Purification Effect of the Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment by Microbial Nanospheres with Different Material Ratios and Dosing Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Microbial Nanospheres
2.1.1. EM Active Calcium Solution
2.1.2. Nano Spheres Carriers
2.1.3. Fixation of Microbes in Nano-Carrier Spheres
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Effects of Ratio of Nanospheres Materials on Aquaculture Wastewater Purification
2.2.2. Effect of Microbial Nanospheres Dosing Methods on Removal OM in Sediment
2.2.3. In Situ Evaluation of the Sediment Bioremediation
2.3. Determination Methods
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
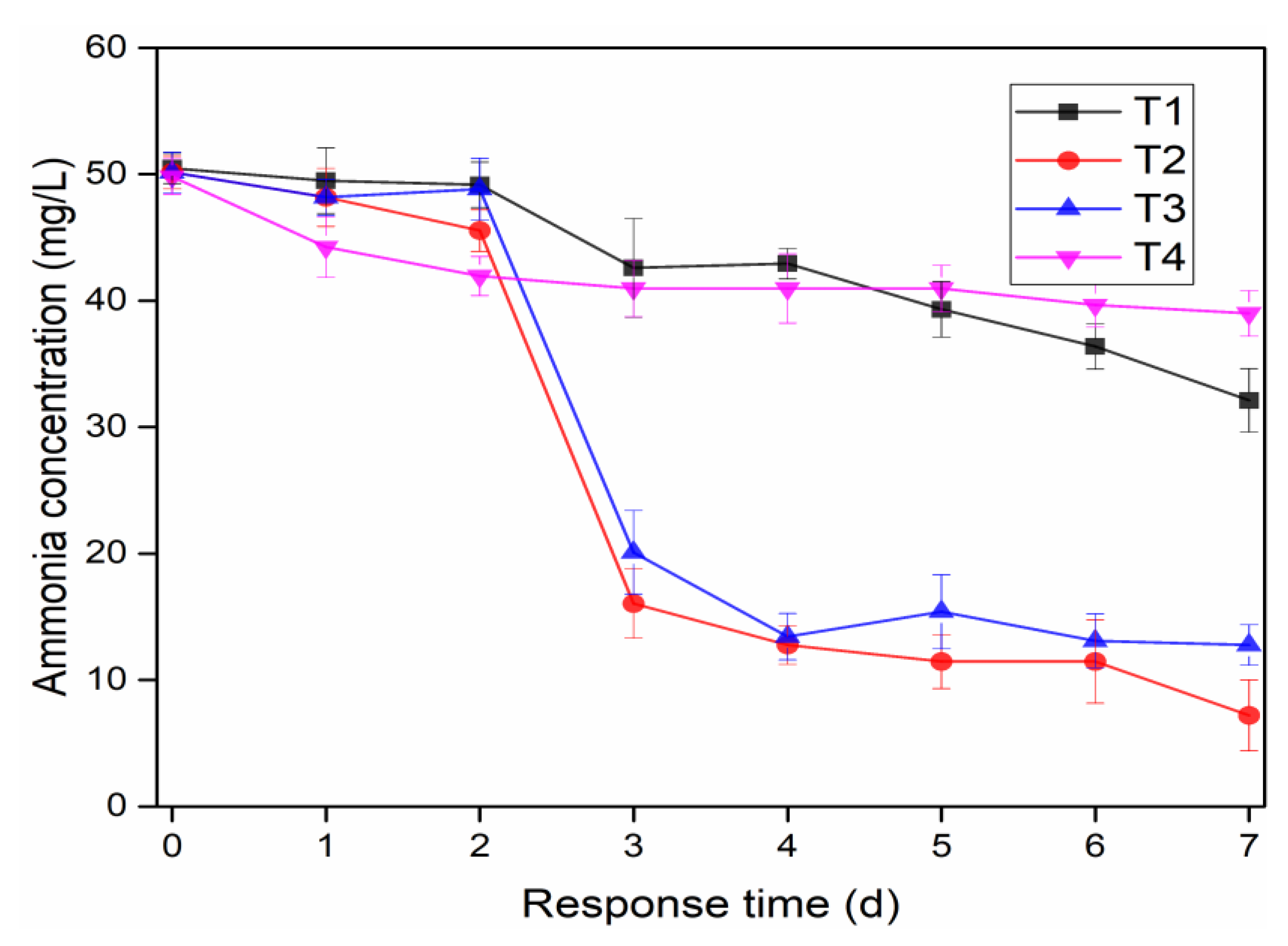
3.1. Effects of Microbial Nanospheres on NH4+-N and TN Removals
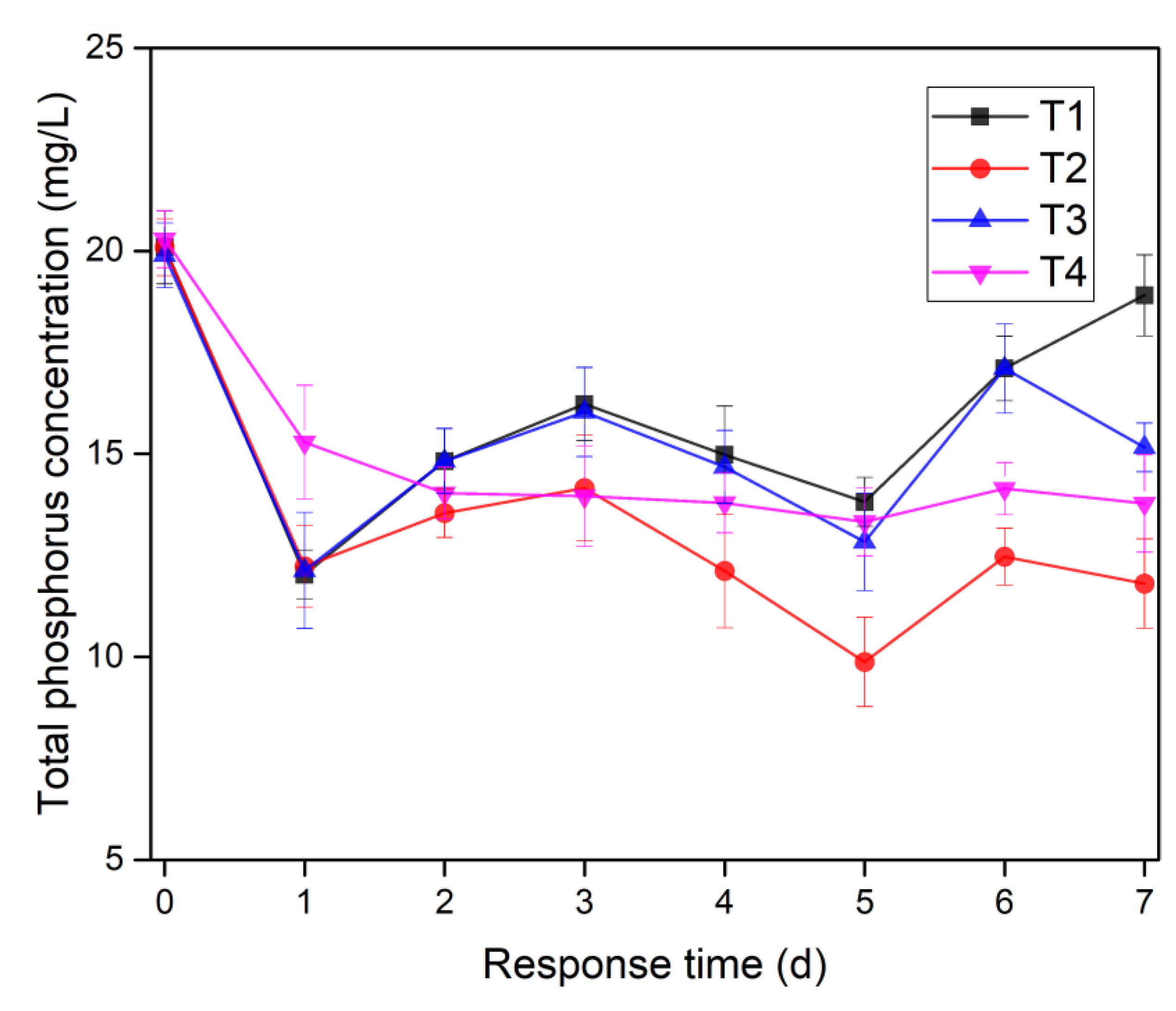
3.2. Effect of Microbial Nanospheres on the Removal of Total Phosphorus
3.3. Effect of Nanospheres With and Without Microbes on the Purification
3.4. Effects of Dosage Methods on Removal of OM in Sediment
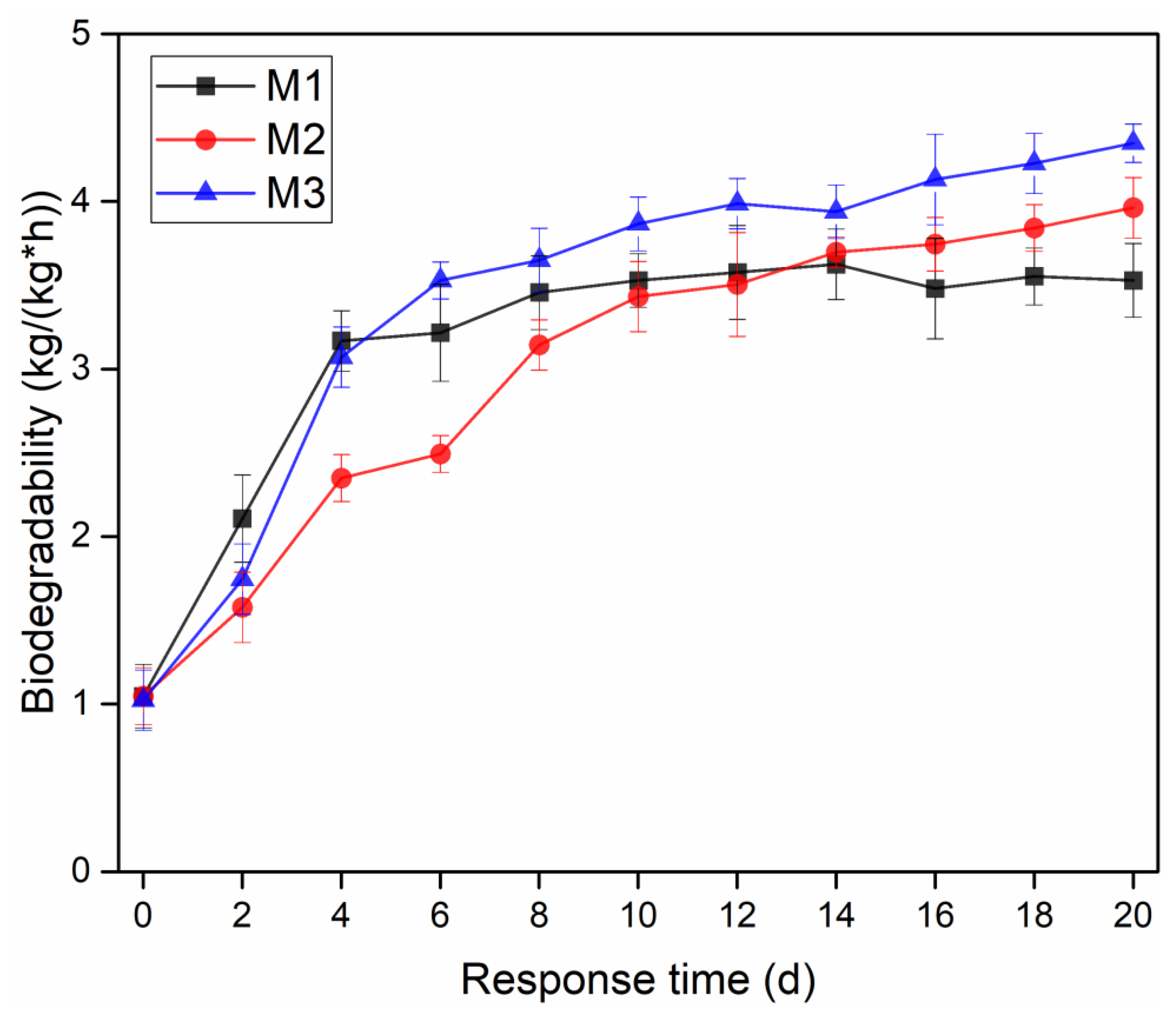
3.5. Effects of Dosage Methods on Biodegradability of Sediment
3.6. Evaluation of Sediment Bioremediation in a Practical Aquaculture Pond
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, H.; Zhu, J.Q.; Li, G. Advances in Water Purification for Pond Freshwater Aquaculture. Adv. Mater. Res. 2018, 955–959, 3928–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.U.; Fan, L.M. Pollution and Control Measures of Aquaculture Environment. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 563–587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lina, L.I.; Chen, M.; Feng, X.; Qin, C.; Tang, G.; Jing, L. Research on total phosphorus and total nitrogen emission status of main pollution sources in China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2015, 43, 416–431. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Fu, L. The recent development of advanced wastewater treatment by ozone and biological aerated filter. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8315–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Weng, Q.; Jindeng, L.U. Purification effect on water with different concentrations of TN by artificial floating bed cultivation of Ipomoea aquatica. J. Hubei Univ. 2016, 43, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y. Review of Constructed Wetland Sludge Treatment Technology. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2017, 54, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Liu, W.J.; Tong, J.; Yan, W.H.; Lu, Q.P.; Tang, J.Q. Ecological Aquaculture Analysis in a Recirculating Water Pond. Fish. Sci. 2010, 78, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.W.; Tucker, C.S.; Rutland, B.L. Performance Evaluation of Four Different Methods for Circulating Water in Commercial-Scale, Split-Pond Aquaculture Systems. Aquac. Eng. 2015, 70, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górski, R.; Kleiber, T. Effect of Effective Microorganisms (EM) on nutrient contents in substrate and development and yielding of rose (Rosa x hybrida) and gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii). Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2010, 17, 505–513. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Cheng, Z.H. Effects of different nutrient concentrations on growth and nutrient absorbance of Gerbera jamesonii growing in substrates at flower budding stage. J. Northwest A F Univ. 2013, 682, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq, A.; Abbasi, M.K.; Hussain, T. Effects of integrated use of organic and inorganic nutrient sources with effective microorganisms (EM) on seed cotton yield in Pakistan. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirwandono, E.; Sitepu, M.; Wahyuni, T.H.; Ginting, N.; Siregar, G.A.; Sembiring, I. Nutrition quality test of fermented waste vegetables by bioactivator local microorganisms (MOL) and effective microorganism (EM4). Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. 2018, 122, 012127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Obbard, J. Ammonia removal from prawn aquaculture water using immobilized nitrifying bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 57, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.F.; Ding, X.F.; Ding, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. Purification of Tail Water by Combination of EM Fungi with Terrestrial Plants. China Water Wastewater 2013, 76, 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; An, L.; Pan, B. Research on Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen from Wastewater by Frozen Immobilized Nitrifying Bacteria. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2004, 23, 1150–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Ping, H. Immobilization of Fenpropathrin Degradating-enzyme by Ca-alginate. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2006, 4, 123–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, T.; Chen, T.; Wille, M.