COVID-19, Storms, and Floods: Impacts of Tropical Storm Cristobal in the Western Sector of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. The First Scenarios
2.2. Flood Resilience Indicators and COVID-19
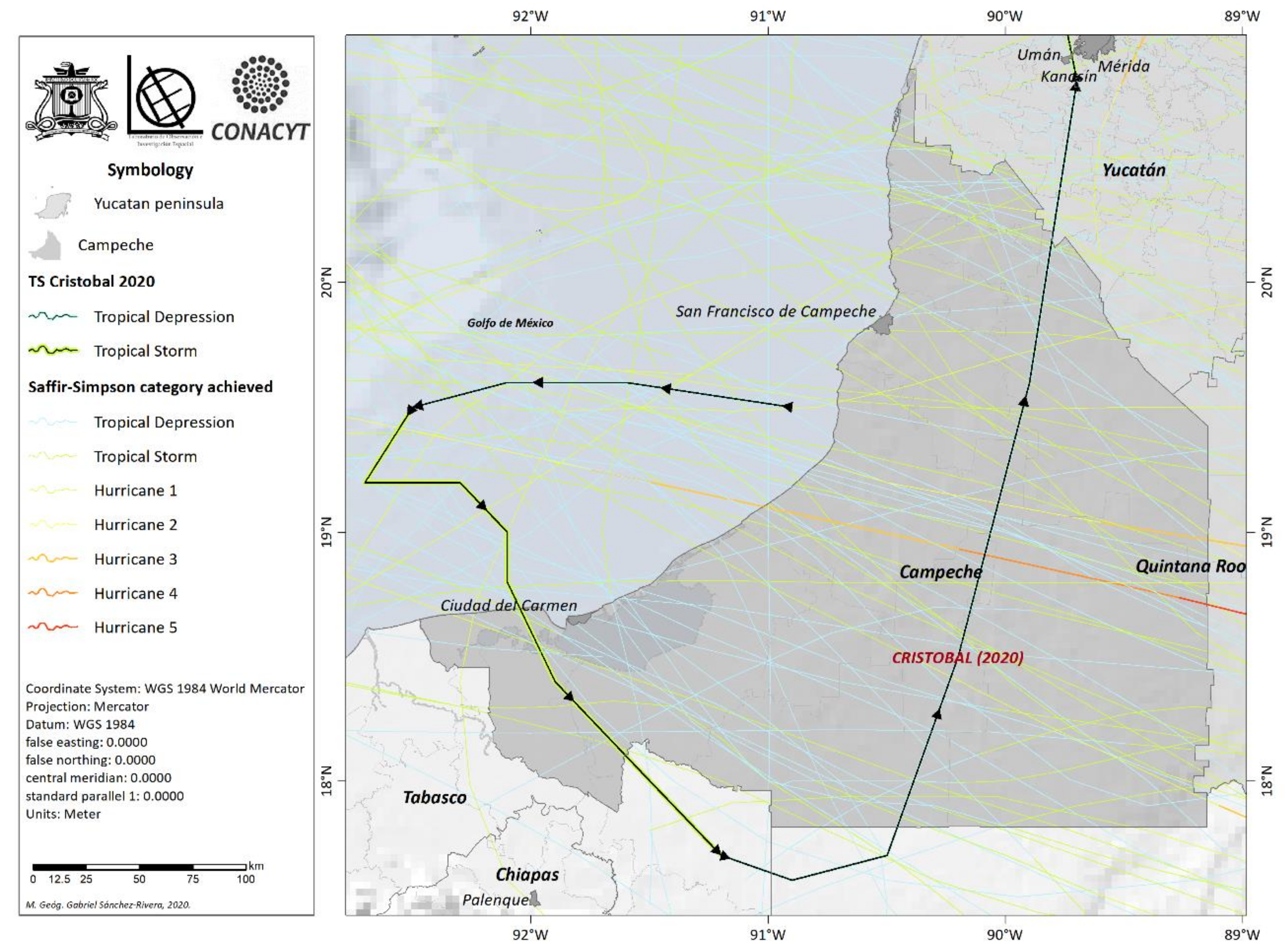
2.3. The Hurricane Season: Tropical Storm Cristobal
3. Materials and Methods
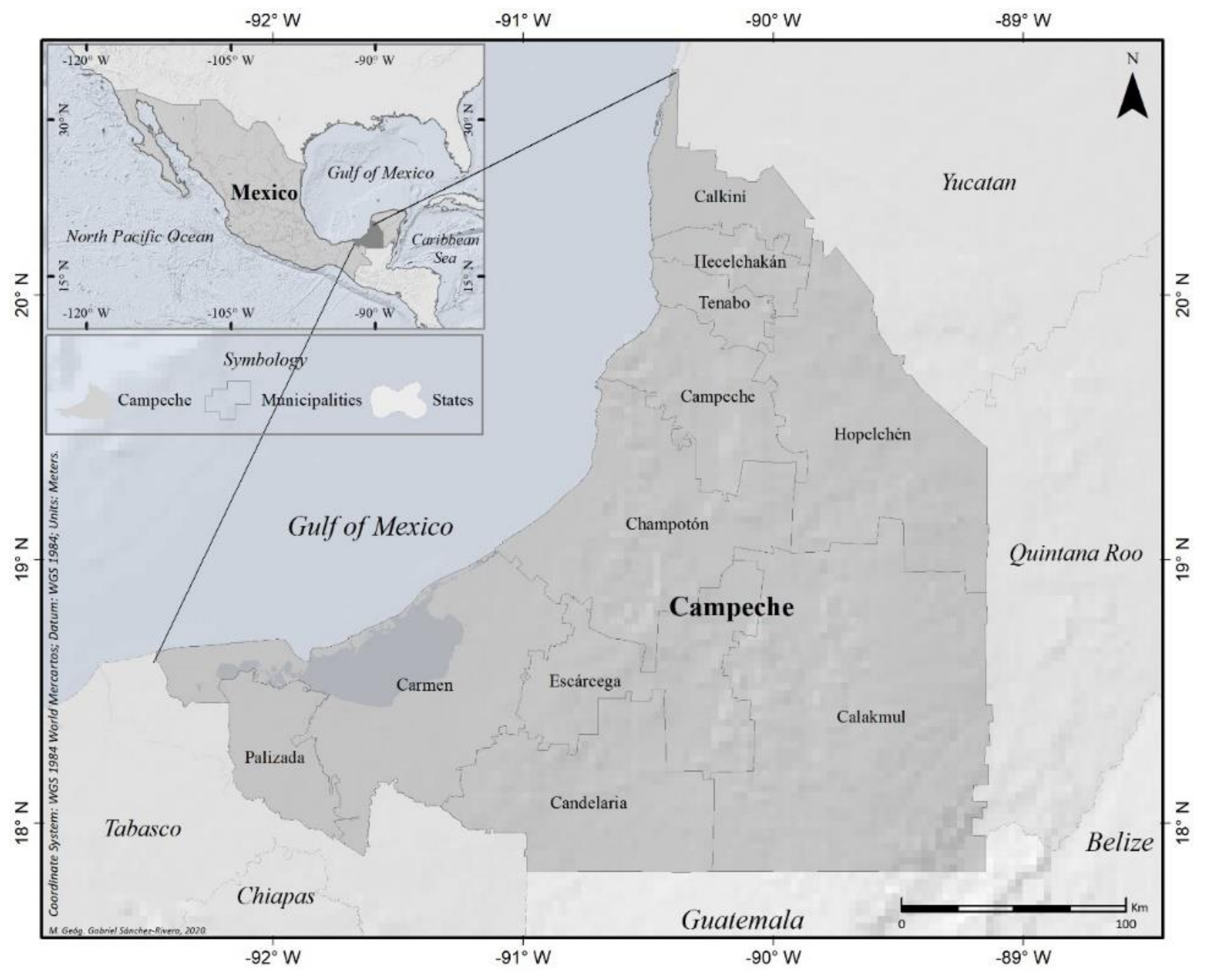
3.1. Study Zone
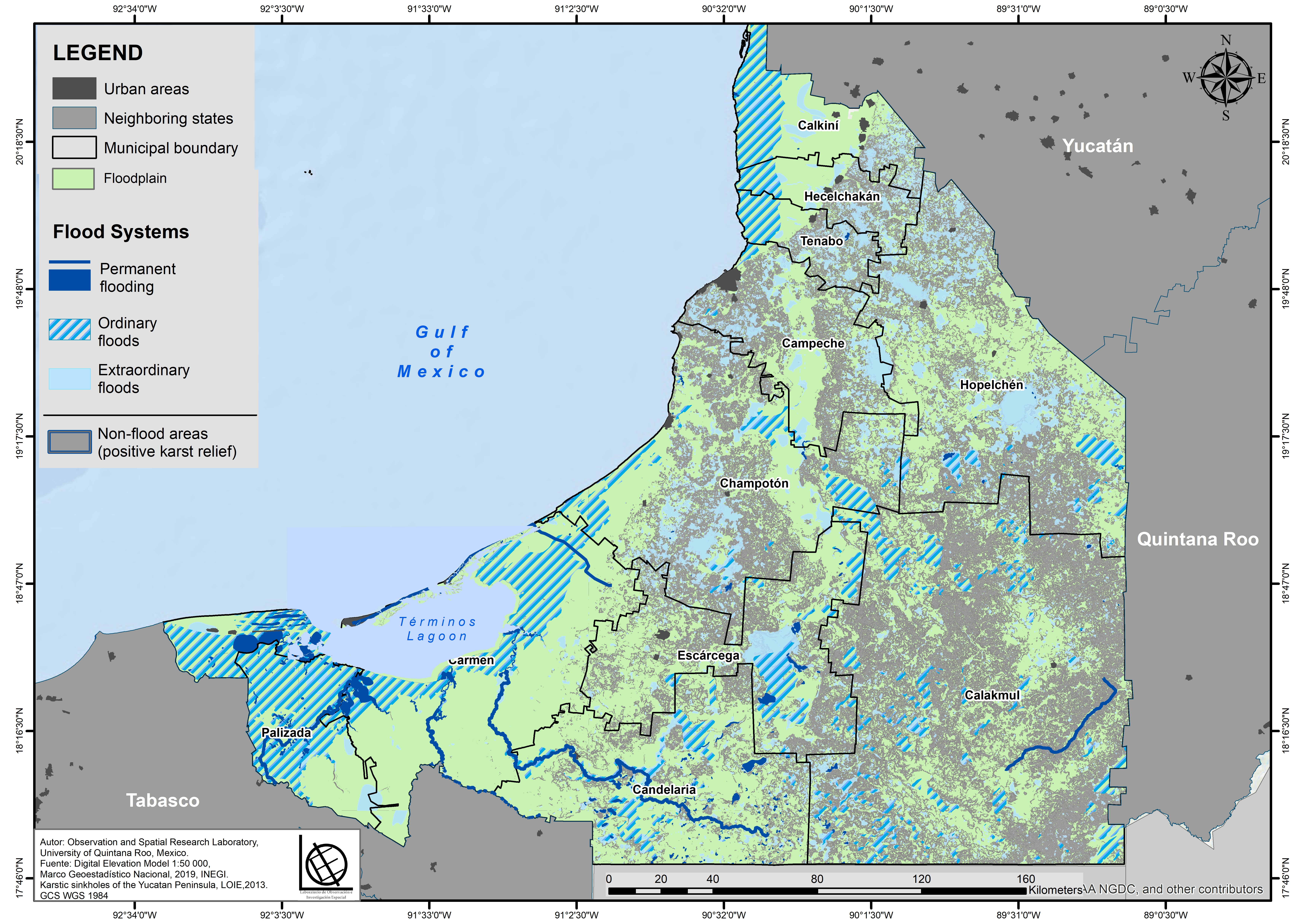
3.2. Data
- The data regarding the trajectories and physical characteristics of the tropical cyclones that impacted the State of Campeche, Mexico, in the period 1851–2019 were obtained from the International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS), a database administered by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The information corresponds to version v04r00 and is available on an internet download portal [45].
