Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Selection of Urbanization Indicators
2.4. RF Regression Model
2.5. Quantifying Ecosystem Services Using Empirical Models
- Food production
- Carbon sequestration and oxygen production
- Water conservation
- Soil conservation
3. Results
3.1. The Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Dynamic Characteristics of Urbanization Levels
3.2. The Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Services in the BTH Urban Agglomeration
3.3. The Comparisons of Simulations between the RF Regression Model and an Empirical Model
4. Discussions
4.1. The Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Characteristics of Urbanization
4.2. The Quantification of the Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Services in the BTH Urban Agglomeration Using the RF Regression Model
4.3. The Comparisons of Simulations between RF Regression and Empirical Models
4.4. Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, S.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Transformation of agricultural landscapes under rapid urbanization: A threat to sustainability in Hang-Jia-Hu region, China. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; van der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, J. Value assessment of ecosystem services in nature reserves in Ningxia, China: A response to ecological restoration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M. Impacts of land use and population density on seasonal surface water quality using a modified geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.R.; Mears, M.; Maltby, L.; Warren, P. Understanding spatial patterns in the production of multiple urban ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 16, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, M.E.; Martone, R.G.; Chan, K.M.A. Human impacts and ecosystem services: Insufficient research for trade-off evaluation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 16, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Luo, Y. Dynamic variations in ecosystem service value and sustainability of urban system: A case study for Tianjin city, China. Cities 2015, 46, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.D.C.; Martínez, P.F.; Martínez, J.M.G.; Martín, J.M.M. Modelling natural capital: A proposal for a mixed multi-criteria approach to assign management priorities to ecosystem. Contemp. Econ. 2020, 14, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, I.J.; Jones, A.P. Contrasting conventional with multi-level modeling approaches to meta-analysis: Expectation consistency in U.K. woodland recreation values. Land Econ. 2003, 79, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, M.A.; Cunha-E-Sá, M.A.; Ducla-Soares, M.M.; Nunes, L.C. Combining averting behavior and contingent valuation data: An application to drinking water treatment in Brazil. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2006, 11, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Hua, J. Heterogeneity in resident perceptions of a bio-cultural heritage in Hong Kong: A latent class factor analysis. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Valuing ecosystem services as productive inputs. Econ. Policy 2007, 22, 178–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, G.; Du, H.; Lu, D.; Mo, L.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Current and potential carbon stocks in Moso bamboo forests in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Chuai, X.; Dai, C.; Lai, L.; Zhang, M. The impact of land use change on the temporospatial variations of ecosystems services value in China and an optimized land use solution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Z.; Zhao, C.X.; Wang, X.L.; Li, J. Study of nitrate leaching and nitrogen fate under intensive vegetable production pattern in northern China. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2009, 332, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoyama, K.; Kamiyama, C.; Morimoto, J.; Ooba, M.; Okuro, T. A review of modeling approaches for ecosystem services assessment in the Asian region. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, N.D.; Burkhard, B.; Nedkov, S. Quantifying and mapping ecosystem services. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.H.; Caldarone, G.; Duarte, T.K.; Ennaanay, D.; Hannahs, N.; Mendoza, G.; Polasky, S.; Wolny, S.; Daily, G.C. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7565–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Crossman, N.; Nedkov, S.; Petz, K.; Alkemade, R. Mapping and modelling ecosystem services for science, policy and practice. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Changes of ecosystem service values in response to land use/land cover dynamics in Munessa-Shashemene landscape of the Ethiopian highlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Yu, W.; Li, W. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Wu, J. Impacts of urban expansion on ecosystem services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China: A scenario analysis based on the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 125, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, S. Urbanization impacts on the structure and function of forested wetlands. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Li, D.