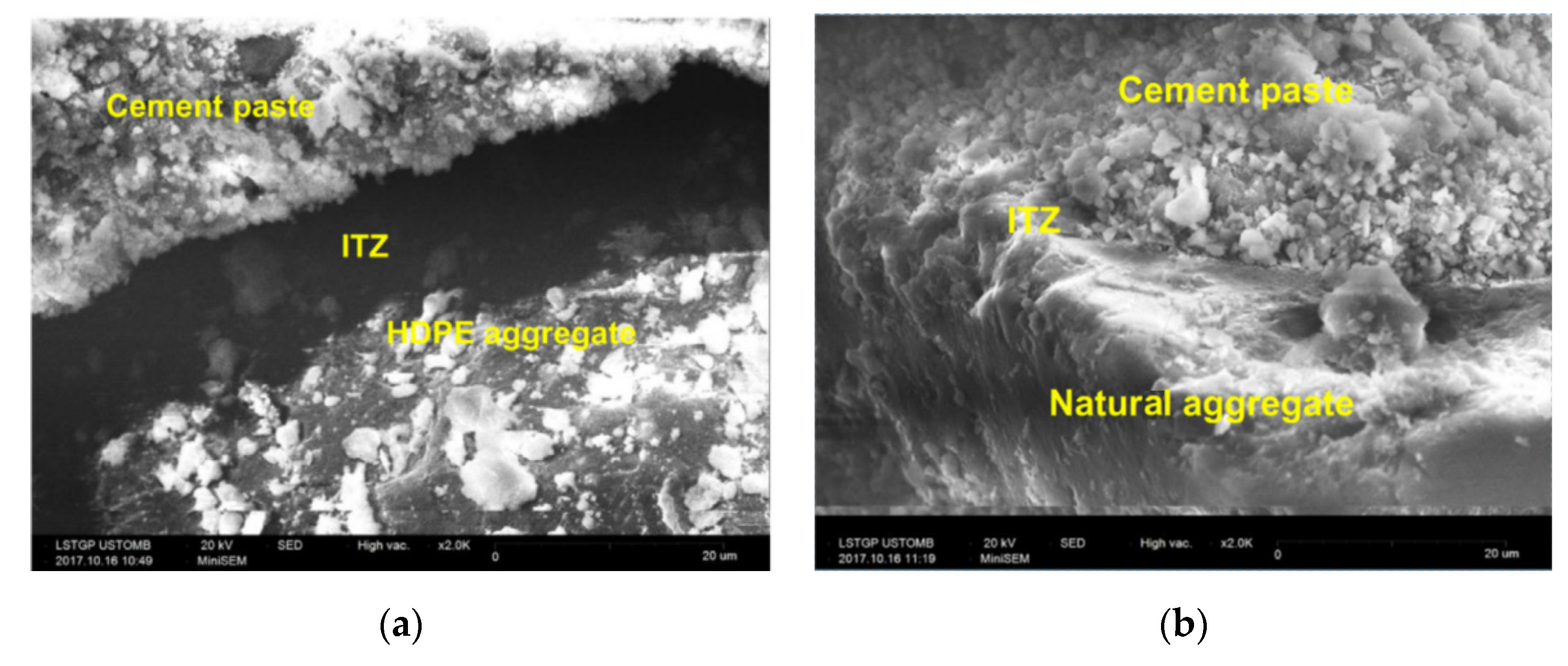
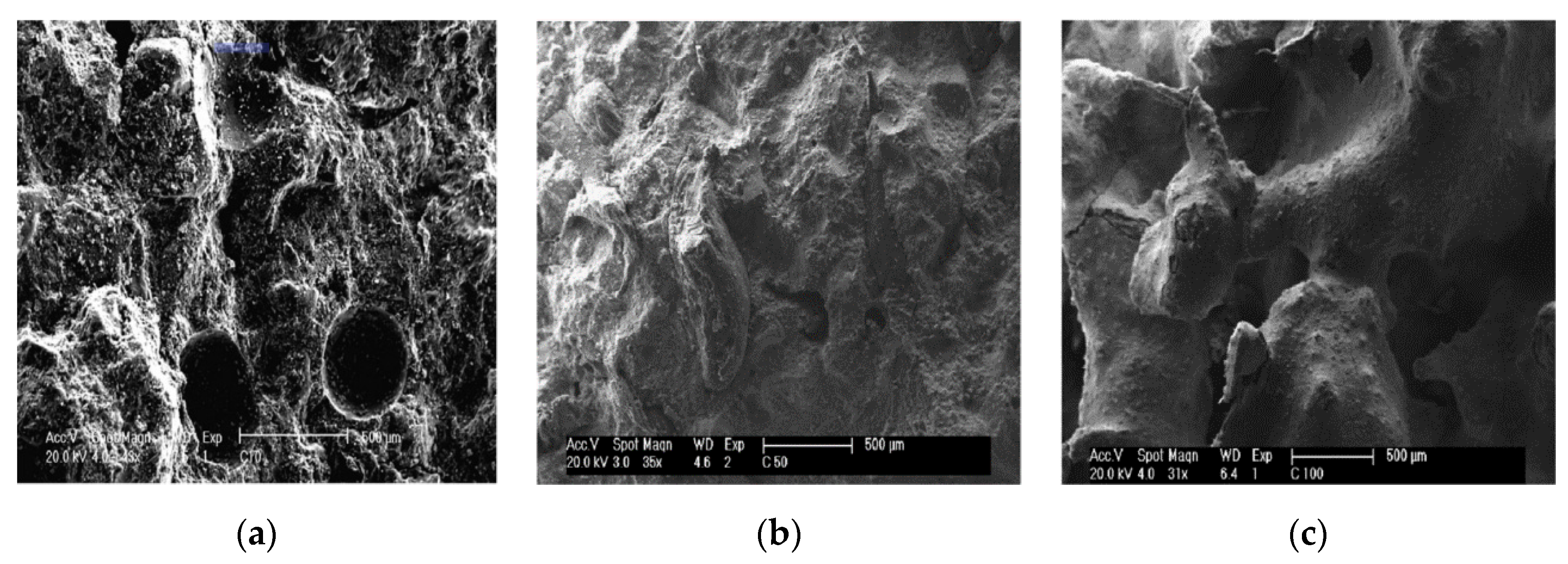
Badache et al. [46] used scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to prove that a decrease in compressive strength was caused by the low density of recycled plastic aggregates, and the interface between the plastic surface and cement-based materials was weaker than in the aggregate, as shown in Figure 10. However, as shown in Figure 9b, concrete with a weight ratio of less than 5% showed higher compressive strength than conventional concrete; however, it was impossible to explain this tendency. Some researchers concluded that there is a small amount of approximately 2% weight ratio replacement [30,34,35,42].
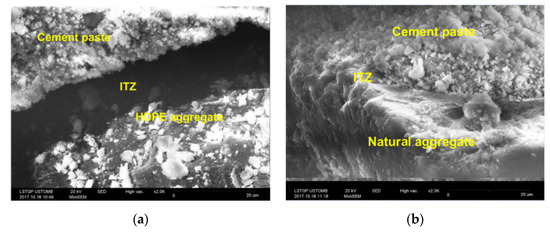
Figure 10.
