Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics
2.4. Aggregate Stability Tests
2.4.1. Measuring Aggregate Stability by Laser Diffraction
2.4.2. Wet Sieving Method
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
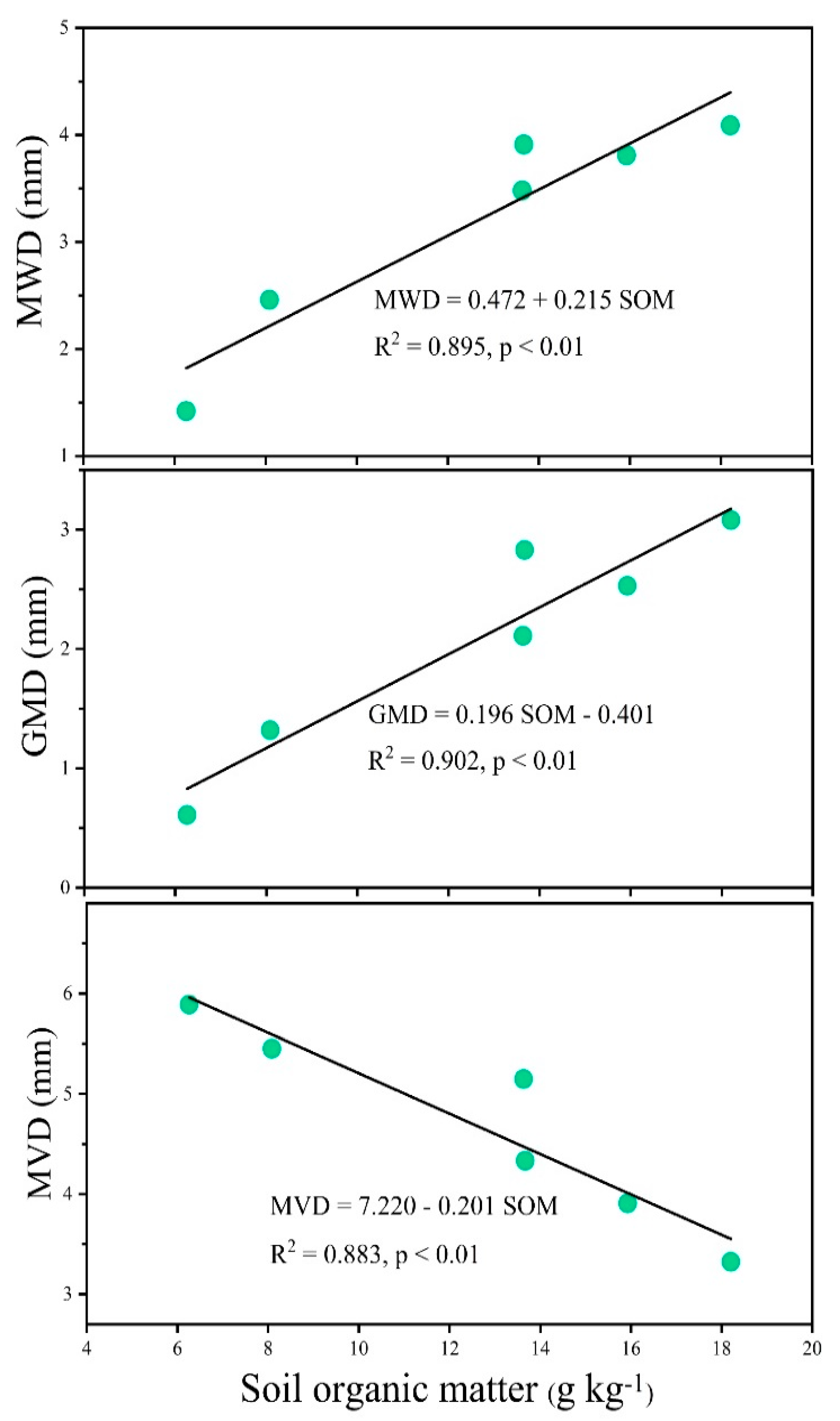
3.1. Soil Organic Matter Dynamic in the WLFZ
3.2. Soil Particle Size Distribution Characteristics in the WLFZ
3.3. Temporal Variation of Soil Aggregate Stability in the WLFZ
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Time Effect of Wetting and Drying Cycles on Soil Aggregate Stability in WLFZ of the TGR
4.2. Effect of Hydrological Regime on Soil Aggregate Stability Changes in the WLFZ
4.3. The Hydrological Regime and Soil Organic Matter Impact on Grain Size Distribution in the WLFZ of the Three Gorge Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rattan, L.; Manoj, K.S. Principles of Soil Physics, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Arrouays, D. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability and erodibility: II. Application to humic loamy soils with various organic carbon contents. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A.C.; Vis, M. Assessing soil aggregate stability by water-drop impact and ultrasonic dispersion. Geoderma 1984, 34, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès, B.; Albrecht, A.; De Noni, G.; Asseline, J.; Roose, E. Relationship between soil erodibility and topsoil aggregate stability or carbon content in a cultivated Mediterranean Highland (Averyon, France). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 1999, 30, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Nacci, S.; Pla, I. Effect of raindrop impact and its relationship with aggregate stability to different disaggregation forces. Catena 2003, 53, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil Structure and Soil Organic Matter: II. A Normalized stability index and the effect of mineralogy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, S.; Silva, A.P.; Dexter, A. factors Contributing to the tensile strength and friability of oxisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezketa, E.; Singer, E.M.