Desertification Control Practices in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Sand Transportation Flux
2.3. Methodological Framework
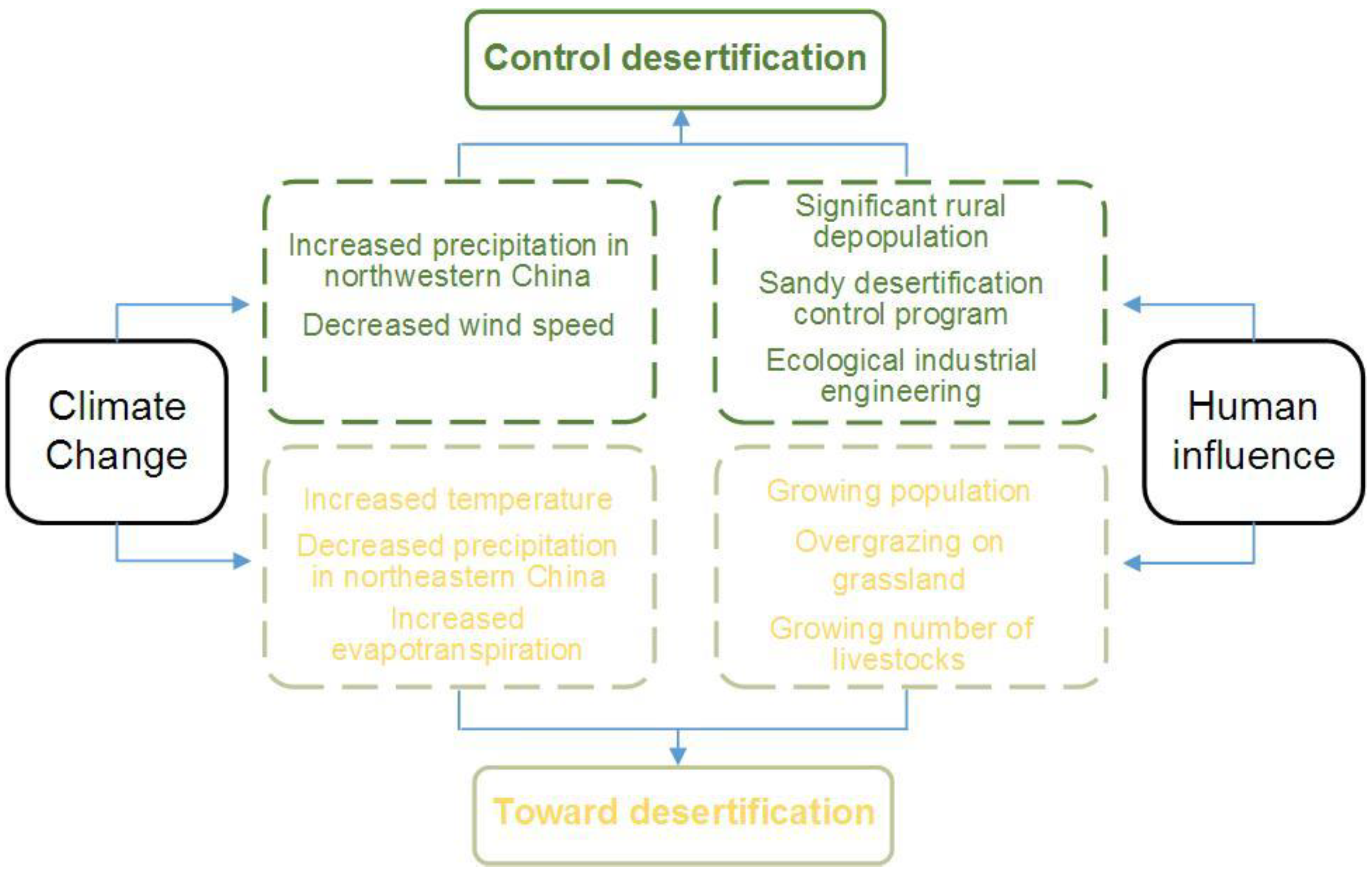
3. Drying and Warming Trends in Desertified Areas
3.1. Differences in the Rainfall between Northeastern and Northwestern China
3.2. Northern China’s Trend of Fast Warming
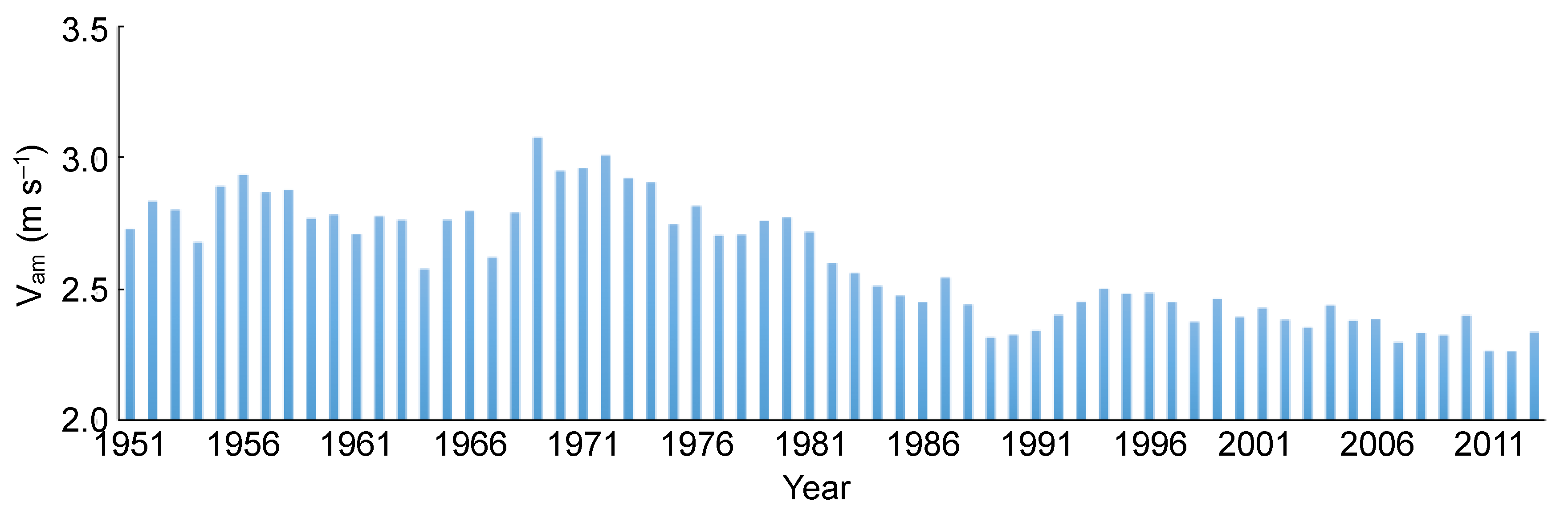
3.3. Northern China’s Decreased Surface Wind
4. Anthropogenic Impact on Desertification
4.1. Growing Population Pressure on Land
4.2. Significant Rural Depopulation
4.3. Overgrazing on Existing Grassland
5. A Series of Proactive Human Responses Playing the Main Role in Desertification Control
5.1. Government-Supported Vegetation Construction in Desertified Areas
5.2. The Great Impact of Ecological Industrial Engineering on Sandy Desertification Control
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Convention to Combat Desertification (ICCD). International Convention to Combat Desertification at United Nations General Assembly; UNCCD: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- GLP (Global Land Project). Science Plan and Implementation Strategy. Available online: www.globalcarbonproject.org/global/pdf/pep/GLP_FINAL_IGBP-IHDP.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- MEA (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment). Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Desertification; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- D’Odorico, P.; Bhattachan, A.; Davis, K.F.; Ravi, S.; Runyan, C.W. Global desertification: Drivers and feedbacks. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dregne, H.; Kassas, M.; Rozanov, B. A new assessment of the world status of desertification. Desertif. Control Bull. 1991, 20, 6–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dregne, H.E.; Cheng, D. Distribution of global desertified land and land consolidation costs. World Desert Res. 1993, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stringer, L. Can the UN Convention to Combat Desertification guide sustainable use of the world’s soils? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ning, D.T.; Smil, V. An estimate of economic loss for desertification in China. China Popul. Resour. Env. 1996, 6, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Soil Protection: The Story Behind the Strategy; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nater, T.; Duchrow, A.; Sörensen, L. Desertification: Coping with Today’s Global Challenges; High-Level Policy Dialogue: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD). Desertification—The Invisible Frontline. 2014. Available online: www.unccd.int/publications/desertification-invisible-frontline-second-edition (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Thomas, D.S.G.; Knight, M.; Wiggs, G.F.S. Remobilization of southern African desert dune systems by twenty-first century global warming. Nature 2005, 435, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, C. Responses of dune activity and desertification in China to global warming in the twenty-first century. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Siyal, P. Spatiotemporal dynamics of land surface temperature and its impact on the vegetation. Civil Eng. J. 2019, 5, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, H.T.; Zin, W.W.; Kyi, C.C.T. Assessment of future climate change projections using multiple global climate models. Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 5, 2152–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.D.; Chen, G.T. Sandy Desertification in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Harris, J.A. Restoration ecology: Repairing the earth’s ecosystems in the new millennium. Restor. Ecol. 2001, 9, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.W.; Zheng, Q.H.; Yu, Y.J. A preliminary study of oasis evolution in the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 55, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.F.; Zhang, D.D. Perceiving desertification from the lay perspective in northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, W.M.; Gabriels, D. Optimal windbreak design for wind- erosion control. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 61, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burciaga, U.M.; Sáez, P.V.; Ayón, F.J.H. Strategies to reduce CO2 emissions in housing building by means of CDW. Emerg. Sci. J. 2019, 3, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. Superficial review about the desertification in the North zone of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1991, 46, 266–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Chen, F.H.; Hasi, E.; Li, J. Desertification in China: An assessment. Earth Sci. Rev. 2008, 88, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkoh, M.B.K. The nature, causes and consequences of desertification in the drylands of Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 1998, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, H. Governing desertification in Mediterranean Europe: The challenge of environmental policy integration in multi–level governance contexts. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Stafford Smith, D.M.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.J.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J. Combating aeolian desertification in northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, S. The concept of desertification and the differentiation of its development. J. Desert Res. 1984, 4, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, H. Desertification in north China: Background, anthropogenic impacts and failures in combating it. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 16, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Grainger, A.; Stafford Smith, D.M.; Bastin, G.; Garcia-Barrios, L.; Fernández, R.J.; Janssen, M.A.; Jürgens, N.; Scholes, R.J.; Veldkamp, A.; et al. Scientific concepts for an integrated analysis of desertification. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y. A preliminary study on the amount and intensity of regional aeolian sand erosion: A case study of Shanxi Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia border area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1999, 66, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.Y.; Skidmore, E.; Hasi, E.; Wagner, L.; Tatarko, J. Dune sand transport as influenced by wind directions, speed and frequencies in the ordos plateau, china. Geomorphology 2005, 67, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Lin, Z.G. Climate of China; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Wang, J.A.; Jin, Y.Y.; Gu, X.T.; Yin, W.X. Climate change regionalization in China (1961–2010). Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kang, E.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, R. Recent and future climate change in northwest China. Clim. Chang. 