- The trajectory of the tropical storm Cristobal was obtained from accumulated wind history data from the National Hurricane Center [46].
- The political limits of Mexico and the topographic vector data (contour lines, depressions, land subject to flooding, bodies of water, and rivers) were determined from the Geostatistical Framework distributed by the National Institute of Statistics, Geography, and Informatics, and 81 topographic charts from the State of Campeche at a scale of 1:50,000 were collected [47].
- Data on the emergency declaration of the Government of Campeche and municipalities affected were obtained. The declaration of emergency was published on 16 June 2020 in the Official Gazette of the Federation [37]. Tropical cyclones emergency bulletins were also released by CENAPRED and the early warning system published by the National Meteorological Service, from which data on precipitation, shelters, impacts generated by floods, and municipalities with declarations of emergency were extracted (issued from 30 May to 8 June 2020).
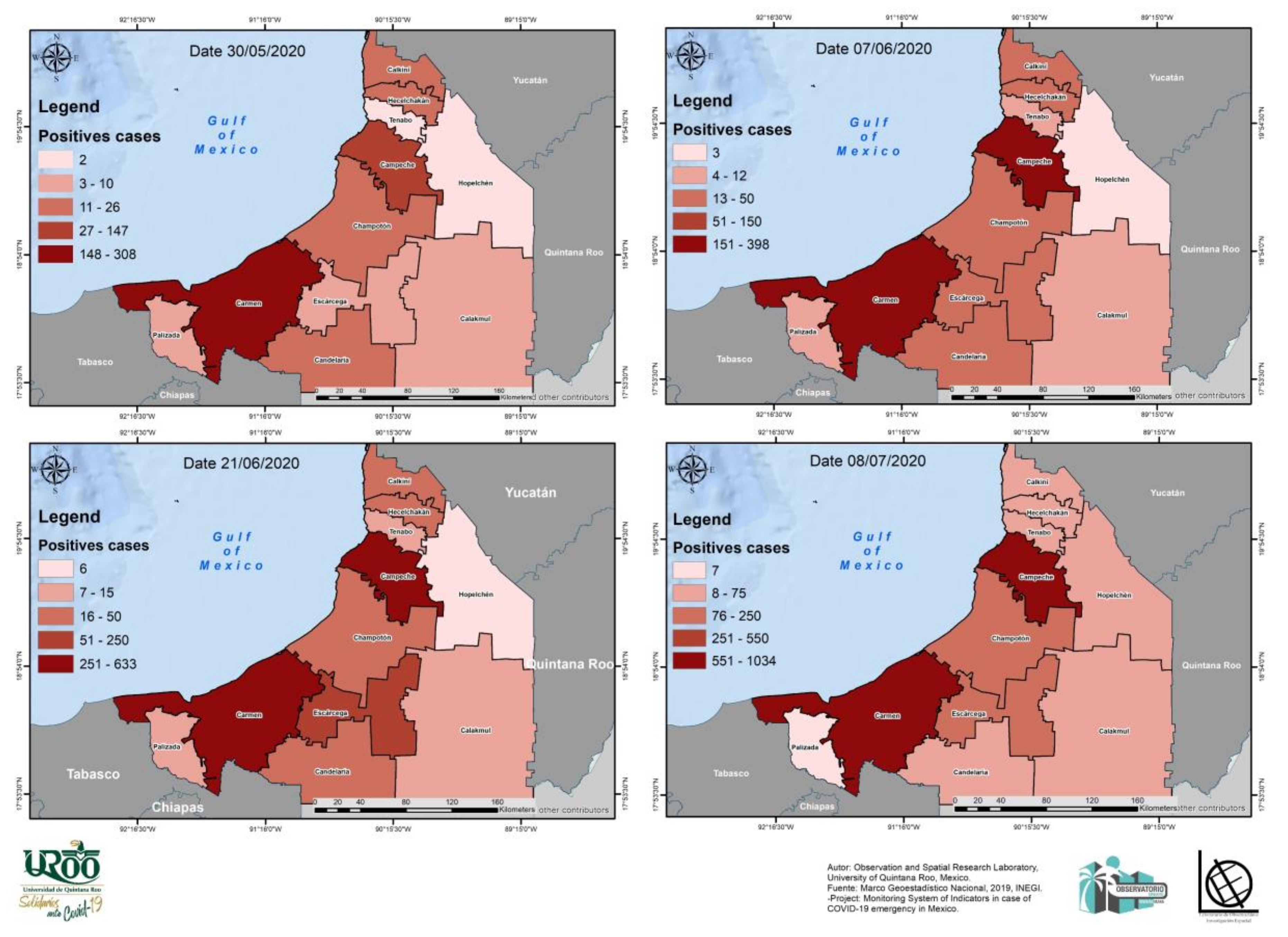
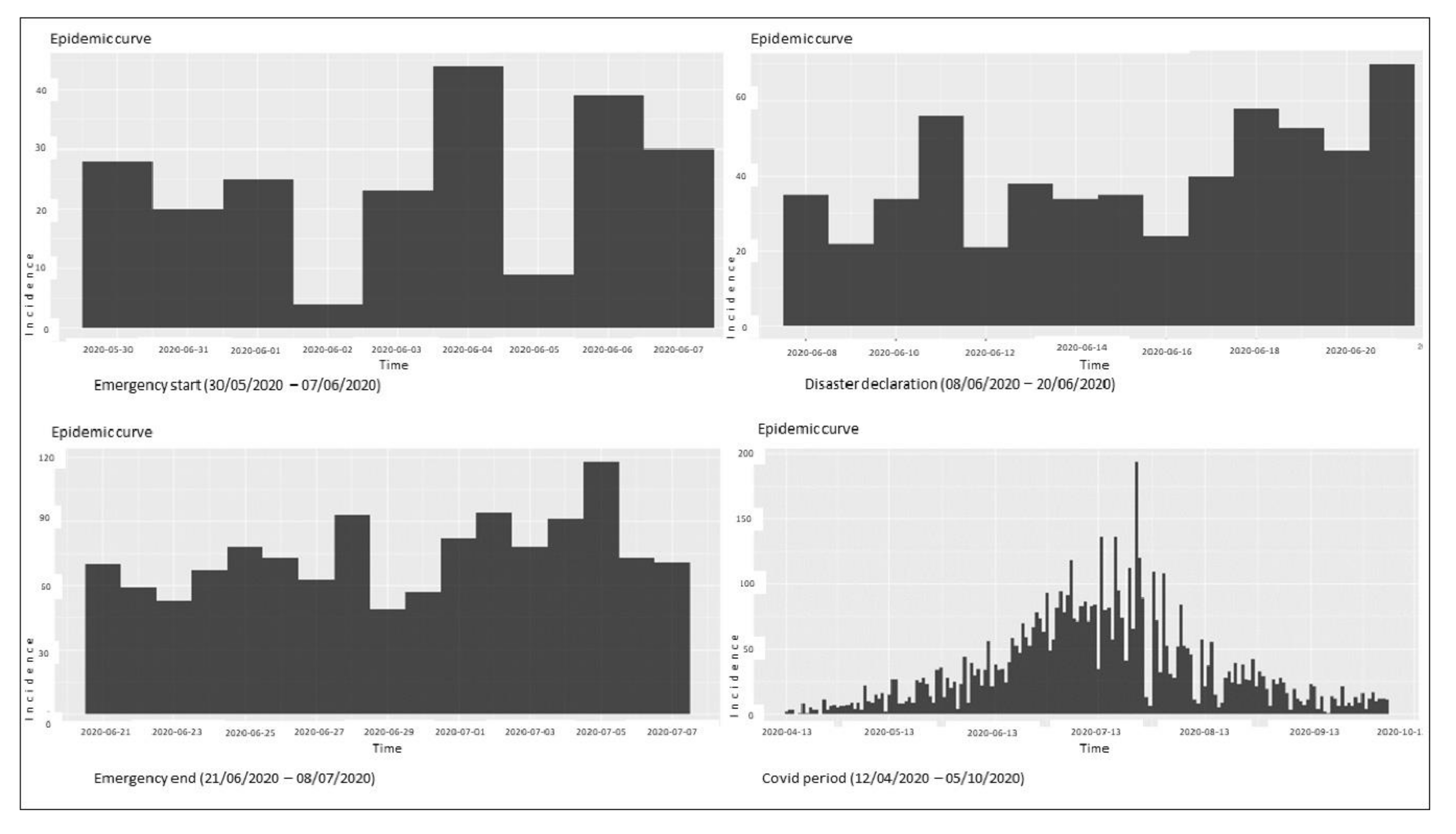
- The data used as a reference for the COVID-19 data were obtained from the historical open data system of the General Directorate of Epidemiology of the Government of Mexico, which included unique identification data on confirmed cases. In this study, the data included were records from 30 May to 30 June 2020 [48] to align with the impact time of the tropical storm Cristobal from 30 May to 6 June, and the following 15 days of possible contagion from 16 to 22 June, as well as 8 days for prospecting and trend comparison, with the above factors depending on the date of the announcement of the end of the contingency issued by the Coordination of Civil Protection of Mexico [41].
