Abstract
Periods of consecutive days with heavy rain of high intensity are common in the red soil region of China, increasing unpredictable risks of soil erosion and non-point source pollution on sloping orchards. Grass cover, as a type of vegetation management, is useful for controlling soil erosion and pollution. However, the potential of different kinds of groundcover plants in combating soil erosion and non-point source pollution remains unclear under the rainfall conditions in this region of China. This study included 7 d of simulated rainfall applied to a set of six treatments: Bare soil control, natural grass, and four groundcover treatments, Trifolium repens, T. repens, and Lolium perenne, Vicia sativa and Festuca elata, Medicago polymorpha, and Cynodon dactylon. The effects of the treatments on runoff volume, and soil, nitrogen, and phosphorus losses were evaluated. The results indicated that greater soil erosion and non-point source pollution occurred over the first 3d of daily 1-h simulated rainfall events. Also, the beneficial effects of the groundcover plants were greater earlier in the 7-d period of daily heavy rain, particularly in reducing runoff and nitrogen loss on the second and third day. Compared with bare soil, all the groundcovers showed a reduction effect in varying degrees, among which T. repens treatment was more effective. T. repens treatment showed an overall reduction in runoff and soil loss by 25.5% and 91.5%, respectively, and total nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus loss by 25.5%, 74.6%, 90.7%, and 81.8%, respectively. These findings indicated that single planting of perennial pasture T. repens with short stems is an effective management option to limit soil erosion and non-point source pollution in sloping citrus orchards of southern China.
1. Introduction
Red soil (equivalent to Ultisols in the Soil Taxonomy System of the USA) occupies about 1.14 million km2 of subtropical China and 79% of this region consists of hilly to mountainous areas [1]. This region is one of China’s most important agricultural regions particularly for growing citrus due to its abundant rainfall and suitable temperatures [2]. However, the area is seriously affected by soil erosion because of the steep terrain, soil properties, abundant rainfall, and improper land management, especially in newly developed orchards [3,4]. In addition, the excessive use of chemical fertilizers, particularly N and P, by fruit growers leads to serious agricultural non-point source pollution under heavy rainfall and over-irrigation [5]. Severe soil erosion and non-point source pollution in orchards will not only cause soil degradation, but also reduced fruit quality, economic value of agriculture and farmer income, failure to achieve sustainable agricultural development goals [6,7,8], and broader adverse environmental effects [9,10]. Therefore, the red soil region is a particularly ecologically vulnerable area of China where development and protection are both crucial [11].
Groundcover vegetation management has proven to be an effective means to limit soil erosion [12,13,14] and N and P loss in runoff [15,16]. N and P are regarded as the main contributors to agricultural non-point source pollution [8]. The benefit of groundcover plants is that they can reduce the rainfall erosivity, increase infiltration, trap sediment, and enhance soil fertility [12,17]. For example, Keesstra et al. (2016) found that simulated rainfall during summer in Mediterranean orchards resulted in an erosion rate under vegetation-covered plots of only 0.02 mg/ha·h, which was significantly lower than in herbicide-treated (0.91 mg/ha·h) and cultivated plots (0.51 mg/ha·h). García-Díaz et al. (2017) investigated nitrogen loss in vineyards with different types of ground covers and found that over the first 2 min of the simulated rainfall, NO3−-N loss in cultivated plots was twice more than that in Brachypodium distachyon-covered plots and 18 times more than that in plots covered with spontaneous vegetation. Various groundcover vegetation can be used in hilly orchards, especially herbaceous plants, most commonly grasses [18], legumes [14], and crucifers [19]. Many groundcover species have also been tested in sloping citrus orchards in the red soil region of China [20,21,22], among which Medicago spp., Paspalum notatum, and Trifolium repens are the most commonly used. Nevertheless, the benefits of groundcovers in reducing soil erosion and non-point source pollution have been clear, and different groundcover species and their mixtures were recommended in sloping citrus orchards in the red soil region of southern China, but few studies have actually compared the relative merits of them in this region.
The processes of soil erosion and nutrient losses in agriculture are extremely dynamic and complicated, which are affected by many factors, for example, the vegetation cover, agricultural practices, rainfall characters, and topography [7,18,23]. Among these factors, rainfall characteristics (generally including rainfall intensity, duration, pattern, and raindrop energy) are particularly important [24,25], with rainfall intensity and frequency as the key factors influencing loss processes. Rainfall events with higher intensity and/or frequency usually generate earlier runoff and higher peak runoff, causing greater soil loss [23] as well as more chemical pollution [26]. Wei et al. (2007) concluded that the rainfall patterns with features such as high intensity, short duration, and high frequency can cause the greatest runoff and sediment loss [27]. Rainfall simulation experiments conducted by Liu et al. (2014) in farmland in China indicated that the N and P losses with surface runoff were strongly positively correlated to rainfall intensity [26]. There is no doubt that heavy rainfall with high frequency can increase the complexity and uncertainty of soil erosion and nutrient loss process. In the red soil region of southern China, high rainfall intensity and amounts occur frequently due to the well-developed monsoon. The annual precipitation is usually 800 to 2500 mm, which is 1.9 to 2.8 times higher than the national mean and 70% of the rainfall events occur from April to September as rainstorms [28], which can lead to severer soil and water loss, non-point source pollution, and further degradation in agriculture land. Under the rainfall conditions in this region, the potential of different groundcover plants for reducing soil erosion and non-point source pollution has not been adequately investigated [20,21]. Understanding the effect of herbaceous plants in reducing runoff, soil, and associated nutrient losses under periods of consecutive days with high-intensity rainfall and the assessment of this land management is crucial for developing further policies for local sustainable agriculture [29].
