1. Introduction
Equal spatial distribution of public services in urban areas is a basic concept of urban studies [
1], and determining the efficiency and adequacy of the spatial distribution of public services is an important element of contemporary urban planning [
2]. The efficiency and importance of the services provided in a city are measured by the quality of the services, how far away they are, and how long it takes to reach them [
3].
The availability and efficiency of services are regarded as indicators of the standard of living in a city. The increasing population makes it necessary to increase services to meet the needs of the population. Most researchers agree that there are levels and patterns of quality of life, and there are also different definitions; for example, the one introduced by Bryan in 2002, that quality of life is determined by the extent to which an urban area meets the requirements of happiness, which depends on good planning and providing appropriate services [
4]. There is no absolute agreement among scientists and policy-makers on the precise definition of quality of life, its individual components, and how plans for enhancing its work. Many reports, projects, and planning data refer to quality of life as the “result” of economic, environmental, social, recreational, and civil conditions [
5].
Studying the quality of the urban environment has gained the attention of many researchers through several studies on different aspects, such as planning private living, and on quality of life in general, such as the Rogerson study on quality of life in the city, illustrating the patterns and parameters of quality of life, the attraction of a city for living, the factors and indicators for measuring and evaluating quality of life, and categorizing the different levels of quality of life using multicriteria techniques [
6].
There are many social science studies focused on monitoring the social indicators of quality of life [
7,
8], for example, regarding human geography and planning, focusing on deprivation in cities [
9], and focusing on health as the main element in studying quality of life in cities in the USA [
10]. There are also those interested in the relationship between economic indicators and quality of life [
11,
12] and in the importance of work in determining quality of life [
13].
A great effort was made in studying urban social geography to evaluate the quality of different habitation environments [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20], and in studying the conditions of deprived areas as the main focus and contemporary urban social geography [
21,
22].
Some studies have focused on monitoring environmental conditions and some personal characteristics of the population, such as water and air pollution and the level of education and health [
23,
24] as an approach to determine quality of life. The Quality of Life Research Group of the geography department at Strathclyde University in Scotland has conducted several studies on quality of life in UK cities. They also studied the problem of measuring quality of life [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29], conducted many experimental studies on the quality of life in urban areas around the world [
30], and published many articles directly related to quality of life. The most important study was that of Pacione, on the quality of the urban environment and human welfare from a social geographic perspective. That study introduced a five-dimensional model of quality of life, illustrating some main definitional and methodological issues that were investigated and providing an evaluation of the potential benefits of research on quality of life and potential advanced results of future research [
31].
Geographic Information System (GIS) tools are very powerful in spatial decision support systems for evaluating the quality of urban life; four main spatial processes are usually used to generate alternative decisions: connectivity [
32], communication [
33], proximity [
34], and overlay [
35]. Multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) is generally used to evaluate multiple parameters. The decision-making process mainly involves four stages: defining the problem, building the preferences of decision-makers, evaluating the alternatives, and determining the best of the alternatives [
36,
37]. Integrating MCDA and GIS is a great contribution that usually yields very useful spatial alternatives to help decision-makers.
Malczewski [
38] defined GIS-based MCDA as a process that combines the preferences of the spatial data and the values law to generate information to be provided to decision-makers [
39,
40,
41,
42,
43]. GIS-based MCDA includes evaluating the spatial decision alternatives that were determined based on the parameters and preferences of decision-makers. Historically, the application of the MCDA technique in GIS goes back to the beginning of the 1990s [
44,
45,
46].
There are many examples in the literature concerning the application of GIS techniques integrated with MCDA. GIS-MCDA can be classified into several types, including multiobjective decision analysis (MODA) and multiattribute decision analysis (MADA). MADA can be performed in many ways, including the linear weighted overlay model, the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), and the ideal point method (IPM).
In the present study, AHP is used. It was developed by Saaty in 1970 and 1980 [
47,
48] to help in the multidecision-making process using a hierarchical system of objectives, aspects, criteria, and alternatives [
37]. A one to nine scale is used to assign weights of importance to the criteria [
49]. AHP is regarded as one of the most popular and widely used tools in scientific research.
Many studies [
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55] established the importance of site analysis in urban and regional planning services. One of the most important tools for site analysis is quantitative modeling for accessibility and location-allocation analysis. This provides quantitative comparisons for evaluating the efficiency of local spatial decisions and generating alternatives, by either suggesting more efficient service systems or enhancing the current ones, because local planning decisions made by those responsible or by the government are often far from ideal [
56,
57,
58,
59,
60].