3.3. Methodology
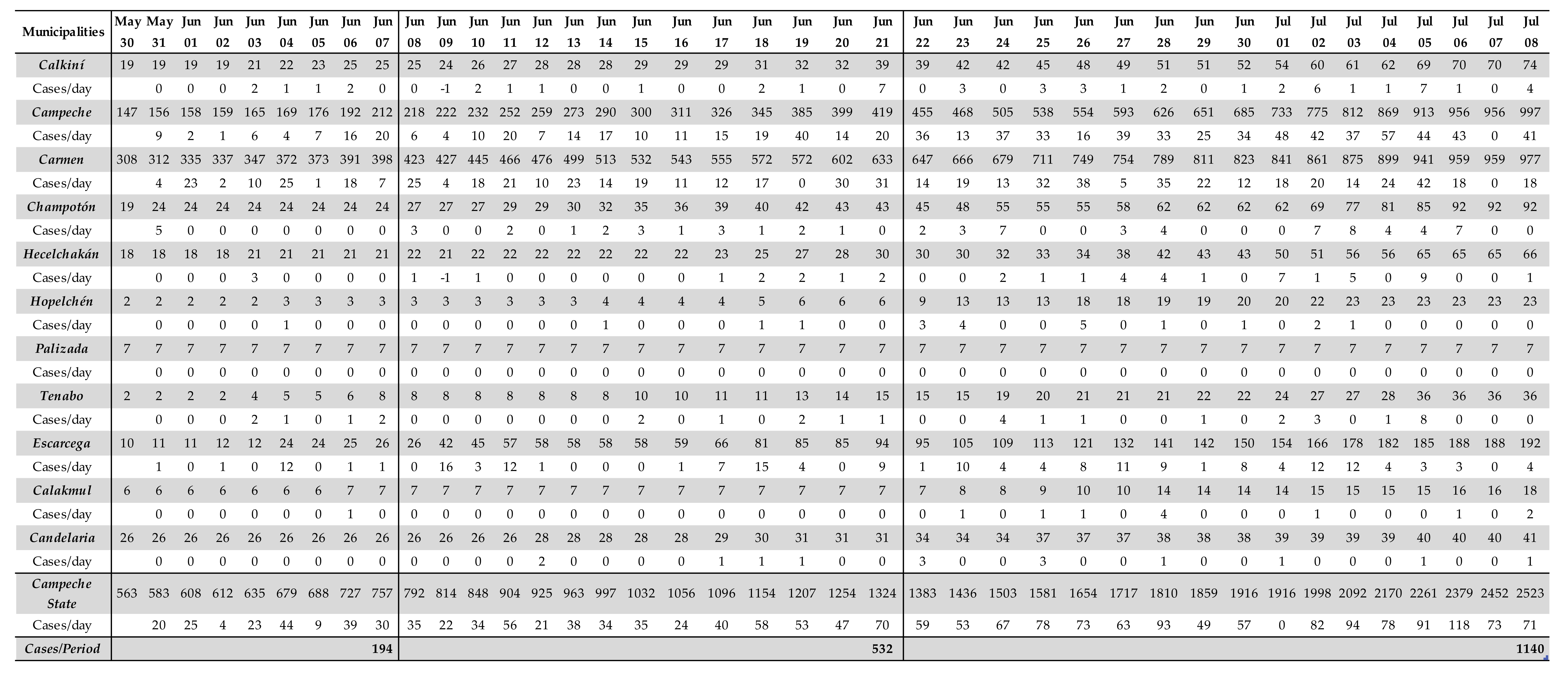
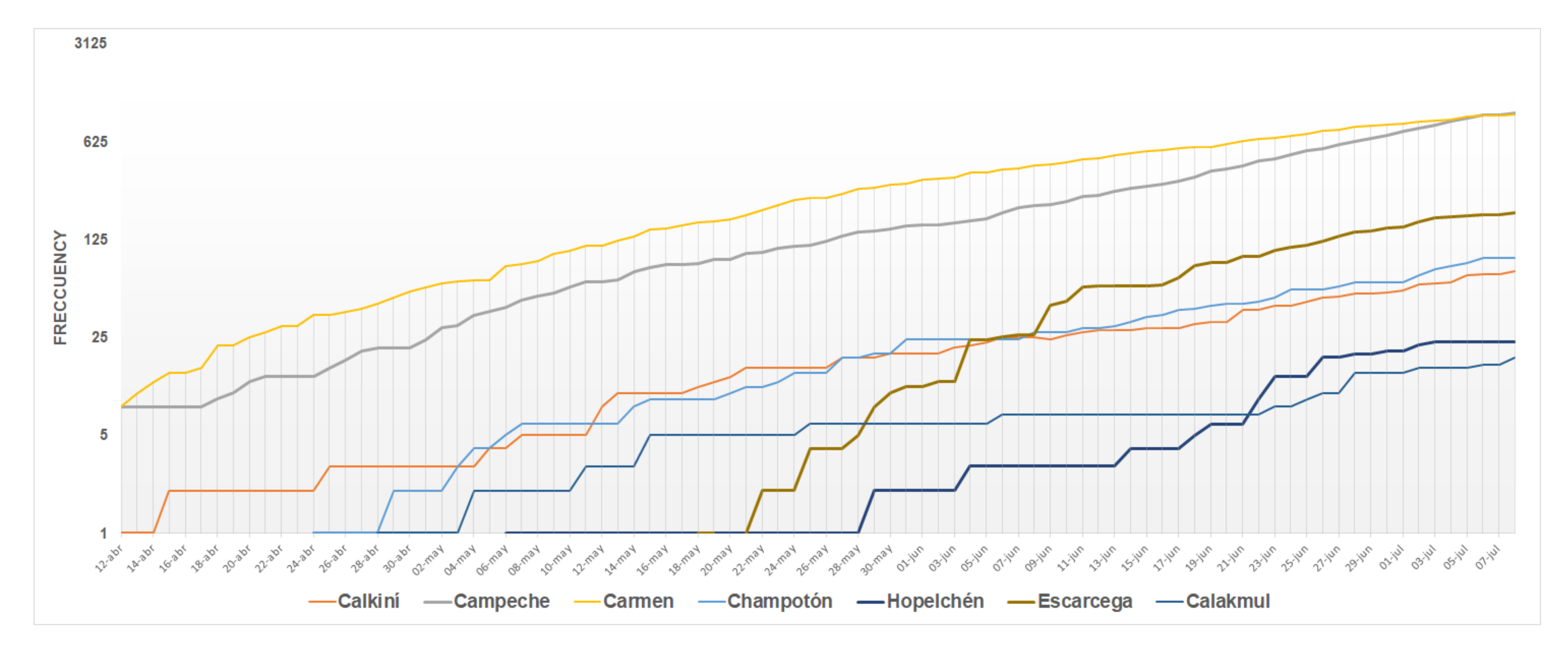
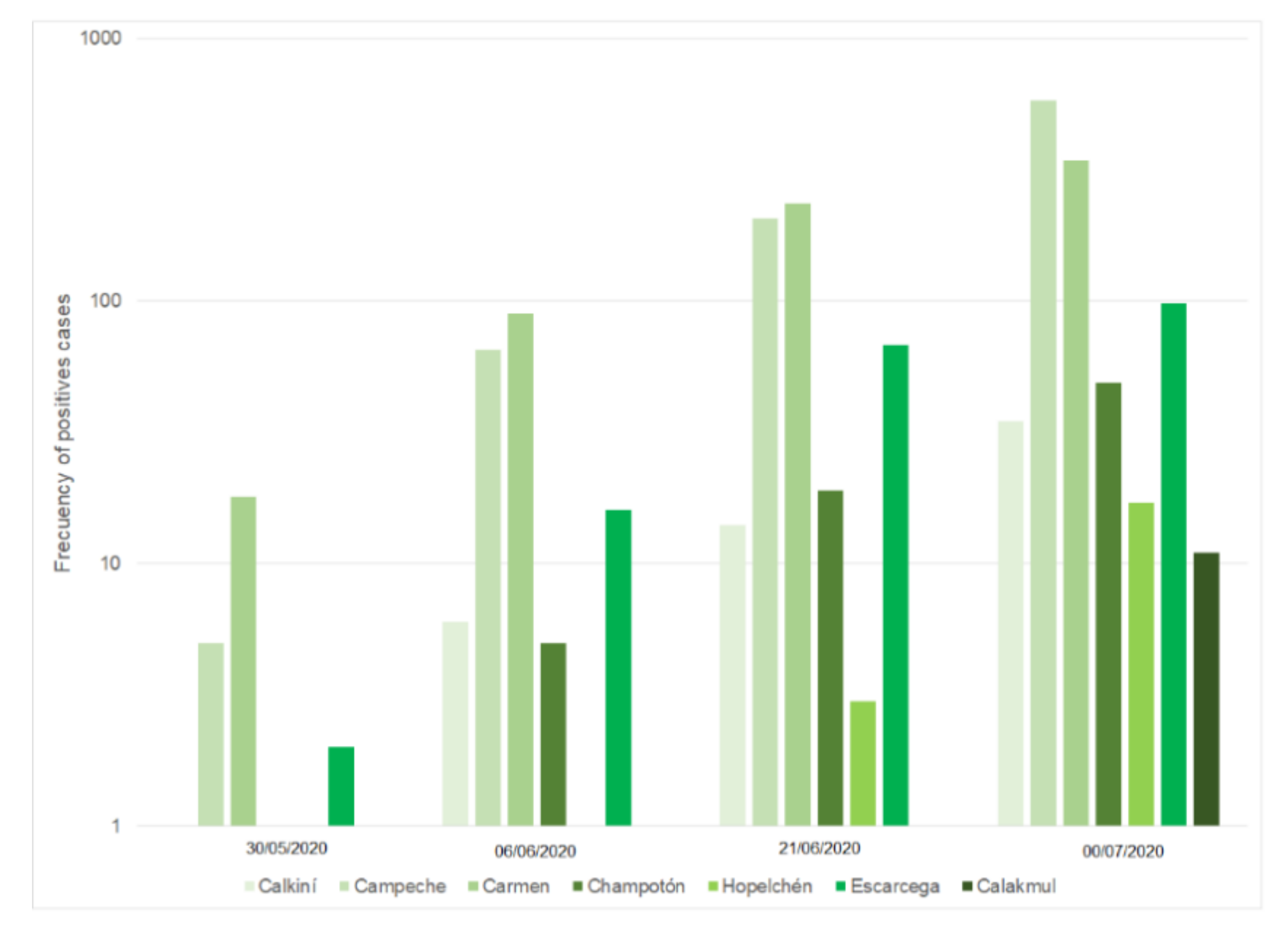
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, J.T.; Gayer, M.; Connolly, M.A. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemonick, D.M. Epidemics after natural disasters. Am. J. Clin. Med. 2011, 8, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kouadio, I.K.; Aljunid, S.; Kamigaki, T.; Hammad, K.; Oshitani, H. Infectious diseases following natural disasters: Prevention and control measures. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, G.D.; Dhar, D.; Nath, D.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Banerjee, R.; Das, S.; Chatterjee, J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak: Some serious consequences with urban and rural water cycle. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, S.H.; Rahman, N.M.; Imtiaz, R.; Gozzer, E.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Ahmed, Y.; Memish, Z.A. Forward planning for disaster-related mass gatherings amid COVID-19. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e379–e380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, R. COVID-19 and dengue: A deadly duo. Trop. Dr. 2020, 50, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Filho, P.R.; Tavares, C.S.S.; Santos, V.S. Factors associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19. A quantitative evidence synthesis of clinical and laboratory data. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 76, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Covert coronavirus infections could be seeding new outbreaks. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, Y.; Lina, B. Coronavirus et COVID-19 Sous titre Du Simple Rhume au Syndrome Respiratoire Aigu Sévère. Available online: https://www.inserm.fr/information-en-sante/dossiers-information/coronavirus-sars-cov-et-mers-cov (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. Q&A on Coronaviruses (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.; McGrath, G. Hurricanes in a Pandemic ‘Absolutely that’s Our Nightmare Scenario’. Available online: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/2020/04/02/hurricane-season-in-june-during-coronavirus-pandemic/5111024002/ (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. Floods. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/floods?fbclid=IwAR1xDiSs8WlRLVyrZzK68m-3lyEQkmDV-_RIz7a0vva4sqOaVBFFWvR4vZ0#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- CENAPRED. Inundaciones; Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres: Mexico, NM, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, C.A.; Caldas, A.; Cleetus, R.; Dahl, K.A.; Declet-Barreto, J.; Licker, R.; Merner, L.D.; Ortiz-Partida, J.P.; Phelan, A.L.; Spanger-Siegfried, E. Compound climate risks in the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The Pacific Islands: Tropical Cyclone Harold—Situation Report May 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/emergencies/resources/documents/resources-detail/en/c/1274007/ (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Ober, K.; Bakumenko, S. Issue Brief: A New Vulnerability: COVID-19 and Tropical Cyclone Harold Create the Perfect Storm in the Pacific. Available online: https://www.refugeesinternational.org/reports/2020/6/1/a-new-vulnerability-COVID-19-and-tropical-cyclone-harold-create-the-perfect-storm-in-the-pacific (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Gutierrez, J. Severe Tropical Storm Vongfong Takes Aim at Philippine Heartland. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/05/15/world/asia/typhoon-vongfong-philippines-luzon.html (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Dasboard for the Western Pacific Region. Available online: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/wprocovid19/ (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- OCHA. Bangladesh: Cyclone Amphan Affects 10 Million People Amid COVID-19. Available online: https://www.unocha.org/story/bangladesh-cyclone-amphan-affects-10-million-people-amid-COVID-19 (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Dema, C. Incessant Rainfall Cause Damage in Tsirang. Available online: https://kuenselonline.com/incessant-rainfall-cause-damage-in-tsirang/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Korosec, M. Tropical Cyclone Amphan (Bay of Bengal) Could Become One of the Most Intense Category 5 on Record in the North Indian Ocean—Major Indian City Kolkata in Its Direct Path. Available online: https://www.severe-weather.eu/tropical-weather/india-cyclone-amphan-bengal-mk/amp/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Nagchoudhary, S.; Ruma, P. Cyclone Kills 14 in India, Bangladesh Leaving Trail of Destruction. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-asia-storm-india/cyclone-kills-14-in-india-bangladesh-leaving-trail-of-destruction-idUSKBN22W0MT (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- NOAA. Tropical Storm Amanda. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/2020/ep02/ep022020.public_a.003.shtml? (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Fedschun, T. China Floods Kill 5 More, as Rainstorms Impact Some 700,000 Residents. Available online: https://www.foxnews.com/world/china-flood-rainstorm-guizhou-hunan-province-weather-flooding (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- IFRC. Hydrological Hazards: General Floods and Flash Floods. Available online: https://www.ifrc.org/en/what-we-do/disaster-management/about-disasters/definition-of-hazard/floods/?fbclid=IwAR0Kid1gMRtM1DScZfEjMNLrGG9SRqFoOANddcnT-aogNTHsUmM_EeVS4rY (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- SEGOB. Manual del Sistema de Alerta Temprana para Ciclones Tropicales (SIAT-CT). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/segob/documentos/manual-del-sistema-de-alerta-temprana-para-ciclones-tropicales-siat-ct (accessed on 17 May 2020).
- UNISDR. Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030. In Proceedings of the 3rd United Nations World Conference on DRR, Sendai, Japan, 14–18 March 2015; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Reghezza-Zitt, M. Utiliser la polysémie de la résilience pour comprendre les différentes approches du risque et leur possible articulation. EchoGéo 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frausto-Martínez, O.; Colín-Olivares, O. Indicadores de Sustentabilidad de la Política de Mares y Costas—México. Rev. Costas 2020, 1, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenayake, C.C.; Mikami, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Jayasinghe, A. Ecosystem services-based composite indicator for assessing community resilience to floods. Environ. Dev. 2018, 27, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzee, I.; Reyers, B. Piloting a social-ecological index for measuring flood resilience: A composite index approach. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.; Qasim, M.; Shrestha, R.P.; Khan, A.N.; Tun, K.; Ashraf, M. Community resilience to flood hazards in Khyber Pukhthunkhwa province of Pakistan. Int. J. Dis. Risk Reduct. 2016, 18, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhong, M.; Hong, Y.; Lin, K. Enhancing community resilience to urban floods with a network structuring model. Saf. Sci. 2020, 127, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalsvig, A.; Barnard, L.T.; Gray, L.; Wilson, N.; Baker, M. Supporting the COVID-19 Pandemic Response: Surveillance and Outbreak Analytics; University of Otago Wellington: Wellington, New Zealand, 2020; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, L.; Honiden, T.; Schumann, A. Indicators for Resilient Cities. OECD Reg. Dev. Work. Pap. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOF. Declaratoria de Emergencia por la Presencia de Lluvia Severa Ocurrida del 30 de Mayo al 5 de Junio de 2020 en 11 Municipios del Estado de Campeche. Available online: http://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5595026&fecha=16/06/2020 (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Aponte, G.P.; de Almeida, P.S.A.; Casarín, R.S.; Bautista, E.; Vanegas, G.P.; Val, R. Diagnóstico de Riesgo por Inundaciones para la Ciudad de Campeche; CENTRO EDOMEX-UAC: Mexico, NM, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ihl, T.; Frausto, O. El cambio Climático y los Huracanes en la Península de Yucatán. In Monitoreo de Riesgo y Desastre Asociados a Fenómenos Hidrometeorológicos y Cambio Climático; Universidad de Quintana: Roo Chetumal, Mexico, 2014; pp. 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lazos-Chavero, E.; Mwampamba, T.H.; García-Frapolli, E. Uncovering links between livelihoods, land-use practices, vulnerability and forests after hurricane Jova in Jalisco, Mexico. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 426, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEGOB. Boletín del Sistema de Alerta Temprana para Ciclones Tropicales SIAT-CT: TT Cristobal AT. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/555732/TT_CRISTOBAL_19_04062020.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- NASA-EO. Cristobal Drenches Central America. Available online: Earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/146817/cristobal-drenches-central-america (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- COESPO. Indicadores Sociodemográficos del estad0 de Campeche 2016–2050. Available online: http://www.coespo.campeche.gob.mx/index.php/13-coespo/199-informacion-estadistica?fbclid=IwAR3NHwhkfai3jnAxWA4GuNeAQf22BQ9N7FwGBVxBCvkJaJaWgd4v8Glc1r8 (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Rivera-Arriaga, E.; López Chan, O.; León Olea, R.; Paredes, J.; Arjona García, M.; Espejel, I.; Zetina, R.; Villalobos Zapata, G. El Ordenamiento de la Zona Costera de Campeche; Educosta: México, NM, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS). Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/ibtracs/index.php (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- NOAA. Tropical Depression Cristobal, Cumulative Wind History. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/refresh/graphics_at3+shtml/113241.shtml?swath#contents (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- INEGI. Datos Topográficos de INEGI a Escala 1:50,000. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/topografia/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- SSA. Datos Abiertos—Bases Históricas. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/salud/documentos/datos-abiertos-bases-historicas-direccion-general-de-epidemiologia (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Cori, A.; Ferguson, N.M.; Fraser, C.; Cauchemez, S. A new framework and software to estimate time-varying reproduction numbers during epidemics. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RC Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CONAGUA. Lluvias Asociadas a Ciclones Tropicales. Available online: https://smn.conagua.gob.mx/es/ciclones-tropicales/lluvias-asociadas-a-ciclones-tropicales (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- CENAPRED. Guía para la Prevención, Preparación y Gestión de las Emergencias en el Contexto del COVID-19; Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (CENAPRED): Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- INIFAP. Perspectiva Climática para la República Mexicana (Junio–Agosto del 2020). Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarios. Available online: http://clima.inifap.gob.mx/lnmysr (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- GOBERNACION. Pronóstico de Lluvias del 1 al 10 de Junio del 2020. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/555136/Pronostico_de_lluvias_a_10_dias_001_junio_2020.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2020).
