Innovative Multidisciplinary Methodology for the Analysis of Traditional Marginal Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
2.1. Marginal Architecture and Sustainability
2.2. Aeolian Landscape and Local Traditional Architecture
- — relationship between natural/anthropic elements of landscape;
- — precautions to ensure adequate comfort conditions;
- — seismic resistance.
- — the orientation of windows;
- — the type of the building envelope;
- — the existence of shading systems;
- — the possibility of natural ventilation.
2.3. Rapid Evaluation Method (REM)
- — the evaluation of the sustainability of the site;
- — the efficient management of resources;
- — the optimization of energy and environmental performance;
- — the comfort of interior spaces;
- — the adoption of sustainable materials;
- — the implementation of appropriate models of management [35].
2.4. Geographic Information System (GIS)
3. Methodology
Structure of the Database on the GIS Platform
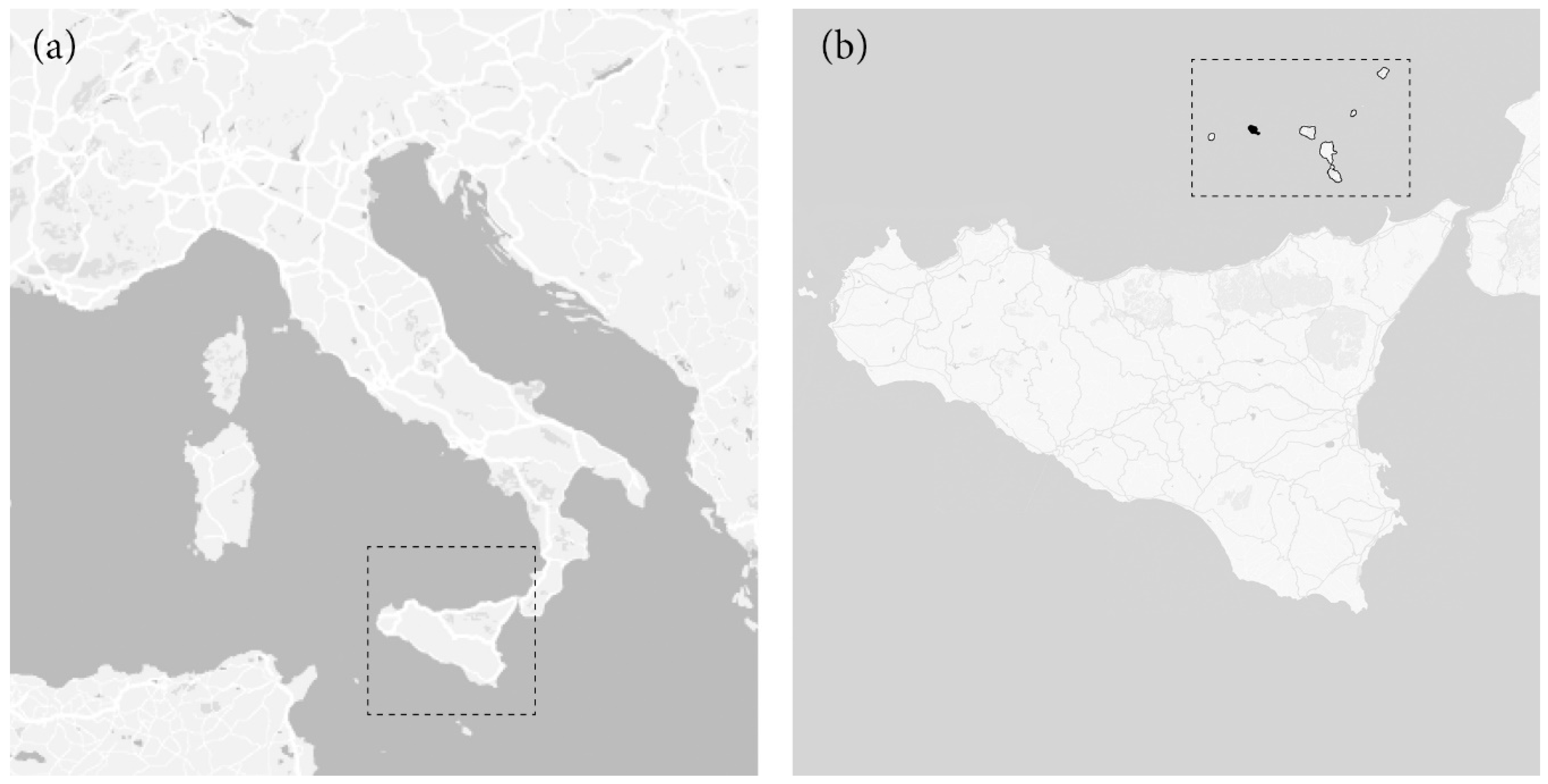
4. Application on the Test-Site
4.1. Filicudi Island Choosing
4.2. Sample Selection
4.3. Features Detection and Weighing
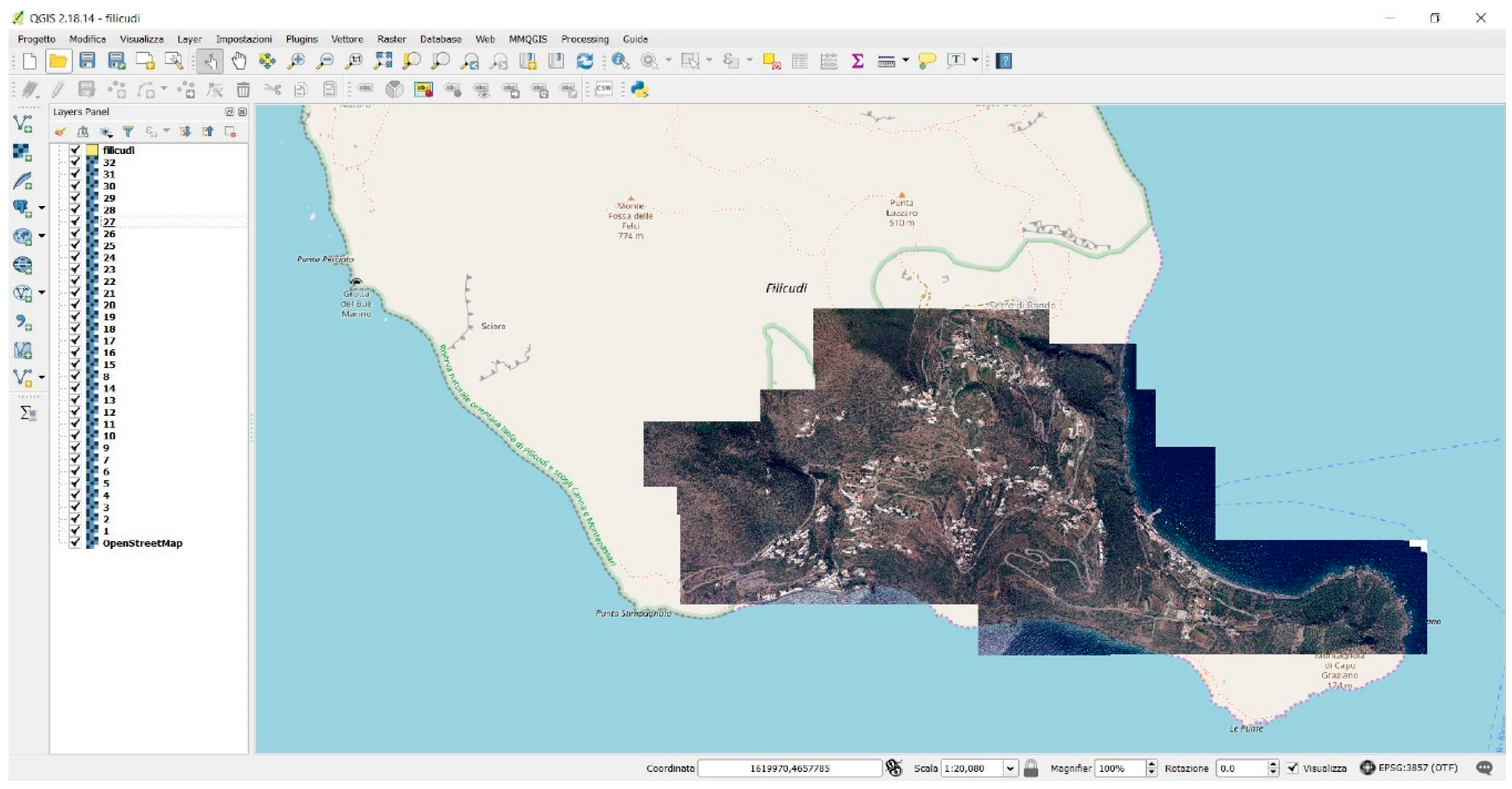
4.4. GIS Platform Processing
4.5. Preliminary Survey
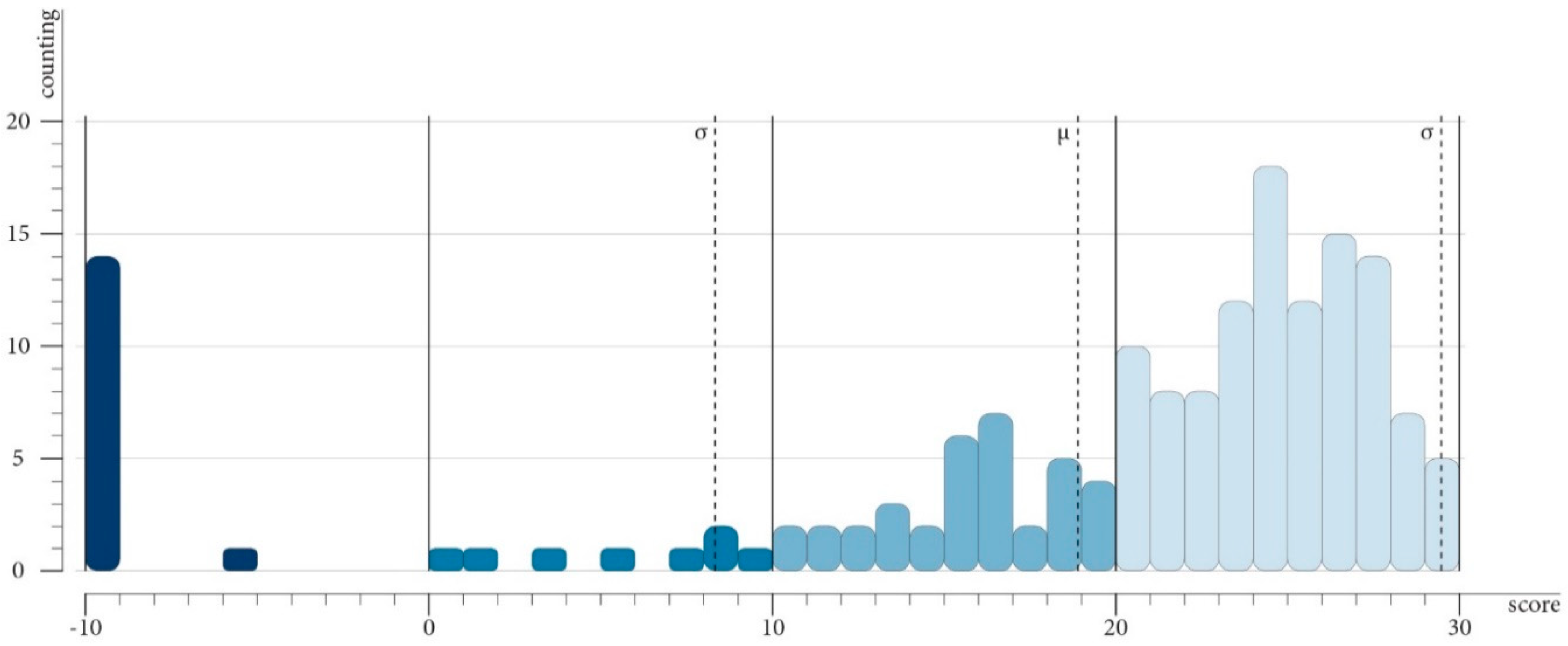
4.6. Tuning
4.7. Detailed Survey
4.8. Discussion Case Selection
5. Discussion
5.1. Findings
5.2. Criticism and Future Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision, Methodology, Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.252; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Foruzanmehr, A.; Vellinga, M. Vernacular architecture: Questions of comfort and practicability. Build. Res. Inf. 2011, 39, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pasquale, L.; Mecca, I. L’architettura vernacolare come modello codificato per il progetto contemporaneo sostenibile. Techne 2016, 12, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Latouche, S. Breve Trattato Sulla Decrescita Serena; Bollati Boringhieri: Torino, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Italian Operative Programs. Available online: http://community-pon.dps.gov.it/areeinterne/progetto-aree-interne/la-strategia-nazionale-per-le-aree-interne/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Padiglione Italia