Saudi cities have witnessed rapid development in various ways regarding urban systems, especially after the discovery of petroleum oil in the 1970s. Development in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) during this period was characterized by random urban expansion and services being distributed in a sporadic manner, limited to districts with higher population density and giving rise to the manifestation of environmental deficiency indicators and the disruption of environmental sustainability. Buraidah city in the Al-Qassim region is regarded as a model for rapidly developing Saudi Arabian cities in both urban and population growth. Buraidah city accounts for about 51% of the total population in the cities of the region and about 37.2% of the population in the whole region. The population doubled about four times during the period 1974–2019. The city dominated the rank–size graph, leaving a large gap with Unaizah city in second place and Al Rass city in third. The urban mass also doubled about 135 times during the period 1910–2019. This resulted in considerable pressure on the public services, which became unable to meet the increasing needs of the population in Buraidah city as a result of the lack of prior planning to contain any potential increase in population. This makes it necessary for decision-makers to take into account the required precautions in order to provide citizens with fairly distributed efficient services.
The present study was aimed at introducing an innovative approach for evaluating the quality of the urban environment in Buraidah city by integrating GIS-based network analysis and multicriteria decision analysis. The service area analysis technique of GIS Network Analysis was applied to the available services in the districts of Buraidah city, while the MCDA technique of GIS was applied to generate a spatial suitability map for quality of life in the districts. The AHP technique was used to determine the criteria weights. The location-allocation model was used to improve the spatial planning of public services in the city by suggesting or allocating new efficient services and enhancing the existing ones.
