Abstract
The acceleration of average temperature of lands and oceans, rising sea level, frequent extreme weather events and ocean acidification denote that climate change is a contemporary pressing dilemma facing the world. Everyday human activities such as open burning, deforestation, burning of fossil fuels and agricultural activities significantly contribute to Earth warming. Preventing the aforementioned activities reduce the greenhouse gas emission to the atmosphere and subsequently slows the changes in climate. Thus, climate change education is integral to educate people on the destructive consequences of their actions to the climate. Past studies revealed that well-established theories and models guided the designing of education to deliver behavioral change in many countries and reportedly improved participants’ knowledge, attitude and motivation. However, these theories and models exist as an after effect of the education and the long-term impact of the initiative frequently not found and less information available on the sustainability of such education. Additionally, effective climate change education is typically context-based and designed based on factors related to local students’ behavior. Hence, this study examined how knowledge and psychological factors such as belief and motivation explain the formation of climate conserving behavior among secondary school students. A total of 221 questionnaires was distributed to 14 years old Malaysian secondary school students to measure knowledge, motivation and belief. The data obtained were later analyzed using the partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) approach. The findings revealed that knowledge (β = 0.259, p < 0.05), belief (β = 0.295, p < 0.05) and motivation (β = 0.546, p < 0.05) positively affects the behavior. These findings reflected that knowledge, belief and motivation collectively explain a total of 65.5% of variances in the formation of climate conserving behavior among Malaysian secondary school students.
1. Introduction
The acceleration of average temperature of land and ocean, rising sea level, frequent extreme weather events and ocean acidification signify that climate change is a contemporary pressing dilemma facing the world [1]. The panels deliberated that the average global temperature likely to reach 1.5 °C between 2030 and 2052. Consequently, the global community expected to experience health, societal and economic destructions on an unprecedented scale due to the surge in the temperature. A wealth of studies in the literature [2,3,4,5] and reports from the global organization on climate change [1,6,7] forwarded firm evidence depicting that the anthropogenic activities are the underlying cause for the spike in the global temperature.
Everyday human activities such as open burning, deforestation [8,9], burning of fossil fuels [8] and agricultural activities [1] significantly contribute to the warming of the Earth. Preventing the aforementioned human activities reduces greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere and subsequently slows climate changes. In such circumstances, climate change education is integral to educate the people on the destructive consequences of their actions to the climate [10,11,12,13,14,15]. The Chapter 36 of Agenda 21 reveals the imperative role of education in preparing the younger generation with crucial knowledge and skills for behavioral change. The knowledge and skills are expected to guide the younger peoples’ actions to conserve the environment [16].
In responding to the above call, in many countries, climate change education focused on secondary level students [17,18,19]. The education with the ultimate aim of changing behavior or developing pro-environmental behavior of students made them realize the need to modify their lifestyle to save the environment from further destruction. The educational initiatives predominately employ well-established theories, models and past literature as a guide in designing the initiatives. The theories and models such as experiential learning [20], constructivist approach [21,22], online inquiry-based learning [23] and socioscientific issues-based instruction [24] predominantly employed in designing climate change education.
Although these initiatives effectively improved participants’ knowledge [20,23,25] attitude [10,26,27,28] and motivation [20,29], the literature did not explicitly document the long term effect and sustainability of the approaches. Frequently, climate change education focuses on the right-after-effect of the activities or programs rather than on the long-term impact of the program. This is likely because framing educational initiatives using common theories result in students learning less relevant content [30]. This contradicts the notion of effective climate change education which is typically context-based and designed considering the factors that explain the behavior of local students [31,32].
Climate change is a significant concern in countries like Malaysia, where the actions of the general public, such as open burning, deforestation and the excessive use of energy, water and transportation [9] are the major contributor to the emission of greenhouse gases. During the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC) in 2015, Malaysia has committed to reducing 35% of the emission intensity by 2030 [15]. The Malaysian Government has framed the National Policy on Climate Change to mitigate climate change by controlling the anthropogenic causes of climate change such as greenhouse gas emissions. However, after nine years of implementing the policy detrimental impacts of climate change notable in the agriculture, forestry, biodiversity, water resources, coastal and marine resources, public health and energy sectors [33]. Tang [33] further said that extreme weather events, increase in average daily temperature, rising sea level and uneven rainfalls denoting climate change is a real and impacting livelihood of the society. The contemporary climate condition of the country suggests a context-based climate change education is required for delivering behavioral change among Malaysian society. Hence, this study was conducted to explore the factors that explain the climate conserving behavior of Malaysian secondary school students.
Specifically, the study aims to measure the effects of secondary level students’ knowledge about climate change, their belief and motivation on committing climate conserving behaviors. A model describing the climate conserving behaviors was recommended based on the combined effects of the variables.
2. Background
2.1. Climate Conserving Behavior
In the literature, the definition of pro-environmental behavior (PEB) varies. The definition differs according to the type of actions either impact or intends oriented behavior [34]. Impact-oriented behavior refers to the behaviors that alter the availability of materials or energy and the structure of dynamic ecosystems. Impact-oriented behavior is performed for the betterment of the environment. Stern further categorized impact and intend oriented behaviors as public and private sphere pro-environmental behaviors. Steg and Vlek [35] refer to pro-environmental behavior as actions that only have a minimal detrimental impact on the environment. In the meta-analysis of a collection of studies that researched on PEB, Kollmuss and Agyeman [36] postulated pro-environmental behavior as “behavior that consciously seeks to minimize the negative impact of one’s actions on the natural and built world” (p. 240). Besides, proposing a definition for PEB, the meta-analysis also documented the development of theories and models explaining PEB beginning from the linear progression model at the earlier times to contemporary use of the theory of planned behavior (TPB) and value-belief-norm theory (VBN) as fundamental theories in comprehending environmental actions.
