Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
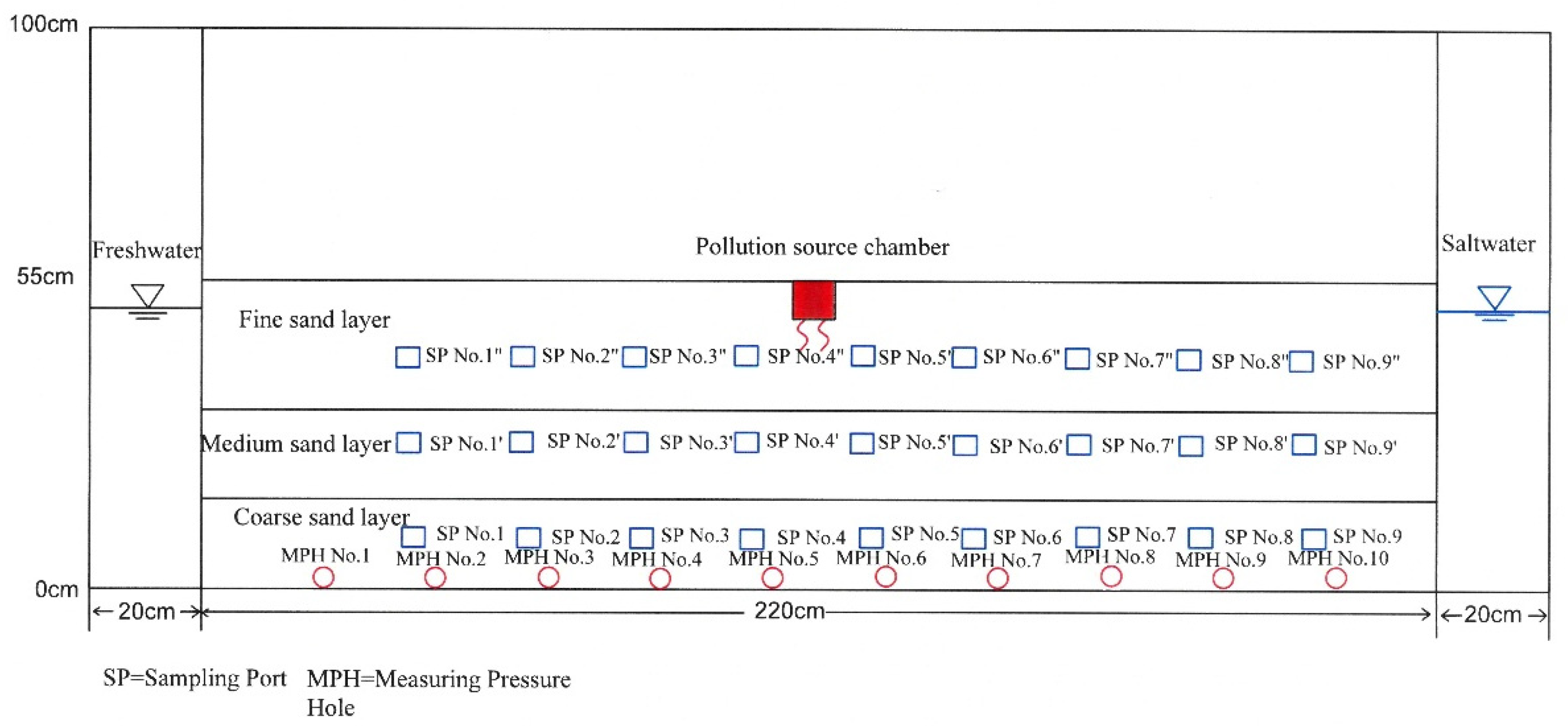
2.1. Laboratory Experiment
2.2. Numerical Model and Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
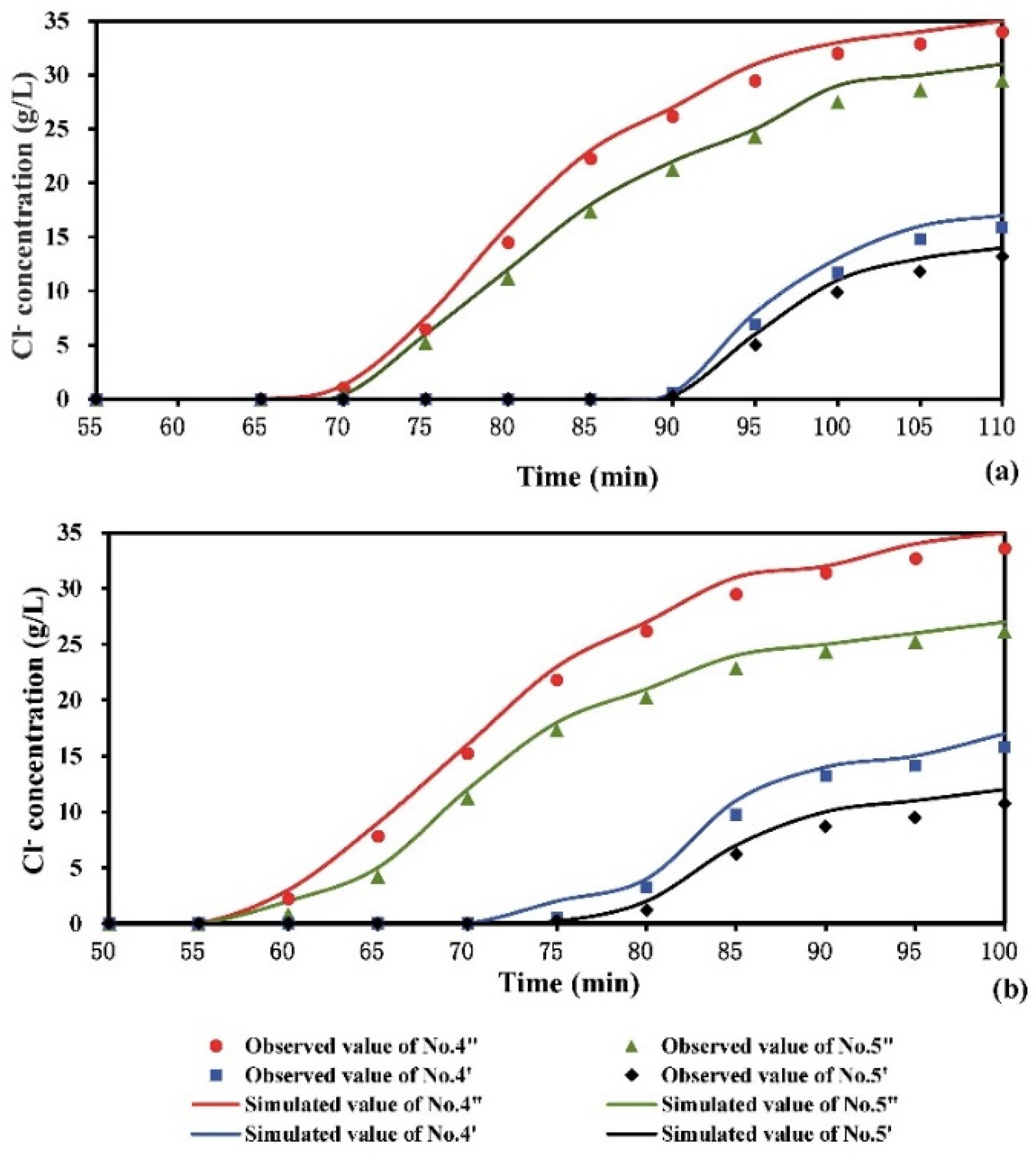
3.1. Numerical Validation
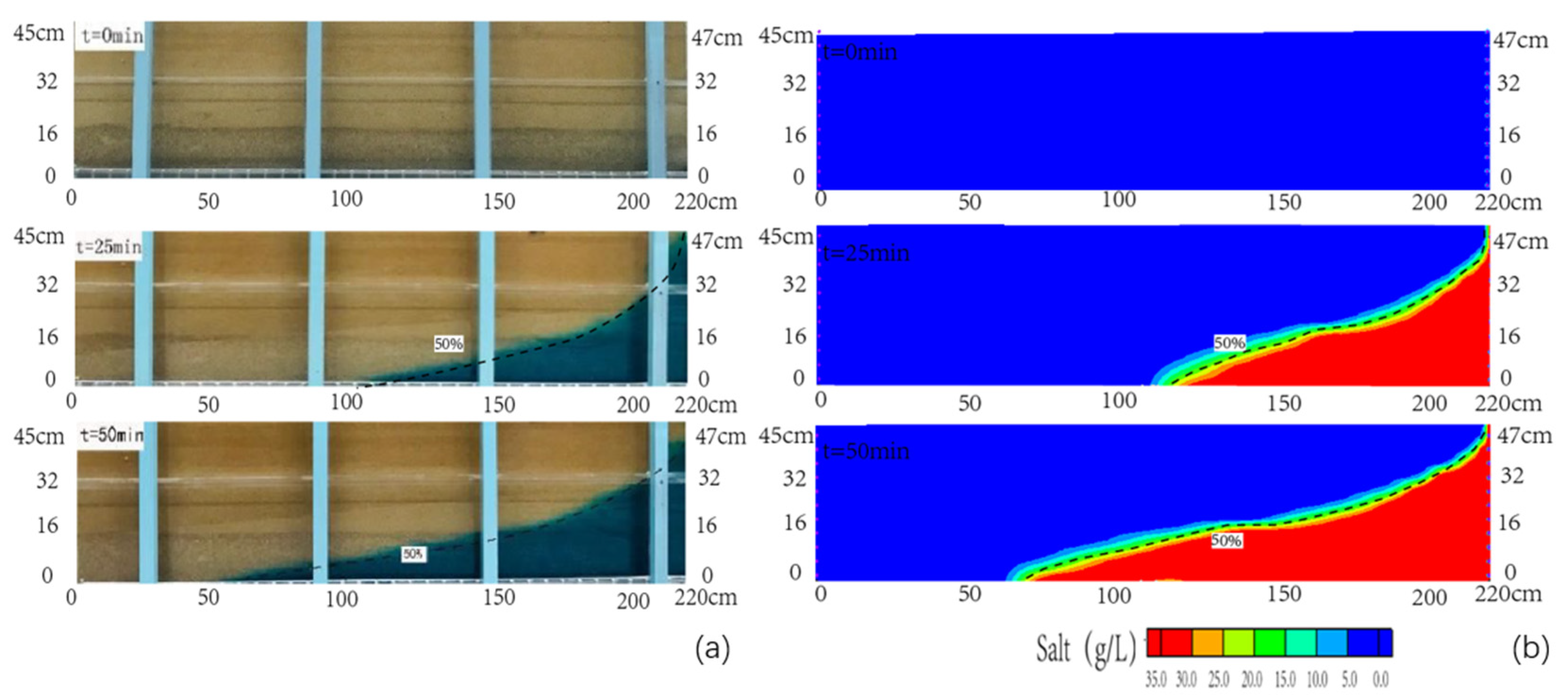
3.2. Seawater Intrusion Effected by Seawater Level Rise
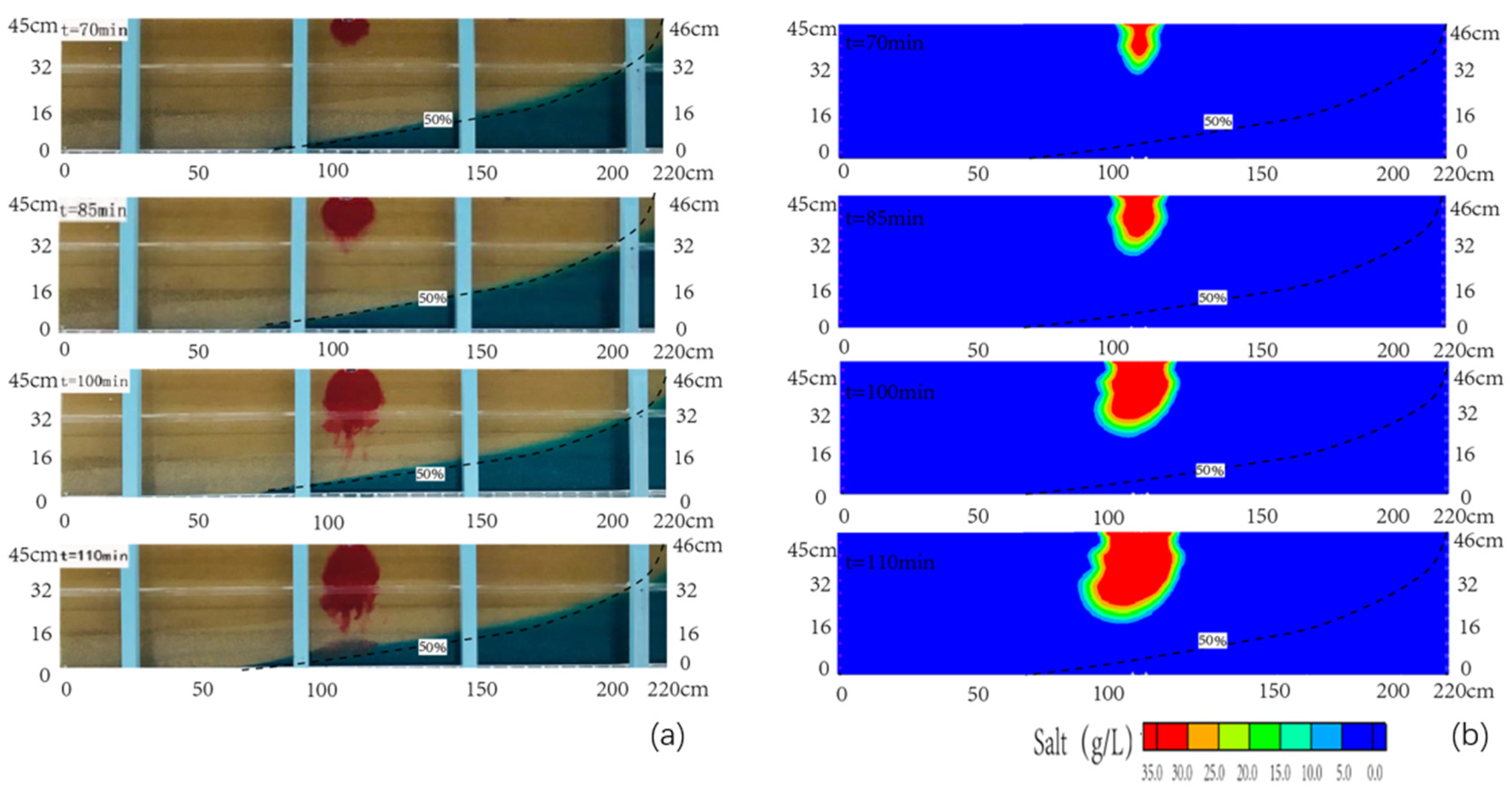
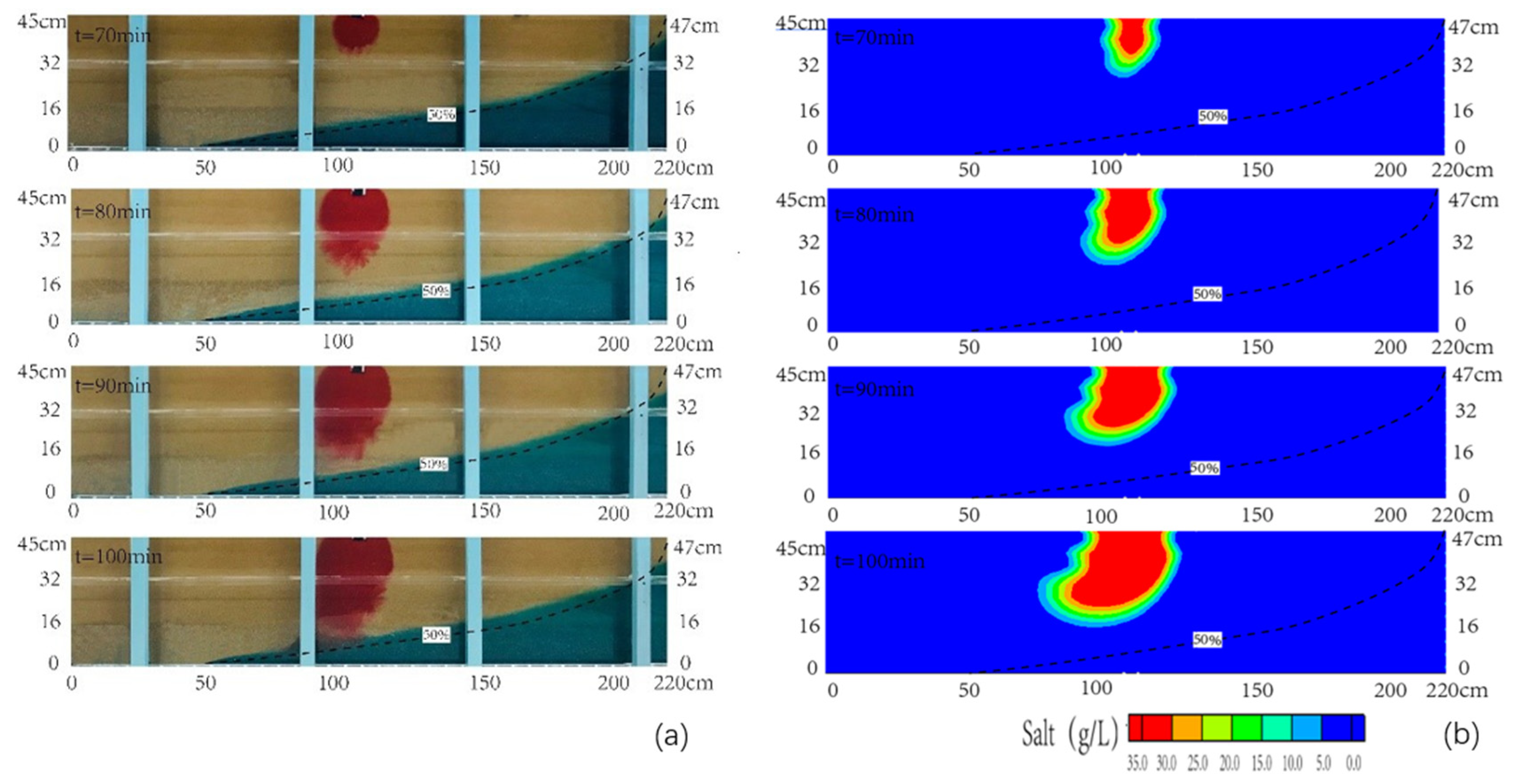
3.3. Contamination Transport Effected by Seawater Level Rise
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.4.1. Effect of Hydraulic Conductivity
3.4.2. Effect of Dispersion
3.4.3. Effect of Contaminant Concentration
3.4.4. Effect of Homogeneous Aquifer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T. Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.N.; Huang, J.W.; Zhou, Z.F.; Wang, J.G. Experiment and numerical simulation of seawater intrusion under the influences of tidal fluctuation and groundwater exploitation in coastal multilayered aquifers. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 2316271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of seawater rise on seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. Ground Water 2014, 52, 264–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.H.; Ataie-Ashtianiab, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.N.; Li, H.L.; Boufadel, M.C.; Sharifi, Y. Hydrodynamics in a gravel beach and its impact on the Exxon Valdez oil. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.L.; Boufadel, M.C. Long-term persistence of oil from the Exxon Valdez spill in two-layer beaches. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufadel, M.; Geng, X.L.; An, C.J.; Owens, E.; Chen, Z.; Lee, K.N.; Taylor, E.; Prince, R.C. A Review on the factors affecting the deposition, retention, and biodegradation of oil stranded on beaches and guidelines for designing laboratory experiments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, S.L.; Unger, D.; Wu, Y.; Jennerjahn, C.T. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 57, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, A.; Weinstein, Y.; Yechieli, Y.; Borisover, M. The influence of fish ponds and salinization on groundwater quality in the multi-layer coastal aquifer system in Israel. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, A.; Weinstein, Y.; Walman, S.; Goldman, M.; Yechieli, Y. The interrelations between a multi-layered coastal aquifer, a surface reservoir (fish ponds) and the sea. Water 2018, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Javadi, A.A. Impact of sea level rise and over-pumping on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.; Robinson, C.; Barry, D.A. Influence of tides and waves on the fate of nutrients in a nearshore aquifer: Numerical simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 73, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Tidal effects on seawater intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T.; Morgan, L.K.; Lu, C. How important is the impact of land-surface inundation on seawater intrusion caused by sea-level rise? Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xin, P.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Seawater intrusion in response to sea-level rise in a coastal aquifer with a general-head inland boundary. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.R.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B. An evaluation of the relative importance of the effects of climate change and groundwater extraction on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers in Atlantic Canada. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y. Saltwater transport under the influence of sea-level rise in coastal multilayered aquifers. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 36, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, J.M.; Hassaoui, J.; Molson, J.; Therrien, R.; Therrien, P.; Chouteau, M.; Ouellet, M. Simulating the impact of climate change on the groundwater resources of the Magdalen Islands, Quebec, Canada. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 3, 400–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehdizadeh, S.S.; Karamalipour, S.E.; Asoodeh, R. Sea level rise effect on seawater intrusion into layered coastal aquifers (simulation using dispersive and sharp-interface approaches). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 138, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Werner, A.D.; Simmons, C.T. Sea-level rise impact on fresh groundwater lenses in two-layer small islands. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5938–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.L.; Lu, C.H.; Ye, Y.; Wu, J.C.; Li, L.; Luo, J. Assessment of the impact of sea-level rise on steady-state seawater intrusion in a layered coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.D.; Howard, W.F. Modeling the transient response of saline intrusion to rising sea levels. Groundwater 2011, 49, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdoulhalik, A.; Ahmed, A.A. Transience of seawater intrusion and retreat in response to incremental water-level variations. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, L.K.; Stoeckl, L.; Werner, A.D.; Post, V.E.A. An assessment of seawater intrusion overshoot using physical and numerical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6522–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Contaminant transport in the aquifers influenced by tide. Aust. Civil Eng. Trans. Institut. Eng. Aust. 2002, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Enot, P.; Barry, D.A.; Li, L.; Binley, A.; Jeng, D.S. Tidal influence on behavior of a coastal aquifer adjacent to a low-relief estuary. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyar, R.; Brovelli, A.; Barry, D.A.; Robinson, C.; Li, L. Transport of variable-density solute plumes in beach aquifers in response to oceanic forcing. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 53, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, A.; Mao, X.; Barry, D.A. Numerical modeling of tidal influence on density-dependent contaminant transport. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Luo, X. Effects of inland water level oscillation on groundwater dynamics and land-sourced solute transport in a coastal aquifer. Coast. Eng. 2016, 114, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Kong, J.; Xin, P.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L. Solute transport influenced by unstable flow in beach aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 125, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohbor, B.; Fahs, M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T. Semi-analytical solutions for contaminant transport under variable velocity field in a coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Experimental investigation of contaminant transport in coastal groundwater. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B. MODSharp: Regional-scale numerical model for quantifying groundwater flux and contaminant discharge into the coastal zone. Environ. Modell Softw. 2007, 22, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Lai, K.H.; Liu, C.W.; Ni, C.F. A novel method for analytically solving multi-species advective–dispersive transport equations sequentially coupled with first-order decay reactions. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, M.; Kosakowski, G.; Jakob, A.; Churakov, S.V. A class of analytical solutions for multidimensional multispecies diffusive transport coupled with precipitation-dissolution reactions and porosity changes. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, WR3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.W.; Clement, T.P. Laboratory and numerical investigation of transport processes occurring above and within a saltwater wedge. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 147, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.T.; Dawson, C.N.; Farthing, M.W.; Hou, T.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Kees, C.E.; Kelley, C.T.; Langtangen, H.P. Numerical simulation of water resources problems: Models, methods, and trends. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 405–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, X.; Chen, J.; Barry, D.A. Influence of a coarse interlayer on seawater intrusion and contaminant migration in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5162–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Kim, U. An upscaled approach for transport in media with extended tailing due to back-diffusion using analytical and numerical solutions of the advection dispersion equation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 182, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahkarami, P.; Liu, L.; Moreno, L.; Neretnieks, I. Radionuclide migration through fractured rock for arbitrary-length decay chain: Analytical solution and global sensitivity analysis. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufadel, M.C.; Xia, Y.Q.; Li, H.L. Modeling solute transport and transient seepage in a laboratory beach under tidal influence. Environ. Modell Softw. 2011, 26, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Boufadel, M.C.; Cui, F. Numerical modeling of subsurface release and fate of benzene and toluene in coastal aquifers subjected to tides. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Boufadel, M.C. A tracer study in an Alaskan gravel beach and its implications on the persistence of the Exxon Valdez oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.N.; Li, H.L.; Boufadel, M.C.; Liu, J. A field experiment and numerical modeling of a tracer at a gravel beach in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; He, W.; Savoy, H.; Dietrich, P.; Kolditz, O.; Rubin, Y.; Schüth, C.; Kalbacher, T. Identifying the influential aquifer heterogeneity factor on nitrate reduction processes by numerical simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 99, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalumera, G.M.; Calamari, D.; Galli, P.; Castgilioni, S.; Crosa, G.; Fanelli, R. Preliminary investigation on the environmental occurrence and effects of antibiotics used in aquaculture in Italy. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, E.A.; Dietze, J.E.; Meyer, M.T.; Kolpin, D.W. Occurrence of Antibiotics in Water from Fish Hatcheries; U.S. Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2002; p. 68.