2. Area of Study
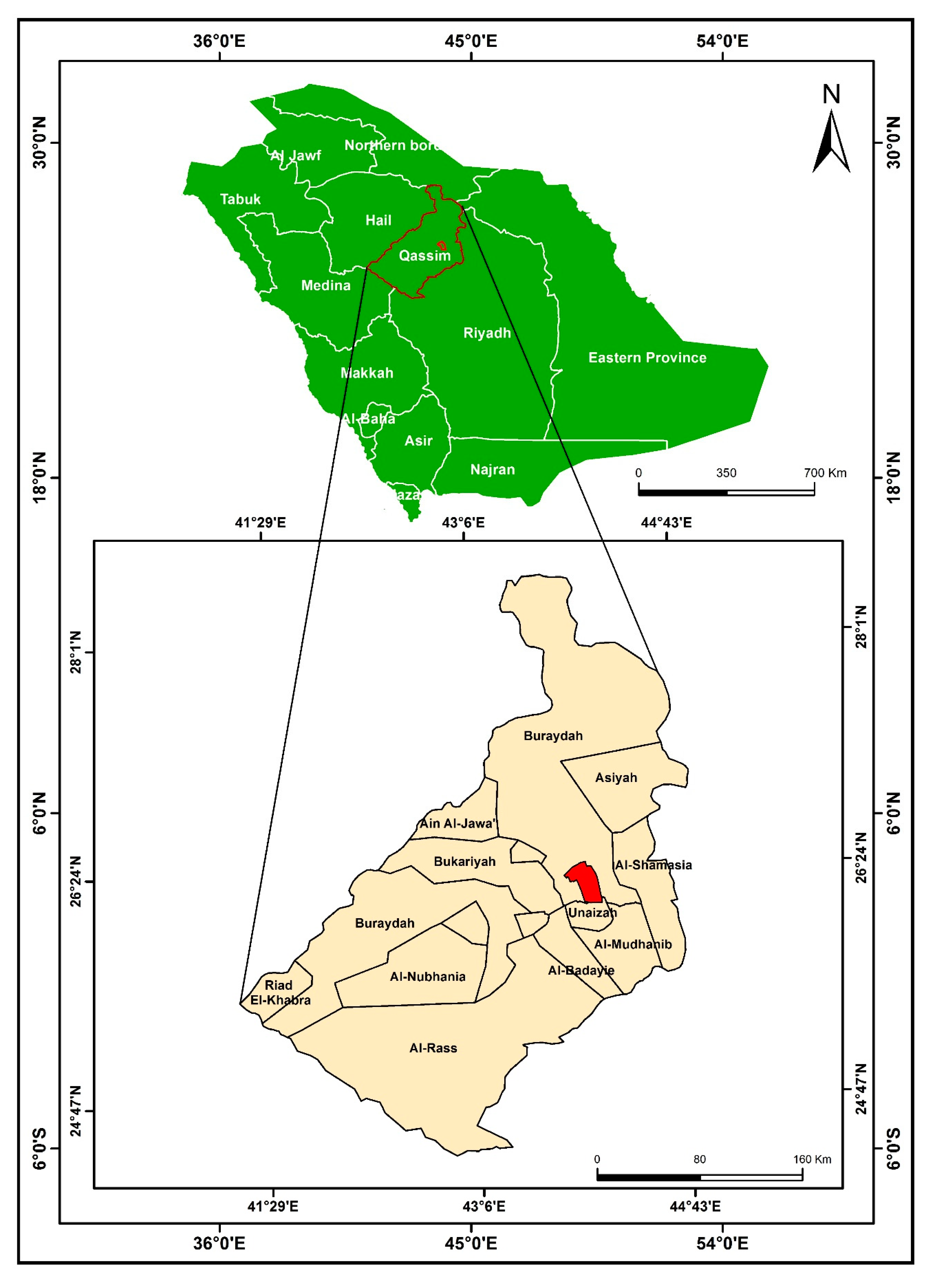
Buraidah city lies in the Al-Qassim region in NW KSA between longitudes 43°42′E to 43°90′E and latitudes 26°10′N to 26°45′N at an elevation ranging from 600 to 650 m above sea level (
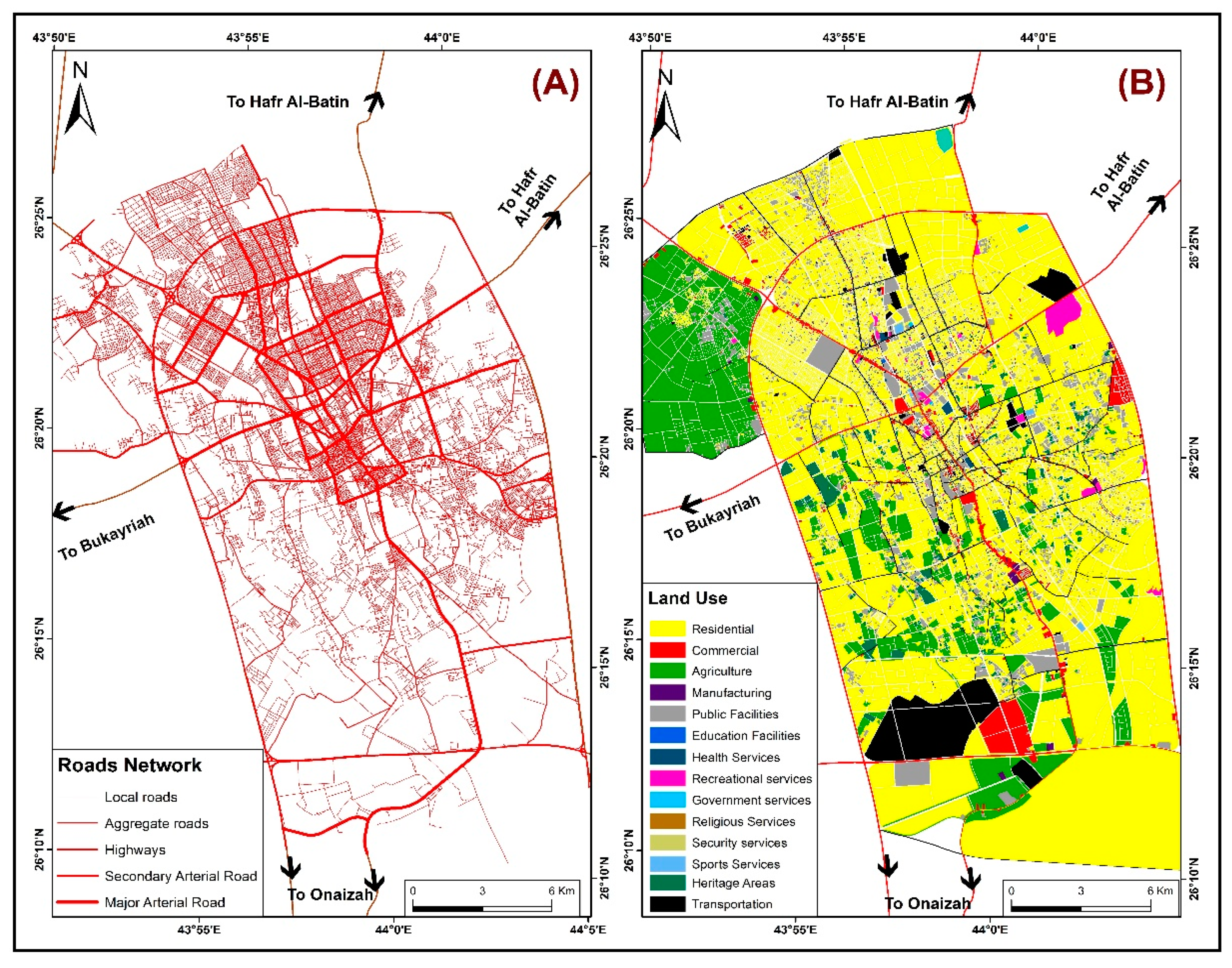
Figure 1). It is the capital and the commercial and administrative center of Al-Qassim. It lies in the center of the largest agricultural zone in KSA. It is regarded as the food basket for KSA, with large farms for the production of wheat, vegetables, and dates. It consists of 70 districts with concentrated services and large trade centers and recreational services, giving rise to large stresses due to the rapidly increasing population from other cities to share these services due to the lack of services in the other cities and villages of Al-Qassim (
Figure 2). As of 2019, the total population in Buraidah city was 59,0312 inhabitants, representing 51% of the total population in all cities in Al-Qassim, and the total urban area was about 42,000 hectares (
Figure 3).
3. Methodology and Data Processing
The methodology of the study (
Figure 4) and the data processing for evaluating the quality of life in Buraidah city depended on three main integrated techniques (accessibility analysis, multicriteria analysis, and the location-allocation model in GIS (ArcGIS v. 10.2)), as follows:
3.1. Input Data for Network Analysis
To conduct network analysis in Buraidah city, the necessary data were obtained from several sources, with standardization of measurements and projections so that the data would be integrated within the Geographic Information System and the spatial data for the study.