Therefore, the objectives of this study were (1) to investigate the effects of different groundcover species on soil erosion in sloping citrus orchards on red soil region of southern China; (2) to investigate the effects of different groundcover species on non-point source pollution under simulated rainfall; and (3) to identify an effective groundcover option for limiting soil erosion and non-point source pollution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Facilities
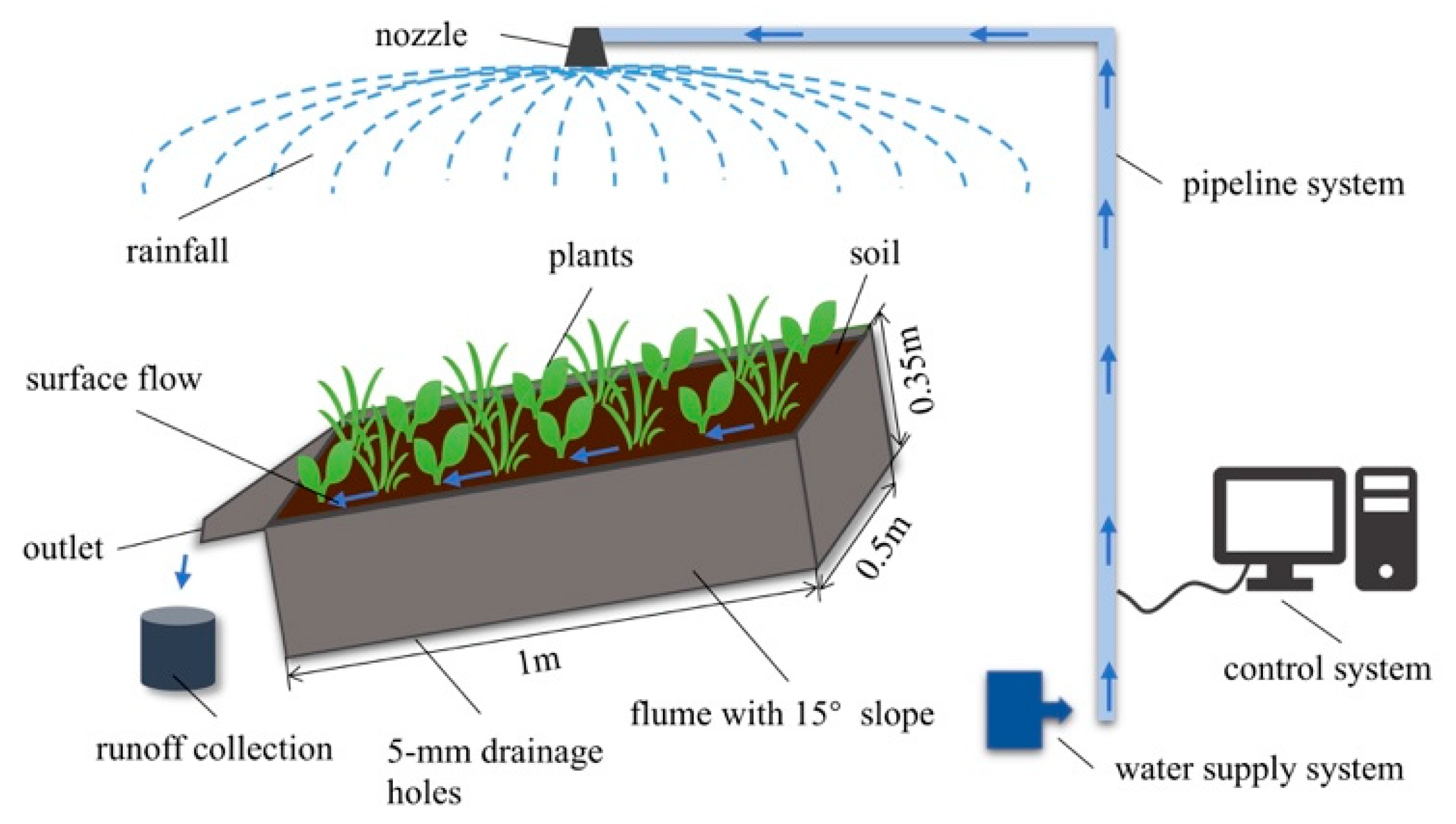
The experiments were conducted under simulated rainfall at the College of Resources and Environment, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China. The simulated rainfall facility (QYJY-503, Qingyuan Xi’an Measurement and Control Technology Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China) consisted of three parts: Control system, water supply system, and pipeline system. The rainfall intensity varied from 15 to 200 mm/h with rainfall uniformity of >80% and droplet size between 0.4 and 0.6 mm. The rainfall simulation process was fully computer controlled. The nozzles were a rotary down spray type, which ensured that the simulated rainfall was similar to natural rainfall (Figure 1).
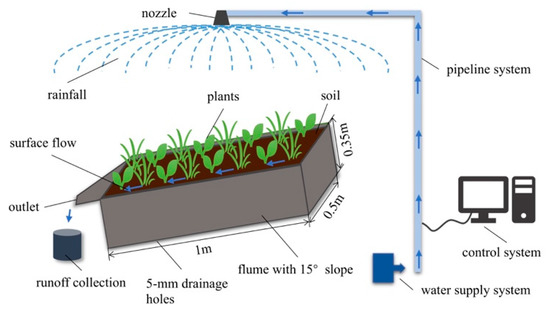
Figure 1.
Simulated rainfall facility.
The experimental soil containers (flumes) were variable-slope steel tanks, 1 × 0.5 × 0.35 m (L × W × D), with slope variable to 15° and the lower part had 5-mm diameter drainage holes.
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
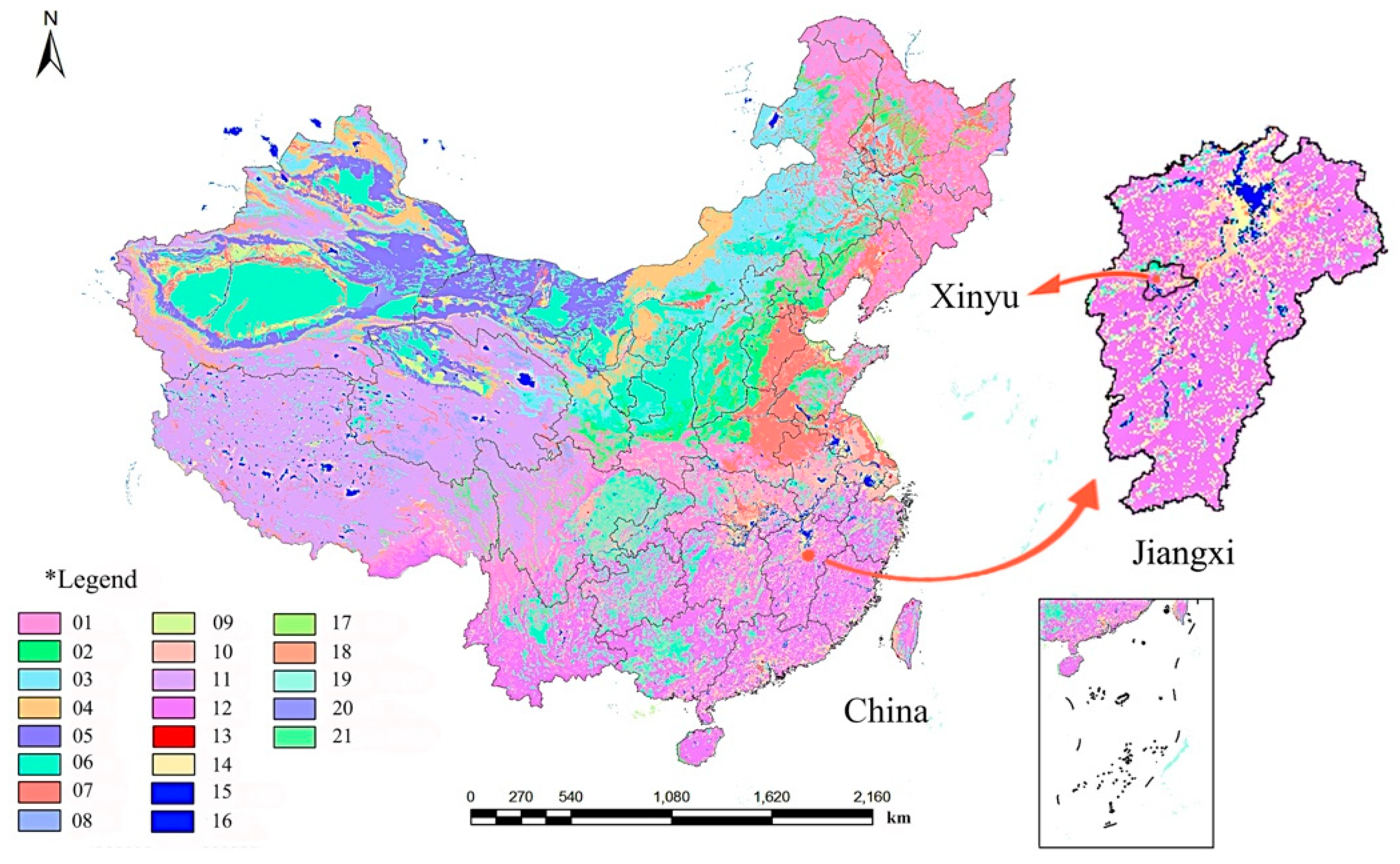
Soil was collected from a citrus orchard on a sloping site in of Xinyu City (114.93 E, 27.8 W), Jiangxi Province, a typical red soil citrus growing areas of China (Figure 2), air-dried until the water content was about 6% to 10%, and passed through a 10-mm sieve to remove coarse rock and organic debris. Afterward, the soil was added in layers (3 × 10-cm layers) and tapped with a wooden block aiming to attain a uniform bulk density of the study site (1.23 g/cm3) and also minimize the differences of soil between the treatments. Each layer of soil was lightly raked before packing the next layer to minimize the discontinuities between layers. Five-centimeter fine sand was evenly spread at the bottom of flumes to facilitate drainage. The soil was wet to field capacity and kept for a week to make it close to the natural soil state before sowing. This soil collecting method was used in previous studies about indoor simulated rainfall experiments [23,30]. The basic physical and chemical properties of the soil are given in Table 1.