SEM images of mortar composites: (a) HDPE aggregate; (b) naturel aggregate [46].
Marzouk et al. [20] analyzed the microstructure of the mortar using SEM and reported that the replacement volume contents of PET aggregates showed a high level of compressibility at 50% or less; furthermore, the porosity of the structure increased when it exceeded 50%, as shown in Figure 11.
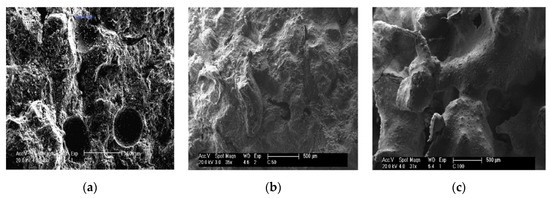
Figure 11.
SEM images of mortar composites containing PET aggregates: (a) 30%; (b) 50%, and (c) 100% [20].
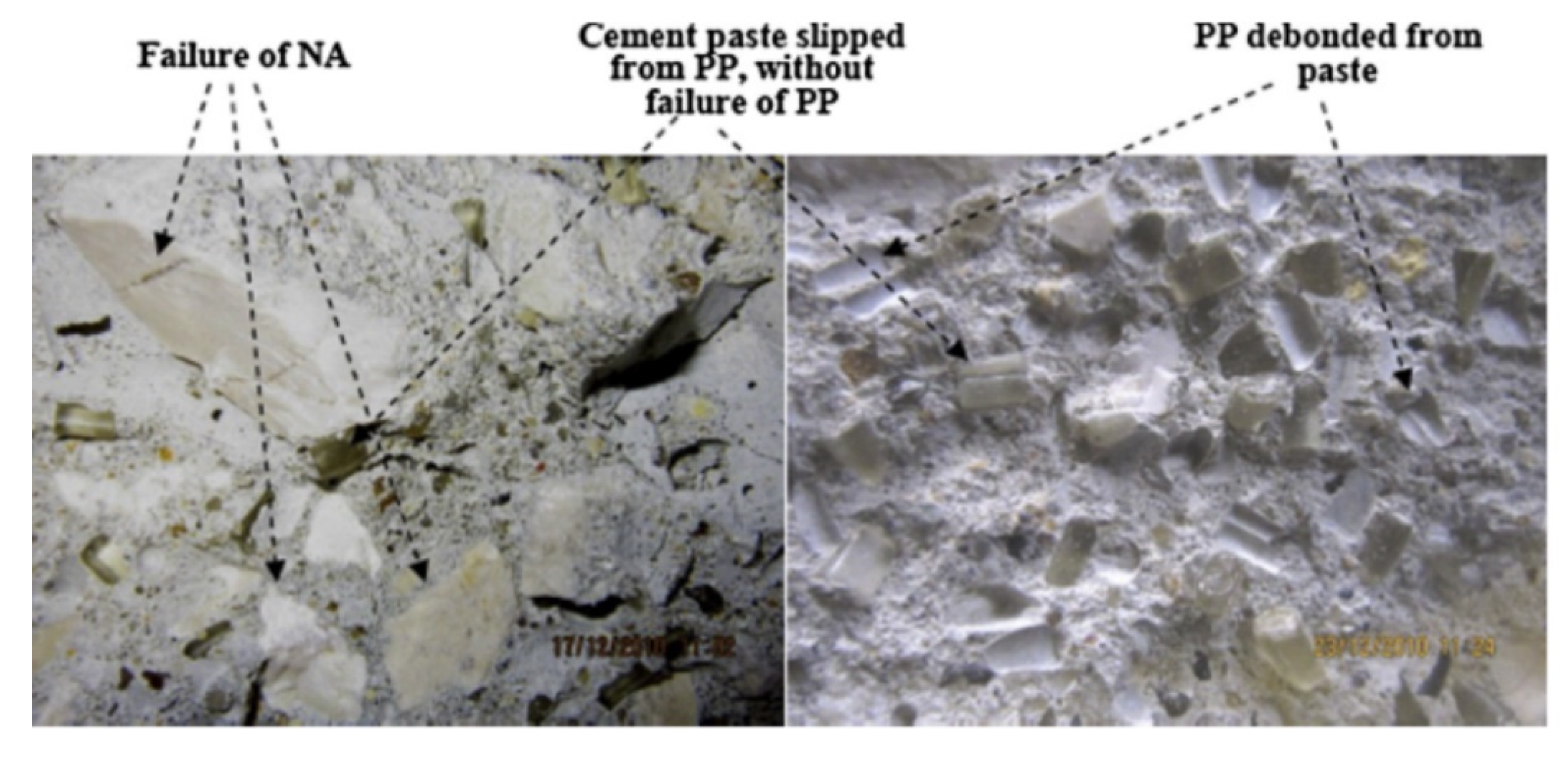
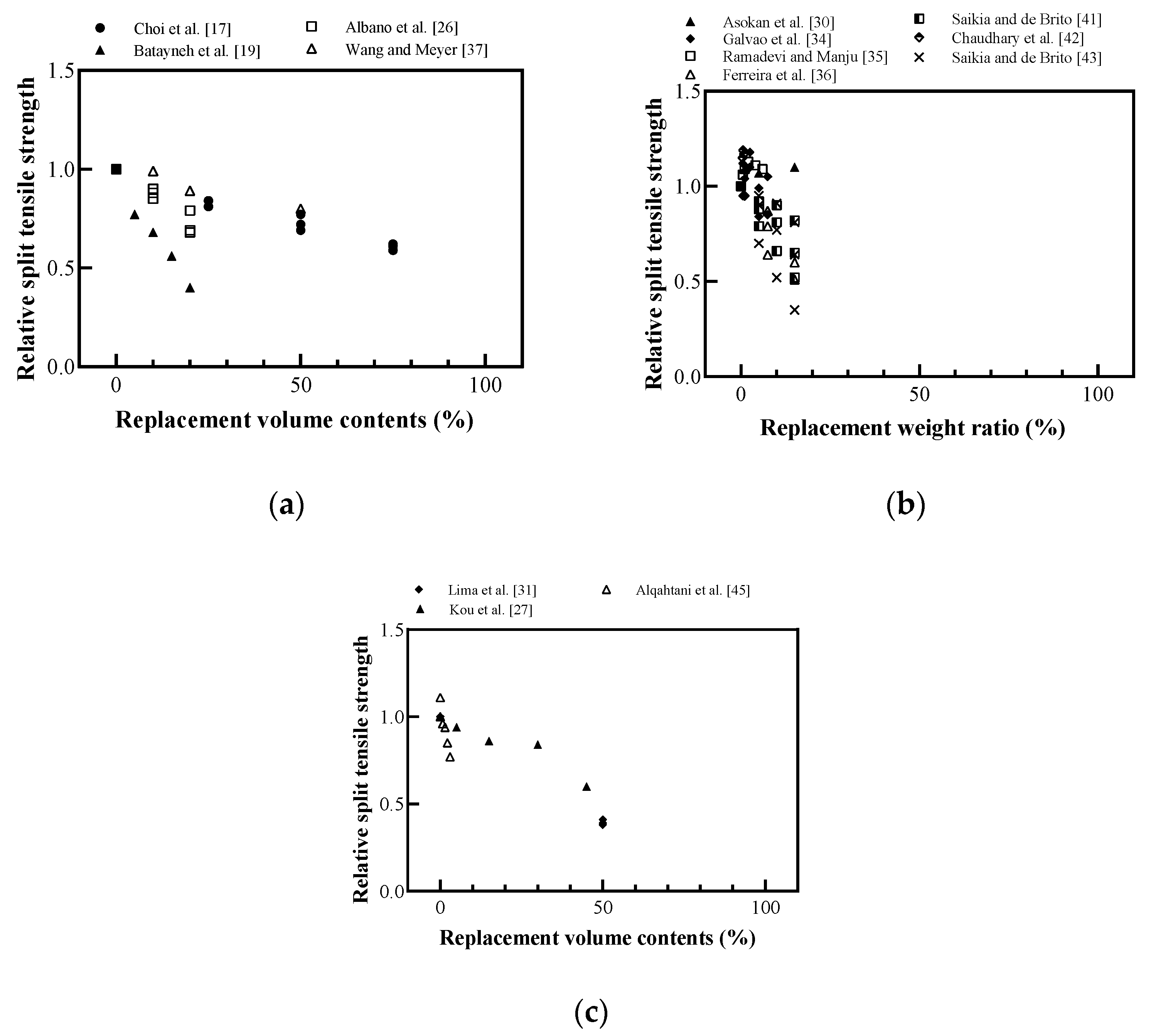
Figure 12 shows the effect of plastic aggregates on the split tensile strength of cement-based materials. The split tensile strength decreased as the replacement ratio of the plastic aggregate increased. Most researchers attributed the decrease in the split tensile strength to the decrease in the adhesion between the plastic aggregate and the cement-based material [26,27,36,41]. Saikia and de Brito [43] reported that the smooth surface of the plastic aggregate and the free