The Linear progression model hypothesized knowledge of particular environmental issues promotes environmental attitude and eventually engender PEB [37]. However, the advocate of environmental education argued that knowledge alone does not necessarily lead to PEB. The demographic, external and internal factors may have some positive and negative influences on PEB [36]. Some studies adapted the TPB, a theory designed for explaining general behaviors in social science [38], considering the integral roles of the external and internal factors for describing PEB [39,40,41]. These studies report the behavioral intention is the immediate antecedent for actual PEB. One’s belief, attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioral control are the factors that explain the pro-environmental behavioral intention. Contradicting to TPB, in which the focus is to demonstrate more general behaviors, Stern, Dietz, Abel, Guagnano and Kalof [42] and Stern [34] proposed Value-Belief-Norm (VBN) theory explaining PEB. VBN theory postulated that the causal chain of values, beliefs and norms inform behavior. The causal relationships between the variables are widely employed to describe specific behaviors such as recycling and energy and water conservation [43]. Few studies have used the VBN theory to describe climate change behavior [44,45].
The actions to mitigate climate change known as climate conservation behaviors include opting for public transport, carpooling, conserving energy at home and recycling. The impact and intend-oriented climate conservation or mitigating behaviors predominantly centered on individuals [46]. The behaviors are largely habitual in which people behave according to past experiences [34]. Combination of various causal factors determines the habits driven private sphere pro-environmental behaviors. Past studies demonstrate that various antecedents inform climate conserving behaviors. The antecedents include belief [44,47,48], motivation [20,49,50] and knowledge [20,25,51,52,53]. Frequently, the causal factors are context-specific and locally relevant. Earlier studies on climate change education involving Malaysian students documented that secondary school students’ knowledge of climate change is instrumental for behavioral change for mitigating climate change [52]. Another study employed climate change education to explore students’ belief that changing their behavior decelerates the climate changes [54]. Motivation is another factor closely related to Malaysian students’ climate conserving behaviors [20]. In the studies mentioned above, the effects of belief, motivation and knowledge on climate conserving behavior have been investigated in isolation. However, VBN and TPB denote that the antecedents collectively inform behavior formation. The ultimate aim of this study is to establish a model that collectively explains the effects of knowledge, belief and motivation on the formation of climate conserving behaviors. Subsequently, the study bridges the gap in the lack of such a model in the literature to explain climate conserving behaviors.
2.2. Knowledge and Climate Conserving Behavior
Advocates of environmental studies accredited knowledge as one of the antecedents for pro-environmental behavior. For instance, Heimlich and Ardoin [55] perceived environmental knowledge as the fundamental factor that triggers behavioral change. Hungerford and Volk [56] further stressed that knowledge is one of the factors that influence behavior modification.
Environmental knowledge is ascribed to the increase in pro-environmental behavior [57]. Findings from another study revealed that students who are equipped with knowledge on how their actions impact the environment embraces more environmentally responsible behaviors [58]. A recent study involving students from Singapore and Germany indicated that outdoor environmental education program increased the participants’ environmental knowledge. The study detailed that the participants with advanced knowledge performed more environmentally friendly behaviors than the others with lesser experience [59].
The literature on climate conserving behavior renders knowledge as one of the critical determining factors of climate conserving behavior. Knowledge is a prerequisite to comprehend the issue of climate change [11]. Anderson [10] claimed that new knowledge requires to modify behavior that could slow the rate of climate change and subsequently decreases the vulnerability of the natural and human system. The individual with a considerable level of knowledge on climate change expressed concern about how their behavior could influence climate change [60,61]. Another study proposed that awareness on the causes and impacts of climate change influence behavioral changes towards protecting the climate [62].
Heimlich and Ardoin [55] said that knowledge that informs pro-environmental behaviors are multifaceted. The multifaceted knowledge consists of system knowledge, action-related knowledge and knowledge on the effectiveness of actions. This knowledge is derived from the combination of both system and action-related knowledge [63]. In researching the three different types of knowledge and climate conserving behaviors, Bofferding and Kloser [64] categorized how climate works as system knowledge. Behaviors that influence the climate system as action-related knowledge and knowing the effectiveness of the behavior in achieving the goals is known as effectiveness knowledge. The three components of knowledge prescribed by Bofferding and Kloser [64] are essential in understanding the science that underlies the climate change-related phenomena. These components help in understanding global warming, greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, acid rain, weather and climate, ocean and climate change and land and climate change [32,51,52,65,66]. The effects of knowledge on pro-environmental behavior documented in the literature guided the researchers in formulating the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Knowledge about climate change-related phenomena such as global warming, greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, acid rain, weather and climate, ocean and land has a significant positive direct effect on the formation of climate conserving behaviors.
2.3. Belief and Climate Conserving Behavior
Belief is another psychological dimension inferred as precedents of pro-environmental behavior [34,67,68] besides cognition. Findings from a study performed with young people in Australia demonstrate that participants who were more pro-environmental had a greater belief that it is the society’s responsibility to safeguard the environment [69]. A study by Schutte and Bhullar [70] with a group of adults shows that individual belief about sustainability-related behavior significantly relates to them performing self-reported behavior.
The literature defines belief in multiple ways. Gagnon Thompson and Barton [68] suggested two conflicting belief systems ‘ecocentrism and anthropocentrism’ explaining the pro-environmental behaviors. Individuals with ecocentric and anthropocentric belief systems perform pro-environmental actions with different justifications. The individuals with the ecocentric belief system support the conservation of the environment due to the inherent value of nature. Anthropocentric individuals care for the environment because the environment enhances their health and well-being [68].
Stern [34] presented belief as a three-dimensional construct. The three dimensions that constitute belief are an individual’s worldview, awareness of adverse consequences and ascription to responsibility. Worldview refers to an individual believe that the human and environment relationship eventually determines the environmentally significant behaviors. Awareness of adverse consequences refers to the belief that the individual is responsible for the outcome of their action that affects human beings and other livings. Ascription of responsibility denotes the steps that one could take to mitigate those consequences. Stern [34] placed the three-dimensional views of belief between values and norms in the value-belief-norm model describing pro-environmental behavior.