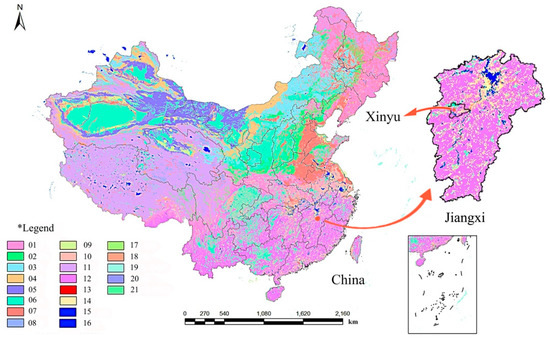
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of soil types in China and Jiangxi. *Legend: (01) leaching soil; (02) semi-leached soil; (03) calcareous soil; (04) arid soil; (05) desert soil; (06) primary soil; (07) semi-aquifer soil; (08) aquifer soil; (09) saline-alkali soil; (10) man-made soil; (11) alpine soil; (12) ferro-alumina (including red soil); (13) urban area; (14) rock; (15) lakes and reservoirs; (16) river; (17) sandbar or island; (18) glacier and snow cover; (19) coral reef or sea island; (20) northwest Salt Shell; (21) coastal saltworks or farms.

Table 1.
Properties of the soil used in the experiments.
Six herbaceous plants selected for the experiment were the common native annual and perennial species found in the orchard selected for the experiment. They had been previously identified as suitable for red soil citrus orchards in the region [31,32], viz. three legumes, T. repens, Vicia sativa, and Medicago polymorpha, and three grasses, Lolium perenne, Festuca elata, and Cynodon dactylon. These species were tested in four treatments, T. repens alone (T), T. repens with L. perenne (TL), V. sativa with F. elata (VF), and M. polymorpha with C. dactylon (MC). Digitaria sanguinalis was included as a natural grass treatment (NG) because it was the most common local weed, and bare soil (BS) was used as a control. Each kind of seed was evenly sown in three repeating flumes and no fertilization was applied in the early stage. They were watered equally and carefully when there was a dry soil surface, avoiding erosion. Details of these treatments are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Details of controls and groundcover treatments.
After the groundcover plants had been growing for about 6 weeks, all treatments were watered uniformly to ensure the same soil moisture content, and 15 g of the compound fertilizer (17% CO(NH2)2 and 17% P2O5) was applied to each flume. This fertilizer and application rate were chosen as it was the typical practice in the citrus orchard.
To evaluate the effects of the treatments, the flumes were set at a slope of 15° because this is a common slope in local citrus orchards [34]. Rainfall intensity was set to 90 mm/h, and applied as 1-h events, 24 h apart for 7 d. Consecutive daily rainfall of high intensity (daily precipitation >50 mm) occurred 82 times from 1961 to 2010 in Jiangxi, China during the rainy season over 3 to 20 d consecutive days and the maximum daily rainfall was 154.3 mm [35,36]. With 24 h between each simulated rainfall events, the 90 mm/h intensity gave 90 mm precipitation per day, which was representative of natural heavy rains in the region.
2.3. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis
Before simulated rainfall, all the flumes were set randomly in the rainfall area. For each rainfall event, the runoff was collected in 60-L containers placed under the outlet of each flume and measured with a water gauge. Three repeated runoff samples mixed with sediments were collected in 500-mL plastic bottles of these containers randomly after resuspension by stirring. Three hundred and seventy-eight samples were collected from the 6 treatments over 7 d.
The sample bottles were capped and kept at 4 °C for 8 h until all suspended soil particles settled. The water samples without sediments were taken from the sample bottles for chemical analysis and the sediments were oven-dried at 105 °C before weighing. For chemical analysis, the total N and P concentrations were assayed by alkaline potassium persulfate oxidation ultraviolet spectrophotometry and ammonium molybdate spectrophotometric methods, respectively [37]. After the water samples were filtered through a 0.45-μm membrane, the NO3−-N and NH4+-N concentrations were assayed by continuous flow analyzer (AA3, SEAL Analytical, Ltd., Norderstedt, Germany).
To compare runoff volumes, soil, and nutrient losses between BS and groundcover treatments, the reduction compared with BS (%) of the different groundcover treatments was calculated by the following equations according to the previous study [38].
where R and R′ are the reduction compared with BS of volume, soil, or nutrient losses (%) on each day and the whole 7-d rainfall period, respectively, M0 and are the runoff, soil, and nutrient losses (L, g, mg) for BS on each day and the whole 7-d rainfall period, respectively, and Mi and are the runoff, soil, and nutrient losses (L, g, mg) of groundcover treatments on each day and the full 7-d rainfall period, respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0 and Microsoft Excel were used to calculate and analyze all the statistics. Regression analysis was performed to show the relationship between rainfall days and daily/accumulated generated runoff, soil, and nutrient losses. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was carried out to determine the differences between the measured parameters for different treatments. Least significant difference (LSD) at P = 0.05 was used to elucidate any significant differences.