Figure 5 and
Table 1 show the types, spatial accuracy, and sources of data.
As for the descriptive data, the lengths of roads and streets were calculated through the Calculate Geometry function in ArcGIS, and accuracy and units were ensured after defining them and the appropriate coordinate system for the region as Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Zone 38N and its compatibility with the geospatially defined visual space, as well as standard 1:5000 field survey maps sourced from the Al-Qassim Region Secretariat of the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs (
Table 1).
The average speed of vehicles on roads was estimated according to their type from the Road Engineering Design Manual in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for 2019, approved by the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs.
The data of residents of the districts in Buraidah were also obtained through the secretariat of the Al-Qassim Region of the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs according to the last population census of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 2019, the population data were matched with the statistics issued in reports of the General Authority for Statistics, and the population density was calculated in each administrative unit (residential district) by calculating the area of the district using Calculate Geometry.
3.2. Service Area Analysis within GIS Network Analysis
3.2.1. Creating Attributes and Setting Network Parameters
The attributes of the network were created (
Table 2), comprising the main data of the roads, including length of the road, allowed speed, waiting time, and time to the end of the road. The speed of arrival depends on the quality and efficiency of the surfaces of roads/streets; their suitability for driving/walking; the topography, geometry, and width of the roads/streets; the presence of paths for walking; traffic lights and signs; and the type of land use on both sides of the roads/streets. These attributes/fields were created in the road network layer.
A. Waiting Time
Waiting time is estimated as the average waiting time according to the type of road. It is difficult to collect field data on waiting time with traffic lights on each street, but it is possible to estimate waiting times based on the type of street: for highways, it is 10% of the travel time, and for main arterial roads it is 30% of travel time, and the speed of traffic decreases due to delays in intersections and the interactions of vehicles. For a secondary arterial road, it is 40% of travel time, and for a synthetic road, it is 50% of travel time due to the possibility of long rows of signals. Time is considered as a weight in ArcGIS Network Analysis, and is unstable in all streets where the speed of access depends on the quality, efficiency, and characteristics of the streets. On high-efficiency streets, the arrival time between two points is shorter. The opposite occurs on dilapidated streets, so street condition is a necessary element when analyzing networks.
B. Road Speed and Time to the End of the Road
The time to the end of the road is calculated by the following formula:
(Road length/Road speed) × 60 + waiting time
This equation includes the length of the road and its type, which determines the average vehicle speed (km/h), which is 120 km/h on highways, 80 km/h on major arterial roads, 60 km/h on secondary arterial roads, and 50 km/h on aggregate roads. The average speed of vehicles was estimated according to their type from the Road Engineering Design Manual of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for 2019, approved by the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs.
When calculating the time to the end of the road in minutes, the length of the road in kilometers is divided by the speed of the road in kilometers per hour and the result is multiplied by 60 to be in minutes. It should be noted that the pedestrian position in the network weights was not determined, because it is difficult to perform accurately in the field. The estimate would be misleading, so the distance weights and the average time spent by vehicles are based on the established speeds on the roads.
3.2.2. Applying Service Area Analysis
The service analysis was performed, the desired services for analysis were selected, and the road network layer and other layers were added to compute their service area.
The service points were loaded with the facilities, and the service area layer was configured with travel times of 5, 10, and 15 minutes. The network was then solved with the model according to the defined times.
The resulting service areas were distributed over the districts of Buraidah city to determine the efficiency of services in each area by computing the percentage of serviced area to total area. Then, the minimum value, maximum value, sum, and mean were calculated, resulting in a layer with two fields for each area showing the minimum and maximum values of time required to reach the service. This showed that there were areas covered by the service within 0 to 5 minutes, other areas within 5 to 10 minutes and 10 to 15 minutes, and areas not covered by the service within the specified maximum time of 15 minutes.
3.2.3. Location-Allocation Analysis
This stage included determining the deficiency of different services and allocating locations for suggested services to correct the deficiency. The location-allocation model was used after building the road network. It was added from the Network Analyst toolbar, and its parameters include impedance weight attribute and value (distance or time), number of facilities (facilities to choose), impedance cutoff, and location-allocation problem type. There are seven types of location-allocation models [
61,
62]. In the present study, the maximum coverage type was used [
63] with the formula
where
is the group of demand points or the time duration or the population as a weight, and
is the location-allocation parameter with a value of either 0 or 1. After setting the parameters of the analysis layer and selecting the “maximize coverage” location-allocation type, the spatial locations of services (facilities) and the demand points were provided for the administrative districts of the study area, represented by point layers in the Network Analysis window. The network was then solved to obtain results and suggestions for new locations of services in all administrative districts of Buraidah city.
