Outdoor Thermal Comfort at a University Campus: Studies from Personal and Long-Term Thermal History Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Site Description
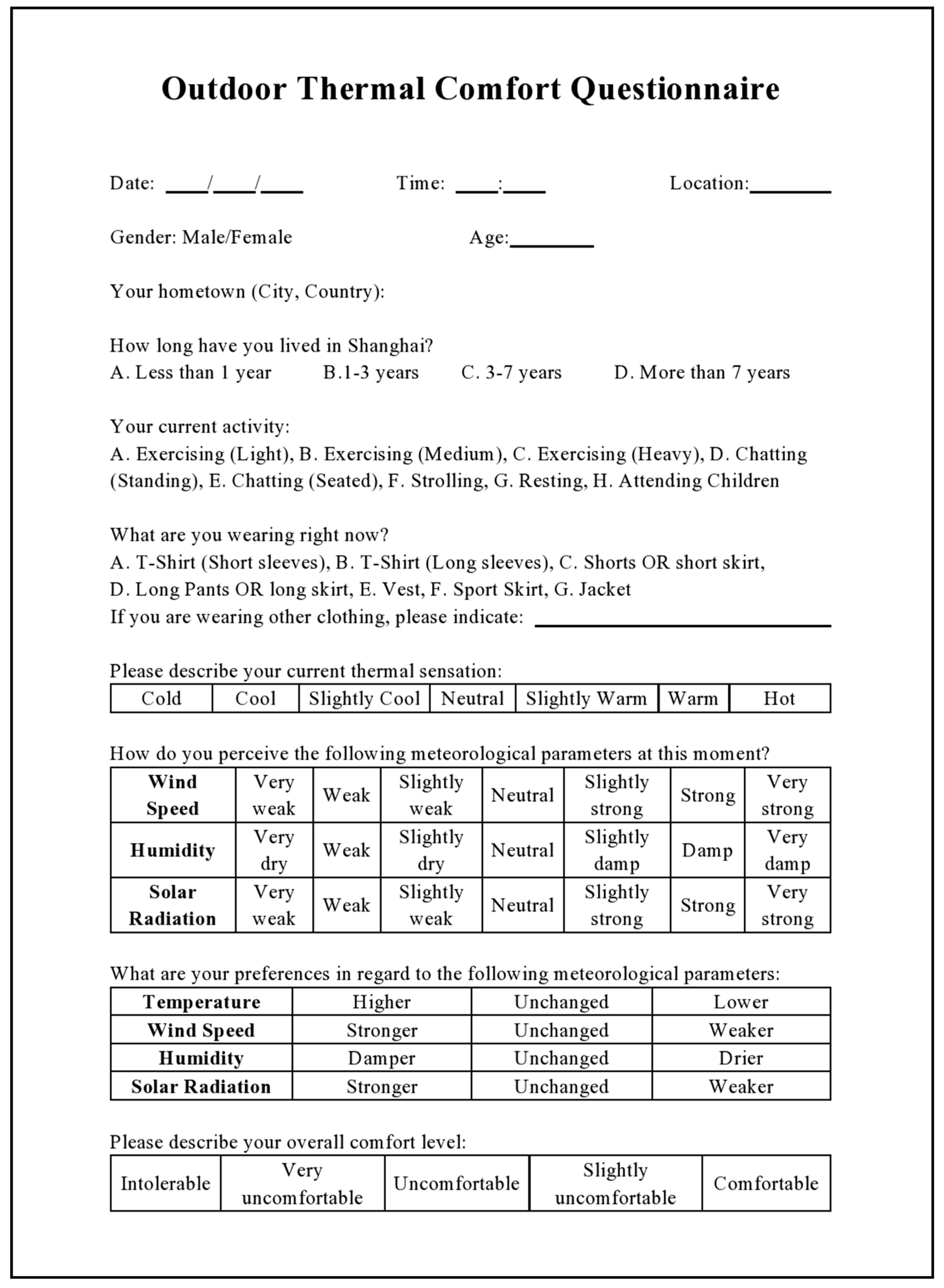
2.2. Field Survey
2.3. Thermal Indices
2.3.1. Physiologically Equivalent Temperature (PET)
2.3.2. Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI)
3. Results
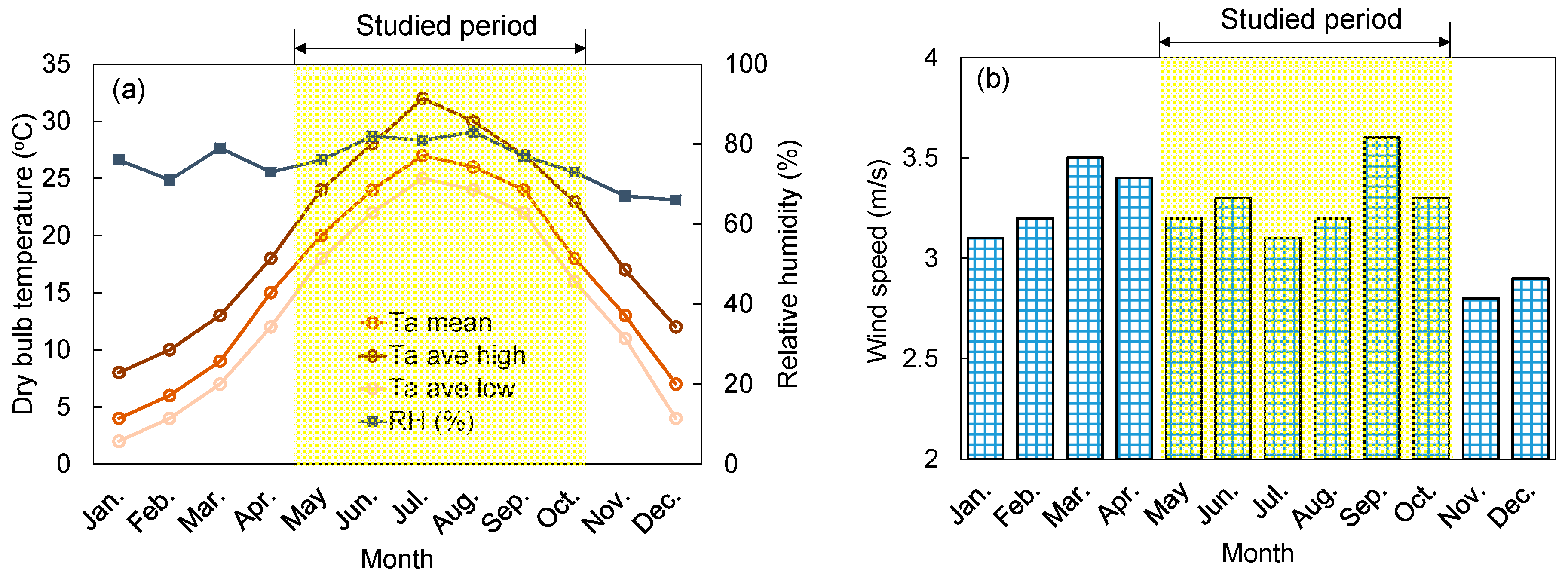
3.1. Climate and Microclimate
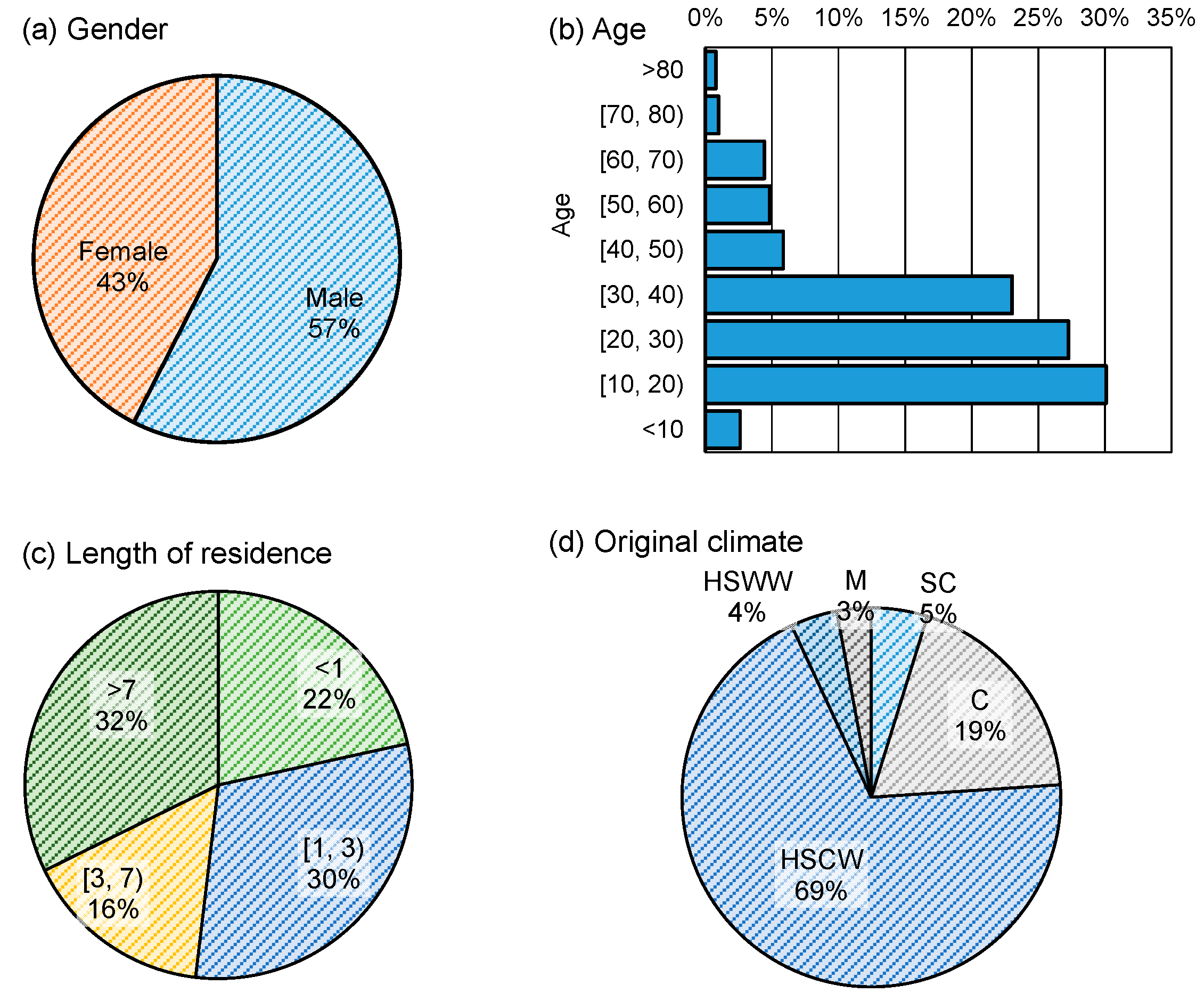
3.2. Demographics of the Interviewees
3.3. General Description of Thermal Comfort
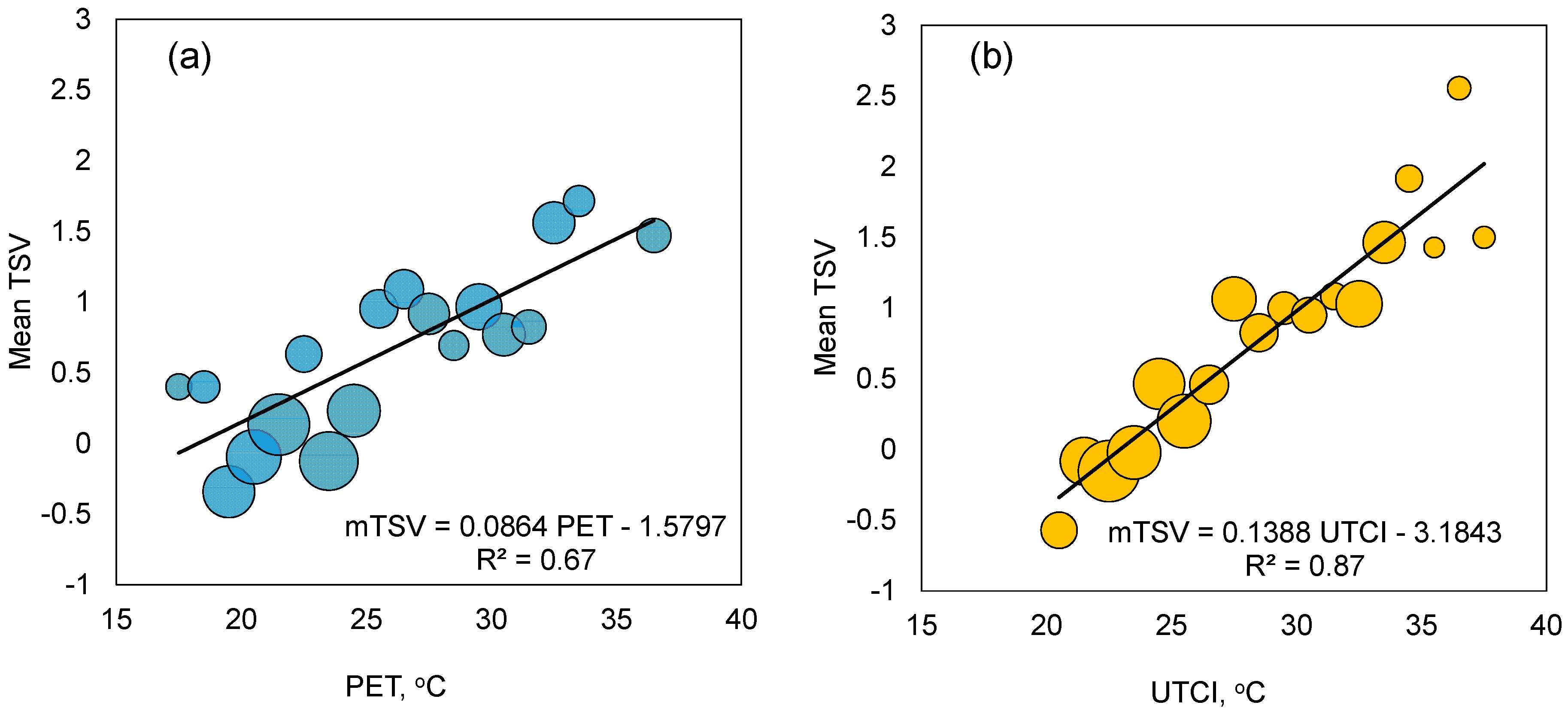
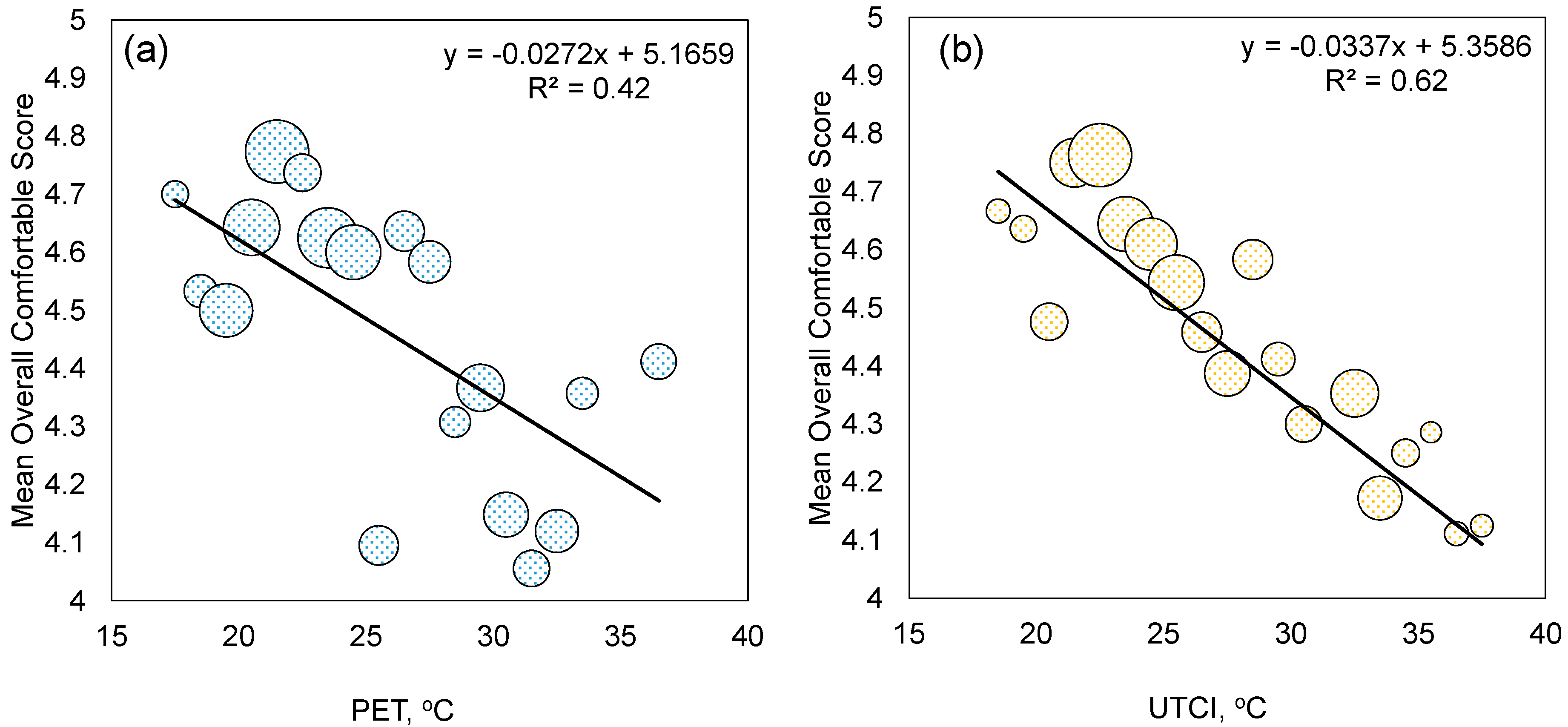
3.4. Correlations between Perceptions and Thermal Indices (PET and UTCI)
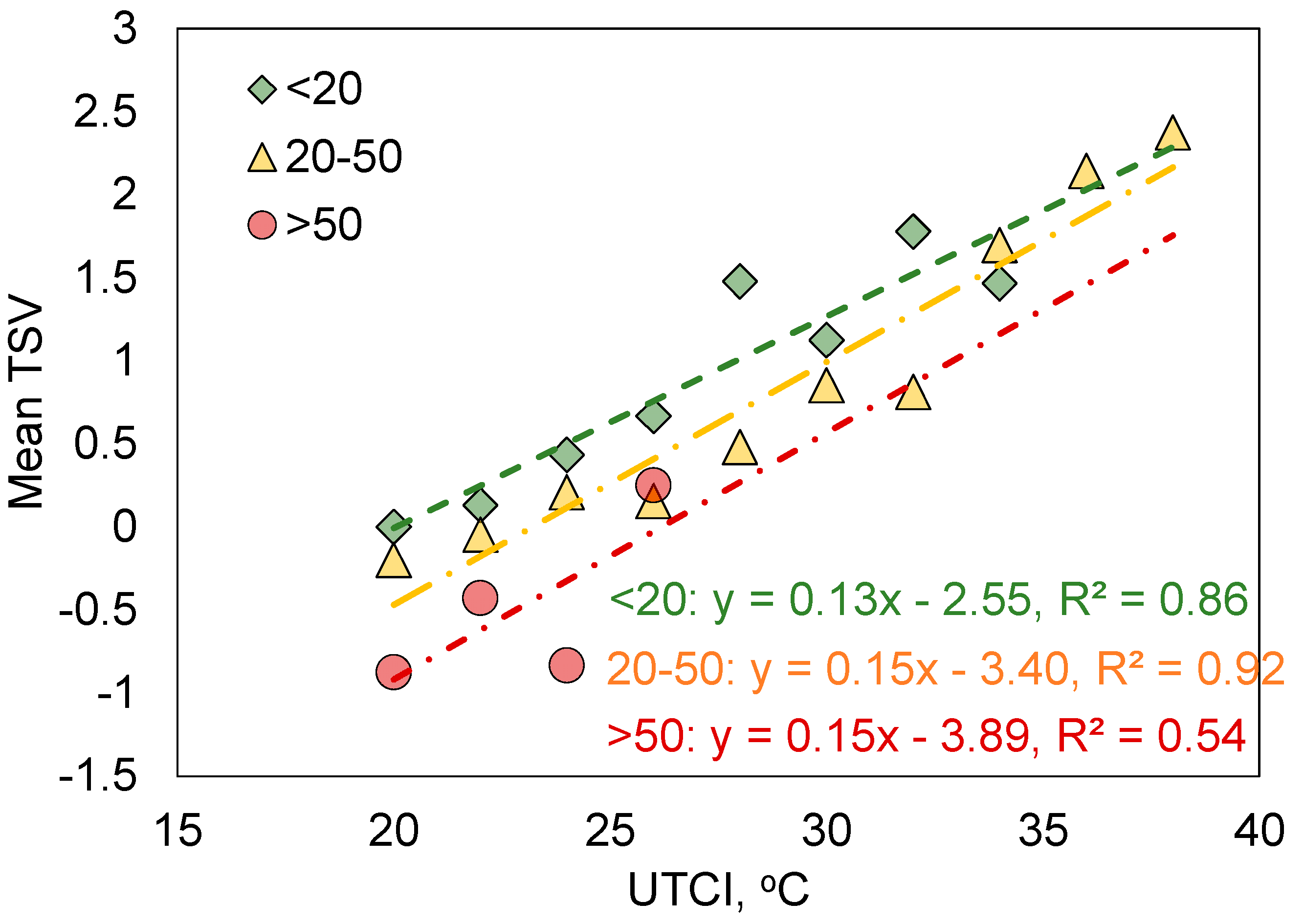
3.5. Influence of Personal Factors
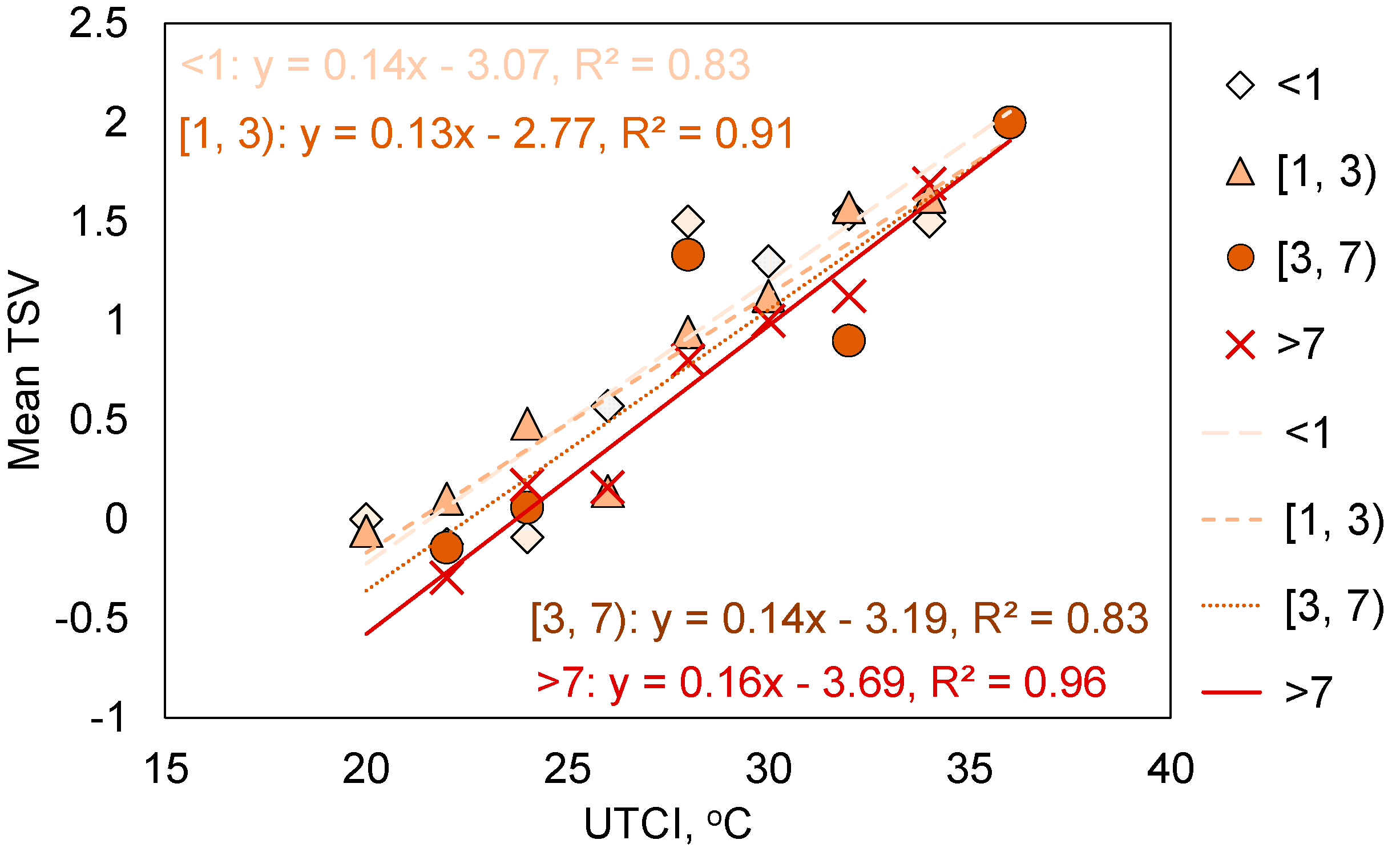
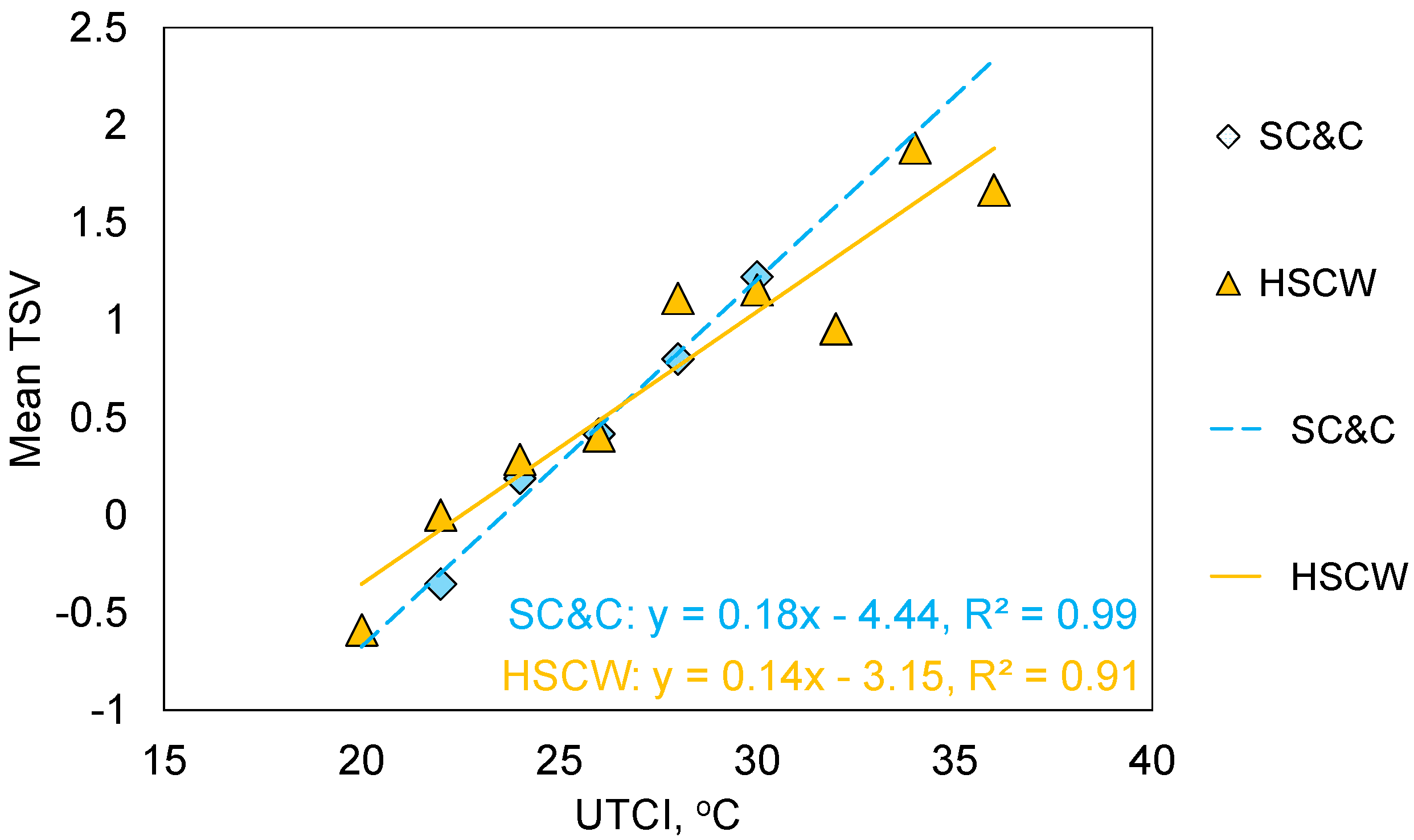
3.6. Influence of Long-Term Thermal History
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparing with Other Studies
4.2. Clothing Behavior
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
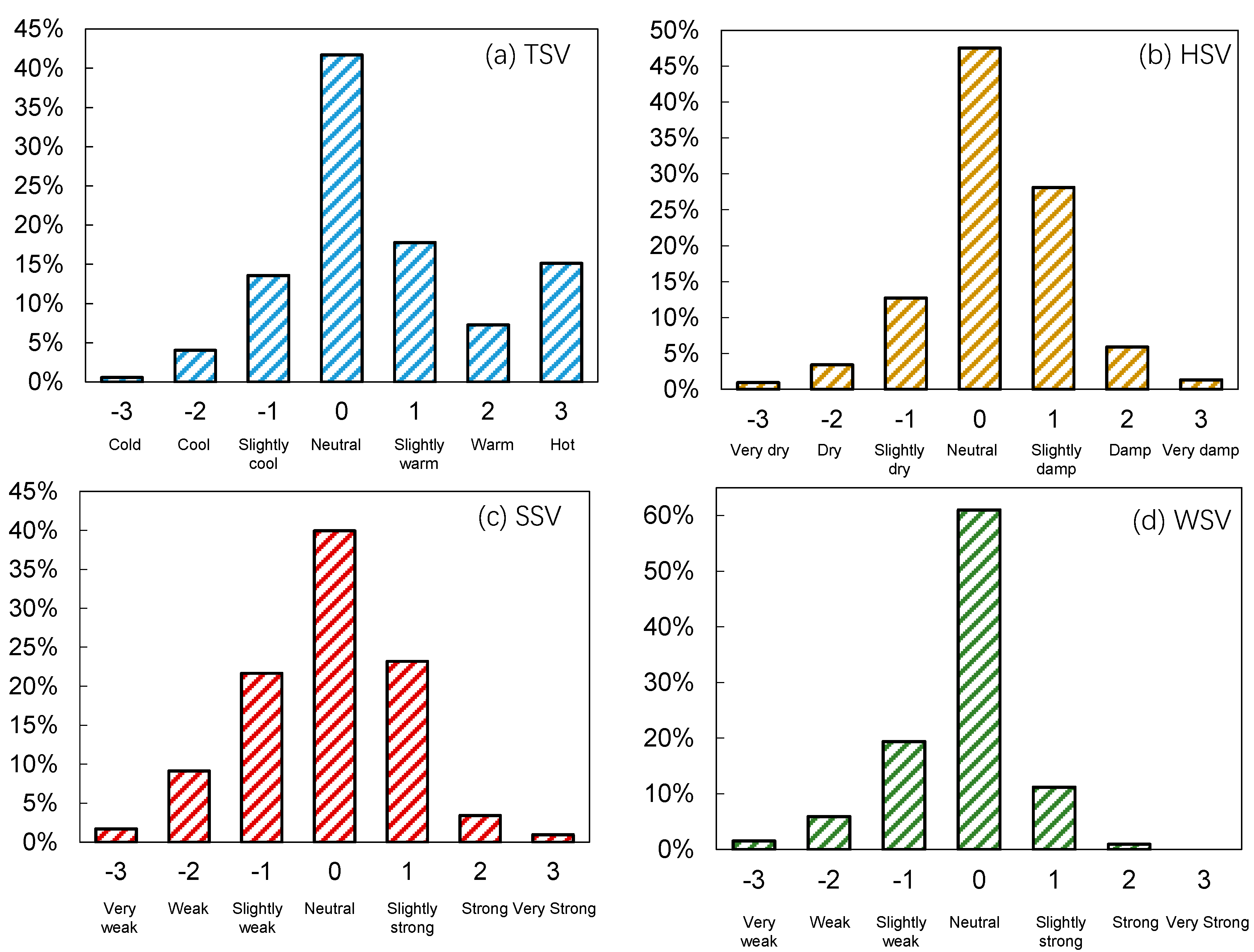
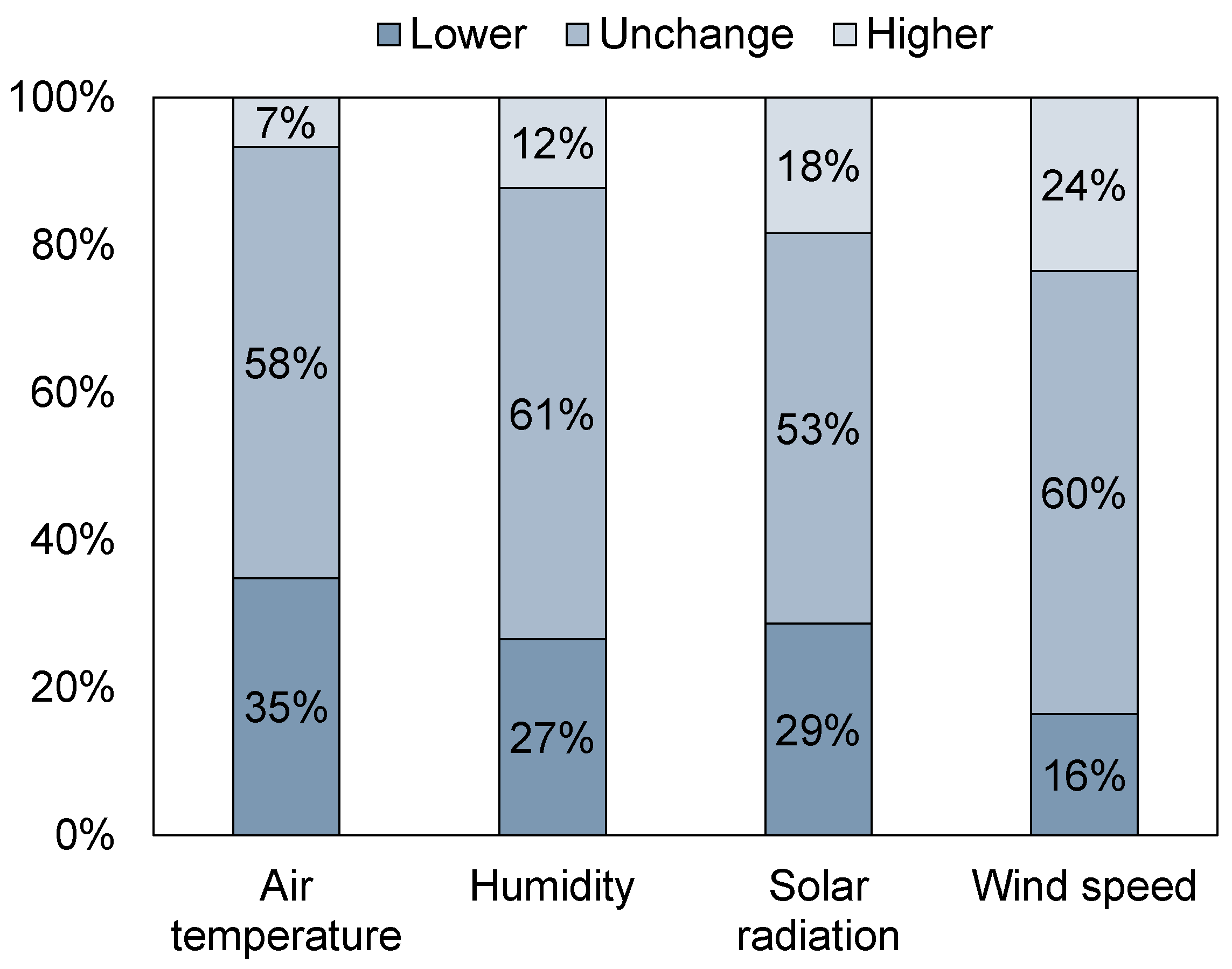
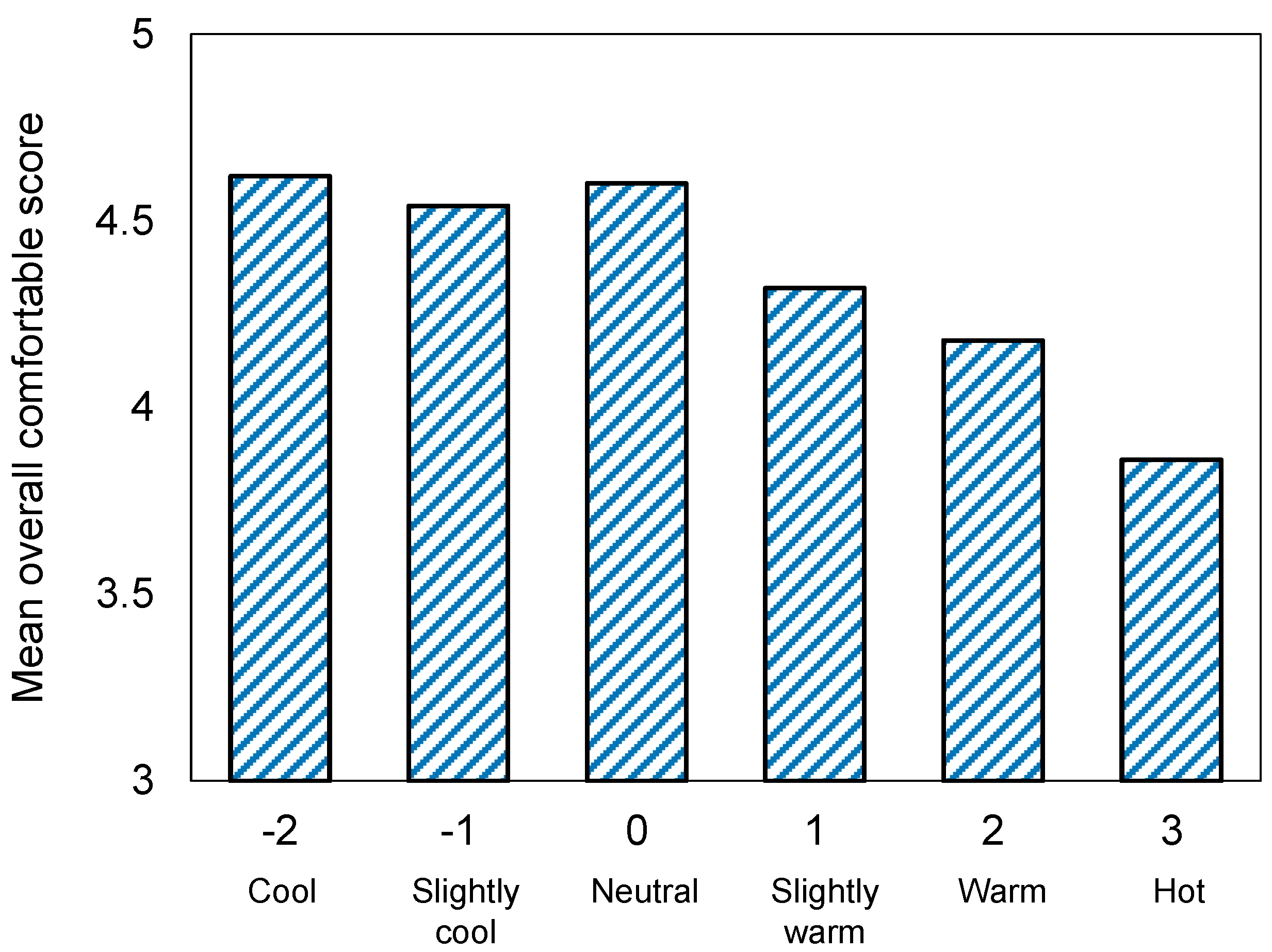
- The occupants generally accepted the outdoor thermal environment. During the survey, 42%, 48%, 40%, and 62% of the respondents perceived the temperature, humidity, solar radiation, and wind as neutral, respectively. In total, 57% of them felt comfortable, and only 1% and 3% stated that the overall comfort level was intolerable or very uncomfortable, respectively.
- UTCI showed a better correlation with the mean thermal sensation than PET did. A 1 K change in UTCI led to a 0.1388 unit change in mean thermal sensation.
- Female respondents demonstrated a higher sensitivity to the outdoor thermal environment than male respondents did. Different age groups had a similar level of sensitivity, while respondents younger than 20 had the highest TSV.