-L.; Zou, X.; Frost, R.L.; Qing, C.; Chen, D. Preparation of iron oxide-based porous ceramsite from goethite and application for city wastewater treatment in biological aerated filters. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmei, L.I.; Pang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gouhao, L.I.; Liu, B.; Qin, Z. Investigation on the optimum preparation process conditions of nano-iron oxide and nano-silicon oxide coated sand. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lin, Z.Z.; Fan, Z.H. Effect of nanometer Al_2O_3 addition on sintering characteristics of clay ceramsite. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2016, 45, 78–100. [Google Scholar]
- Min, X.; Ran, Z.; Gong, X.; Li, C.; Dong, W.; Xia, D. Denitration and adsorption mechanism of heat-treated bamboo charcoal. J. Environ. Chem. 2017, 5, 6194–6200. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.U.; Bian, L.; Qin, G.; Qian, X.U. Investigation on Structure and Properties of PP/Nano-( Bamboo Charcoal) Composite. Plastics 2017, 12, 678–698. [Google Scholar]
- Soudejani, H.T.; Heidarpour, M.; Shayannejad, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Afyuni, M. Composts Containing Natural and Mg-Modified Zeolite: The Effect on Nitrate Leaching, Drainage Water, and Yield. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2019, 47, 1123–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shao, X.H.; Mao, J.Q.; Mao, X.Y.; Yin, C.; Tang, Z.L.; Wang, T. Preliminary Study on Purification of Aquaculture Wastewater by Microbial Nano-Silica Ball. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 955–959, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmenta Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality of Total Nitrogen Determination of the Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion of Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry; Ministry of Environmenta Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. The Determination of Water Quality of Ammonia Nitrogen Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry; Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Chen, J.; Lu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, M. Effects of overlying water aeration on phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in surface sediment. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 21, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angassa, K.; Leta, S.; Mulat, W.; Kloos, H.; Meers, E. Organic Matter and Nutrient Removal Performance of Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands Planted with Phragmite karka and Vetiveria zizanioide for Treating Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Li, K.; Jiang, D. Study on effect of polluted sediments bioremediation on water body bioremediation of polluted urban rivers. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 3, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.B.; Han-Ling, Y.E.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, Q.S. Study on technology for preparing biological bamboo charcoal and its application. Technol. Water Treat. 2008, 22, 4423–4441. [Google Scholar]
- Safwat, S.M. Performance of moving bed biofilm reactor using effective microorganisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Z.; Wei, C.; Wu, W. Nitrogen removal performance and functional genes distribution patterns in solid-phase denitrification sub-surface constructed wetland with micro aeration. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, M. Denitrifying and phosphorus accumulating mechanisms of denitrifying phosphorus accumulating organisms (DPAOs) for wastewater treatment-A review. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2015, 55, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Jia, L.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Kirumba, G. Comparison of quartz sand, anthracite, shale and biological ceramsite for adsorptive removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; Zhang, D.; Dai, L.L.; Dai, X.H. Research on Application of Microbial Carriers in an Anaerobic Digestion System. 2018, 11, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.X.; Ma, F.; Zhao, Q.L.; Li, W.G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jia, J. Removal of trace organic pollutants by immobilized microbe on biological activated carbon. J. Northeast. Norm. Univ. 2000, 32, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, L.-J.; Yun, L.-J.; Tang, F.; Zhao, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Zeng, X.; Luo, Q.-F. Removal of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Organic Pollutants From Water Using Seeding Type Immobilized Microorganisms. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Chen, T.-H.; Qing, C.; Xie, J.J.; Frost, R.L. Development and application of Palygorskite porous ceramsite in a biological aerated filter (BAF). Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.S.; Chiou, I.-J.