3.3. GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Analysis
3.3.1. Criteria Definition
The first stage of multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) is concerned with combining information and data from several criteria for decision-making purposes [
64]. The criteria influencing the quality of urban life in Buraidah city were determined and selected based on the local and international literature and personal interviews [
65], and services were determined. The weights of preferences were determined for the seven services using the AHP method: health services (hospital (H), health center (HC), ambulance facility (AF)), educational services (elementary school (ES), middle school (MS), high school (HS), university (U)), security services (SE), government services (GO), religious services (RE), sports services (SP), and recreational services (RS).
3.3.2. Criteria Weighing
The process of assigning weights to the criteria is one of the most sensitive points in this type of analysis. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used for criteria weights, as this method proved its high efficiency in solving complex problems [
66]. It was introduced by Saaty [
47,
48] (
Table 3) and is very helpful in decision-making.
The AHP underwent successive stages of generating a pairwise comparison matrix with criteria values from 1 to 9, as shown in
Table 3. The diagonal must equal 1, as it represents the comparison of one criterion against itself, and values above the diagonal are the inverse of those below it. After the numerical comparison, the sum of the columns is obtained and then divided by the total sum to obtain the relative weight.
3.3.3. First Stage: Assigning Criteria Preference Values Based on Saaty’s Table
The preferences are determined in the AHP based on pairwise comparisons, which are based on evaluating each element/criterion against all other elements/criteria in a specific hierarchal level. The element is a specific character, such as a variable or evaluation parameter, and the reference comparison point is an element at the top of the hierarchal chain.
The preference matrix is a result of pairwise comparisons of all elements at a specific hierarchy level. Formula (2) indicates a matrix of n × n dimensions where n is the number of elements being compared. Formula (3) is an expression of the principle of preference, in which two identical elements compared to each other are not differentiated by preference, and the difference in preferences is expressed by the number 1, so all values of the elements on the diagonal of the matrix are equal to 1 (
Table 4).
3.3.4. Second Stage: Percentage of Preference Value for Each Parameter
A. Percentage of preference value
The percentage of preference values between two parameters where one is in a column and the other is in a row can be determined using the formula
where
is the percentage of preference and
is the value of preference between two parameters in column and row, respectively, and
is the total sum of the column parameter.
All percentages for all parameters were computed, and are presented in
Table 5.
B. Values of relative weights
The relative weight values are determined using the formula
where
is the value of the relative weight for the row parameter,
is the sum of percentages of preference values for a row parameter, and
is the final value of sum
for all rows.
3.3.5. Third Stage: Verification Index for Calculating Consistency Mathematically
First, consistency is computed using the formula:
where
is the square root of the pairwise comparison matrix mean and n is the number of parameters or criteria.
The consistency is 0.05; the closer the result to 0, the more confident the consistency index, and vice versa.
Second, the consistency index percentage is calculated by the formula
where R is the random consistency index based on the number of criteria taken from
Table 7.
The value of the random consistency index based on
Table 7 is equal to 1.49, because the number of criteria used is more than 10. The percentage of the consistency index is 0.05/1.49 = 0.03 = 3%.
The consistency values must be in a range not exceeding 0.1 (10%), as values higher than 0.1 mean more conflict in consistency.
3.4. Spatial Suitability Model for Standard of Living for Quality of Life Map
After preparing the parameters in the suitable formats, they are multiplied by their weights and then summed together by a simple math process using the raster calculator in the GIS environment. The sum is calculated, the spatial analyst tool group is selected, then the map algebra group, and finally the raster calculator.
After determining the weights of parameters, areas with high coverage by all public services were determined, considering the best areas in the city in terms of quality of life. A field or attribute was created to determine the percentage of each area from the services, with the formula of field area in the service area layer/area of district × 100, to obtain the best Buraidah districts for service coverage and hence quality of life through the spatial suitability map.
Table 8 lists the classification parameters of the final suitability map.
Figure 6 shows the structure of the multicriteria analysis model for evaluating the quality of urban life in districts with the best standard of living in the city.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Accessibility Analysis of Public Services in Buraidah City
4.1.1. Accessibility Analysis of Educational Services
The results of the data analysis of educational services (
Figure 7 and
Table 9) revealed that there are two districts not covered by educational services, representing 2.9% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 1016 inhabitants, or 0.2% of the total population in the city. The other 68 districts (97.1%), with 589,296 inhabitants (99.8%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of university services within five minutes includes 15 districts, representing 21.43% of the 70 districts in Buraidah city, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 29 districts (41.43%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 52 districts (74.28%). The coverage area of high school services within five minutes includes 59 districts representing 84.29% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 64 districts (91.43%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 66 districts (94.29%).
The coverage area of middle school services within five minutes includes 34 districts, representing 48.57% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 48 districts (68.57%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 64 districts (91.43%). The coverage area of elementary school services within five minutes includes 64 districts, representing 91.43% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 66 districts (94.29%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 68 districts (97.1%).