water at the surface of the plastic aggregate can cause a weaker bonding between these particles and the cement paste, as shown in Figure 13. When fine aggregates were replaced with plastic aggregates at the same water–cement ratio, free water that did not react with the cement increased because of the decreased water absorption, thereby causing increased porosity, and consequently decreased tensile strength.
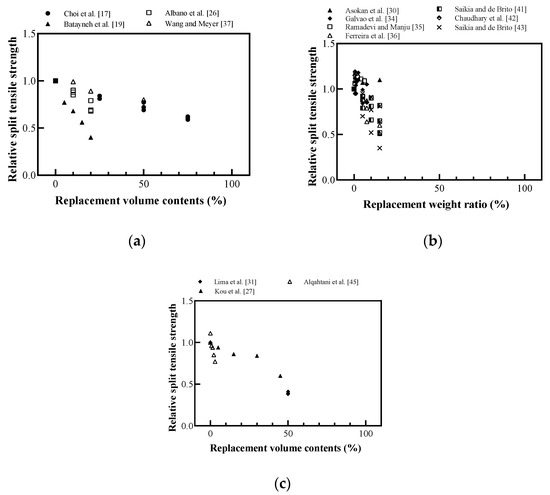
Figure 12.
Relative split tensile strength of cement-based materials with recycled plastic aggregate: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Choi et al. [17], Batayneh et al. [19], Asokan et al. [24], Albano et al. [26], Kou et al. [27], Lima et al. [31], Galvão et al. [34], Ramadevi and Manju [35], Ferreira et al. [36], Wang and Meyer [37], Saikia and de Brito [41], Chaudhary et al. [42], Saikia and de Brito [43], Alqahtani et al. [45]).
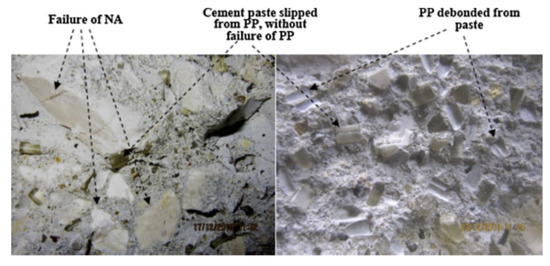
Figure 13.
Concrete specimens with plastic aggregate after failure in the splitting strength test [43].
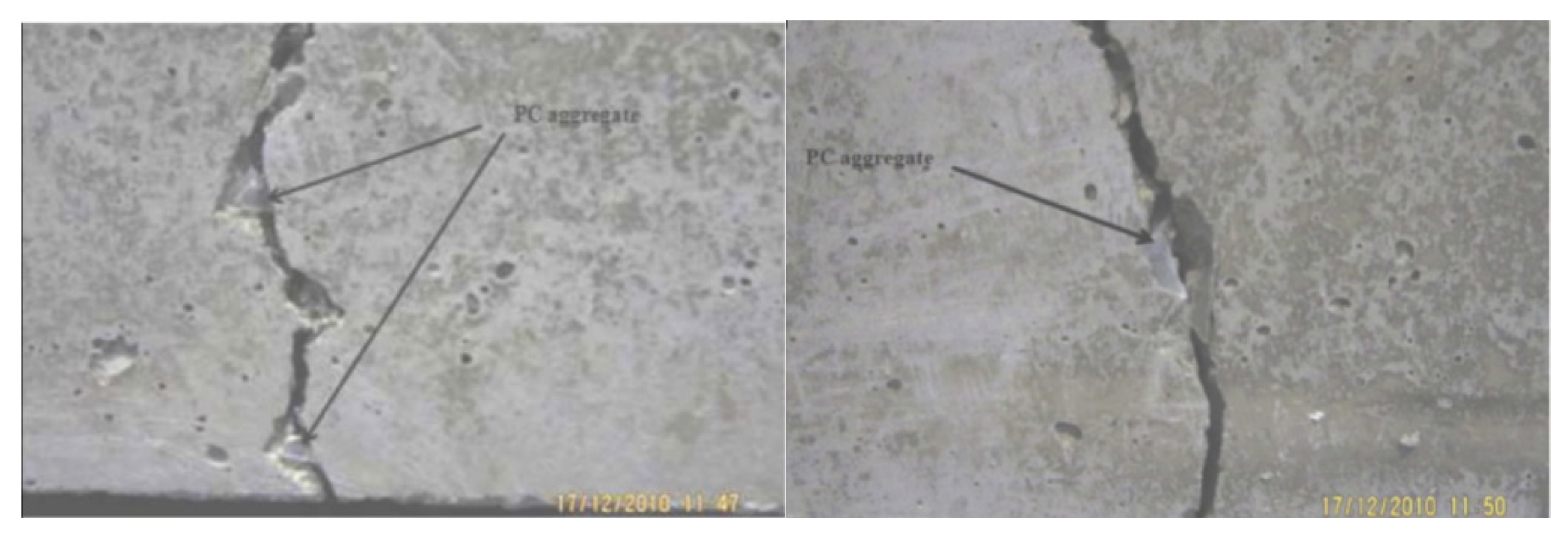
