Abstract
Sustainable societies need to consider the connection between knowledge management (KM) and healthcare as a critical issue for social development. They need to investigate how to create knowledge and identify possible predictors of knowledge-sharing behavior that can support a hospital’s sustainable knowledge-management strategy. KM strategies could help managers to increase the performance of hospitals and other healthcare organizations. The purpose of this paper is to present a valid and reliable questionnaire about KM in healthcare organizations. We develop a new knowledge-management questionnaire based on the use of an extensive literature review and health professionals’ consensus. The Applied Knowledge Management Instrument (AKMI) questionnaire was pilot tested and retested on a small group of employees of healthcare organizations (n = 31). After the pilot process, a larger group of health professionals (n = 261) completed the questionnaire. Further investigation resulted in item reduction and verification of the dimensions of AKMI. Finally, we explore the psychometric properties of the developed tool. The developed questionnaire seems to be reliable, valid, and suitable to be used for studying the suggested nine dimensions of KM: perceptions of KM, intrinsic and extrinsic motivations, knowledge synthesis and sharing, cooperation, leadership, organizational culture, and barriers. The developed questionnaire can help policymakers and hospital administrators collect information about KM processes in healthcare organizations and this can result in higher performance of health organizations.
1. Introduction
Knowledge is a valuable resource for the growth of individuals and organizations. It represents a cognitive framework that makes possible the meaning and understanding of raw data and information [1] and sometimes leads to wisdom [2]. Scientists distinguish two types of knowledge, explicit and implicit [3,4,5]. Explicit knowledge can be expressed through words, numbers, or figures and represents the tip of an iceberg. Most of our knowledge is tacit, and it is hard to formulate and share. It is what Michael Polanyi [6] said: “We can know more than we can tell”.
The cornerstone of knowledge creation and transfer theory was introduced by Nonaka and Takeuchi [5] with the SECI model. Since knowledge increases with interaction, it can be articulated and amplified in various entities where individuals cooperate, like businesses and other organizations, making them sustainable [7]. In the past, scientists insisted on the personal character of knowledge. Next, many agreed that organizational culture exists, especially the heuristic knowledge that is developed by employees while working. Organizational knowledge is achievable when organizations sustain a spirit of cooperation, motivate their personnel, and encourage them to innovate, which means that they have competent management [8].
Management embraced knowledge and, around the 1990s, a contemporary business philosophy attracted the interest of executive officers, researchers, and scholars. In this way, the interest in knowledge management (KM) has grown and has been sustained. An increasing amount of digitized information is available because the decision-maker allows an organization to outperform its competitors. The complexity of modern business needs proper information to minimize errors and ensure future success [9], and the need for quality and best economic outcomes within the business strategy management framework [10].
The definition and conceptualization of knowledge management are not easily distinguished [11] mainly because of the two disjointed approaches that identify KM as technology-centered and people-centered. The first suggests that KM resembles information system management, which uses high technology to make information available and accessible at the right time for the users. The latter focuses on managing knowledge via human resource management practices [12]. The perspective of this article is human-orientated. Like other scientists, we believe that information and communication systems are tools for effective knowledge management and that attention should be focusing on the human, organizational and cultural aspects of knowledge management [13]. Healthcare organizations are examples of the balance between humans and engines. Even if the provision of health services relies on modern technologies, health professionals take the final decision for the diagnosis and treatment of the patient.
As Peter Drucker, the renowned professor, stated [14], “Hospitals are the most complex human organizations ever derived … and the fastest-growing in all developed countries”. Even medium-sized hospitals occupy hundreds of employees from various scientific fields, educational backgrounds, socioeconomic status, and occasionally different cultures. Different groups of employees often have their regulations, perspectives, requirements, and accreditation. Still, they have to interact, cooperate, share information, transform it into knowledge, and perform efficiently to provide high-quality services to the patients and their caregivers. Consequently, it is difficult to share experiences and make comparisons between healthcare settings and other types of organization, and these should be studied independently via their social context and norms.
Healthcare agencies are late adopters of KM philosophy compared to the business sector [15]. Therefore, healthcare experts have just recently started to show interest in research for evaluating the existence and quality of a knowledge environment in hospitals. In 2015, we conducted a systematic review of knowledge management practices in healthcare settings. We accessed three databases (Medline, Cinahl, and Health Source: nursing/academic edition) for 10 years (1/1/2004-25/11/2014) and retrieved 604 articles, of which 20 articles were eligible for analysis. Most of the studies had a qualitative approach, and researchers collected data through interviews with a small number of individuals or focus groups. Details about preparation, analysis, and results of our systematic review are published [16]. We confirmed that quantitative research about KM in a healthcare settings is scarce, and there is a lack of an integrated self-administered questionnaire for health professionals who work in healthcare organizations.
Academics and practitioners from other scientific fields have developed appropriate questionnaires for KM [17]. Still, to our knowledge, no one has until now introduced a reliable quantitative tool that explores KM elements in healthcare organizations.
The purpose of this study is to develop and test a questionnaire to learn more about knowledge management in healthcare settings. We aim to create a tool that could explore attitudes, emotions, cognition, intention or behavior, and identify motivators of and barriers to employees about KM.