- Longer residence length led to a higher overall comfort rating and lower thermal sensation. Interviewees from severe cold and cold climate regions were more sensitive to the changes in UTCI than occupants from hot summer and cold winter climate regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Population Reference Bureau. 2020 World Population Data Sheet; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, J.; Hong, B.; Zhang, T.; Huang, B.; Niu, J. Outdoor thermal benchmarks and their application to climate‒responsive designs of residential open spaces in a cold region of China. Build. Environ. 2020, 169, 106592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, M.; Lykoudis, S. Use of outdoor spaces and microclimate in a Mediterranean urban area. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Chen, B.; Liu, K. Quantification of the influence of thermal comfort and life patterns on outdoor space activities. Build. Simul. 2019, 13, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-P.; Tsai, K.T.; Hwang, R.L.; Matzarakis, A. Quantification of the effect of thermal indices and sky view factor on park attendance. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 107, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aram, F.; Solgi, E.; Baghaee, S.; Higueras García, E.; Mosavi, A.; Band, S.S. How parks provide thermal comfort perception in the metropolitan cores; A case study in Madrid Mediterranean climatic zone. Clim. Risk Manag. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aram, F.; Solgi, E.; Garcia, E.H.; Mosavi, A. Urban heat resilience at the time of global warming: Evaluating the impact of the urban parks on outdoor thermal comfort. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larriva, M.T.B. Outdoor Thermal and acoustic comfort in autumn for senior citizens in public spaces in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Seo, B.M.; Yoon, Y.B.