3. Results
3.1. Process of Soil Erosion and Non-Point Source Pollution on Bare Soil
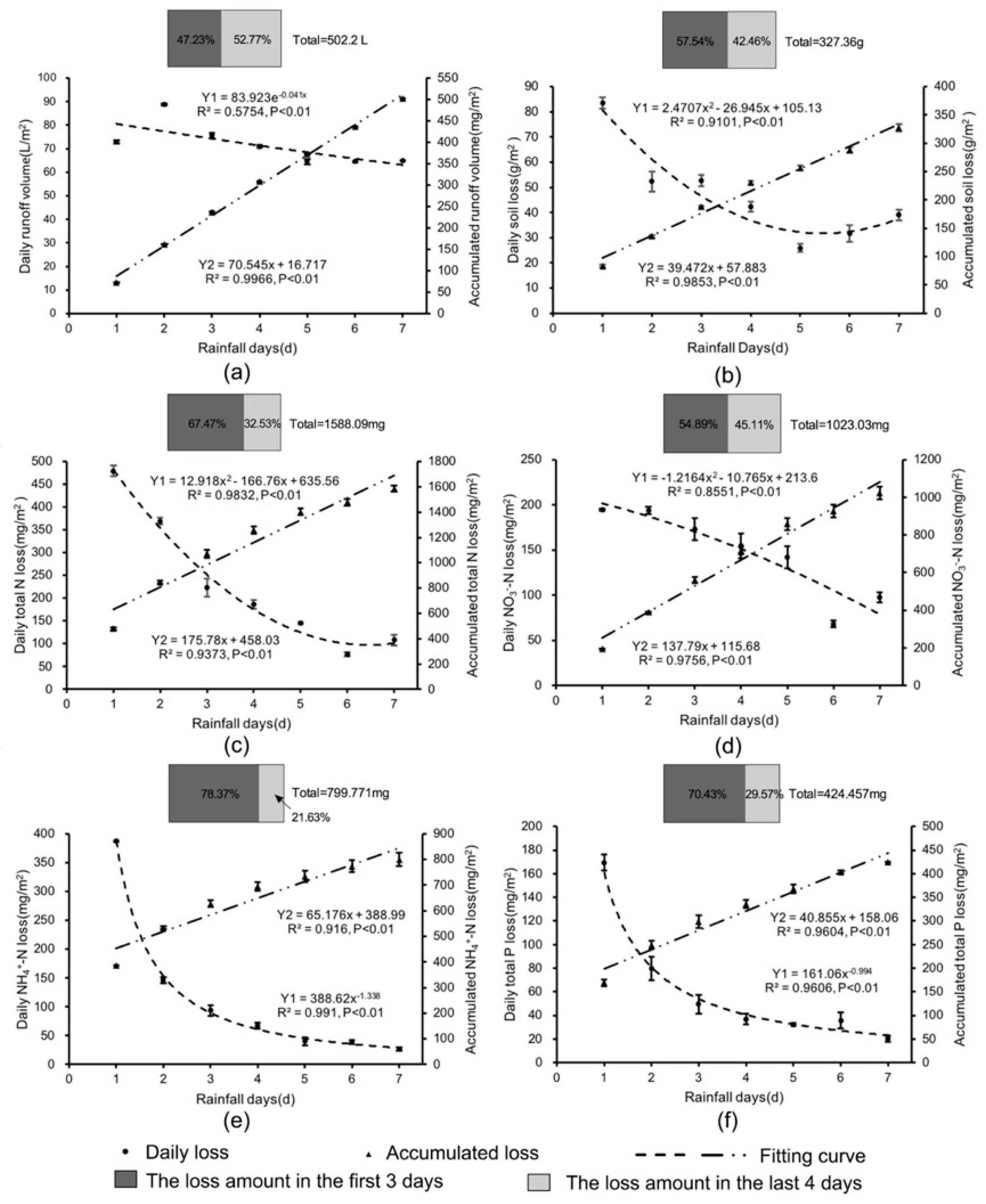
Over the seven days of simulated rainfall, the runoff volume for BS increased on the first two days, then decreased slowly, reaching the lowest volume on the fifth day, and then stabilized. The soil, total N, and NO3−-N loss for BS showed a similar trend that the loss amount was highest on the first day followed by a decline, reaching the lowest on the fifth or sixth day and rising again. The NO3−-N and total P loss was also highest on the first day and kept declining until the end of the rainfall period (Figure 3).
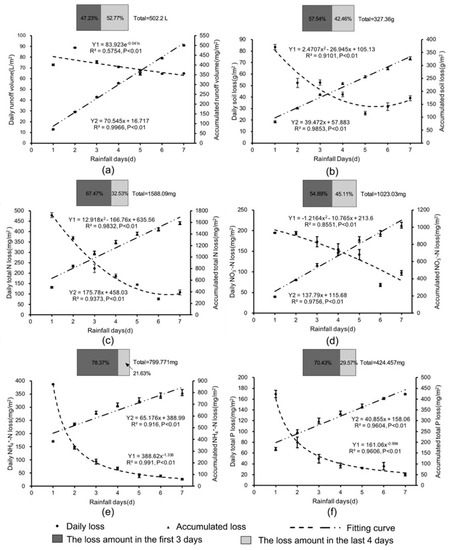
Figure 3.
Process and distribution of losses of runoff (a), soil (b), N (c–e), and P (f) over time on bare soil. The boxes compare the losses over the first three days and the final four days.
Figure 3 also shows scatter plot graphs for the relationship between rainfall days and daily/accumulated generated runoff, soil and nutrient losses, and there was a very significant regression relationship between rainfall days and the loss (P < 0.01). The best regression equations were selected based on determination coefficients of the line of best fit. For the runoff loss, the dominant equation was in the form of the exponential function, and for the soil, total N, and NO3−-N loss, the response functions were quadratic and the relationship tended to be power function for NO3−-N and total P loss. There was a significant linear regression relationship between rainfall days and accumulated soil, runoff, and nutrient losses (P < 0.01).
The total soil and nutrient losses over the first three days were higher than that over the final four days, and the combined runoff volume in the two time periods was similar (Figure 3).