2. Methods
2.1. Questionnaire Design
Rattray and Jones [18] claimed that researchers who design a questionnaire should use various resources, such as discussions with experts, proposals of participants, and an extensive literature review to increase the face and content validity. Before creating this questionnaire, we conducted a systematic review of the literature [16]. This review identified six critical elements of KM in healthcare settings: perceptions of KM, synthesis, dissemination, collaboration, means of KM, and leadership. Furthermore, it detected several barriers, which restrict the implementation of knowledge management practices. These findings stimulated us to attempt the development of a questionnaire, which we named the Applied Knowledge Management Instrument or AKMI. The word “AKMI” is similar to the English word acme, which has a Greek origin and means the highest point or peak. We chose this name to stress that effective knowledge management could lead hospitals and other healthcare units to top performance.
2.2. Ethical Issues
The study protocol received approval by the scientific and the border committee of the General Hospital of Messinia, Greece. We composed a letter stating that the completion of the questionnaire is voluntary, and that we will protect the privacy of human subjects while collecting, analyzing, and reporting data by anonymity [19]. Furthermore, we clearly announced the purpose of the study, the significance of the contribution of each employee, and that the completion of the questionnaire will have a positive impact on the hospital and science in general [20]. A cover letter stated a brief definition of KM to clarify the term for those who were not familiar with it. In this way, we motivated potential participants to complete the questionnaire.
2.3. Research Tool
2.3.1. Selection of the Factors
We selected the following factors of knowledge management for healthcare settings for analysis: perceptions about KM, intrinsic motives, extrinsic motives, knowledge synthesis, dissemination, cooperation, leadership, culture, and barriers. The items of the factors consisted of closed-ended statements, and participants completed AKMI by reporting their level of agreement on a five-point Likert scale. The first statement, for example, is, “Each hospital should implement KM politics.” There is only one open-ended question, which asks, “In your opinions, which are the three most important barriers of knowledge management,” to identify KM obstacles. Furthermore, the questionnaire had questions for job satisfaction, self-efficacy, and state anxiety, and six items for demographics. These questions were the last to diminish the possibility of drop-outs [18].
2.3.2. Perceptions about Knowledge Management (KM)
The theory of reasoned action assumes that there is a relationship between attitudes and volitional behavior [21]. As a result, a positive attitude or perception towards KM could lead to action like knowledge creation or sharing. Chang et al. [22] claimed that better comprehension of KM improves employees’ performance at hospitals. Another study revealed that a positive attitude for KM could give a competitive advantage and can increase innovation [23]. Another supposition is the existence or absence of a correlation between positive perceptions about KM and self-efficacy, as it appears in a sample of librarians in Israel [17]. This factor consists of five items.
2.3.3. Motives
Motives activate individuals to fulfill their needs [24]. If the reward from a specific action is endogenous (e.g., feeling of satisfaction), the motivation is intrinsic, and if it is exogenous (e.g., financial compensation), the motive is extrinsic [25]. The exploration of the motivations that drive employees to knowledge creation and sharing is one of the main goals of our study. Two factors are needed to represent motives; one for the intrinsic features and one for the extrinsic characteristics. Each latent factor consists of four items.
At the intrinsic motives, the person draws satisfaction from other external rewards, like the challenge of completing a difficult task. It is hard but possible for managers to handle intrinsic motives [26]. Comprehension of human behavior could help managers. For instance, people seek purposes to fulfill their life, and a shared goal promotes collaborative relationships. On the contrary, the lack of use places a psychological burden on employees [27]. Intrinsic motives for participating in KM procedures could be the satisfaction of having and transmitting knowledge, and the joy of helping others [28].
The reinforcement theory suggests that individuals are motivated when their behavior is reinforced positively (with rewards) or negatively (with the reduction or removal of positive rewards) [29]. The theory has received some criticism, but tangible rewards are significant motivators for other methods as well [25]. Recorded extrinsic motives for KM are personal, professional, and financial rewards for participating in KM procedure, work safety and stability, and other ways of individual support. Effects of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation on employees’ knowledge-sharing intentions were examined in Taiwan, using structural equation modeling. The sample was 172 employees of a big group of firms [30]. A comparison of these results with participants from a Greek public hospital could be rather interesting.
2.3.4. Knowledge Synthesis
Knowledge synthesis is a fundamental element of KM [31] and healthcare settings [14]. Results showed many ways of creating knowledge, such as interactions of colleagues [32], formal and informal meetings [33], and recorded evidence [34]. The synthesis will attempt to clarify which groups of employees are more involved in the process and whether it connects strongly with other factors like perceptions, culture [35], or leadership [36], in different environments besides hospitals.
2.3.5. Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration
Knowledge sharing through collaboration is fundamental for KM because it can be carried out by all employees, regardless of their ability to create knowledge. Next, we will examine whether this factor (using five items) relates to various motives. Furthermore, we will test if knowledge sharing correlates with personal and demographic characteristics [37]. The “openness” to cooperation will also be examined [38] with four items, as stated in the case that collaboration among different groups of health professionals increases the likelihood of innovation [39]. Pezeshki Rad et al. [40] designed a questionnaire for knowledge sharing at the Iranian Ministry of Agriculture that had some interesting questions, which we modified and adopted for this factor.
2.3.6. Leadership
Leaders have a significant impact on businesses and organizations. They are expected to ease access to information, encourage innovation, and empower employees to implement KM practices [41]. The way they act is fundamental to the success of knowledge sharing [42]. They should build a culture of knowledge [43], reinforce continuous learning, and create communication channels [22]. Leaders have the power to provide support and rewards [43]. Factor “leadership,” which consists of three items, will be tested for correlations with culture, extrinsic motives, and self-efficacy, to clarify its impact on KM.