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, J.M.; Lee, K.H. Heating energy performance and part load ratio characteristics of boiler staging in an office building. Front. Energy 2018, 13, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, R.K.; Kumar, M.; Dhingra, A.K. A comprehensive review of greenhouse shapes and its applications. Front. Energy 2017, 13, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talele, S.; Traylor, C.; Arpan, L.; Curley, C.; Chen, C.F.; Day, J.; Feiock, R.; Hadzikadic, M.; Tolone, W.J.; Ingman, S.; et al. Energy modeling and data structure framework for Sustainable Human-Building Ecosystems (SHBE)—A review. Front. Energy 2018, 12, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wen, F.; Xu, Y. A comprehensive energy solution for households employing a micro combined cooling, heating and power generation system. Front. Energy 2018, 12, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Lian, Z.; Liu, W.; Guo, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q. A comprehensive review of thermal comfort studies in urban open spaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, D.; Hou, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, Z.A.; Zhang, G.; Shi, L. Outdoor thermal comfort of urban park—A Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hong, B.; Jiang, R.; An, L.; Zhang, T. Outdoor thermal comfort of shaded spaces in an urban park in the cold region of China. Build. Environ. 2019, 155, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liang, J.; Sun, C.; Han, Y. Summer outdoor thermal comfort in urban commercial pedestrian streets in severe cold regions of China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Hou, T.; Fu, J.; Wei, Y. The effects of microclimate parameters on outdoor thermal sensation in severe cold