What Type of Industrial Agglomeration Is Beneficial to the Eco-Efficiency of Northwest China?
Abstract
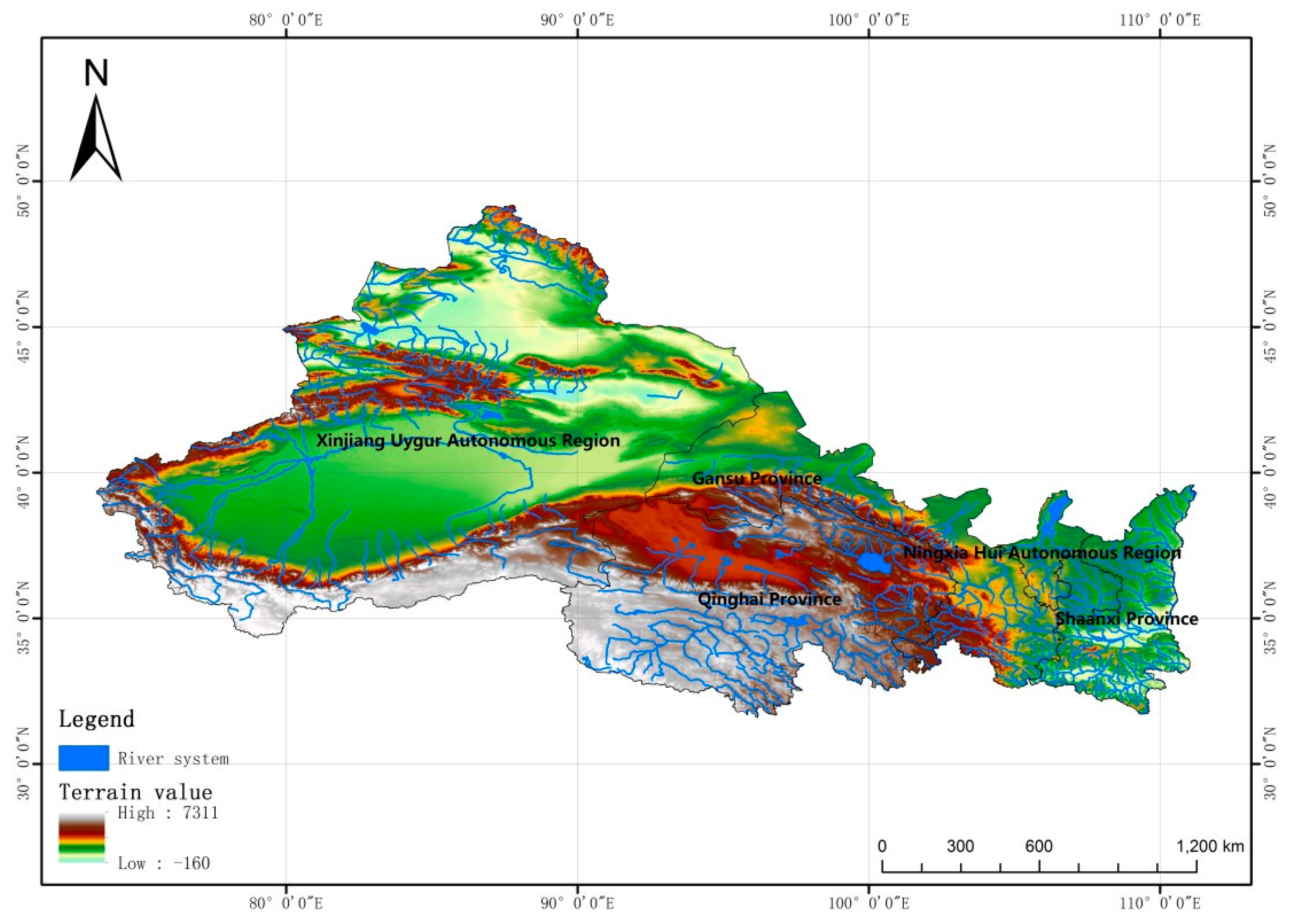
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Measuring Methods for Industrial Agglomeration
2.1.2. Measuring Methods for Industrial Eco-Efficiency
2.1.3. Panel Tobit Regression Model
2.2. Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Industrial Agglomeration in Northwest China 2006–2018
3.2. Level of Industrial Eco-Efficiency in Northwest China 2006–2018
3.3. Influence of Industrial Agglomeration on Eco-Efficiency in Northwest China
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, F.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Lv, L.; Li, Y. Comparison and Analysis of Future Heavy Precipitation and Extremely Heavy Precipitation in Seven Major Regions of China from 2010 to 2099 under the Background of Geoengineering. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2019, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Chen, X.; Lan, Q. An Analysis of Coupling Degree between Economic Development and Ecological Environment in Northwest China along the Silk Road Economic Belt: An Empirical Test Based on DEA Entropy-Weight TOPSIS Model. Int. Bus. 2018, 5, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Dong, M. On Influence of Resources and Environment upon Economic Development in Northwest China. J. Northwest Minzu Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2018, 1, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Cao, H. Evaluation of Industrial Development and Policies in Northwestern China in the Past 70 Years from the Perspective of Low-carbon Economy. J. Lanzhou Univ. Soc. Sci. 2019, 47, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.; Qi, S.; Liang, B.; LIu, X. Analysis of ecological sensitivity of five provinces in northwestern China. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2019, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Li, L. The History, Achivement and Future Path of Green Development in the 20 Years of the Development of Western China. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 48, 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Allenby, B.R.; Richards, D.J. The Greening of Industrial Ecosystems; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allenby, B.R. Industrial Ecology; Prentice Hall Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 261, pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Graedal, T.E.; Allenby, B.R. Industrial Ecology and the Automobile; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Frosch, R.A.; Gallopoulos, N.E. Strategies for manufacturing. Sci. Am. 1989, 261, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W. Ecological Industry:Theory, Practice and Prospects. Econ. Probl. 2014, 11, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gong, X. Literature Review of Industrial Ecologization. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2013, 32, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Bi, J. Industrial Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Chen, W. Industrial Ecology in China. Retrospect and prospect. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7158–7167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shi, X. A review of industrial ecology based on GIS. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Nieminen, E.; Linke, M.; Tobler, M.; Beke, B.V. EU COST Action 628: Life cycle assessment (LCA) of textile products, eco-efficiency and definition of best available technology (BAT) of textile processing. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willison, J.H.M.; Côté, R.P. Counting biodiversity waste in industrial eco-efficiency: Fisheries case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollands, N.; Lermit, J.; Patterson, M. Aggregate eco-efficiency indices for New Zealand-A principal components analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 73, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehni, M. WBCSD Project on Eco-efficiency Metrics & Reporting; State of Play Report; World Business Council for Sustainable Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Hu, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and spatial interaction of regional eco-efficiency in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidheiny, S.; Stigson, B. Eco-efficiency: Creating More Value with Less Impact; World Business Council for Sustainable Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L. Environmental Regulations, Foreign Direct investment and Industrial Agglomeration—Evidence from Provincial Panel Data of China. Ind. Econ. Rev. 2018, 9, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhuang, G. Spatial and Temporal Impact of Industrial Agglomeration on eco-efficiency in Bohai Economic Rim—A Study Based on Environmental Regulation. Econ. Surv. 2020, 37, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Research on regional totalfactor eco-efficiency of China: Measurement and determinants. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, X. The spatio-temporal evolutionary characteristics and regional differences in affecting factors analysis of China’s urban eco-efficiency. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.; Yao, S. Convergence and differentiation characteristics on agro-eco-efficiency in China from a spatial perspective. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Q.; Liang, Q. Spatio-tempo-ral difference of marine eco-efficiency and identification of its response relationship with marine industrial structure in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, M.; Zhan, Y. Spatial evolution of marineeco-efficiency and its influential factors in China coastal regions. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Miao, Z. Progress in Chinese and International Industrial Ecological Engineering Development. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 8, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Wang, R.; Zhou, C.; Liang, J. Review of eco-efficiency accounting method and its applications. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Peng, H.; Cao, F. Circular Economy and Industrial Eco-efficiency Indicator System. Urban Environ. Urban Ecol. 2003, 16, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Dyckhoff, H.; Allen, K. Measuring eco-efficiency with data envelopment analysis (DEA). Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 132, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J. Ecoefficiency: How data envelopment analysis can be used by managers and researchers. In Environmentally Conscious Manufacturing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4193, pp. 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama, H.; Weber, W.L. A directional slacks-based measure of technical inefficiency. Socio Econ. Plan. Sci. 2010, 43, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Evaluation of low carbon transformation process for Chinese provinces. Econ. Res. J. 2012, 47, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yao, P. Industrial agglomeration and eco-efficiency: An empirical analysis based on different main function zones. J. Southeast Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2020, 22, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z. Exploration on the Distribution of Economic Activity: Technology Spillover, Environmental Pollution and Trade Liberalization. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2015, 35, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Qin, T.; Tong, J.; Sun, D. Industrial agglomeration, urban agglomeration and water consumption. Soft Sci. 2018, 32, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Xie, S. Can industrial agglomeration promote pollution agglomeration? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 246, 118960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, C. Impact of spatial agglomeration on industrial pollution emissions intensity in China. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.; Yao, D. The causal relationship and determinants of industrial agglomeration and urban labor productivity. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2008, 25, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Shen, K. The government intervention, the economic agglomeration and the energy efficiency. Manag. World 2013, 10, 6–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. An Analysis on the Spatio-Temporal Difference and Convergence of China’s Industrial Eco-efficiency. Macroeconomics 2020, 7, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Zheng, M.; Sun, J. The Impact of Industrial Agglomeration on Haze Pollution of Key Urban Agglomerations in China. Soft Sci. 2020, 34, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, C. Research on Dynamic Relationship between Industrial Agglomeration and Urban eco-efficiency. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2019, 36, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Luan, X.; Song, Y. The Impact of High-Tech Industry Agglomeration on Green Economy Efficiency—Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, K. Water-energy nexus within urban agglomeration: An assessment framework combining the multiregional input-output model, virtual water and embodied energy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Specialization, diversity and their impacts on China’s provincial industrial pollution emissions. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 586–599. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A. Principles of Economics; MacMillan: London, UK, 1890. [Google Scholar]