Alla Biennale Architettura 2018. Available online: http://www.arcipelagoitalia.it/home (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Cucinella, M. Arcipelago Italia. Progetti Per Il Futuro Dei Territori Interni Del Paese. Padiglione Italia Alla Biennale Architettura 2018; Quodlibet: Macerata, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, A.G. Traditional Buildings: A Global Survey of Structural Forms and Cultural Functions; I.B. Tauris & Co. Ltd.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marini, S. Nuove Terre. Architetture e Paesaggi Dello Scarto; Quodlibet Studio: Macerata, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bauman, Z. Modernità Liquida; Editori Laterza: Roma, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- European Landscape Convention, Florence 2000. Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/landscape/the-european-landscape-convention (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- VVITA. Rural Forward Platform. Available online: https://sites.google.com/view/vvita/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Ciaschi, A.; De Iulio, R. Aree Marginali e Modelli Geografici di Sviluppo. Teorie e Esperienze a Confronto; Sette Città: Viterbo, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Di Maggio Alleruzzo, M.T. Modificazioni ed usure dello spazio vissuto nell’arcipelago eoliano. In Atlante dei Beni Etno-Antropologici Eoliani; Todesco, S., Ed.; E.D.A.S. Edizioni Dr. Antonino Sfameni: Messina, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Cascio, G. Architetture Eoliane; Litografia Lombardo Milazzo: Lipari, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Maramai, A.; Graziani, L.; Tinti, S. Tsunamis in the Aeolian Islands (southern Italy): A review. Mar. Geol. 2005, 215, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Perricone, M. Tecniche costruttive storiche del patrimonio edilizio eoliano. In Archivio Storico Messinese; University of Toronto Libraries: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1995; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Curzio, M. Il patrimonio architettonico delle Isole Eolie. Notazioni su caratteri, tutela ed interventi conservativi. In Atlante dei Beni Etno-Antropologici Eoliani; Todesco, S., Ed.; E.D.A.S. Edizioni: Messina, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza, V. The Aeolian houses of Filicudi: An example of spontaneous sustainable architecture. Il Progetto Sostenibile. RICERCA e Tecnologie per L’ambiente Costruito 2014, 34, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasio, G. L’architettura tradizionale delle Isole Eolie. In Atlante dei Beni Etno-Antropologici Eoliani; Todesco, S., Ed.; E.D.A.S. Edizioni Dr. Antonino Sfameni: Messina, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza, V. Aeolian Houses—Design of an Innovative Teaching Module; Edicom Edizioni: Gorizia, Italy, 2018; pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza, V. Spontaneous Architecture and Energetic Sustainability: The Aeolian Homes of Filicudi Isle. In Proceedings of the ZEMCH-12, Glasgow, UK, 20–22 August 2012; pp. 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Giuffrè, A. Sicurezza e Conservazione dei Centri Storici—Il Caso Ortigia; La Terza: Bari, Italy, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Grecchi, M.; Malighetti, L.E. Ripensare il Costruito. Il Progetto di Recupero e Rifunzionalizzazione Degli Edifici; Maggioli Editore: Rimini, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Haapio, A.; Viitaniemi, P. A critical review of building environmental assessment tools. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, H. The Evaluation of Historic Buildings; Published under authority of the Minister of the Environment: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Roulet, C.A.; Flourentzou, F.; Labben, H.H.; Sanamouris, M.; Koronaki, I.; Dascalaki, E.; Richalet, V. ORME: A multicriteria rating methodology for buildings. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, T.; Kumar, R.P.; Singth, A.P.; Rastogi, B.K.; Kumar, S. Earthquake Vulnerability Assessment of Existing Buildings in Gandhidham and Adipur Cities Kachchh, Gujarat (India). Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 41, 336–353. [Google Scholar]