2.3.7. Culture
Knowledge culture represents the factor with the most items (nine items). Here, it is examined if a healthcare setting supports innovation, research, and cultivates a learning environment. Organizational culture is a broad term that refers to ideologies, practices, norms, and social behaviors. It gives integration and differentiation opportunities [44]. Sibbald et al. [45] found that leadership and organizational culture are instrumental in supporting knowledge management procedures in hospitals. We will also examine the relationship between corporate culture and perceptions of employees about KM.
2.3.8. Barriers
Even if administrators and employees might have the best intentions to create and share knowledge, there are often obstacles complicating their efforts. Most studies exploring the subject have a qualitative orientation [46,47,48]. Likewise, we chose an open-ended question of AKMI to reveal more barriers to implementing KM in hospitals. Still, we also entered three items for the quantitative part of the scale.
2.4. Pilot Study
We initially developed a pilot questionnaire of 38 questions. Then, we asked the opinion of three experts from the Hospital. The first expert was a medical doctor, who was the manager of a public Health Center, and responsible for the continuous education of physicians who undertake their internship. The second expert was the administrative manager of a General Hospital, an expert in Hospital Administration. The third expert was a registered nurse with a Master’s degree in special education [49]. After the discussions, the number of questions increased to 64.
The extensive questionnaire of the 64 questions was pilot tested in a sample of 31 employees (physicians, nurses, midwives, health visitors, and administrative staff) who work at two public health centers and a public Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Center. The participants (24 females and 7 males) had a mean of 19.82 years of working experience (SD 7.99) and a mean age of 45.42 (SD 6.72) years.
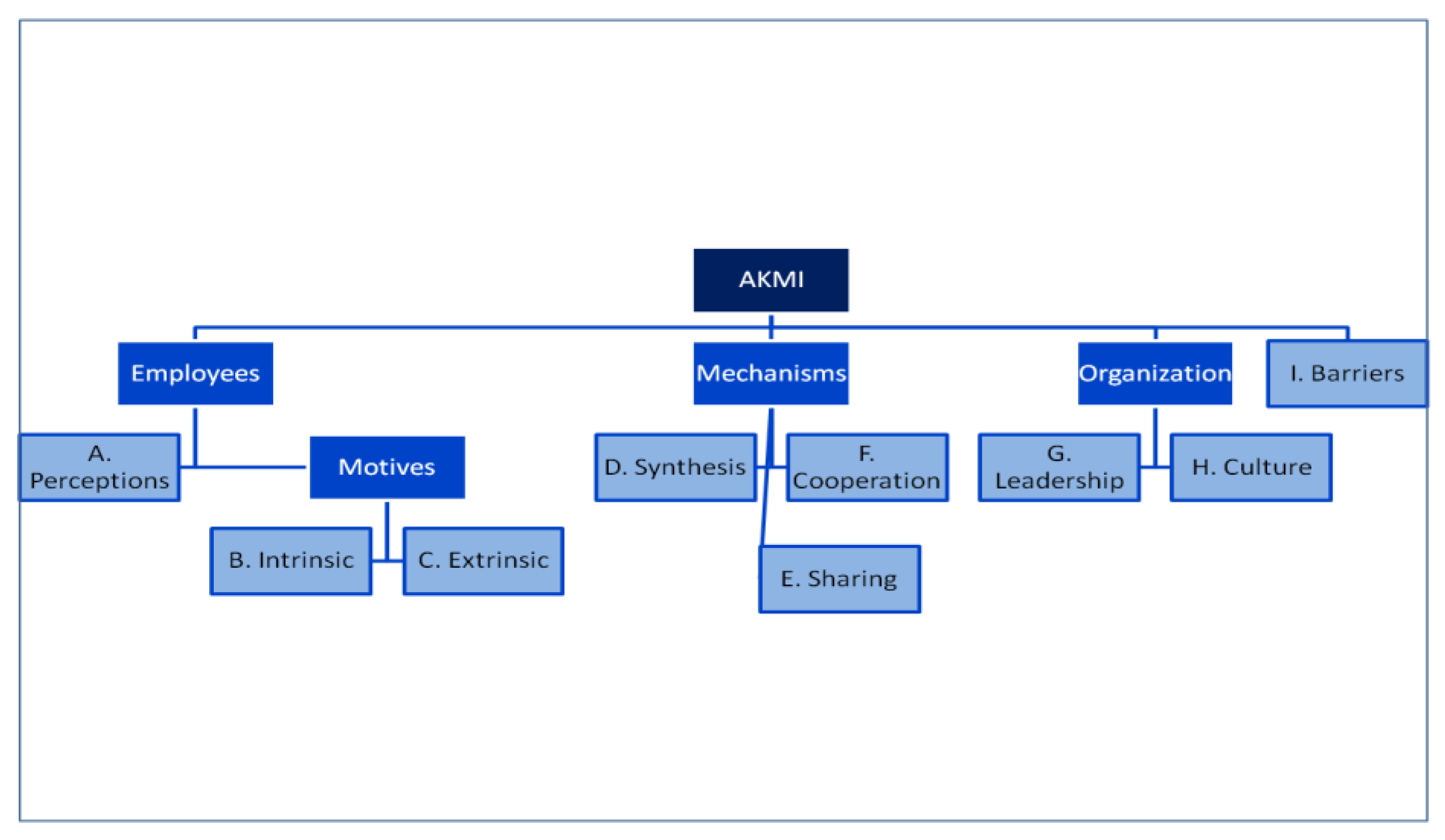
The questionnaire was completed for a second time 15 days later by the same group of people. Test-retest was measured with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC, two-way mixed model on absolute agreement) [50] for all the questions except the demographics. The results of ICC are interpreted according to the scores as follows: <0.40 poor, 0.40–0.49 adequate, 0.60–0.74 good, 0.75–1.00 excellent [51]. The ICC of our study was excellent (ICC average measures: mean 0.904, min 0.717, max 1.000). For the questions answered by the Likert scale, we measured Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient wıth mean value equals to 0.905 [52]. Figure 1 shows the dimensions of AKMI.
