Abstract
The Industrial Internet of things (IIoT) helps several applications that require power control and low cost to achieve long life. The progress of IIoT communications, mainly based on cognitive radio (CR), has been guided to the robust network connectivity. The low power communication is achieved for IIoT sensors applying the Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) with the Sigfox, NBIoT, and LoRaWAN technologies. This paper aims to review the various technologies and protocols for industrial IoT applications. A depth of assessment has been achieved by comparing various technologies considering the key terms such as frequency, data rate, power, coverage, mobility, costing, and QoS. This paper provides an assessment of 64 articles published on electricity control problems of IIoT between 2007 and 2020. That prepares a qualitative technique of answering the research questions (RQ): RQ1: “How cognitive radio engage with the industrial IoT?”, RQ2: “What are the Proposed architectures that Support Cognitive Radio LPWAN based IIOT?”, and RQ3: What key success factors need to comply for reliable CIIoT support in the industry?”. With the systematic literature assessment approach, the effects displayed on the cognitive radio in LPWAN can significantly revolute the commercial IIoT. Thus, researchers are more focused in this regard. The study suggests that the essential factors of design need to be considered to conquer the critical research gaps of the existing LPWAN cognitive-enabled IIoT. A cognitive low energy architecture is brought to ensure efficient and stable communications in a heterogeneous IIoT. It will protect the network layer from offering the customers an efficient platform to rent AI, and various LPWAN technology were explored and investigated.
1. Introduction
LPWAN provides long-distance communication for rural and urban areas to support IIoT devices considered by a 10-year provision time to acclimate IIoT applications with higher extensibility and availability of intelligent monitoring infrastructure for a small portion of data exchanges. LoRa is favorable to use with smart sensing applications working on the IIoT non-authored spectrum [1]. NBIoT is suitable for supporting agriculture and environmental data collection and observations; industrial data tracking and monitoring; inventory tracking; smart billing; and smart buildings, smart metering, and smart cities. Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication uses the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technique for data communication; the other IIoT applications used in healthcare, smart agriculture, intelligent home, smart vehicles, smart city, smart gadgets, and industries use the cognitive LPWAN, LoRA, Sigfox [2,3,4,5,6,7]. Figure 1 shows the various sectors of IIoT applications. There is a need to mix most LPWAN technologies in heterogeneous IIoT applications to provide more efficient and convenient intelligent services. In heterogeneous IIoT applications, there is a need to mix most LPWAN technologies to provide more efficient and convenient intelligent services. This will be deployed by cognitive LPWAN [8].
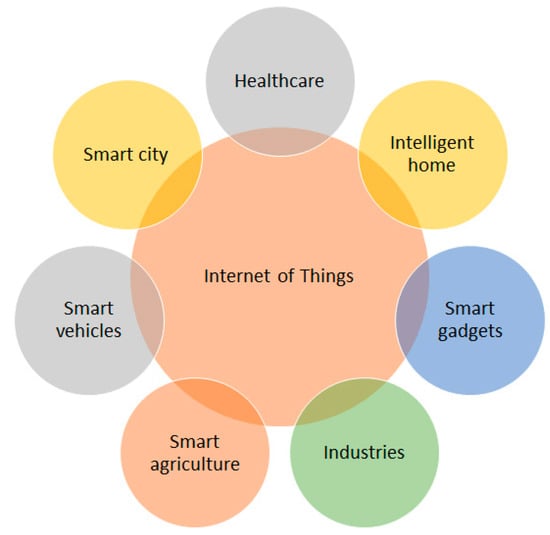
Figure 1.
Various sectors of IIoT applications.
Cognitive LPWAN will provide promising IIoT systems strategies and improve spectrum usage to increase network performance. The use of cognitive radio will help overcome the limitations due to several IIoT infrastructure things. Cognitive devices in LPWAN can work collaboratively more than available spectrum allocations. The LPWANs can share channels and events because of the extra traffic packets within the specific event area, thereby striving to block the channel concurrently [9,10,11]. The most sophisticated Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), based on applications for smart cities, industries, metering, and home architectures, are required to transmit data over long distances, consume low energy, and to be cheaper and highly scalable [12,13,14]. However, the design mechanism requires maintaining the existing cellular communication technologies.
Thus, it has been a recent research prospect to meet-up all the above requisites related to IIoT-based applications, and due to the importance of the matter, newer and more suitable communication technologies such as Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) started to appear with no delay. LPWAN is currently being utilized in numerous applications based on Industrial IoT (IIoT) due to their merits of offering low power consumption rates, long transmission range, low cost, simplified network topology, scalable and simple deployment, small data frame sizes [14], and thin infrastructure; even though it has low data rates [15]. According to the estimation provided in [16], 800 million IIoT devices may become connected over LPWAN standards by 2022 due to the good qualities and advantages of LPWAN. However, there is a concern that most LPWAN will typically suffer from spectra congestion due to their major deployment in the unlicensed Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) band [17]. This demerit may cause increased interference, limited scalability, spectral inefficiency, and reduced transmission range to LPWAN systems [18].
