Global Imbalances: The Role of Institutions, Financial Development and FDI in the Context of Financial Crises
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data and Variables
3.1.1. Quality of Institutions
3.1.2. Financial Development
3.1.3. Foreign Direct Investment
3.1.4. Openness
3.1.5. Financial Crisis
3.1.6. Income per Capita and Growth
3.1.7. Fiscal Balance
3.1.8. Initial Net Foreign Asset Position and Oil Balance
3.1.9. Demographics
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
4. Results
4.1. FDI, the Quality of Institutions and Financial Crisis
4.2. The Role of Financial Development
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Name | Source |
|---|---|
| Current account | International Monetary Fund |
| GDP | World Bank |
| Per capita income | World Bank |
| Exports and imports | International Monetary Fund |
| Fiscal balance (net lending) | International Monetary Fund |
| Exchange rate | International Monetary Fund |
| Financial Development Indices | Svirydzenka (2016) |
| Population data | United Nations |
| Net Foreign Asset Position | Lane and Milesi-Ferretti (2007) |
| Institutional Quality Index | Kuncic (2013) |
| Financial crises | Laeven and Valencia (2018) |
| Oil balance | Energy Information Agency (EIA); OPEC |
| FDI | World Bank |
| Current Account | Per capita Income | Δ% Per capita Income | Fiscal Balance | Lagged NFA | Youth Dep. | Elderly Dep. | Oil Balance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current account | 1000 | |||||||
| Per capita income | 0413 | 1000 | ||||||
| Δ% Per capita income | 0089 | −0167 | 1000 | |||||
| Fiscal balance | 0524 | 0167 | 0183 | 1000 | ||||
| Lagged NFA | 0574 | 0475 | −0026 | 0283 | 1000 | |||
| Youth dep. | −0207 | −0715 | 0104 | 0036 | −0397 | 1000 | ||
| Elderly dep. | 0090 | 0779 | −0237 | −0152 | 0262 | −0795 | 1000 | |
| Oil balance | 0028 | 0105 | −0123 | 0154 | −0162 | 0212 | −0056 | 1000 |
| Current Account | Per capita Income | Δ% Per capita Income | Fiscal Balance | Lagged NFA | Youth Dep. | Elderly Dep. | Oil Balance | |
| Openness | 0535 | 0168 | 0155 | 0362 | 0456 | −0197 | −0045 | −0365 |
| Financial crisis | −0007 | 0049 | −0231 | −0153 | 0054 | −0137 | 0049 | −0007 |
| Financial crisis*openness | 0024 | 0032 | −0236 | −0121 | 0040 | −0154 | 0057 | −0007 |
| FDI | 0164 | 0543 | −0155 | −0111 | 0156 | −0371 | 0495 | 0106 |
| Economic Institutions | 0197 | 0773 | −0220 | 0132 | 0361 | −0644 | 0674 | −0128 |
| Legal Institutions | 0209 | 0836 | −0181 | 0015 | 0367 | −0735 | 0762 | −0127 |
| Political Institutions | 0175 | 0826 | −0171 | −0015 | 0334 | −0704 | 0788 | −0077 |
| Financial development | 0304 | 0731 | −0072 | 0032 | 0447 | −0772 | 0638 | −0197 |
| Financial Institutions | 0198 | 0732 | −0136 | −0070 | 0393 | −0800 | 0692 | −0186 |
| Openness | Financial Crisis | Financial Crisis* Openness | FDI | Economic Institutions | Legal Institutions | Political Institutions | Financial Development | |
| Openness | 1000 | |||||||
| Financial crisis | −0139 | 1000 | ||||||
| Financial crisis× openness | −0024 | 0833 | 1000 | |||||
| FDI | −0201 | 0023 | 0021 | 1000 | ||||
| Economic Institutions | 0298 | −0032 | 0013 | 0318 | 1000 | |||
| Legal Institutions | 0170 | 0025 | 0040 | 0439 | 0863 | 1000 | ||
| Political Institutions | 0109 | −0018 | 0433 | 0008 | 0828 | 0941 | 1000 | |
| Financial development | 0251 | 0094 | 0484 | 0086 | 0686 | 0726 | 0687 | 1000 |