- Baggio, C.; Bernardini, A.; Colozza, R.; Corazza, L.; Della Bella, M.; Di Pasquale, G.; Dolce, M.; Goretti, A.; Martinelli, A.; Orsini, G.; et al. Field Manual for post-earthquake damage and safety assessment and short term countermeasures (AeDES). 2007. Available online: https://www.eeri.org/wp-content/uploads/Italy/EUR%2022868%20(2007)%20Field%20Manual%20for%20post-earthquake%20damage%20assessment.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Italian Civil Protection. Available online: http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/risk-activities/seismic-risk/activities (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- GBCB. Green Building Council. Available online: https://new.usgbc.org/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- BREEAM. BREEAM Official Web Page. Available online: https://www.breeam.com/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- DGNB. DNGB International Application. Available online: https://www.dgnb.de/de/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Arbizzani, E. Tecnica e Tecnologia dei Sistemi Edilizi; Maggioli Editore: Milano, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, E.; Carlucci, S.; Cornaro, C.; Bohne, R.A. An Analysis of the Most Adopted Rating Systems for Assessing the Environmental Impact of Buildings. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, G.; Maas, G.; Huyghe, J.; Oostra, M. Criticism on Environmental Assessment Tools. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Belgrade, Serbia, 28 September–2 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, U. Sustainability Assessment in the Construction Sector: Rating Systems and Rated Buildings. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 20, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, A. GIS. Metodi e Strumenti Per un Nuovo Governo Della Città e Del Territorio; Maggioli Editore: Milano, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, L.; Cavallini, P.; Frigeri, A.; Furieri, A.; Marchesini, I.; Neteler, M. GIS Open Source. Grass GIS, Quantum GIS e SpatialLite. Elementi di Software Libero Applicato al Territorio; Dario Flaccovio Editore: Palermo, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.Y.M. 5D GIS virtual heritage. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 111, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristy, G. The impact of urban sprawl on cultural heritage in Herat, Afghanistan: A GIS analysis. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2018, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, A.; Patania, F.; Capizzi, A.; Nocera, F.; Galesi, A. A proposed methodology for estimating the performance of small wind turbines in urban areas. Sustain. Energy Build. 