As an aftermath, the necessity to mitigate the above limitations has encouraged the recent paradigm shift to integrate Cognitive Radio (CR) in LPWAN. The maturity of the study of CR has happened recently, intending to improve efficiency and spectral utilization in wireless communication systems; CR can automatically detect available channels in a wireless spectrum and alter its transmission parameters to ensure improved communication and radio operating behavior [19]. CR has gained better consideration under new IEEE standards such as IEEE 802.15.2, IEEE 802.22, and IEEE Standards Coordinating Committee (SCC) due to the capability of CR to solve some problems related to wireless communications, e.g., interference, delayed network deployment, and spectral efficiency [20,21,22,23]. Moreover, CR has been utilized in many IIoT-based applications [24], e.g., improving the Quality of Service (QoS) in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)-based smart grid applications [25]. Cognitive radio has also made its mark to mitigate interference in industrial WSNs (IWSNs) and fulfills the QoS requirement by improving the latency, transmission, and frame losses challenges [26].
This analysis aims to research the literature on cognitive radio in LPWAN for industrial IoT. We investigate different studies providing different backgrounds for study and their relationships. The following research questions (RQ): RQ1: “How cognitive radio engage with the industrial IoT?”, RQ2: “What are the Proposed architectures that Support Cognitive Radio LPWAN based IIOT?”, and RQ3: What key success factors need to comply for reliable CIIoT support in the industry?”.
The main contribution of this paper is a systematic literature assessment on a long variety of extensive location (LoRa), Sigfox era, long time evolution class m (LTE-m) [27], and narrowband internet of things (NBIoT) in low electricity extensive location LPWAN technology with an unlicensed spectrum [28,29]. Cognitive LPWAN allows industrial IoT applications for smart city services to access different wireless connectivity and selects appropriate communication technologies to achieve the best interaction experience [30,31,32].
The article is organized as consisting of three sections. Section 2 presents a comprehensive study on methods, material and methods, where it discusses the data collection, searching, and selecting the papers, and covers a depth review on cognitive-enabled industrial IoT applications, methods with pros and cons. Section 2 also answered each of the research questions and highlighted the deployment’s significance, the determinant factors for designing, and modeling cognitive-enabled industrial IoT frameworks. Section 3 presents the concluding remarks, with future scope for this work being suggested.
2. Materials and Methods
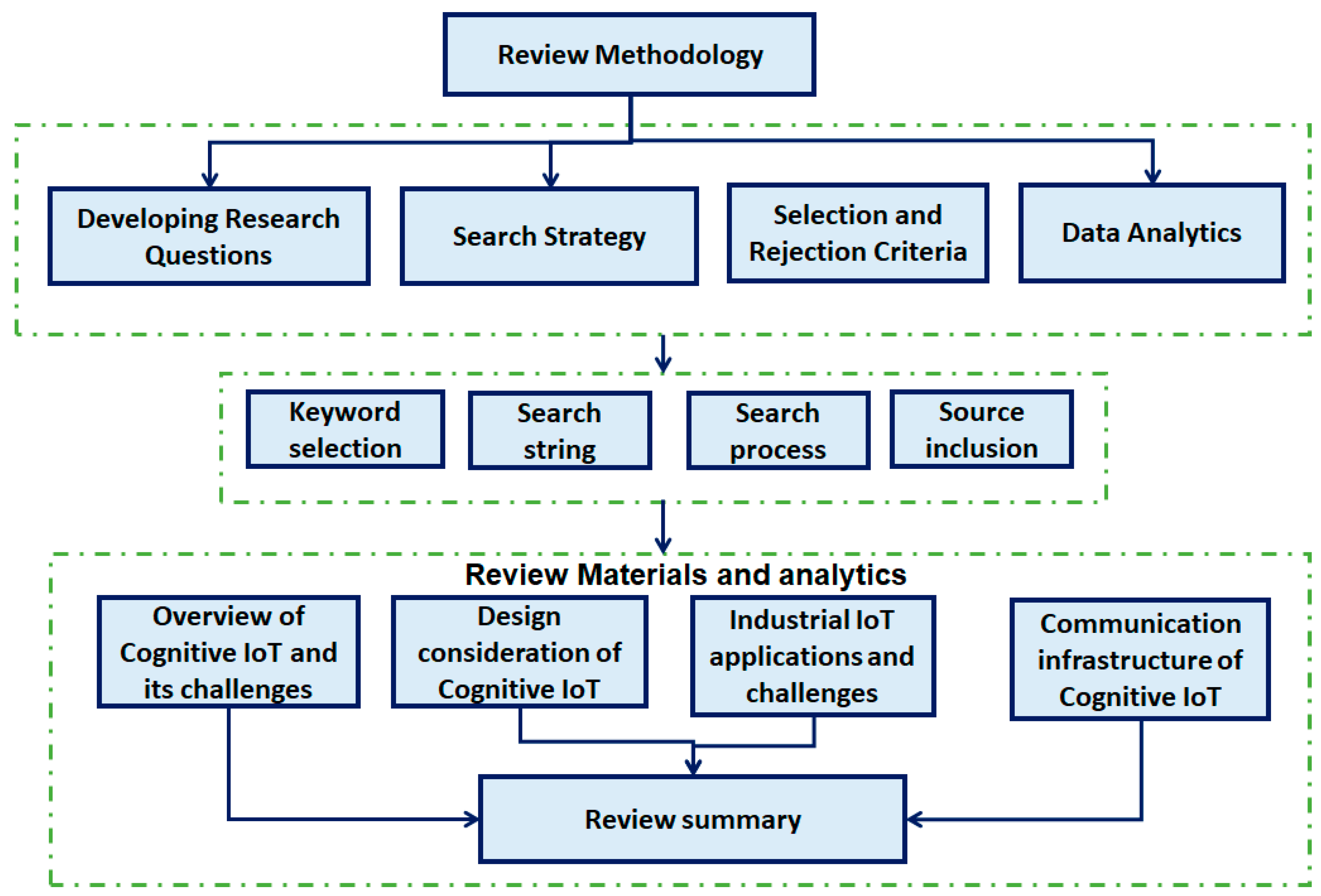
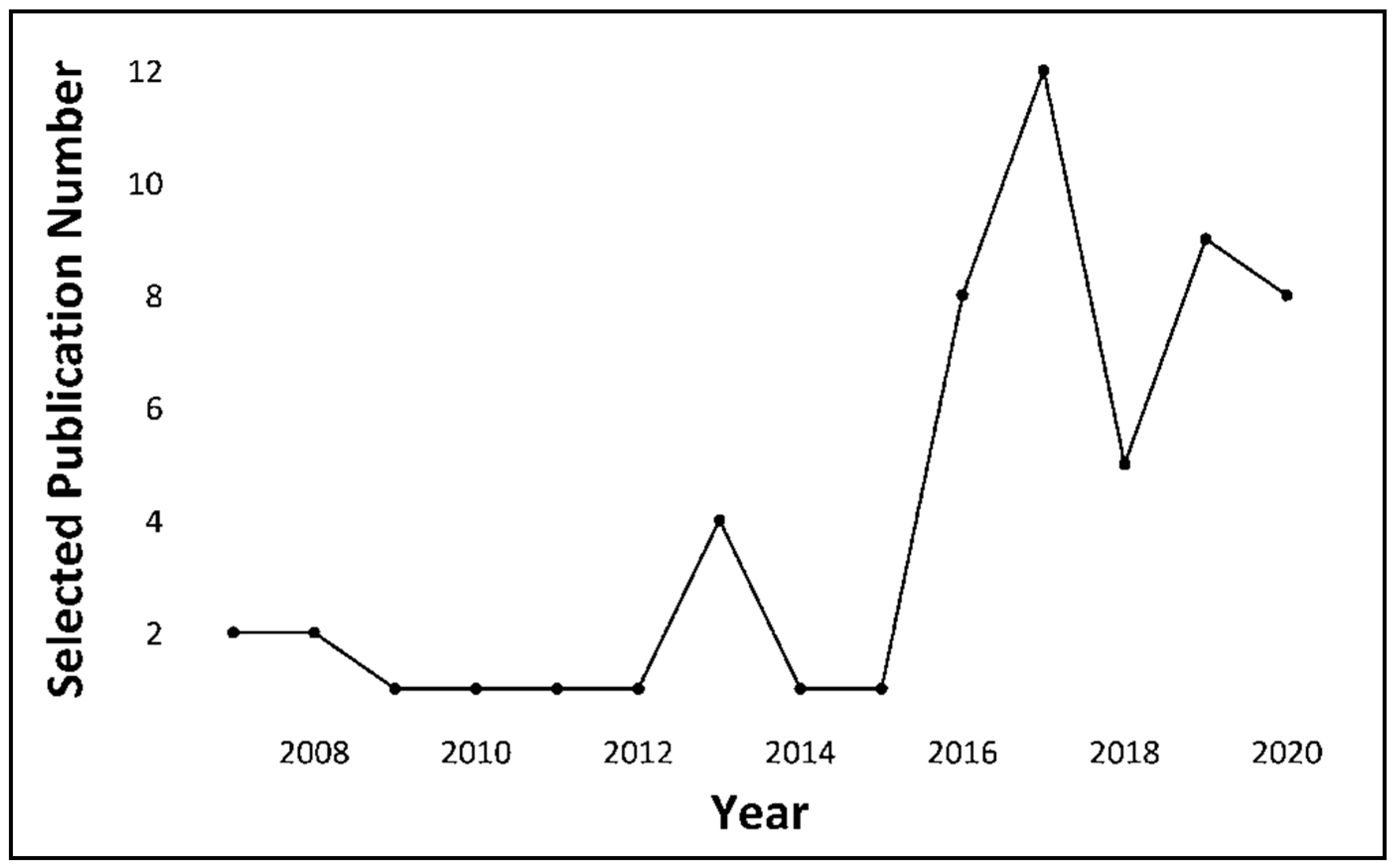
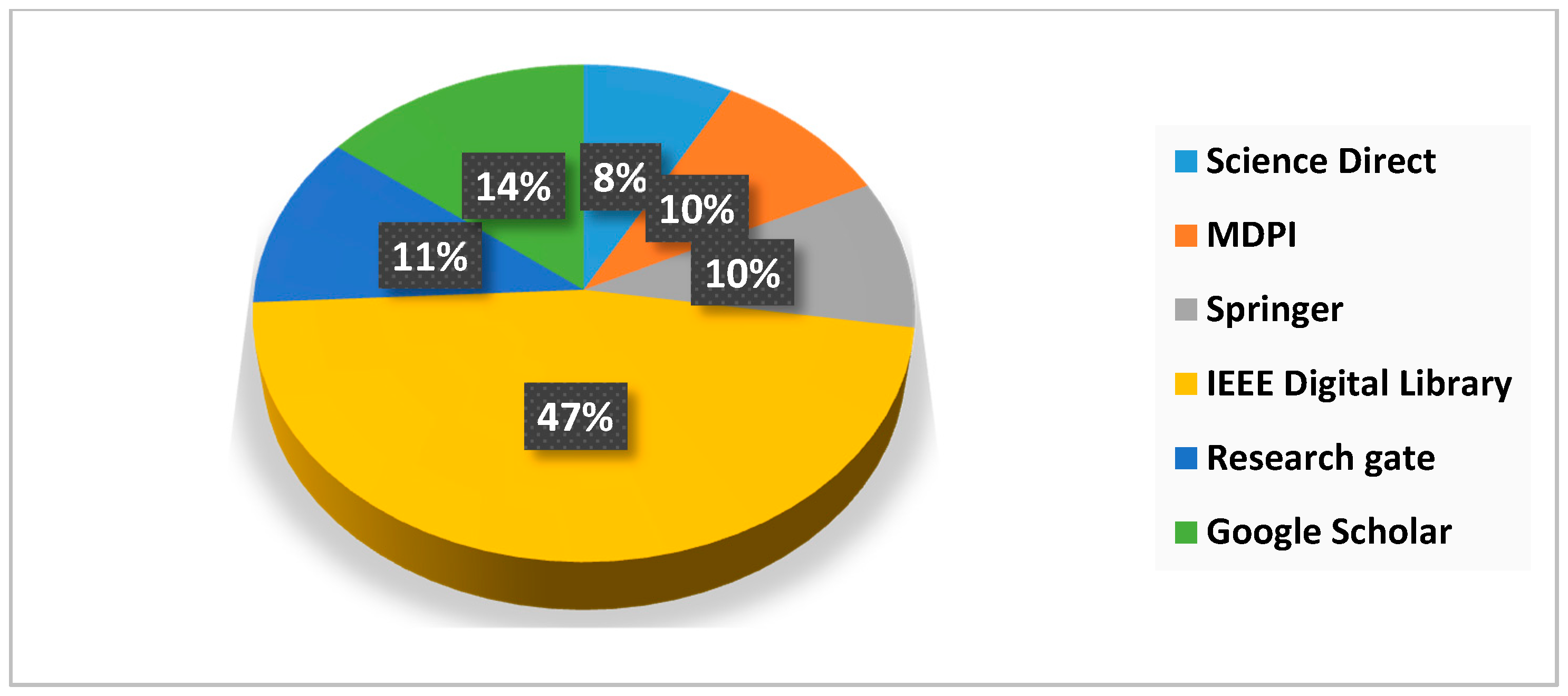
This study considers the systematic review technique a suitable approach to address particular research questions by applying the several phases that can be categorized into three parts—preparation, leading, and reporting the review. Figure 2 presents the overall review methodology for cognitive-enabled IIoT methods for different industrial applications. The data/paper selection methodology for the year and the source is illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
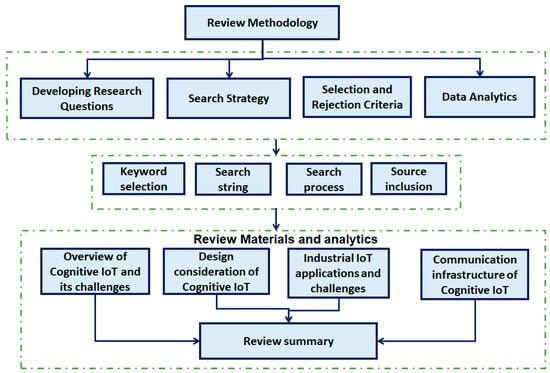
Figure 2.
Review methodology.
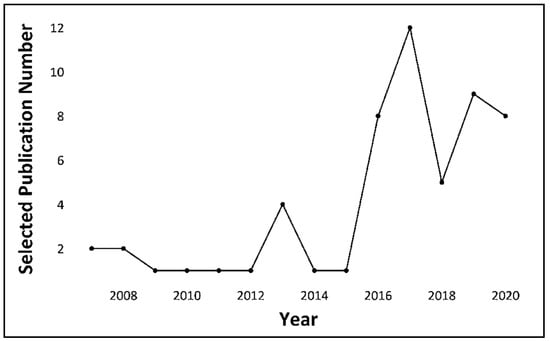
Figure 3.
Selected publication over the years (2007–2020).
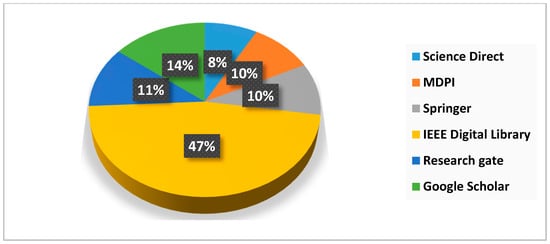
Figure 4.
Sources of publication that have been considered for review.
This study’s review methodology focused on the existing approaches, techniques, and design principles of industrial IIoT applications in LPWAN. All the relevant data (journals and conferences within 2007–2020) were collected and arranged during the first phase (preparation phase): the background and formulated research questions RQ1, RQ2, and RQ3. The review of the existing methods components and data sources are highlighted in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 1.
Comparison Technologies of Low Power WAN [10,13,18,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,33,34].

Table 2.
Summarized comparative analysis of CR LWPAN technologies for the Industrial IoT applications [16,17,22,35,36,37].

Table 3.
Summary of Industrial IoT features with the various parameter requirements [16,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61].

Table 4.
Summary of the different Cognitive Industrial IoT technologies and applications.
2.1. How Cognitive Radio Engage with the Industrial IoT?
The Cognitive Radio (CR) technologies for the Industrial IoT (IIoT) have been impressive. Many researchers have been considering the CR-based IIoT for industrial applications and proposing several approaches, techniques, and design principles using the LPWAN. In this section, the standards, protocols, devices, and methodologies will be discussed to articulate the engagement of CR in IIoT applications.