- Guo, W.; Langevin, C.D. User’s guide to SEAWAT: A computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variabledensity groundwater flow. In Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; p. 434. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, C.D.; Shoemaker, W.B.; Guo, W. MODFLOW-2000, the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model: Documentation of the SEAWAT-2000 Version with Variable Density Flow Process (VDF) and the Integrated MT3DMS Transport Process (IMT). U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 3–426.
- Bakker, M.A. Dupuit formulation for modeling seawater intrusion in regional aquifer system. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Bill, X.H.; Burnett, W.C.; Santos, I.R.; Chanton, J.P. Submarine groundwater discharge driven by tidal pumping in a heterogeneous aquifer. Ground Water. 2009, 47, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hu, B.X.; Xu, Z.X.; Li, X.; Tong, J.X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.X.; Miao, J.J.; Liu, H.W.; Ma, Z. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


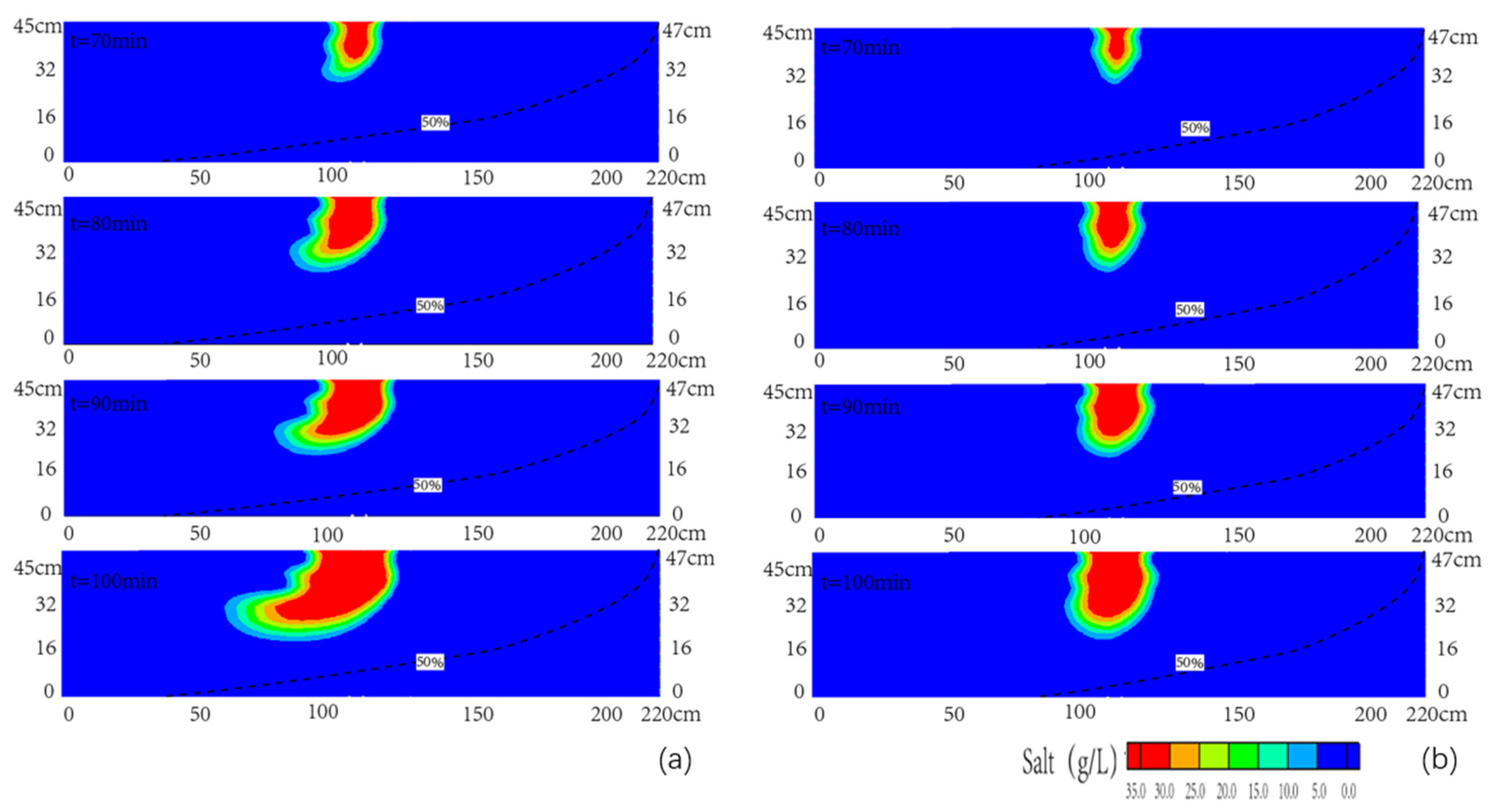

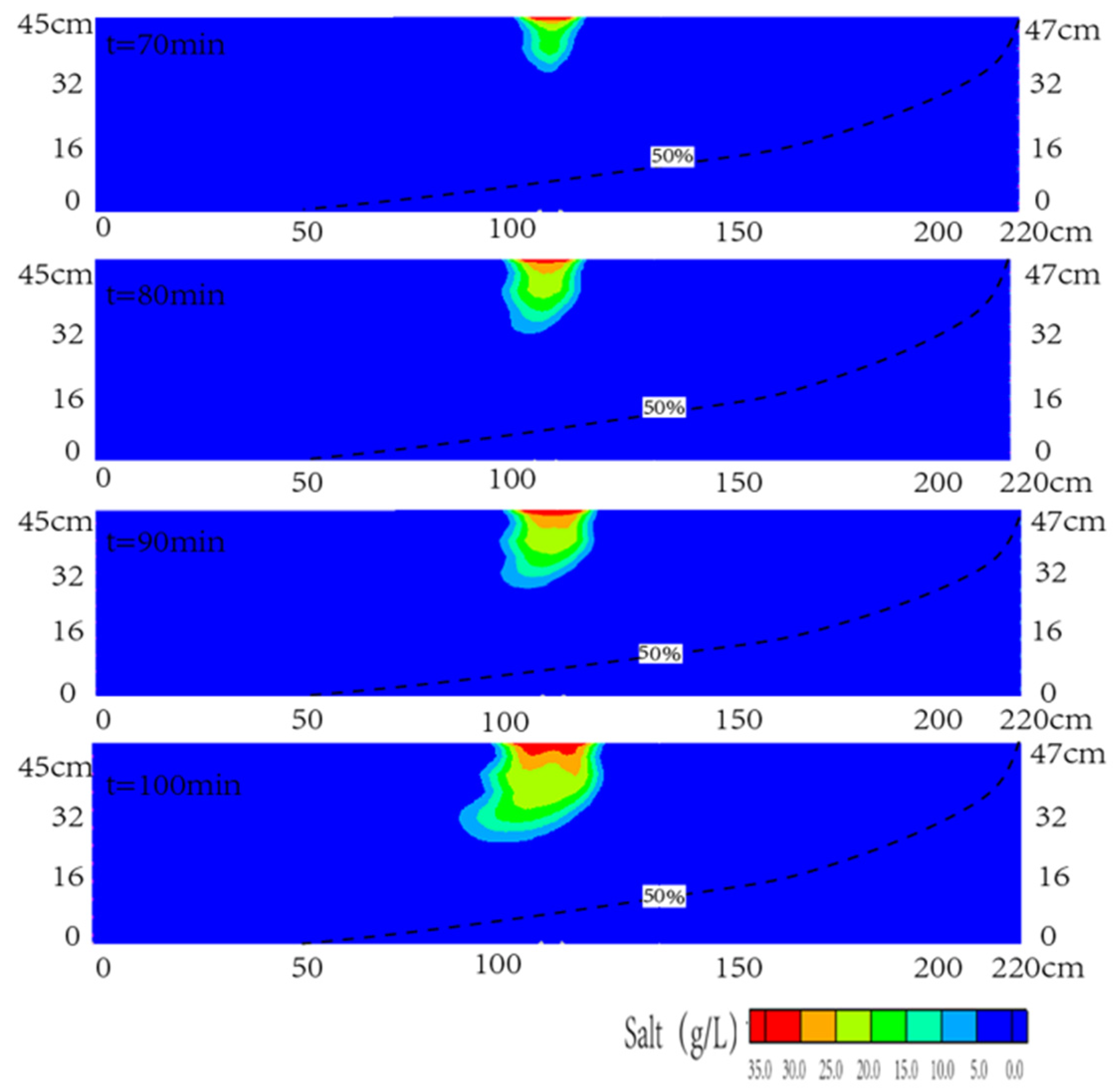
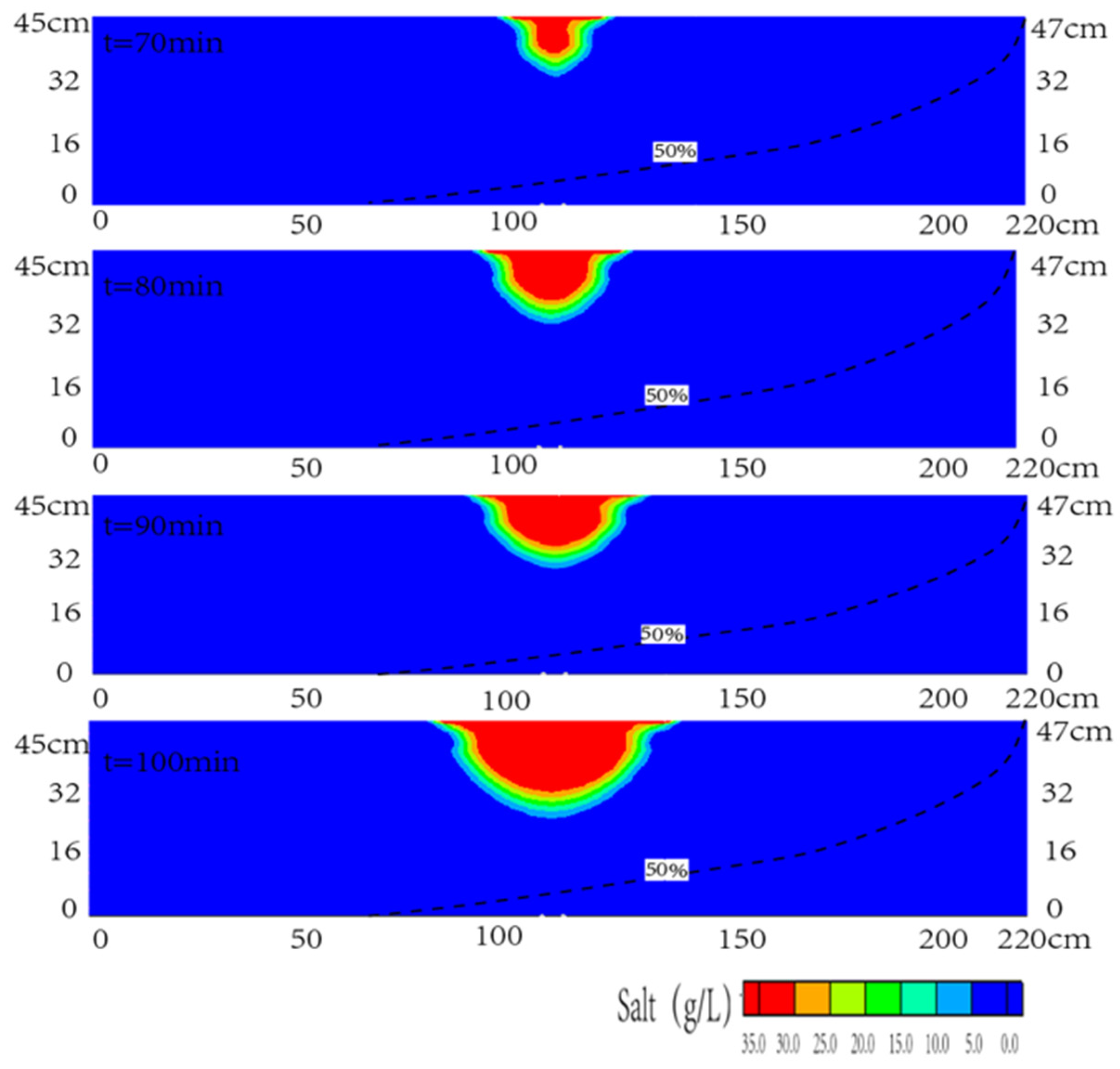
| Parameter | Definition | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | Hydraulic Conductivity | m/s | 4.6 × 10−5 (fine sand layer) |
| 2.9 × 10−4 (medium sand layer) | |||
| 6.9 × 10−4 (coarse sand layer) | |||
| µ | Specific Yield | - | 0.2 (fine sand layer) |
| 0.25 (medium sand layer) | |||
| 0.30 (coarse sand layer) | |||
| Specific Storage | 1/m | 10−5 | |
| Density of the Freshwater | kg/m3 | 1.0 × 103 | |
| Density of the Seawater | kg/m3 | 1.02 × 103 | |
| n | Porosity | - | 0.3 |
| Longitudinal Dispersivity | m | 0.1 | |
| Transverse Dispersivity | m | 0.01 | |
| Molecular Diffusion Coefficient in Porous Media | m2/s | 10−9 | |
| t | Time Period | min | 110 for Case 1 100 for Case 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, Z. Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239838
Guo Q, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Hu Z. Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer. Sustainability. 2020; 12(23):9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239838
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qiaona, Yahui Zhang, Zhifang Zhou, and Zili Hu. 2020. "Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer" Sustainability 12, no. 23: 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239838
APA StyleGuo, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Z., & Hu, Z. (2020). Transport of Contamination under the Influence of Sea Level Rise in Coastal Heterogeneous Aquifer. Sustainability, 12(23), 9838. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239838