| Financial Institutions | 0226 | 0088 | 0084 | 0435 | 0717 | 0768 | 0755 | 0936 |
References
- King, M. Speech by Mervyn King, Governor of the Bank of England, to the CBI Dinner, East Midlands Conference Centre, Nottingham—20 January 2009. Available online: https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/-/media/boe/files/speech/2009/mervyn-king-to-cbi-dinner (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Blanchard, O.J. Current Account Deficits in Rich Countries. SSRN Electron. J. 2007, 54, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanchard, O.; Milesi-Ferretti, G.M. Global Imbalances: In Midstream? IMF Staff Position Note 2009, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernanke, B. The Global Saving Glut and the U.S. Current Account. Remarks at the Sandridge Lecture; Virginia Association of Economics: Richmond, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chinn, M.D.; Ito, H. Current Account Balances, Financial Development and Institutions: Assaying the World ‘Savings Glut’. SSRN Electron. J. 2005, 26, 546–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gossé, J.-B.; Serranito, F. Long-run determinants of current accounts in OECD countries: Lessons for intra-European imbalances. Econ. Model. 2014, 38, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubik, B.T.A.; Sablik, T. Should We Worry about Trade Imbalances? Econ. Brief. Fed. Reserv. 2017, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, H.; Nitsch, V. The Euro’ s Effect on Trade Imbalances. IMF Work. Pap. 2010, 10, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Milesi-Ferretti, G.-M.; Tressel, T. External Imbalances in the Euro Area. IMF Work. Pap. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghyrou, M.G.; Chortareas, G. Current Account Imbalances and Real Exchange Rates in the Euro Area. Rev. Int. Econ. 2008, 16, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdelger, T.; Kandil, M. Determinants of the current account balance in the United States. Appl. Econ. 2012, 44, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R. A threshold model of the US current account. Econ. Model. 2015, 48, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M. What Drives China’s Current Account? SSRN Electron. J. 2010, 32, 856–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadiku, L.; Fetahi-Vehapi, M.; Sadiku, M.; Berisha, N. The Persistence and Determinants of Current Account Deficit of FYROM: An Empirical Analysis. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 33, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Rault, C. Budgetary and External Imbalances Relationship: A Panel Data Diagnostic. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1291170 (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Belke, A.; Dreger, C. Current Account Imbalances in the Euro Area: Does Catching up Explain the Development? Rev. Int. Econ. 2013, 21, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, M.D.; Prasad, E.S. Medium-term Determinants of Current Accounts in Industrial and Developing Countries: An Empirical Exploration. SSRN Electron. J. 2003, 59, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Jochem, A. Determinants of Current Account Developments in the Central and East European EU Member States—Consequences for the Enlargement of the Euro Area. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2785215 (accessed on 27 September 2020).