2.1.1. LPWAN for IIoT
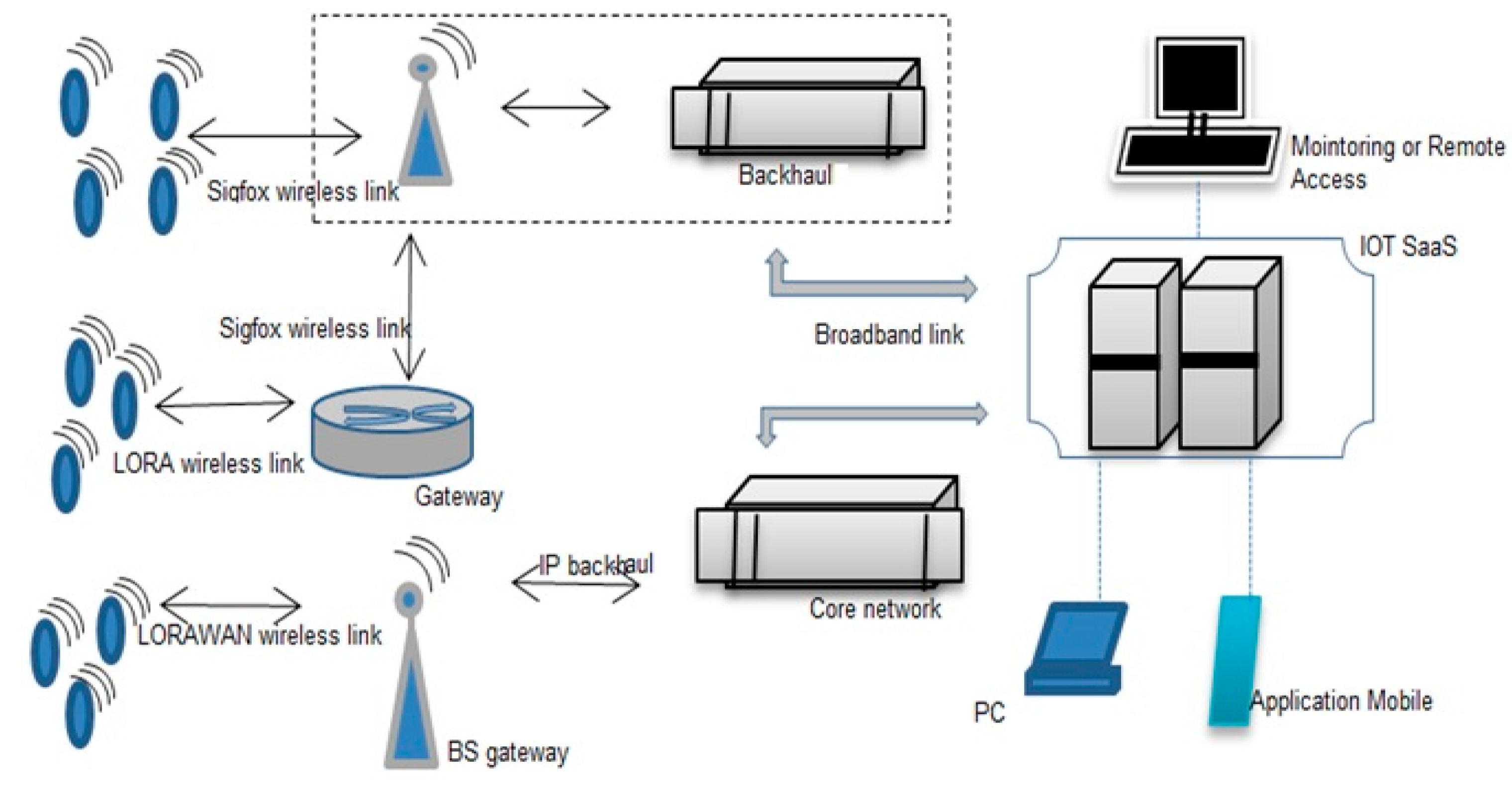
LPWAN is considered an efficient technology for IIoT applications, which promises high-energy efficiency and coverage capability with low power consumption [31]. The LPWAN approaches such as Sigfox, LoRA, NBIoT, and other licensed cellular IIoT technologies standardized by 3GPP such as eMTC (LTE-Cat-M1) and 5G cellular IIoT are all represented for IIoT applications and expected to be part of the new 5G framework by 2020 [32]. Multiple access levels have been applied using LPWAN for IIoT applications. In a mixed LPWAN network, Sigfox can collect the IIoT data using LoRaWAN [33] intermediary devices to facilitate connectivity to the IIoT core network, as shown in Figure 5. The LTE and 5G as wireless Access technology based on the Internet of Things connect the cells such as NBIoT, WiFi, and LoRa [38]. The comparison is shown in Table 1.
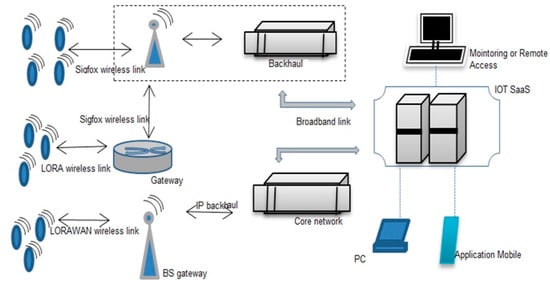
Figure 5.
Mixed LPWAN for IIoT architecture [32,33,34].
In Mixed LPWAN, device management functions are: registration, authentications, data traffic, speed transmission, and bandwidth performance using the core network. The consistency of network servers in LPWAN occurs to control the LoRaWAN base stations’ traffic flow to provide received payload [39]. Base stations forward the collected data to the IIoT SaaS to manage the database contents.
Generally, LPWA networks are suffering from latency limitations that are mitigated, and the highest rate demand is replaced by long coverage range and low consumption [40]. The inverse demand for the two technologies such as IIoT concerns big applications, and it is accessing that traditional cellular networks will still be a resolution, for example, non-energy-constrained issues that request high data rates [41]. CR delivers capacity through spectrum sensing. So, CR obtains the best frequency through the interaction with its radio setting [42]. That is very important for CR to increase the frequency utilization for scare radio resources. Lately, research has been projected using multiple access technologies for unlicensed frequency allocation [43].
IIoT system can control the frequency dynamically using cognitive radio power that maximizes radio utilization and system performance. In CR LPWANs, the radio channel between the licensed networks and the unlicensed BS only can take place within the cellular radio coverage area [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. For convenient resource allocation by following QoS rules, the channel bandwidth allocation in LPWAN is made well-defined in wireless applications [45,46,47]. Hence, LPWANs face no difficulties during serving the traffic for wireless applications, even though QoS has strict requirements [48]. Moreover, CR-LPWAN is seen to be efficient whenever the primary radio network (PRN) system’s radio spectrum remains underutilized, even though it has various resources. Therefore, the dynamic spectrum access is essential for efficiently managing the spectrum in CR-LPWANs for IIoT sensor nodes densely deployed [44]. Spectrum sensing functionality is the factor that distinguishes CR-LPWAN from conventional WSN.
CR can adjust the operating parameters of its spectrum sensing capability dynamically; utilizing this can determine the vacant bands [45]. CR manages these vacant bands efficiently to improve the utilization of the overall spectrum. There are two distinct categories of radio: active region using licensed bands and active region unlicensed bands. Likewise, radio users can be classified into two types—Licensed PUs and Unlicensed CUs [46]. The unlicensed CUs can use available licensed channels, only if no interference is caused for the licensed users. The unlicensed CUs in CU-WPLAN use the IoT devices to detect licensed PU’s activity through spectrum sensing whenever licensed PUs use the available licensed channels. Therefore, CR should have the capability to operate both in licensed and unlicensed bands, as PUs cannot fully take advantage of the licensed spectrum bands [47].
2.1.2. Cognitive LPWAN
LPWAN technology is a low range revolutionary system for IIoT low-powered sensor devices that operate in a short distance area [48]. Thus, LPWAN technologies are up-and-coming for low power consumption, coverage, and low costs. Cognitive LPWAN operates multiple LPWAN technologies as a combination in one backbone network that achieves efficient user experiences using AI services [49]. It can provide stable communication between people and things together in heterogeneous IIoT. Cognitive LPWAN expands subscribers with more performance and relief smart services by enhancing cognitive LPWAN technologies for various applications of smart cities, Internet of vehicles, and smart home with the AI mechanisms [50].
The cognitive devices or users need to detect the spectrum before the unused spectrum’s occupation using a detection technology to determine an inactive frequency spectrum. After access to the available spectrum, cognitive users need to perceive other channels to prepare the primary users to achieve transparent transfer and prevent cognitive-communication [51,52,53]. The benefit of using cognitive radio in LPWAN is to use sufficient spectrum and efficient energy and resource availability when using the unused opportunistic licensed spectrum [10]. Smart sensors that use a cognitive radio can access the IIoT network through LPWAN base stations responsible for receiving, storing [54], and processing data from other nodes and distributing the different requests on the network. Smart sensor nodes use a specific low power, low-speed, long-range network—typically LPWAN networks [55]. In long-range and lower power consumption applications and cellular LPWAN technologies such as LTE, NBIoT is used. A dynamic spectrum access scheme is used in such networks to allow unlicensed users to access unused licensed bands dynamically. Cognitive radio with dynamic spectrum access provides a solution for increasing spectrum utilization in cognitive LPWAN [56].
The fusion of different LPWA technologies offers cognitive-LPWAN (C-LPWAN), an entirely new set of the application domain, as it can make intelligent services more comfortable and efficient for the users. The C-LPWAN based on an AI-enabled engine has been presented in [57]. According to this study, C-LPWAN can ensure superior advantages over known LPWAN technologies by minimizing energy consumption and delay. The architecture of C-LPWAN incorporates different LPWAN technologies, and by utilizing precise calculation, analysis, and distributed cloud support, it can choose the best suitable technology for each application [58].
2.1.3. Cognitive Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The growth of IIoT applications in different aspects will require enabling protocols and more spectrum due to different kinds of devices, sensors, and things that can be connected to the Internet. Available spectrum will become rare relative to this phenomenal growth, especially in the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical Bands. Technologies such as LoWPAN and ZigBee depend on ISM bands that are not sufficient for their needs for a spectrum [59]. Cognitive radio in IIoT with dynamic spectrum access can be more aggressive, in which multiple users can simultaneously use a channel if only it satisfies the predefined quality condition. The use of cognitive technology in IIoT will help to bring control to IIoT growth issues in the case of channels distribution among devices shared with infrastructure-based development through radio connections [60].
The operational planning for Cognitive IIoT fundamentally characterizes the interactivities of mainly five essential cognitive functions: intelligence cycle, large data test, logic knowledge, derivation, and detection. Intelligent systems decide for resolution and request services supplying similar signals useful for the IIoT model [61,62]. Cognitive processing in IIoT network based on cellular backbone architecture as shown in Figure 6 enables IIoT devices to determine its action [63]. This can be accomplished by exchanging local event information between the sensor nodes and servers. Besides, IIoT devices can exchange control data for spectrum allocation and channel determination for handover. The radio sensing integration with cloud-enabled services can assist as self-reconfigurable IIoT resolutions for an implementation application [64].