cities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Fukuda, H.; Zhou, D.; Wang, M. A Study of the pedestrianized zone for tourists: Urban design effects on humans’ thermal comfort in Fo Shan City, Southern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayoshi, M.; Kanda, M.; Shi, R.; De Dear, R. Outdoor thermal physiology along human pathways: A study using a wearable measurement system. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q. Measurements and predictions of the skin temperature of human subjects on outdoor environment. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q. Modelling dynamic thermal sensation of human subjects in outdoor environments. Energy Build. 2017, 149, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.S.; Jeong, M.A. Morphology of pedestrian roads and thermal responses during summer, in the urban area of Bucheon city, Korea. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2016, 60, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, M.; Steemers, K. Thermal comfort and psychological adaptation as a guide for designing urban spaces. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amindeldar, S.; Heidari, S.; Khalili, M. The effect of personal and microclimatic variables on outdoor thermal comfort: A field study in Tehran in cold season. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, E.L.; Drach, P. Identifying potential effects from anthropometric variables on outdoor thermal comfort. Build. Environ. 2017, 117, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Ridley, I. The effect of individual and social environments on the users thermal perceptions of educational urban precincts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 26, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, E.L.; Rossi, F.A. Effect of personal and microclimatic variables on observed thermal sensation from a field study in southern Brazil. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Shashua-Bar, L.; Keller, R.; Gil-Ad, R.; Yaakov, Y.; Lukyanov, V.; Bar, P.; Tanny, J.; Cohen, S.; Potchter, O.; et al. Urban outdoor thermal perception in hot arid Beer Sheva, Israel: Methodological and gender aspects. Build. Environ. 2019, 160, 106169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner-Cendrowska, K.; Blazejczyk, K. Impact of selected personal factors on seasonal variability of recreationist weather perceptions and preferences in Warsaw (Poland). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, W.N. Studies of thermal comfort and space use in an urban park square in cool and cold seasons in Shanghai. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Olofsson, T.; Nair, G.; Kabanshi, A. Outdoor thermal comfort under subarctic climate of north Sweden—A pilot study in Umeå. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. ASHRAE Handbook (SI), Fundamentals; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Höppe, P. The physiological equivalent temperature—A universal index for the biometeorological assessment of the thermal environment. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1999, 43, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendritzky, G.; De Dear, R.; Havenith, G. UTCI—Why another thermal index? Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.; Rutz, F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments: Basics of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzarakis, A.; Rutz, F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments—Application of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppe, P. Heat balance modelling. Experientia 1993, 49, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, D.; Havenith, G.; Brode, P.; Kampmann, B.; Jendritzky, G. UTCI-Fiala multi-node model of human heat transfer and temperature regulation. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brode, P.; Fiala, D.; Blazejczyk, K.; Holmer, I.; Jendritzky, G.; Kampmann, B.; Tinz, B.; Havenith, G. Deriving the operational procedure for the Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Liu, W.; Gan, T.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q. A review of mitigating strategies to improve the thermal environment and thermal comfort in urban outdoor spaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Bureau, Climate Information Center, Climate Data Office and Tsinghua University, Department of Building Science and Technology. China Standard Weather Data for Analyzing Building Thermal Conditions; China Building Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Thermal Design Code for Civil Building; Technical Report No. GB50176-2016; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Lai, D.; Guo, D.; Hou, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, Q. Studies of outdoor thermal comfort in northern China. Build. Environ. 2014, 77, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, P.F. The effect of personal and microclimatic variables on outdoor thermal comfort: A field study in a cold season in Lujiazui CBD, Shanghai. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.P.; De Dear, R.; Hwang, R.L. Effect of thermal adaptation on seasonal outdoor thermal comfort. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantavou, K.; Theoharatos, G.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D. Outdoor thermal sensation of pedestrians in a Mediterranean climate and a comparison with UTCI. Build. Environ. 2013, 66, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villadiego, K.; Velay-Dabat, M.A. Outdoor thermal comfort in a hot and humid climate of Colombia: A field study in Barranquilla. Build. Environ. 