- Gruber, J.W.; Kamin, S.B. Explaining the Global Pattern of Current Account Imbalances. SSRN Electron. J. 2005, 26, 500–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abbas, S.M.A.; Bouhga-Hagbe, J.; Fatás, A.; Mauro, P.; Velloso, R.C. Fiscal Policy and the Current Account. IMF Econ. Rev. 2011, 59, 603–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluedorn, J.C.; Leigh, D. Revisiting the Twin Deficits Hypothesis: The Effect of Fiscal Consolidation on the Current Account. IMF Econ. Rev. 2011, 59, 582–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.W.; Kamin, S.B. Do Differences in Financial Development Explain the Global Pattern of Current Account Imbalances? SSRN Electron. J. 2008, 17, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.; Smith, R. Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J. Econ. 1995, 68, 79–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunčič, A. Institutional quality dataset. J. Inst. Econ. 2014, 10, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarida, R. G7 Current Account Imbalances: Sustainability and Adjustment; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Svirydzenka, K. Introducing a New Broad-based Index of Financial Development. IMF Work. Pap. 2016, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romelli, D.; Terra, C.; Vasconcelos, E.X. Current Account and Real Exchange Rate Changes: The Impact of Trade Openness. SSRN Electron. J. 2014, 105, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, J.A.; Cavallo, E.A. Does Openness to Trade Make Countries More Vulnerable to Sudden Stops, or Less? Using Gravity to Establish Causality. SSRN Electron. J. 2004, 27, 1430–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Joy, M.M.; Lisack, N.M.; Lloyd, S.M.; Reinhardt, D.M.; Sajedi, R.M.; Whitaker, S.M. Mind the (Current Account) Gap. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeven, L.; Valencia, F. Systemic Banking Crises Revisited. IMF Work. Pap. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erauskin, I. Savings, the size of the net foreign asset position, and the dynamics of current accounts. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2015, 39, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H. A Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimator and a Direct Test for Heteroskedasticity. Econometrica 1980, 48, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, O.J.; Milesi-Ferretti, G.M. (Why) Should Current Account Balances Be Reduced? SSRN Electron. J. 2011, 60, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, P.; Ferretti, G.M.M. External Adjustment and the Global Crisis. Extern. Adjust. Global Crisis 2011, 88, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, F.G.; Unsal, D.F. It is not your fault, but it is your problem: Global financial crisis and emerging markets. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 2017, 69, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalassinos, E.I.; Thalassinos, Y. Financial Crises and e-Commerce: How Are They Related. SSRN Electron. J. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrrawal, P.; Waggle, D.; Sandweiss, D.H. Suicides as a response to adverse market sentiment (1980–2016). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snipes, M.; Cunha, T.M.; Hemley, D.D. An empirical investigation into the relationship between changes in the business cycle and the incidence of suicide. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2011, 38, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumhof, M.; Laxton, D. Fiscal deficits and current account deficits. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 2013, 37, 2062–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
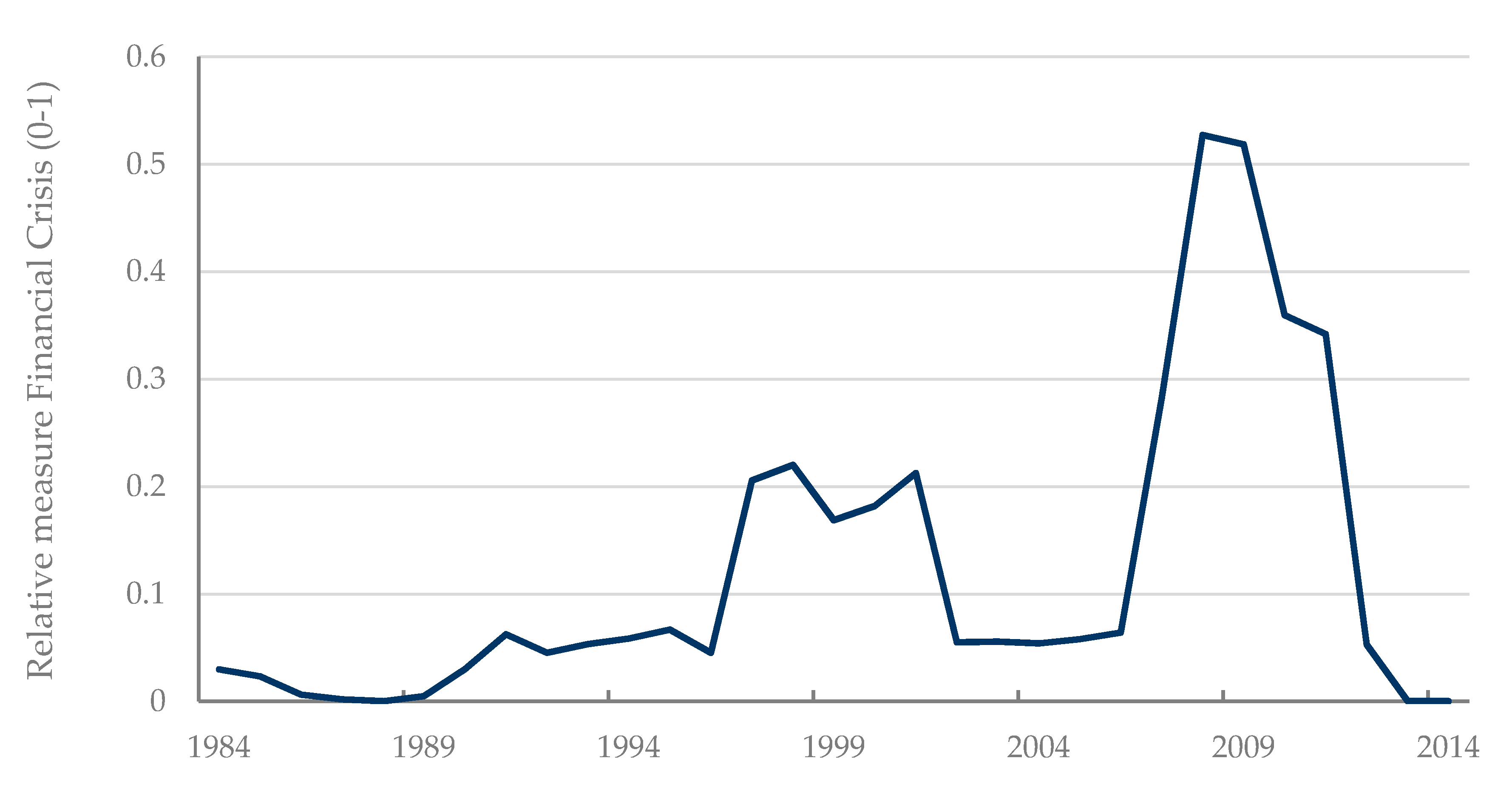

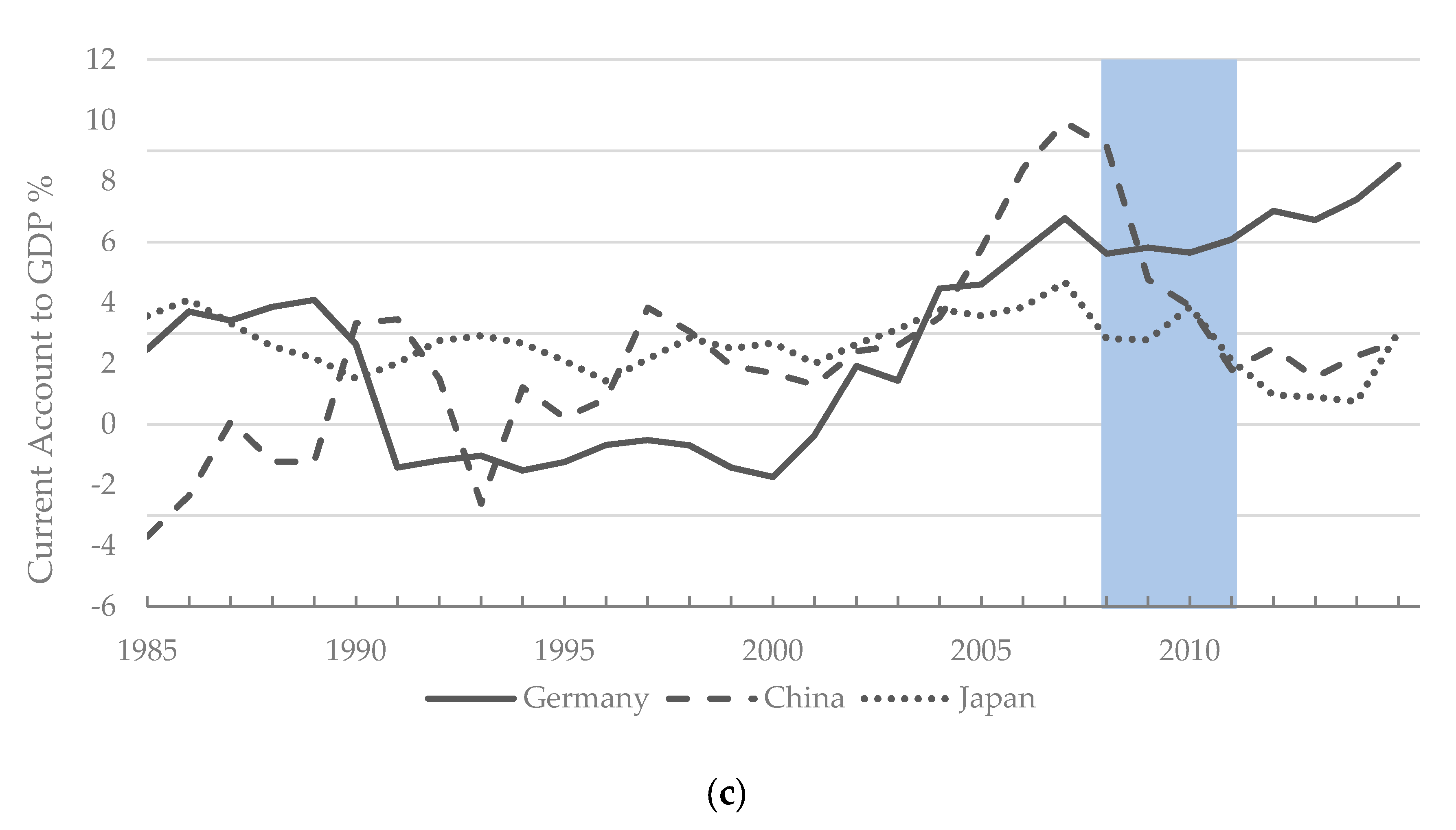


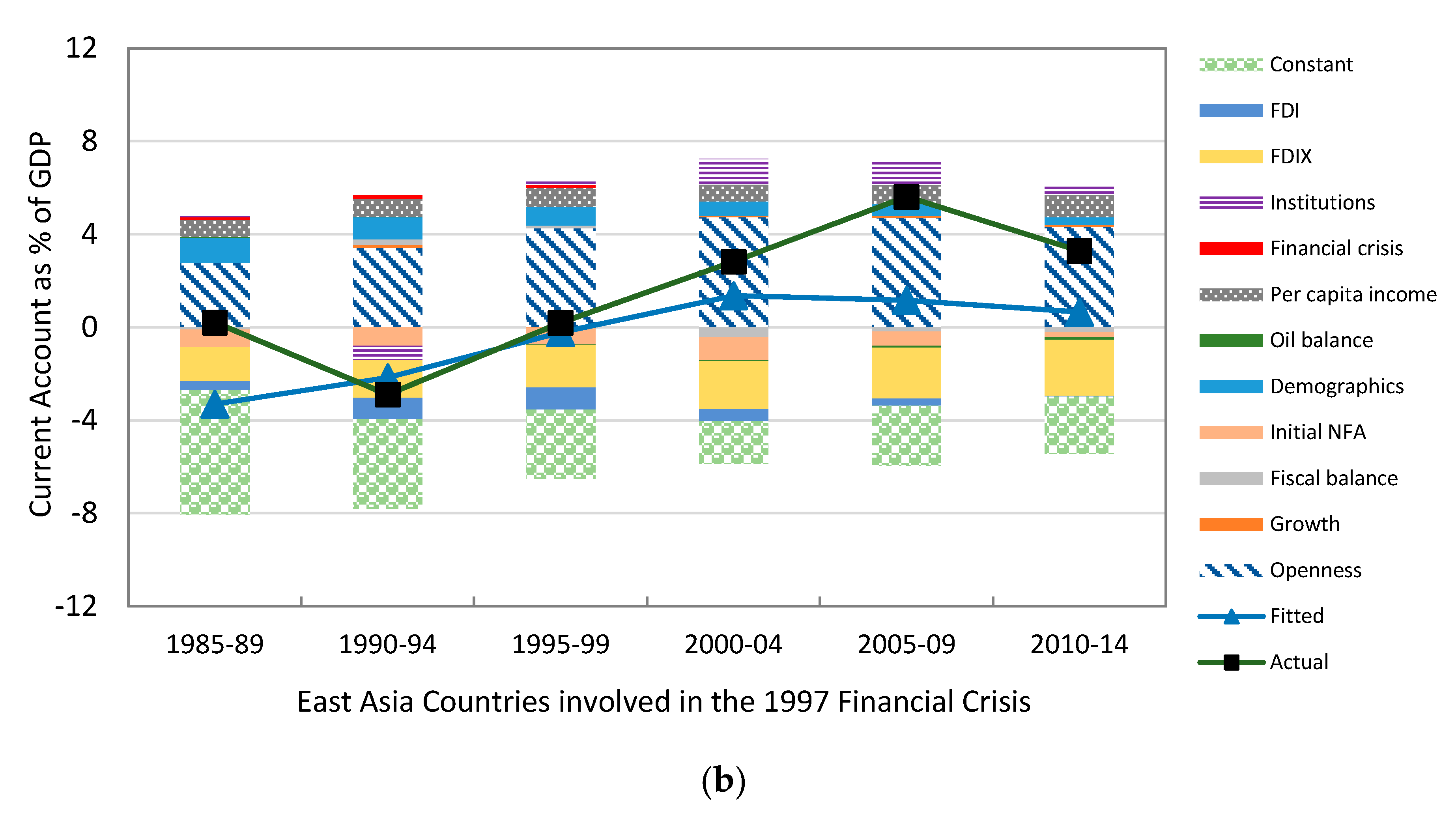
| Author | Country | Period | Determinants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gossé and Serranito (2014) | OECD countries | 1974–2009 | Exchange rate (−), credit level (−), RGDP (−), oil balance (+), terms of trade (+), labour productivity (+) |