4.1.2. Accessibility Analysis of Health Services
The results of the data analysis of health services (
Figure 8 and
Table 9) revealed that there are nine districts not covered by health services, representing 12.9% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 8854 inhabitants, or 1.5% of the total population. The other 61 districts (87.1%), with 581,458 inhabitants (98.5%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of hospital services within five minutes includes six districts, representing 8.57% of the 70 districts in Buraidah city, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 16 districts (22.86%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 36 districts (55.43%). The coverage area of health center services within five minutes includes 36 districts, representing 51.43% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 53 districts (75.71%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 61 districts (87.14%). The coverage area of ambulance facility services within five minutes includes 15 districts, representing 21.43% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 20 districts (28.57%), and within 15 minutes the coverage included 32 districts (45.71%).
4.1.3. Accessibility Analysis of Government Services
The results of the data analysis of government services (
Figure 8 and
Table 9) revealed that there are 18 districts not covered by government services, representing 25.7% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 134,199 inhabitants, or 22.7% of the total population. The other 52 districts (75.3%), with 456,113 inhabitants (77.3%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of government services within five minutes includes eight districts, representing 11.44% of the 70 districts in Buraidah city, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 19 districts (27.14%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 33 districts (47.14%).
4.1.4. Accessibility Analysis of Religious Services
The results of the data analysis of religious services (
Figure 9 and
Table 9) revealed that there are two districts not covered by religious services, representing 2.9% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 1016 inhabitants, or 0.2% of the total population. The other 68 districts (97.1%), with 589,296 inhabitants (99.8%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of religious services within five minutes includes 54 districts, representing 77.14% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 59 districts (84.29%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 63 districts (90%).
4.1.5. Accessibility Analysis of Security Services
The results of the data analysis of security services (
Figure 9 and
Table 9) revealed that there are 12 districts not covered by security services, representing 17.1% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 95,260 inhabitants, or 16.1% of the total population. The other 58 districts (83.9%), with 495,052 inhabitants (82.9%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of security services within five minutes includes 12 districts, representing 17.14% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 29 districts (41.34%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 47 districts (67.14%).
4.1.6. Accessibility Analysis of Recreational Services
The results of data analysis of recreational services (
Figure 9 and
Table 9) revealed that there are 11 districts not covered by recreational services, representing 15.7% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 95,740 inhabitants, or 16.2% of the total population. The other 59 districts (84.3%), with 494,572 inhabitants (83.8%), are in the coverage area of these services. The coverage area of recreational services within five minutes includes 17 districts, representing 24.29% of the 70 districts in Buraidah city, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 42 districts (60%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 60 districts (68.74%).
4.1.7. Accessibility Analysis of Sports Services
The results of data analysis of sports services (
Figure 9 and
Table 9) revealed that there are 20 districts not covered by sports services, representing 28.6% of all districts in Buraidah city, with a population of 180,228 inhabitants, or 30.5% of the total population. The other 50 districts (71.4%), with 410,084 inhabitants (69.5%), are in the coverage area of these services.
The coverage area of sports services within five minutes includes 10 districts, representing 14.28% of the 70 districts, within 10 minutes the coverage includes 26 districts (37.14%), and within 15 minutes the coverage includes 41 districts (58.57%).
4.2. Analysis of Standards of Living for Quality of Life Map
4.2.1. Districts with High Quality of Life
These are represented by districts with very high spatial suitability of 100%, including 31 districts (44.29%) with 362,223 inhabitants, representing 71.59% of the total population in Buraidah city living in an area of 96.22 km
2, or 19.24% of the total area of the city. Al Janoub, Al Khalij, As Sadah, Al Helal, Al Agibah, Al Basatien, An Nasim, Al Maota, At Talem, and Al Garidah are the most important districts in this category. They are old midtown districts that have benefited from continuous development projects in the area (
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
The services in these districts vary between commercial, residential, religious, and government services. The Saudi Electricity Company, Buraidah Central Hospital, the General Directorate of Education, As Sadah cemetery/tombs, King Fahd Specialist Hospital, the General Health Affairs Directorate, King Fahd Park, the Ministry of Media, and the College of Food and Environmental Technology are the most important services in these districts.
The spatial distribution of public services in Buraidah city is influenced by population growth. The population doubled about four times during 1974–2019, from 150,906 inhabitants in 1974 to 590,312 in 2019. The population increase was accompanied by urban expansion, as the urban mass of the city doubled about 135 times during 1910–2019, from 312 hectares in 1910 to 42,000 hectares in 2019. The population is found to be concentrated in the old city center, with a density of more than 11,000 persons/km2, and the density decreases toward the east, south, and west to fewer than 1300 persons/km2.
4.2.2. Districts with Good Quality of Life
These are represented by districts with high spatial suitability of 80%–100%. This category includes 20 districts (28.6%) with 87,012 inhabitants, representing 17.20% of the total population in Buraidah city living in an area of 168.92 km
2, or 33.78% of the total area of the city. Al Ghadeer, As Salmeyiah, Ar Rawaby, Howailan, Wasit, Khodaira, As Salam, Ad Dahy, Al Moraideseyah, and Khab Ath Thanian are the most important districts in this category, and they are newly founded districts (
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
These districts have been developed since 2007, and their area increased from 0.52 km2 before 1910 to 239.6 km2 in 2007, or a total increase of 239.08 km2 during this period. These districts are characterized by the presence of main arterial roads that share in the large urban expansion of the city. The First Northern Ring and Internal Southern Ring roads are among the most important roads in the area. These districts are also characterized by relatively high population density, ranging from 6501 to 11,000 persons/km2.