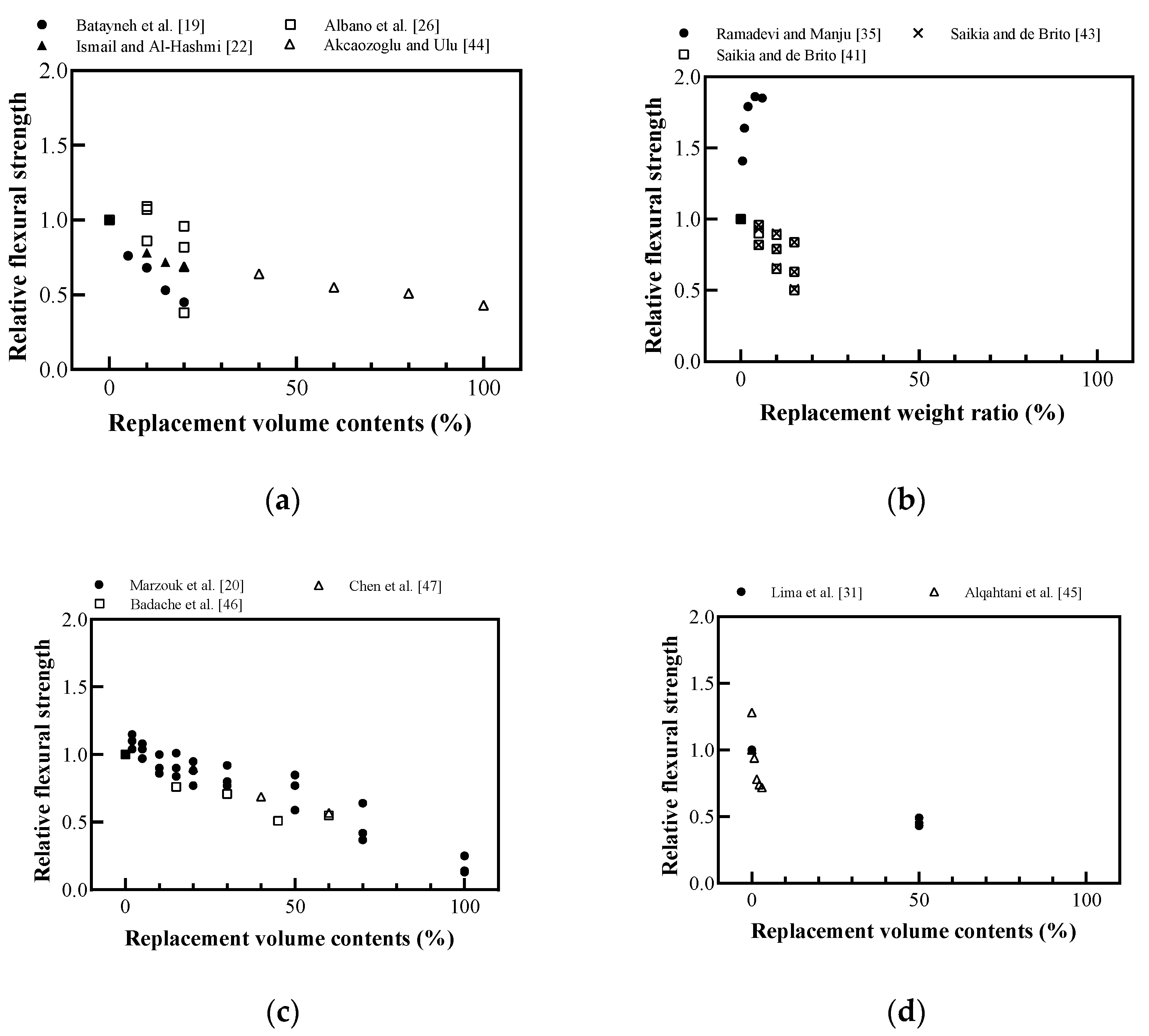
Figure 14 shows the effect of the plastic aggregate on the flexural strength of cement-based materials. Flexural strength also showed the same tendency as compressive strength and split tensile strength. Saikia and de Brito [43] reported that crushed plastic aggregates bridged cracks and prevented the brittle failure of the specimens, as shown in Figure 15.
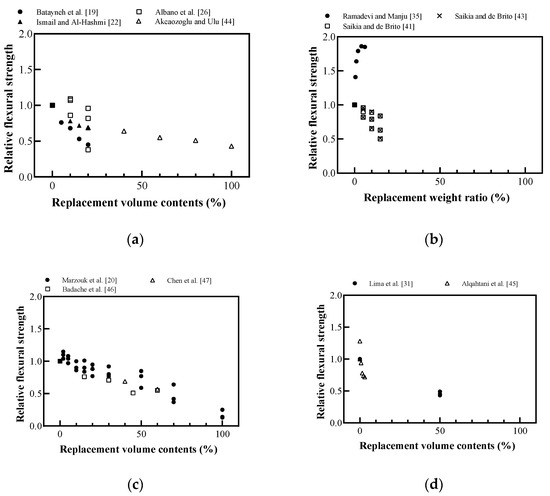
Figure 14.
Relative flexural strength of cement-based materials with recycled plastic aggregate: (a) replaced volume in concrete; (b) replaced weight in concrete; (c) replaced volume in mortar; (d) replaced volume in lightweight concrete (redrawn using Batayneh et al. [19], Marzouk et al. [20], Ismail and Al-Hashmi [22], Albano et al. [26], Lima et al. [31], Ramadevi and Manju [35], Saikia and de Brito [41], Saikia and de Brito [43], Akçaözoğlu and Ulu [44], Alqahtani et al. [45], Badache et al. [46], Chen et al. [47]).

Figure 15.
Cracking in a concrete specimen containing crushed plastic aggregate after flexural test [43].