3.2. Runoff and Soil Loss
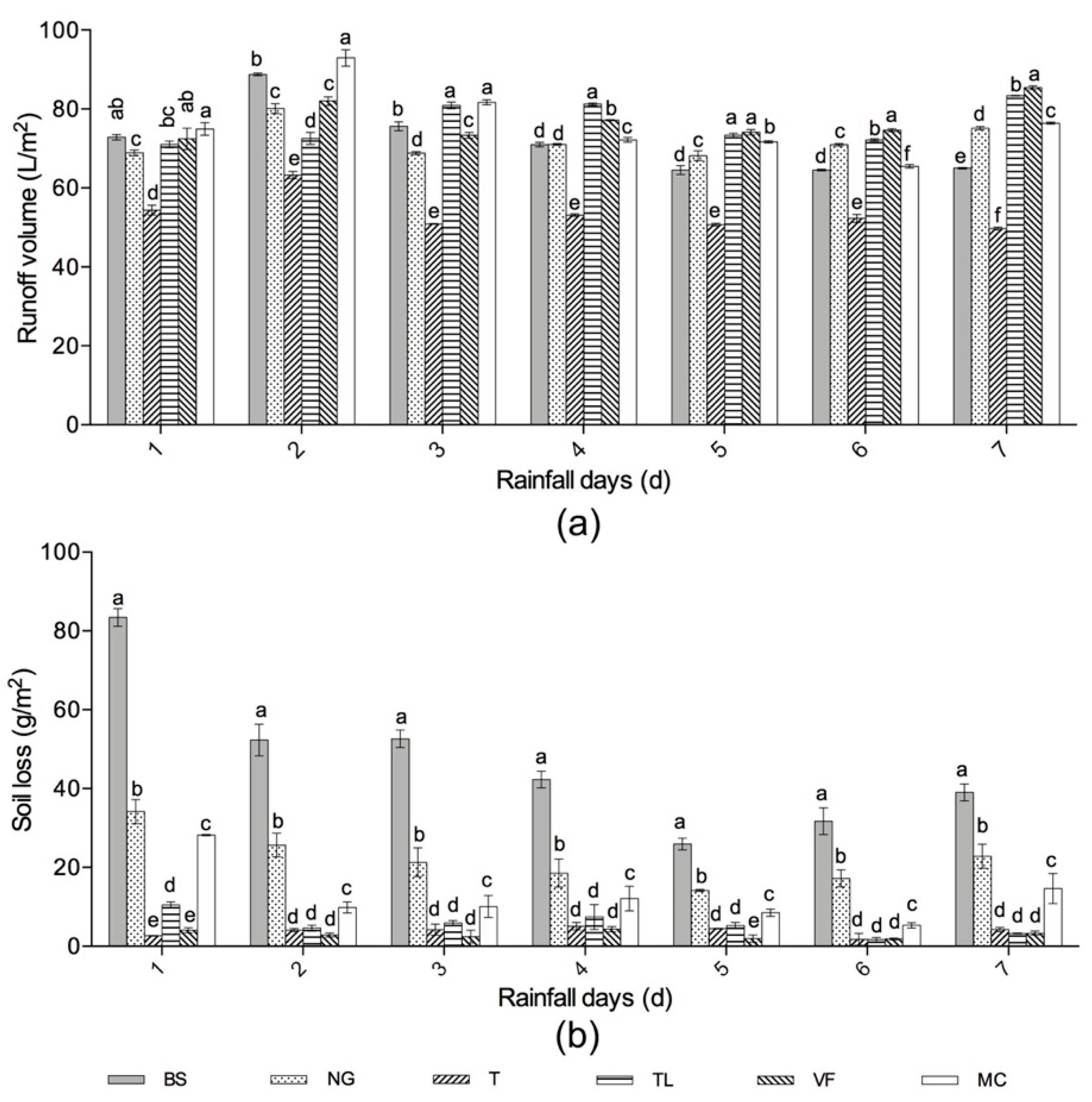
The runoff volume of T and NG was significantly lower than that for BS (P < 0.05) over the seven days, while the difference between the other three groundcovers and BS was not significant on the first day (Figure 4a). N and VF showed reductions only over the first three days, TL showed the reduction only over the first two days, and the runoff volume of MC was always higher than that for BS. The total reduced runoff volume of T compared with BS in the seven days was the most, which was 127.98 L/m2 with a percentage of 25.48% (Table 3).
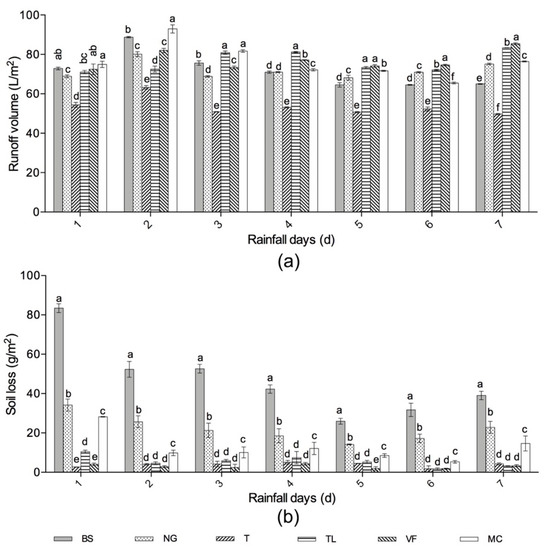
Figure 4.
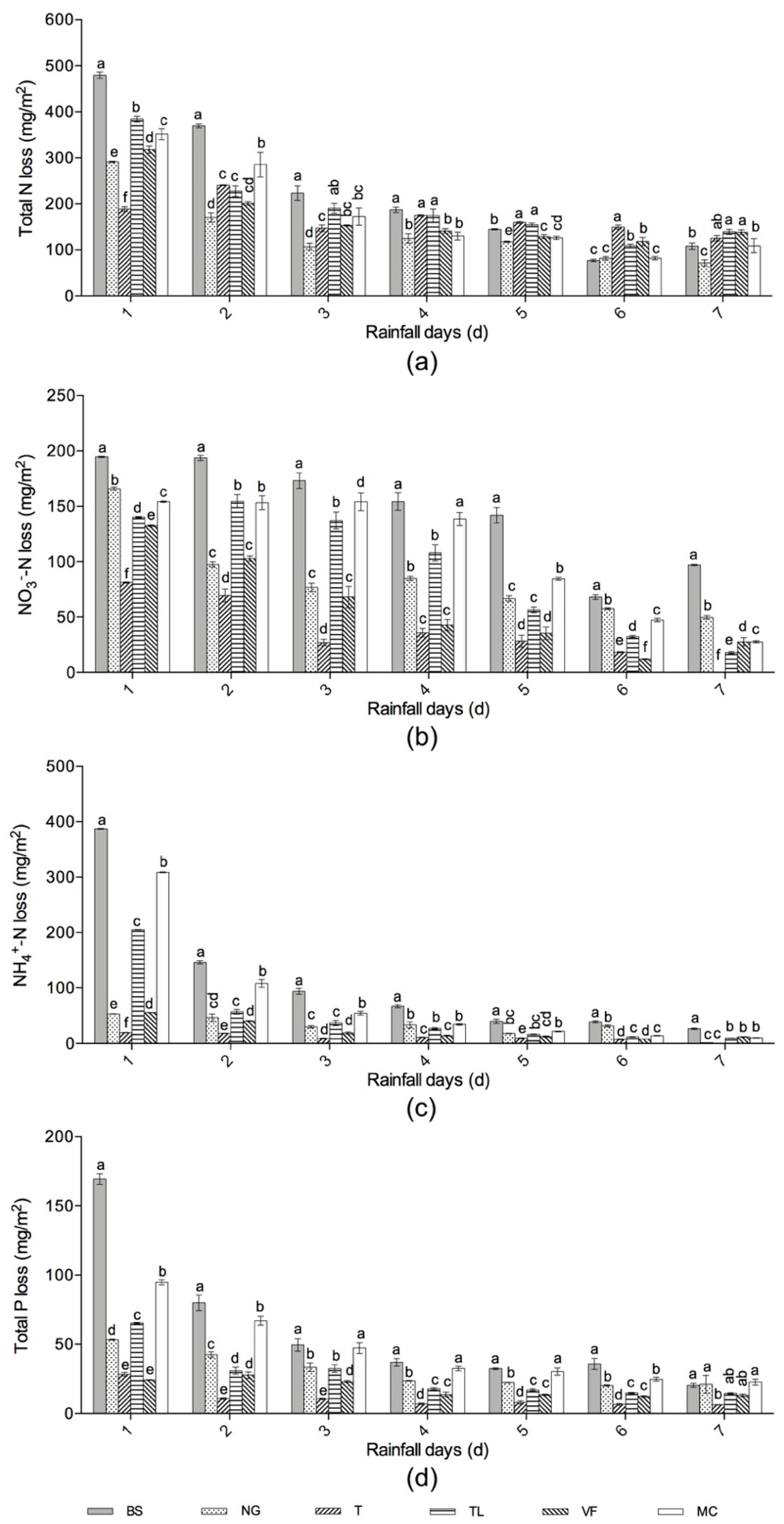
Comparison of runoff (a) and soil loss (b) between different groundcover treatments and bare soil during a seven-day period of consecutive heavy daily rainfall. Error bars indicate standard deviations and different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA (calculated each rainfall day). Treatment codes are BS, bare soil; NG, natural grass, T, Trifolium repens; TL, T.repens and Lolium perenne; VF, Vicia sativa and Festuca elata; and MC, Medicago polymorpha and Cynodon dactylon.