Dunlap and Van Liere [67], in their earlier work, presented belief as beliefs about humanity’s ability to upset the balance of nature, the existence of limits to growth for human societies and humanity’s right to rule over the rest of nature. Dunlap, Van Liere, Mertig and Jones [71] added two new facets and expanded the description of belief. The two new facets of belief are the likelihood of ecocrises and antihuman exemptionalism (the belief that humans are not exempt from the laws of nature). The New Ecological Paradigm presented a five dimensions of belief which is widely used to measure environmental belief [72,73] and appeared to have more robust psychometric features and it is theoretically better grounded. Landon, Woosnam, Keith, Tarrant, Rubin and Ling [74] advocated that NEP appropriately measures the belief about climate change.
The belief climate change is anthropogenic entails people to demonstrate climate conserving behavior to decelerate climate changes [75]. A study done by Karpudewan [44] proves that there is a significant positive relationship between students’ beliefs and climate conserving behaviors. Experimental research indicates that a moderate positive relationship exists between students’ climate change beliefs and intention to take action to reduce climate change [76]. In the same study, the moderate relationship then turns to a strong positive relationship after students in the treatment group exposed to hands-on activities. A recent study done in Czech with upper primary and secondary level students confirmed that students’ belief directly explains up to 18% of their willingness to act to alleviate global warming [48].
The literature concerning belief in environmental studies revealed that belief is instrumental in explaining behavior. The literature mentioned above guided the formulation of the hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Belief, as measured using five facets of NEP has a positive direct effect on the formation of climate conserving behavior.
2.4. Motivation and Climate Conserving Behavior
Motivation is a factor that drives humans to perform behavior. Self-determination theory (SDT) is the prominent motivational theory that describes the degree of behavior regulations and the corresponding motivation [77,78]. The authors employed SDT to propose a continuum on quality of motivation ranging from non-self-determined to self-determined motivation. The lowest point of the continuum is amotivation which is the non-self-determined motivation. The absence of external or internal forces for regulating the behavior results in amotivation. Different degrees of regulation of external and internal forces result in self-determined motivation. The second level of motivation in the SDT continuum after amotivation is extrinsic motivation. Extrinsic motivation refers to performing the behaviors for obtaining both positive and negative distinctive outcomes than the real intention of the activity. Based on the degree of internationalization of the forces, extrinsic motivation is classified as external, introjected, identified and integrated regulations. Behaviors that arise from external regulations are motivated by external forces and performed to avoid punishment to secure rewards. Introjected regulations direct the actions towards satisfying ego to refrain from guilt and embarrassment. Identified regulations refer to the behaviors performed to reflect self-identity. When the individuals fully assimilate the identified regulation within them, the resulting behaviors are integrated within the individual’s value system. Intrinsic motivation, the highest point of the continuum referred to as self-determined motivation, reflects the behaviors performed for accomplishing the inert satisfaction of the individual.
Past studies demonstrated positive relationships between different types of motivation and pro-environmental behavior. For instance, a study involving a group of undergraduate students revealed that self-determined motivation promoted lasting pro-environmental behaviors [79]. Similar findings were also documented in a study involving students from Australia [80]. Enhancement of pre-service teachers’ intrinsic and extrinsic motivation encouraged the development of pro-environmental behaviors [81]. A study involving undergraduate students from Iran revealed that intrinsic and extrinsic rewards of environmentally unfriendly behaviors as the direct determinants of pro-environmental behavior [82]. Pongiglione [83] identified barriers for the lacking motivation for adopting pro-environmental behaviors among adults. The studies discussed above indicate that motivation as the antecedent for developing pro-environmental behaviors [84,85]. Motivation is also integral for adopting climate conserving behaviors. For instance, van der Linden [86] called for studies investigating the role of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation for sustaining energy conservation behavior as a measure to address climate change. van Valkengoed and Steg [50] performed a series of meta-analyses using data from 106 studies involving 23 countries to illustrate the key motivating factors that explain climate conserving behaviors’ adaptation. The review of past studies on self-determination theory and studies relating to motivation and behavior guided the formulation of the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Motivation presented in the self-determined motivation continuum has a significant positive effect on the formation of climate conserving behavior.
3. Methodology
3.1. Methods
This study investigated the effects of knowledge, beliefs and motivation on the formation of climate conserving behaviors among Malaysian secondary school students. For this purpose, the study employed SmartPLS 3.0 Ringle, Christian M. Wende, Sven and Becker [87] to test the three hypotheses and the research model (Figure 1) formulated from reviewing the literature.
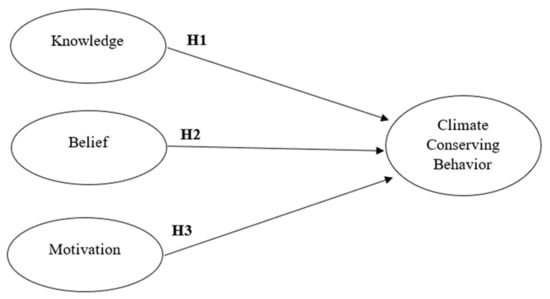
Figure 1.
Research Model of the Study.
3.2. Research Design and Sample
This study utilized a cross-sectional survey design. The survey design is deemed appropriate as the survey requires collecting data from several secondary schools. The students between 14 to 15 years enrolled in secondary schools in Malaysia represent the study population. The convenient sampling strategy was employed to locate the four schools from the Northern Region of Malaysia to participate in the study. A total of 221 students from the four schools participated in this study. The sample size, n = 221, meets the ten times rules of a number of arrowheads pointing at a latent variable. The sample size is also bigger than the minimum sample size required at the significant level of 5% and minimum R2 of 0.10 for the statistical power of 80% [88]. The G*Power calculator indicated that a minimum sample size of 103 is necessary for the study. The sample size n = 221 adequate and full fills the requirement for the minimum sample size.
3.3. Instrumentation
The study employed the Climate Change Knowledge Inventory (CCKI) to measure knowledge, the New Ecological Paradigm (NEP) scale to measure belief, the Motivation Towards Environment Scale (MTES) for measuring motivation and the Self-Reported Climate Conserving Behavior questionnaire to gauge behavior. Table 1 provides details about the four instruments used in this study.

Table 1.
Sources of the instruments and distributions of items in the questionnaires.