| Duncan (2015) | The United States | 1973–2012 | Fiscal surplus (+), productivity (−), TFP volatility (+), relative price of oil (−), real exchange rate (−), real interest rate (+) |
| Huntington (2015) | World (91 countries) | 1984–2009 | Government surplus (−), oil trade (+), trade openness (+), age dependency (−) |
| Duncan (2016) | US | 1973–2012 | Output below long-run trend: GDP cycle (−), output above long-run trend: GDP cycle (+) |
| Romelli, Terra and Vasconcelos (2018) | World (181 countries) | 1970–2011 | Openness (+), exchange rate (+) |
| 1985–1989 | 1990–1994 | 1995–1999 | 2000–2004 | 2005–2009 | 2010–2014 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current account (% of GDP) | −0.71 | −0.81 | −0.26 | 1.12 | 0.75 | 0.16 |
| Per capita income (2010 USD) | 17,059 | 18,399 | 20,150 | 22,313 | 24,772 | 25,485 |
| Δ% Real per capita income | 2.27 | 1.89 | 2.29 | 1.86 | 1.94 | 2.13 |
| Lagged NFA (% of GDP) | −25.72 | −25.31 | −25.08 | −22.21 | −19.55 | −16.87 |
| Openness (% of GDP) | 60.51 | 63.31 | 70.68 | 78.79 | 85.30 | 87.08 |
| Youth dependency ratio (×100) | 49.91 | 46.51 | 43.41 | 40.01 | 36.89 | 34.31 |
| Elderly dependency ratio (×100) | 12.80 | 13.52 | 14.26 | 14.97 | 15.75 | 16.78 |
| Oil balance (% of GDP) | −0.80 | −0.24 | −0.11 | −0.18 | −0.52 | −0.99 |
| FDI (% of GDP) | −0.52 | −0.85 | −1.22 | −1.00 | −0.53 | −1.19 |
| Economic Institutions (Score ×100) | NA | 48.00 | 51.00 | 42.00 | 32.00 | 37.00 |
| Political Institutions (Score ×100) | NA | 62.00 | 59.00 | 59.00 | 59.00 | 65.00 |
| Legal Institutions (Score ×100) | NA | 47.00 | 57.00 | 48.00 | 46.00 | 53.00 |
| Financial Development Index (FDIX) | 34.52 | 38.05 | 45.78 | 51.76 | 56.82 | 56.62 |
| Financial Institutions Index (FIIX) | 45.47 | 48.36 | 52.47 | 55.87 | 59.65 | 62.57 |
| Financial Crises Dummy a | 15 | 34 | 33 | 26 | 35 | 32 |
| GDP-Weighted Crisis Dummy | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.15 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per capita income | 0.013 * | 0.030 *** | 0.023 *** | 0.020 ** | 0.028 *** |