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Testing a new procedure for measuring water-stable aggregation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1996, 60, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J. Effect of drying—wetting cycles on aggregate breakdown for yellow—brown earths in karst areas. Geoenviro. Disasters 2017, 4, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemper, W.D.; Chepil, W.S. Size distribution of aggregates. In Methods of Soil Analysis part 1, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy-Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; Volume 9, pp. 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, E.Y. A direct method of aggregate analysis of soils and a study of the physical nature of erosion losses. Am. Soc. Agron. 1936, 28, 337–351. [Google Scholar]
- Gyawali, A.J.; Stewart, R.D. An improved method for quantifying soil aggregate stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Legout, C.; De Danieli, S.; Daumergue, N.; Cécillon, L. Comparison of infrared spectroscopy and laser granulometry as alternative methods to estimate soil aggregate stability in Mediterranean badlands. Geoderma 2016, 271, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Poleto, C.; Baginski, Á.J.; da Silva, V.R. Aggregation of subtropical soil under liming: A study using laser diffraction. Rev. Bras. Ciência do Solo 2010, 34, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virto, I.; Andez-ugalde, O.F. Role of organic matter and carbonates in soil aggregation. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, J.; Xia, J.; Shen, C. Variation of soil aggregation along the weathering gradient: Comparison of grain size distribution under different disruptive forces. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Impact of drying-wetting cycles on the soil aggregate stability of Alfisols in southwestern China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, L.; Ji, L. Spatial analysis of soil aggregate stability in a small catchment of the Loess Plateau, China: II. Spatial prediction. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 192, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, A.R.; Dexter, W.H. Changes in soil aggregate water stability induced by wetting and drying cycles in non-saturated soil. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, B.D. Rates of change of soil structure under different cropping systems. Adv. Soil Sci. 1990, 12, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, T.; Yuhai, B.; Xiubin, H.; Huaidong, Z.; Zhijing, C.; Peng, G.; Ronghua, Z.; Yunhua, H.; Xinbao, Z. Sedimentation and associated trace metal enrichment in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Hefting, M.; Clement, J.C.; Dowrick, C.; Cosandey, A.C.; Bernal, S.; Cimpian, C.; Tatur, A.; Burt, T.P.; Pinay, G. Water table elevation controls on soil nitrogen cycling in riparian wetlands along a European climatic gradient. Biogeochemistry 2004, 67, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Fu, B.; Collins, A.L.; Wen, A.; He, X.; Bao, Y. Developing a sustainable strategy to conserve reservoir marginal landscapes following routine flow regulation marginal landscape. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, S. The Implication of land-use/land-cover change for the declining soil erosion risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xibao, X.; Yan, T.; Guishan, Y.; Hengpeng, L.; Wizhong, S. Soil erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Soil Res. 2011, 49, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.J.; Tang, Q.; Bao, Y.H.; He, X.B.; Tian, F.X.; Lu, F.Y.; Wang, M.; Raheel, A. Effects of seasonal water-level fluctuation on soil pore structure in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Tang, Q.