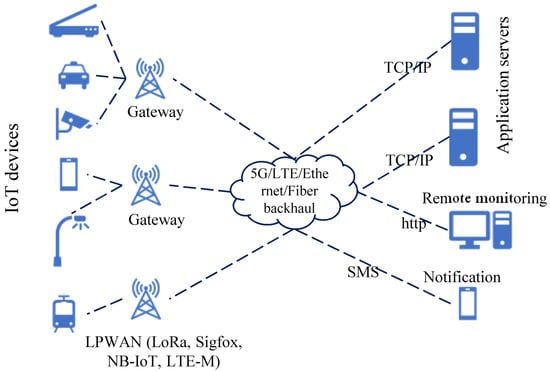
Figure 6.
Cognitive-enabled LPWAN Technologies for IIoT [61,62,63].
Another cognitive IIoT consideration is the use of coexistence performance of hot spot indoor with LTE [65]. The coexistence system of ZigBee and LTE will promise more performance explored through the different communication networks since LTE offers low density in rural regions and ZigBee high density for urban regions. The integration between LTE and ZigBee configuration will introduce a new approach to different spectrum bands in one architecture without the spectrum sharing aspect [66].
In cognitive IIoT in LTE access technology, the spectrum sensing is a process that enables Secondary Users (SUs) to sense the spectrum with a given probability to detect and protect the signal from Primary Users (PUs) possibly in noisy environments [67]. It should be that the PUs signal must be identified for SUs communication at the desired interference level. For perfect sensing performance, two metrics, the probability of misdetection and false alarm, should be considered in cognitive IIoT system evaluation [64]. False alarm represents that SU discovers that the idle PU is active, which can miss transmission opportunity. The following equation determines the probability of false alarm [68]:
where C represents the complementary distribution function of a standard Gaussian, denotes the spectrum sensing threshold, is the channel power noise, T denotes the spectrum sensing time, and fs indicates the sampling rate of the channel. The detection probability of an arbitrary SU i is derived as follows [69]:
where represents the SINR of the PU’s signal measured at the SU. The misdetection probability for SU can be written by:
Cognitive radio performance can affect the sensing ability during the detection process of the active SUs. Multipath fading problems in wireless channels that appeared in PUs will make SUs fail in the process of PUs detection, which will push the SUs to cause much interference to the PUs in their successive transmissions [70]. Either SU in its neighborhood can detect PUs to be active or inactive during the process of spectrum sensing; the clear channel probability (Pcc) for SUs with which the channel is free from the incumbent PUs, can be obtained by the following equation:
where and respectively refer to the probabilities of false alarm and misdetection for SU. H1 is the probability of active PUs in the neighborhood of SU, and H0 is the probability of inactive neighboring PUs. SUs energy detector suggested declaring the activity or inactivity of incumbent PUs with probability and probability , respectively.
2.1.4. IIoT LPWAN Cognitive Radio Bands
Primary radio networks (PRNs) and cognitive radio based on LPWANs are deployed for the two different categories of radio frequency. The PRNs are mobile cellular networks where the radio-licensed bands are often observed to be underutilized. Cognitive LPWANs can deploy with PRNs at a specific frequency band. The channel radio between primary and cognitive LPWAN becomes a place within the primary radio distance [71]. The primary licensed users can only use the radio bands allocated in Primary Radio. The PRN frequency systems for cognitive LPWANs apply the CU where the frequency is unutilized. That is, CUs can differentiate and exploit these spectrum holes occurring in the PRN radiofrequency. Specifically, CU can exploit the spectrum hole occurring to transmit an opportunistic technique that does not interfere with all Primary Users [72].
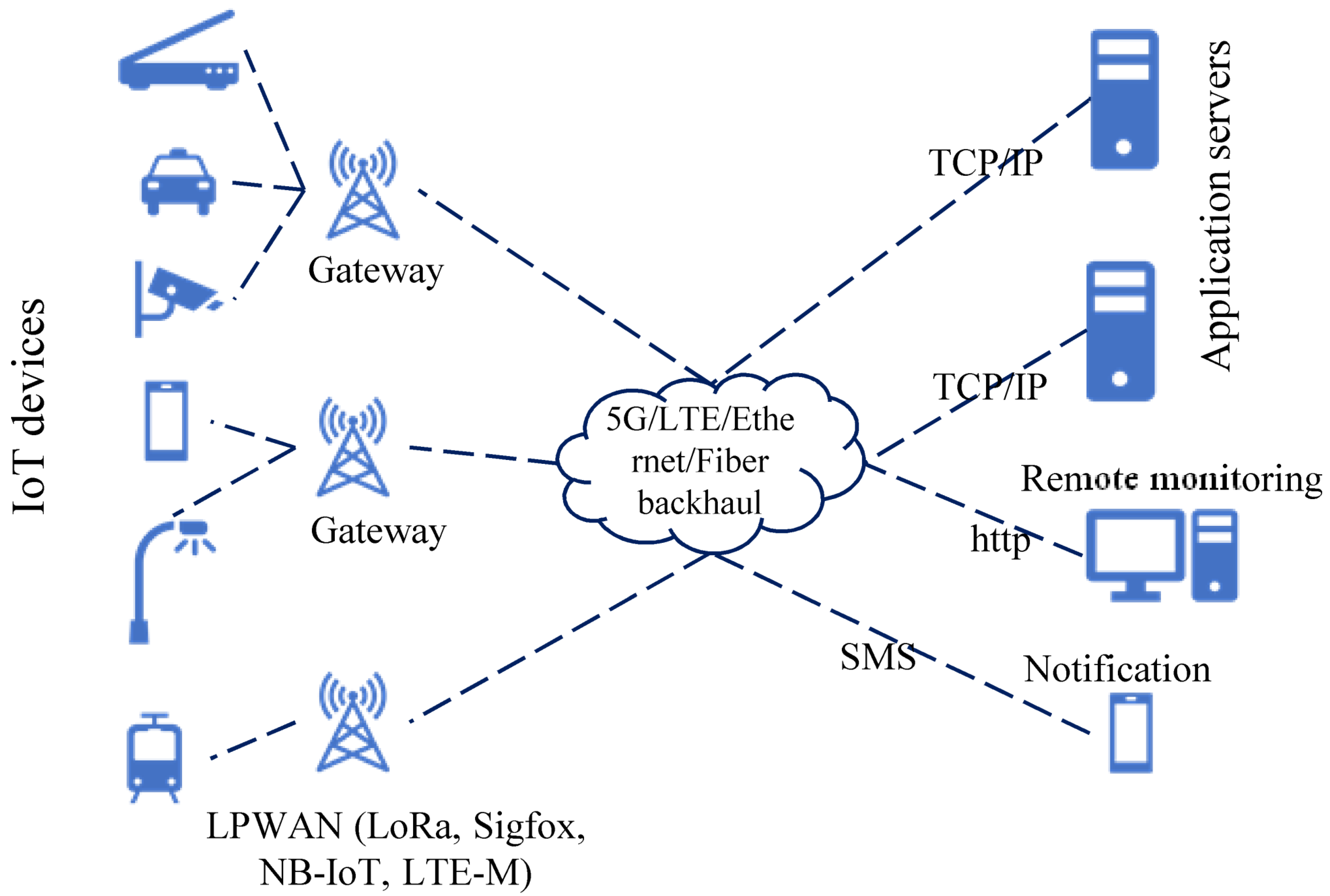
The sensor system transmits its information values to the cell LPWAN, applying spectrum availability through cognitive energy radio. Figure 6 shows a set of different IIoT end nodes, which depend on LPWAN and may include Smart cities. End nodes communicate with CR-LPWAN gateway (GW) by the LPWAN network. The coverage region of the Cognitive LPWAN is possibly primary user (PU) communication, as shown in Figure 7. For example, a PU network belongs to a cellular network or TV network. The Cognitive LPWAN operates within the PU’s coverage region via determining transmitting opportunistically over white spaces on a non-interference resource. Data rate coming from the end nodes by white spaces progresses through the CR-LPWAN GW to an IIoT network, which includes all devices on the Internet. A geo-position database with different application servers can be accessed via the Cognitive LPWAN gateway to significantly determine white spaces’ obtainability to recognize application, determining control commands significantly [73]. The information is finally transmitted to the server that is unspecific in Figure 5 for cognitive radio based on the IIoT.
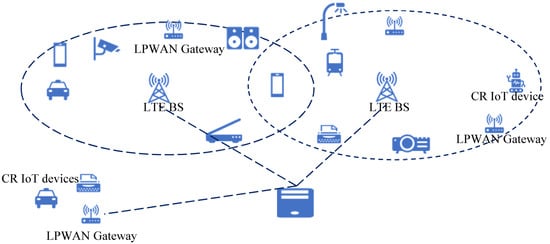
Figure 7.
Radiofrequency network architecture [72,73].
2.1.5. Spectrum Allocation
The radio frequency spectrum allocation to unlicensed users depends on the central spectrum in cognitive IIoT-based LPWAN. Although a centralized sensing technique is available for collecting information on free frequencies, sometimes decentralized sending technique also plays a part. The spectrum availability is scanned by the transceiver on the IIoT device and sent by access points using a specified network. This spectrum access process allows allocating a specific spectrum channel to a certain cognitive user on the IIoT device based on availability [74]. In spectrum access, the radio technique for unlicensed frequency users to effectively access the unutilized licensed bands to decrease the new frequency bands or white area is recognized as the dynamic access frequency band.
In this platform, frequency band unlicensed users essentially use unused licensed frequency bands without damage. When the frequency licensed band of the user initiates the frequency band, the frequency band unlicensed user has to create the free frequency band and transmit it to another inactive radio. The Cognitive Radio techniques and frequency spectrum dynamic access platform significantly improve resolution for upgrading frequency utilization in the cognitive radio [75]. Dynamic access is a technique wherein the frequency spectrum holes in spectrum radio allocation mean the radio spectrum is used proactively. Fixed allocation sources based totally on the static spectrum get right of entry to be unsuitable for cooperating with spectrum radio disabilities anticipated to proportion sources.
On the contrary, dynamic resource allocation functions well using spectrum holes or spectrum accessible bandwidth, by applying several approaches. Various shared radio resources have distinctive structures and can allocate several constant frequency bandwidths to numerous structures. The media access control (MAC) or channel allocation in LPWANs are better to explain so that the percentage of resources can turn out to be dependent on special SINR within the wireless software; the LPWANs can contribute to the Wi-Fi applications with difficult QoS demands [76].