2012, 12, 539–548. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, A.; Patania, F.; Nocera, F.; Capizzi, A.; Galesi, A. GIS-based decision support for solar photovoltaic planning in urban environment. Sustain. Energy Build. 2013, 22, 865–874. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano, A.; Nocera, F.; D’Amico, A.; Spataru, C. Geographical information system as a support tool for sustainable Energy Action Plan. Energy Procedia 2015, 83, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mauro, A.; Greco, M.; Grimaldi, M. A Formal definition of Big Data based on its essential features. Libr. Rev. 2016, 65, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, E. An integrated GIS platform architecture for spatiotemporal big data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 94, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ren, Y. Integrated application of BIM and GIS: An overview. Procedia Eng. 2017, 196, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, I.; Del Giudic, M.; Zerbinatti, M. A database for the architectural heritage recovery between Italy and Switzerland. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 40, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, A.; Yaagoubi, R.; Boehm, J. Integration of Jeddah historical BIM and 3D GIS for documentation and restoration of historical monument. In Proceedings of the 25th International CIPA Symposium 2015 (XL-5/W7), Taipei, Taiwan, 31 August 2015–4 September 2015; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J. A GIS-based cultural heritage study framework on continuous scales: A case study on 19th century military industrial heritage. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-5/W7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadanza, E.; Turillazzi, B.; Terzaghi, F.; Marzi, L.; Giuntini, A.; Sebastian, R. The Streamer European Project. Case study: Careggi Hospital in Florence. In 6th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 649–652. [Google Scholar]
- Roman Empire. Available online: https://www.romanoimpero.com/2010/12/marco-vitruvio-pollione-80-23-ac.html (accessed on 29 November 2019).