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X. Soil erosion in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bao, Y.; Nan, H.; Xiong, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Tillage pedogenesis of purple soils in southwestern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2009, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources; Reports No. 106; International Union of Soil Science: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhai, B.; He, X.; Anbang, W.; Peng, G.; Qiang, T.; Dongchun, Y.; Yi, L. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in a typical disturbance zone of China’s Three Gorges Reservoir. Catena 2018, 169, 128–139. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, S.; Jiang, P.; Chang, S.X.; Song, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, L. Soil Organic Carbon in Particle Size and Density Fractionations under Four Forest Vegetation-Land Use Types in Subtropical China. Forest 2014, 5, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, R.H.; Hu, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, F.; He, X. Soil nutrients in relation to vertical roots distribution in the riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, B.G.; Wragg, J.; Lark, R.M. Application of a novel method for soil aggregate stability measurement by laser granulometry with sonication. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate stability and size. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods-Agronomy Monograph, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy-Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, K.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Huang, P. Soil types differentiated their responses of aggregate stability to hydrological stresses at the riparian zones of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 20, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.W.; Nyle, C.B. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK, 2017; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mulia, D.J.; Huyck, L.M.; Reganold, J.P. Temporal variation in aggregate stability on conventional and alternative farms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denef, K.; Johan, S.; Heleen, B.; Serita, D.F.; Edward, T.E.; Roel, M.; Keith, P. Influence of dry-wet cycles on the interrelationship between aggregate, particulate organic matter, and microbial community dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Garza, M.R.; Bryan, R.B.; Voroney, P. Influence of wetting and drying cycles and maize residue addition on the formation of water stable aggregates in Vertisols. Geoderma 2009, 151, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.A.; Shouliders, F.E. Effect of drying and freezing soils on carbon dioxide production, available mineral nutrients, aggregation, and bacterial population. Soil Sci. 1961, 91, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Cockroft, B.; Uren, N.C. The stability of soil aggregates as affected by organic materials, microbial activity and physical disruption. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1978, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzehei, T.A. Soil structure. In Handbook of Soil Sciences: Properties and Processes, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boix-fayos, C.; Calvo-cases, A.; Imeson, A.C.; Soriano-Soto, M. Influence of soil properties on the aggregation of some mediterranean soils and the use of aggregate size and stability as land degradation indicators. Catena 2001, 44, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Soil aggregate size distribution and stability of farmland as affected by dry and wet sieving methods. Zemdirb. Agric. 