The location of the city at the intersections of vital roads/highways has influenced activities and services in the city, making it an administrative, commercial, and service center for the whole area.
The development that began in the core of the city then extended to the outskirts and the related corridors of development. King Abdel Aziz Road (Al Khobaib) and As Senaa’h Street, along with the other longitudinal and latitudinal corridors that represent the initial extension of the city, are among the most important shared corridors in the city’s development. They are oriented in the northwestern direction for about 13 km, in the northern direction for about 6 km, in the northeastern direction for about 5 km, in the eastern direction for about 7.5 km, and in the western direction for about 4.5 km.
4.2.3. Districts with Moderate Quality of Life
These are represented by districts with moderate spatial suitability of 60%–80%. This category includes nine districts (12.86%) with 29,610 inhabitants, representing 5.85% of the total population in Buraidah city living in an area of 87.08 km
2, or 17.41% of the total area of the city (
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
These nine districts are Al Khodr, Ar Rewak, Al Qaseimah, Al Mroj, Al Oraidemy, Ash Shafaq, An Naql, and Al Faroq. These are newly founded districts developed after 2007, and their area has increased by 10,414.9 hectares. These districts are characterized by a low population density of 1301–3200 persons/km2. The low population density is attributed to the deficiency in services, as they are newly founded districts. It is noticed that most of these are residential districts only, with no other distinguished services. The direction of urban growth in these districts is toward the north and northwest, except the industrial city, which was constructed to the west of Wadi El Ramma, which is located southeast of the city and is considered the main reason for the ceasing of development in this area.
4.2.4. Districts with Low Quality of Life
These are districts with low spatial suitability of 40%–60%. This category comprises six districts (8.57%) with 23,918 inhabitants, representing 4.7% of the total population in Buraidah city living in an area of 86.42 km
2, or 17.28% of the total area of the city. These districts are Al Yarmok, Ar Remal, Al Marwah, Al Losaib, Ash Shafaq, and Ash Shaqqah. These are newly founded districts developed after 2007, and their area has increased by 20,414.9 hectares. These districts are characterized by a very low population density of fewer than 1300 persons/km
2, and this is attributed to the deficiency in services, as they are newly founded districts. It is noticed that most of these districts are residential only, with no other distinguished services due to the presence of Wadi El Ramma, which is located southeast of the city and is considered the main reason for the ceasing of development in this direction (
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
4.2.5. Districts with Very Low Quality of Life
These are districts with very low spatial suitability of less than 40%. This category comprises four districts (5.71%) with 3237 inhabitants, representing 0.64% of the total population in Buraidah city living in an area of 61.46 km
2, or 12.29% of the total area of the city. These districts are Al Andalos Al Yarmok, Ar Remal, and Al Marwah. These are newly founded districts with no sufficient services, and are characterized by a very low population density of fewer than 1300 persons/km
2 (
Figure 10 and
Table 10).
4.3. Improving the Spatial Planning of Quality of Life in the Urban Environment in Buraidah City Based on the Location-Allocation Model
The location-allocation model tries to find the best locations for services and is regarded as a very powerful tool for planning public utilities. Its application was previously limited by the unavailability of data; now the data are available thanks to the land information systems in most KSA cities. Allocating services equally in the districts of Buraidah city is an effective approach to maximize social welfare and improve or generate planning alternatives by either suggesting new effective services or enhancing the existing ones [
65,
66]. In the present study, the maximize coverage location-allocation model type was used, with a response time of no more than 15 minutes. The results were as follows:
There are 67 districts covered by university services, or 95.7% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern part of the city; consequently, it is suggested that two additional universities should be allocated in the eastern and southwestern parts of the city (
Figure 11 and
Table 11).
There are 67 districts covered by high school services, or 95.7% of the 70 districts in the city. Consequently, it is suggested that additional high schools should be allocated in the southern part of the city to ensure coverage of all districts. In addition, an elementary school and middle school are proposed (
Figure 11 and
Table 11).
There are 62 districts covered by hospital services, or 88.6% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern and central parts of the city; consequently, it is suggested that two more hospitals should be allocated in the eastern and southern parts of the city to ensure coverage of all districts. In addition, a health center is suggested (
Figure 11 and
Table 11).
There are 62 districts covered by ambulance facility services, or 88.6% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the eastern and central parts; consequently, it is suggested that two more ambulance facilities should be allocated in the southern and southwestern parts to cover all districts (
Figure 11 and
Table 10).
There are 63 districts covered by security services, or 90% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern and central parts of the city. It is suggested that two more security services should be allocated in the southern and southwestern parts to cover all districts (
Figure 12 and
Table 11).
There are 60 districts covered by government services, or 85.7% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern parts. It is suggested that two more courts should be allocated in the eastern and southwestern parts to cover all districts (
Figure 12 and
Table 11).