- Frenken, K.; Oort, F.V.; Verburg, T.N. Related Variety, Unrelated Variety and Regional Economic Growth. Reg. Stud. 2007, 41, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, J. The Economy of Cities; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H. Modern Regional Economics; Economic & Management Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. Inter-industry technology spillover effects in China: Evidence from 35 industry sectors. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.T.; Lovell, C.A.K. A global Malmquist productivity index. Econ. Lett. 2005, 88, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G. Data Envelopment Analysis: Methods and MaxDEA Software; Intellectual Property Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 200–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Y. The Influencing Factors of Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Efficiency in China from the Perspective of Green Development—An Empirical Study Based on Super-efficiency DEA and Tobit Models. Manag. Rev. 2020, 32, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of China’s inter provincial industrial eco-efficiency. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Department of Industry Statistics, National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Industry Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- National Bureau of Statistics; Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. China Statistical Yearbook on Environment; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Statistics Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; NBS Sarvey Office in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Statistics Bureau of Shaanxi; NBS Sarvey Office in Shaanxi. Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Statistics Bureau of Gansu; NBS Sarvey Office in Gansu. Gansu Development Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Statistics Bureau of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region; NBS Sarvey Office in Ningxia; National Bureau of Statistics. Ningxia Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Statistics Bureau of Qinghai; NBS Sarvey Office in Qinghai. Qinghai Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2006–2018.
- Shan, H. Re-estimating the capital stock of China: 1952-2006. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2008, 25, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. Resource-Based Economy: Theory Explanation, Internal Mechanism and Application Research. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Fan, M.; Yang, L. How does resource industry dependence affect economic development efficiency. Manag. World 2013, 2, 32–63. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y. Performance evaluation of China’s provincial ecological management. Stat. Res. 2017, 34, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Gai, M. Study on efficiency and effect of ecological undesirable outputs SBM model of Bohai Bay Area based on factors. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2018, 34, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Shan, B.; Ma, J.; Deng, W. Surface Water Environmental Carrying Capacity in Water-Deficient Areas: A Case Study on Jingjinji and the Five Northwestern Provinces and Autonomous Regions in China. Strateg. Study CAE 2017, 19, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
| Variable Type | Variable Name | Variable Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input indicator | Natural resource input | Water consumption | Total industrial water |
| Land consumption | Area of industrial construction land | ||
| Energy consumption | Total industrial energy consumption | ||
| Social and economic factor input | Labor input | Number of industrial employees | |
| Capital input | Industrial fixed assets | ||
| Output indicator | Desirable output | Economic value creation | Industrial value added |
| Undesirable output | Wastewater discharge | COD emissions industrial wastewater | |
| Ammonium nitrogen emissions from industrial wastewater | |||
| Waste gas discharge | SO2 emissions from industrial emissions | ||
| Smoke (dust) emissions from industrial waste gas | |||
| Solid waste discharge | Emissions from industrial solid waste | ||
| Type | Region | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Shaanxi | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.50 |
| Qinghai | 1.15 | 1.13 | 1.09 | 1.08 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | |
| Ningxia | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.91 | |
| Gansu | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.71 | |
| Xinjiang | 1.10 | 1.03 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.79 | |
| Mean | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.77 | |
| Related diversification | Shaanxi | 1.77 | 1.78 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 1.81 | 1.73 | 1.74 | 1.83 | 1.83 | 1.83 | 1.82 | 1.82 | 1.81 |
| Qinghai | 1.51 | 1.47 | 1.39 | 1.45 | 1.43 | 1.3 | 1.30 | 1.3 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.29 | |