Table 3.
Percentage reduction in runoff volume and soil loss of different groundcover treatments relative to the bare soil control.
The soil loss was significantly reduced by all the groundcovers over the seven days (P < 0.05) (Figure 4b). Their reductions compared with BS remained stable over 60% except for NG and the reduction effects of T, TL, and VF were similar. VF reduced the most soil loss by 306.64 g/m2 (93.34%), and the value of T was very close to it (300.87 g/m2, 91.49%) (Table 3).
It was found that different groundcovers were more effective in reducing soil loss than runoff, with the reduction being better in the early in the seven-day period (days 1 to 3). T showed a better effect both on reducing runoff and soil loss than other groundcovers.
3.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss
Compared with BS, total N loss was significantly lower in all groundcover treatments (P < 0.05) over the first two days, but the difference between the groundcovers and BS was not significant over the following four days (Figure 5a). The reduction compared with BS (%) of five groundcovers changed over days, treatment T and TL, and treatment N, VF, and MC did not have any reduction effect on the fifth and sixth day, respectively. The reduced total N loss of NG over the seven days was the most (625.16 mg/m2) with a percentage of 39.37%, followed by T (404.40 mg/m2, 25.47%) and VF (309.48 mg/m2, 24.59%) (Table 4).
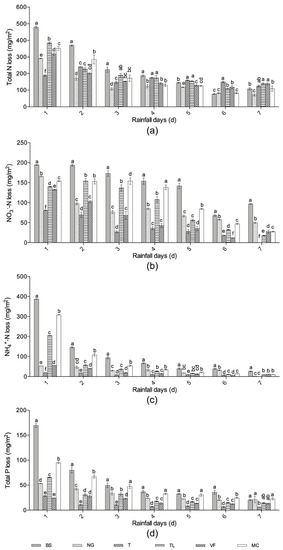
Figure 5.
Comparison of total N (a), NO3—N (b), NH4 + -N (c), total P (d) loss between different grass-covered plots and bare soil during a seven-day period of consecutive heavy daily rainfall. Error bars indicate standard deviations and different letters above the bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA (calculated each rainfall day). Treatment codes are BS, bare soil; NG, natural grass, T, Trifolium repens; TL, T.repens and Lolium perenne; VF, Vicia sativa and Festuca elata; and MC, Medicago polymorpha and Cynodon dactylon.

Table 4.
Percentage reduction in nutrient losses of different groundcover treatments relative to the bare soil control.
The effect of different groundcovers on the NO3−-N loss was significant (P < 0.05) compared with BS, and there were also significant differences among the groundcover treatments (Figure 5b). All the treatments showed positive reduction effect compared with BS (%), especially in the last three days (over 40%). T reduced the most NO3−-N loss by 97.11 mg/m2 (74.59%), followed by VF (601.86 mg/m2, 58.83) (Table 4).
NH4+-N loss was significantly (P < 0.05) lower in all groundcover treatments compared with BS, but there were no significant differences between the groundcover treatments after the second day (Figure 5c). Regarding the reduction compared with BS (%) for T, VF was higher over the seven days, at around 70% to 90%, and it was around 50% for NG, TL, and MC. The reduced total NH4+-N loss over the seven days of T was the most, by 725.47 mg/m2 compared with BS (90.71%), and the following was VF (638.46 mg/m2, 79.83%) (Table 4).
Significant reduction effects on total P loss of each groundcover treatment was seen on the first and sixth days (P < 0.05), and on the second to fifth days, except for MC, the other groundcovers reduced total P loss significantly (P < 0.05), but it was not significant on the seventh day, and there were no significant differences among the groundcover treatments (Figure 5d). The reduction effect of each groundcover on total P loss was more positive in the initial two days than that of the following days, and the total P loss of NG and MC were higher than BS on the seventh day. T reduced the most total P loss in the seven days (347.05 mg/m2, 72.89%), followed by VF (297.05 mg/m2, 69.98%) (Table 4).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of the Simulated Rainfall Pattern on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Losses
In this study, the seven consecutive days with 1-h rainfall of an intensity of 90 mm/h represented the typical extreme natural rain in the rainy season in Jiangxi, China [35,36]. Our study quantified the loss process of runoff, sediment, and agricultural nutrients on bare red soil from this simulated rainfall and showed a very significant regression relationship between rainfall days and the loss (P < 0.01) (Figure 3).
The runoff was higher on the second day of rainfall than the first day because the infiltration and hydraulic conductivity decreased due to the development of a previously described sealing phenomenon [39,40]. Such changes in the hydraulic properties of the soil might also cause changes in the runoff and sediment loss during the subsequent rainfall. The sediment loss showed a declining trend during the intermittent 3-h rainfall, which is similar to the results of Montenegro et al. (2013) [41]. However, the dynamics of runoff volume and sediment loss change differed to those reported by Wang et al. (2018) for rainfall after the second day; this might be attributed to different soil properties and plot size in their study [39]. These factors are reported in previous studies to influence on runoff and sediment yield [42].
Environmental contamination from fertilizers occurs with runoff and sediment loss, which will accumulate in depressions or enter downstream rivers, lakes, and reservoirs [9]. The N and P losses were higher over the first three days in our study, which means the severe non-point source pollution can occur in the early stage of periods of consecutive daily rainfall. Previous studies have also reported that the highest P or N loss in runoff occurs during the initial stage of rainfall events [43]. For example, a field experiment conducted by Smith et al. (2007) showed that the mean soluble P and NH4+-N concentrations of the inorganic fertilizer treatments were greater in runoff that occurred one to four days after application rather than in the later rainfall events [44]. Shuman et al. (2002) found NO3−-N loss(mg) in runoff had a decrease in the simulated rainfall of 24, 72, 96, and 168 hours after fertilizer, which is consistent with the decrease in our study in the seven-day period. The increase of NO3−-N loss on the last day may suggest that nitrification was occurring in soils [45], and this may also be the reason for the increasing trend of total N loss on the 6th d.