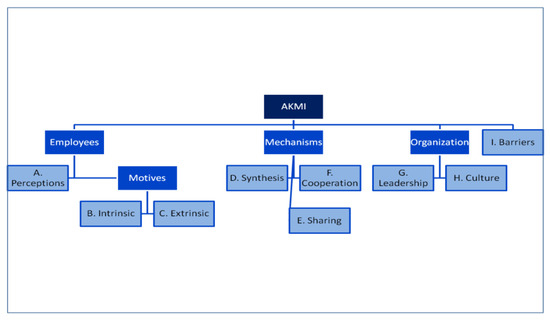
Figure 1.
The architecture of Applied Knowledge Management Instrument (AKMI).
2.5. Data Analysis
Data were collected and entered on Microsoft Excel and analyzed with SPSS v22 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA). Missing values were less than 3.2% for each item (overall missing values less than 4‰). We conducted Little’s MCAR test, which indicated that values were missing completely at random. Therefore no entry was excluded from the analysis, and missing values were not replaced because sometimes imputation techniques for handling missing data result in biased estimates [53,54]. Reverse coding questions were recoded into different variables before further analysis.
To test whether data were appropriate for factor analysis, we measured the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) coefficient (KMO = 0.696). Furthermore, we carried out Barlett’s test of sphericity, which showed a significant p-value <0.001. Both tests indicated that the dataset was suitable for factor analysis [55]. Furthermore, the sample size of the dataset was larger than 250, which is a prerequisite for obtaining reliable results [56].
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
This study took place from February to June of 2015 at General Hospital of Kalamata, which is a medium-sized public hospital with 300 beds, and the biggest (out of two) from a rural area of 200,000 inhabitants in Messinia, Greece. In 2015, the hospital had approximately 700 employees, of which 30% were males and 70% females. We asked 300 employees to participate in the study, and 261 employees agreed and completed the questionnaire (87% response rate). Even if there is no rule of thumb for the ideal sample size for testing a newly developed scale, a sample size of more than 200 people is acceptable [57].
Demographics of participants as regards gender, age, professional status, and working experience resembled the rest of the employees, who did not participate (Table 1). The completion time was 10–15 minutes.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the 261-employee sample.
3.2. Validity
Face validity is a measure for the suitability of the project. It concerns the appropriateness, sensibility, or relevance of a test and its items and evaluates how it appears to the people who undertake it. Even if face validity seems an ambiguous term, it is essential for the success of a test or scale [58]. Many participants reported that our questionnaire was exciting and comprehensive. Additionally, they realized how effective knowledge management is and stated that they could participate more in knowledge sharing in the future. Content validity is a characteristic associated with the scale’s adequacy for the measurement of the concept under consideration. It can only be checked subjectively through its approval by connoisseurs [59]. Our questionnaire was a subject of extended discussions at the pilot phase with three experienced health professionals with various educational and professional backgrounds, to ensure content validity. Additionally, we performed a factor analysis to establish construct validity [60].
3.3. Exploratory Factor Analysis
We conducted factor analysis, with extract method Alpha factoring, which resulted in 19 components with an eigenvalue greater than 1.0 that explained 52.8% of the variance. Due to low scoring, we removed a group of questions regarding “facilities” and nine more items. Most of the single items we excluded were reverse coded, and that means that they confused the participants. Following principal component factoring and varimax rotation, we repeated the analysis with a forced nine-factor solution. This time, the solution explained 56.87% of the variance. Table 2 illustrates results from factor analysis.

Table 2.
Exploratory factor analysis of the knowledge-management (KM) dimensions.