The planner ought to decide a mac protocol of CR based on IIoT, based totally on numerous vital requirements. Firstly, IIoT devices are unique in using massive data, higher cost, communique vicinity, electricity consumption, and communication devices. Secondly, the checked radio frequency band is widespread. Many essential operators play approximately the function of choosing a mac protocol for the IIoT machine. The operators are communication probability, delays, and power consumption. Therefore, purposeful MAC protocol has to tolerate decrease fees, decrease complexity, and low strength intake. A mac protocol has to be as much as the correct errors. For example, this work [77] offers a comprehensive evaluation among mac types of standards, IEEE 802. 11ah, and IEEE 802.15.4.
The requirements are consistent with its structures. The IEEE 802.15.4 is a better deployable system than the IEEE 802.11ah or IEEE 802.14 because of its energy saving and networkability permits regulating a huge number of IIoT devices system in unlicensed 2.4 using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). Numerous smart devices allow MAC protocols, for instance, slotted aloha and acquainted Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA); and orthogonal frequency division multiple Access (OFDMA) and Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) were deployed for IIoT LPWAN systems for applying the spectrum [78]. For instance, a CSMA/CA MAC protocol [79].
Cognitive LPWAN is an especially designed dynamic radio where the primary radio network (prn) structures with a huge number of radio sources become underutilized; so the cognitive radio LPWANs, the green get admission to is primary to the dynamic spectrum control for being closely deployed within the IoT [80]. The cognitive LPWAN is superb from the conventional interference standpoint through spectrum sensing implementation [81]. Cognitive radio locates the restricted bands anywhere and functions, adjusting its processing variable parameters, by dynamically controlling radio band utilization.
2.2. What Are the Proposed Architectures That Support Cognitive Radio LPWAN Based IIoT?
Architectures that Support Cognitive Radio LPWAN-based IIOT are discussed in the following subsections:
2.2.1. Cognitive IIoT LPWAN Architectures
Cognitive Radio LPWAN supports artificial intelligent application services, such as automatic driving and smart houses [16]. The heterogeneous wireless communication technologies can be used for the design and implementation of the IIoT infrastructure. To design the IIoT infrastructure for the unlicensed LoRa and Sigfox, the short coverage area BLE and WiFi; and cellular technologies, LTE-m, NBIoT, and 5G, have been suggested [82]. The coverage area of narrowband IoT is less than a distance of 15 km, whereas Bluetooth BLE is less than a length of 10 m; WiFi is less than 100 m; Long Range LoRa is less than 20 km; LTE is less than 11 km; and 5Gis less than 15 km [83]. The performance parameters such as distance, high data rate, bandwidth, and sensor capacity are discussed in Table 1. The limitations of the different implementations of narrowband IoT base stations using the LTE infrastructures are highlighted. Using LTE radio wave resources can save the power consumption of WAN applications as well as costs. Long Range LoRa is mostly used for cognitive interconnection and transmission and other implementation applications for its enhancement of the unlicensed spectrum. Table 2 presented a summarized comparative analysis of CR LWPAN technologies for the critical Industrial IoT applications. The NBIoT supports environment AI monitoring in smart cities. The WiFi technology supports smart home as AI home, Machine-to-Machine wireless communication technology, and other implementation applications; LoRa supports smart sensing, smart home, and M2M communication technology [84].
Table 3 presents Industrial IoT characteristics with different parameter requirements (L: Low; M: Medium; H: High). For example, for environments WPWAN CIIoT applications, the power needed is medium due to the scattering of devices around the area; the random distribution probabilities of the long and short distances between the sensor and gateway are similar. Link capacity needed is high due to huge reporting sensors. Coverage is medium as well because for environmental applications, usually the coverage is smaller than cities and larger than campuses. The cost needed is high due to the nature of the environment’s application usually at the remote side where no network deployment is available. CR potential interference to other primary users is low, which is due to the environment’s application usually at the remote side where there is rarely another network to be deployed at remote or jungle areas, and even though it happens that another foreign network has deployed, the number of devices would not be large.
2.2.2. Architecture and Domain of CR-Based IIoT
CR based on IIoT region and IIoT articles should have the intellectual office to make smart goals on the range and perform smart administration by breaking down system circumstances. In [85], a CR method was proposed to improve M2M interchanges. Substantial scale IIoT applications make vast volumes of information, yet this information is unfilled and unambiguous with reliable data. An information CR dependent on IIoT structure empowers interpretation for the executive’s information and insightful assurance work. Intellectual condition aware structure-based public IoT (pIoT) diminishes to overhead, where pIoT is free and dynamic, as it depends on the open connections between articles. Status obtaining is trailed by information identification and information mining methods to identify diverse follow-up conditions. This helps in the evaluation of administrations. After this, many approaches have appeared with different concerns and functioned for accurate decisions [86].
Virtual objects (VOs) are created in [87] to speak to sensors. This model applied sensor information and used the data. The system design has sensors, controllers, a focal center point, a server, and a client layer. A composite virtual article speaks to a gathering of VOs that have discernment with semantic interoperability. The purchaser level gives an interface to clients to collaborate with the framework for application utilization. A Distributed Internet like Architecture for Things (DIAT), because of three-level engineering, can bolster the secure expansion of various heterogeneous gadgets. The layered design manages security and adaptability also. Intellectual capacity acknowledges perceptive choices with a self-governing administration arrangement. Psychological capacities are consolidated at all three dimensions, bringing about a stack called IIoT Daemon. With the expansion of sensors in IIoT comes the issue of vitality proficiency. One arrangement is to choose vitality effective passageways. This is accomplished through diversion hypothesis and disseminated learning. In any case, the structure must be adaptable and less perplexing in the calculation. Software-defined radio (SDR) innovation for the remote IIoT stage was considered in [88].
2.2.3. The Architecture of U-LTE Cognitive Radio for IIoT
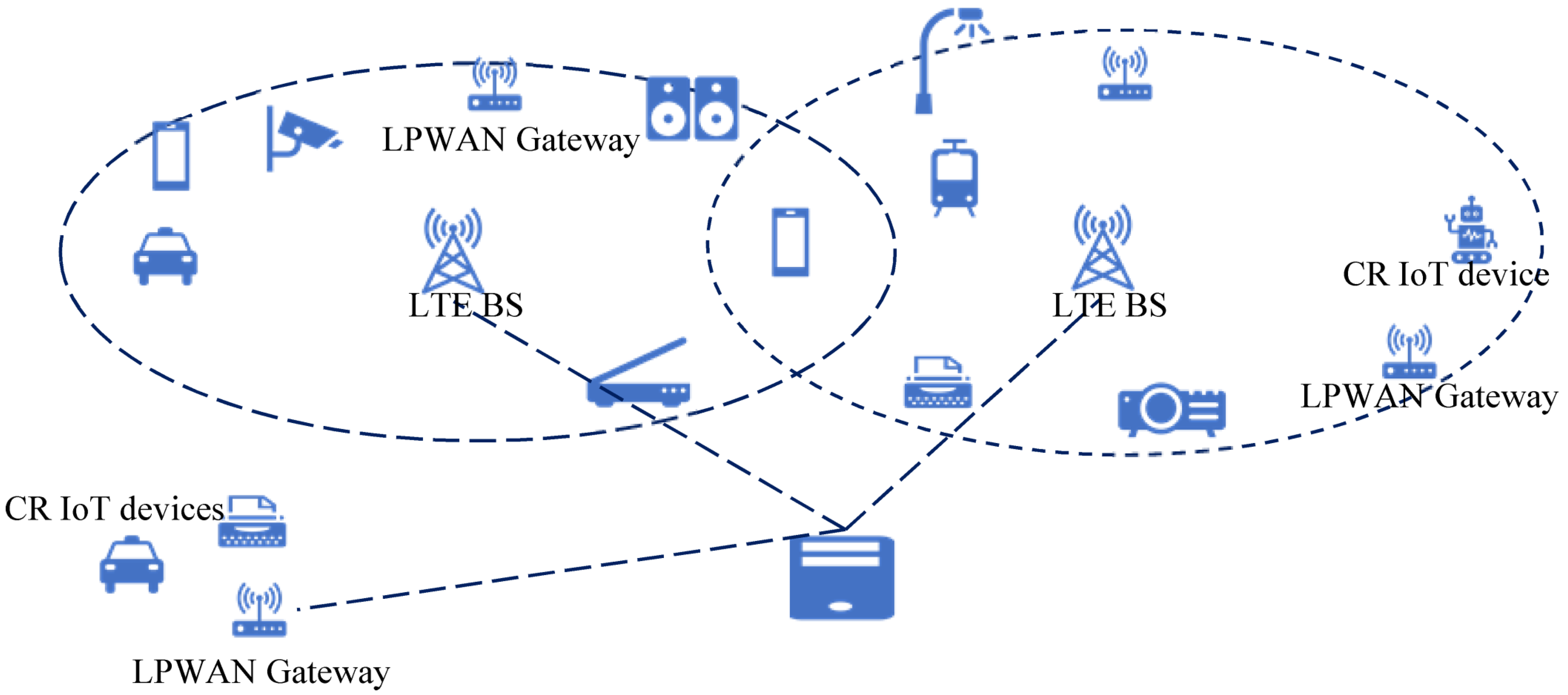
Unlicensed LTE (U-LTE) bands provide an attractive opportunity to satisfy subcarriers, enabling access to 5 GHz for IIoT. These bands coexist with other Wi-Fi/IoT users. The coexistence between U-LTE and IoT requires a protocol to listen before talk (LBT) with cognitive radio [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]. The differences between LTE and IoT in PHY/MAC can cause continuous interference to Wi-Fi/IoT systems. Unlicensed band operation needs the component to be within the regulatory requirements of a given area deployment state of affairs of U-LTE at the side of IIoT person device and devices, by using speaking with Wi-Fi to get AP to use the unlicensed spectrum, form a femtocell, and grow to be number one customers. United states in a small cell with eNodeB utilize unlicensed spectrum and grow to be secondary customers. In U-LTE, the unlicensed spectrum is handiest for downlink site visitors and the operations that include making sure reliable communications and checking the provision of intended unlicensed channels are achieved through eNodeB [89].
In the coexistence of U-LTE with Wi-Fi/IoT system as shown in Figure 8, the LTE and Wi-Fi/IoT randomly generate multiple signals with respective energy and transmission time. Free channels could be allotted to the transmission between the respective source and sink where the machine architectures of U-LTE cognitive radio for IIoT occupy idle channels and transmit for its respective period [90]. The contention adoption via the wireless based on mac protocol with a random access mechanism will find that the medium busy most of the time and have high back off.
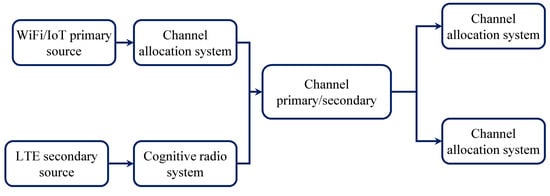
Figure 8.
Coexistence of U-LTE Cognitive Radio/IIoT [88,90].