2014, 75, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, T.; Hermida, M.A. Effects of thermophysiological and non-thermal factors on outdoor thermal perceptions: The Tomebamba Riverbanks case. Build. Environ. 2018, 138, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, N.; Salleh, E.; Jaafar, M.Z.; GhaffarianHoseini, A. Thermal comfort conditions of shaded outdoor spaces in hot and humid climate of Malaysia. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lan, L.; Tang, J.; Wan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z. Bed heating improves the sleep quality and health of the elderly who adapted to no heating in a cold environment. Energy Build. 2020, 210, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Lian, Z.; Chen, P. Evaluation on the performance of quilts based on young people’s sleep quality and thermal comfort in winter. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Wargocki, P.; Lian, Z. Quantitative measurement of productivity loss due to thermal discomfort. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Ma, T.; Lian, Z.; De Dear, R. Perceptual and physiological responses of elderly subjects to moderate temperatures. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Lian, Z. Impact of wooden versus nonwooden interior designs on office workers’ cognitive performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2020, 127, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Tsuzuki, K.; Liu, Y.F.; Lian, Z.W. Thermal environment and sleep quality: A review. Energy Build. 2017, 149, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
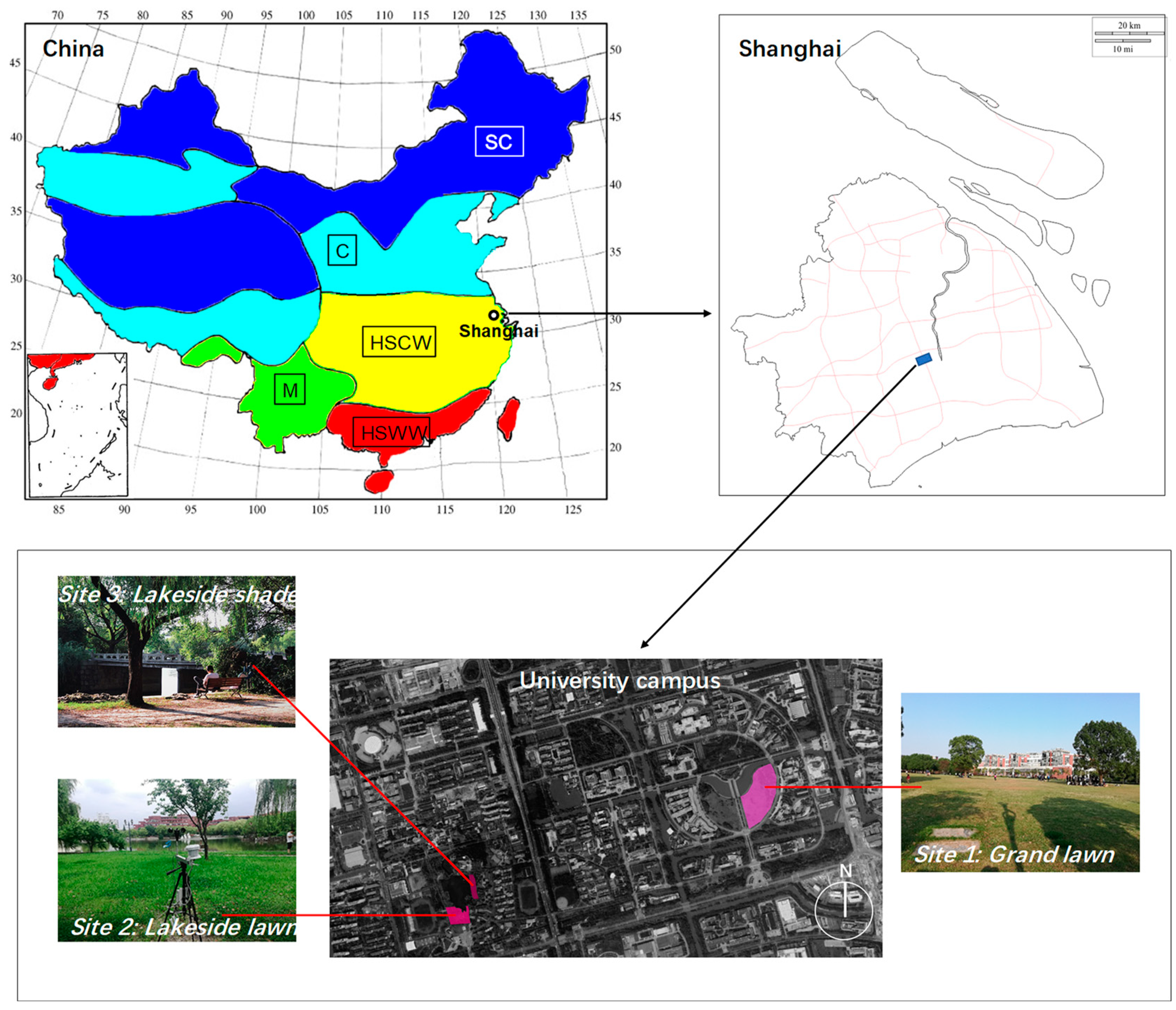


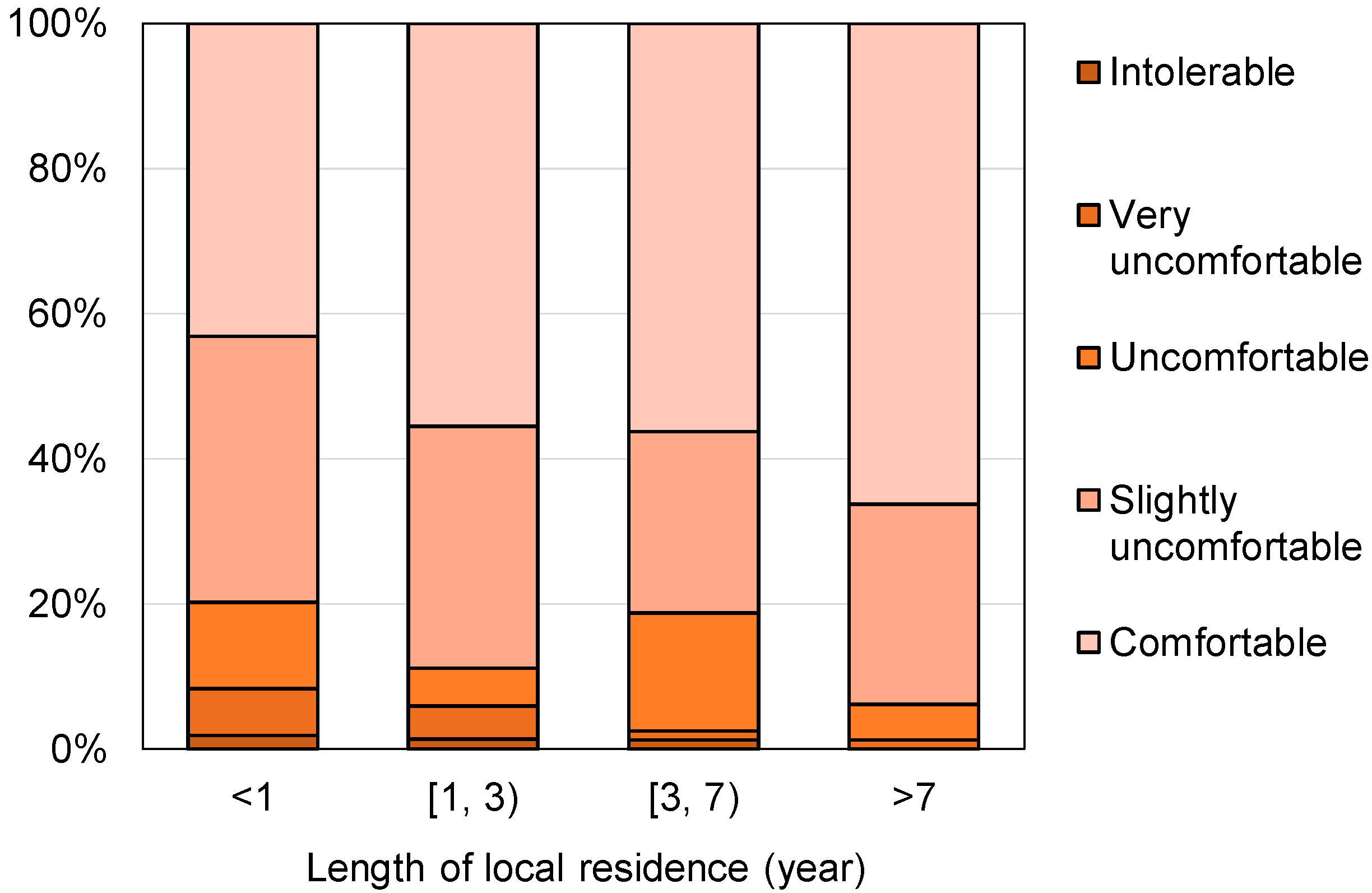


| Parameter | Sensor | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature | S-THB-M002 | −40–75 °C | ±0.2 K at 20 °C |
| Relative humidity | S-THB-M002 | 0–100% | ±3% |
| Wind speed | S-WSET-A | 0–45 m/s | ±1.1 m/s |
| Global radiation | S-LIB-MOO3 | 0–1280 W/m2 | ±10 W/m2 or ±5% |