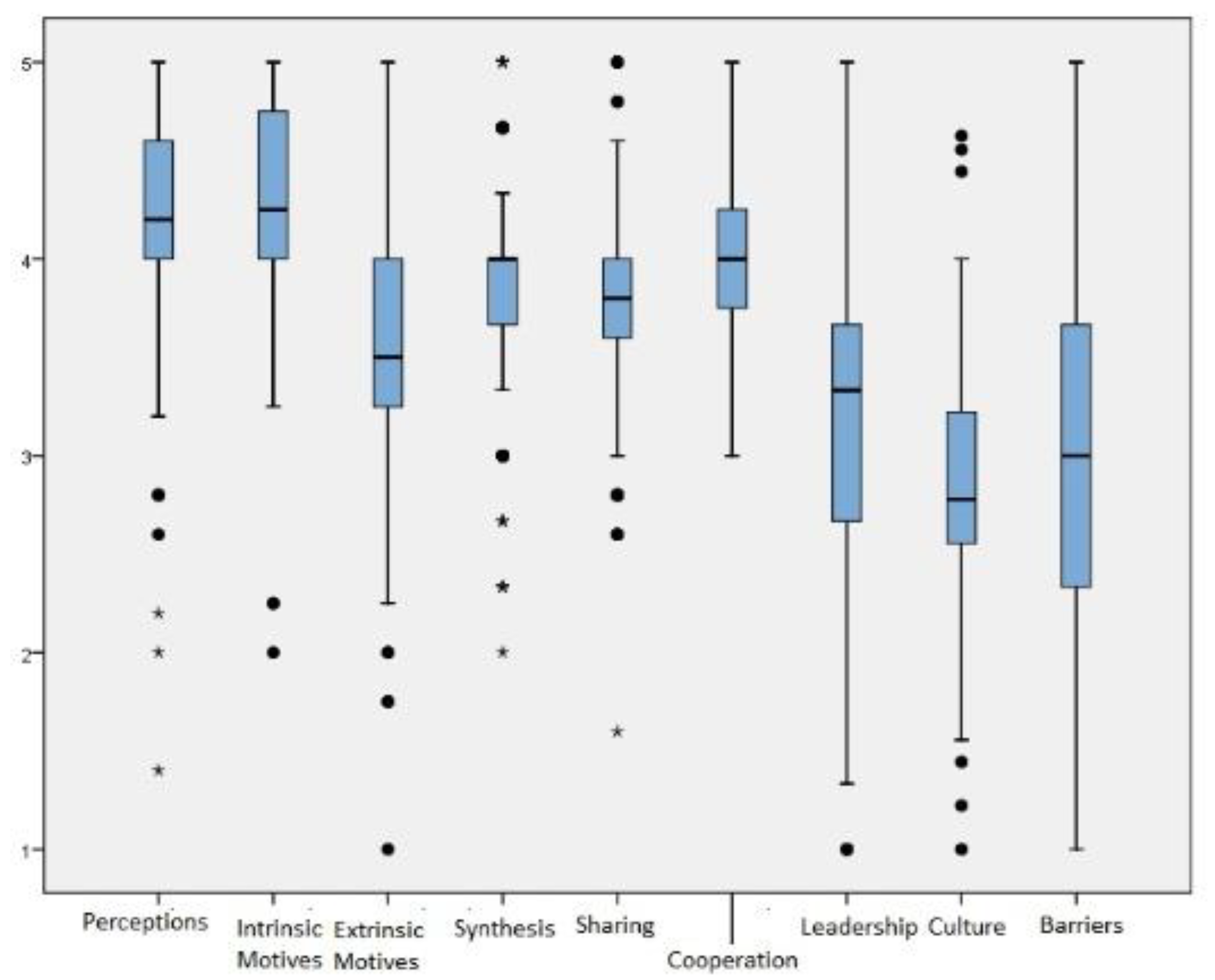
The estimate for the internal consistency of the entire questionnaire (Cronbach’s alpha) was 0.802. Each dimension had the following Cronbach’s α: perceptions—0.724, intrinsic motivation—0.626, extrinsic motivation—0.739, knowledge synthesis—0.652, knowledge sharing—0.570, cooperation—0.567, leadership—0.717, culture—0.821, barriers—0.664. Median, interquartile range, and outliers of the results from the nine dimensions of AKMI are presented in Figure 2, and the final version of AKMI with preliminary results is shown in Table 3.
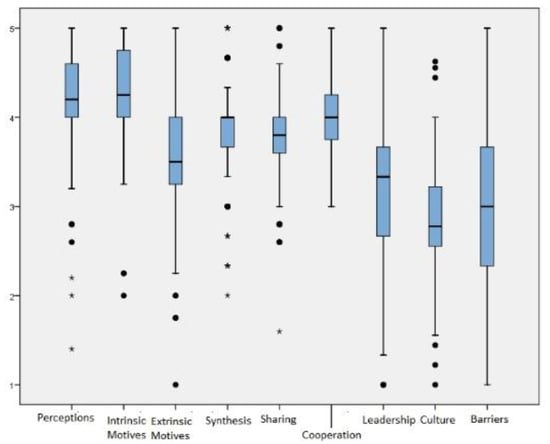
Figure 2.
Boxplots of the nine dimensions.

Table 3.
The final version of the Applied Knowledge Management Instrument.
We further estimated the polychoric inter-correlations among the AKMI subscales and reported significant correlations between factors. Table 4 shows the estimated polychronic intercorrelations.

Table 4.
Polychronic inter-correlations between factors.
4. Discussion
This research aimed to develop a questionnaire to understand the concepts of knowledge management and to investigate the organizational factors that affect all aspects of the knowledge creation process within hospitals.
Knowledge management is related to sustainability, organizational learning, knowledge transfer, quality of care and safety, type of motivations, and barriers, all of which will affect the level of service.
4.1. Knowledge Management and Sustainability
The application of knowledge management can lead to a sustainable healthcare system, and leaders can achieve the goals of their organizations [61]. It is important to note that the knowledge management process can be significantly related to improvements in the quality of healthcare as well as the organizational-level of social and economic outcomes, as stated by Popa [10,62]. Doctors may process the information related to the healthcare industry, and based on their experience and knowledge, can improve the quality of the system and the management of their patients. Moreover, patients can increase their knowledge from various sources like the internet, social media, and other medical staff. In this way, patients can determine or change their behavior and thoughts and demand the best possible service. The optimal management of the knowledge process affects the quality of a system.
Social stainability issues in healthcare facilities is another aspect which is explained by [63,64]. An organization with collaboration can apply knowledge management to share information to make healthcare organizations sustainable.
4.2. Knowledge Management and Human Resources
Knowledge is also regarded as organizational culture, skills, reputation, intuition, and codified theory that influences human behavior and thoughts [65,66]. There is also a concern about the current and future status of human resources management in healthcare organizations [67] and the impact of human resources information systems technology. Each organization will need to use HR practices that will balance evidence from data, its objectives, individual factors, and Human Resources Information systems. Organizations are becoming increasingly aware of the importance of employees in gaining and maintaining competitive advantage.