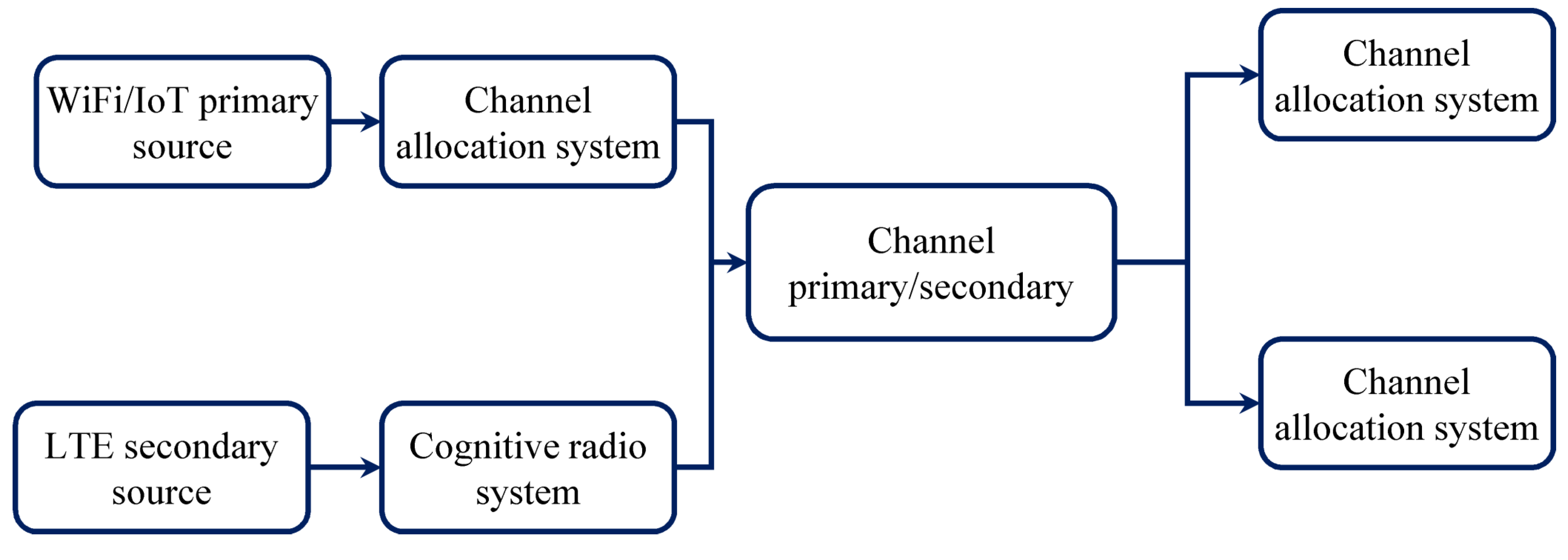
Within the cognitive radio utility in such coexistence architecture, wireless/IIoT can be considered as a primary user (pu) and U-LTE because of the secondary consumer (su). The alerts come from IIoT assets that occupy the channels following their own MAC protocol employing the channel allocation device. While U-LTE indicators will comply with the requirements channels through the cognitive radio machine. The cognitive radio system can be prepared on LTE base station, which gets a transmission request from LTE resources and then discovers the unfastened channels utilizing estimated idle channel threshold by way of measuring the energy degree for the duration of the listening duration [91].
2.2.4. Architectures of NBIoT Cognitive Radio
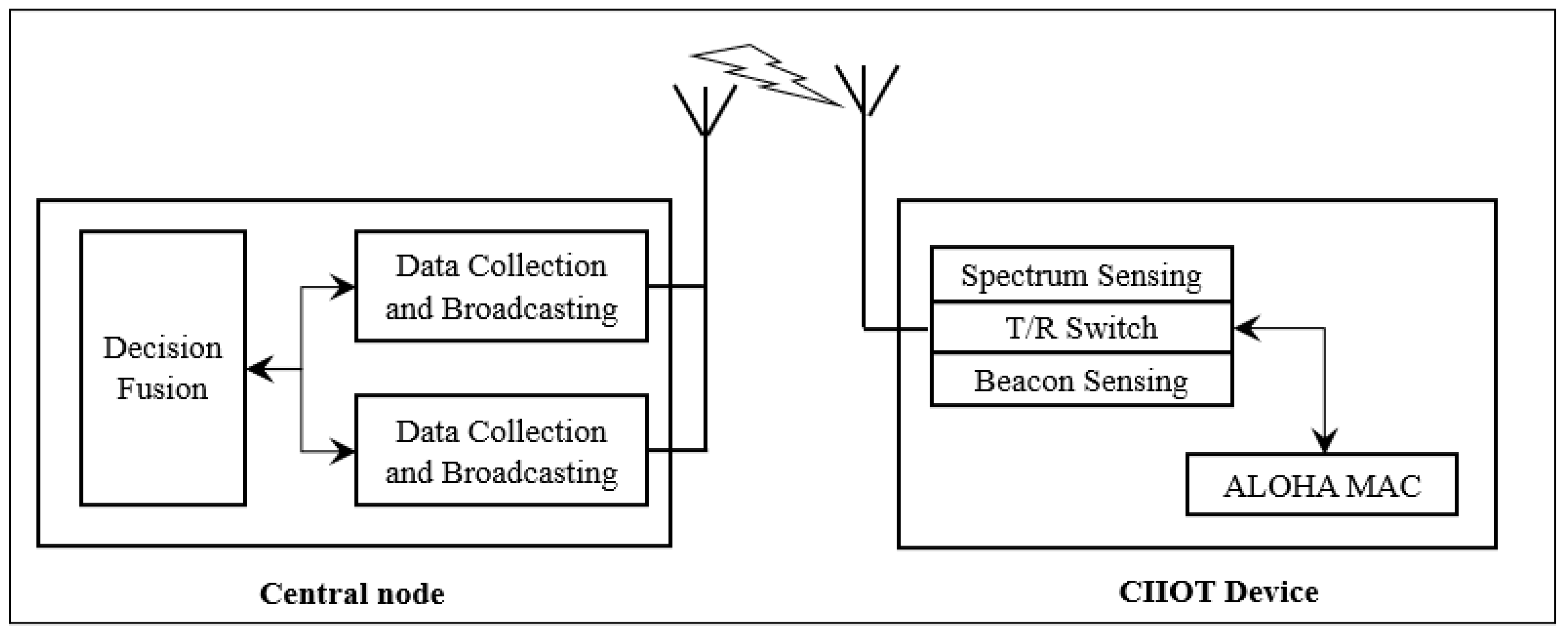
New 3GPP technology standardized in LTE known as NBIoT has gained more attention for IIoT applications. NBIoT enables a wide range of services for M2M communication for stable connectivity among IIoT devices, which are desirable to access the medium at any time. The IIoT traffic involves small data packets that can be subject to excessive collision due to many devices. The use of cognitive radio with random access strategies is done to reduce congestion in the network [92]. In addition, the cognitive radio will promise to meet the requirements of future IIoT spectrum by identifying vacant channels dynamically, and the networks of CR-IIoT will offer collaborative sensing at a low rate and provide support needs of channels for information exchanges between cognitive radio users and the central node for the IIoT, as shown in Figure 9 below.
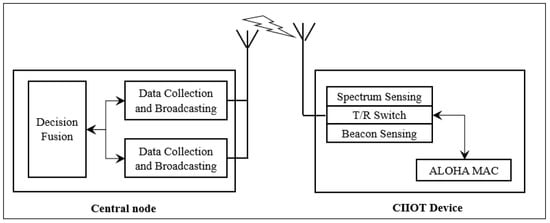
Figure 9.
Collaborative sensing of IIoT device in NBIoT Cognitive Radio system [91,92].
In NBIoT cognitive radio, energy saving should be considered to reduce the system realization cost for cognitive radio users; this is due to comparing the energy detected on a channel with the local threshold. Matched filter detection can be used as an optical signal detection mechanism to maximize the SNR of the recovered primary user (PU) signal. In such a network, the received signal can be represented as y(n) affected by the noise u(n) thatis assumed to be a complex Gaussian distribution function with zero mean and known variance given by E) = . The received signal at NBIoT cognitive radio device denoted by S(n) with zero mean and known variance can be given by E) = [32]. The shared signal-to-noise ratio at a certain group of NBIoT cognitive radio devices is given by:
In this system, all devices assumed are assigned to different groups of sensed frequencies based on their packet priority and sensing SNR, such that devices with the same sensing abilities were assigned to the same group. The decision variable of the energy detector for collected Ns recovered signals can be written as follows.
when T() follows Gaussian distribution Collaborative sensing, all devices in NBIoT cognitive radio will transmit their local detection information to the central node to take the final decision on the presence of the PU signal, and then the decision is communicated to all devices. The collaborative sensing system set to times is known as sensing time and collaborative sensing time for sensing and communicating sensing information to and from the central node. This scheme will provide more accurate sensing decisions, especially under the low SNR scenario.
2.3. What Key Success Factors Need to Comply for Reliable CIIoT Support in the Industry?
The key success factors for reliable CIIoT are discussed in this section. The IIoT can be built and operated with the development of other technologies using the Internet connection. The use of cloud and distributed computing, remote sensor system, and actuator systems’ significance toward reliable cognitive IIoT is reviewed in the following subsections [93].
2.3.1. CIIoT with Fog and Clouds
Distributed computing is another rising plan, and it accepts that the future world will join the “everything as an administration” model dependent on the sharing of assets through the cloud. Individuals will approach any administration, whenever and wherever with the assistance of the Web association. Be that as it may, access to these assets is an incredible test. Distributed computing has three noteworthy administration models: framework as an administration, stage as an administration, and programming as an administration [94]. Notwithstanding these models, detecting as an administration is additionally proposed. Also, haze registering conveys the administrations near the end clients; that is why it is essential to consider such cloud administrations (correspondence, stockpiling, arrangement, and the executives) at the edge of a system. Utilizing psychological capacity and CRN with its dynamic range of abilities, can consolidate with distributed computing to convey IIoT administration provisioning to the real world [95].
2.3.2. CIIoT Remote Sensor Systems
Remote sensor systems (WSNs) have officially demonstrated their helpfulness as of late. Scaled downsize and minimal effort have made sensors a significant wellspring of data gathering. The need to know whenever and anywhere has bolstered the idea that they are joining in IIoT structures [96]. Notwithstanding, data recovery from these sensors remains a test in the substantial-scale topographical arrangement or in-home applications because of range accessibility and obstruction. Besides, assets constrained sensors to produce and transmit crude information rather than expansive and valuable information streams. WSN information can be valuable for little-scale applications, yet it might have issues in the IIoT setting. In this manner, WSNs mix with CRNs and give foundationless and self-composed systems that have great potential for IIoT applications. Cognitive Radio with Actuator Systems (WSANs) performs activities indicated by condition detecting [56,62,64,66,67,68,72,73,74,75]. Their impromptu nature gives the least physical expansion and for the most part, results in a solitary assignment. Joining WSANs in IIoT needs a more comprehensive vision. Transmitting activities to actuators in an opportune and proficient way is a major obstacle. NFC and RFID have generally been appropriate for WSANs; nevertheless, a subjective info-communication viewpoint is additionally researched to improve the IIoT system [97].