Climate Change Knowledge Inventory (CCKI) comprises 25 items. Students stated their understanding of global warming, greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, acid rain, weather and climate, ocean and climate change and land and climate change on a scale of 1 to 5. Following Hoppe, Taddicken and Reif’s [92] recommendation the scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) was employed to ascertain students’ knowledge. The items in the knowledge inventory have been adapted from the original work of Arslan, Cigdemoglu, and Moseley [89] and Libarkin, Gold, Harris, McNeal and Bowles [90].
The New Ecological Paradigm (NEP) scale consisted of 15 items [71]. The 15 items have been categorized into five subscales, the reality of limits of growth (1, 6, 11), anti-anthropocentrism (2, 7, 12), the fragility of nature’s balance (3, 8, 13), rejection of exemptionalism (4, 9, 14) and the possibility of an eco-crisis (5, 10, 15). The students responded to items in the NEP, using a 5-points Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly agree) to 5 (strongly disagree). The NEP scale is widely employed to measure belief due to its high internal consistency.
The researchers obtained the original version of the Motivation Towards Environment Scale (MTES) from Pelletier, Tuson, Green-Demers, Noels, and Beaton [91]. The original version of MTES consisted of 24-items categorized into six subscales. The six subscales correspond to the different types of motivation indicated in the self-determination continuum. Each subscale consisted of four items: Intrinsic motivation (1–4), integrated regulation (5–8), identified regulation (9–12), introjected regulation (13–16), external regulation (17–20) and amotivation (21–24). The items were rated using a 5-points Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (does not correspond at all) to 5 (correspond exactly). MTES is known to possess a high level of reliability. For this reason, MTES has been widely used to measure motivation towards the environment (e.g., [20,93])
Climate conserving behaviors in this study is measured using eight self-reported behavior items. The items focus on actions that decelerate the rate of climate change. The items in the self-reported climate conserving behaviors instrument were adapted from Dijkstra and Goedhart [28]. The students specified their degree of agreement to the climate change conserving behaviors using the 5-points Likert scale varying from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree).
Prior to this study, a pretesting was conducted to gauge the reliability of the instruments. For the pretesting purpose, 40 lower secondary students aged between 14 to 15 years from a secondary school, six expert teachers and two climate change experts from a university participated. A Cronbach’s alpha (α) = 0.755 for NEP, α = 0.816 for MTE and α = 0.725 was obtained for the Self-reported Climate Conserving Behaviors Measures. For Climate Change Knowledge Inventory, the Cronbach’s alpha values ranging from 0.7 to 0.9 denote the instruments are reliable for measuring knowledge, belief, motivation and behavior. The teachers and climate change experts indicated that the instruments are appropriate in terms of content and understandable for local students.
4. Data Collection
The study began with the researchers contacting the State Education Department seeking permission to perform research in schools. The State Education Department assisted the researchers with randomly assigning schools. The researchers then contacted the schools recommended by the state education department. The researchers visited the schools and discussed the research’s aim and procedures of the research with the school principals and the participating teachers. The teachers helped in administering the questionnaires to the students. Researchers contacted the assigned teacher from each school and hand over the questionnaires and collected back the answered questionnaires after two weeks.
5. Data Analysis
The objective of partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) is to maximize the explained variance of the endogenous latent construct (dependent variable) [94]. In the context of this study, the endogenous latent construct or dependent variable refers to climate change conserving behavior. PLS-SEM allows an explanation of exogenous latent constructs (independent variables) on the endogenous latent construct (dependent variable).
A PLS path model comprises of measurement and structural models formulated in testing the hypotheses. The measurement model exhibits the effects between the latent variables (construct) and the manifested variables (items). The structural model demonstrates the impact of the latent variables [95]. In this study, the manifest variables are knowledge (measured as K1 through K25), belief (measured as B1 through B15), motivation towards the environments (measured as M1 through M24) and climate conserving behavior (measured as CCB1 through CCB8). The four latent variables in this study are knowledge about climate change, belief, motivation and climate conserving behavior.
6. Results
6.1. Assessment of Measurement Model
The loading values of nine items from the knowledge inventory (K11, K13, K16, K17, K19, K20, K21, K24, K25) and one item from the motivation scale (M17) are lower than 0.5. For assessing the measurement model, items with loading values below 0.5 are removed [95]. The AVE values for knowledge, belief, motivation and climate conserving behaviors are more than the recommended threshold value of 0.5. Since the AVE values are greater than the threshold value of 0.5, the items with loading values of below 0.7 in all the questionnaires were retained for further analysis [96]. The CR values above 0.9 recorded for all the subscales infers that the items in the knowledge, belief, motivation and climate conserving behaviors possesses a relatively high level of internal consistency [95]. Table 2 shows the outcome of the measurement model assessment.

Table 2.
Assessment of Measurement Model.
The Fornell and Lacker Criterion, cross-loading comparisons and Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio were employed to analyze the discriminant validity of the measurement model.
The findings of discriminant analysis using Fornell and Lacker Criterion, as shown in Table 3 reveals that all the constructs exhibit satisfactory discriminant validity [97]. This is because the square root of AVE is larger than the correlations for all reflective constructs. The comparisons of the cross-loadings between constructs reveal that all the items load higher on its construct but lower on the other constructs. Table 4 illustrates the findings obtained from cross-loading comparisons.

Table 3.
Discriminant Validity using Fornell and Lacker Criterion.

Table 4.
Cross-Loadings.
Table 5 presents the findings of the analysis of discriminant validity obtained from Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio (HTMT) technique developed by Henseler, Ringle, and Sarstedt [98]. As shown in Table 5, all the values fulfil the criterion of HTMT90 [99] and HTMT85 [100]. This indicates that discriminant validity has been ascertained.

Table 5.
Discriminant Validity using Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio (HTMT) Criterion.
6.2. Assessment of Structural Model
Prior to evaluating the structural model, it is crucial to ensure that there is no lateral collinearity issue in the structural model. According to Kock and Lynn [101], although the criteria of discriminant validity (vertical collinearity) are met, lateral collinearity issue (predictor-criterion collinearity) may sometimes mislead the findings in a stealth way, because it can mask the strong causal effect in the model. This typically happens when two variables that are hypothesized to be causally related measures the same construct [102]. Table 6 presents the outcome of the lateral collinearity assessment. All the inner variance inflator factor (VIF) values for the independent variables (knowledge, belief and motivation) are less than 5, indicating lateral multicollinearity is not a concern in the study [95].