The competitiveness of a healthcare organization depends on the effectiveness of its knowledge management [62], and the knowledge-sharing process helps sustainable engagement in healthcare.
4.3. Knowledge Management and Organisational Learning
With knowledge management, healthcare leaders can understand how collective learning enhances the quality and safety improvement of hospitals. Organizations can support the process of internal learning if the goal is the improvement of their services. External knowledge acquisition often occurs through processes involving people. Knowledge management can help to reduce errors. For example, effective control is achieved using a clinical decision-support system. As a result, the potential reduction of medical errors can affect the improvement of healthcare delivery.
For example, research suggests that collective learning plays a role in improvement [68]. Specifically, cooperative learning is the process of gaining information which helps the capabilities in groups and organizations. Another process is collective learning, which has to do with the understanding and skills in groups and organizations [68,69]. Collective learning differs from individual learning because it requires individuals to analyze and interpret organizational experience [68].
The implementation of knowledge management can be thought of in two different ways [70,71]. The first is that there is a possibility that knowledge management to increase the autonomy of the medical staff by enhancing knowledge access. Knowledge sharing can lead to knowledge creation. On the other hand, controlling activities of the team can decrease collective intelligence. The excess of autonomy can encourage individuals to destabilize the organization, and there is a chance for them to act against the interests of the organization.
4.4. Knowledge Management and the Developed Questionnaire
Scientific interest in the various aspects of knowledge management can allow the connection of past results and the creation of knowledge. The findings and their implications should be addressed in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted. Perceptions of knowledge management were examined for another group of professionals, such as librarians in India [72] and other sectors, like construction and design companies in Spain [73]. Comparisons have been made between the perceptions of employees about knowledge management from small and large organizations in the United Kingdom [74]. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations of KM were explored by researchers from various scientific fields [30,75]. There is still a debate in this field if external rewards can be considered as drivers for knowledge sharing, and our questionnaire aspires to clarify this issue. Knowledge creation, sharing, and cooperation are amongst the most researched topics in this area. However, in the healthcare sector, the focuses were mainly qualitatively analyzed [16], even if there are a small number of surveys, e.g., [37]. As regards leadership, studies have indicated individual styles of leadership to be significantly associated with the art of KM practices [76]. Zheng et al. [77] suggest that KM fully mediates the impact of organizational culture, and Leidner et al. [78] claim that organizational culture influences knowledge management initiatives. Based on these findings, we will subsequently create a model to determine the correlation structure of KM dimensions using a structural equation modeling procedure.
We think that self-efficacy plays an essential role in knowledge sharing. Until now, self-efficacy is mainly correlated with computer skills and knowledge-management systems [79] and less with occupational self-efficacy. With our dataset, we could check for significant connections between occupational self-efficacy and intentions to create or share knowledge.
The barriers of knowledge management procedure will be studied using the information we have collected with a closed and open-ended question. We asked health professionals to name the three most essential barriers according to their experience about the implementation of knowledge management in their organizations. The rationale of the task is to reveal existing barriers, especially in their working environment, and understand the correlations of barriers with the rest of the dimensions of the set-up questionnaire, e.g., leadership, and organizational culture.
The main advantage for the use of a specific knowledge-management instrument for healthcare units concerning a standard KM questionnaire is that the former takes into account the sui generis nature of the healthcare environment and the particular type of working relationships among health professionals. Additionally, the design of AKMI was done cautiously, with carefully examined methodological steps of an exhaustive literature review, pilot testing and retesting extended discussions with health professionals, and item reduction with factor analysis according to the main findings. The completion time was acceptable, and the dropouts were practically non-existent. Finally, participants spontaneously expressed their content after completed the questionnaire by stating that “this was their first step to actively participating in the knowledge-management process.”
In terms of limitations, there are some caveats about specific dimensions of the questionnaire due to a just fair Cronbach’s alpha score. Furthermore, our study does not permit premature generalization of the results obtained.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this paper describes the process of development and validation of a questionnaire with nine dimensions of knowledge management in healthcare organizations, perceptions of knowledge management, intrinsic and extrinsic motives, knowledge creation and sharing, cooperation, leadership, culture, and barriers. The introduction with AKMI makes a novel contribution to the study of KM in the area of healthcare organizations, adopting a social orientation at which employees and managers are the protagonists for successful KM in contrast to systems and sophisticated structures. Thus, AKMI has theoretical and practical implications. Universities may use the scale to explore knowledge management as a social process, at which people are the drivers of knowledge, smoothing the transitions from academia to practice. Similarly, it is useful to managers who need to know how they could motivate their personnel to engage in knowledge creation and sharing in an unimpeded way, in a working environment where innovation is supported.