3.2.2. Effect of Recycled Plastic Fibers
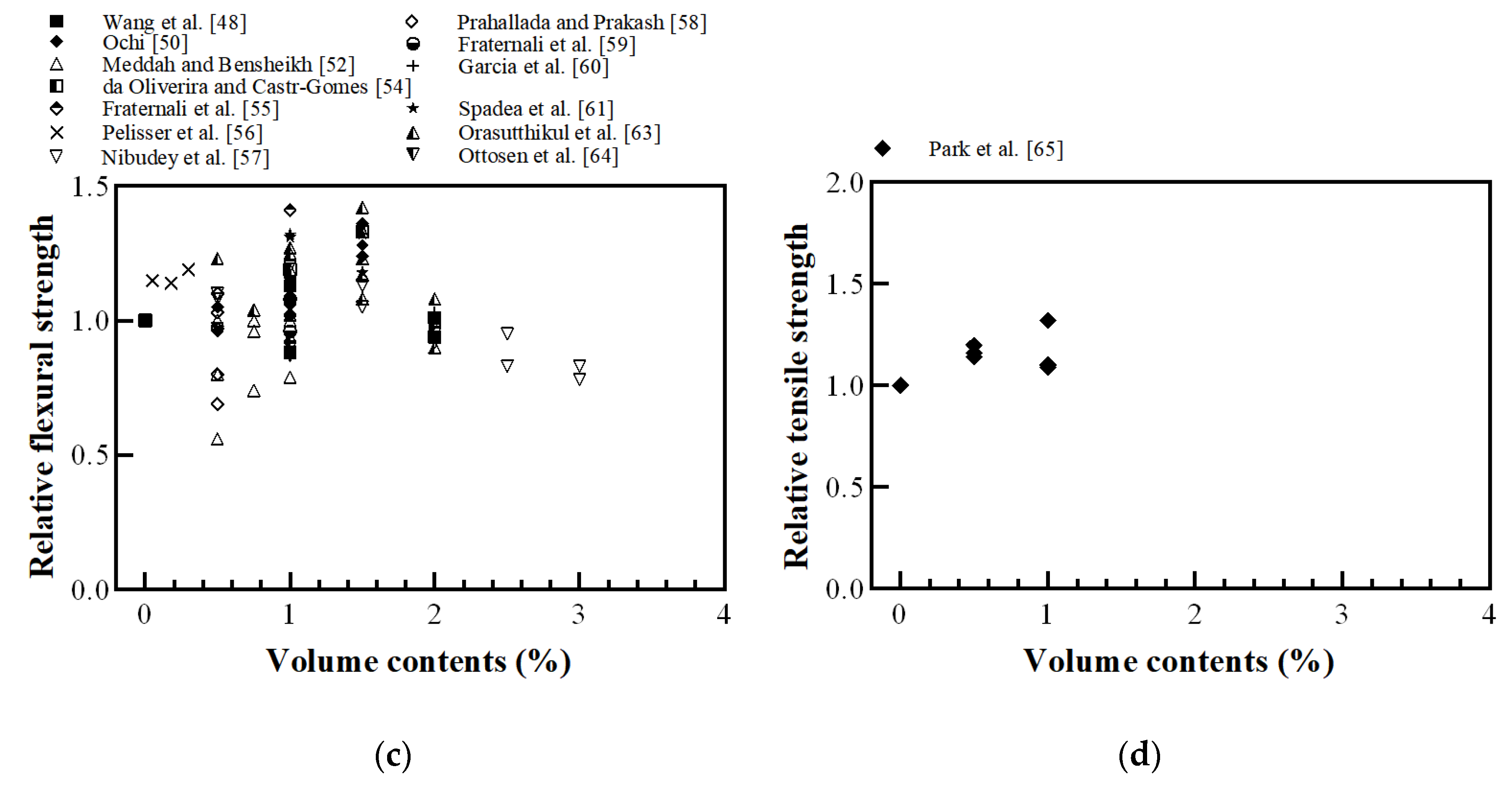
Figure 16 shows the effect of recycled plastic fibers on the mechanical properties of FRC. When the volume ratio of recycled plastic FRC exceeded 2%, the compressive strength tended to be lower than that of cement-based materials without fiber, as shown in Figure 16a. However, up to 2%, the mechanical properties showed different trends depending on the shape of the recycled plastic fibers. Fraternali et al. [55] reported that when 1% of different recycled PET fibers was added, the compressive strength increased when the specific gravity of the recycled PET FRC was higher than that of the conventional concrete without fibers. Spadea et al. [62] reported that the compressive strength decreased because highly deformable plastic fibers may assume the role of voids in the cementitious matrix when compressive forces are applied. Prahallada and Prakash [58] reported that the aspect ratio of fiber increased over 50, and the compressive strength decreased at the same volume contents. Therefore, the compressive strength of recycled plastic FRC is related to the fiber density and aspect ratio.
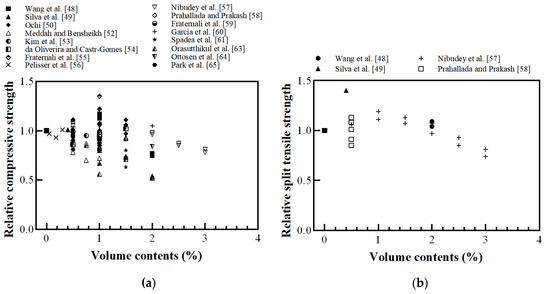
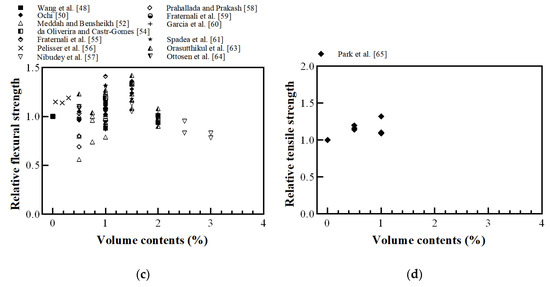
Figure 16.
Relative mechanical properties of FRC with recycled plastic fiber: (a) compressive strength; (b) spilt tensile strength; (c) flexural strength; (d) direct tensile strength (Wang et al. [48], Silva et al. [49], Ochi [50], Meddah and Bensheikh [52], Kim et al. [53], de Oliveira and Castro-Gomes [54], Fraternali et al. [55], Pelisser et al. [56], Nibudey et al. [57], Prahallada and Prakash [58], Fraternali et al. [59], García et al. [60], Spadea et al. [62], Orasutthikul et al. [63], Ottosen et al. [64], Park et al. [65]).
The split tensile strength and flexural strength increased as the fiber volume content increased by 1% and 1.5%, respectively. However, as the fiber volume increased from 1.5% to 3.0%, the flexural strength decreased [49,57,63]. Orasutthikul et al. [63] reported the forming ball problem when higher fiber volume contents were used or when the fiber was not well distributed, which directly affected the flexural strength.