Table 6.
Lateral Collinearity Assessment.
In this study, literature guided the formulation of three direct hypotheses between the latent variables. The researchers generated t-statistics using SmartPLS 3.0 bootstrapping function to test the three hypotheses at the significance level of 0.05. The assessment of the path coefficient, as presented in Table 7, shows t-values ≥ 1.645 for all three paths. The findings imply that the effects are significant at the level of 0.05 [95]. Precisely, the predictors of knowledge (β = 0.259, p < 0.05), belief (β = 0.295, p < 0.05) and motivation (β = 0.546, p < 0.05) has a positive direct effect on the formation of climate conserving behaviors. Thus, H1, H2 and H3 are supported. The result demonstrates that motivation is the most significant predictor of climate conserving behaviors, followed by belief and knowledge. The R2 value of 0.655 above 0.26 indicates a substantial model [103]. The path diagram in Figure 2 shows that the combination of knowledge, belief and motivation explains 65.5% of the variances in the formation of climate conserving behaviors.

Table 7.
Hypothesis Testing.
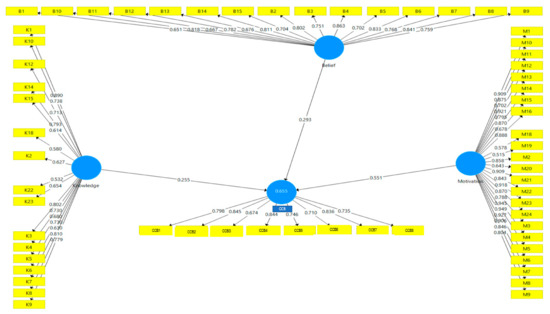
Figure 2.
Path Diagram shows the variances in the pro-environmental behavior (PEB) explained by all the exogenous construct.
The effect size (f2) was assessed to estimate the influence of independent latent variables on the dependent variable. According to Cohen [103], values of 0.02, 0.15 and 0.35 correspond to small, medium and substantial effect sizes. Findings in Table 7 suggest that motivation has a considerable effect (f2 = 0.683) on forming climate conserving behaviors. Both knowledge (f2 = 0.165) and belief (f2 = 0.218) show a moderate impact on the formation of climate conserving behaviors.
The predictive relevance of the model is examined using the blindfolding procedure. The Q2 = 0.383 larger than 0, suggest that the model has a substantial predictive relevance [95,104]. The reported effect size of knowledge (q2 = 0.057) on CCB and effect size of belief (q2 = 0.078) on CCB infers that both knowledge and belief produce weak effect. On the contrary, the effect size of motivation (q2= 0.216) on CCB is relatively large [95].
7. Discussion
The scarcity of information about the antecedents that inform climate conserving behaviors of Malaysian secondary students has prompted the researchers in performing this study. Subsequently, the study bridges the gap, on the absence of literature documenting the collective influence of knowledge about the environment, the belief that humans and nature are interconnected and self-determined motivation on formations of climate conserving behavior. The study documents several significant findings.
Firstly, the study reveals that knowledge about climate change has a significant positive direct effect on the formation of climate conserving behavior. The significant direct positive effects of knowledge on behavior documented in this study are parallel with other studies which reported knowledge is fundamental to trigger behavioral change [55] and behavior modification [56]. The findings also correspond to the claim that knowledge is a prerequisite to change behaviors to conserve the climate. Although the effect of knowledge on behavior is significant, the effect appeared small. Kim, Kim and Thapa [105] deliberated that the multidimensional perspective of knowledge contributes to the weak effect. Kim, Kim and Thapa [105] claim reflects the weak effect of knowledge on behavior in this study. This is because the knowledge component in this study reflects the multidimensional perspective as it measures students’ knowledge on climate change-related phenomena such as global warming, greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion, acid rain, weather and climate, ocean and climate change, land and climate change. Similar components of knowledge emerged in earlier studies that have investigated knowledge on climate change [32,51,52,65,66].
Secondly, the current study reveals the effects of human belief on climate conserving behaviors. The belief that there are ample resources in nature for them to extensively use the resources. Humans extensively exploit the limited resources available in nature and significantly affects the formation of climate conserving behavior in a positive direction. The findings mirror the claims made by environmental advocates that belief is crucial for developing pro-environmental behavior [34,67,68]. In the later years, the empirical findings of several studies confirm the claims made by the advocators that belief affects formation of climate conserving behaviors [44,48,75,76]. Although belief significantly affects behaviors, the effect is notably small. This is because students agree with the five facets of NEP, which represents the belief in this study. In other words, the students agree that climate and humans are interconnected, humans are not dominant over nature, human activities contribute to the excessive emission of greenhouse gases and exploitation of limited natural resources available in nature. However, to a larger extent, the students did not translate their agreement to the five facets of NEP into behavior [44,74].
Thirdly, the current study dictates that motivation significantly affects behavior formation in a positive direction. The finding echoes the idea that motivation drives individuals towards performing targeted actions [79,80,81]. The results of the current study corroborated earlier studies which demonstrate significant positive effects of different types of motivation and environmental behaviors including climate conserving behaviors [50,79,80,81,83,84,85,86]. This nature of the Malaysian secondary curriculum explains the considerable large effect size of motivation. Environmental education has been integrated across several subjects offered at the secondary level [106]. Education informs the students that human action largely contributes to the destruction of the environment. Knowing humans are responsible for protecting and conserving nature, different types of regulations, as indicated in SDT continuum, affected students’ pro-environmental behaviors environment. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation are associated with different kinds of regulations that determine the ultimate behavior.