Hospitals, as part of their operations, need to use knowledge-management systems to facilitate their operations’ sustainably. Learning is an essential process, which is related to knowledge management [80]. The knowledge-creation process can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage process. However, few studies have empirically investigated how individual characteristics and organizational work practices influence knowledge sharing [81]. The knowledge creation process is vital for sustainability [82], and social media have an impact on this process [83]. Knowledge management enablers such as organizational structure, information technology (IT), strategy, and culture can be essential factors for the sustainability process of any healthcare organization. Different categories of healthcare employees have their role within sustainable operations, and human resources managers are encouraged to recruit people with the right qualifications to apply knowledge management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.K. and M.A.T.; methodology, F.K. and M.A.T.; software, I.K. and F.K.; data curation I.K. and F.K., I.K.; writing—original draft preparation, I.K.; writing—review and editing, M.A.T.; supervision, M.A.T.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the participants of the survey.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zins, C. Conceptual approaches for defining data, information, and knowledge. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2007, 58, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackoff, R.L. From Data to Wisdom. J. Appl. Syst. Anal. 1989, 16, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.A. The role of tacit and explicit knowledge in the workplace. J. Knowl. Manag. 2001, 5, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, H. Tacit and Explicit Knowledge; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Polanyi, M. The Tacit Dimension; Anchor Books: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Sanguankaew, P.; Vathanophas Ractham, V. Bibliometric review of research on knowledge management and sustainability, 1994–2018. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukas, H.; Vladimirou, E. What is organizational knowledge? J. Manag. Stud. 2001, 38, 973–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, J. Knowledge management in health care. J. Health Care Financ. 2005, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, I.; Ștefan, S.C. Modeling the Pathways of Knowledge Management Towards Social and Economic Outcomes of Health Organizations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begoña Lloria, M. A review of the main approaches to knowledge management. Knowl. Manag. Res. Pract. 2008, 6, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hislop, D. Knowledge Management in Organizations: A Critical Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Šajeva, S. The analysis of key elements of socio-technical knowledge management system. Econ. Manag. 2010, 15, 765–774. [Google Scholar]
- Drucker, P. Managing in the Next Society; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kothari, A.; Hovanec, N.; Hastie, R.; Sibbald, S. Lessons from the business sector for successful knowledge management in health care: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2011, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitri, I.; Talias, M.A.; Bellali, T. Knowledge management practices in healthcare settings: A systematic review. Int. J. Health Plann. Manag. 2017, 32, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharony, N. Librarians’ Attitudes toward Knowledge Management. Coll. Res. Libr. 2011, 72, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray, J.; Jones, M.C. Essential elements of questionnaire design and development. J. Clin. Nurs. 2007, 16, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissett, A.F. Designing a questionnaire. Send a personal covering letter. BMJ 1994, 308, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.; Bonetti, D.; Clarkson, J.; Ramsay, C. Improving trial questionnaire response rates using behaviour change theory. Trials 2015, 16, P92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, I.; Ajzen, I. Belief, Attitude, Intention and Behaviour: An Introduction to Theory and Research; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Hsu, P.-F.; Li, M.-H.; Chang, C.-C. Performance evaluation of knowledge management among hospital employees. Int. J. Health Care Qual. Assur. 2011, 24, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, A.; Dube, T.; Rensleigh, C. Knowledge management awareness in a research and development facility: Investigating employee perceptions. S. Afr. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslow, A.H. A theory of human motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1943, 50, 370–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, S.B.; Shanks, N.H. Introduction to Health Care Management, 2nd ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Denver, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, J. Impact of total quality management on corporate sustainability through the mediating effect of knowledge management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.W. Intrinsic Motivation at Work: What Really Drives Employee Engagement; Berrett-Koehler Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bednarczyk, T.K. Human resources and motivation in knowledge management. Manag. Prod. Eng. Rev. 2010, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, B.F. Science and Human Behavior; New Impression edition; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-F. Effects of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation on employee knowledge sharing intentions. J. Inf. Sci. 2007, 33, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colnar, S.; Dimovski, V.; Bogataj, D. Knowledge Management and the Sustainable Development of Social Work. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Scott, J.E. Comparing knowledge management in health-care and technical support organizations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzano, A.J.; Ohman-Strickland, P.A.; Patel, M. What can family medicine practices do to facilitate knowledge management? Health Care Manag. Rev. 2008, 33, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrish, K.; McDonnell, A.; Nolan, M.; Guillaume, L.; Kirshbaum, M.; Tod, A. The role of advanced practice nurses in knowledge brokering as a means of promoting evidence-based practice among clinical nurses. J. Adv. Nurs. 2011, 67, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auernhammer, J.; Hall, H. Organizational culture in knowledge creation, creativity and innovation: Towards the Freiraum model. J. Inf. Sci. 2013, 40, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M. Effect of Leadership Behaviors on Knowledge Creation in Indian Organizations. Delhi Bus. Rev. 2013, 14, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Hong, S.A. Factors affecting hospital employees‘ knowledge sharing intention and behavior, and innovation behavior. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2014, 5, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nembhard, I.M. All teach, all learn, all improve?: The role of interorganizational learning in quality improvement collaboratives. Health Care Manag. Rev. 2012, 37, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.M. Integration of health and social care: A case of learning and knowledge management. Health Soc. Care Community 2012, 20, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki rad, G.; Alizadeh, N.; Zamani Miandashti, N.; Shabanali Fami, H. factors influencing knowledge sharing among personnel of agricultural extension and education organization in iranian ministry of jihad-e agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 13, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Mohamed, S. Leadership behaviors, organizational culture and knowledge management practices: An empirical investigation. J. Manag. Dev. 2011, 30, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-C.; Cheng, K.