2.3.3. CIIoT with D2D and M2M Technologies
The developing increment in the number of gadgets has transformed the concentration into M2M correspondence rather than human-to-human (H2H) correspondence. A few gadgets such as mobiles, workstations, and sensors can engage in data communication without the requirement for human intercession. Reliance on machine information has made M2M correspondence significant for future IIoT systems [54,72]. Therefore, the self-configurable systems for inter-device communication methods are necessary [73,74,75]. Moreover, the system resource must be shared between M2M and established H2H interchanges coordinating CRNs [98]. The summary of the cognitive radio technologies for different IIoT applications is presented in Table 4.
2.3.4. Cognitive Engine
Cognitive Engine (CE) is a central feature of CR that acknowledges intelligent argumentation and learning on the software radio system and executes the entire cognitive sequence. CE uses the radio resource cognitive engine and cognitive data engine [20,56,62]. Radio resource development for the lifetime multi-paradigm flow of data in the technology networks is performed with data automatic operating power and by implementing the data intelligently. The cognitive data engine could organize the communication allocation resources and allocation network resources [21,62,72,73,74,75] of heterogeneous IoT and remote access cloud, and create the actual time returns of the overall data allocation resources to the cognitive data engine.
3. Conclusions and Future Work
The IIoT helps several applications that require power control and low cost to achieve long life. The development of the IIoT communication technologies base on CR has achieved high ability for industrial network stable connectivity. An efficient and appropriate smart service in smart cities, i.e., advanced health care, automatic driving, and users, can currently easily access such IIoT. This paper focuses on smart wireless technologies based on cognitive radio wireless medium with low power wide area LPWAN unlicensed spectrum using LoRa, Sigfox, LTE-M, and NBIoT. Various cognitive IIoT applications have been studied, with their techniques, protocols, and the model success determinant parameters with their significance being identified. Cognitive LPWAN allows smart city services to access other wireless access points and selects appropriate communication technologies to achieve the best user experience. Our future study for the research area is to develop a framework that facilitates less energy, long-run devices, and the highest possible data rate using the cognitive Internet of Things for the industrial solution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.N.; R.A.S.; M.K.H.; E.S.A. and R.A.M.; methodology, M.K.H.; R.A.S.; M.A.H. and S.I.; software, R.A.S.; M.K.H. and M.A.H.; validation, R.A.S.; M.K.H. and E.H.; formal analysis, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; R.A.M.; E.S.A.; investigation, N.N.; R.A.S.; resources, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; R.A.M.; E.S.A.; E.H. and S.I.; data curation, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; R.A.M.; E.S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, N.N.; R.A.S. and M.K.H.; writing—review and editing, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; R.A.M.; E.S.A.; E.H.; I.M.; K.A.Z.A. and S.I.; visualization, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; supervision, R.A.S.; M.K.H.; project administration, M.K.H.; funding acquisition, M.K.H.; I.M. and K.A.Z.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the research grant of Malaysia’s Ministry of Higher Education and Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) under the grant GGPM 2020-028, and GUP-2019-062 respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Abbreviations
| 3GPP | Third Generation Partnership Project |
| 5G | Fifth Generation |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BLE | Bluetooth Low Energy |
| CIIoT | Cognitive Radio IIoT |
| CR | Cognitive Radio |
| CRLPWAN | Cognitive Radio Low Power Wide Area Network |
| CSMA | Carrier Sense Multiple Access |
| CU | Cognitive User |
| eMTC | Enhanced Machine Type Communication |
| FHSS | Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ISM | Industrial, Scientific, and Medical |
| IWSNs | Interference in Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks |
| LoRA | Bi-directional Long Short-term Memory |
| LoRaWAN | Low Range Wide Area Network |
| LPWAN | Low Power Wide Area Network |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| M2M | Machine-to-Machine |
| MAC | Media Access Control |
| NB-IoTNBIoT | Narrow Band Internet of Things |
| OFDMA | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access |
| PU | Primary User |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| RQ | Research Question |
| SCC | IEEE Standards Coordinating Committee |
| SDR | Software-defined radio |
| SINR | Signal to Interference Noise Ratio |
| U-LTE | Unlicensed LTE |
| VOs | Virtual objects |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
References
- Shafiq, M.; Ahmad, M.; Afzal, M.K.; Ali, A.; Irshad, A.; Choi, J.-G. Handshake Sense Multiple Access Control for Cognitive Radio-Based IoT Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P. Towards Cognitive Radio in Low Power Wide Area Network for Industrial IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 July 2019; Volume 1, pp. 947–950. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, K.; Chen, M. Big Data Analytics for Cloud/IoT and Cognitive Computing; Wiley: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Somov, A.; Dupont, C.; Giaffreda, R. Supporting Smart-City Mobility with Cognitive Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the Future Network and Mobile Summit, Lisboa, Portugal, 3–5 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Z.E.; Saeed, R.A.; Ghopade, S.N.; Mukherjee, A. Energy Optimization in LPWANs by using Heuristic Techniques. In LPWAN Technologies for IoT and M2M Applications; Chaudhari, B.S., Zennaro, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 11; ISBN 9780128188804. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.J.A.; Hamzah, M.I.; Yasin, M.H.M.; Tahar, M.M.; Haron, Z.; Ensimau, N.K.E. The UKM Students Perception towards Cyber Security. Creative Educ. 2018, 10, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P. Cognitive Radio in Low Power Wide Area Network for IoT Applications: Recent Approaches, Benefits and Challenge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 7489–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulogeorgos, A.A.; Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) for Internet of Things (IoT) Applications: Research Challenges and Future Trends. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.07449. [Google Scholar]
- Augustin, A.; Yi, J.; Clausen, T.; Townsley, W.M. A Study of LoRa: Long Range & Low Power Networks for the Internet of Things. Sensors 2016, 16, 1466. [Google Scholar]
- Insider, B.I. Ericsson just Took a Significant Step toward Delivering Cellular-Based IoT. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/ericsson-just-took-a-significant-step-toward-delivering-cellular-based-iot-2016-11 (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Akpakwu, G.A.; Silva, B.J.; Hancke, G.P.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A Survey on 5G Networks for the Internet of Things: Communication Technologies and Challenges. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3619–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejlgaard, B.; Lauridsen, M.; Nguyen, H.; Kovacs, I.Z.; Mogensen, P.; Sorensen, M. Coverage and Capacity Analysis of Sigfox, LoRa, GPRS and NBIoT. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, Australia, 4–7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mercier, B.; Fodor, V.; Thobaben, R.; Beferull-Lozano, B. Sensor Networks for Cognitive Radio: Theory and System Design. In Proceedings of the ICT Mobile and Wireless Communications, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–12 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, B.-K. Dynamic Spectrum Access for Internet of Things Service in Cognitive Radio-Enabled LPWANs. Sensors 2017, 17, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awin, F.; Alginahi, Y.M.; Abdel-Raheem, E.; Tepe, K. Technical Issues on Cognitive Radio-Based Internet of Things Systems: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 97887–97908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, B.S.; Zennaro, M.; Borkar, S. LPWAN Technologies: Emerging Application Characteristics, Requirements, and Design Considerations. Futur. Internet 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, B.S.; Zennaro, M. (Eds.) LPWAN Technologies for IoT and M2M Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, D.; Rahman, M.; Saifullah, A. Low-Power Wide-Area Networks: Opportunities, Challenges, and Directions. In Proceedings of the Workshop Program of the 19th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, Varanasi, India, 4–7 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kelaidonis, D.; Somov, A.; Foteinos, V.; Poulios, G.; Stavroulaki, V.; Vlacheas, P.; Demestichas, P.; Baranov, A.; Biswas, A.R.; Giaffreda, R. Virtualization and Cognitive Management of Real-World Objects in the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Green Computing and Communications, Besancon, France, 20–23 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tragos, E.Z.; Angelakis, V. Cognitive Radio Inspired M2M Communications. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC), New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 24–27 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adelantado, F.; Vilajosana, X.; Tuset-Peiro, P.; Martinez, B.; Melia-Segui, J.; Watteyne, T. Understanding the Limits of LoRaWAN. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, M.; Nitti, M.; Pilloni, V.; Atzori, L.; Giusto, D.; Popescu, V.; Alexandru, M. Distributed Spectrum Sensing for Indoor Broadcasting Services Using an IoT Platform. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), Cagliari, Italy, 7–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, G.A.; Gungor, V.C.; Akan, O.B. A Cross-Layer QoS-Aware Communication Framework in Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks for Smart Grid Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Mancuso, V.; Ali, S.; Marsan, M.A. Stop and forward: Opportunistic local information sharing under walking mobility. Ad Hoc Netw. 2018, 78, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ahmed, M.M.; Hashim, A.H.A.; Razzaque, A.; Islam, S.; Pandey, B. A Novel Artificial Intelligence Based Timing Synchronization Scheme for Smart Grid Applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.Z.; Hassan, R. The implementation of internet of things using testbed in the UKMNET environment. Asia Pac. J. Inf. Technol. Multimed. 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Badri1, I.; Abdellaoui, M. Spectral Sensing & Multi-Objective Spectrum Allocation over MIMO-OFDMA Based on 5G Cognitive WSSNs for IoT Intelligent Agriculture. IJMER 2018, 6, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Parvez, I.; Sarwat, A.I. A Spectrum Sharing based Metering Infrastructure for Smart Grid Utilizing LTE and WiFi. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 2019, 4, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Islam, S.; Khalifa, O.O.; Hashim, A.-H.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Razzaque, A.; Pandey, B. Design and Evaluation of a Multihoming-Based Mobility Management Scheme to Support Inter Technology Handoff in PNEMO. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 1133–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervonen, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pieska, S.; Jämsä, J.; Heikkila, M. Cognitive Internet-of-Things Solutions Enabled by Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th IEEE Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Vietri sul Mare, Italy, 5–7 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, J.; Cerdan-Cartagena, F.; Muro, J.S.; Ybarra-Moreno, J. Design and Implementation of a Mixed IoT LPWAN Network Architecture. Sensors 2019, 19, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.P.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, S.W. Cognitive Radio Wireless Sensor Networks: Applications, Challenges and Research Trends. Sensors 2013, 13, 11196–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyan, M.; Reddy, V.; Jitesh, K.; Ashif, S.; Ravikumar, C.V.; Kalapraveen, B. LPWAN Technologies for IoT Deployment. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Rachedi, A. When Cognitive Radio meets the Internet of Things? In Proceedings of the International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Liu, K.J.R. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing: A Game Theoretical Overview. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2007, 45, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa, J.; Sanchez-Iborra, R.; Rodriguez-Rey, P.; Bernal-Escobedo, L.; Skarmeta, A.F. LPWAN-based vehicular monitoring platform with a generic IP network interface. Sensors 2019, 19, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.E.; Tokikawa, D.W.; Rebelatto, J.L.; Brante, G. Comparison between LoRa and NB-IoT coverage in urban and rural Southern Brazil regions. Ann. Telecommun. 