| (0.007) | (0.009) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.009) | |
| Δ% Real per capita income | 0.148 | 0.056 | 0.131 | 0.076 | 0.039 |
| (0.080) | (0.114) | (0.119) | (0.124) | (0.117) | |
| Fiscal balance | 0.208 *** | 0.282 ** | 0.210 ** | 0.226 ** | 0.263 *** |
| (0.079) | (0.083) | (0.091) | (0.093) | (0.081) | |
| Lagged NFA | 0.028 *** | 0.022 ** | 0.026 *** | 0.026 *** | 0.0235 *** |
| (0.006) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.007) | (0.007) | |
| Youth dependency | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.048 | 0.036 | 0.056 |
| (0.035) | (0.036) | (0.037) | (0.036) | (0.037) | |
| Elderly dependency | −0.058 | −0.011 | −0.034 | −0.060 | −0.001 |
| (0.099) | (0.103) | (0.114) | (0.112) | (0.105) | |
| Oil | 0.055 | 0.024 | 0.088 | 0.016 | 0.067 |
| (0.113) | (0.087) | (0.097) | (0.153) | (0.098) | |
| Openness | 0.037 *** | 0.045 *** | 0.040 *** | 0.036 *** | 0.047 *** |
| (0.008) | (0.007) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Financial crisis | −0.115 * | −0.071 * | −0.104 * | −0.096 * | −0.069 * |
| (0.059) | (0.042) | (0.055) | (0.053) | (0.041) | |
| Financial crisis ×openness | 0.001 * | 0.001 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.001 |
| (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.001) | |
| FDI | 0.454 ** | 0.410 * | 0.405 | 0.418 * | 0.345 |
| (0.230) | (0.242) | (0.255) | (0.249) | (0.235) | |
| Economic Institutions | −0.026 *** | −0.031 *** | |||
| (0.006) | (0.008) | ||||
| Legal Institutions | −0.013 ** | 0.005 | |||
| (0.006) | (0.010) | ||||
| Political Institutions | −0.843 | 0.002 | |||
| (0.570) | (0.009) | ||||
| Time dummies | 1990–1994 | 1990–1994 * | 1990–1994 | 1990–1994 | 1990–1994 * |
| 1995–1999 | 1995–1999 *** | 1995–1999 ** | 1995–1999 * | 1995–1999 ** | |
| 2000–2004 ** | 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 ** | 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 *** | |
| 2005–2009 | 2005–2009 ** | 2005–2009 * | 2005–2009 ** | 2005–2009 ** | |