| Air Temperature (Ta, °C) | Relative Humidity (RH, %) | Wind Speed (Va, m/s) | Global Radiation (G, W/m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1: Grand lawn (May, June, July, October) | Mean | 24.5 | 68.3 | 0.9 | 239.0 |
| Max. | 33.1 | 79.7 | 3.5 | 1115.6 | |
| Min. | 19.2 | 46.6 | 0.0 | 1.9 | |
| Site 2: Lakeside lawn (June, July, October) | Mean | 27.3 | 64.9 | 0.4 | 232.4 |
| Max. | 32.8 | 78.4 | 2.0 | 1025.6 | |
| Min. | 20.9 | 47.3 | 0.0 | 13.1 | |
| Site 3: Lakeside shade (June, July, October) | Mean | 24.7 | 63.0 | 0.2 | 100.2 |
| Max. | 31.8 | 78.8 | 1.5 | 745.6 | |
| Min. | 20.7 | 46.8 | 0.0 | 3.1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, J.; Hu, X.; Sani, S.N.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Chai, L.; Lai, D. Outdoor Thermal Comfort at a University Campus: Studies from Personal and Long-Term Thermal History Perspectives. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219284
Xue J, Hu X, Sani SN, Wu Y, Li X, Chai L, Lai D. Outdoor Thermal Comfort at a University Campus: Studies from Personal and Long-Term Thermal History Perspectives. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):9284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219284
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Jiao, Xiao Hu, Shu Nuke Sani, Yuanyuan Wu, Xinyu Li, Liang Chai, and Dayi Lai. 2020. "Outdoor Thermal Comfort at a University Campus: Studies from Personal and Long-Term Thermal History Perspectives" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 9284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219284
APA StyleXue, J., Hu, X., Sani, S. N., Wu, Y., Li, X., Chai, L., & Lai, D. (2020). Outdoor Thermal Comfort at a University Campus: Studies from Personal and Long-Term Thermal History Perspectives. Sustainability, 12(21), 9284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219284