Next, the study reveals that the three constructs of knowledge about climate change, believing human and nature are the interconnected and self-determined motivation that arises from one’s inert feelings in combination exhibited significant positive effects in developing climate conserving behaviors. The three constructs in combination explain 65.5% of variances in the formation of climate conserving behavior among Malaysian secondary school students. The point to note here is that knowledge and belief in the silo generated small effects on behavior. However, in the combined state, greater effects were established. This infers that demographic, external and internal factors are integral in forming climate conserving actions [36]. The contemporary local extreme weather conditions, the adverse effects of climate change on lay peoples’ everyday living, the impact on the peoples’ income and the abrupt change in the lifestyle influences the students’ decision making about their behavior. Additionally, the model that dictates the collective effects of knowledge, belief and motivation on behavior complements the use of existing prominent theories, namely TPB and VBN, in describing the climate conserving behaviors.
8. Conclusions
The study has several significant contributions to the literature. Firstly, the study reports the collective effects of knowledge, belief and motivation on behavior formation. The collective effects of the variables identified in the current study contribute to the literature. This is because literature predominately documented the role of the three variables in forming behaviors in isolation [20,25,48,50,52,54]. Secondly, the study attempted to include knowledge as one of the variables. In the past various other factors ruled out to influence behavior [27,29,48,49]. The current research informs that knowledge distinctively has a small effect. However, in combination with belief and motivation, knowledge plays an instrumental role. Thirdly, the study reports that self-determined motivation largely contributes to climate conserving behavior formation. The findings on the motivation bridge the gap on the availability of minimal literature associating climate change behavior and motivation.
Throughout the research, stringent measures have been undertaken to control the internal and external threats to the validity of the research. However, the study exhibits several limitations. One of the limitations is the sample size and characteristics of the sample. The sample size and characteristics limit the generalization of the findings to other parts of the country. The sample size (n = 221) of the study is sufficient to test the hypothesis and to develop a model [88]. The sample that participated in this study are from the Northern Region of the country. The samples represent the populations of lower secondary students in the country because Malaysia practices centralized education system. The schools throughout the country implement the same curriculum provided by the Ministry of Education to the students [106]. However, to improve the validity of the model further study is recommended involving a large sample size with students from different parts of the country.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and N.S.M.A.K.; Data curation, N.S.M.A.K.; Formal analysis, M.K. and N.S.M.A.K.; Funding acquisition, M.K.; Methodology, M.K. and N.S.M.A.K.; Supervision, M.K.; Validation, M.K. and N.S.M.A.K.; Writing—original draft, M.K. and N.S.M.A.K.; Writing—review & editing, M.K., N.A. and N.S.M.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded through Research University Grant provided by Universiti Sains Malaysia. The grant number is [1001/PGURU/8016082].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Roberts, H.O.P., Skea, D., Shukla, J., Pirani, P.R., Moufouma-Okia, A., Péan, W., Pidcock, C., Connors, R., et al., Eds.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, S.C. Communicating Climate Change: History, Challenges, Process and Future Directions. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Williams, A.P.; Barbero, R. Global Emergence of Anthropogenic Climate Change in Fire Weather Indices. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernesto, R.-C. Chapter 2 A Review of the Current Science of Climate Change. In Tourism and the Implications of Climate Change: Issues and Actions; Schott, C., Ed.; Bridging Tourism Theory and Practice; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezér, M.A. Computer Models and the Evidence of Anthropogenic Climate Change: An Epistemology of Variety-of-Evidence Inferences and Robustness Analysis. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part A 2016, 56, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Global Anthropogenic Non-CO; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E. Climate Change Caused by Human Activities Is Happening and It Already Has Major Consequences. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law 2018, 36, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junsheng, H.; Akhtar, R.; Masud, M.M.; Rana, M.S.; Banna, H. The Role of Mass Media in Communicating Climate Science: An Empirical Evidence. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A. Climate Change Education for Mitigation and Adaptation. J. Educ. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 6, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liarakou, G.; Athanasiadis, I.; Gavrilakis, C. What Greek Secondary School Students Believe about Climate Change? Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2011, 6, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A. Global Climate Change: What Has Science Education Got to Do with It? Sci. Educ. 2012, 21, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, A.; Shepardson, D.P.; Hirsch, A.; Niyogi, D.; Jignesh, M.; Top, S. The Need to Introduce System Thinking in Teaching Climate Change. Sci. Educ. 2017, 25, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, R.B.; Nicholls, J.; Whitehouse, H. What Is Climate Change Education? Curric. Perspect. 2017, 37, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). In The Paris Agreement; UNFCCC: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNCED. UN Conference on Environment and Development. In Agenda 21—Action Plan for the Next Century; UNCED: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, V. Western Australian High School Students’ Understandings about the Socioscientific Issue of Climate Change. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, B.; Sesto, V.; García-Rodeja, I. An Investigation of Secondary Students’ Mental Models of Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect. Res. Sci. Educ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Pascua, L. Singapore Students’ Misconceptions of Climate Change. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2016, 25, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpudewan, M.; Mohd Ali Khan, N.S. Experiential-Based Climate Change Education: Fostering Students’ Knowledge and Motivation towards the Environment. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2017, 26, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepardson, D.P.; Roychoudhury, A.; Hirsch, A.S.; Top, S.M. Students’ Conception of a Climate System. In Teaching and Learning about Climate Change: A Framework for Educators; Shepardson, D.P., Roychoudry, A., Hirsch, A.S., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinfried, S.; Aeschbacher, U.; Rottermann, B. Improving Students Conceptual Understanding of the Greenhouse Effect Using Theory-Based Learning Materials That Promote Deep Learning. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2012, 21, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, K.S.; Libarkin, J.C.; Ledley, T.S.; Bardar, E.; Haddad, N.; Ellins, K.; Dutta, S. The Role of Research in Online Curriculum Development: The Case of EarthLabs Climate Change and Earth System Modules. J. Geosci. Educ. 2014, 62, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, A.; Sadler, T.; Kinslow, A.; Zangori, L.; Friedrichsen, P. Climate Change as an Issue for Socio-Scientific Issues Teaching and Learning. Teach. Learn. Clim. Chang. A Framew. Educ. 2017, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, K.T.; Nils Peterson, M.; Bondell, H.D. Developing a Model of Climate Change Behavior among Adolescents. Clim. Chang. 