| 2010–2014 | 2010–2014 ** | 2010–2014 ** | 2010–2014 * | 2010–2014 ** | |
| Root mean square error | 2.925 | 2.631 | 2.807 | 2.875 | 2.610 |
| Time dummies joint test | 13.590 * | 16.700 *** | 12.970 ** | 14.450 ** | 17.310 *** |
| Hausman test | – | 16.610 | 0.920 | 39.210 *** | 14.100 |
| VIF test | 2.690 | 3.310 | 3.390 | 3.370 | 4.470 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per capita income | 0.021 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.019 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.014 * |
| (0.007) | (0.009) | (0.007) | (0.009) | (0.007) | |
| Δ% Per capita income | 0.145 | 0.051 | 0.132 | 0.033 | 0.165 |
| (0.125) | (0.118) | (0.124) | (0.116) | (0.125) | |
| Fiscal balance | 0.193 ** | 0.255 *** | 0.396 ** | 0.231 *** | 0.197 ** |
| (0.079) | (0.081) | (0.075) | (0.078) | (0.081) | |
| Lagged NFA | 0.028 *** | −0.023 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.022 *** | 0.029 *** |
| (0.006) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.007) | (0.006) | |
| Youth dependency | 0.038 | 0.042 ** | 0.020 | 0.019 | 0.063 * |
| (0.040) | (0.039) | (0.039) | (0.039) | (0.037) | |
| Elderly dependency | −0.054 | −0.006 | −0.051 | −0.015 | −0.033 |
| (0.101) | (0.107) | (0.952) | (0.102) | (0.103) | |
| Oil balance | 0.007 | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.049 | 0.055 |
| (0.114) | (0.103) | (0.115) | (0.104) | (0.117) | |
| Openness | 0.039 *** | 0.047 *** | 0.039 *** | 0.048 *** | 0.037 *** |
| (0.009) | (0.008) | (0.313) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Financial crisis | −0.117 ** | −0.073 * | −0.120 ** | −0.078 * | −0.116 ** |
| (0.054) | (0.040) | (0.054) | (0.040) | (0.059) | |
| Financial crisis ×openness | 0.002 ** | 0.001 | 0.002 ** | 0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | |
| FDI | 0.541 ** | 0.405 * | 0.500 ** | 0.390 | 0.435 * |
| (0.245) | (0.251) | (0.231) | (0.236) | (0.234) | |
| Financial Development (FDIX) | −0.058 ** | −0.042 * | |||
| (0.023) | (0.022) | ||||
| Financial Institutions (FIIX) | −0.059 *** | −0.060 *** | |||