- QGIS User Guide, Release 2.8. Available online: https://docs.qgis.org/2.8/pdf/en/QGIS-2.8-UserGuide-en.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2019).
- Filicudi Island. Available online: https://www.filicudi.info/isolafilicudi/isola-filicudi (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Piano di gestione UNESCO Isole Eolie, Regione Siciliana. 2014. Available online: http://www.regione.sicilia.it/beniculturali/dirbenicult/pianogestioneeolie.html (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Smart Filicudi. Available online: http://www.smartisland.eu/replicabilita/eolie/filicudi.html (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- 3D Metric Web Site. Available online: https://3dmetrica.it/sistemi-di-riferimento/ (accessed on 29 November 2019).
- Geo Repository Web Site. Available online: http://georepository.com/crs_3857/WGS-84-Pseudo-Mercator.html (accessed on 29 November 2019).
- Bertolin, C.; Caliò, I.; Finocchiaro, L.; Gagliano, A.; Hărmănescu, M.; Mandrescu, E.C.; Margani, G.; Mihăilă, M.; Panait, A.; Sapienza, V.; et al. VVITA Project—Sustainable and inclusive development of strategies to vitalize villages through innovative architecture technologies. In Proceedings of the 4th Biennal of Architectural and Urban Restoration (BRAU4); Cicop Italia: Florence, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- DOCET, Evaluation Software. Available online: http://www.docet.itc.cnr.it/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Solarity Web Site. Available online: http://www.solaritaly.enea.it/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Wind Finder Web Site. Available online: http://www.windfinder.com (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Eastman, C.; Teicholz, P.; Sacks, R.; Liston, K. BIM Handbook. A guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers and Contractors; Di Giuda, G.M., Villa, V., Eds.; Hoepli: Milano, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, A.; Feligioni, E. Come Redigere il Capitolato Informativo Secondo la Metodologia BIM; Dario Flaccovio Editore: Palermo, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]














| Macro frameworks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Data | Geometry | Supplementary Data | Building | Structure | Energy |
| Toponomastic data | Building topology data | Data carried out through post-processing | Architecture building features and integration into the natural environment | Structural and stability features | Data on environmental energy performance |
| BUILDING Features (alias) | Functions | STRUCTURE Features (alias) | Functions | ENERGY Features (alias) | Function | SCORING Features (alias) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellular aggregation score | CASE WHEN "b_b_01" = ’cluster’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "b_b_01" = ’row’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | construction features score | CASE WHEN "s_b_01" = ’mixed’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "s_b_01" = ’reinforced concrete’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | surface/volume score | CASE WHEN "e_b_01" = ’≤ 0.6’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "e_b_01" = ’0.6 < S/V ≤ 1.2’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | BUILDING SCORE | "b_b_s_01" + "b_b_s_02" + "b_b_s_03" + "b_b_s_04" + "b_b_s_05" + "b_b_s_06" + "b_b_s_07" + "b_b_s_08" + "b_a_s_01" + "b_a_s_02" + "b_a_s_03" + "b_a_s_04" + "b_a_s_05" + "b_a_s_06" + "b_a_s_07" + "b_a_s_08" + "b_a_s_09" + "b_a_s_10" |
| relation with the slope score | CASE WHEN "b_b_02" = ’aligned’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | foundation score | CASE WHEN "s_b_02" = ’horizontal’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | facade hue score | CASE WHEN "e_b_02" = ’light’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | ||
| architectural shape score | CASE WHEN "b_b_03" = ’cubic cells’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | layout organization score | CASE WHEN "s_b_03" = ’cellular type’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | external shading score | CASE WHEN "e_b_03" = ’yes’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | STRUCTURE SCORE | "s_b_s_01" + "s_b_s_02" + "s_b_s_03" + "s_b_s_04" + "s_b_s_05" + "s_b_s_06" + "s_b_s_07" + "s_b_s_08" + "s_a_s_01" + "s_a_s_02" + "s_a_s_03" + "s_a_s_04" + "s_a_s_05" + "s_a_s_06" + "s_a_s_07" + "s_a_s_08" + "s_a_s_09" + "s_a_s_10" |