2007, 80, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.K.; Zhai, P.; Zhang, Q. Variations in droughts over China: 1951–2003. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L04707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.M.; Zou, X.K. Changes of temperature and precipitation and their effects on drought in China during 1951–2003. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2005, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J.; Yan, P.; Yuan, Y. The driving force analyses of the blown-sand activity in northern China. Quat. Sci. 2001, 21, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y. Detection, causes and projection of climate change over China: An overview of recent progress. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 24, 954–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hou´erou, H.N. Climate change, drought and desertification. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 133–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.D. Concept, cause and control of desertification in China. Quat. Sci. 1998, 18, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M. Sandy desertification: Borne on the wind. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 20, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, S. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956–2004. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Chen, F.H.; Dong, Z.B. The relative role of climatic and human factors in desertification in semiarid China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2006, 16, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dickinson, R.E.; Tian, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, Q.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B. Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. Proc. Natl. A Sci. 2004, 101, 9540–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. The distribution, regionalization and prospect of China’s population. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1990, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.L.; Feng, Z.M. Population distribution of China based on GIS: Classification of population densities and curve of population gravity centers. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization of the United Nations (UNESCO), World Meteorological Organization (WMO). World Map of Desertification at a Scale of 1: 25 000000; United Nation: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Ma, H. Monitoring and evaluation of grassland-livestock balance in pastoral and semi-pastoral counties of China. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Desertification combating during the past 60 years in China. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 7, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Shi, P.; Zhang, G.; Qu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Desertification and blown sand disaster in China. J. Agric. Sci. Techol. A 2016, 6, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- State Forestry Administration. Opinions of the State Forestry Administration on deepening the construction and reform of the Three North Shelterbelt Development Program. 2014. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/sbj/5055/1549/4.html (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- State Forestry Administration. China Forestry Statistical Yearbook; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2001–2011.