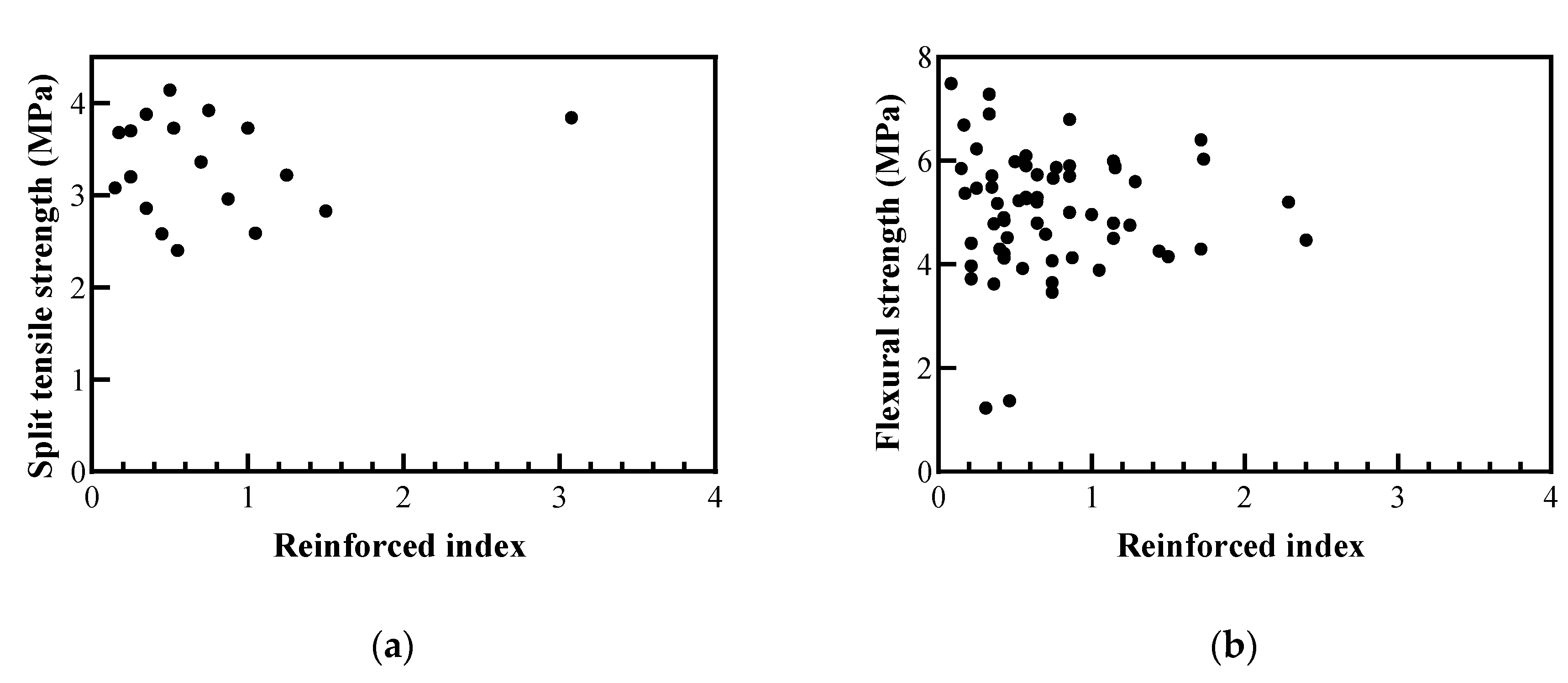
To confirm the appropriate fiber aspect ratio and fiber volume ratio, the reinforced index was calculated as
where Vf, Lf, Df, and Lf/Df are the fiber volume content, fiber length, fiber diameter, and aspect ratio. The relationship between the split tensile strength and flexural strength is shown in Figure 17.
Reinforced index = Vf Lf / Df = Vf
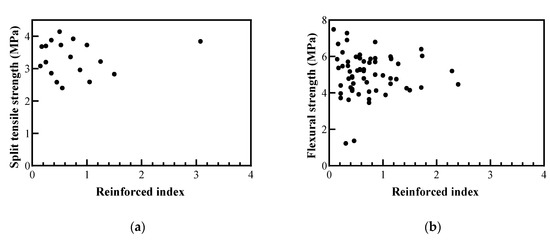
Figure 17.
Effect of fiber reinforced index: (a) on split tensile strength; (b) on flexural strength.
Yu et al. [69] reported that the tensile strength of FRC increased as the fiber-reinforced index increased. However, the split tensile strength and flexural strength of the recycled plastic FRC were not significantly related to the reinforced index. Therefore, it is necessary to study why recycled plastic fiber reinforcement has no effect on the reinforced index and to determine how to fabricate recycled plastic fibers to improve tensile strength. Although Park et al. [65] conducted a direct tensile test using recycled waste fishing nets, as shown in Figure 16d, the direct tensile test results are still insufficient, and the analysis remains difficult. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a direct tensile test on recycled plastic fibers in future studies.
3.3. Comparison of Properties Between Virgin and Recycled Plastics for Construction Materials
In the study, in which virgin plastic was used as an aggregate, EPS material was mainly used to manufacture lightweight concrete. In recent years, research on manufacturing aggregates from virgin plastic has not been actively conducted. The reason is that even if virgin plastic is used, the disadvantages of recycled plastic aggregate cannot be overcome and the strength decrease due to density reduction occurs equally [23]. However, Alqahtani et al. [45] reported that the density of concrete with recycled LLDPE aggregate, which replaced volcanic lightweight coarse aggregate, increased, while compressive strength, flexural strength, and splitting tensile strength decreased by 15–62%, 27–44%, and 12–31%, respectively. Studies on recycled plastic aggregates to produce lightweight concrete are continuously being published; however, plastic aggregates are not widely used.
On the other hand, virgin plastic fibers have been used in specific structures such as high-rise buildings, protection facilities, tunnel lining, foundations, and concrete pavements [69,81,82,83,84,85,86]. PP is a representative plastic virgin material used to reinforce the tensile resistance of cement-based materials, and PET and PE are typically used for recycling [87]. These virgin plastic fibers and recycled fibers are the same in that they are plastic materials, but the decrease in tensile strength is minor compared to fibers of the same material during the recycling process [73,88]. Hence, there are studies examining the mechanical behavior of currently used virgin plastic fibers and recycled plastic fibers in cement-based materials [53,55,63]. Kim et al. [53] compared the performance of recycled PET fiber and concrete reinforced with commercial PP fiber. As a result of the comparative evaluation, which led to similar results at the same amount of volume ratio when using PET recycled fibers compared to PP virgin fibers, they concluded that the use of recycled fibers was possible. Fraternali et al. [55] performed a comparative evaluation by using reinforcing recycled PET fiber and commercial PP fiber in concrete. As a result, high-strength PET fiber can significantly increase the compressive and flexural strength compared to unreinforced concrete and PP fiber-reinforced concrete. However, corrugated recycled PET fibers have proven to be advantageous in terms of ductility. Orasutthikul et al. [63] compared and evaluated the reinforcing effect of recycled nylon fiber, PET fiber, and virgin PVA fiber. In their results, embossed recycled PET fibers showed higher compressive strength and ductility than virgin PVC fibers. These results indicate that recycled fibers could be used to reinforce the mechanical performance of cement-based materials, and plastics collected from the ocean can also be used to replace virgin plastics with appropriate pretreatment.
4. Concluding Remarks
We investigated existing research on cement-based materials fabricated by recycling plastic waste to confirm whether ocean plastic waste can be used for these materials. The methods and the physical and mechanical properties of plastic recycling were reviewed in detail.
Most studies targeted plastic waste collected on land and, therefore, an automated manufacturing process is required for application to ocean waste. Although some studies have recycled ocean plastics, the manufacturing process was carried out manually. In future studies, a method that can recycle ocean plastics through an automated manufacturing process should be developed. Methods for using recycled plastic for cement-based materials were largely classified into those using aggregates and fibers. Plastic recycled aggregates were used to replace coarse and fine aggregates to reduce the weight of cement-based materials. Plastic recycled fibers were used to enhance the tensile resistance of cement-based materials. Cement-based materials with plastic aggregates and fibers exhibit reduced workability and density. To solve this problem, it is necessary to study a method that can effectively treat the surface of pulverized plastic and an appropriate reinforcing volume ratio of fibers.