Therefore, more attention should be given to the early period (say the first one to three days) of a period of consecutive daily rainfall after fertilizer application when soil erosion and nutrient losses potentials are much higher. Furthermore, some measures such as groundcover management should be used to reduce the severity of soil erosion and agricultural non-point source pollution during the rainy season.
4.2. Effect of Different Groundcovers on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Losses
The different groundcovers chosen in our study were effective in reducing soil erosion and decreasing nutrient losses according to the total reductions over the seven-day period except for runoff volume (Table 3).
Planting with single species (T. repens) was the most effective treatment for reducing soil erosion, which decreased runoff and sediment yield by 25.5% and 91.5% over the seven-day period, respectively. Novara et al. (2011) also reported that legume cover significantly reduced soil loss by 74.94% compared to bare soil after conventional tillage [14]. The groundcover plants can reduce soil erosion by protecting the soil surface against splash erosion and soil detachment, reducing the velocity and erosivity of surface flow, and increasing the infiltration by roots [19,46]. The surface coverage of all the groundcover treatments was similar in this experiment, so their root development might have an important role in this process, which needs further exploration. Increased runoff can be caused by lower infiltration [47], which can vary between plant species [48]. Legumes can increase infiltration capacity and hydraulic conductivity because decaying taproots of legumes form stable macropores while grasses do not [49]. The observation of Mytton et al. (1993) showed that water infiltration was higher under T. repens due to a higher fraction of soil pores greater than 60 µm with porosity being equal compared to grasses [50]. In addition, due to the root proliferation, which increases soil organic matter content and favors soil fauna such as earthworms, legumes can enhance water flow through soil [51]. This mechanism might explain how the single species of legume (T. repens) used in this study achieved the best effect on soil erosion control consistent with the studies mentioned above.
The N and P losses during the rainfall period were decreased the most by the T. repens treatment. The N and P in fertilizers can be absorbed by vegetation cover and reduce the nitrate loss by runoff [52,53]. Relatively higher effectiveness of T. repens in reducing N and P losses was also found in other research [13,48].
On the whole, T. repens and V. sativa with F. elata showed a better efficiency of reducing runoff, sediment, and nutrient losses. However, VF treatment needs more work because it produces higher stems, so it needs to be mowing during the growing season (Table 2). T. repens is shorter, can fertilize the soil, and is easily managed, so is considered to be a suitably cultivated legume for orchard floors in hilly areas of southern China [32,54,55]. Therefore, we recommend a legume with short stems such as T. repens as a suitable choice for groundcover in citrus orchards on red soil slopes. However, our study did not analyze the effect of T. repens on the ecological environment (e.g., biocommunity), fruit yield, and water competition between the groundcover and citrus trees. Therefore, further studies need to be conducted to evaluate the effect of a Trifolium spp. as a groundcover in the hilly orchards in the red soil region. Also, the effect of mixed sowing of different legumes on soil erosion and contamination control in sloping citrus orchards should be explored.
4.3. Dynamics of the Reduction Effect of Different Groundcovers under Frequent Heavy Rainfall
The reduction effect varied during the seven-day period of consecutive daily rainfall (Table 3 and Table 4). The groundcovers had a clearly reduced runoff only over the first three days, which differs from most studies that reported vegetation cover can reduce the surface runoff during rainfall over a longer period [12,13]. This might be because of the different rainfall types, which will cause a series of changes in soil and plants. For example, through our observations, plants would be forced to the ground under the impact of raindrops with strong kinetic energy under prolonged rainfall, which will be likely to strengthen the stem flow or leaf drainage [56], causing the phenomena of high runoff with low sediment or nutrient losses. Abrantes et al. (2018) also found a reduction effect of 70% with mulching on surface runoff and sediment in the second rainfall (16% and 53%, respectively), which was significantly lower than that in the first rainfall (83% and 92%, respectively) [57].
Meanwhile, the mixed groundcovers in our study showed a gradually diminishing effect on reducing total N loss, and a negative effect was even observed over the last three days. The reduction in P loss fluctuated over the seven-day period (Table 4). The mechanism may be complex, relating to the nutrient element properties, change of physical properties on slopes and erosion forms, and also shoot and root morphology of the groundcover [13,15]. It may also be affected by the relative loss in the velocity of contaminants between bare soil and vegetated treatments. Further research is needed to investigate these changes under different periods of rain to provide a theoretical basis for developing appropriate and sustainable measures for soil erosion and nutrient losses control.
5. Conclusions
In a simulated rainfall experiment, we investigated the performance of five different grass covers for soil conservation and non-point pollution control. Our results showed that a period of consecutive heavy daily rainfall can cause severe soil erosion and pollution, especially early in the period (first one to three days). All groundcovers evaluated effectively reduced soil, N, and P losses over the full seven-day period, but not runoff volume. While the reduction in losses varied during the experiment, the reduction on runoff and total N loss was negative after the first three days. We concluded that single Trifolium sp. with short stems, such as T. repens, is likely to be a more effective groundcover options than other common groundcovers to mitigate soil erosion and non-point pollution losses from the sloping citrus orchards in the red soil region of southern China. Simultaneously, it is also necessary to avoid inorganic fertilizer application before periods of consecutive daily rainfall; even though the groundcovers can provide some control, it may not be sufficient in particularly wet periods. The application of inorganic fertilizer can be incorporated into the local comprehensive pollution prevention and control system, and the development of the long-term effective pollution prevention strategy. These findings have important implications for combating soil erosion and non-point pollution caused by extended periods of heavy rainfall in the region.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, N.Z.; data curation, visualization, Q.Z.; resources, validation, funding acquisition, Y.L. and M.Z.; investigation, W.L. and C.C.; project administration, supervision, funding acquisition, Y.X.; writing—review and editing, C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (NO.2017YFC0505605).