2018, 151, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, F.; Klima, K.; Posen, I.D.; Azevedo, I.M.L. A New Approach of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Outreach in Climate Change, Energy, and Environmental Decision Making. Sustainability 2015, 8, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M.T.J.; Powell, R.B.; Hallo, J.C. A Review of the Foundational Processes That Influence Beliefs in Climate Change: Opportunities for Environmental Education Research. Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.M.; Goedhart, M.J. Development and Validation of the ACSI: Measuring Students’ Science Attitudes, pro-Environmental Behaviour, Climate Change Attitudes and Knowledge. Environ. Educ. Res. 2012, 18, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, A.C.; Meyer, M.A. Teaching Urban High School Students Global Climate Change Information and Graph Interpretation Skills Using Evidence from the Scientific Literature. J. Geosci. Educ. 2009, 57, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, M.C.; Plate, R.R.; Oxarart, A.; Bowers, A.; Chaves, W.A. Identifying Effective Climate Change Education Strategies: A Systematic Review of the Research. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 4622, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandar, R.; Poyyamoli, G. Activity-Based Water Resources and Climate Change Education Among School Students in Puducherry. In Climate Change and the Sustainable Use of Water Resources; Leal Filho, W., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 557–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruneau, D.; Gravel, H.; Bourque, W.; Langis, J. Experimentation with a Socio-Constructivist Process for Climate Change Education. Environ. Educ. Res. 2003, 9, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. Climate Change in Malaysia: Trends, Contributors, Impacts, Mitigation and Adaptations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, P.C. Psychology and the Science of Human-Environment Interactions. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steg, L.; Vlek, C. Encouraging Pro-Environmental Behaviour: An Integrative Review and Research Agenda. J. Environ. Psychol. 2009, 29, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmuss, A.; Agyeman, J. Mind the Gap: Why Do People Act Environmentally and What Are the Barriers to pro-Environmental Behavior? Environ. Educ. Res. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.; Harrison, C.M.; Filius, P. Environmental Communication and the Cultural Politics of Environmental Citizenship. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Sp. 1998, 30, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.-K.; Ellinger, A.E.; Hadjimarcou, J.; Traichal, P.A. Consumer Concern, Knowledge, Belief, and Attitude toward Renewable Energy: An Application of the Reasoned Action Theory. Psychol. Mark. 2000, 17, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotch, C.; Hall, T. Understanding Nature-related Behaviors among Children through a Theory of Reasoned Action Approach. Environ. Educ. Res. 2004, 10, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Hwang, Y. Predictors of Pro-Environmental Behaviors of American and Korean Students: The Application of the Theory of Reasoned Action and Protection Motivation Theory. Sci. Commun. 2012, 35, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.C.; Dietz, T.; Abel, T.; Guagnano, G.A.; Kalof, L. A Value-Belief-Norm Theory of Support for Social Movements: The Case of Environmentalism. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 1999, 6, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fielding, K.S.; Hornsey, M.J. A Social Identity Analysis of Climate Change and Environmental Attitudes and Behaviors: Insights and Opportunities. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpudewan, M. The Relationships between Values, Belief, Personal Norms, and Climate Conserving Behaviors of Malaysian Primary School Students. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-F. An Examination of the Value-Belief-Norm Theory Model in Predicting pro-Environmental Behaviour in Taiwan. Asian J. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 18, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Media Use, Environmental Beliefs, Self-Efficacy, and pro-Environmental Behavior. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamp, K.; Boyes, E.; Stannistreet, M. Global Warming Responses at the Primary Secondary Interface 1. Students’ Beliefs and Willingness to Act. Aust. J. Environ. Educ. 2009, 25, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, M.; Fiedor, D.; Frajer, J.; Hercik, J.; Jurek, M. Czech Students and Mitigation of Global Warming: Beliefs and Willingness to Take Action. Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, L.T.O.; Chow, A.S.Y.; Fok, L.; Yu, K.-M.; Chou, K.-L. The Effect of Self-Determined Motivation on Household Energy Consumption Behaviour in a Metropolitan Area in Southern China. Energy Effic. 2017, 10, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valkengoed, A.M.; Steg, L. Meta-Analyses of Factors Motivating Climate Change Adaptation Behaviour. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzin, A.M.; Anastasio, D.; Sahagian, D.; Peffer, T.; Dempsey, C.; Steelman, R. Investigating Climate Change Understandings of Urban Middle-Level Students. J. Geosci. Educ. 2014, 62, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpudewan, M.; Roth, W.-M.; Chandrakesan, K. Remediating Misconception on Climate Change among Secondary School Students in Malaysia. Environ. Educ. Res. 2015, 21, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-S.; Lin, K.-Y.; Guu, Y.-H.; Chang, L.-T.; Lai, C.-C. The Effect of Hands-on ‘Energy-Saving House’ Learning Activities on Elementary School Students’ Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behavior Regarding Energy Saving and Carbon-Emissions Reduction. Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 19, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpudewan, M.; Roth, W.M.; Abdullah, M.N.S.B. Enhancing Primary School Students’ Knowledge about Global Warming and Environmental Attitude Using Climate Change Activities. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2015, 37, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimlich, J.E.; Ardoin, N.M. Understanding Behavior to Understand Behavior Change: A Literature Review. Environ. Educ. Res. 2008, 14, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungerford, H.R.; Volk, T.L. Changing Learner Behavior through Environmental Education. J. Environ. Educ. 1990, 21, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, R.; Fien, J.; Packer, J. Program Effectiveness in Facilitating Intergenerational Influence in Environmental Education: Lessons From the Field. J. Environ. Educ. 2001, 32, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harness, H.; Drossman, H. The Environmental Education through Filmmaking Project. Environ. Educ. Res. 2011, 17, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Dierkes, P. Evaluating Three Dimensions of Environmental Knowledge and Their Impact on Behaviour. Res. Sci. Educ. 2019, 49, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, A.; Chang, C.H. Promoting Pro-Environmental Behaviour in a Community in Singapore–from Raising Awareness to Behavioural Change. Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 25, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, R.; Le Grange, L.; Beets, P. Climate Change Science: The Literacy of Geography Teachers in the Western Cape Province, South Sfrica. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2015, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halady, I.R.; Rao, P.H. Does Awareness to Climate Change Lead to Behavioral Change? Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2010, 2, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, J.; Kaiser, F.G.; Wilson, M. Environmental Knowledge and Conservation Behavior: Exploring Prevalence and Structure in a Representative Sample. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2004, 37, 1597–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bofferding, L.; Kloser, M. Middle and High School Students’ Conceptions of Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies. Environ. Educ. Res. 2015, 21, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepardson, D.P.; Niyogi, D.; Choi, S.; Charusombat, U. Seventh Grade Students’ Conceptions of Global Warming and Climate Change. Environ. Educ. Res. 2009, 15, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, A.; Stanisstreet, M.; Boyes, E. Turkish Students’ Ideas about Global Warming. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2008, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap, R.E.; Van Liere, K.D. The “New Environmental Paradigm”. J. Environ. Educ. 1978, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon Thompson, S.C.; Barton, M.A. Ecocentric and Anthropocentric Attitudes toward the Environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 1994, 14, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, K.S.; Head, B.W. Determinants of Young Australians’ Environmental Actions: The Role of Responsibility Attributions, Locus of Control, Knowledge and Attitudes. Environ. Educ. Res. 2012, 18, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, N.S.; Bhullar, N. Approaching Environmental Sustainability: Perceptions of Self-Efficacy and Changeability. J. Psychol. 2017, 151, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, R.E.; Van Liere, K.D.; Mertig, A.G.; Jones, R.E. New Trends in Measuring Environmental Attitudes: Measuring Endorsement of the New Ecological Paradigm: A Revised NEP Scale. J. Soc. Issues 2000, 56, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawcroft, L.J.; Milfont, T.L. The Use (and Abuse) of the New Environmental Paradigm Scale over the Last 30 Years: A Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, R.E. The New Environmental Paradigm Scale: From Marginality to Worldwide Use. J. Environ. Educ. 2008, 40, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, A.C.; Woosnam, K.M.; Keith, S.J.; Tarrant, M.A.; Rubin, D.M.; Ling, S.T. Understanding and Modifying Beliefs about Climate Change through Educational Travel. J. Sustain. Tour. 2019, 27, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, A.; Paloniemi, R. Does Belief Matter in Climate Change Action? Public Underst. Sci. 2011, 22, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.; Knezek, G. Impact of Middle School Student Energy Monitoring Activities on Climate Change Beliefs and Intentions. Sch. Sci. Math. 2018, 118, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Overview of Self-Determination Theory: An Organismic-Dialectical Perspective. In Handbook of Self-Determination Research; University of Rochester Press: Rochester, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Osbaldiston, R.; Sheldon, K.M. Promoting Internalized Motivation for Environmentally Responsible Behavior: A Prospective Study of Environmental Goals. J. Environ. Psychol. 2003, 23, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, A.N.; Fielding, K.S.; Louis, W.R. Environmentally Active People: The Role of Autonomy, Relatedness, Competence and Self-Determined Motivation. Environ. Educ. Res. 2016, 22, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpudewan, M.; Roth, W.M.; Ismail, Z. The Effects of “Green Chemistry” on Secondary School Students’ Understanding and Motivation. Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 2013, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, A.; Maleksaeidi, H. Pro-Environmental Behavior of University Students: Application of Protection Motivation Theory. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongiglione, F. Motivation for Adopting Pro-Environmental Behaviors: The Role of Social Context. Ethics Policy Environ. 2014, 17, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, A.R. Motivating Pro-Environmental Behavior: The Use of Feedback and Peer Education to Promote Energy Conservation in an Organizational Setting; Vanderbilt University: Nashville, TN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Balundė, A.; Perlaviciute, G.; Steg, L. The Relationship Between People’s Environmental Considerations and Pro-Environmental Behavior in Lithuania. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, S. Intrinsic Motivation and Pro-Environmental Behaviour. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Becker, J.-M. “SmartPLS 3.” Boenningstedt SmartPLS GmbH 2015. Available online: http://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 6 March 2020).
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; SAGE: Thousands Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, H.O.; Cigdemoglu, C.; Moseley, C. A Three-Tier Diagnostic Test to Assess Pre-Service Teachers’ Misconceptions about Global Warming, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion, and Acid Rain. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2012, 34, 1667–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libarkin, J.C.; Gold, A.U.; Harris, S.E.; McNeal, K.S.; Bowles, R.P. A New, Valid Measure of Climate Change Understanding: Associations with Risk Perception. Clim. Chang. 2018, 150, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, L.G.; Tuson, K.M.; Green-Demers, I.; Noels, K.; Beaton, A.M. Why Are You Doing Things for the Environment? The Motivation Toward the Environment Scale (MTES)1. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 28, 437–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, I.; Taddicken, M.; Reif, A. What Do People Know about Climate Change—And How Confident Are They? On Measurements and Analyses of Science Related Knowledge. J. Sci. Commun. 2018, 17, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Darner, R. An Empirical Test of Self-Determination Theory as a Guide to Fostering Environmental Motivation. Environ. Educ. Res. 2012, 18, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a Silver Bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousands Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Babin, B.J.; Krey, N. Covariance-Based Structural Equation Modeling in the Journal of Advertising: Review and Recommendations. J. Advert. 2017, 46, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A New Criterion for Assessing Discriminant Validity in Variance-Based Structural Equation Modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.H.; Malhotra, A.; Segars, A.H. Knowledge Management: An Organizational Capabilities Perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2001, 18, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N.; Lynn, G.S. Lateral Collinearity and Misleading Results in Variance-Based SEM: An Illustration and Recommendations. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2012, 13, 546–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramayah, T.; Cheah, J.; Chuah, F.; Ting, H.; Memon, M.A. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using SmartPLS 3.0: An Updated and Practical Guide to Statistical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Singapore: Pearson, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Cha, J. Partial Least Squares. In Advanced Methods of Marketing Research; Bagozzi, R., Ed.; Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 52–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.; Thapa, B. Influence of Environmental Knowledge on Affect, Nature Affiliation and Pro-Environmental Behaviors among Tourists. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Education Malaysia [MOE]. Secondary School Standard Curriculum: Form 2 Science Curriculum and Assessment Standard Document; Curriculum Development Centre, Ministry of Education: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).