2020, 107, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, T. Evaluation of soil aggregate microstructure and stability under wetting and drying cycles in two Ultisols using synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 149, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Hamilton, S. Seasonal soil aggregate stability variation in relation to rainfall and temperature under Mediterranean conditions. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms. 2009, 34, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Collins, A.L.; Wen, A.; He, X.; Bao, Y.; Yan, D. Particle size differentiation explains flow regulation controls on sediment sorting in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron., J.; Kay, B.D. Rate of response of structural stability to a change in water content: Influence of cropping history. Soil Tillage Res. 1992, 25, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézketa, E. Soil Aggregate Stability: A Review. J. Sustain. Agric. 1999, 14, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. The effects of timing of inundation on soil physical quality in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Shi, D.; Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, T. Soil stability characteristics of mulberry lands at hydro-fluctuation belt in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, C.; Graf, F. Soil permeability, aggregate stability and root growth: A pot experiment from a soil bioengineering perspective. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.S.; Ha, L.S.; Wen, Z.Z.; Tong, H.Z. Fractal features of soil particle size distribution and the implication for indicating desertification. Geoderma 2004, 122, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yaron, B.; Calvet, R.; Prost, R. Soil Pollution, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 100–125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Bao, Y.H.; Wei, J.; He, X.B.; Tang, Q.; de Dieu Nambajimana, J. Fractal characterization of sediment particle size distribution in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant. and Soil. 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, E.; Sakin, E.D. Relationships between particle size distribution and organic carbon of soil horizons in the Southeast area of Turkey. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2015, 47, 526–530. [Google Scholar]

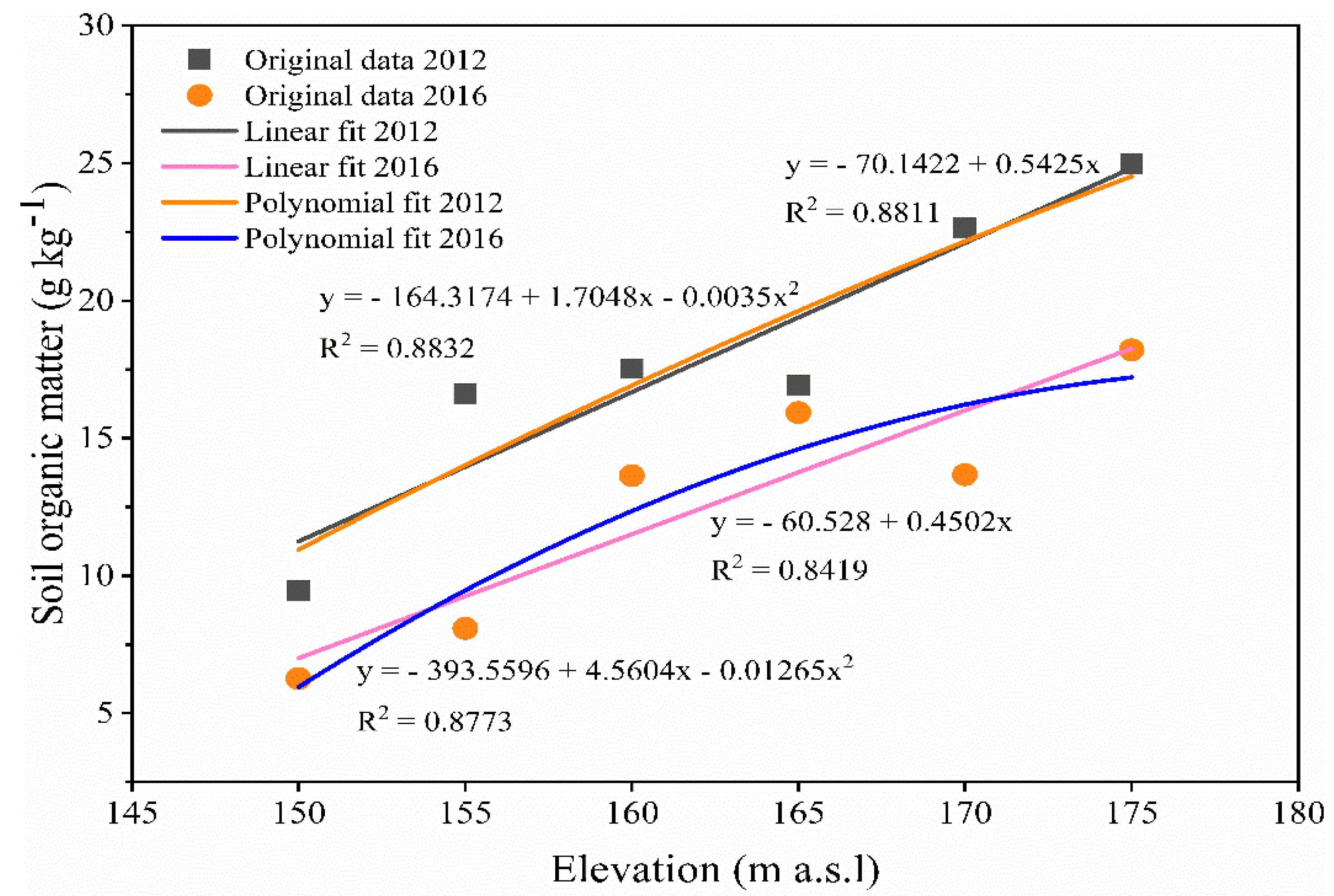
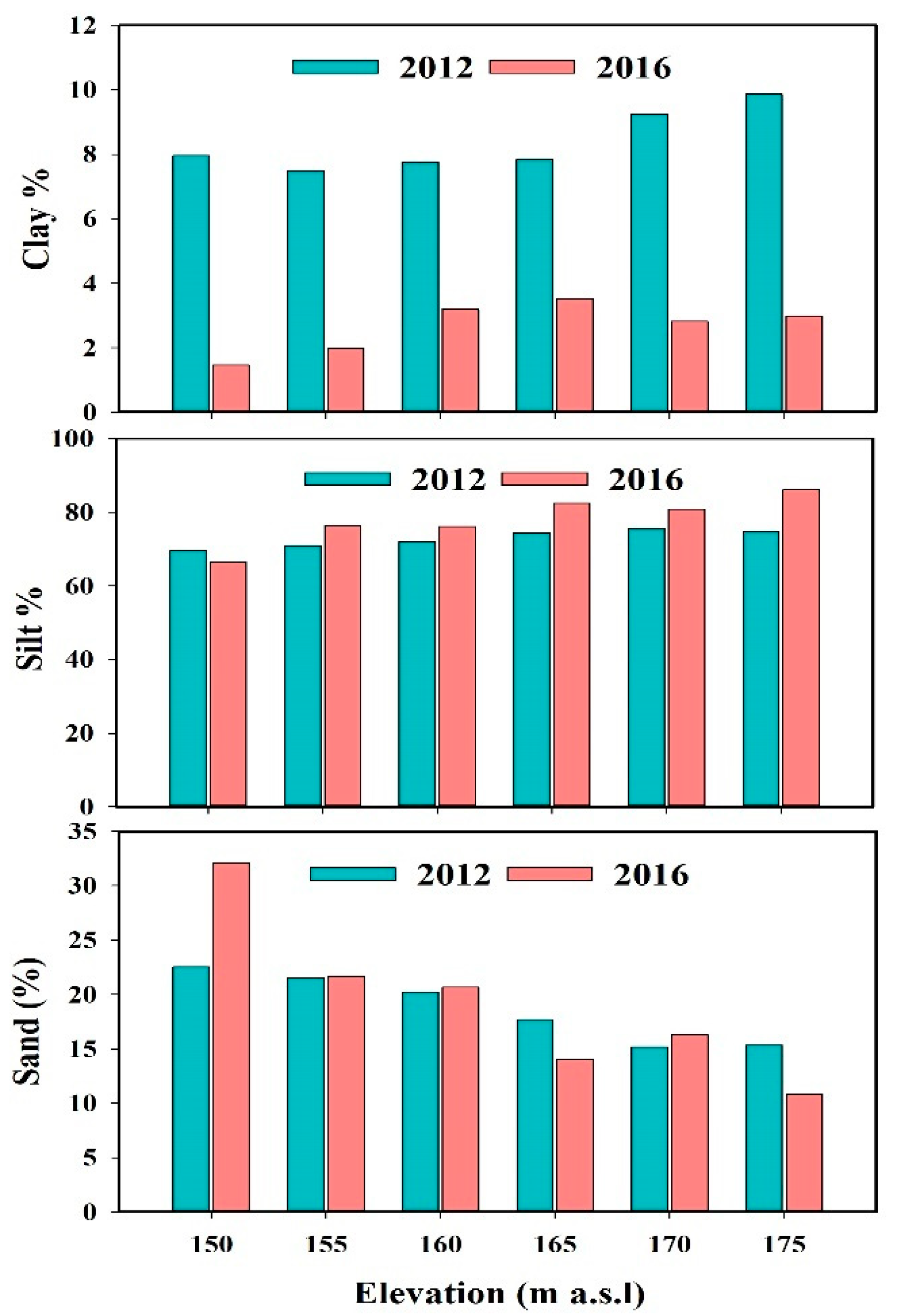

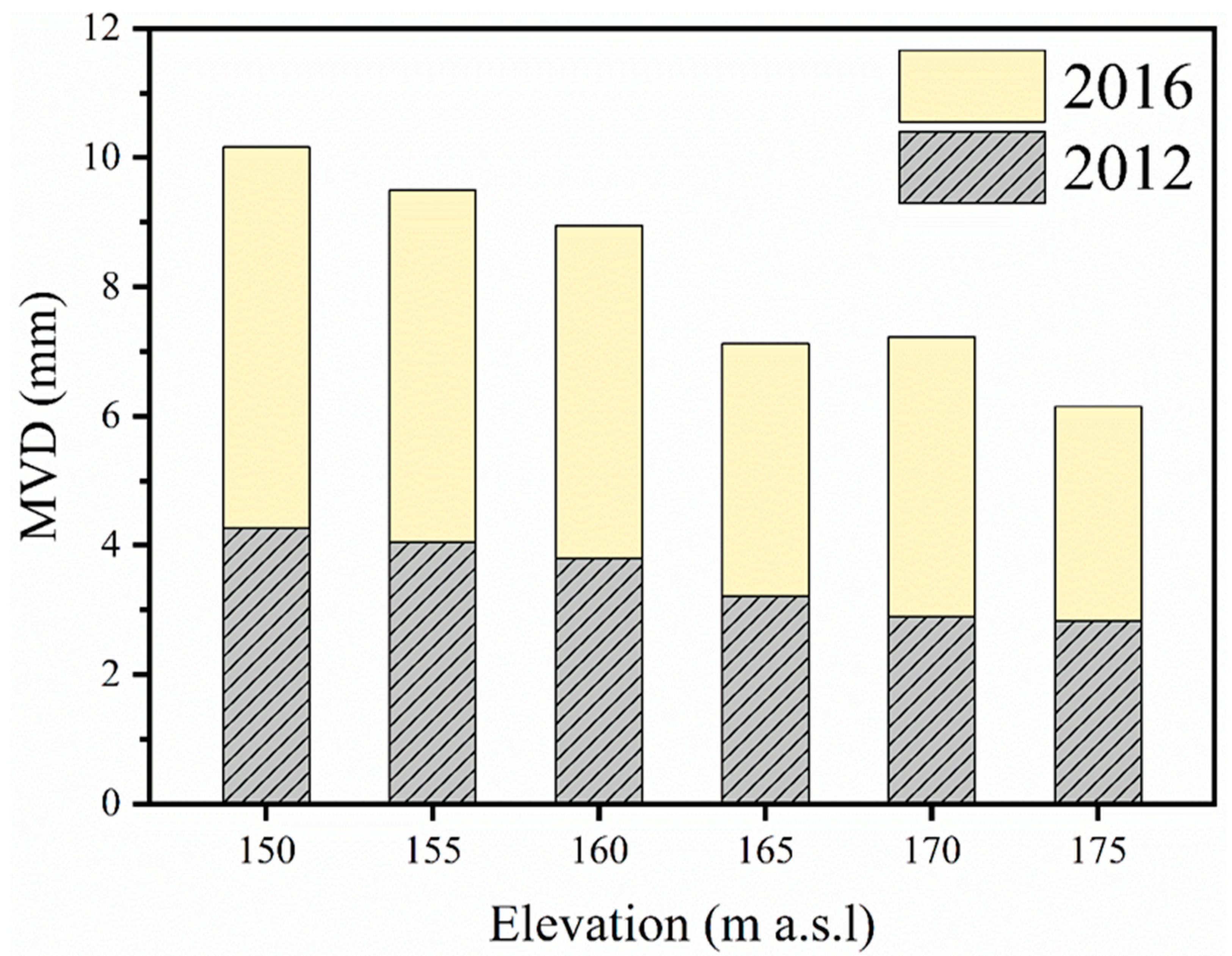
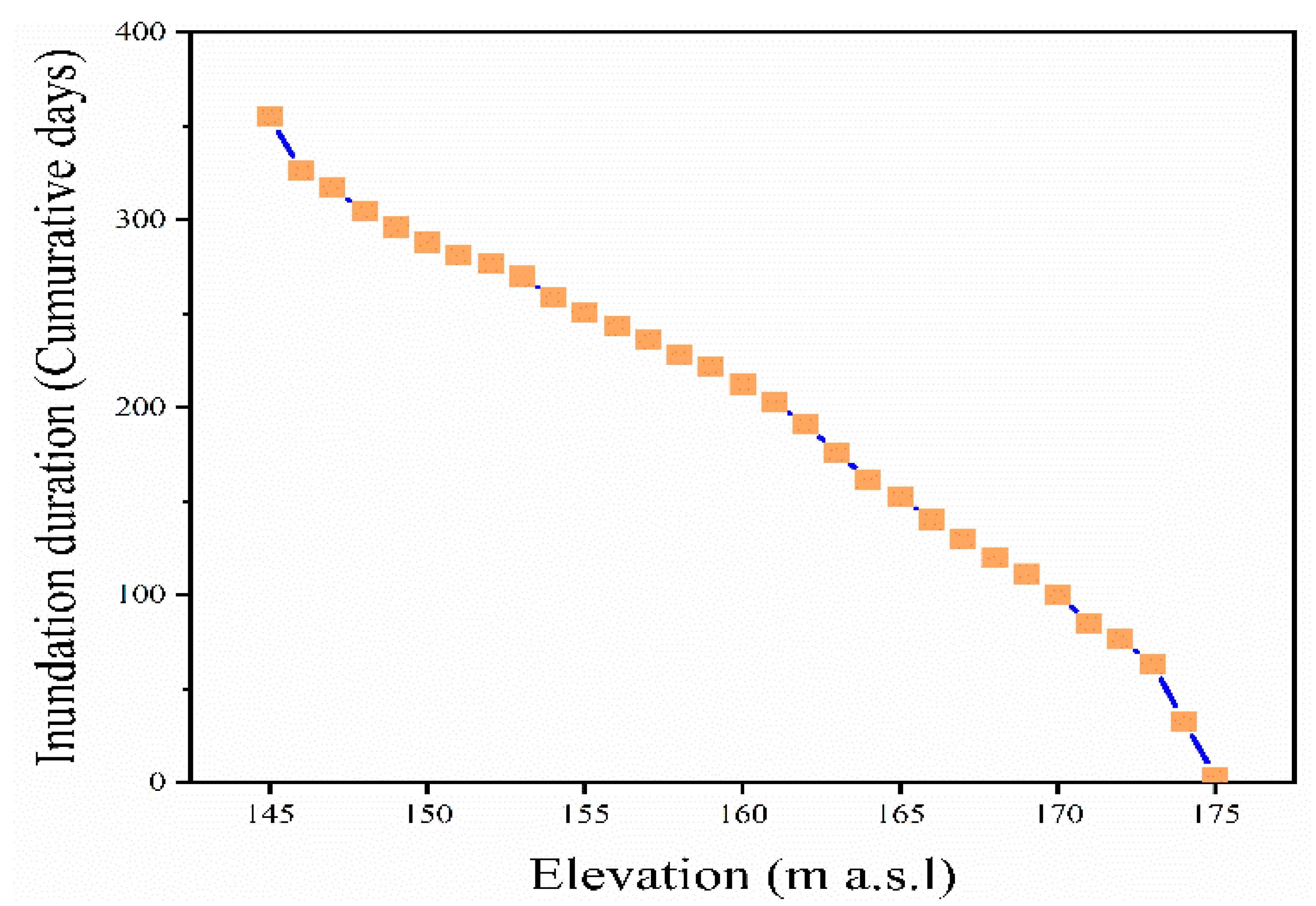
| Elevation (m a.s.l) | Annual Inundation Time/Day | Inundation Depth (m) | Land Use | Soil Type | Slope Gradient/° | Main Vegetation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 288 | 25 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb. |
| 155 | 250 | 20 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb. |
| 160 | 212 | 15 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder |
| 165 | 152 | 10 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder, Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop. |
| 170 | 100 | 5 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder, Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop. |
| 175 | 3 | <0.5 | Grassland | Purple soil | 3 | Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder, Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop. |
| Year | Clay | Silt | Sand | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 0.77 | 0.86 * | −0.89 * | |
| SOM | ||||
| 2016 | 0.52 | 0.91 * | −0.89 * |
| Variable | Year | Means | t | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVD | 2012 | 3.50 ± 0.61 a | −2.46 | 10 | 0.03 |
| 2016 | 4.67 ± 0.98 b | ||||