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y. Spatially non-stationary response of ecosystem service value changes to urbanization in Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Huo, J. Studies of the relationship between city size and urban benefits in China based on a panel data model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Crittenden, J.C.; Li, F.; Lu, Z.; Dou, X. Urban expansion simulation and the spatio-temporal changes of ecosystem services, a case study in Atlanta Metropolitan area, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ren, X.; Che, Y.; Yang, K. A Coupled SD and CLUE-S Model for Exploring the Impact of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study in Baoshan District, Shanghai, China. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Christopher Culberson, J.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random Forest: A Classification and Regression Tool for Compound Classification and QSAR Modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hong, W.; Qiu, R.; Hong, T.; Chen, C.; Wu, C. Geographic variations of ecosystem service intensity in Fuzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Ye, X.; Lee, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, K. Effects of urbanization on ecosystem service values in a mineral resource-based city. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Ye, X.Y.; Qi, Z.F.; Zhang, H. Impacts of land use/land cover change and socioeconomic development on regional ecosystem services: The case of fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, China. Cities 2013, 31, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Tianjin Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Tianjin Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Tianjin Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Tianjin Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Tianjin Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press (CSP) Publishing: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Realizing China’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, P.; Bielza, C.; Larranaga, P. Random Forests for Regression as a Weighted Sum of k-Potential Nearest Neighbors. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 25660–25672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, D.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, T.; Chen, H. Spatio-temporal assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services: Case study of Nanjing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Zhao, X. Projecting the impacts of urban expansion on simultaneous losses of ecosystem services: A case study in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Z.X. Natural and human impacts on ecosystem services in Guanzhong—Tianshui economic region of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6803–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Fu, B.; Feng, X.; Hou, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. The tradeoff and synergy between ecosystem services in the Grain-for-Green areas in Northern Shaanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, W.R. Computation of direct runoff amounts from storm rainfall. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Publ. 1963, 63, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, H. Derivation and validation of leaf area index maps using NDVI data of different resolution satellite imageries. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3826–3834. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC: The Erosion-Productivity Impact Calculator, 1.0 Model Documentation; Technical Bulletin; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Li, X.S.; Ji, C.C.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, N.N.; Wu, B.F. Dynamics of water and soil loss based on remote sensing and GIS: A case study in Chicheng County of Hebei Province. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 1723–1729. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatio-temporal investigation of the interactive relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: Case study of the Jingjinji urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. China and the World Trade Organization; CPG Publishing: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Tang, B.S. Institutional change and diversity in the transfer of land development rights in China: The case of Chengdu. Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.-S.; Woodworth, M.D. China’s Urban Speed Machine: The Politics of Speed and Time in a Period of Rapid Urban Growth. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2018, 42, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China. Constitution of the People’s Republic of China; NPC Publishing: Beijing, China, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.J.C. Urban administrative restructuring, changing scale relations and local economic development in China. Polit. Geogr. 2005, 24, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, F. China’s changing economic governance: Administrative annexation and the reorganization of local governments in the Yangtze River Delta. Reg. Stud. 2006, 40, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.S. Institutional innovations, asymmetric decentralization, and local economic development: A case study of Kunshan, in post-Mao China. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2007, 25, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, J. Planning the competitive city-region: The emergence of strategic development plan in China. Urban Aff. Rev. 2007, 42, 714–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Ho, S.P.S. The state, land system, and land development processes in contemporary China. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2005, 95, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, F.; Zheng, S. Impact of urbanization process on ecosystem service value in China. Res. Soil. Water. Conserv. 2019, 26, 352–359. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. The coupling relationship between the ecosystem service value of farmland and urbanization in Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone. Master’s Thesis, Shaanxi Normal University, Xian, Shaanxi, June 2015. [Google Scholar]


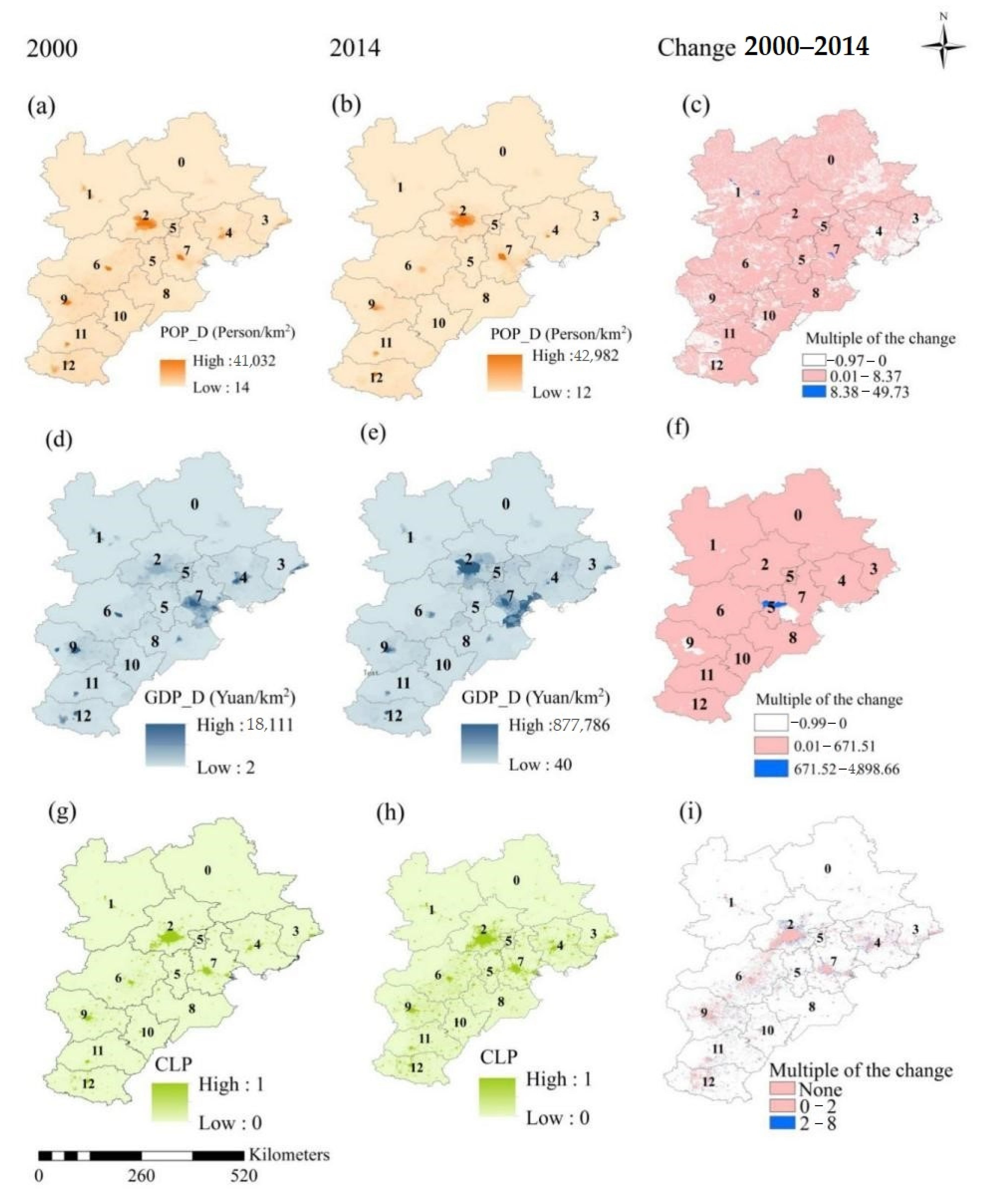
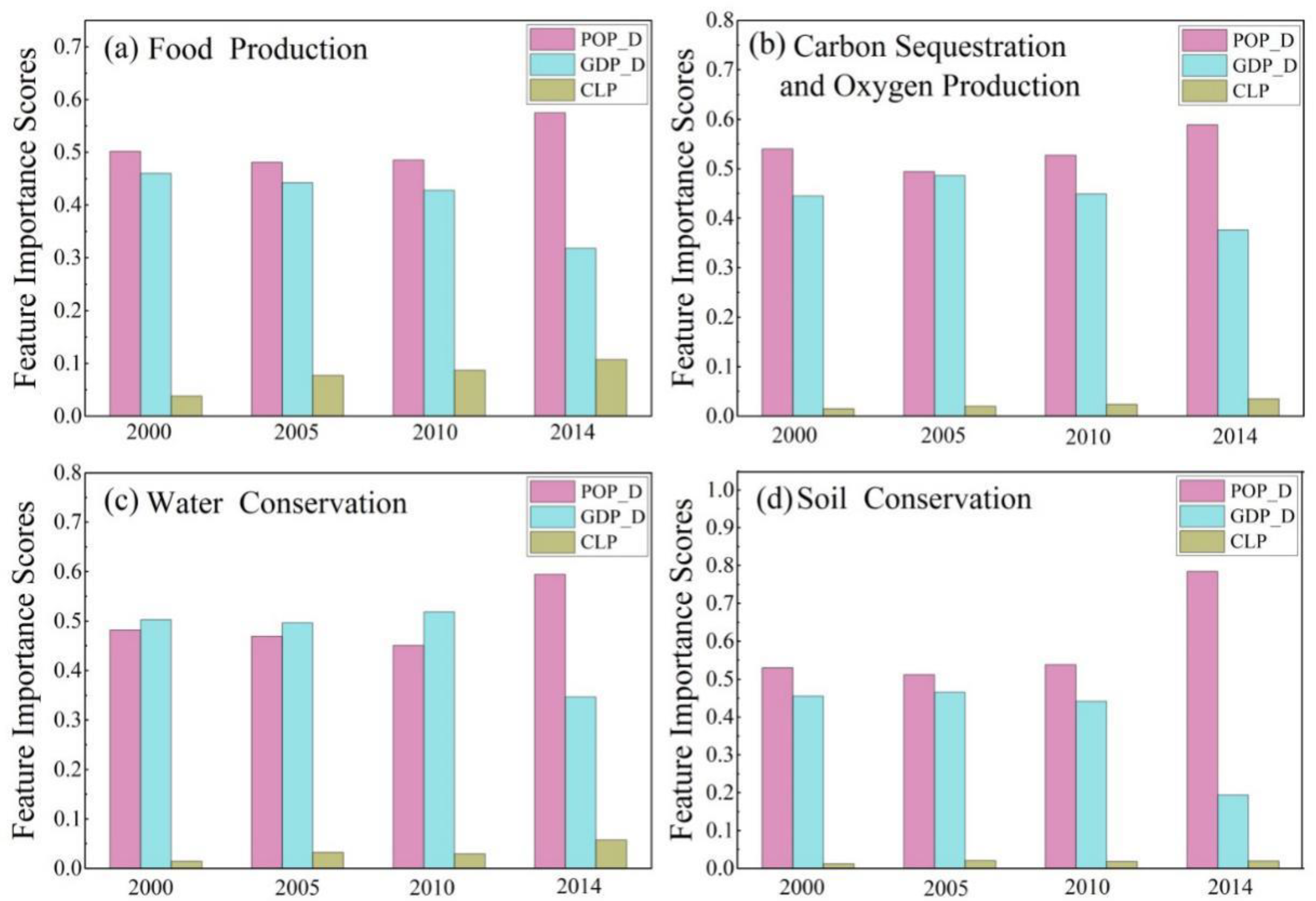
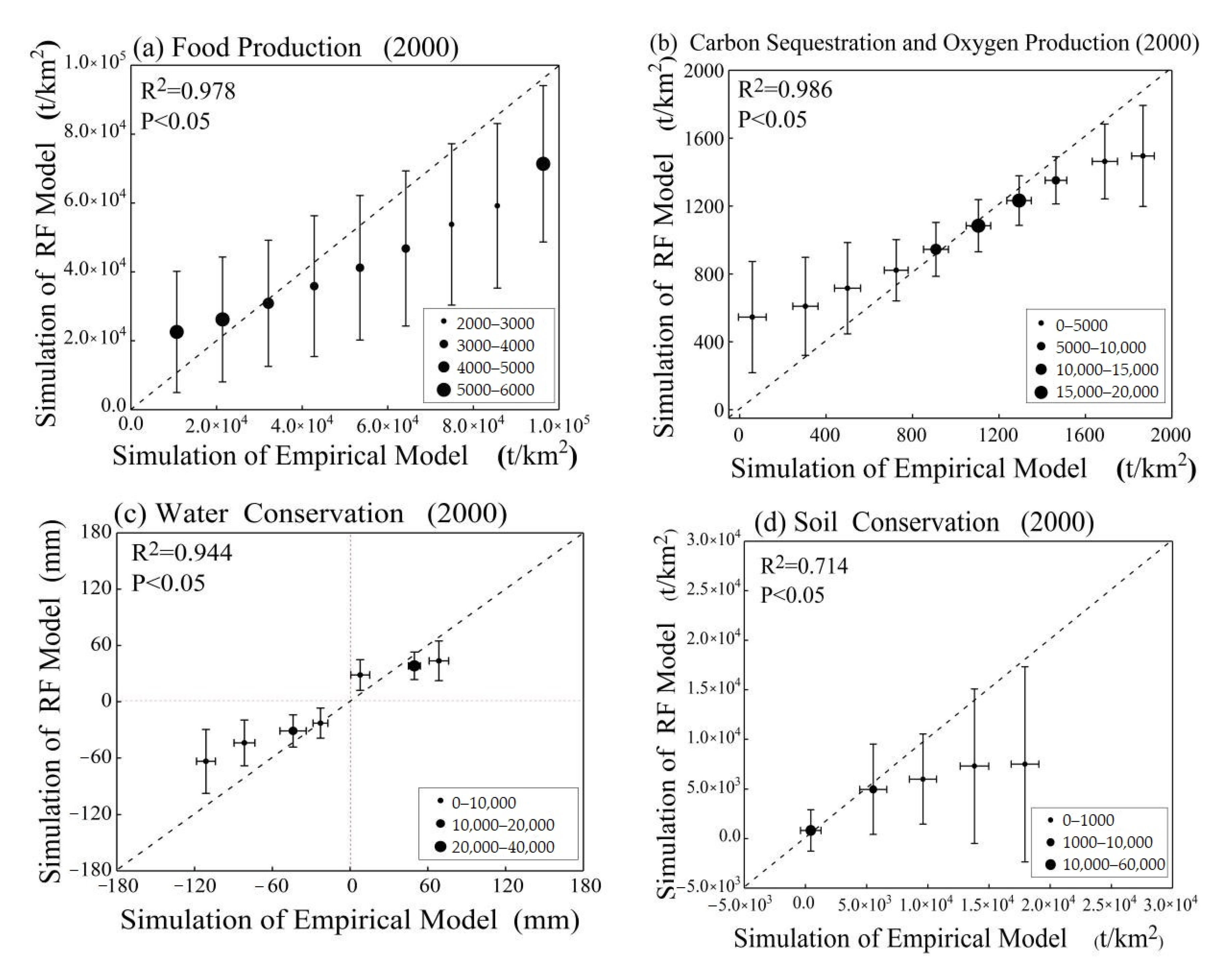
| Indicators | Property and Role | |
|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | POP_D (person/km2) | Reflect population urbanization |
| GDP_D (yuan/km2) | Reflect economic urbanization | |
| CLP | Reflect the situation of construction land expansion | |
| Ecosystem Service | Food Production (t/km2) | Provisioning service of ecosystem service function |
| Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Production (t/km2) | Regulating service of ecosystem service function | |
| Water Conservation (mm) | Provisioning service of ecosystem service function | |
| Soil Conservation (t/km2) | Supporting service of ecosystem service function | |
| Levels | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2014 | 2000–2014 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POP_D (person/km2) | 343.61 | 376.20 | 427.21 | 443.62 | 29.11 |
| GDP_D (yuan/km2) | 344.44 | 728.82 | 1306.84 | 3130.86 | 808.97 |
| CLP | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 166.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Mou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Peng, C. Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410233
Liu S, Yang M, Mou Y, Meng Y, Zhou X, Peng C. Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014. Sustainability. 2020; 12(24):10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410233
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shan, Mingxia Yang, Yuling Mou, Yanrong Meng, Xiaolu Zhou, and Changhui Peng. 2020. "Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014" Sustainability 12, no. 24: 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410233
APA StyleLiu, S., Yang, M., Mou, Y., Meng, Y., Zhou, X., & Peng, C. (2020). Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014. Sustainability, 12(24), 10233. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410233