| Ningxia | 1.34 | 1.32 | 1.31 | 1.32 | 1.37 | 1.35 | 1.33 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 1.37 | 1.36 | 1.36 | 1.35 | |
| Gansu | 1.55 | 1.46 | 1.43 | 1.41 | 1.40 | 1.35 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.34 | 1.35 | 1.36 | 1.36 | 1.39 | |
| Xinjiang | 1.60 | 1.55 | 1.58 | 1.57 | 1.63 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.59 | 1.60 | 1.58 | 1.58 | 1.56 | |
| Mean | 1.55 | 1.52 | 1.50 | 1.51 | 1.53 | 1.46 | 1.45 | 1.47 | 1.48 | 1.49 | 1.48 | 1.48 | 1.48 | |
| Unrelated diversification | Shaanxi | 1.24 | 1.25 | 1.24 | 1.23 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.21 |
| Qinghai | 1.24 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.31 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 1.34 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.30 | |
| Ningxia | 1.30 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.33 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.33 | 1.34 | 1.33 | 1.32 | 1.32 | |
| Gansu | 1.31 | 1.29 | 1.28 | 1.28 | 1.27 | 1.25 | 1.24 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.18 | |
| Xinjiang | 1.18 | 1.17 | 1.18 | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 1.25 | 1.29 | 1.25 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.29 | 1.28 | |
| Mean | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 1.28 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.27 | 1.27 | 1.26 |
| Region | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaanxi | 0.97 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 1.04 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.00 | 1.11 | 1.13 |
| Qinghai | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| Ningxia | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.56 |
| Gansu | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| Xinjiang | 0.96 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 1.11 | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.21 |
| Meane | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 2.72 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Explanatory Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| spe | −0.433 *** | −1.862 ** | ||||
| (−2.85) | (−2.25) | |||||
| spe2 | 0.813 | |||||
| (1.56) | ||||||
| rd | −0.147 | −4.376 *** | ||||
| (−1.13) | (−2.97) | |||||
| rd2 | 1.45 *** | |||||
| (2.65) | ||||||
| urd | −0.436 * | −0.287 | ||||
| (−1.95) | (−0.07) | |||||
| urd2 | −0.061 | |||||
| (−0.06) | ||||||
| pgdp | −0.174 *** | −0.162 *** | −0.117 *** | −0.146 *** | −0.088 * | −0.087 * |
| (−3.75) | (−3.49) | (−2.74) | (−3.45) | (−1.98) | (−1.79) | |
| pgdp2 | 0.036 *** | 0.034 *** | 0.029 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.025 *** | 0.025 *** |
| (4.65) | (4.39) | (3.84) | (4.47) | (3.27) | (3.21) | |
| estu | −0.944 *** | −0.999 *** | −0.963 *** | −0.936 *** | −0.934 *** | −0.935 *** |
| (−5.51) | (−5.76) | (−5.57) | (−5.89) | (−5.65) | (−5.51) | |
| open | −0.162 | −0.196 | 0.047 | 0.026 | 0.279 | 0.279 |
| (−0.22) | (−0.25) | (0.06) | (0.04) | (0.38) | (0.38) | |
| tech | 6.78 ** | 7.609 ** | 6.975 ** | 5.073 * | 6.781 ** | 6.804 ** |
| (2.17) | (2.44) | (2.14) | (1.75) | (2.10) | (2.05) | |
| envir | 2.825 | 3.25 | 4.180 | 2.662 | 6.967 ** | 6.954 ** |
| (0.89) | (1.07) | (1.27) | (0.82) | (1.98) | (1.96) | |
| mark | 0.019 * | 0.008 | 0.022 * | 0.018 * | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| (1.68) | (0.58) | (1.85) | (1.67) | (1.01) | (1.01) | |
| Constant | 1.762 *** | 2.413 *** | 1.454 *** | 4.546 *** | 1.776 *** | 1.677 |
| (8.28) | (5.39) | (6.27) | (4.01) | (5.98) | (0.53) | |
| Observations | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Number of ID | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Pei, T.; Wang, T.; Hao, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Yang, C. What Type of Industrial Agglomeration Is Beneficial to the Eco-Efficiency of Northwest China? Sustainability 2021, 13, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010163
Gao L, Pei T, Wang T, Hao Y, Li C, Tian Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Song W, Yang C. What Type of Industrial Agglomeration Is Beneficial to the Eco-Efficiency of Northwest China? Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010163
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Lei, Taowu Pei, Tielong Wang, Yue Hao, Chao Li, Yu Tian, Xu Wang, Jingran Zhang, Weiming Song, and Chao Yang. 2021. "What Type of Industrial Agglomeration Is Beneficial to the Eco-Efficiency of Northwest China?" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010163
APA StyleGao, L., Pei, T., Wang, T., Hao, Y., Li, C., Tian, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Song, W., & Yang, C. (2021). What Type of Industrial Agglomeration Is Beneficial to the Eco-Efficiency of Northwest China? Sustainability, 13(1), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010163