| (0.018) | (0.018) | ||||
| Economic Institutions | −0.028 *** | −0.028 *** | |||
| (0.008) | (0.008) | ||||
| Legal Institutions | 0.006 | 0.004 | |||
| (0.010) | (0.010) | ||||
| Political Institutions | 0.002 | 0.006 | |||
| (0.009) | (0.009) | ||||
| Exchange rate | 0.363 * | ||||
| (0.145) | |||||
| Time dummies | 1990–1994 | 1990–1994 ** | 1990–1994 | 1990–1994 * | 1990–1994 |
| 1995–1999 ** | 1995–1999 *** | 1995–1999 * | 1995–1999 ** | 1995–1999 | |
| 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 *** | 2000–2004 ** | |
| 2005–2009 ** | 2005–2009 *** | 2005–2009 ** | 2005–2009 *** | 2005–2009 | |
| 2010–2014 ** | 2010–2014 ** | 2010–2014 *** | 2010–2014 *** | 2010-2014 | |
| Root mean square error | 2.842 | 2.568 | 2.855 | 2.545 | 2.906 |
| Time dummies joint test | 21.640 *** | 20.950 *** | 19.840 *** | 22.950 *** | 12.73 ** |
| Hausman test | 13.490 | 36.120 ** | - | 91.610 *** | 39.500 *** |
| VIF test | 3.000 | 4.710 | 2.890 | 4.620 | 2.630 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, C.A.; Ordeñana, X.; Vera-Gilces, P.; Jiménez, A. Global Imbalances: The Role of Institutions, Financial Development and FDI in the Context of Financial Crises. Sustainability 2021, 13, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010356
Silva CA, Ordeñana X, Vera-Gilces P, Jiménez A. Global Imbalances: The Role of Institutions, Financial Development and FDI in the Context of Financial Crises. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010356
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Carlos A., Xavier Ordeñana, Paul Vera-Gilces, and Alfredo Jiménez. 2021. "Global Imbalances: The Role of Institutions, Financial Development and FDI in the Context of Financial Crises" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010356
APA StyleSilva, C. A., Ordeñana, X., Vera-Gilces, P., & Jiménez, A. (2021). Global Imbalances: The Role of Institutions, Financial Development and FDI in the Context of Financial Crises. Sustainability, 13(1), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010356