- UNEP. Review of the Kubuqi Ecological Restoration Project: A Desert Green Economy Pilot Initiative; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L. Desert to Oasis: Elion’s Way to Ecological Prosperity. 2017. Available online: http://china.chinadaily.com.cn/2017-07/19/content_30168874.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Miao, L.; Moore, J.C.; Zeng, F.; Lei, J.; Ding, J.; He, B.; Cui, X. Footprint of research in desertification management in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Forestry Administration. China Forestry Development Report; Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Li, J.; Feldman, M.W.; Li, S.; Daily, G.C. Rural household income and inequality under the Sloping Land Conversion Program in western China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7721–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.J.; He, B.; Cui, X.F. Did China’s grain for green project benefit to labor structure adjustment? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 3, 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Alxa Bureau of Statistics. Alxa Statistical Yearbook; China’s statistics database: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Feng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Yu, T.; Yin, Z.; Cao, S. Combating desertification through economic development in northwestern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.S.; Na, R.S.; Dong, X.B.; Yu, B.H. The dynamic change of herdsmen well-being and ecosystem services in grassland of Inner Mongolia: Take Xilinguole League as example. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.C.; Huang, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, X. Study on the forming of “small and olded-tree” and the transforming way in the loess plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 1, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Zhang, X. Soil moisture ecological environment of artificial vegetation on steep slope of loess region in north shaanxi province, china. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 3769–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.H.; Guo, L.J.; Liu, G.B. Species diversity and community stability of populus simonii plantations in different habitats in hilly area of the loess plateau. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2007, 27, 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.L.; Zhang, R.Z. Zonation of Vegetation in the Practices of Ecological Restoration of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sino-Africa Joint Research Center (SAJOREC). 2013. Available online: http://www.sinafrica.cas.cn/English/About/Introduction/ (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC). Beijing Action Plan (2019–2021). 2018. Available online: https://www.focac.org/eng/zywx_1/zywj/t1594297.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- China-Arab States Technology Transfer Center (CASTTC). 2014. Available online: http://en.casttc.org (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- China’s State Forestry Administration (CSFA). Memorandum of Understanding between China’s State Forestry Administration and the Arab League (Arab Center for arid area and dryland Research) on Cooperation in Desertification Monitoring and Control. 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2014-06/09/content_2697262.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- China-Arab States Cooperation Forum (CASCF). 