2020, 75, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavric, A.; Popa, V. Internet of Things and LoRaTM Low-Power Wide-Area Networks: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems (ISSCS), Iasi, Romania, 13–14 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, S.; Park, J.H. A combined network control approach for the edge cloud and LPWAN-based IoT services. Concurr. Comput. Pr. Exp. 2020, 32, e4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ismail, A.; Islam, S.; Hashim, W.; Ahmed, M.M.; Memon, I. A Novel HGBBDSA-CTI Approach for Subcarrier Allocation in Heterogeneous Network. Telecommun. Syst. 2019, 70, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, M.; Nguyen, H.; Vejlgaard, B.; Kovacs, I.Z.; Mogensen, P.; Sorensen, M. Coverage Comparison of GPRS, NBIoT, LoRa, and Sigfox in a 7800 km2 Area. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Sydney, Australia, 4–7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, B.; Borkar, S. Design considerations and network architectures for low-power wide-area networks. In LPWAN Technologies for IoT and M2M Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MN, USA, 2020; pp. 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Hasan, M.K.; Kabir, S.R.; Abdullah, S.N.H.S.; Sadeq, M.J.; Hossain, E. HSIC Bottleneck based Distributed Deep Learning Model for Load Forecasting in Smart Grid with A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 222977–223008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.; Hossain, E.; Faruque, H.M.R.; Sultan, T. IoT Based Smart Energy Management in Residential Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Advances in Science, Engineering and Robotics Technology (ICASERT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 3–5 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, M.; Mody, A.N.; Martinez, R.; Rodriguez, C.; Reddy, R. IEEE Standards Supporting Cognitive Radio and Networks, Dynamic Spectrum Access, and Coexistence. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2008, 46, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.T.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Guo, M. Delay-minimized routing in mobile cognitive networks for time-critical applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeyi, J.; Markus, E.D.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Technology Coexistence in LPWANs-A Comparative Analysis for Spectrum Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Q.; Wei, W. Cognitive Internet of Things: Concepts and Application Example. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 2012, 9, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, K.; Obata, K.; Mizutani, K.; Harada, H. Development and Field Experiment of Wide Area Wi-SUN System based on IEEE 802.15.4g. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Reston, VA, USA, 12–14 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.B.; Ali, E.S.; Saeed, R.A. Intelligence IoT Wireless Networks. In Intelligent Wireless Communications; IET Book Publisher: Bangalore, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Reisslein, M. Cognitive Radio for Smart Grids: Survey of Architectures, Spectrum Sensing Mechanisms, and Networking Protocols. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2016, 18, 860–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Zheng, Y.; He, J.; Kong, W.; Zou, S. A duplex current-reusedcmos lna with complementary derivative superposition technique. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2017, 45, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, R. Analog-to-digital converter survey and analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1999, 17, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivado, D.S. LogiCORE IP Product Guide Fast Fourier Transform v9.0. 2017. Available online: https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/ip_documentation/xfft/v9_0/pg109-xfft.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Hasan, M.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Abdalla, A.H.; Ramli, H.A.; Islam, S.; Hashim, W.; Badron, K. Cluster-based spectrum sensing scheme in heterogeneous network. In Theory and Applications of Applied Electromagnetics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Ismail, D.; Modekurthy, V.P.; Saifullah, A. Implementation of LPWAN over white spaces for practical deployment. In Proceedings of the IoTDI ‘19: International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P. Low Power Wide Area Network, Cognitive Radio and the Internet of Things: Potentials for Integration. Sensors 2020, 20, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttlebee, W.H. Software-defined radio: Facets of a developing tech-nology. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1999, 6, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P. A comparativeanalysis of local and global adaptive threshold estimation techniques forenergy detection in cognitive radio. Phys. Commun. 2018, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, A.C.; Vidhyapriya, R.; Vivekanandan, C.; Sangaiah, A.K. Enhancing 4G Co-existence with Wi-Fi/IoT using Cognitive Radio. Cluster Comput. 2019, 22, 11295–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, N.; Hossain, E.; Ahamed, S.I. A Qualitative Study on the United States Internet of Energy: A Step Towards Computational Sustainability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69003–69037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onumanyi, A.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Hancke, G.P. Adaptive threshold techniques for cognitive radio-based low power wide area network. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020, 31, e3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlacheas, P.; Giaffreda, R.; Stavroulaki, V.; Kelaidonis, D.; Foteinos, V.; Poulios, G.; Demestichas, P.; Somov, A.; Biswas, A.R.; Moessner, K. Enabling smart cities through a cognitive management framework for the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 51, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmammar, B. Internet of Things and Cognitive Radio: Motivations and Challenges. Int. J. Organ. Collect. Intell. (IJOCI) 2019, 11, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykas, T.; Kasslin, M.; Cummings, M.; Kang, H.; Kwak, J.; Paine, R.; Reznik, A.; Saeed, R.; Shellhammer, S.J. Developing a standard for TV white space coexistence: Technical challenges and solution approaches. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2012, 19, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Yousoff, S.H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Hashim, A.H.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Islam, S. Phase offset analysis of asymmetric communications infrastructure in smart grid. Elektron. Elektrotech. 2019, 25, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.A.; Khatun, S.; Ali, B.; Abdullah, K. Ultra-Wideband Interference Mitigation using Cross-layer Cognitive Radio. In Proceedings of the 2006 IFIP IEEE Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks (WOCN’06), Bangalore, India, 11–13 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, R.; Qamar, F.; Hasan, M.K.; Aman, A.H.M.; Ahmed, A.S. Internet of Things and Its Applications: A Comprehensive Survey. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, G.; Xu, Y.; Feng, S.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Long, K. Cognitive Internet of Things: A New Paradigm Beyond Connection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, I.; Shaikh, R.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Hassan, R.; Haq, A.U.; Zainol, K.A. Protect Mobile Travelers Information in Sensitive Region Based on Fuzzy Logic in IoT Technology. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, R.; Saeed, R.A.; Alsaqour, R.; Abdallah, Y. Study on Energy Detection-based Cooperative Sensing in Cognitive Radio Networks. J. Netw. 2013, 8, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Abdalla, A.-H.; Ramli, H.A.M.; Hashim, W.; Islam, S. Throughput Maximization for the Cross-Tier Interference in Heterogeneous Network. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2016, 22, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Islam, S.; Hashim, W.; Pandey, B. Dynamic spectrum allocation scheme for heterogeneous network. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Hasan, M.K.; Mokhtar, R.; Salih, S.K.A.; Hashim, W. Throughput Enhancement for WLAN TV White Space in Coexistence of IEEE 802.22. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewobi, S.S.; Hancke, G.P. A survey of cognitive radio handoff schemes, challenges and issues for industrial wireless sensor networks (CR-IWSN). J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 97, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W. 5G Mobile Communications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-34206-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeq, A.S.; Hassan, R.; Al-Rawi, S.S.; Jubair, A.M.; Aman, A.H.M. A Qos Approach for Internet Of Things (Iot) Environment Using Mqtt Protocol. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Cybersecurity (ICoCSec), Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, 25–26 September 2019; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.B.; Ali, E.S.; Mokhtar, R.A.; Saeed, R.A.; Chaudhari, B.S. NB-IoT: Concepts, Applications, and Deployment Challenges. In LPWAN Technologies for IoT and M2M Applications; Chaudhari, B.S., Zennaro, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 6; ISBN 9780128188804. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, R.S.; Wei, Y.; Hwang, S.-H. A survey on LPWA technology: LoRa and NB-IoT. ICT Express 2017, 3, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwewe, T.M.; Mbuya, C.F.; Hancke, G.P., Jr. Using Cognitive Radio for Interference-Resistant Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks: An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1466–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yuan, J.; Torlak, M. Network Throughput Optimization for Random Access Narrowband Cognitive Radio Internet of Things (NB-CR-IoT). IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 3, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, U.; Kulkarni, P.; Sooriyabandara, M. Low Power Wide Area Networks: An Overview. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Willkomm, D.; Abusubaih, M.; Gross, J.; Vlantis, G.; Gerla, M. Cognitive Radios for Dynamic Spectrum Access—Dynamic Frequency Hopping Communities for Efficient IEEE 802.22 Operation. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2007, 45, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shao, L.; Tang, J. Wireless IoT Platform Based on SDR Technology. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Green Computing and Communications and IEEE Internet of Things and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bankov, D.; Khorov, E.; Lyakhov, A. On the limits of LoRaWANchannel access. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Engineering and Telecommunication (EnT), Dolgoprudny, Russia, 29–30 November 2016; pp. 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.; Sohail, M.F.; Ghauri, S.A.; Qureshi, I.M.; Aqdas, N. Cognitive radio based Smart Grid CommunicationNetwork. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 72, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Rachedi, A. Cognitive-Radio-Based Internet of Things: Applications, Architectures, Spectrum RelatedFunctionalities, and Future Research Directions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Saifullah, A. A comprehensive survey on networkingover tv white spaces. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.07120. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, P.; Singh, K.D.; Bonnin, J.M. Cognitive radio for M2M and Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Commun. 2016, 94, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, U.; Bounceur, A.; Clavier, L. A study of LoRa low power and wide area network technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Fez, Morocco, 22–24 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Lee, W.-Y.; Vuran, M.C.; Mohanty, S. NeXt generation/dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2006, 50, 2127–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, A.; Rahman, M.; Ismail, D.; Lu, C.; Chandra, R.; Liu, J. Snow: Sensor network over white spaces. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems CD-ROM, New York, NY, USA, 14 November 2016; pp. 272–285. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah, A.; Rahman, M.; Ismail, D.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Chandra, R. Low-Power Wide-Area Network Over White Spaces. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2018, 26, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantacci, R.; Marabissi, D. Cognitive spectrum sharing: An enabling wireless communication technology for a wide use of smart systems. Future Internet 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohize, H.; Dlodlo, M. A Channel Hopping Algorithm for Guaran-teed Rendezvous in Cognitive Radio Ad Hoc Networks Using Swarm Intelligence. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 96, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongare, A.; Hesling, C.; Bhatia, K.; Balanuta, A.; Pereira, R.L.; Iannucci, B.; Rowe, A. OpenChirp: A Low-Power Wide-Area Networking Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerComWorkshops), Big Island, HI, USA, 13–17 March 2017; pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Miao, Y.; Jian, X.; Wang, X.; Humar, I. Cognitive-LPWAN: Towards intelligent wireless services in hybrid low powerwide area networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2018, 3, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Harras, K.A.; Zegura, E.; Ammar, M. Local and low-costwhite space detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 503–516. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).