Acknowledgments
Sincere thanks to the researchers from the Experimental Center of Subtropical Forestry, China Academy of Forest for providing the study materials and guidance on herbaceous planting. This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (NO.2017YFC0505605), to which the authors are most grateful.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, X. Effects of weed management practices on orchard soil biological and fertility properties in southeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, J.G.; Wang, Q.Z.; Liao, G.Q.; Au, J.; Allard, J.L. Ecological and economic benefits of vegetation management measures in citrus orchards on red soils. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, D.; Dong, L.; Shi, X.; Warner, E.; Gu, Z.; Sun, J. Regional soil erosion assessment from remote sensing data in rehabilitated high density canopy forests of southern China. Catena 2014, 123, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Morera, A.G.; Bodí, M.B. Soil and water losses from new citrus orchards growing on sloped soils in the western Mediterranean basin. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2009, 34, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norse, D. Non-point pollution from crop production: Global, regional and national issues. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Colazo, J.C.; Buschiazzo, D. The impact of agriculture on soil texture due to wind erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Jordán, A.; Cerdà, A. Effects of soil management techniques on soil water erosion in apricot orchards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimotta, A.; Cozzi, M.; Romano, S.; Lazzari, M. Soil Loss, productivity and cropland values gis-based analysis and trends in the Basilicata region (Southern Italy) from 1980 to 2013. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, F.; Norse, D.; Zhu, Z. Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: Causes and mitigation measures. Ambio 2012, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.; Bach, M.; Hartmann, H.; Spiteller, M.; Frede, H.G. Point-and nonpoint-source pesticide contamination in the Zwester Ohm catchment, Germany. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, M.; Wang, P. Land use/cover change in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China: Reconciling the land use conflicts between development and protection. Catena 2019, 175, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Bienes, R.; Eldridge, D.J.; Marques, M.J. Vegetation cover reduces erosion and enhances soil organic carbon in a vineyard in the central Spain. Catena 2013, 104, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blavet, D.; De Noni, G.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Leonard, M.; Maillo, L.; Laurent, J.Y.; Asseline, J.; Arshad, M.A.; Roose, E. Effect of land use and management on the early stages of soil water erosion in French Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Liu, G.B.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, Y.X. Effects of vegetation cover and rainfall intensity on sediment-associated nitrogen and phosphorus losses and particle size composition on the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 66, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Han, W.; Liu, D.; Gan, X. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses by runoff erosion: Field data monitored under natural rainfall in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2016, 147, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguas, E.V.; Arroyo, C.; Lora, A.; Guzmán, G.; Vanderlinden, K.; Gómez, J.A. Exploring the linkage between spontaneous grass cover biodiversity and soil degradation in two olive orchard microcatchments with contrasting environmental and management conditions. Soil 2015, 1, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, A.; Bienes, R.; Sastre, B.; Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Cerdà, A. Nitrogen losses in vineyards under different types of soil groundcover. A field runoff simulator approach in central Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repullo-Ruibérriz de Torres, M.A.; Ordóñez-Fernández, R.; Giráldez, J.V.; Márquez-García, J.; Laguna, A.; Carbonell-Bojollo, R. Efficiency of four different seeded plants and native vegetation as cover crops in the control of soil and carbon losses by water erosion in olive orchards. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, T.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xie, N.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z.; Lin, Y. Influence of zonal grass on non-point source pollution control in orchard. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Z.; Huang, Q. Preliminary study on non-point source pollution of soil erosion in navel orange orchard in southern Jiangxi Province. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, M.; Liang, B.; Dong, J.; Li, J. Effects of orchard grass on nitrogen surface accumulation and runoff loss. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Römkens, M.J.; Helming, K.; Prasad, S.N. Soil erosion under different rainfall intensities, surface roughness, and soil water regimes. Catena 2002, 46, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Peng, M.; Qiao, S.; Ma, X.Y. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield characteristics of bare loess soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Cerdà, A. Contribution of raindrop impact to the change of soil physical properties and water erosion under semi-arid rainfalls. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, P.; Shen, Z. Runoff characteristics and nutrient loss mechanism from plain farmland under simulated rainfall conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Huang, Z.; Wu, D.; Gui, L. The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Exploring optimal measures to reduce soil erosion and nutrient losses in southern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonella, D.; Maurizio, L.; Mario, C.; Severino, R. Soil Erosion Modelling on Arable Lands and Soil Types in Basilicata, Southern Italy. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10408, pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, S.A.; Abrantes, J.R.C.D.B.; Coelho, C.D.O.A.; Keizer, J.J.; de Lima, J.L.M.P. Comparing topsoil charcoal, ash, and stone cover effects on the postfire hydrologic and erosive response under laboratory conditions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Fang, Z.; Shimizu, K. Effects of weed communities with various species numbers on soil features in a subtropical orchard ecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 102, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z. How to interplant and grass in citrus orchards. New Rural Technol. 2017, 8, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Chen, H.; Qin, R.; Lin, R.; Wu, Z.; Cui, H. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.A.; Kong, L.; Wagan, B. Effects of land use and slope gradient on soil erosion in a red soil hilly watershed of southern China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14309–14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Shan, J.; Wu, S.; Yin, J. The climatic characteristics of persistent heavy rainfall in Jiangxi and its large-scale circulation background. Meteorol. Sci. 2013, 33, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, X. Characteristics of continuous heavy rainfall in Jiangxi flood season and medium-term forecasting model. Meteorology 2004, 30, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Methods of Soil and Agro-Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 127–332. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Helmers, M.J. Effects of vegetation cover of natural grassland on runoff and sediment yield in loess hilly region of China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; You, W.; Fan, J.; Jin, M.; Wei, X.; Wang, Q. Effects of subsequent rainfall events with different intensities on runoff and erosion in a coarse soil. Catena 2018, 170, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Moghadam, E.S.; Darvishan, A.K. Effects of subsequent rainfall events on runoff and soil erosion components from small plots treated by vinasse. Catena 2016, 138, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, A.D.A.; Abrantes, J.R.C.B.; De Lima, J.L.M.P.; Singh, V.P.; Santos, T.E.M. Impact of mulching on soil and water dynamics under intermittent simulated rainfall. Catena 2013, 109, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-de las Heras, M.; Nicolau, J.M.; Merino-Martín, L.; Wilcox, B.P. Plot-scale effects on runoff and erosion along a slope degradation gradient. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuman, L.M. Phosphorus and nitrate nitrogen in runoff following fertilizer application to turfgrass. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Owens, P.R.; Leytem, A.B.; Warnemuende, E.A. Nutrient losses from manure and fertilizer applications as impacted by time to first runoff event. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.L.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Quemada, M. The role of cover crops in irrigated systems: Water balance, nitrate leaching and soil mineral nitrogen Accumul. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, J.E.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M. Effects of vegetation stems on hydraulics of overland flow under varying water discharges. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Cao, L.; Liang, Y. Infiltration and runoff generation under various cropping patterns in the red soil region of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Zhang, Z.N.; Wang, D.; Shi, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.J. Interactions of soil water content heterogeneity and species diversity patterns in semi-arid steppes on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.A.L.; Quinton, J.N.; Hess, T.M. Below-ground relationships of soil texture, roots and hydraulic conductivity in two-phase mosaic vegetation in South-East Spain. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 52, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytton, L.R.; Cresswell, A.; Colbourn, P. Improvement in soil structure associated with white clover. Grass Forage Sci. 1993, 48, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Roscher, C.; Jensen, B.; Eisenhauer, N.; Baade, J.; Attinger, S.; Hildebrandt, A. How do earthworms, soil texture and plant composition affect infiltration along an experimental plant diversity gradient in grassland? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.L.; Quemada, M. Replacing bare fallow with cover crops in a maize cropping system: Yield, N uptake and fertiliser fate. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.; Sharpley, A. Phosphorus transport in overland flow in response to position of manure application. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Y. Protection methods to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus losses from sloping citrus land in the three Gorges area of China. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; An, Y. A comparison of the effect of three grass species on controlling non-point polution in orchards. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2015, 24, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Puigdefábregas, J. The role of vegetation patterns in structuring runoff and sediment fluxes in drylands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2005, 30, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.R.; Prats, S.A.; Keizer, J.J.; de Lima, J.L. Effectiveness of the application of rice straw mulching strips in reducing runoff and soil loss: Laboratory soil flume experiments under simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).