2018. Available online: http://www.chinaarabcf.org/chn/lthyjwx/bzjhywj/dbjbzjhy/t1577002.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- MFA (Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People’s Republic of China). Joint Statement of Cooperation on Sustainable Forest Management, Combating Desertification and Wildlife Conservation. 2012. Available online: https://www.fmprc.gov.cn/mfa_eng/wjdt_665385/2649_665393/t931397.shtml (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People’s Republic of China (MFA). One Belt and One Road Joint Action to Combating Desertification. 2016. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/72/content-881674.html (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP). UN and Partners Renew Efforts to Support Green Economy Projects in Deserts and Drylands. 2013. Available online: https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/un-and-partners-renew-efforts-support-green-economy-projects-0 (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Bao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Bao, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, L.; Long, C.; Kong, Z.; Peng, P.; Xiao, J.; Lu, Q. Desertification: China provides a solution to a global challenge. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2017, 4, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People’s Republic of China (MFA). Workshop on Desertification Control in English Speaking African Countries. 2014. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/586/content-689383.html (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Cheng, Z. Tree by Tree, China Rolls Back Deserts. 2007. Available online: http://www.chinese-embassy.org.uk/eng/zt/Features/t367033.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Gansu Desert Control Research Institute (GDCRI). Workshop on Sustainable Development of Water Resources in Arid Areas of Developing Countries. 2016. Available online: http://www.gsdcri.com/?thread-421-1.html (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Bao, Y.; Yang, L.; Long, C.; Kong, Z.; Peng, P.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Q. Review of 60 years combating desertification in China and prospects on it. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
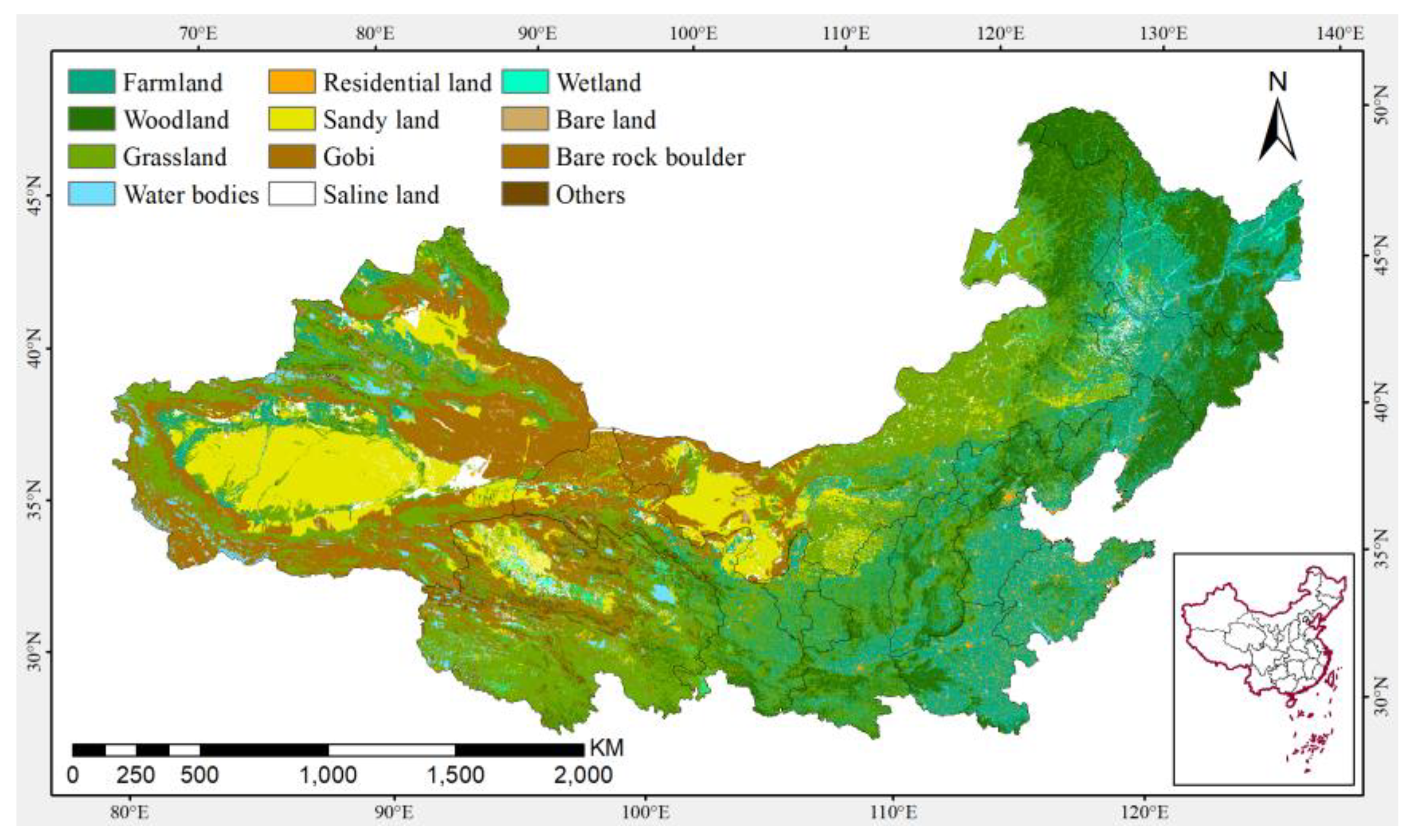





| Years | Total Area of Desertified Land (million km2) | Total Area of Sandy Desertified Land (million km2) | The Average Annual Increase/Decrease Rate of Sandy Desertified Land (km2/year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2.612 | 1.7212 | – 1980 |
| 2009 | 2.624 | 1.7311 | – 1717 |
| 2004 | 2.636 | 1.7396 | – 1283 |
| 1999 | 2.674 | 1.7431 | + 3436 |
| 1994 | 2.622 | 1.6889 | + 2460 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, Y.; Shi, P.; Han, G.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G. Desertification Control Practices in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083258
Lyu Y, Shi P, Han G, Liu L, Guo L, Hu X, Zhang G. Desertification Control Practices in China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Yanli, Peijun Shi, Guoyi Han, Lianyou Liu, Lanlan Guo, Xia Hu, and Guoming Zhang. 2020. "Desertification Control Practices in China" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083258
APA StyleLyu, Y., Shi, P., Han, G., Liu, L., Guo, L., Hu, X., & Zhang, G. (2020). Desertification Control Practices in China. Sustainability, 12(8), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083258