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, D. Lightweight properties and pore structure of foamed material made from sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 19, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Tang, W. Performance of physical and chemical methods in the co-reduction of internal phosphorus and nitrogen loading from the sediment of a black odorous river. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Ren, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of metals in the sediments of Xiaoqing River, Jinan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15001–15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shao, X.; Xu, M.; Cheng, S. Bioremediation of nitrogen- and phosphorus-polluted aquaculture sediment by utilizing combined immobilized effective microorganisms and sediment aeration technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankhah, S.; Ali, A.A.; Soudi, M.R.; Gharavi, S.; Ayati, B. Highly efficient phenol degradation in a batch moving bed biofilm reactor: Benefiting from biofilm-enhancing bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Weng, Q.; Jindeng, L.U. Effects of intermittent aeration on pollutants removal in subsurface wastewater infiltration system. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ingerslev, F.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Biodegradability properties of sulfonamides in activated sludge. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 19, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lan, Q.; Lei, H.; Tao, B.; Qiang, Y.; Zhang, M. In situ biochemical technology to control black-odor of polluted sediments in tidal river. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, S665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Wu, H. Enhanced long-term organics and nitrogen removal and associated microbial community in intermittently aerated subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G.; Haines, B.L. Biodegradability of Dissolved Organic Matter in Forest Throughfall, Soil Solution, and Stream Water. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, L. Regulating Effect of Multi-stage Biological Purification on Water Quality in a Closed Recirculating Aquaculture System. Fish. Sci. 2017, 66, 488–501. [Google Scholar]
- Labatut, R.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Scott, N.R. Biochemical methane potential and biodegradability of complex organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 102, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Lv, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, W.; Wu, S. Intensified organics and nitrogen removal in the intermittent-aerated constructed wetland using a novel sludge-ceramsite as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 2% Ca2+ Liquid (mL) | EM Stock Solution (mL) | Molasses (mL) | Deionized Water (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 64 |