- CONAGUA. Presenta el Servicio Meteorológico Nacional Balance de las Tormentas Tropicales Amanda y Cristobal; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- SEPROCI. Reporte de la Comisión de Evaluación de Daños del Meteoro Cristobal. Secretaria de Protección Civil de Campeche. Available online: http://www.seprocicam.gob.mx/index.php/comunicacion-social/1385-reunion-con-el-comite-de-ayuda-de-desastres-y-emergencia-nacionales-cadena (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Quigley, M.C.; Attanayake, J.; King, A.; Prideaux, F. A multi-hazards earth science perspective on the COVID-19 pandemic: The potential for concurrent and cascading crises. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2019, 1, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwatari, M.; Koike, T.; Hiroki, K.; Toda, T.; Katsube, T. Managing disasters amid COVID-19 pandemic: Approaches of response to flood disasters. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 6, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Active Date | Affected Country |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical Cyclone Harold | 1–10 April | The Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji, Tonga |
| Typhoon Vongfong | 10–18 May | The Philippines, the Palau Islands |
| Tropical Storm Arthur | 16–20 May | The USA (Florida and South Carolina), Cuba, the Bahamas |
| Tropical Cyclone Amphan | 16–21 May | India (West Bengal, Odisha, Andaman Islands), Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Bhutan |
| Tropical Storm Bertha | 27 and 28 May | The USA (Florida and South Carolina) |
| Tropical Storm Amanda | 30 and 31 May | El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Belize, Costa Rica, Mexico |
| Tropical Storm Cristobal | 2–10 June | Guatemala, El Salvador, Belize, Nicaragua, Honduras, Mexico (Yucatan, Quintana Roo, Veracruz, Campeche), the USA (Luisiana, Mississippi, Florida) |
| Indicator | Definition | Importance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive cases and scattering | Number of new local positive cases of COVID-19 during the emergency period | In times of crisis, evacuation and accumulation of people in tightly confined locations for flood-related safety reasons can increase contagion. | [35] |
| Active hostels and number of populations per hostel | Implementation of hostels during the contingency period | During a flood, people at risk sites have very few shelter options. The magnitude of the natural disaster phenomenon and the limited conditions of withdrawal associated with the study area’s morphological context requires populations to take refuge in structures capable of resisting the phenomenon. There is a need for the capacity of structures to accommodate enough people while allowing them to maintain social distancing and hygiene measures. | [36] |
| Activating early warning system | Number of emergency early warning releases | This early warning system involves an alert system through the mass media (newsletters), commissioning of temporary shelters, evacuation of risk zones, safeguarding of material resources to be used for the rehabilitation of affected systems, implementation of programs to ensure sufficient supply of drinking water, food, fuels, and electricity, and suspension of school activities and maritime and coastal activities. | [27] |
| Declaration of emergency and disaster | Emergency declaration | Emergency declarations allow a crisis to be alleviated and authorities to be given the resources to meet the health, food, and shelter needs of the affected population. | [37] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frausto-Martínez, O.; Aguilar-Becerra, C.D.; Colín-Olivares, O.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Hafsi, A.; Contreras-Tax, A.F.; Uhu-Yam, W.D. COVID-19, Storms, and Floods: Impacts of Tropical Storm Cristobal in the Western Sector of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9925. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239925
Frausto-Martínez O, Aguilar-Becerra CD, Colín-Olivares O, Sánchez-Rivera G, Hafsi A, Contreras-Tax AF, Uhu-Yam WD. COVID-19, Storms, and Floods: Impacts of Tropical Storm Cristobal in the Western Sector of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Sustainability. 2020; 12(23):9925. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239925
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrausto-Martínez, Oscar, Cesar Daniel Aguilar-Becerra, Orlando Colín-Olivares, Gabriel Sánchez-Rivera, Adel Hafsi, Alex Fernando Contreras-Tax, and Wilberth David Uhu-Yam. 2020. "COVID-19, Storms, and Floods: Impacts of Tropical Storm Cristobal in the Western Sector of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico" Sustainability 12, no. 23: 9925. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239925
APA StyleFrausto-Martínez, O., Aguilar-Becerra, C. D., Colín-Olivares, O., Sánchez-Rivera, G., Hafsi, A., Contreras-Tax, A. F., & Uhu-Yam, W. D. (2020). COVID-19, Storms, and Floods: Impacts of Tropical Storm Cristobal in the Western Sector of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Sustainability, 12(23), 9925. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239925