-L.; Chao, M.; Tseng, H.-M. Team innovation climate and knowledge sharing among healthcare managers: Mediating effects of altruistic intentions. Chang. Gung Med. J. 2012, 35, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.T.; Cegarra-Navarro, J.G. Implementing Knowledge Management Practices in Hospital-in-the-Home Units. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2008, 23, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Kayworth, T.R.; Leidner, D.E. An Empirical Examination of the Influence of Organizational Culture on Knowledge Management Practices. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2005, 22, 191–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbald, S.L.; Wathen, C.N.; Kothari, A. An empirically based model for knowledge management in health care organizations. Health Care Manag. Rev. 2016, 41, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, J.; Shurong, T.; Ahmad, N.; Waheed, A.; Khan, S. Barriers to knowledge management in the health sector of Pakistan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbins, M.; DeCorby, K.; Twiddy, T. A knowledge transfer strategy for public health decision makers. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. 2004, 1, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tan, B.; Chang, S. An exploratory model of knowledge flow barriers within healthcare organizations. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, C.A. Questionnaire construction and question writing for research in medical education. Med. Educ. 1988, 22, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donders, A.R.T.; van der Heijden, G.J.M.G.; Stijnen, T.; Moons, K.G.M. Review: A gentle introduction to imputation of missing values. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, A.; Ernstmann, N.; Ommen, O.; Wirtz, M.; Manser, T.; Pfeiffer, Y.; Pfaff, H. Psychometric properties of the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture for hospital management (HSOPS_M). Bmc Health Serv. Res. 2011, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacCallum, R.C.; Widaman, K.F.; Zhang, S.; Hong, S. Sample size in factor analysis. Psychol. Methods 1999, 4, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L.; Kottner, J. Recommendations for reporting the results of studies of instrument and scale development and testing. J. Adv. Nurs. 2014, 70, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, I.B.; Craighead, W.E. The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gotzamani Katerina, D. An empirical study of the ISO 9000 standards’ contribution towards total quality management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2001, 21, 1326–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, W.; Freidel, K.; Schucher, B.; Baumann, H.; Wiebel, M.; Matthys, H.; Petermann, F. The Severe Respiratory Insufficiency (SRI) Questionnaire: A specific measure of health-related quality of life in patients receiving home mechanical ventilation. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2003, 56, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, J.; Shurong, T.; Ahmad, N.; Afridi, S.; Khan, S.; Mahmood, K. Promoting healthcare sustainability in developing countries: Analysis of knowledge management drivers in public and private hospitals of Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, S.C.; Popa, I.; Dobrin, C.O. Towards a model of sustainable competitiveness of health organizations. Sustainability 2016, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, A.; Marić, J. Towards Socially sustainable Healthcare Facilities – the Role of Evidence-based Design in Regeneration of Existing Hospitals in Serbia. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolongo, S.; Gola, M.; Di Noia, M.; Nickolova, M.; Nachiero, D.; Rebecchi, A.; Settimo, G.; Vittori, G.; Buffoli, M. Social sustainability in healthcare facilities: A rating tool for analysing and improving social aspects in environments of care. Annali Dell’Istituto Superiore Sanita 2016, 52, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.; Andriani, P. Managing knowledge associated with innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2003, 56, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.M.; Elrehail, H.; Alatailat, M.A.; Elçi, A. Knowledge management, decision-making style and organizational performance. J. Innov. Knowl. 2019, 4, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursunbayeva, A. Human resource technology disruptions and their implications for human resources management in healthcare organizations. Bmc Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, S.; Benzer, J.; Hamdan, S. Improving health care quality and safety: The role of collective learning. J. Healthc. Leadersh. 2015, 7, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, B.; March, J.G. Organizational Learning. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 1988, 14, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, C.; Dudezert, A. Knowledge management systems, Autonomy and control: How to regulate? A case-study in an industrial company. In Materiality, Rules and Regulation; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2015; pp. 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, M.; Tian, A.W.; Soo, C.; Zhang, B.; Ho, K.S.B.; Hosszu, K. Different motivations for knowledge sharing and hiding: The role of motivating work design. J. Organ. Behav. 2019, 40, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, P.D.; Du Toit, A.S.A. Perceptions on the use of a corporate business incubator to enhance knowledge management at Eskom. S. Afr. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2013, 10, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Forcada, N.; Fuertes, A.; Gangolells, M.; Casals, M.; Macarulla, M. Knowledge management perceptions in construction and design companies. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, R. SME and large organisation perceptions of knowledge management: Comparisons and contrasts. J. Knowl. Manag. 2001, 5, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, M. How Do Rewards and Management Styles Influence the Motivation to Share Knowledge? 2008. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1098881 (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- Singh Sanjay, K. Role of leadership in knowledge management: A study. J. Knowl. Manag. 2008, 12, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yang, B.; McLean, G.N. Linking organizational culture, structure, strategy, and organizational effectiveness: Mediating role of knowledge management. J. Bus. Res. 2010, 63, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorothy, L.; Maryam, A.; Timothy, K. The Role of Culture in Knowledge Management: A Case Study of Two Global Firms. Int. J. E-Collab. 2006, 2, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y. How reward, computer self-efficacy, and perceived power security affect knowledge management systems success: An empirical investigation in high-tech companies. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, A.S.; Linderman, K.W.; Schroeder, R.G. Method and psychological effects on learning behaviors and knowledge creation in quality improvement projects. Manag. Sci. 2007, 53, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, F.; Kamariotou, M.; Talias, M.A. Corporate Sustainability Strategies and Decision Support Methods: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, C.; Wu, Y.J. Knowledge creation process and sustainable competitive advantage: The role of technological innovation capabilities. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, F.; Jaafar Noor, I.; Ainin, S. Social media’s impact on organizational performance and entrepreneurial orientation in organizations. Manag. Decis. 2016, 54, 2208–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).