| Treatment | NBC Powder (%) | Zeolite Powder (%) | Pond Sediment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 5 | 15 | 80 |
| T2 | 10 | 15 | 75 |
| T3 | 15 | 15 | 70 |
| Properties | BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Average Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 38.82 | 4.2 | 6.54 | 0.32 |
| T2 | 45.01 | 4.0 | 7.32 | 0.41 |
| T3 | 46.92 | 3.6 | 7.56 | 0.42 |
| Water Quality Index | pH | NH4+-N (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 8.0 | 50.2 | 55.8 | 20.3 |
| Sampling Point | Testing Index | Time (Days) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Pond I | OM/g·kg−1 | 70.4 | 70.3 | 72.1 | 73.7 | 74.0 | 75.1 | 76.2 |
| G/kg·(kg·h)−1 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 1.21 | |
| ST/cm | 20.3 | 20.6 | 20.5 | 20.8 | 21.1 | 21.5 | 21.4 | |
| Pond II | OM/g·kg−1 | 70.6 | 68.7 | 65.1 | 64.1 | 56.8 | 55.4 | 48.2 |
| G/kg·(kg·h)−1 | 0.98 | 1.23 | 1.89 | 1.98 | 2.87 | 2.98 | 3.12 | |
| ST/cm | 20.1 | 20.0 | 19.7 | 19.2 | 17.9 | 17.0 | 16.8 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, L.; Elbashier, M.M.A. Purification Effect of the Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment by Microbial Nanospheres with Different Material Ratios and Dosing Methods. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041462
Shao Y, Zhong H, Wang L, Elbashier MMA. Purification Effect of the Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment by Microbial Nanospheres with Different Material Ratios and Dosing Methods. Sustainability. 2020; 12(4):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041462
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Yalu, Hua Zhong, Liangkai Wang, and Mohammed M.A. Elbashier. 2020. "Purification Effect of the Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment by Microbial Nanospheres with Different Material Ratios and Dosing Methods" Sustainability 12, no. 4: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041462
APA StyleShao, Y., Zhong, H., Wang, L., & Elbashier, M. M. A. (2020). Purification Effect of the Aquaculture Wastewater and Sediment by Microbial Nanospheres with Different Material Ratios and Dosing Methods. Sustainability, 12(4), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041462