As the amount of recycled plastic aggregate increased, the compressive strength, tensile strength, and flexural strength of cement-based materials decreased. The recycled plastic aggregate lowered the density and increased porosity of the cement-based material. Therefore, to use recycled plastic as an aggregate, only materials with a relatively high density among plastic materials should be used; however, this is inefficient, except for special purposes such as lightweight concrete. Recycled plastic fibers reduced the compressive strength but improved the shrinkage resistance and tensile strength; to effectively improve tensile strength, a volume content of less than 1.5% should be added to prevent balling fibers. In some studies, the overall trend was similar to that of virgin plastic fiber, and recycled fibers showed a higher reinforcing effect than virgin plastic fibers. Furthermore, an appropriate aspect ratio should be determined based on the type of plastic to be used. Consequently, ocean plastics for cement-based materials are necessary to automate the recycling process and ensure material consistency after recycling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.O.K.; methodology, M.O.K.; validation, J.K.P.; investigation, J.K.P.; resources, M.O.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K.P.; visualization, J.K.P.; supervision, M.O.K.; project administration, M.O.K.; funding acquisition, M.O.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST), project number PE99833. The authors express their gratitude to the KIOST (385, Haeyang-ro, Yeongdo-gu, Busan 49111, Republic of Korea).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cressey, D. The plastic ocean. Nature 2016, 536, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C.; Tse, H.F.; Fok, L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.I.; Kim, M.O.; Park, J.K. Development of marine waste recycling technologies for the lifetime extension of marine and coastal structures. Mag. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2020, 65, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries. Available online: https://www.meis.go.kr/mli/business/collectStat.do (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S. A Study on Resources Circulation for Marine Debris of Aquaculture Farm; Korea Maritime Institute: Busan, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nonato, R.V.; Mantelatto, P.E.; Rossell, C.E.V. Integrated production of biodegradable plastic, sugar and ethanol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khardenavis, A.A.; Kumar, M.S.; Mudliar, S.N.; Chakrabarti, T. Biotechnological conversion of agro-industrial wastewaters into biodegradable plastic, poly b-hydroxybutyrate. Biores. Technol. 2007, 98, 3579–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestria, E.; Menicaglia, V.; Ligorinia, V.; Fulignatib, S.; Gallettib, A.M.R.; Lardicci, C. Phytotoxicity assessment of conventional and biodegradable plastic bags using seed germination test. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Phil. Trans. R Soc. B. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Products from Waste Fishing Nets Accessories, Clothing, Footwear, Home Ware, Recreation. Available online: http://www.circularocean.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Circular-Ocean_Research_Products_FINAL_02-02-18.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Malloy, R.; Desai, N.; Wilson, C.; Swan, C.; Jansen, D.; Kashi, M. High carbon fly ash/mixed thermoplastic aggregate for use in lightweight concrete. In Proceedings of the Society of Plastics Engineering, Annual Technical Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 6–10 May 2001; pp. 2743–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Elzafraney, M.; Soroushian, P.; Deru, M. Development of energy-efficient concrete buildings using recycled plastic aggregates. J. Archit. Eng. 2005, 11, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Use of recycled plastic in concrete: A critical review. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juki, M.I.; Awang, M.; Annas, M.M.K.; Boon, K.H.; Othman, N.; Kadir, A.A.; Roslan, M.A.; Khalid, F.S. Relationship between compressive, splitting tensile and flexural strength of concrete containing granulated waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles as fine aggregate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 795, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R.; Singh, S.S.; Huber, C.O.; Brodersen, B.S. Use of post-consumer waste plastics in cement-based composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaa, B.; Ravindrarajah, R.S. Engineering properties of lightweight concrete containing crushed expanded polystyrene waste. In Proceedings of the Fall Meeting, Symposium MM: Advances in Materials for Cementitious Composites. Materials Research Society, Boston, MA, USA, 1–3 December 1997; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.W.; Moon, D.J.; Chung, J.S.; Cho, S.K. Effects of waste PET bottles aggregate on the properties of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukaitis, A.; Zurauskas, R.; Kerien, J. The effect of foam polystyrene granules on cement composite properties. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, M.; Marie, I.; Asi, I. Use of selected waste materials in concrete mixes. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.Y.; Dheilly, R.; Queneudec, M. Valorization of post-consumer waste plastic in cementitious concrete composites. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyakapo, P.; Panyakapo, M. Reuse of thermosetting plastic waste for lightweight concrete. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Z.Z.; Al-Hashmi, E.A. Use of waste plastic in concrete mixture as aggregate replacement. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, A.; Demirboğa, R. A novel material for lightweight concrete production. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Osmani, M.; Price, A.D. Assessing the recycling potential of glass fibre reinforced plastic waste in concrete and cement composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.W.; Moon, D.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lachemi, M. Characteristics of mortar and concrete containing fine aggregate manufactured from recycled waste polyethylene terephthalate bottles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, C.; Camacho, N.; Hernandez, M.; Matheus, A.; Gutierrez, A. Influence of content and particle size of waste pet bottles on concrete behavior at different w/c ratios. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Lee, G.; Poon, C.; Lai, W. Properties of lightweight aggregate concrete prepared with PVC granules derived from scraped PVC pipes. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remadnia, A.; Dheilly, R.; Laidoudi, B.; Quéneudec, M. Use of animal proteins as foaming agent in cementitious concrete composites manufactured with recycled PET aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3118–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçaözoğlu, S.; Atiş, C.D.; Akçaözoğlu, K. An investigation on the use of shredded waste PET bottles as aggregate in lightweight concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, P.; Osmani, M.; Price, A.D. Improvement of the mechanical properties of glass fibre reinforced plastic waste powder filled concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.R.L.; Leite, M.B.; Santiago, E.Q.R. Recycled lightweight concrete made from footwear industry waste and CDW. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigione, M. Recycling of PET bottles as fine aggregate in concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraj, A.B.; Kismi, M.; Mounanga, P. Valorization of coarse rigid polyurethane foam waste in lightweight aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, J.C.A.; Portella, K.F.; Joukoski, A.; Mendes, R.; Ferreira, E.S. Use of waste polymers in concrete for repair of dam hydraulic surfaces. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadevi, K.; Manju, R. Experimental investigation on the properties of concrete with plastic PET (bottle) fibres as fine aggregates. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.; de Brito, J.; Saikia, N. Influence of curing conditions on the mechanical performance of concrete containing recycled plastic aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Meyer, C. Performance of cement mortar made with recycled high impact polystyrene. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; De Brito, J.; Saikia, N. Influence of curing conditions on the durability-related performance of concrete made with selected plastic waste aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 35, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herki, A.; Khatib, J.; Negim, E. Lightweight concrete made from waste polystyrene and fly ash. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 21, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Z.; Li, P. Physical and mechanical properties of mortar using waste Polyethylene Terephthalate bottles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Waste polyethylene terephthalate as an aggregate in concrete. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.; Srivastava, V.; Agarwal, V. Effect of waste low density polyethylene on mechanical properties of concrete. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2014, 3, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Mechanical properties and abrasion behaviour of concrete containing shredded PET bottle waste as a partial substitution of natural aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçaözoğlu, S.; Ulu, C.; Akçaözoglu, S.; Ulu, C. Recycling of waste PET granules as aggregate in alkaliactivated blast furnace slag/metakaolin blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 58, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.K.; Ghataora, G.; Khan, M.I.; Dirar, S. Novel lightweight concrete containing manufactured plastic aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badache, A.; Benosman, A.S.; Senhadji, Y.; Mouli, M. Thermo-physical and mechanical characteristics of sand-based lightweight composite mortars with recycled high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, L. The influence of nano-SiO2 and recycled polypropylene plastic content on physical, mechanical, and shrinkage properties of mortar. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 6960216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zureick, A.H.; Cho, B.S.; Scott, D. Properties of fibre reinforced concrete using recycled fibres from carpet industrial waste. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 4191–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.D.; Betioli, A.M.; Gleize, P.; Roman, H.R.; Gomez, L.; Ribeiro, J. Degradation of recycled PET fibers in Portland cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, T.; Okubo, S.; Fukui, K. Development of recycled PET fiber and its application as concrete-reinforcing fiber. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.J.; Park, C.G.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, S.W.; Won, J.P. Effects of the geometry of recycled PET fiber reinforcement on shrinkage cracking of cement-based composites. Compos. Part B 2008, 39, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddah, M.S.; Bencheikh, M. Properties of concrete reinforced with different kinds of industrial waste fibre materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3196–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Yi, N.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.J.; Song, Y.C. Material and structural performance evaluation of recycled PET fiber reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, L.A.P.; Castro-Gomes, J.P. Physical and mechanical behaviour of recycled PET fibre reinforced mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Ciancia, V.; Chechile, R.; Rizzano, G.; Feo, L.; Incarnato, L. Experimental study of the thermo-mechanical properties of recycled PET fiberreinforced concrete. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelisser, F.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Roman, H.R. Mechanical properties of recycled PET fibers in concrete. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibudey, R.; Nagarnaik, P.; Parbat, D.; Pande, A. Strength and fracture properties of post consumed waste plastic fiber reinforced concrete. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Environ. Infrastruct. Eng. Res. Dev. 2013, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Prahallada, M.C.; Prakash, K.B. Effect of different aspect ratio of waste plastic fibres on the properties of fibre reinforced concrete-an experimental investigation. Int. J. Adv. Res. IT Eng. 2013, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fraternali, F.; Spadea, S.; Berardi, V.P. Effects of recycled PET fibres on the mechanical properties and seawater curing of Portland cement-based concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.; Vegas, I.; Cacho, I. Mechanical recycling of GFRP waste as short-fiber reinforcements in microconcrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kaushik, R.; Sharma, T. Effect of PET fibres different aspect ratio on fresh and mechanical properties of cement concrete. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Young Researchers and Graduates Symposium (YRGS 2014), Bangkok, Thailand, 31 July–1 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Spadea, S.; Farina, I.; Carrafiello, A.; Fraternali, F. Recycled nylon fibers as cement mortar reinforcement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasutthikul, S.; Unno, D.; Yokota, H. Effectiveness of recycled nylon fiber from waste fishing net with respect to fiber reinforced mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Svensson, S.J.; Bertelsen, I.M.G. Discarded nylon fishing nets as fibre reinforcement in cement mortar. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 231, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.O. Mechanical behavior of waste fishing net fiber-reinforced cementitious composites subjected to direct tension. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, I.C. Options for Closing the Loop for Plastic Debris—Environmental Analysis of Beach Clean-up and Waste Treatments. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rajankar, S.A.; Chavhan, A.D.; Metem, S.G.; Marodkar, H.R.; Dhanvij, P.D.; Shende, C.J. Extraction of strip from waste PET (Plastic) bottles. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 2020, 3, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Tuladhar, R.; Shi, F.; Combe, M.; Collister, T.; Sivakugan, N. Use of macro plastic fibres in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J.; Xu, Q.F. Direct tensile properties of engineered cementitious composite: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.O. Pullout behavior of recycled waste fishing net fibers embedded in cement mortar. Materials 2020, 13, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.T.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, G.H. Mechanical behavior of lightweight soil reinforced with waste fishing net. Geotext. Geomembr. 2008, 26, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.M. Low-Cost Fishing Net-Reinforced Cement Matrix Overlay for Substandard Concrete Masonry in Coastal Areas. Master’s Thesis, University of South Carolina, Columbia, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen, I.M.G.; Ottosen, L.M. Engineering properties of fibers from waste fishing nets. In Proceedings of the International RILEM Conference on Materials, Systems and Structures in Civil Engineering: Conference Segment on Cold Region Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 15–29 August 2016; pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sigvardsen, N.M. Use of discarded fishing nets as near surface mounted reinforcement for prolonging lifetime of existing structures. In Grøn Dyst 2016, Kgs; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.C.; Lo, Y.; Nadeem, A. Mechanical and drying shrinkage properties of structural-graded polystyrene aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, I.M.G.; Ottosen, L.M.; Fischer, G. Quantitative analysis of the influence of synthetic fibres on plastic shrinkage cracking using digital image correlation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongtanakitcharoen, T.; Naaman, A.E. Unrestrained early age shrinkage of concrete with polypropylene, PVA, and carbon fibers. Mater. Struct. 2007, 40, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchey, F.L. The use of recycled polymer fibers as secondary reinforcement in concrete structures. J. Constr. Educ. 1998, 3, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pelisser, F.; Neto, A.B.S.S.; Rovere, H.L.L.; Pinto, R.C.A. Effect of the addition of synthetic fibers to concrete thin slabs on plastic shrinkage cracking. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tulaian, B.S.; Al-Shannag, M.J.; Al-Hozaimy, A.M. Recycled plastic fibers for minimizing plastic shrinkage cracking of cement based mortar. Int. Sch. Sci. Res. Innov. 2014, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Banthia, N.; Fujikake, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Gupta, R. Fiber-reinforced cement composites: Mechanical properties and structural implications. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8395461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.O.; Bordelon, A.C. Age-dependent properties of fiber-reinforced concrete for thin concrete overlays. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.O.; Bordelon, A.C.; Lee, N.K. Early-age crack widths of thin fiber reinforced concrete overlays subjected to temperature gradients. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.O.; Bordelon, A. Fiber Effect on Interfacial Bond between Concrete and Fiber-Reinforced Mortar. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2591, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.O.; Bordelon, A. Determination of Total Fracture Energy for Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. ACI Spec. Publ. 2015, 300, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.O.; Bordelon, A.; Lee, M.K.; Oh, B.H. Cracking and failure of patch repairs in RC members subjected to bar corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.F.; Teixeira, B.A.N.; Agnelli, J.A.M.; Manrich, S. Characterization of effluents through a typical plastic recycling process: An evaluation of cleaning performance and environmental pollution. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2005, 45, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Khatib, J.; Kaur, I. Use of recycled plastic in concrete: A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1835–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).