There are 64 districts covered by sports services, or 91.4% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern and central parts. It is suggested that one more sports services should be allocated in the southwestern part of the city to cover all districts (
Figure 12 and
Table 11).
There are 64 districts covered by recreational services, or 91.4% of the 70 districts in the city. These districts are concentrated in the northern parts. To cover all districts, it is suggested that one more should be allocated in the southeastern part of the city (
Figure 12 and
Table 11).
5. Recommendations
In order to narrow the quality of life gap between districts in Buraidah city, the study recommends enhancing services (facilities) in the city by redistributing services according to the amount and needs of the population in order to serve all districts equally and efficiently. This requires correcting the current deficiency, which is estimated in this study to be 16 services: one high school, one elementary school, one middle school, two universities, one sports service, two security services, two courts, two hospitals, one health center, one park, and two ambulance facilities.
New, comprehensive housing centers that serve as focal points to fill the current gap in the quality of life in the city should be developed through five main areas: inside and around the city center, in the northwest along Al-Khabib Street (Al Safraa), in the northeast (Al Faizia), east of the truck road, and in the southeast (Al Dahie), with upgrading and improvement of residential areas built with mud by gradually rebuilding and adding roads, parking, and better social and public services while maintaining some important buildings.
An integrated commercial, cultural, and government center should be established on the land located east of the princedom building and the hospital (in the center of the city), with three other commercial centers to the northwest of the city on the Medina road, in the northeast on the Tarifa road, and in the southeast in Al-Sharqi on Riyadh Road in the Al-Dahie area.
The current commercial center should be improved and upgraded by rebuilding the market and renovating old shops and offices in the surrounding streets and adding new buildings, providing parking and associated services; a central park heading from east to west should be established, containing agricultural areas, gardens, and open squares for government use; and a longitudinal park complementary to the central park should be established from north to south (Crown Prince Park) along the west side of the truck road.
Two industrial zones should be established, the first in the center of the city, extending the current workshop area west of Al-Khabib Street, and the second south of the city to the east of Aniza Road, and a large commercial/industrial area east of the city should be added to these areas that meets the requirements of those who need large areas such as car dealers, for equipment, storage, and warehouses.
We also recommend providing decision-makers with the results of this study for consideration in strategic urban planning and sustainable urban development plans to enhance the efficiency of infrastructure according to the needs of the population of Buraidah city. It is also recommended that the methodology of this study, using accessibility analysis and GIS spatial and statistical analysis techniques, along with standards of urban planning, be approached in the planning of public utilities in similar cities.
6. Conclusions
The nature of the formation of the city of Buraidah and its emergence as a vital center at the intersections of important roads in the center of the KSA affected the growth of activities and services in the study area, and over time this area became an administrative, service, and commercial center for the vast urban environment represented by the area of Qassim. The growth of this center occurred organically and then extended on the axes emanating from it, the most important of which is King Abdul Aziz Road (Al-Khabib), and the other longitudinal and transverse axes that represent the first extensions of the city. The great development and urbanization attracted investments in the city. Different fields emerged in secondary centers associated with the main axis of movement and spread in different sizes, until they took on the current spatial distribution, consisting of a main center and secondary centers linked by the axes of movement, with the problems of fragmentation of the urban mass, lack of services, and poor distribution. Within the city’s districts, the available services are unable to meet the growing needs of the population, as a result of the lack of planning to contain potential increases in the population, which has become an inevitable assessment of the quality of life of the city for planners, decision-makers, and development officials to take measures to achieve all the services that citizens desire, characterized by fair geographical distribution among the districts.
Aggravating the quality of life map is that the city of Buraidah in the Al-Qassim region is a model of rapidly growing Saudi Arabian cities in both population and urban growth. The population of Buraidah city doubled about four times during 1974 to 2017, accompanied by urban expansion about 135 times during 1910 to 2019. The population density increased in the districts of the old center of the city and decreased toward the eastern, southern, and western parts of the city. The increased population led to a random distribution of services, resulting in a sharp deficiency of urban and environmental services in some areas of the city.
The results of accessibility analysis of public services in the city revealed that two districts (2.9%) are not covered by educational services, nine districts (12.9%) are not covered by health center services, 18 districts (25.7%) are not covered by government services, two districts (2.9%) are not covered by religious services, 12 districts (17.1%) are not covered by security services, 11 districts (15.7%) are not covered by recreational services, and 20 districts (28.6%) are not covered by sports services.
The results of the final suitability map to determine districts with the best standard of living according to the provided services revealed that living standards in the city are very good, as there are around 51 districts with very high and high living levels, representing 72.9% and inhabited by 449,235 people, while about 19 districts have moderate, low, and very low levels, representing 27.1% or 56,765 people. Narrowing the quality of life gap and improving spatial planning requires correcting the current deficiency in services, which is estimated in this study to be 16 services: one high school, one elementary school, one middle school, two universities, one sports service, two security services, two courts, two hospitals, one health center, one park, and two ambulance facilities.