Earthworm Burrowing Activity and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Soil Moisture Conditions from the Loess Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Characterization of Earthworm Burrows
2.3. Soil Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Earthworm Burrows
3.2. Soil Aggregate Formation
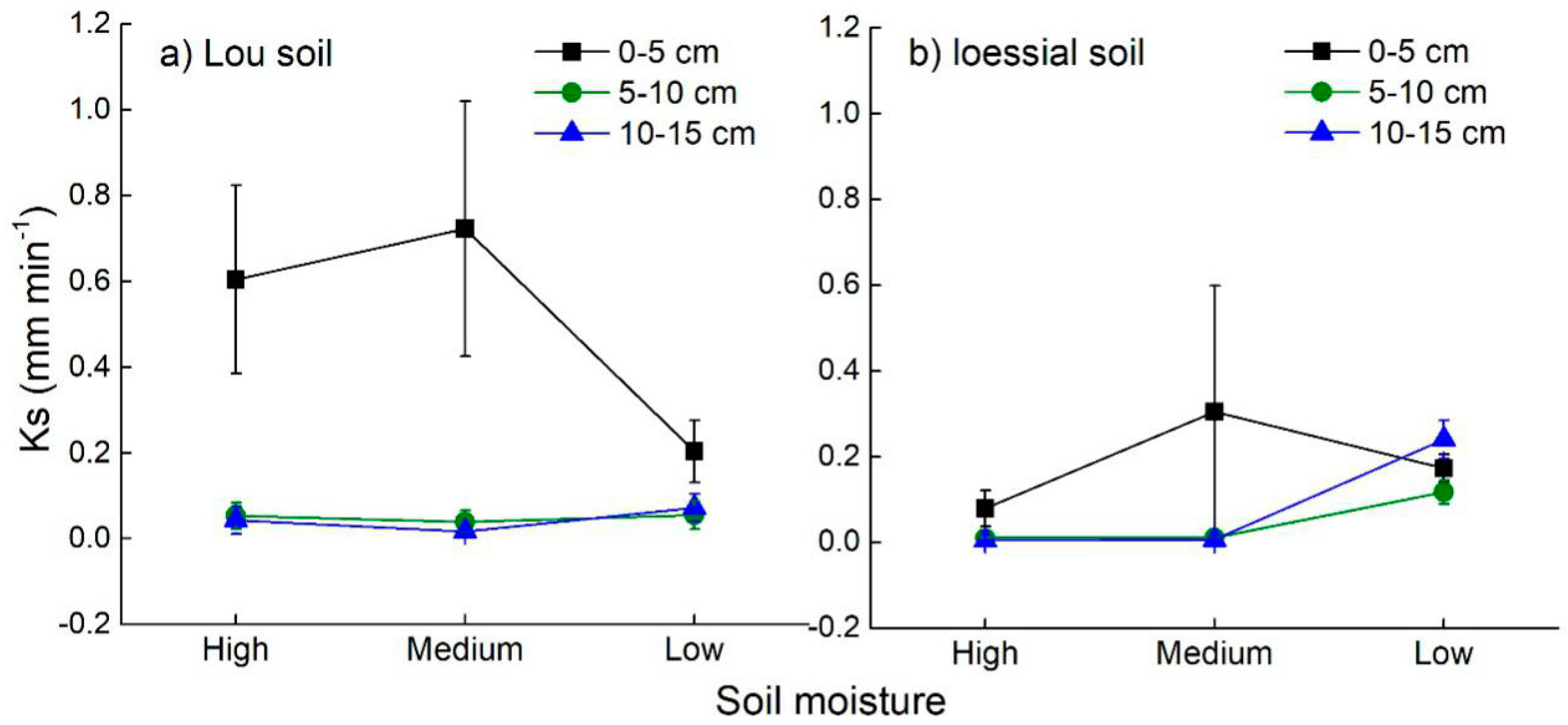
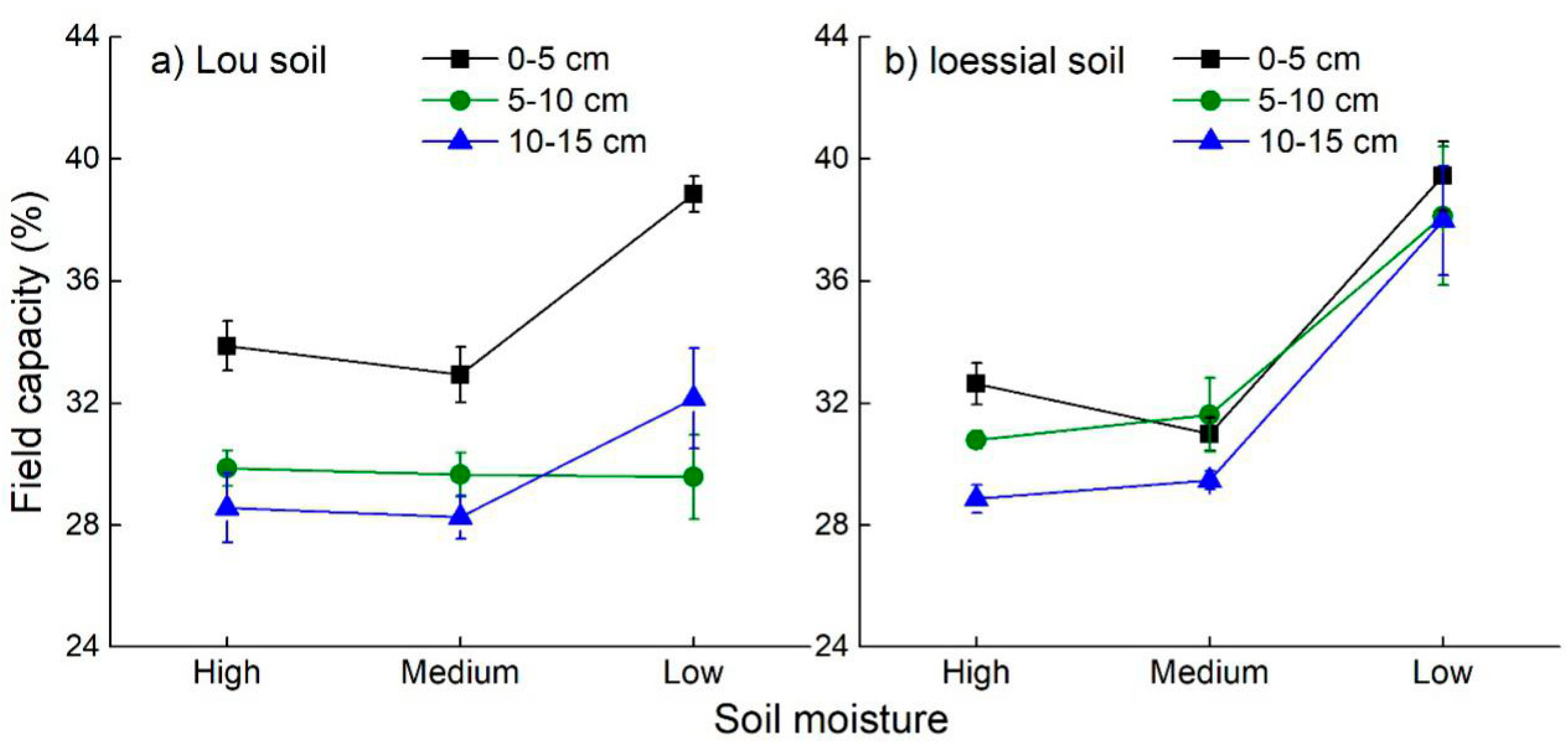
3.3. Soil Hydraulic Characteristics
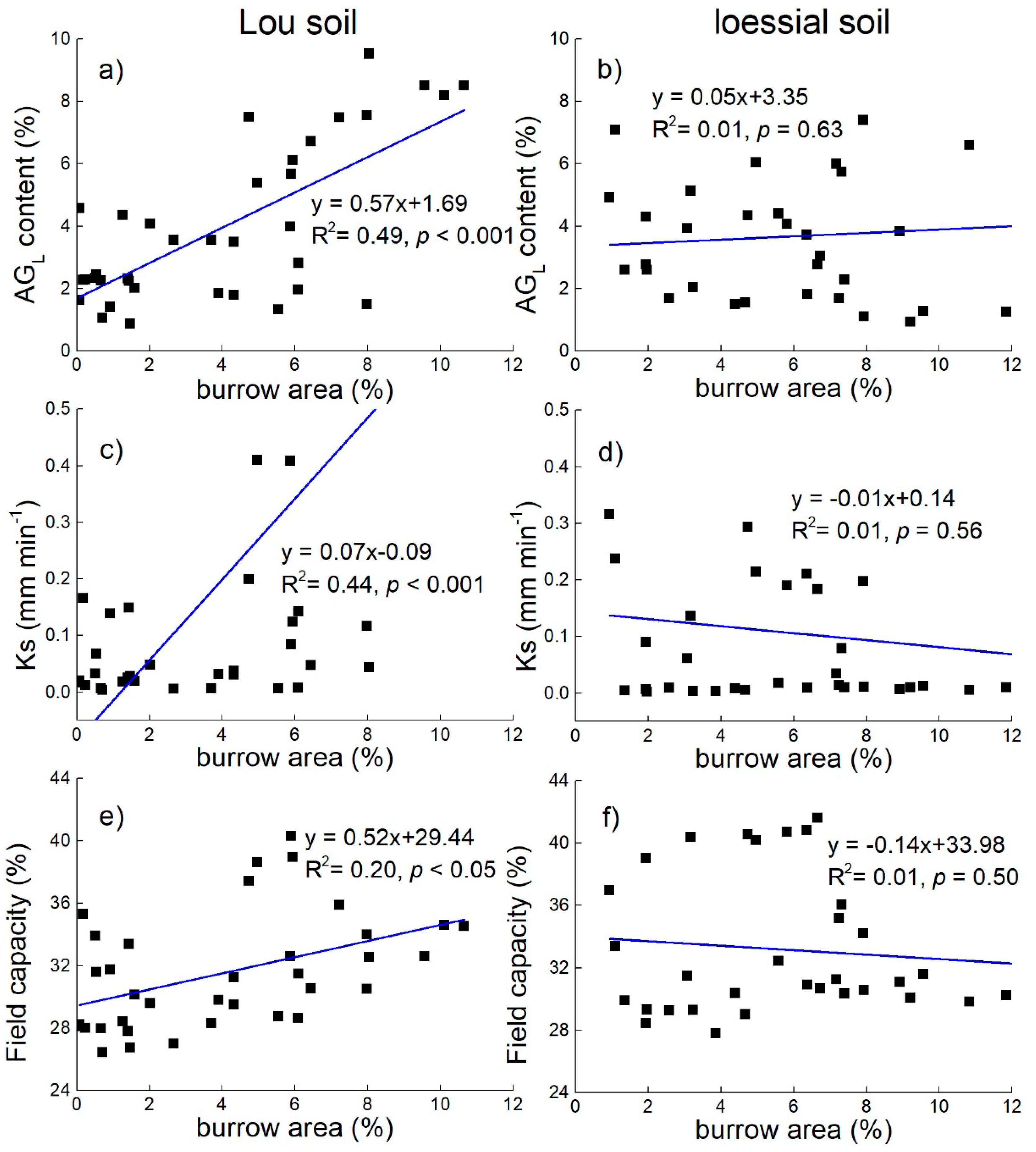
3.4. Effect of Earthworm Activity on Soil Aggregation and Hydraulic Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavelle, P.; Aubert, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Bureau, F.; Margerie, P.; Mora, P.; Rossi, J.P. Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire–Leung, S.E.; Gupta, S.C.; Moncrief, J.F. Water and solute movement in soil as influenced by macropore characteristics: 2. Macropore tortuosity. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 41, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capowiez, Y.; Cadoux, S.; Bouchant, P.; Ruy, S.; Roger–Estrade, J.; Richard, G.; Boizard, H. The effect of tillage type and cropping system on earthworm communities, macroporosity and water infiltration. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, G.; Felten, D.; Vohland, M.; Emmerling, C. Impact of ecologically different earthworm species on soil water characteristics. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E. Earthworms: Their Ecology and Relationships with Soils and Land Use; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, L.; Heppelthwaite, V.; Mcglinchy, A. The effect of environmental parameters on growth, cholinesterase activity and glutathione S–transferase activity in the earthworm (Apporectodea caliginosa). Biomarkers 2000, 5, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstrup, M. Sensitivity of life history parameters in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa to small changes in soil water potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, A. Burrowing ability of the earthworm Aporrectodea longa limited by soil compaction and water potential. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1991, 11, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, W.J.; Williams, D.L. Interactive effects of soil moisture and food on growth and aerobic metabolism in Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1992, 102A, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, L.R.; Lilleskov, E.A. Introduced earthworm species exhibited unique patterns of seasonal activity and vertical distribution, and Lumbricus terrestris burrows remained usable for at least 7 years in hardwood and pine stands. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, J.M.; Whalen, J.K. Earthworm burrowing in laboratory microcosms as influenced by soil temperature and moisture. Pedobiologia 2006, 50, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiunov, A.V.; Hale, C.M.; Holdsworth, A.R.; Vsevolodova–Perel, T.S. Invasion Patterns of Lumbricidae Into the Previously Earthworm–free Areas of Northeastern Europe and the Western Great Lakes Region of North America. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, M.; Orgiazzi, A.; Gardi, C.; Römbke, J.; Jänsch, S.; Keith, A.M.; Neilson, R.; Boag, B.; Schmidt, O.; Murchie, A.K.; et al. Mapping earthworm communities in Europe. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 97, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, H.; Six, J.; Hendrix, P.F. Interactive effects of functionally different earthworm species on aggregation and incorporation and decomposition of newly added residue carbon. Geoderma 2006, 130, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouquet, P.; Podwojewski, P.; Bottinelli, N.; Jérôme, M.; Ricoy, M.; Orange, D.; Tran, T.D.; Valentin, C. Above–ground earthworm casts affect water runoff and soil erosion in Northern Vietnam. Catena 2008, 74, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, J.; Turski, M.; Hajnos, M.; Świeboda, R. Pore structure, stability and water repellency of earthworm casts and natural aggregates in loess soil. Geoderma 2015, 243–244, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, J.P.; Butters, G.; Barbarick, K.A.; Stromberger, M.E. Effects of Aporrectodea caliginosa on soil hydraulic properties and solute dispersivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, J.; Berdeni, D.; Grayson, R.; Guest, E.J.; Holden, J.; Lappage, M.G.; Prendergast–Miller, M.T.; Robinson, D.A.; Turner, A.; Leake, J.R.; et al. Effect of earthworms on soil physico–hydraulic and chemical properties, herbage production, and wheat growth on arable land converted to ley. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capowiez, Y.; Dittbrenner, N.; Rault, M.; Triebskorn, R.; Hedde, M.; Mazzia, C. Earthworm cast production as a new behavioural biomarker for toxicity testing. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneda, S.; Ohkubo, S.; Wagai, R.; Yagasaki, Y. Soil temperature and moisture–based estimation of rates of soil aggregate formation by the endogeic earthworm Eisenia japonica (Michaelsen, 1892). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindell, R.P.; Mckenzie, B.M.; Silvapulle, M.J.; Tisdall, J.M. Relationships between casts of geophagous earthworms (Lumbricidae, Oligochaeta) and matric potential. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 18, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.S.; Fraser, P.M. The effects of three earthworm species on soil macroporosity and hydraulic conductivity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 10, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastardie, F.; Capowiez, Y.; de Dreuzy, J.-R.; Cluzeau, D. X–ray tomographic and hydraulic characterization of burrowing by three earthworm species in repacked soil cores. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 24, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottinelli, N.; Zhou, H.; Capowiez, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Jouquet, P.; Peng, X.H. Earthworm burrowing activity of two non–Lumbricidae earthworm species incubated in soils with contrasting organic carbon content (Vertisoil vs. Ultisol). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Lin, H.; Schmidt, J. Quantitative relationships between soil macropore characteristics and preferential flow and transport. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, G. Identification et Quantification In Situ des Interactions Entre la Biodiversité Lombricienne et la Bioporosité dans le Contexte Polyculture Breton. Influence sur le Fonctionnement Hydrodynamique du sol; Université de Rennes 1: Rennes, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson–Maynard, J.L.; Umiker, K.J.; Guy, S.O. Earthworm dynamics and soil physical properties in the first three years of no–till management. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, J.; Hodson, M.E. Impact of different earthworm ecotypes on water stable aggregates and soil water holding capacity. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Shao, M.A. Advances and perspectives on soil water research in China’s Loess Plateau. Earth–Sci. Rev. 2019, 199, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shao, M.A.; Jia, Y. Characteristics of Soil Evaporation and Temperature under Aggregate Mulches Created by Burrowing Ants (Camponotus japonicus). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shao, M.A.; Jia, Y.; Jia, X.; Huang, L. Small–scale observation on the effects of the burrowing activities of mole crickets on soil erosion and hydrologic processes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 261, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, G.; Bhardwaj, P. Comparative studies on biomass production, life cycles and composting efficiency of Eisenia fetida (Savigny) and Lampito mauritii (Kinberg). Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 92, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capowiez, Y.; Bottinelli, N.; Jouquet, P. Quantitative estimates of burrow construction and destruction, by anecic and endogeic earthworms in repacked soil cores. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 74, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A.; Dirksen, C. Hydraulic conductivity of saturated soils. In Methods of Soil Analysis. ASA and SSSA; Klute, A., Ed.; Wiley: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 694–700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. Soil desiccation for Loess soils on natural and regrown areas. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, R.E. A Direct Method of Aggregate Analysis of Soils and a Study of the Physical Nature of Erosion Losses. J. Am. Soc. Agron. 1936, 28, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, J. The determination of organic carbon in soils by dichromate mixtures. Trans. Int. Congr. Soil Sci. 1950, 1, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.; Nam, S.; Kim, S.; Bajagain, R.; Jeong, S.; An, Y. Changes in soil properties after remediation influence the performance and survival of soil algae and earthworm. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.P.; Schmidt, O. The feeding ecology of earthworms—A review. Pedobiologia 2007, 50, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, W.D.; Subler, S.; McCoy, E.L. The influence of earthworm community structure on the distribution and movement of solutes in a chisel–tilled soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 21, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scullion, J.; Malik, A. Earthworm activity affecting organic matter, aggregation and microbial activity in soils restored after opencast mining for coal. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, O.; Kohli, L.; Schuler, B.; Zever, J. Surface cast production by the earthworm Aporrectodea nocturna in a pre–alpine meadow in Switzerland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1996, 22, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasiah, V.; Kay, B.D.; Martin, T. Variation of structural stability with water content: Influence of selected soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panabokke, C.R.; Quirk, J.P. Effect of initial water content on stability of soil aggregates in water. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaëns, T. Degradation dynamics of surface earthworm casts in grasslands of the eastern plains of Colombia. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, L.; Jiménez, J.J.J.; Torres, E.A.; Amézquita, E.; Decaëns, T. Rainfall impact effects on ageing casts of a tropical anecic earthworm. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiptalo, M.J.; Butt, K.R. Occupancy and geometical properties of Lumbricus terrestris L. burrows affecting infiltration. Pedobiologia 1999, 43, 782–794. [Google Scholar]
- Bastardie, F.; Cannavacciuolo, M.; Capowiez, Y.; Dreuzy, J.R.D.; Bellido, A.; Cluzeau, D. A new simulation for modelling the topology of earthworm burrow systems and their effects on macropore flow in experimental soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchart, E.; Alegre, J.; Duboisset, A.; Lavelle, P.; Brussaard, L. Effects of earthworms on soil structure and physical properties. In Earthworm Management in Tropical Agroecosystems; Lavelle, P., Brussaard, L., Hendrix, P., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, CT, USA, 1999; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Blouin, M.; Lavelle, P.; Laffray, D. Drought stress in rice (Oryzasativa L.) is enhanced in the presence of the compacting earthworm Millsonia anomala. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayos, C.B. The roles of texture and structure in the water retention capacity of burnt Mediterranean soils with varying rainfall. Catena 1997, 31, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, Y. Soil hydro–physical characteristics and water retention function of typical shrubbery stands in the Yellow River Delta of China. Catena 2017, 156, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
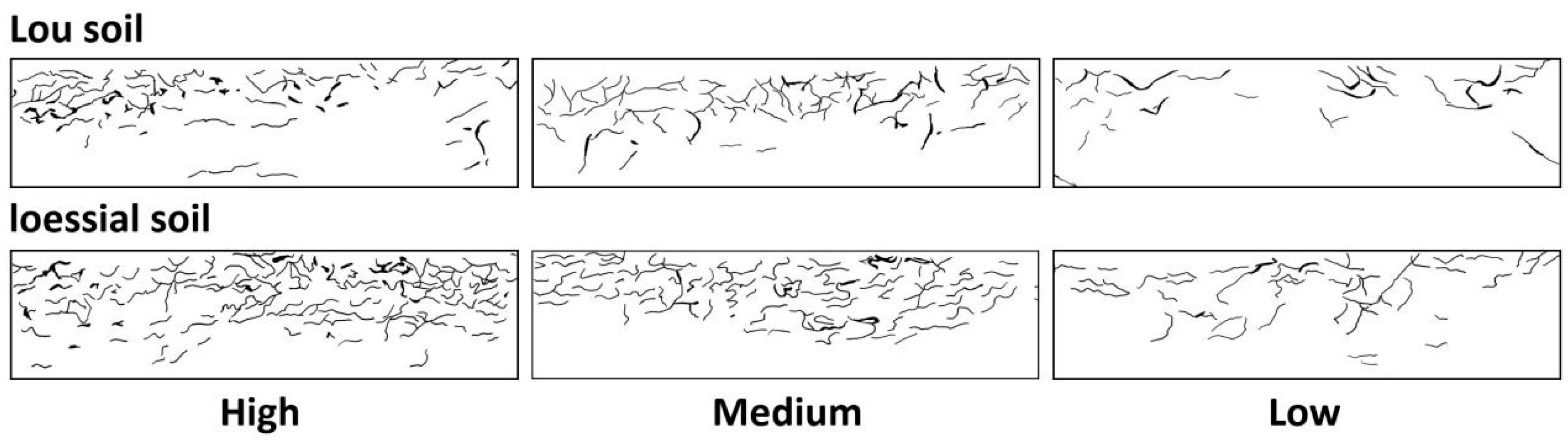

| Lou Soil | Loessial Soil | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Medium | Low | High | Medium | Low | |
| 0–5 cm | ||||||
| Area of burrows (%) | 2.96 ± 0.26 a | 2.54 ± 0.32 ab | 1.79 ± 0.10 b | 3.38 ± 0.51 a | 2.67 ± 0.39 ab | 2.04 ± 0.17 b |
| Area of macropores (%) | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.06 a | 0.05 ± 0.02 ab | 0 b |
| Number of branches | 15.75 ab | 20.25 a | 6 b | 29.75 a | 16.25 b | 11.75 b |
| 5–10 cm | ||||||
| Area of burrows (%) | 1.66 ± 0.17 a | 1.84 ± 0.32 a | 0.62 ± 0.11 b | 3.52 ± 0.37 a | 2.52 ± 0.20 a | 1.24 ± 0.34 b |
| Area of macropores (%) | 0.10 ± 0.05 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0 |
| Number of branches | 6.50 a | 7.75 a | 1.50 b | 25.50 a | 10.25 b | 6 b |
| 10–15 cm | ||||||
| Area of burrows (%) | 0.16 ± 0.07 | 0.32 ± 0.12 | 0.22 ± 0.09 | 0.76 ± 0.18 | 1.24 ± 0.16 | 0.57 ± 0.35 |
| Area of macropores (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0 |
| Number of branches | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 2.25 | 4.50 | 1.50 |
| Total layer (0–15 cm) | ||||||
| Number of burrows | 64 a | 54 ab | 37 b | 64.5 a | 58.75 ab | 34 b |
| Area of burrows (%) | 4.78 ± 0.30 a | 4.70 ± 0.30 a | 2.63 ± 0.20 b | 7.66 ± 0.81 a | 6.43 ± 0.60 a | 3.84 ± 0.81 b |
| Area of macropores (%) | 0.25 ± 0.04 a | 0.15 ± 0.08 ab | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.10 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 ab | 0 b |
| Number of branches | 22.50 a | 28.50 a | 7.75 b | 57.50 a | 31 b | 19.25 b |
| Number of Burrows | Area of Burrows (%) | Area of Macropores (%) | AGL (%) | AGS (%) | Ks (mm min−1) | Field Capacity (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | |
| Soil moisture | 8.98 | 0.002 | 23.51 | <0.001 | 10.16 | <0.001 | 7.72 | 0.001 | 0.32 | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0.75 | 33.76 | <0.001 |
| Soil type | 0.02 | 0.90 | 27.08 | <0.001 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.86 | 0.36 | 11.01 | 0.002 | 1.74 | 0.19 | 3.518 | 0.07 |
| Soil depth | — | — | 90.91 | <0.001 | 10.56 | <0.001 | 83.16 | <0.001 | 0.06 | 0.94 | 9.52 | <0.001 | 32.57 | <0.001 |
| Soil moisture × soil type | 0.15 | 0.86 | 1.76 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.80 | 4.05 | 0.02 | 4.45 | 0.02 | 1.70 | 0.20 | 3.90 | 0.03 |
| Soil moisture × soil depth | — | — | 5.25 | 0.001 | 3.07 | 0.02 | 9.80 | <0.001 | 0.41 | 0.80 | 1.57 | 0.20 | 1.88 | 0.13 |
| Soil type × soil depth | — | — | 3.33 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.71 | 7.61 | <0.001 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 3.42 | 0.04 | 7.51 | 0.001 |
| Soil moisture × soil type × soil depth | — | — | 1.26 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.92 | 0.25 | 0.91 | 1.86 | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, S.; Shao, M.; Wang, J. Earthworm Burrowing Activity and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Soil Moisture Conditions from the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219303
Wen S, Shao M, Wang J. Earthworm Burrowing Activity and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Soil Moisture Conditions from the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(21):9303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219303
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Shuhai, Ming’an Shao, and Jiao Wang. 2020. "Earthworm Burrowing Activity and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Soil Moisture Conditions from the Loess Plateau, China" Sustainability 12, no. 21: 9303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219303
APA StyleWen, S., Shao, M., & Wang, J. (2020). Earthworm Burrowing Activity and Its Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties under Different Soil Moisture Conditions from the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability, 12(21), 9303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219303