| volume addiction score | CASE WHEN "b_b_04" = ’less than 10%’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "b_b_04" = ’less than 40%’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | number of floors score | CASE WHEN "s_b_04" = ’1’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "s_b_04" = ’2’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | orientation score | CASE WHEN "e_b_04" = ’N - S’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "e_b_04" = ’NE - SW/NW - SE’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | ||
| perimeter walls score | CASE WHEN "b_b_05" = ’plastered’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "b_b_05" = ’exposed stone’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | staircase score | CASE WHEN "s_b_05" = ’outside’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "s_b_05" = ’none’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | thermal phaseshift score | CASE WHEN "e_b_05" = ’10 h - 15 h’ THEN ’2’ WHEN "e_b_05" = ’5 h - 10 h’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’0’ END | ENERGY SCORE | "e_b_s_01" + "e_b_s_02" + "e_b_s_03" + "e_b_s_04" + "e_b_s_05" + "e_b_s_06" + "e_b_s_07" + "e_b_s_08" + "e_a_s_01" + "e_a_s_02" + "e_a_s_03" + "e_a_s_04" + "e_a_s_05" + "e_a_s_06" + "e_a_s_07" + "e_a_s_08" + "e_a_s_09" + "e_a_s_10" |
| green essences score | CASE WHEN "b_b_06" = ’traditional’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | largest cell score | CASE WHEN "s_b_06" = ’≤ 30 mq’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | overhangs score | CASE WHEN "e_b_06" = ’yes’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | ||
| pulere score | CASE WHEN "b_b_07" = ’in use’ THEN ’4’ WHEN "b_b_07" = ’not in use’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | plan regularity score | CASE WHEN "s_b_07" = ’good’ THEN ’4’ WHEN "s_b_07" = ’moderate’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | daylighting score | CASE WHEN "e_b_07" = ’FLDm > 4’ THEN ’4’ WHEN "e_b_07" = ’2 < FLDm ≤ 4’ THEN ’2’ ELSE ’0’ END | TOTAL SCORE | "b_score" + "s_score" + "e_score" |
| bagghiu score | CASE WHEN "b_b_08" = ’yes’ THEN ’4’ ELSE ’0’ END | height regularity score | CASE WHEN "s_b_08" = ’yes’ THEN ’4’ ELSE ’0’ END | natural ventilation score | CASE WHEN "e_b_08" = ’yes’ THEN ’4’ ELSE ’0’ END | ||
| pavements score | CASE WHEN "b_a_01" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | type of soil score | CASE WHEN "s_a_01" = ’rock’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | U walls score | CASE WHEN "e_a_01" = ’≤ 1.5’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| roof score | CASE WHEN "b_a_02" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | masonry quality score | CASE WHEN "s_a_02" = ’good’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | U roof score | CASE WHEN "e_a_02" = ’≤ 1.5’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| pulere shape score | CASE WHEN "b_a_03" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | walls thickness score | CASE WHEN "s_a_03" = ’≥ 50 cm’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | U windows score | CASE WHEN "e_a_03" = ’≤ 3.5’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| horizontal shading score | CASE WHEN "b_a_04" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | walls slimness score | CASE WHEN "s_a_04" = ’≤ 12’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | shutters score | CASE WHEN "e_a_04" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| facade color score | CASE WHEN "b_a_05" = ’traditional’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | walls on slople score | CASE WHEN "s_a_05" = ’no’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | rainwater collection score | CASE WHEN "e_a_05" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| door jambs and lintel score | CASE WHEN "b_a_06" = ’traditional’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | connections efficiency score | CASE WHEN "s_a_06" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | photovoltaic panels score | CASE WHEN "e_a_06" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| windows shape score | CASE WHEN "b_a_07" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | damages or cracks score | CASE WHEN "s_a_07" = ’no’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | solar thermal score | CASE WHEN "e_a_07" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| windows frame score | CASE WHEN "b_a_08" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | openings for cell score | CASE WHEN "s_a_08" = ’≤ 2’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | cooling system score | CASE WHEN "e_a_08" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| windows shutters score | CASE WHEN "b_a_09" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | large arches score | CASE WHEN "s_a_09" = ’no’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | heating system score | CASE WHEN "e_a_09" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | ||