| D10 | 2012 | 3.50 ± 0.61 a | −4.42 | 10 | 0.01 |
| 2016 | 4.67 ± 0.98 b | ||||
| D50 | 2012 | 17.49 ± 2.07 a | 0.54 | 10 | 0.59 |
| 2016 | 16.23 ± 5.22 a | ||||
| D90 | 2012 | 71.31 ± 10.83 a | −1.33 | 10 | 0.21 |
| 2016 | 87.11 ± 26.79 a | ||||
| SOM | 2012 | 18.02 ± 5.40 a | 1.86 | 10 | 0.09 |
| 2016 | 12.63 ± 34.58 a | ||||
| Clay | 2012 | 8.35 ± 0.95 a | 11.26 | 10 | 0.001 |
| 2016 | 2.65 ± 0.78 b | ||||
| Silt | 2012 | 72.90 ± 2.40 a | −1.75 | 10 | 0.11 |
| 2016 | 78.08 ± 6.83 a | ||||
| Sand | 2012 | 18.74 ± 3.14 a | −0.15 | 10 | 0.88 |
| 2016 | 19.25 ± 7.46 a |
| Elevation (m) | MWD (mm) | GMD (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 150 | 1.42 ± 0.28 a | 0.61 ± 0.19 a |
| 155 | 2.46 ± 0.28 b | 1.32 ± 0.29 b |
| 160 | 3.48 ± 0.22 c | 2.11 ± 0.25 c |
| 165 | 3.81 ± 0.18 d | 2.53 ± 0.25 d |
| 170 | 3.91 ± 0.14 d,e | 2.83 ± 0.14 e |
| 175 | 4.09 ± 0.24 e,f | 3.08 ± 0.39 e,f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nsabimana, G.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; Nambajimana, J.d.D.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Khurram, D. Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219107
Nsabimana G, Bao Y, He X, Nambajimana JdD, Wang M, Yang L, Li J, Zhang S, Khurram D. Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):9107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219107
Chicago/Turabian StyleNsabimana, Gratien, Yuhai Bao, Xiubin He, Jean de Dieu Nambajimana, Mingfeng Wang, Ling Yang, Jinlin Li, Shujuan Zhang, and Dil Khurram. 2020. "Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 9107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219107
APA StyleNsabimana, G., Bao, Y., He, X., Nambajimana, J. d. D., Wang, M., Yang, L., Li, J., Zhang, S., & Khurram, D. (2020). Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sustainability, 12(21), 9107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219107