| pluvials score | CASE WHEN "b_a_10" = ’congruent’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | floors rigidity score | CASE WHEN "s_a_10" = ’wood or steel’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END | vegetation score | CASE WHEN "e_a_10" = ’yes’ THEN ’1’ ELSE ’-1’ END |
| BUILDING | STRUCTURE | ENERGY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular aggregation | cluster row isolated | +2 +1 0 | Construction features | mixed reinforced concrete isolated | +2 +1 0 | Surface/Volume | ≤0.6 0.6 < S/V ≤ 1.2 >1.2 | +2 +1 0 |
| Relation with the slope | aligned transversal | +2 0 | Foundation | horizontal slope | +2 0 | Facade hue | Light dark | +2 0 |
| Architectural shape | cubic cells other | +2 0 | Layout organization | cellular type other type | +2 0 | Horizontal shading | yes no | +2 0 |
| Volume addiction | less than 10% less than 40% more than 40% | +2 +1 0 | Number of floors | 1 2 >2 | +2 +1 0 | Orientation | N – S NE - SW/NW – SE E - W | +2 +1 0 |
| Perimeter walls | plastered exposed stone other | +2 +1 0 | Staircase | outside none inside | +2 +1 0 | Thermal phaseshift | 10 h–15 h 5 h–10 h <5 h | +2 +1 0 |
| Green essences | traditional not traditional | +2 0 | Largest cell | ≤30 m2 >30 m2 | +2 0 | Overhangs | yes no | +2 0 |
| Pulere | in use not in use none | + 4 +2 0 | Plan regularity | good moderate no | +4 +2 0 | Daylighting | FLDm > 4 2 < FLDm ≤ 4 FLDm ≤ 2 | +4 +2 0 |
| Bagghiu | yes no | +4 0 | Height regularity | yes no | +4 0 | Natural ventilation | yes no | +4 0 |
| BUILDING | STRUCTURE | ENERGY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pavements | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Type of soil | rock soft | +1 −1 | U walls | ≤1.5 >1.5 | +1 −1 |
| Roof | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Masonry quality | good poor | +1 −1 | U roof | ≤1.5 >1.5 | +1 −1 |
| Pulere shape | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Walls thickness | ≥50 cm <50 cm | +1 −1 | U windows | ≤3.5 >3.5 | +1 −1 |
| Horizontal shading | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Walls slimness | ≥12 <12 | +1 −1 | Shutters | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Facade color | traditional not traditional | +1 −1 | Walls on slope | no yes | +1 −1 | Rainwater collection | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Door jambs and lintel | traditional not traditional | +1 −1 | Connections efficiency | no yes | +1 −1 | Photovoltaic panels | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Windows shape | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Damages or cracks | no yes | +1 −1 | Solar thermal | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Windows frame | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Openings for cell | ≤ 2 > 2 | +1 −1 | Cooling system | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Shutters | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Large arches | no yes | +1 −1 | Heating system | yes no | +1 −1 |
| Pluvials | congruent not congruent | +1 −1 | Floors rigidity | wood or steel other | +1 −1 | Vegetation | yes no | +1 −1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvagna, S.; Gagliano, A.; Greco, S.; Rodonò, G.; Sapienza, V. Innovative Multidisciplinary Methodology for the Analysis of Traditional Marginal Architecture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041285
Calvagna S, Gagliano A, Greco S, Rodonò G, Sapienza V. Innovative Multidisciplinary Methodology for the Analysis of Traditional Marginal Architecture. Sustainability. 2020; 12(4):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041285
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvagna, Simona, Antonio Gagliano, Sebastiano Greco, Gianluca Rodonò, and Vincenzo Sapienza. 2020. "Innovative Multidisciplinary Methodology for the Analysis of Traditional Marginal Architecture" Sustainability 12, no. 4: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041285
APA StyleCalvagna, S., Gagliano, A., Greco, S., Rodonò, G., & Sapienza, V. (2020). Innovative Multidisciplinary Methodology for the Analysis of Traditional Marginal Architecture. Sustainability, 12(4), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041285








